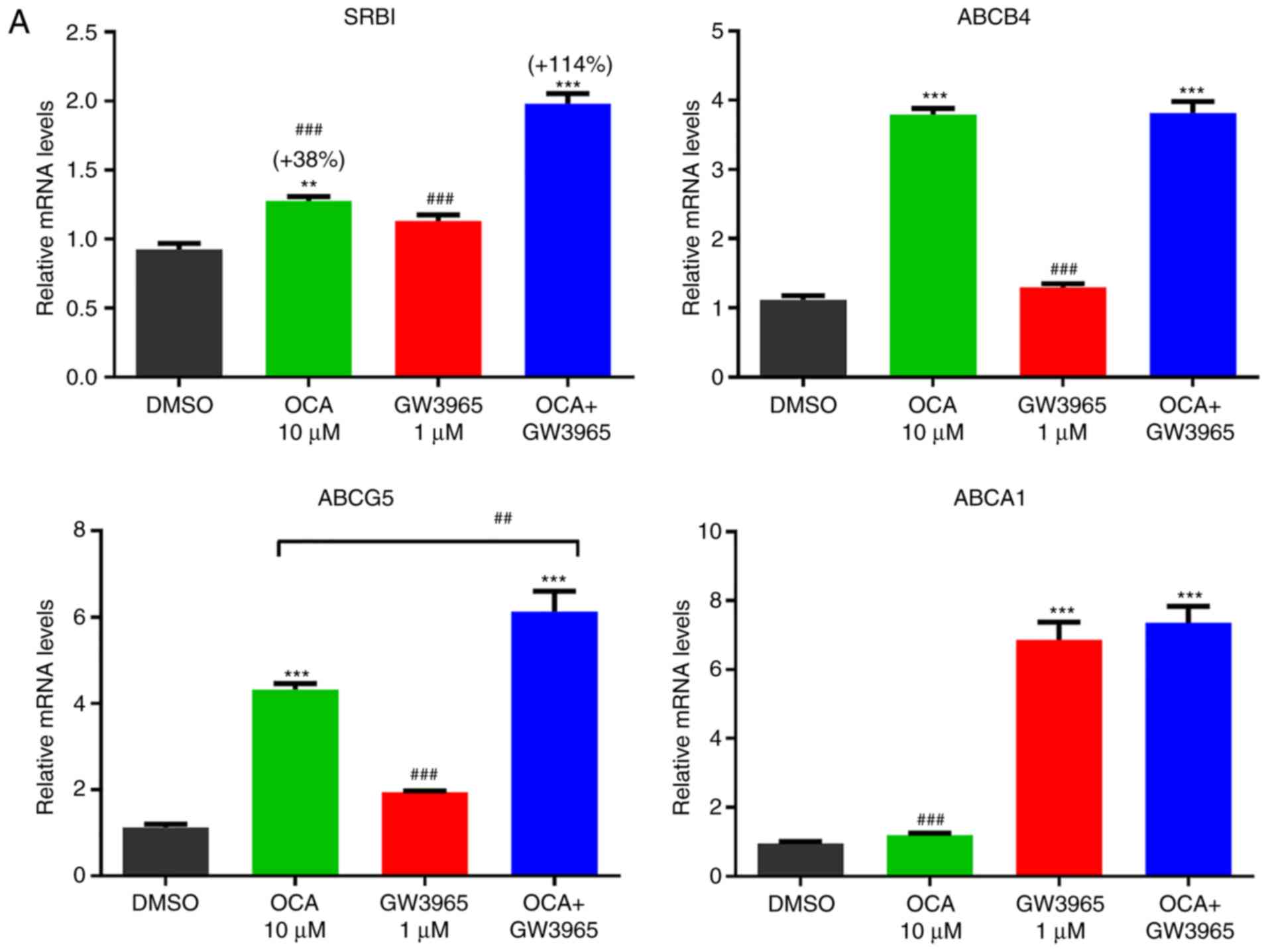
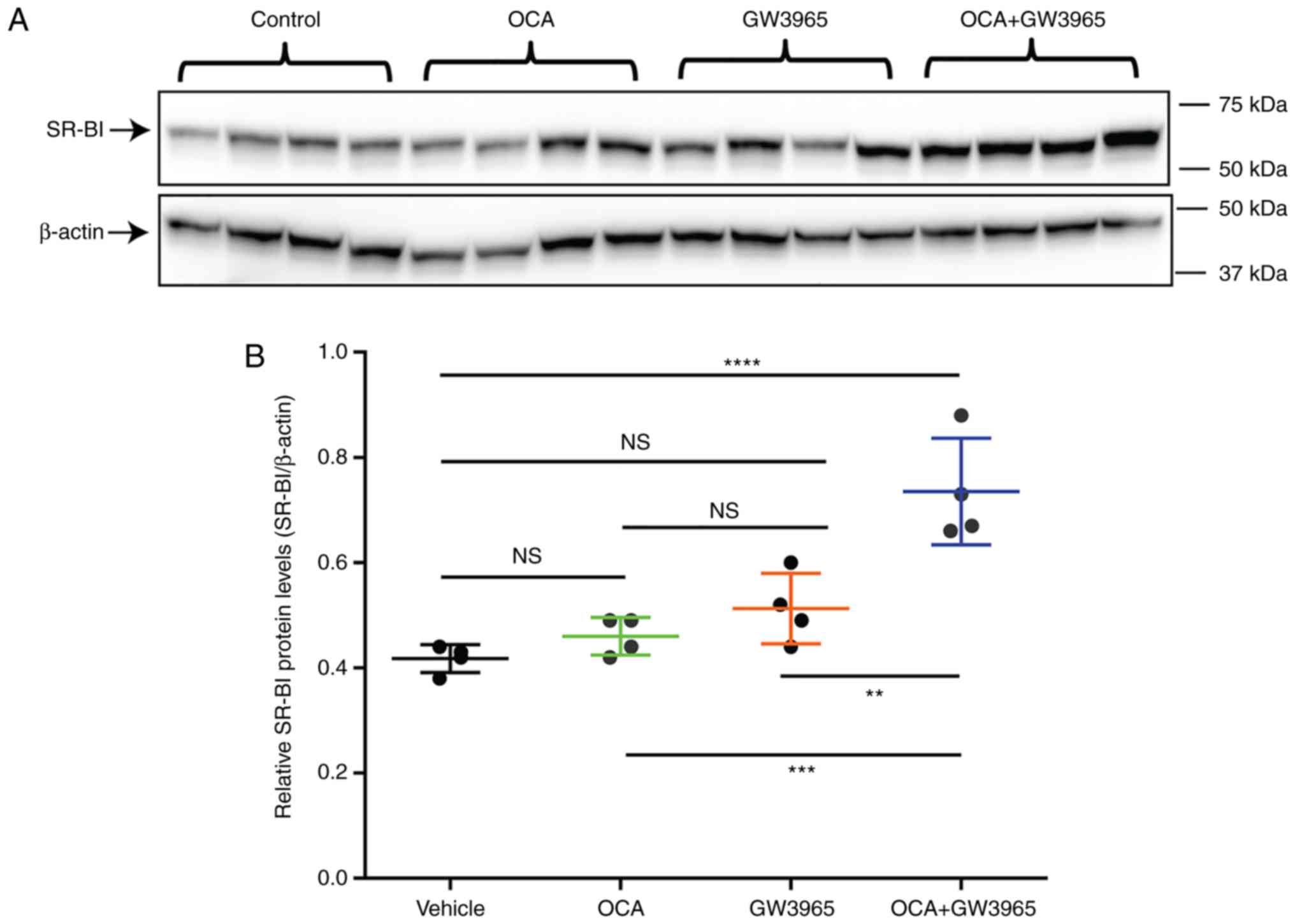
|
1
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE,
Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW,
et al: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by
farnesol metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lefebvre P, Cariou B, Lien F, Kuipers F
and Staels B: Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in
metabolic regulation. Physiol Rev. 89:147–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM,
Lambert G and Gonzalez FJ: Targeted disruption of the nuclear
receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell.
102:731–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li G, Thomas AM, Williams JA, Kong B, Liu
J, Inaba Y, Xie W and Guo GL: Farnesoid X receptor induces murine
scavenger receptor Class B type I via intron binding. PLoS One.
7:e358952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laffitte BA, Kast HR, Nguyen CM, Zavacki
AM, Moore DD and Edwards PA: Identification of the DNA binding
specificity and potential target genes for the farnesoid
X-activated receptor. J Biol Chem. 275:10638–10647. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calkin AC and Tontonoz P: Transcriptional
integration of metabolism by the nuclear sterol-activated receptors
LXR and FXR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:213–224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thomas AM, Hart SN, Kong B, Fang J, Zhong
XB and Guo GL: Genome-wide tissue-specific farnesoid X receptor
binding in mouse liver and intestine. Hepatology. 51:1410–1419.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhan L, Liu HX, Fang Y, Kong B, He Y,
Zhong XB, Fang J, Wan YJ and Guo GL: Genome-wide binding and
transcriptome analysis of human farnesoid X receptor in primary
human hepatocytes. PLoS One. 9:e1059302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Acton S, Rigotti A, Landschulz KT, Xu S,
Hobbs HH and Krieger M: Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI
as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science. 271:518–520. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rigotti A, Trigatti BL, Penman M, Rayburn
H, Herz J and Krieger M: A targeted mutation in the murine gene
encoding the high density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor scavenger
receptor class B type I reveals its key role in HDL metabolism.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:12610–12615. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brodeur MR, Luangrath V, Bourret G,
Falstrault L and Brissette L: Physiological importance of SR-BI in
the in vivo metabolism of human HDL and LDL in male and female
mice. J Lipid Res. 46:687–696. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zanoni P, Khetarpal SA, Larach DB,
Hancock-Cerutti WF, Millar JS, Cuchel M, DerOhannessian S, Kontush
A, Surendran A, Saleheen D, et al: Rare variant in scavenger
receptor BI raises HDL cholesterol and increases risk of coronary
heart disease. Science. 351:1166–1171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rizzo G, Passeri D, De Franco F, Ciaccioli
G, Donadio L, Orlandi S, Sadeghpour B, Wang XX, Jiang T, Levi M, et
al: Functional characterization of the semisynthetic bile acid
derivative INT-767, a dual farnesoid X receptor and TGR5 agonist.
Mol Pharmacol. 78:617–630. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hambruch E, Miyazaki-Anzai S, Hahn U,
Matysik S, Boettcher A, Perović-Ottstadt S, Schlüter T, Kinzel O,
Krol HD, Deuschle U, et al: Synthetic farnesoid X receptor agonists
induce high-density lipoprotein-mediated transhepatic cholesterol
efflux in mice and monkeys and prevent atherosclerosis in
cholesteryl ester transfer protein transgenic low-density
lipoprotein receptor (-/-) mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 343:556–567.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Yin L, Anderson J, Ma H, Gonzalez
FJ, Willson TM and Edwards PA: Identification of novel pathways
that control farnesoid X receptor-mediated hypocholesterolemia. J
Biol Chem. 285:3035–3043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Chong HK, Infante AM, Seo YK, Jeon TI,
Zhang Y, Edwards PA, Xie X and Osborne TF: Genome-wide
interrogation of hepatic FXR reveals an asymmetric IR-1 motif and
synergy with LRH-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:6007–6017. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chao F, Gong W, Zheng Y, Li Y, Huang G,
Gao M, Li J, Kuruba R, Gao X, Li S and He F: Upregulation of
scavenger receptor class B type I expression by activation of FXR
in hepatocyte. Atherosclerosis. 213:443–448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong B, Young M, Liu X, Singh AB and Liu
J: Regulation of lipid metabolism by obeticholic acid in
hyperlipidemic hamsters. J Lipid Res. 58:350–363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Repa JJ and Mangelsdorf DJ: The role of
orphan nuclear receptors in the regulation of cholesterol
homeostasis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 16:459–481. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Apfel R, Benbrook D, Lernhardt E, Ortiz
MA, Salbert G and Pfahl M: A novel orphan receptor specific for a
subset of thyroid hormone-responsive elements and its interaction
with the retinoid/thyroid hormone receptor subfamily. Mol Cell
Biol. 14:7025–7035. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jakobsson T, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA and
Steffensen KR: Liver X receptor biology and pharmacology: New
pathways, challenges and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
33:394–404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maxwell KN, Soccio RE, Duncan EM, Sehayek
E and Reslow JL: Novel putative SREBP and LXR target genes
identified by micro-array analysis in liver of cholesterol-fed
mice. J Lipid Res. 44:2109–2119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grefhorst A, Oosterveer MH, Brufau G,
Boesjes M, Kuipers F and Groen AK: Pharmacological LXR activation
reduces presence of SR-B1 in liver membranes contributing to
LXR-mediated induction of HDL-cholesterol. Atherosclerosis.
222:382–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B,
Haltmeier M, Klingenhoff A, Frisch M, Bayerlein M and Werner T:
MatInspector and beyond: Promoter analysis based on transcription
factor binding sites. Bioinformatics. 21:2933–2942. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cartharius K: MatInspector: Analysing
Promoters for Transcription Factor Binding Sites. The Nuts &
Bolts Series. DNA Press. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E
and Werner T: MatInd and MatInspector: New fast and versatile tools
for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 23:4878–4884. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Dong B, Park SW, Lee HS, Chen W and
Liu J: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha plays a critical role in
PCSK9 gene transcription and regulation by the natural
hypocholesterolemic compound berberine. J Biol Chem.
284:28885–28895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Malerød L, Juvet LK, Hanssen-Bauer A,
Eskild W and Berg T: Oxysterol-activated LXRalpha/RXR induces
hSR-BI-promoter activity in hepatoma cells and preadipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 299:916–923. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong B, Kan CF, Singh AB and Liu J:
High-fructose diet down-regulates long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 3
expression in liver of hamsters via impairing LXR/RXR signaling
pathway. J Lipid Res. 54:1241–1254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schuetz EG, Strom S, Yasuda K, Lecureur V,
Assem M, Brimer C, Lamba J, Kim RB, Ramachandran V, Komoroski BJ,
et al: Disrupted bile acid homeostasis reveals an unexpected
interaction among nuclear hormone receptors, transporters, and
cytochrome P450. J Biol Chem. 276:39411–39418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schultz JR, Tu H, Luk A, Repa JJ, Medina
JC, Li L, Schwendner S, Wang S, Thoolen M, Mangelsdorf DJ, et al:
Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 14:2831–2838.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ding L, Pang S, Sun Y, Tian Y, Yu L and
Dang N: Coordinated actions of FXR and LXR in metabolism: From
pathogenesis to pharmacological targets for type 2 diabetes. Int J
Endocrinol. 2014:7518592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu TT, Makishima M, Repa JJ, Schoonjans K,
Kerr TA, Auwerx J and Mangelsdorf DJ: Molecular basis for feedback
regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol Cell.
6:507–515. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsukuma KE, Bennett MK, Huang J, Wang L,
Gil G and Osborne TF: Coordinated control of bile acids and
lipogenesis through FXR-dependent regulation of fatty acid
synthase. J Lipid Res. 47:2754–2761. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peet DJ, Turley SD, Ma W, Janowski BA,
Lobaccaro JM, Hammer RE and Mangelsdorf DJ: Cholesterol and bile
acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol
receptor LXR alpha. Cell. 93:693–704. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Malerød L, Sporstøl M, Juvet LK, Mousavi
A, Gjøen T and Berg T: Hepatic scavenger receptor class B, type I
is stimulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
305:557–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schoonjans K, Annicotte JS, Huby T,
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Ueda Y, Chapman J and Auwerx J: Liver
receptor homolog 1 controls the expression of the scavenger
receptor class B type I. EMBO Rep. 3:1181–1187. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|