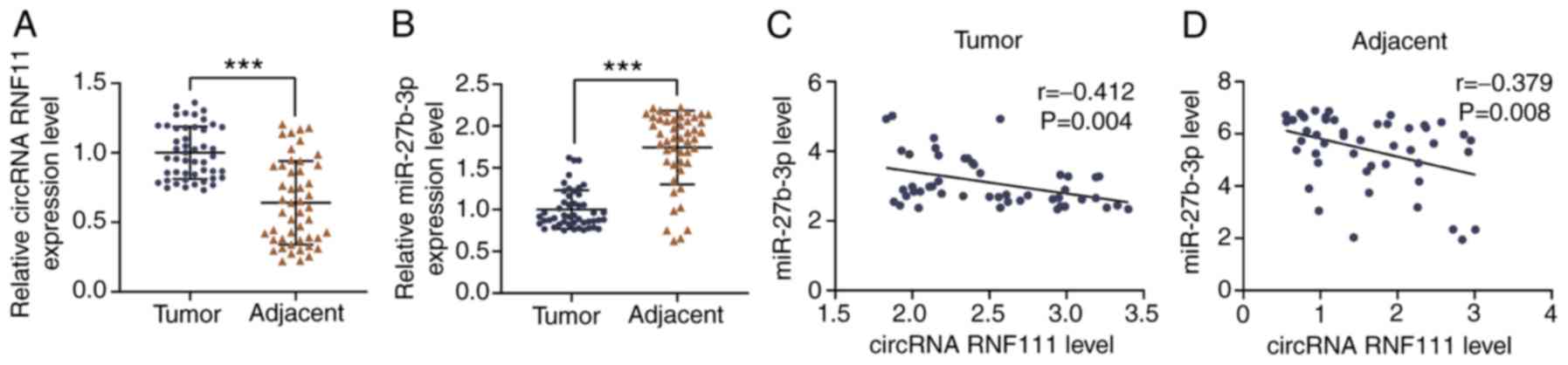
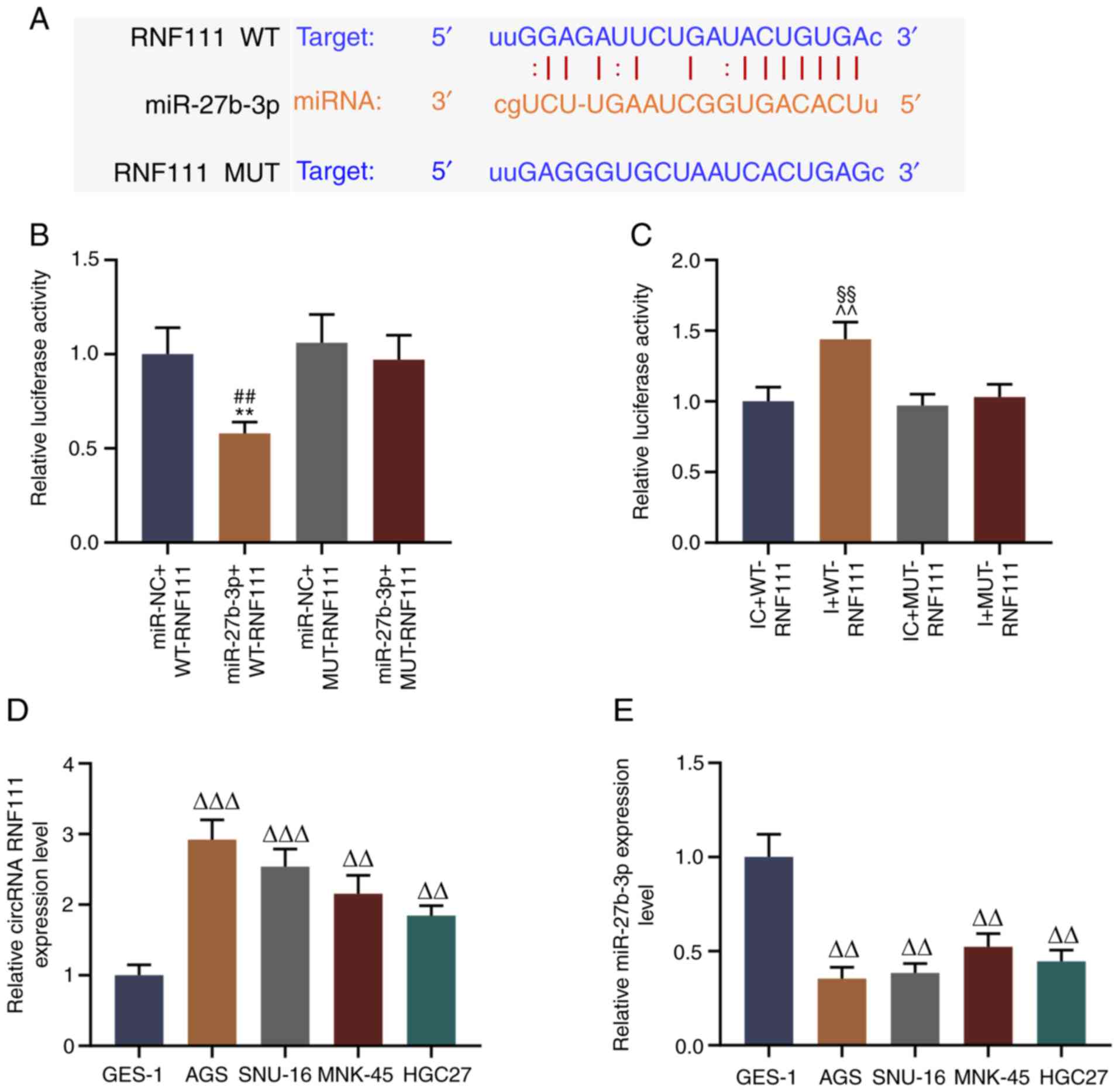
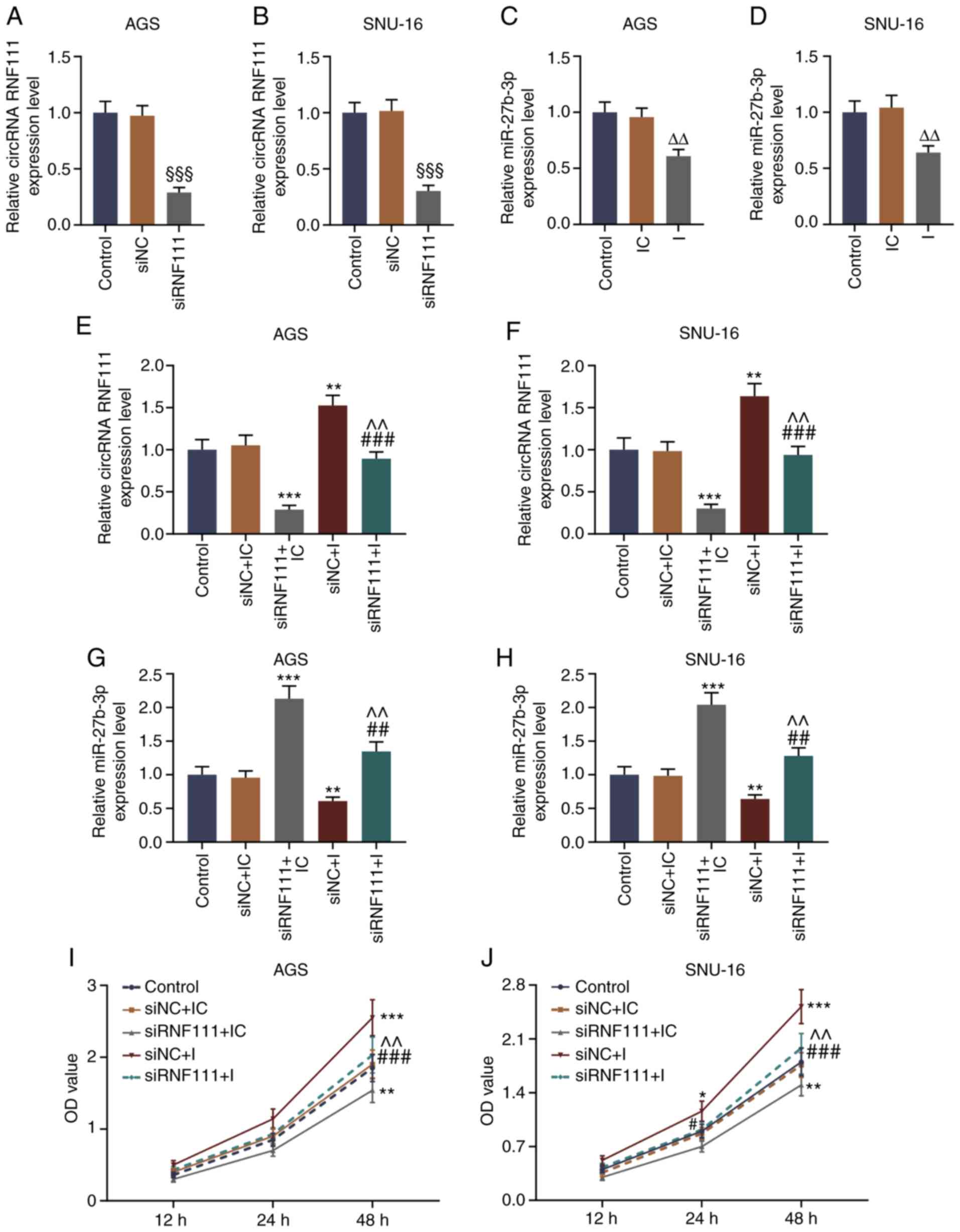
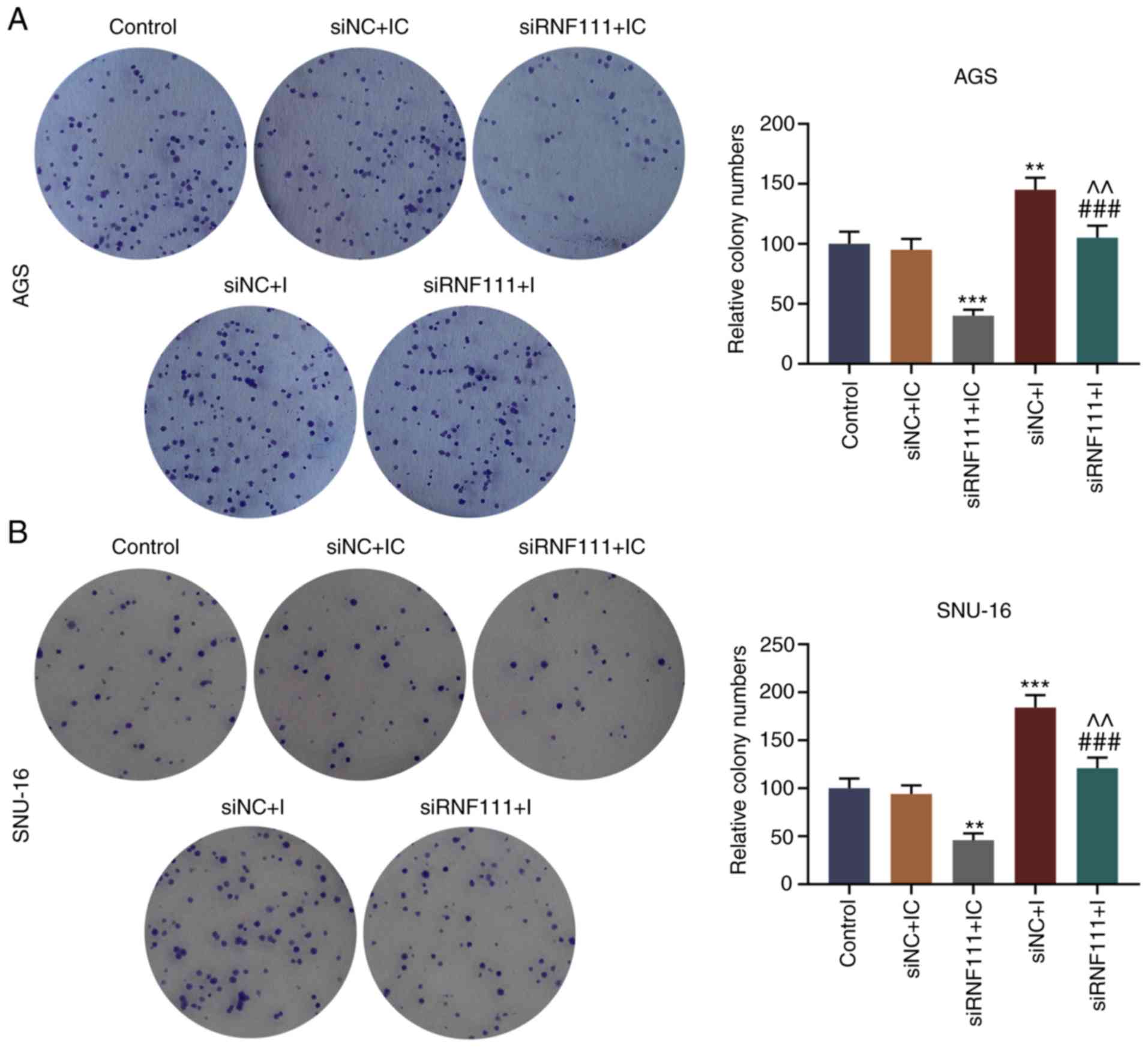
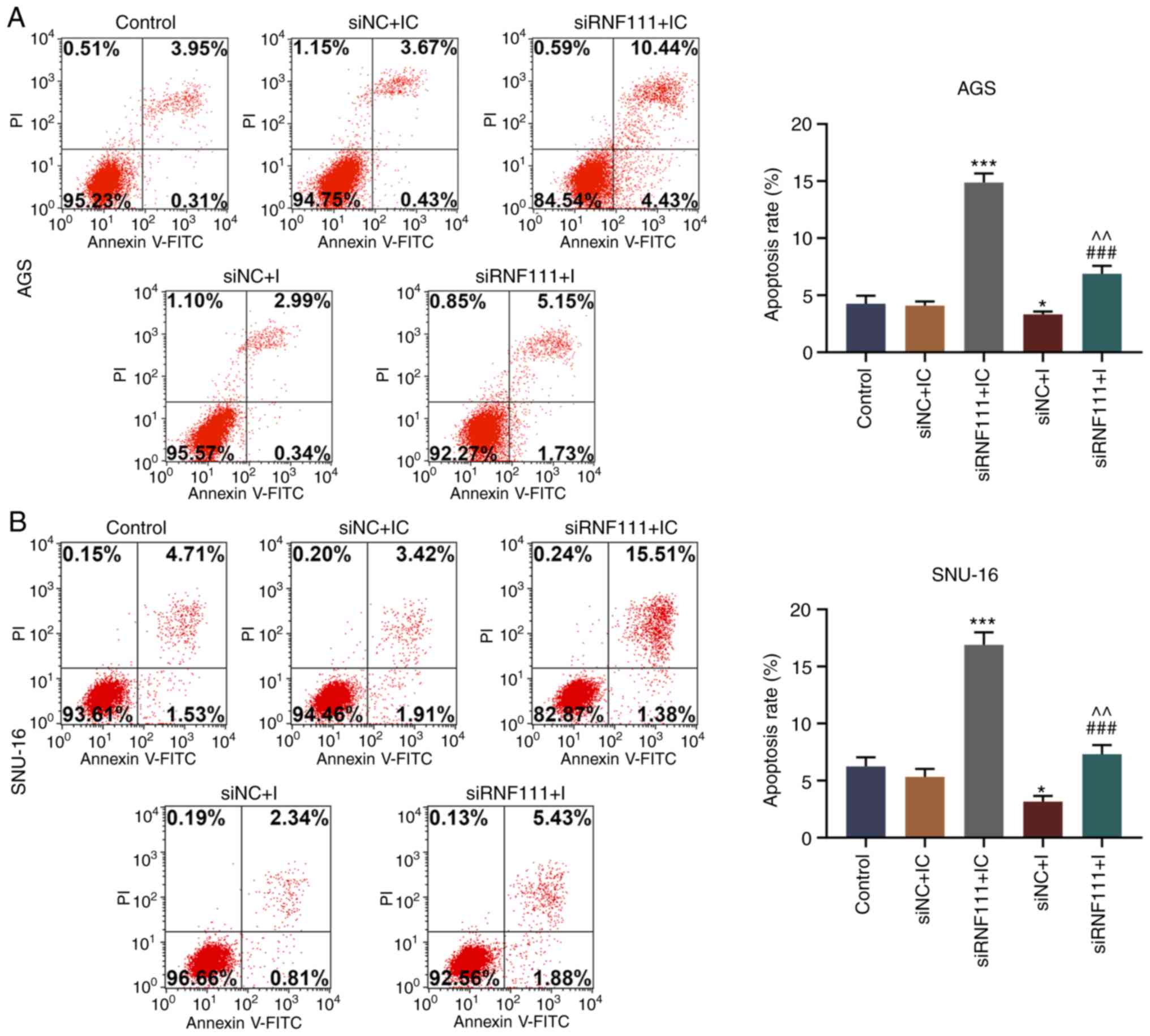
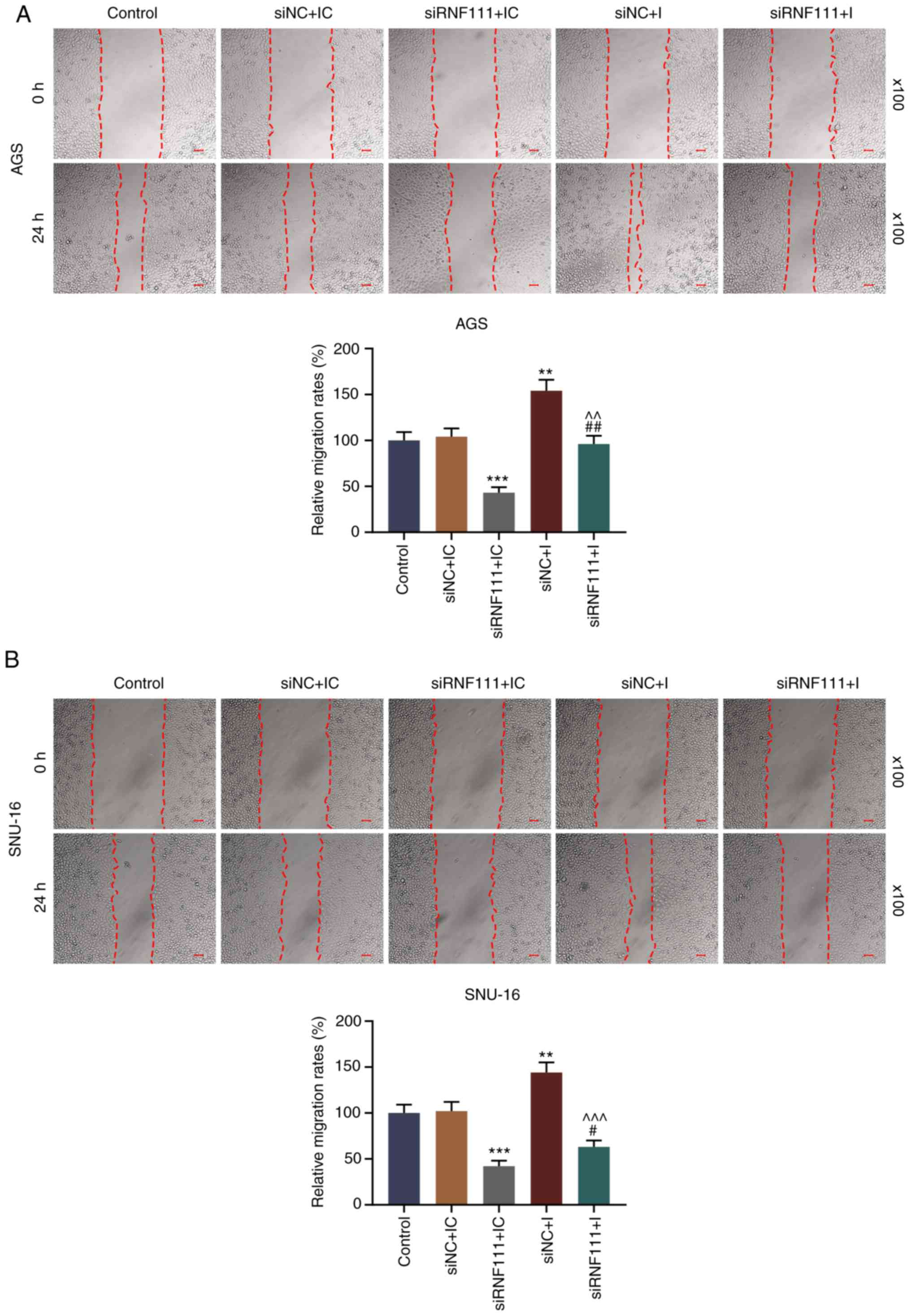
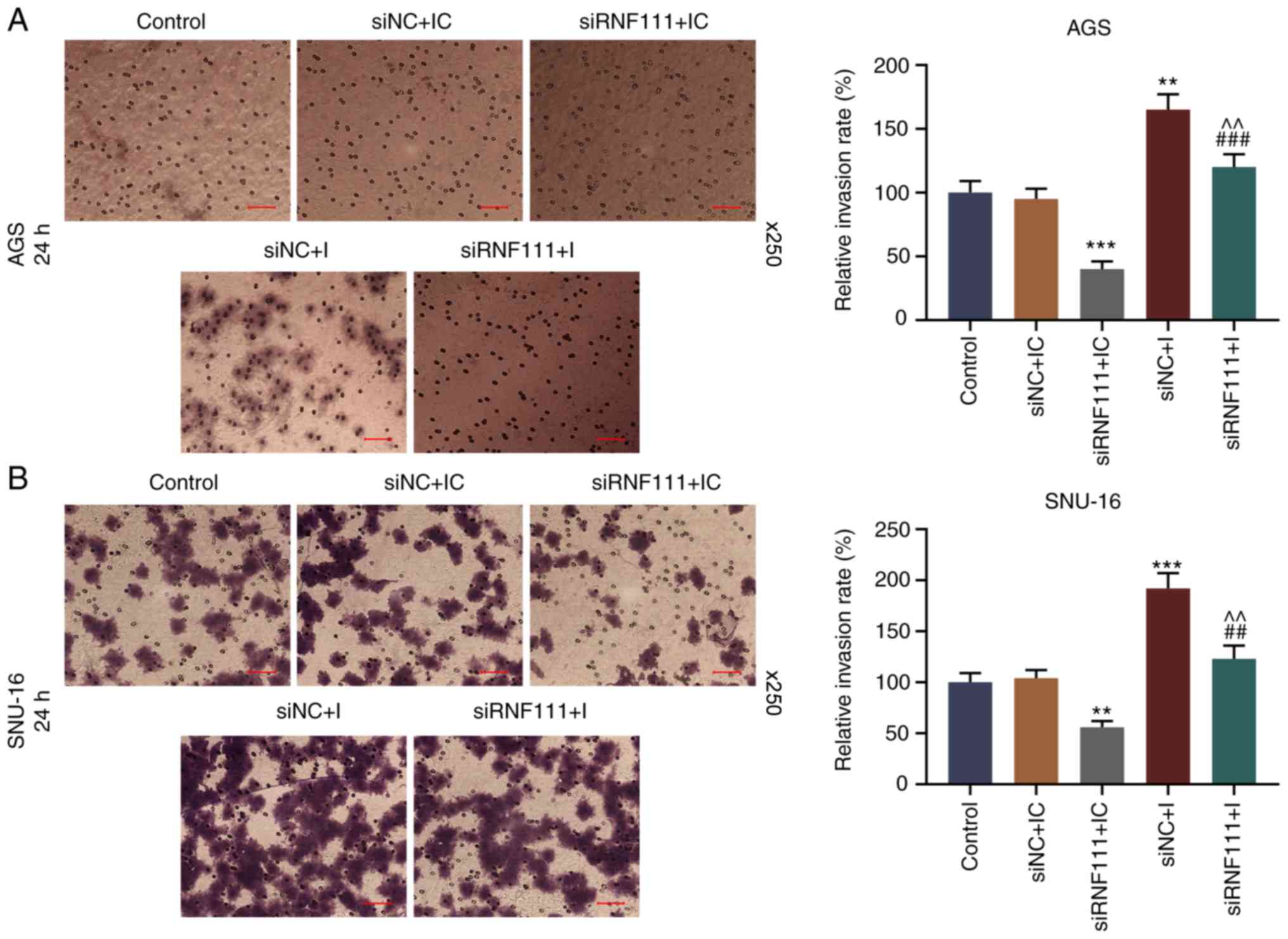
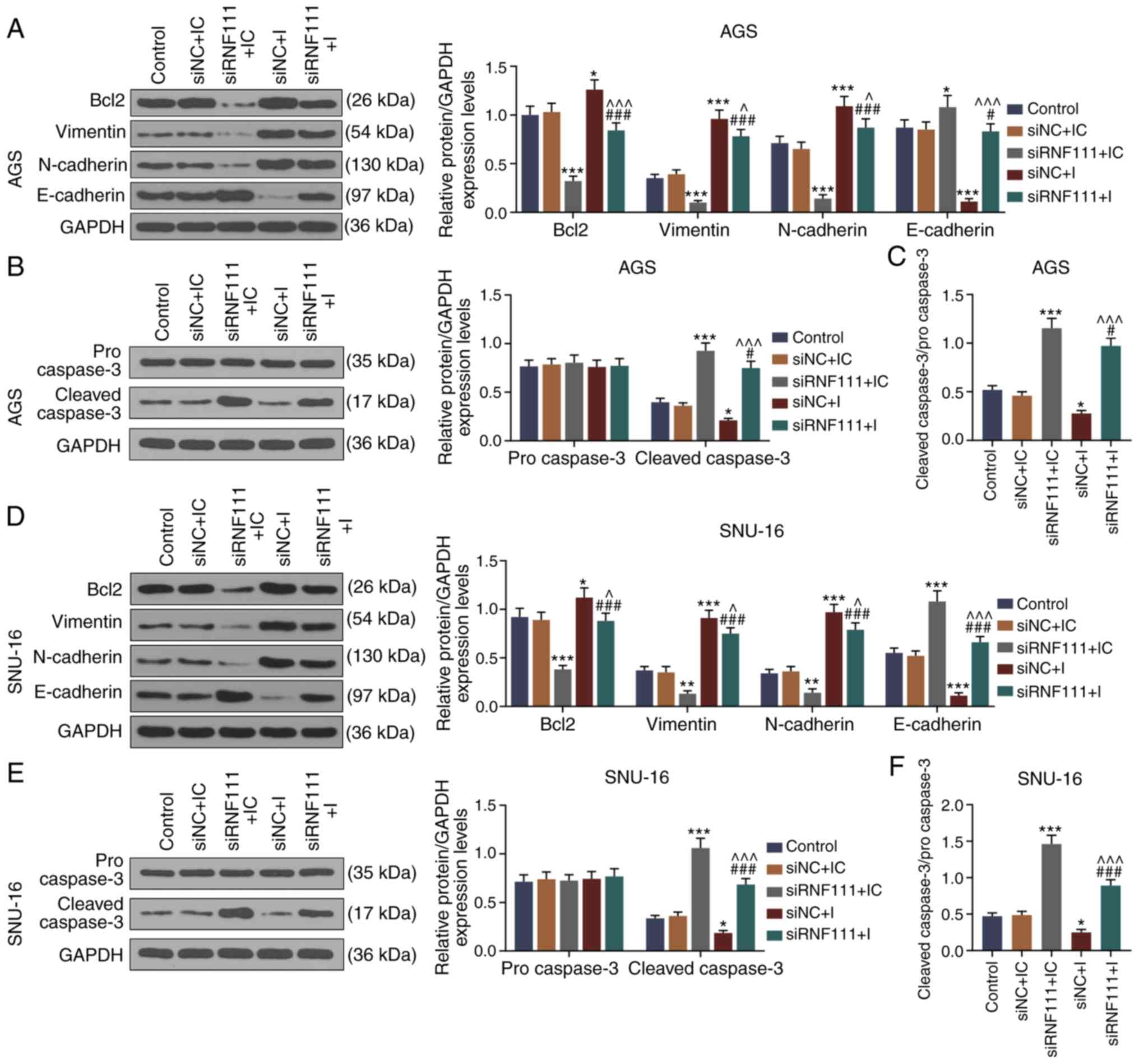
|
1
|
Correa P: Gastric cancer: Overview.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 42:211–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S,
Freedman ND and Kamangar F: Gastric cancer: Descriptive
epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:700–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ang TL and Fock KM: Clinical epidemiology
of gastric cancer. Singapore Med J. 55:621–628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sano T: Gastric cancer: Asia and the
world. Gastric Cancer. 20(Suppl 1): S1–S2. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function
and role in human diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Patop IL and Kadener S: circRNAs in
cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 48:121–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Rong D, Sun H, Li Z, Liu S, Dong C, Fu K,
Tang W and Cao H: An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis
in human diseases. Oncotarget. 8:73271–73281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong Z, Huang M, Lv M, He Y, Duan C,
Zhang L and Chen J: Circular RNA MYLK as a competing endogenous RNA
promotes bladder cancer progression through modulating VEGFA/VEGFR2
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 403:305–317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR,
Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N and
Kadener S: circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 56:55–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y,
Qian C, Lin Y, Liu X, Huang M, et al: Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as
the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. . Hepatology. 66:1151–1164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Lin RC and McMullen
JR: miRNA therapeutics: A new class of drugs with potential
therapeutic applications in the heart. Future Med Chem.
7:1771–1792. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shin VY and Chu KM: MiRNA as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10432–10439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang YY, Zhao P, Zou TN, Duan JJ, Zhi R,
Yang SY, Yang DC and Wang XL: Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001982
promotes breast cancer cell carcinogenesis through decreasing
miR-143. DNA Cell Biol. 36:901–908. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fang Q, Chen X and Zhi X: Long non-coding
RNA (LncRNA) urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1) increases
multi-drug resistance of gastric cancer via downregulating miR-27b.
Med Sci Monit. 22:3506–3513. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh C and Roy-Chowdhuri S: Quantitative
real-time PCR: Recent advances. Methods Mol Biol. 1392:161–176.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Western
blotting: An introduction. Methods Mol Biol. 1312:17–30. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Röcken C: Molecular classification of
gastric cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 17:293–301. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Patop IL, Wüst S and Kadener S: Past,
present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 38:e1008362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Liu H, Li W, Yu J, Li J, Shen Z,
Ye G, Qi X and Li G: CircRNA_100269 is downregulated in gastric
cancer and suppresses tumor cell growth by targeting miR-630. Aging
(Albany NY). 9:1585–1594. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tang W, Fu K, Sun H, Rong D, Wang H and
Cao H: CircRNA microarray profiling identifies a novel circulating
biomarker for detection of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:1372018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shao Y, Li J, Lu R, Li T, Yang Y, Xiao B
and Guo J: Global circular RNA expression profile of human gastric
cancer and its clinical significance. Cancer Med. 6:1173–1180.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li P, Chen S, Chen H, Mo X, Li T, Shao Y,
Xiao B and Guo J: Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker
in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 444:132–136.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, He J, Chen
B, Lyu D, Zheng B, Xu Y, Long Z, et al: Circular RNA profile
identifies circPVT1 as a proliferative factor and prognostic marker
in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 388:208–219. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Arnaiz E, Sole C, Manterola L,
Iparraguirre L, Otaegui D and Lawrie CH: CircRNAs and cancer:
Biomarkers and master regulators. Semin Cancer Biol. 58:90–99.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen
B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al: Circular RNA profiling reveals
an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging
multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 7:112152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sui W, Shi Z, Xue W, Ou M, Zhu Y, Chen J,
Lin H, Liu F and Dai Y: Circular RNA and gene expression profiles
in gastric cancer based on microarray chip technology. Oncol Rep.
37:1804–1814. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tao J, Zhi X, Zhang X, Fu M, Huang H, Fan
Y, Guan W and Zou C: miR-27b-3p suppresses cell proliferation
through targeting receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1
in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun Y, Xu T, Cao YW and Ding XQ: Antitumor
effect of miR-27b-3p on lung cancer cells via targeting Fzd7. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:4113–4123. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hedrick E, Mohankumar K and Safe S:
TGFβ-induced lung cancer cell migration is NR4A1-dependent. Mol
Cancer Res. 16:1991–2002. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen H, Yang T, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H,
Tong X, Yang WT, Zhao J, Gu Y, Chen Y and Zhang HT: RNF111/Arkadia
is regulated by DNA methylation and affects TGF-β/Smad signaling
associated invasion in NSCLC cells. Lung Cancer. 90:32–40. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma V, Antonacopoulou AG, Tanaka S,
Panoutsopoulos AA, Bravou V, Kalofonos HP and Episkopou V:
Enhancement of TGF-β signaling responses by the E3 ubiquitin ligase
arkadia provides tumor suppression in colorectal cancer. Cancer
Res. 71:6438–6449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK,
Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF and Sharpless NE: Circular RNAs are
abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA.
19:141–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL and
Brown PO: Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression.
PLoS Genet. 9:e10037772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P,
Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss
R, et al: Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant,
conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 58:870–885. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maass PG, Glažar P, Memczak S, Dittmar G,
Hollfinger I, Schreyer L, Sauer AV, Toka O, Aiuti A, Luft FC and
Rajewsky N: A map of human circular RNAs in clinically relevant
tissues. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:1179–1189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li H, Lv B, Kong L, Xia J, Zhu M, Hu L,
Zhen D, Wu Y, Jia X, Zhu S and Cui H: Nova1 mediates resistance of
rat pheochromocytoma cells to hypoxia-induced apoptosis via the
Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 40:1125–1133. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Petrova YI, Schecterson L and Gumbiner BM:
Roles for E-cadherin cell surface regulation in cancer. Mol Biol
Cell. 27:3233–3244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Derycke LD and Bracke ME: N-cadherin in
the spotlight of cell-cell adhesion, differentiation,
embryogenesis, invasion and signalling. Int J Dev Biol. 48:463–476.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|