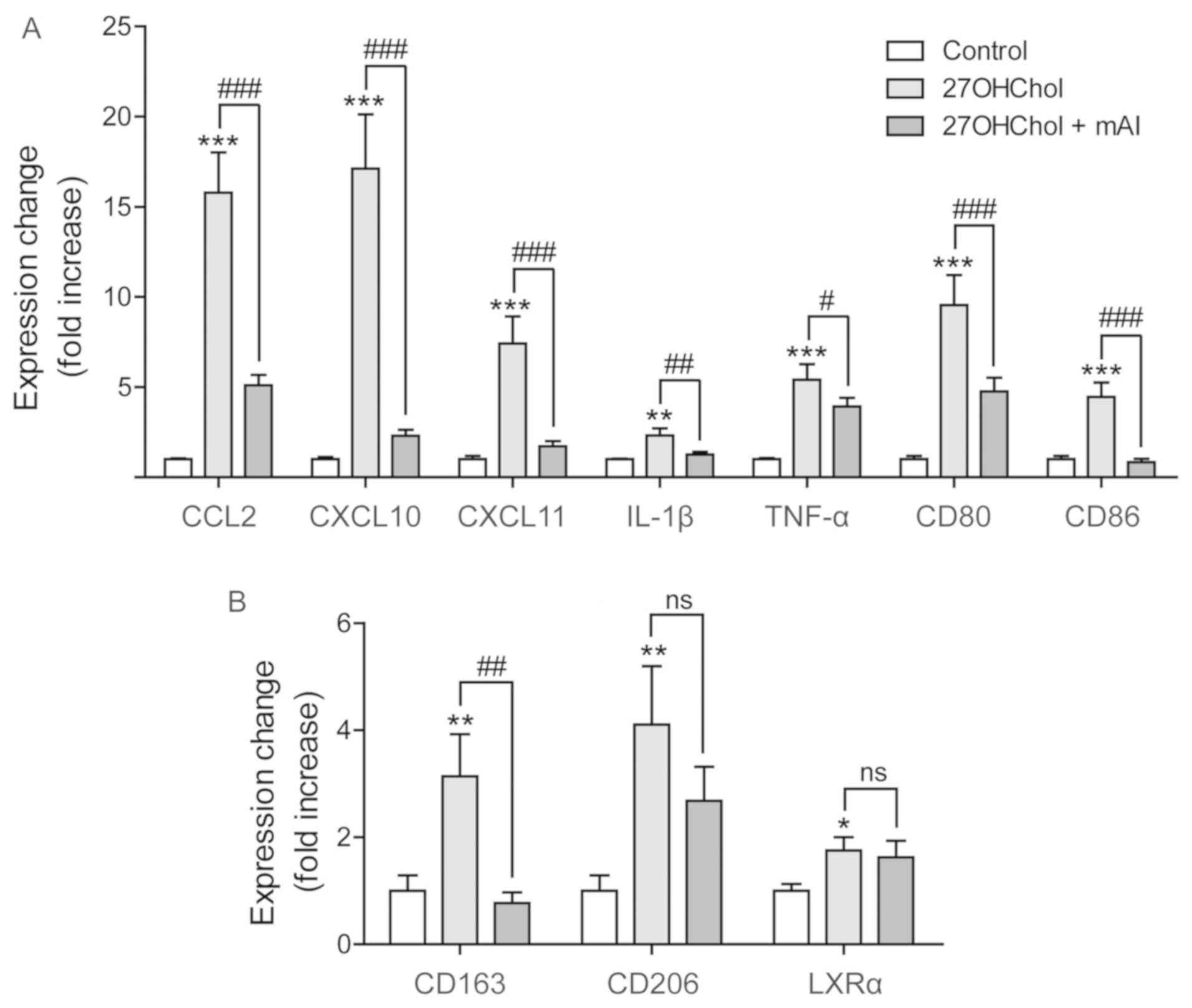
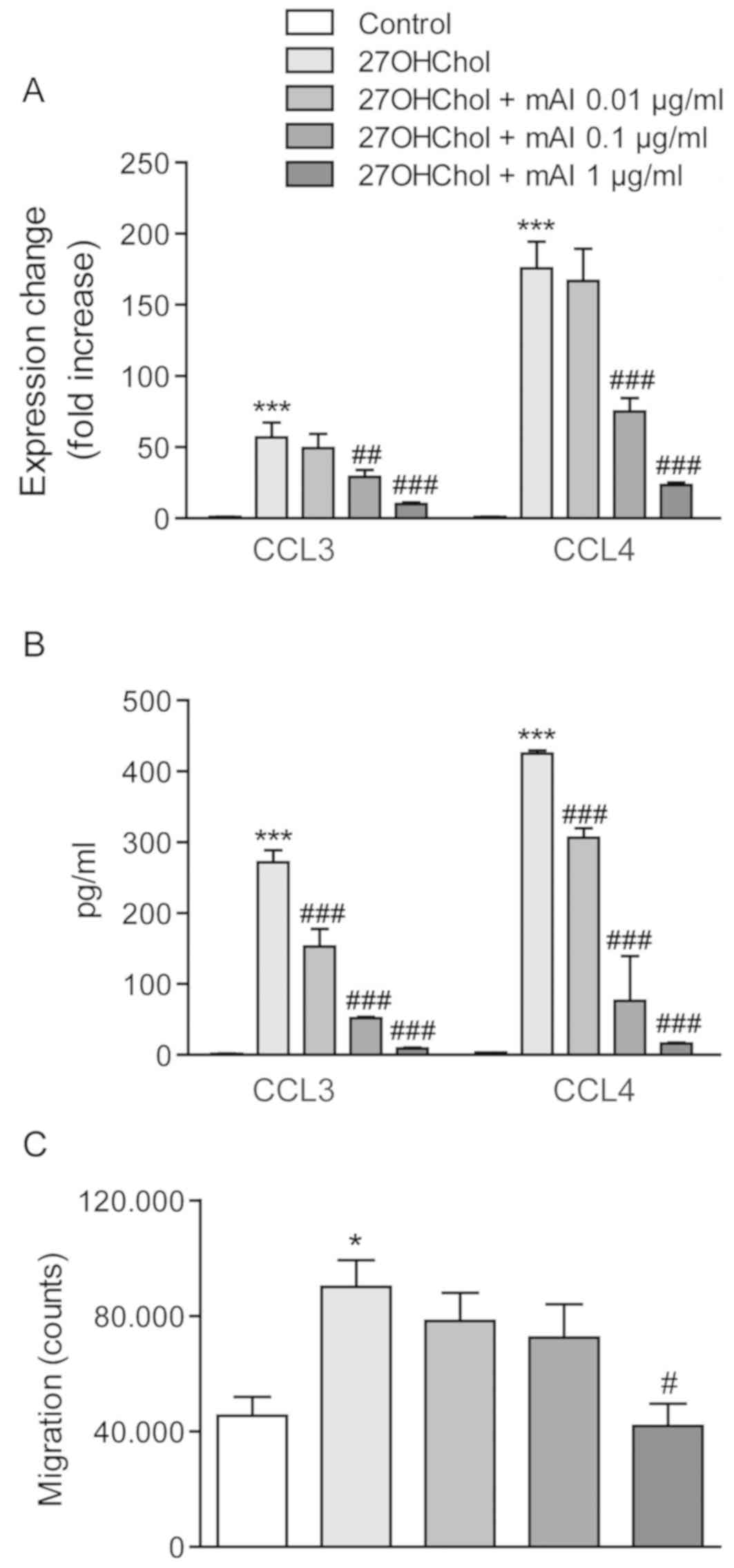
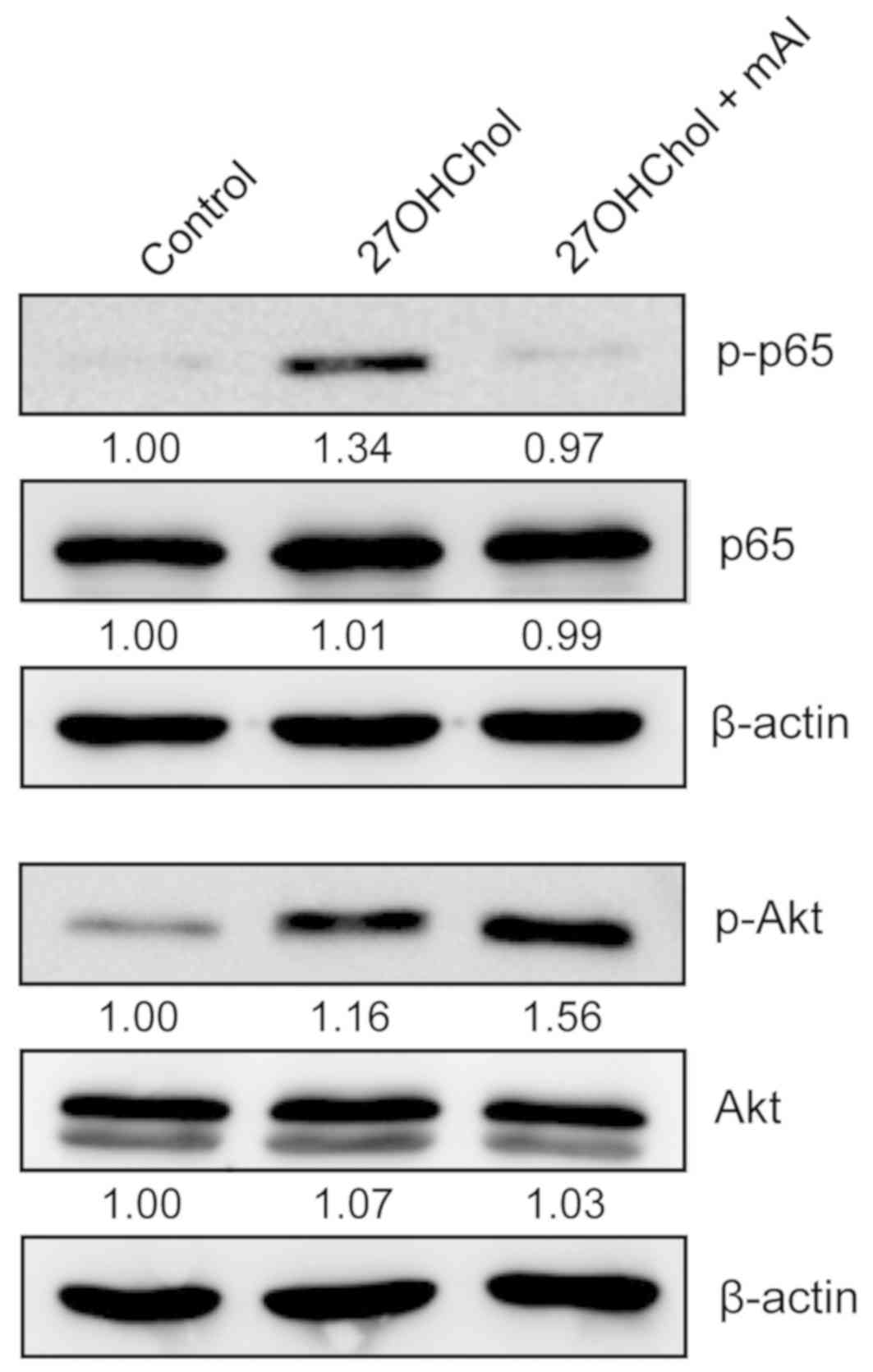
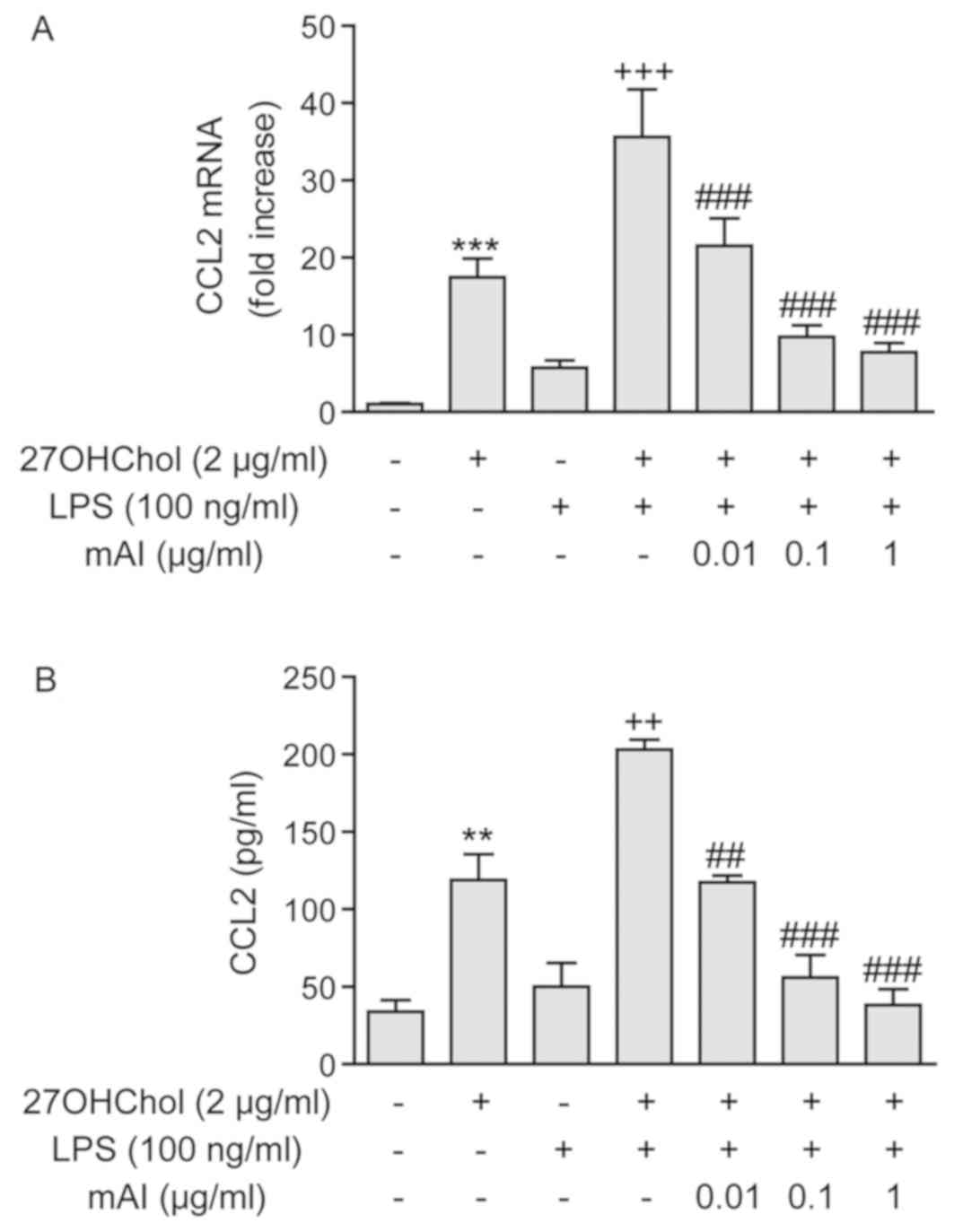
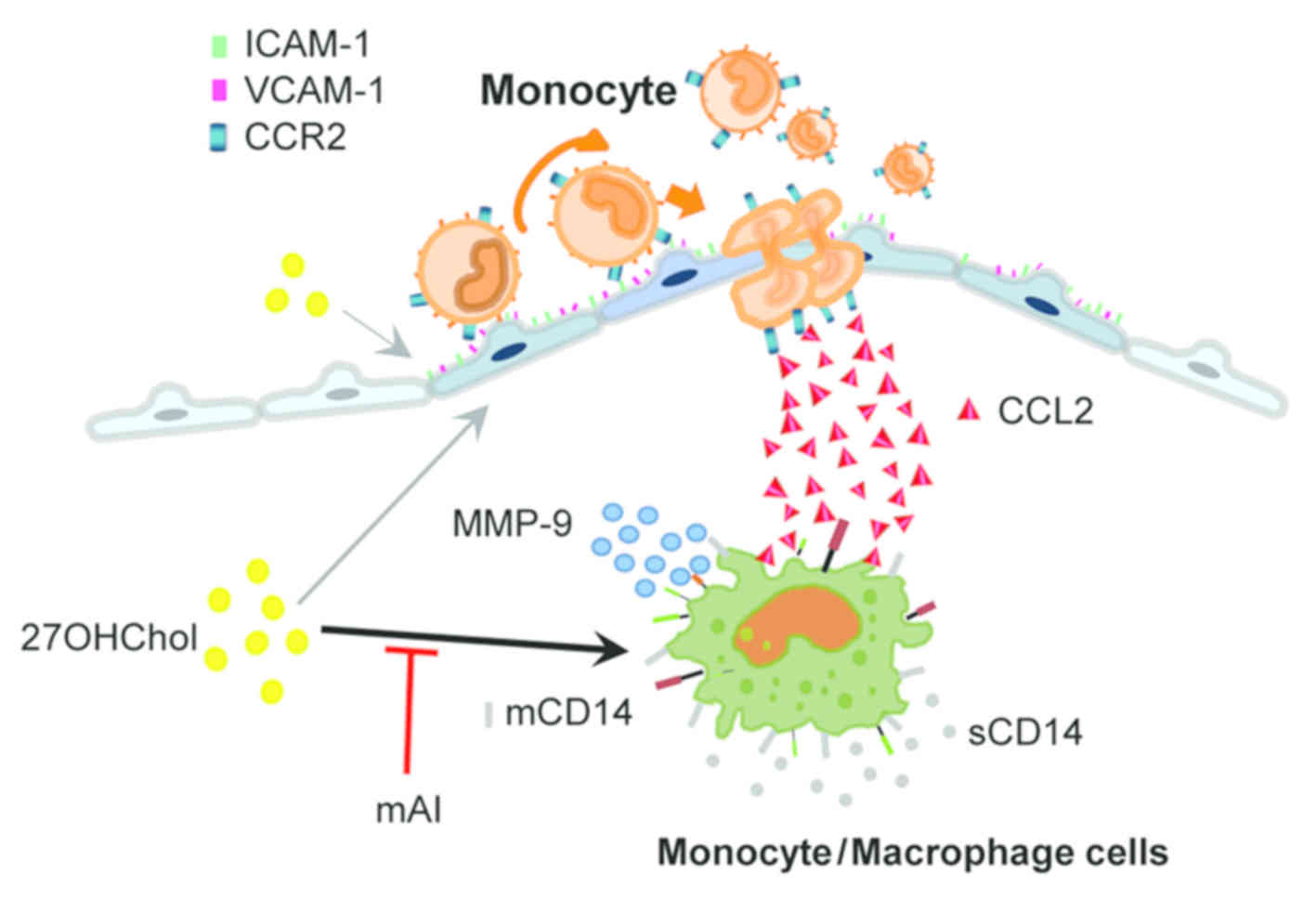
|
1
|
Xin LT, Yue SJ, Fan YC, Wu JS, Yan D, Guan
HS and Wang CY: Cudrania tricuspidata: An updated review on
ethnomedicine, phytochemistry and pharmacology. RSC Advances.
7:31807–31832. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jeong GS, Lee DS and Kim YC:
Cudratricusxanthone A from Cudrania tricuspidata suppresses
pro-inflammatory mediators through expression of anti-inflammatory
heme oxygenase-1 in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:241–246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lim JY, Hwang BY, Hwang KW and Park SY:
Methylalpinu- misoflavone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation in microglial cells by the NF-kappaB and MAPK
signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 26:1948–1956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cho EJ, Yokozawa T, Rhyu DY, Kim SC,
Shibahara N and Park JC: Study on the inhibitory effects of Korean
medicinal plants and their main compounds on the
1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhy-drazyl radical. Phytomedicine. 10:544–551.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee IK, Kim CJ, Song KS, Kim HM, Koshino
H, Uramoto M and Yoo ID: Cytotoxic benzyl dihydroflavonols from
Cudrania tricuspidata. Phytochemistry. 41:213–216. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou YS, Hou AJ and Zhu GF: Isoprenylated
xanthones and flavonoids from Cudrania tricuspidata. Chem
Biodivers. 2:131–138. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Brown AJ and Jessup W: Oxysterols and
atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 142:1–28. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gargiulo S, Gamba P, Testa G, Leonarduzzi
G and Poli G: The role of oxysterols in vascular ageing. J Physiol.
594:2095–2113. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Garcia-Cruset S, Carpenter KL, Guardiola
F, Stein BK and Mitchinson MJ: Oxysterol profiles of normal human
arteries, fatty streaks and advanced lesions. Free Radic Res.
35:31–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SM, Kim BY, Eo SK, Kim CD and Kim K:
27-Hydroxy- cholesterol up-regulates CD14 and predisposes monocytic
cells to superproduction of CCL2 in response to lipopolysaccharide.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:442–450. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Morello F, Saglio E, Noghero A, Schiavone
D, Williams TA, Verhovez A, Bussolino F, Veglio F and Mulatero P:
LXR-activating oxysterols induce the expression of inflammatory
markers in endothelial cells through LXR-independent mechanisms.
Atherosclerosis. 207:38–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Umetani M, Ghosh P, Ishikawa T, Umetani J,
Ahmed M, Mineo C and Shaul PW: The cholesterol metabolite
27-hydroxycholesterol promotes atherosclerosis via proinflammatory
processes mediated by estrogen receptor alpha. Cell Metab.
20:172–182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SM, Kim BY, Lee SA, Eo SK, Yun Y, Kim
CD and Kim K: 27-Hydroxycholesterol and 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol
trigger a sequence of events leading to migration of
CCR5-expressing Th1 lymphocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
274:462–470. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim SM, Lee SA, Kim BY, Bae SS, Eo SK and
Kim K: 27-Hydroxycholesterol induces recruitment of monocytic cells
by enhancing CCL2 production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
442:159–164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martinez FO and Gordon S: The M1 and M2
paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:132014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Italiani P and Boraschi D: From monocytes
to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs. functional differentiation.
Front Immunol. 5:5142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stöger JL, Gijbels MJ, van der Velden S,
Manca M, van der Loos CM, Biessen EA, Daemen MJ, Lutgens E and de
Winther MP: Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in
human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 225:461–468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park D, Park I, Lee D, Choi YB, Lee H and
Yun Y: The adaptor protein Lad associates with the G protein beta
subunit and mediates chemokine-dependent T-cell migration. Blood.
109:5122–5128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hiep NT, Kwon J, Kim DW, Hwang BY, Lee HJ,
Mar W and Lee D: Isoflavones with neuroprotective activities from
fruits of Cudrania tricuspidata. Phytochemistry. 111:141–148. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim BY, Son Y, Lee J, Choi J, Kim CD, Bae
SS, Eo SK and Kim K: Dexamethasone inhibits activation of
monocytes/macrophages in a milieu rich in 27-oxygenated
cholesterol. PLoS One. 12:e01896432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Manicone AM and McGuire JK: Matrix
metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 19:34–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bhatt D and Ghosh S: Regulation of the
NF-κB-mediated transcription of inflammatory genes. Front Immunol.
5:712014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Loetscher P, Uguccioni M, Bordoli L,
Baggiolini M, Moser B, Chizzolini C and Dayer JM: CCR5 is
characteristic of Th1 lymphocytes. Nature. 391:344–345. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Romagnani S: T-cell subsets (Th1 versus
Th2). Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 85:9–18; quiz 18-21. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hanania R, Sun HS, Xu K, Pustylnik S,
Jeganathan S and Harrison RE: Classically activated macrophages use
stable microtubules for matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9)
secretion. J Biol Chem. 287:8468–8483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kirkland TN and Viriyakosol S:
Structure-function analysis of soluble and membrane-bound CD14.
Prog Clin Biol Res. 397:79–87. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Christian F, Smith EL and Carmody RJ: The
Regulation of NF-κB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells. 5:1–19.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Heo W, Kim SM, Eo SK, Rhim BY and Kim K:
FSL-1, a Toll-like receptor 2/6 agonist, induces expression of
interleukin-1 alpha in the presence of 27-hydroxycholesterol.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 18:475–480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|