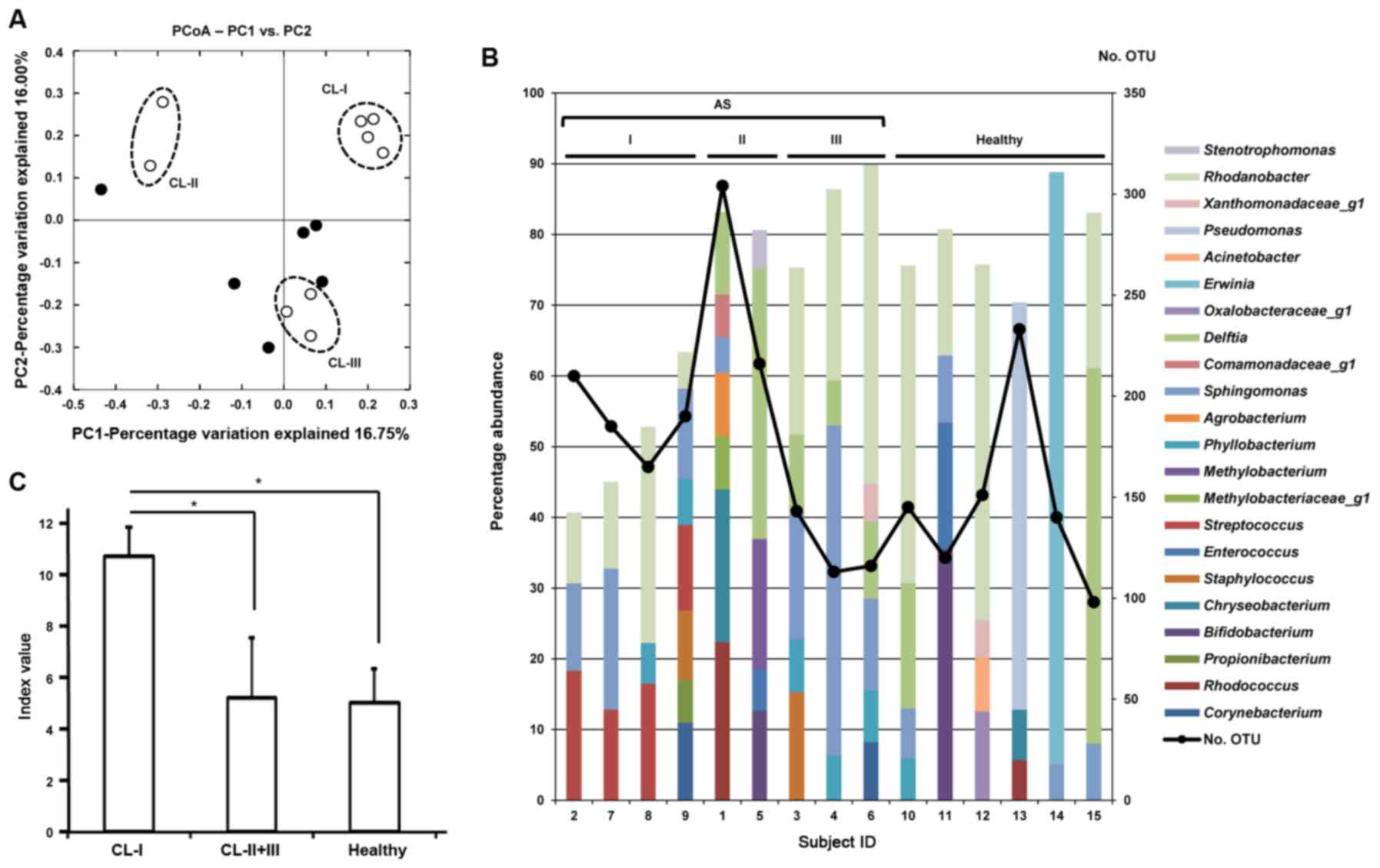
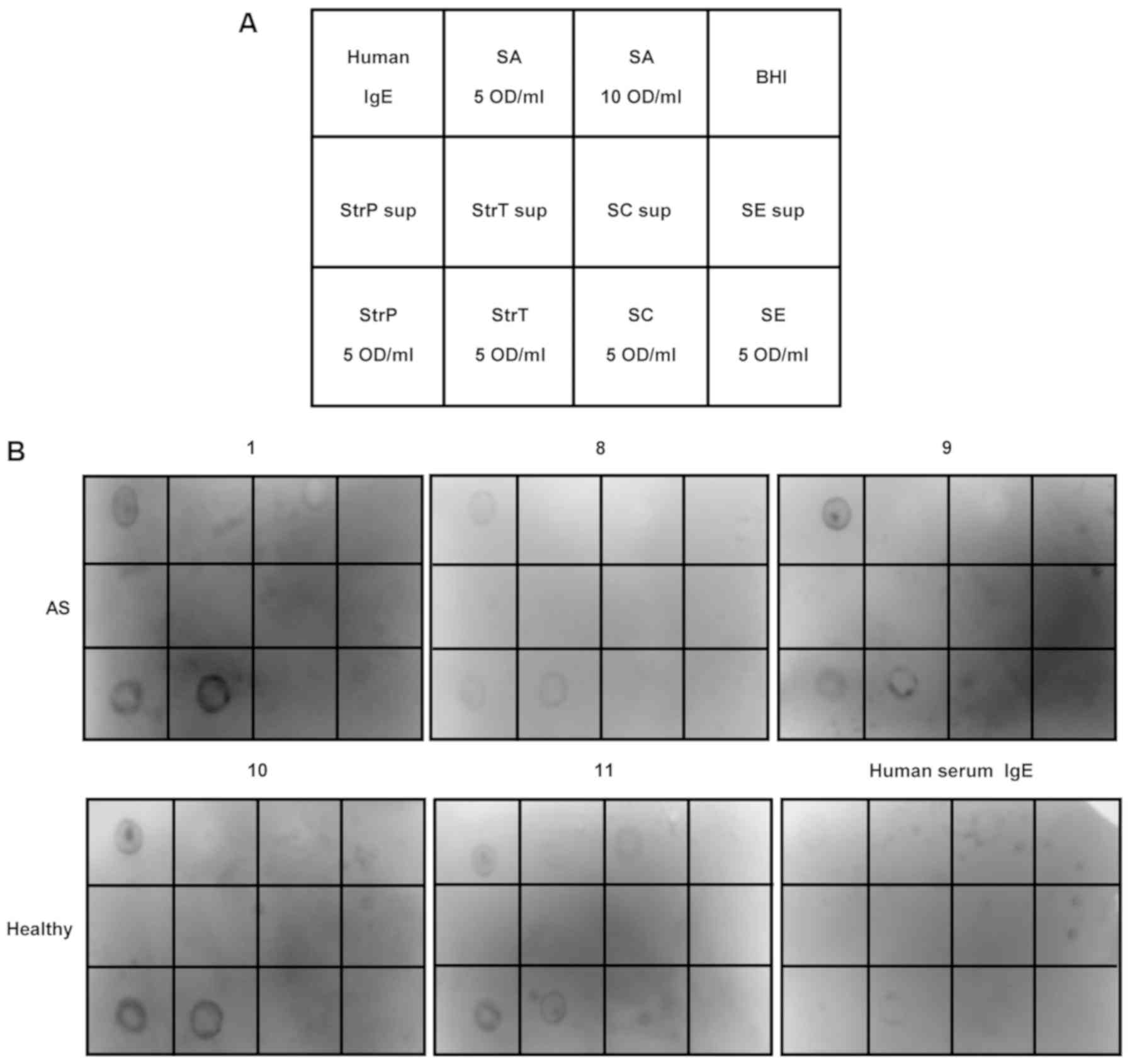
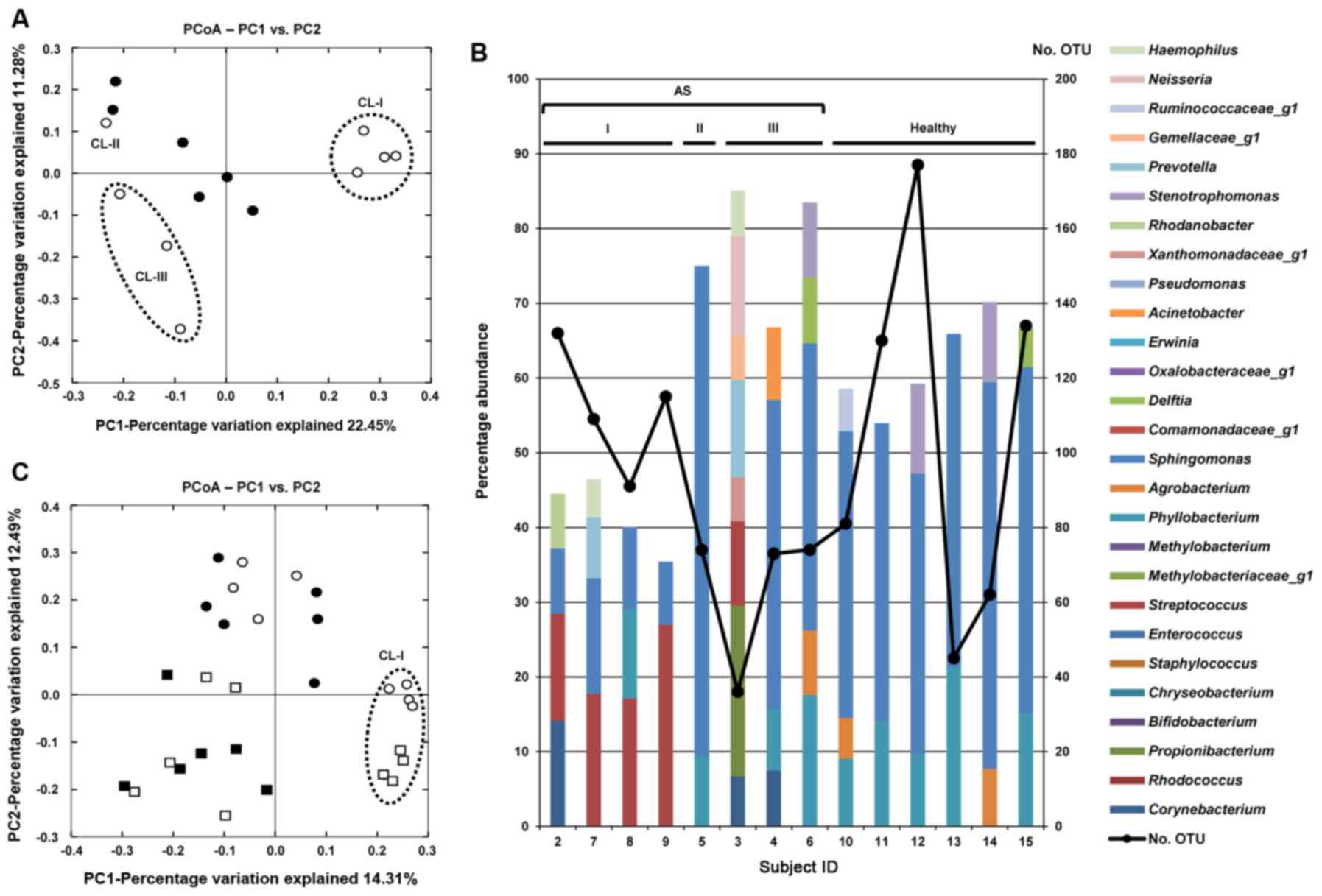
|
1
|
Skotnitsky CC, Naduvilath TJ, Sweeney DF
and Sankaridurg PR: Two presentations of contact lens-induced
papillary conjunctivitis (CLPC) in hydrogel lens wear: Local and
general. Optom Vis Sci. 83:27–36. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Solomon A: Allergic manifestations of
contact lens wearing. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 16:492–497.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan ME, Demirci G, Pearce D, Jalbert I,
Sankaridurg P and Willcox MD: Contact lens-induced papillary
conjunctivitis is associated with increased albumin deposits on
extended wear hydrogel lenses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 506:951–955. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tagliaferri A, Love TE and Szczotka-Flynn
LB: Risk factors for contact lens-induced papillary conjunctivitis
associated with silicone hydrogel contact lens wear. Eye Contact
Lens. 40:117–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shin H, Price K, Albert L, Dodick J, Park
L and Dominguez-Bello MG: Changes in the eye microbiota associated
with contact lens wearing. MBio. 7:e001982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amann RI, Ludwig W and Schleifer KH:
Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of indivisual
microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev. 59:143–169.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Human Microbiome Project Consortium:
Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome.
Nature. 486:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahmed S, Macfarlane GT, Fite A, McBain AJ,
Gilbert P and Macfarlane S: Mucosa-associated bacterial diversity
in relation to human terminal ileum and colonic biopsy samples.
Appl Environ Microbiol. 73:7435–7442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grice EA, Kong HH, Renaud G, Young AC;
NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Bouffard GG, Blakesley RW,
Wolfsberg TG, Turner ML and Segre JA: A diversity profile of the
human skin microbiota. Genome Res. 18:1043–1050. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dong Q, Brulc JM, Iovieno A, Bates B,
Garoutte A, Miller D, Revanna KV, Gao X, Antonopoulos DA, Slepak VZ
and Shestopalov VI: Diversity of bacteria at healthy human
conjunctiva. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:5408–5413. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eguchi H, Hotta F, Kuwahara T, Imaohji H,
Miyazaki C, Hirose M, Kusaka S, Fukuda M and Shimomura Y:
Diagnostic approach to ocular infections using various techniques
from conventional culture to next-generation sequencing analysis.
Cornea. 36(Suppl 1): S46–S52. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang Y, Yang B and Li W: Defining the
normal core micro-biome of conjunctival microbial communities. Clin
Microbiol Infect. 22:643.e7–643.e12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bakhtiar SM, LeBlanc JG, Salvucci E, Ali
A, Martin R, Langella P, Chatel JM, Miyoshi A, Bermúdez-Humarán LG
and Azevedo V: Implications of the human microbiome in inflammatory
bowel diseases. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 342:10–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini
V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI: An obesity-associated gut microbiome
with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 444:1027–1031.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiacchierini E, Restuccia D and Vinci G:
Evaluation of two different extraction methods for chromatographic
determination of bioactive amines in tomato products. Talanta.
69:548–555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Morita H, Kuwahara T, Ohshima K, Sasamoto
H, Itoh K, Hattori M, Hayashi T and Takami H: An improved DNA
isolation method for metagenomic analysis of the microbial flora of
the human intestine. Microbes Environ. 22:214–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T,
Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M and Glöckner FO: Evaluation of general
16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and
next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:e12013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Aronesty E: Comparison of sequencing
utility programs. Open Bioinformatics J. 7:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Navas-Molina JA, Peralta-Sánchez JM,
González A, McMurdie PJ, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Xu Z, Ursell LK, Lauber
C, Zhou H, Song SJ, et al: Advancing our understanding of the human
microbiome using QIIME. Methods Enzymol. 531:371–444. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Edgar RC: Search and clustering orders of
magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 26:2460–2461. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use soft-ware 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dantam J, McCanna DJ, Subbaraman LN,
Papinski D, Lakkis C, Mirza A, Berntsen DA, Morgan P, Nichols JJ
and Jones LW: Microbial contamination of contact lens storage cases
during daily wear use. Optom Vis Sci. 93:925–932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boost MV and Cho P: Microbial flora of
tears of orthokeratology patients, and microbial contamination of
contact lenses and contact lens accessories. Optom Vis Sci.
82:451–458. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yung MS, Boost M, Cho P and Yap M:
Microbial contamination of contact lenses and lens care accessories
of soft contact lens wearers (university students) in Hong Kong.
Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 27:11–21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Willcox MD, Power KN, Stapleton F, Leitch
C, Harmis N and Sweeney DF: Potential sources of bacteria that are
isolated from contact lenses during wear. Optom Vis Sci.
74:1030–1038. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu YT, Zhu H, Harmis NY, Iskandar SY,
Willcox M and Stapleton F: Profile and frequency of microbial
contamination of contact lens cases. Optom Vis Sci. 87:E152–E158.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Willcox MD, Carnt N, Diec J, Naduvilath T,
Evans V, Stapleton F, Iskandar S, Harmis N, de la Jara PL and
Holden BA: Contact lens case contamination during daily wear of
silicone hydrogels. Optom Vis Sci. 87:456–464. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McLaughlin-Borlace L, Stapleton F,
Matheson M and Dart JK: Bacterial biofilm on contact lenses and
lens storage cases in wearers with microbial keratitis. J Appl
Microbiol. 84:827–838. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Staley JT and Konopka A: Measurement of in
situ activities of nonphotosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic and
terrestrial habitats. Annu Rev Microbiol. 39:321–346. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eguchi H, Hotta F, Kuwahara T,
Nakayama-Imaohji H, Kusaka S and Shimomura Y: Acute
keratoconjunctivitis due to contamination of contact lens care
solution with histamine-producing Raoultella species. A case
report. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e93102017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Nichols KK: Patient-reported symptoms in
dry eye disease. Ocul Surf. 4:137–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Belmonte C: Pain, dryness, and itch
sensations in eye surface disorders are defined by a balance
between inflammation and sensory nerve injury. Cornea. 38(Suppl 1):
S11–S24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stapleton F, Stretton S, Sankaridurg PR,
Chandoha H and Shovlin J: Hypersensitivity responses and contact
lens wear. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 26:57–69. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhao Z, Fu H, Skotnitsky CC, Sankaridurg
PR and Willcox MD: IgE antibody on worn highly oxygen-permeable
silicone hydrogel contact lenses from patients with contact
lens-induced papillary conjunctivitis (CLPC). Eye Contact Lens.
34:117–121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barishak Y, Zavaro A, Samra Z and
Sompolinsky D: An immunological study of papillary conjunctivitis
due to contact lenses. Curr Eye Res. 3:1161–1168. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bisgaard H, Hermansen MN, Buchvald F,
Loland L, Halkjaer LB, Bønnelykke K, Brasholt M, Heltberg A,
Vissing NH, Thorsen SV, et al: Childhood asthma after bacterial
colonization of the airway in neonates. N Engl J Med.
357:1487–1495. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jounio U, Juvonen R, Bloigu A,
Silvennoinen-Kassinen S, Kaijalainen T, Kauma H, Peitso A,
Saukkoriipi A, Vainio O, Harju T and Leinonen M: Pneumococcal
carriage is more common in asthmatic than in non-asthmatic young
men. Clin Respir J. 4:222–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Teo SM, Mok D, Pham K, Kusel M, Serralha
M, Troy N, Holt BJ, Hales BJ, Walker ML, Hollams E, et al: The
infant airway micro-biome in health and disease impacts later
asthma development. Cell Host Microbe. 17:704–715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Q, Cox M, Liang Z, Brinkmann F,
Cardenas PA, Duff R, Bhavsar P, Cookson W, Moffatt M and Chung KF:
Airway microbiota in severe asthma and relationship to asthma
severity and phenotypes. PLoS One. 11:e01527242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kloepfer KM, Lee WM, Pappas TE, Kang TJ,
Vrtis RF, Evans MD, Gangnon RE, Bochkov YA, Jackson DJ, Lemanske RF
Jr, et al: Detection of pathogenic bacteria during rhinovirus
infection is associated with increased respiratory symptoms and
exacerbations of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 133:1301–1307.
e1–e3. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Green BJ, Wiriyachaiporn S, Grainge C,
Rogers GB, Kehagia V, Lau L, Carroll MP, Bruce KD and Howarth PH:
Potentially pathogenic airway bacteria and neutrophilic
inflammation in treatment resistant severe asthma. PLoS One.
9:e1006452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weisenseel P and Prinz JC: Incidental
detection of S. pyogenes-DNA in psoriatic skin by PCR. Arch
Dermatol Res. 296:573–576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Valdimarsson H, Thorleifsdottir RH,
Sigurdardottir SL, Gudjonsson JE and Johnston A: Psoriasis-as an
autoimmune disease caused by molecular mimicry. Trends Immunol.
30:494–501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Prinz JC: Psoriasis vulgaris-a sterile
antibacterial skin reaction mediated by cross-reactive T cells? An
immunological view of the pathophysiology of psoriasis. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 26:326–332. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gudjonsson JE, Thorarinsson AM,
Sigurgeirsson B, Kristinsson KG and Valdimarsson H: Streptococcal
throat infections and exacerbation of chronic plaque psoriasis: A
prospective study. Br J Dermatol. 149:530–534. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gray TB, Cursons RT, Sherwan JF and Rose
PR: Acanthamoeba, bacterial, and fungal contamination of contact
lens storage cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 79:601–605. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Devonshire P, Munro FA, Abernethy C and
Clark BJ: Microbial contamination of contact lens cases in the west
of Scotland. Br J Ophthalmol. 77:41–45. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|