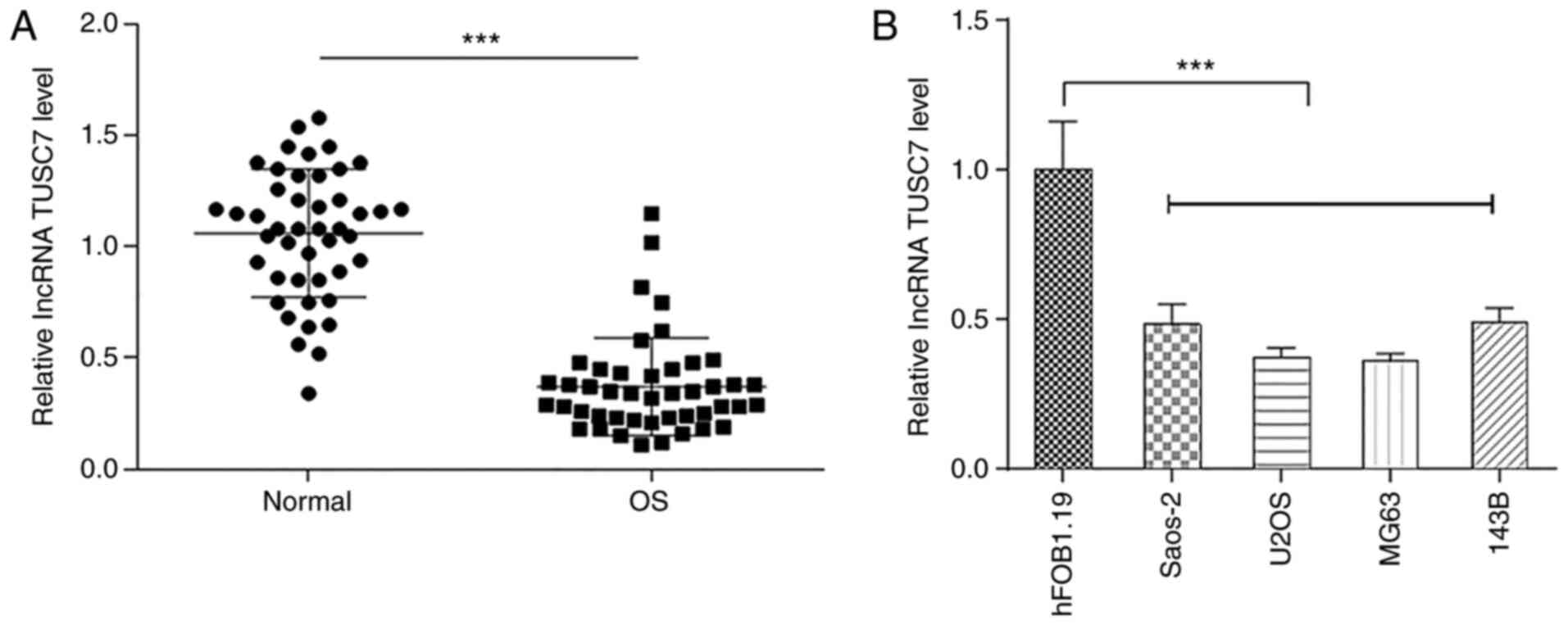
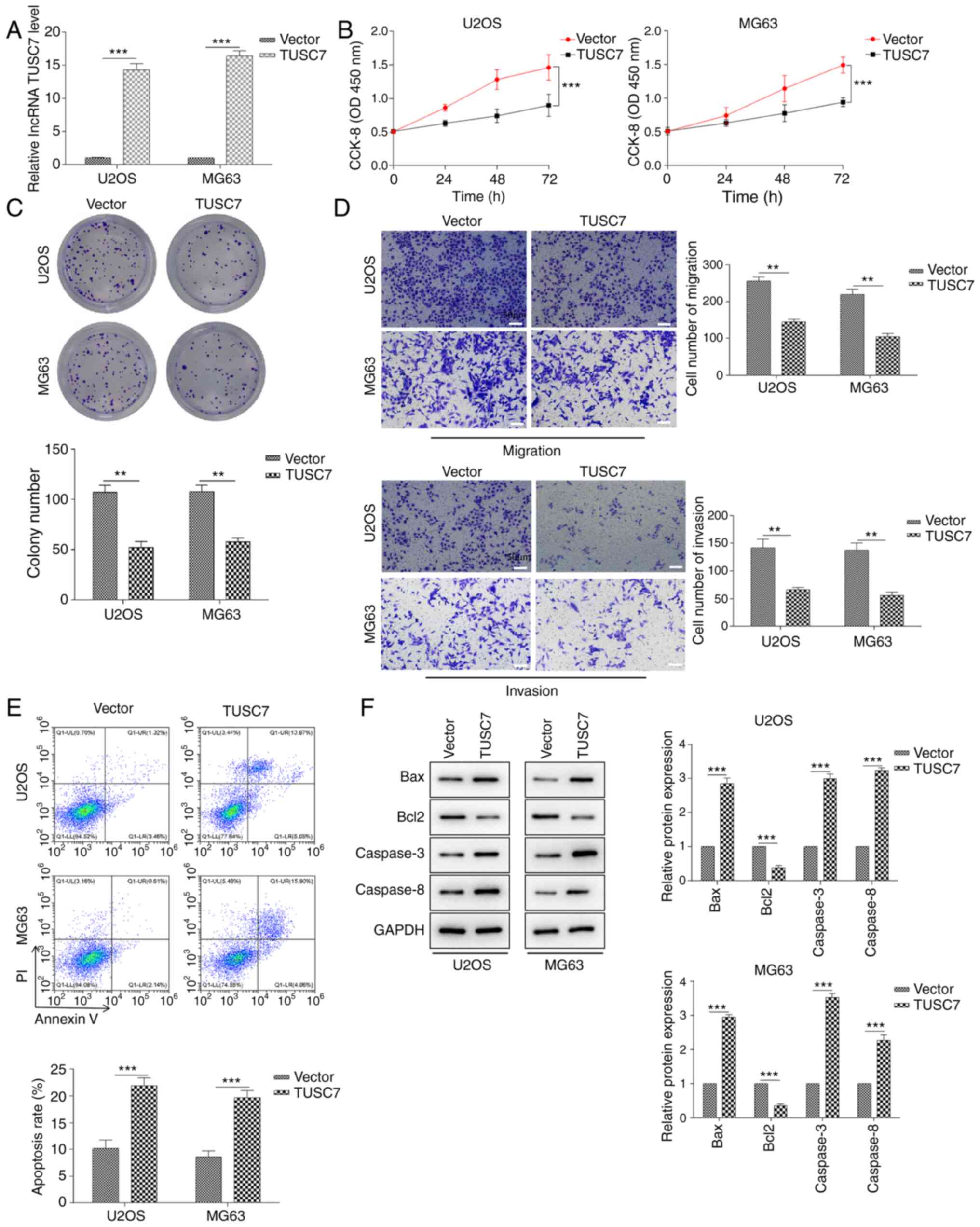
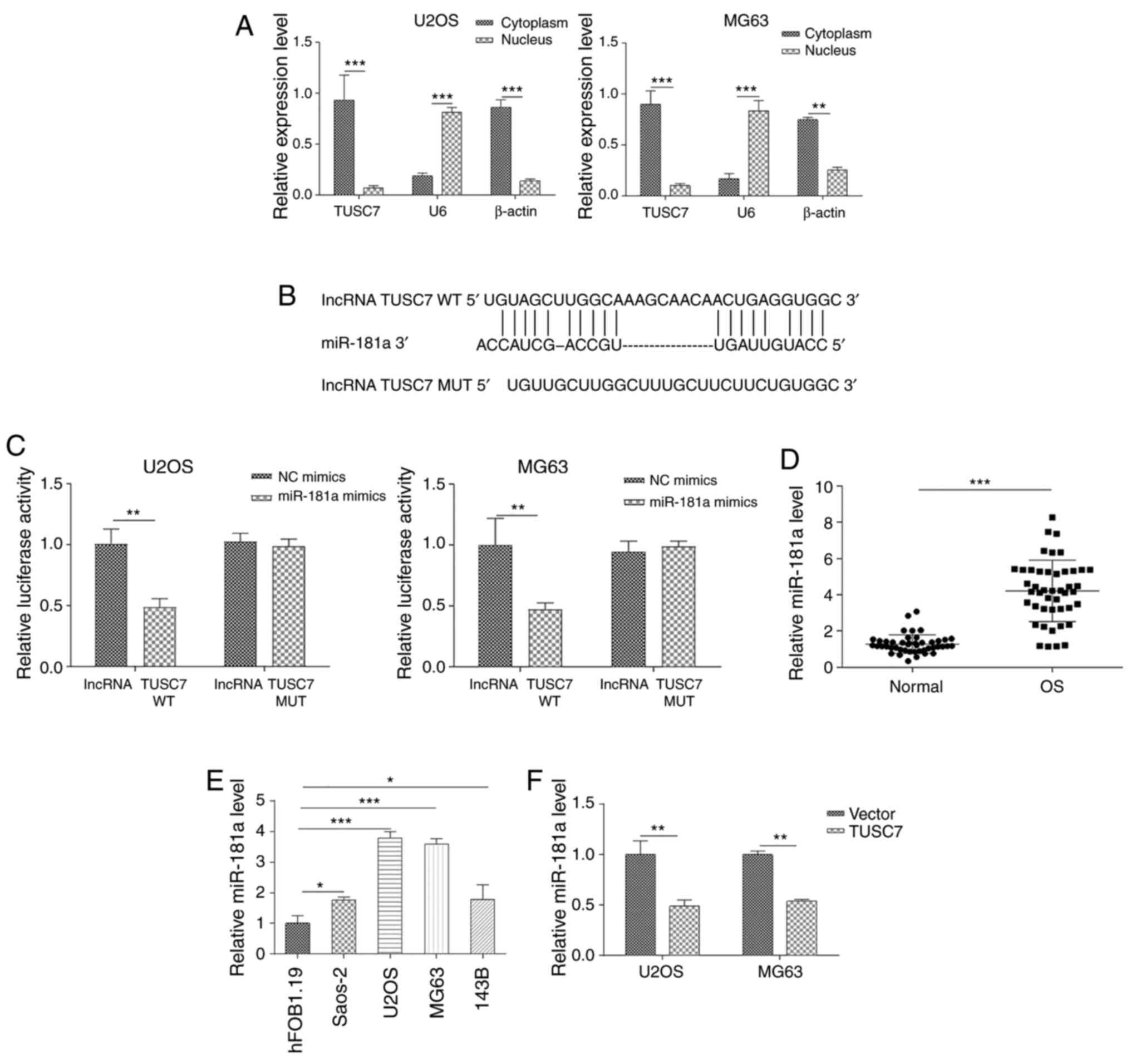
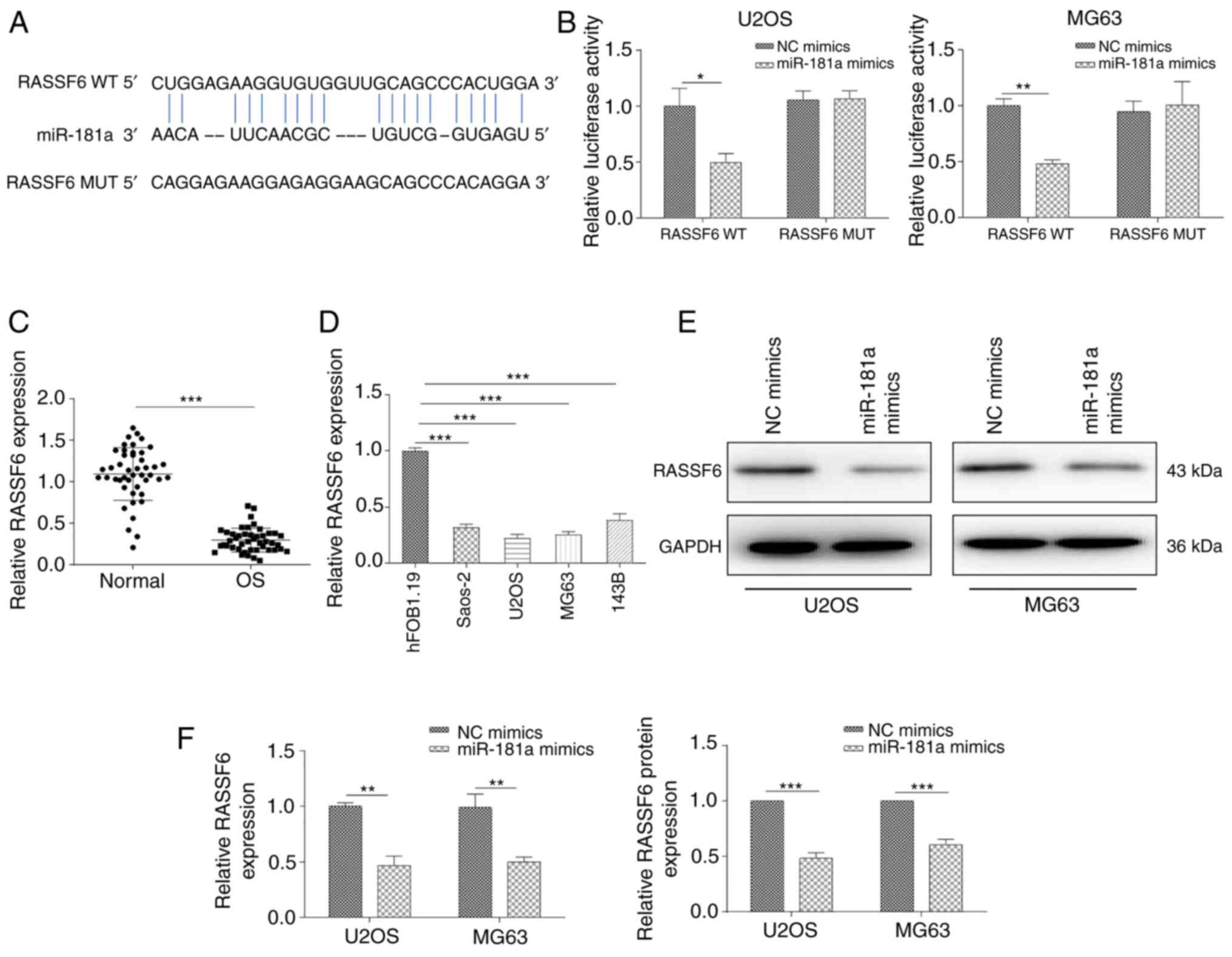
|
1
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P and
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: Current treatment and a collaborative
pathway to success. J Clin Oncol. 33:3029–3035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iwamoto Y, Tanaka K, Isu K, Kawai A,
Tatezaki S, Ishii T, Kushida K, Beppu Y, Usui M, Tateishi A, et al:
Multiinstitutional phase II study of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
osteosarcoma (NECO study) in Japan: NECO-93J and NECO-95J. J Orthop
Sci. 14:397–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou W, Hao M, Du X, Chen K, Wang G and
Yang J: Advances in targeted therapy for osteosarcoma. Discov Med.
17:301–307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Simpson S, Dunning MD, de Brot S,
Grau-Roma L, Mongan NP and Rutland CS: Comparative review of human
and canine osteosarcoma: Morphology, epidemiology, prognosis,
treatment and genetics. Acta Vet Scand. 59:712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP and
Pauler FM: Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA
transcription. BMC Biol. 11:592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Yu X and Shen J: Long non-coding
RNAs: Emerging players in osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 37:2811–2816.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu S, Gong Y, Yin Y, Xing H and Zhang N:
The multiple function of long noncoding RNAs in osteosarcoma
progression, drug resistance and prognosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
127:1101412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim LJ, Wong SYS, Huang F, Lim S, Chong
SS, Ooi LL, Kon OL and Lee CG: Roles and regulation of long
noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
79:5131–5139. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu KP, Ma XL and Zhang CL: LncRNA ODRUL
contributes to osteosarcoma progression through the miR-3182/MMP2
axis. Mol Ther. 25:2383–2393. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qu Z and Li S: Long noncoding RNA
LINC01278 favors the progression of osteosarcoma via modulating
miR-133a-3p/PTHR1 signaling. J Cell Physiol. Jan 29–2020.Epub ahead
of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Zhang C and Wang X: Long noncoding
RNA DLEU1 aggravates osteosarcoma carcinogenesis via regulating the
miR-671-5p/DDX5 axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:3322–3328.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren W, Chen S, Liu G, Wang X, Ye H and Xi
Y: TUSC7 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Am J
Transl Res. 9:4026–4035. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yue L and Guo J: LncRNA TUSC7 suppresses
pancreatic carcinoma progression by modulating miR-371a-5p
expression. J Cell Physiol. 2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chang ZW, Jia YX, Zhang WJ, Song LJ, Gao
M, Li MJ, Zhao RH, Li J, Zhong YL, Sun QZ and Qin YR:
LncRNA-TUSC7/miR-224 affected chemotherapy resistance of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating DESC1. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 37:562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cong M and Jing R: Long non-coding RNA
TUSC7 suppresses osteosarcoma by targeting miR-211. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201902912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu ZJ, Huang P, Chong YX, Kang LX, Huang
X, Zhu ZX and Nie L: MicroRNA-181a promotes proliferation and
inhibits apoptosis by suppressing CFIm25 in osteosarcoma. Mol Med
Rep. 14:4271–4278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ba Z, Gu L, Hao S, Wang X, Cheng Z and Nie
G: Downregulation of lncRNA CASC2 facilitates osteosarcoma growth
and invasion through miR-181a. Cell Prolif. 51:e124092018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jones KB, Salah Z, Del Mare S, Galasso M,
Gaudio E, Nuovo GJ, Lovat F, LeBlanc K, Palatini J, Randall RL, et
al: miRNA signatures associate with pathogenesis and progression of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:1865–1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Savary G, Dewaeles E, Diazzi S, Buscot M,
Nottet N, Fassy J, Courcot E, Henaoui IS, Lemaire J, Martis N, et
al: The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS Is a reservoir of FibromiRs with
major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-β and pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 200:184–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao G, Yao J, Kong D, Ye C, Chen R, Li L,
Zeng T, Wang L, Zhang W, Shi X, et al: The long noncoding RNA
TTTY15, which is located on the Y chromosome, promotes prostate
cancer progression by sponging let-7. Eur Urol. 76:315–326. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yamamura S, Imai-Sumida M, Tanaka Y and
Dahiya R: Interaction and cross-talk between non-coding RNAs. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 75:467–484. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Lopez-Urrutia E, Bustamante Montes LP,
Ladron de Guevara Cervantes D, Perez-Plasencia C and Campos-Parra
AD: Crosstalk between long non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs:
Deciphering molecular mechanisms of master regulators in cancer.
Front Oncol. 9:6692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
National Research Council (US): Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
28
|
Thomson DW and Dinger ME: Endogenous
microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet.
17:272–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Li X and Yang H: LINC00612
functions as a ceRNA for miR-214-5p to promote the proliferation
and invasion of osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res.
392:1120122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chi Y, Wang D, Wang J, Yu W and Yang J:
Long non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of cancers. Cells.
8:10152019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Xu D, Ihira K,
Konno Y, Kobayashi N, Todo Y and Watari H: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1
drives aggressive endometrial cancer progression via
miR-361-regulated networks involving STAT3 and tumor
microenvironment-related genes. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao CC, Jiao Y, Zhang YY, Ning J, Zhang
YR, Xu J, Wei W and Kang-Sheng G: Lnc SMAD5-AS1 as ceRNA inhibit
proliferation of diffuse large B cell lymphoma via Wnt/β-catenin
pathway by sponging miR-135b-5p to elevate expression of APC. Cell
Death Dis. 10:2522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu F, Yuan JH, Huang JF, Yang F, Wang TT,
Ma JZ, Zhang L, Zhou CC, Wang F, Yu J, et al: Long noncoding RNA
FTX inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis
by binding MCM2 and miR-374a. Oncogene. 35:5422–5434. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu W, Liu P, Gao H, Wang X and Yan M:
Long non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
impairing miR-140-5p-mediated FBN1 inhibition. Mol Oncol.
14:2660–2677. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xia P, Gu R, Zhang W and Sun YF: lncRNA
CEBPA-AS1 over-expression inhibits proliferation and migration and
stimulates apoptosis of OS cells via notch signaling. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 19:1470–1481. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang G, Wang M, Li X, Wu J, Chen S, Du N,
Li K, Wang J, Xu C, Ren H, et al: TUSC7 suppression of Notch
activation through sponging MiR-146 recapitulated the asymmetric
cell division in lung adenocarcinoma stem cells. Life Sci.
232:1166302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Duan X, Wu Y, Zhang Z and Lu Z:
Identification and analysis of dysregulated lncRNA and associated
ceRNA in the pathogenesis of keloid. Ann Transl Med. 8:2222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Volodko N, Gordon M, Salla M, Ghazaleh HA
and Baksh S: RASSF tumor suppressor gene family: Biological
functions and regulation. FEBS Lett. 588:2671–2684. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iwasa H, Jiang X and Hata Y: RASSF6; the
putative tumor suppressor of the RASSF family. Cancers (Basel).
7:2415–2426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhu N, Si M, Yang N, Jing Y, Fu Y, Zhao X,
Lin Z and Yang G: Overexpression of RAS-association domain family 6
(RASSF6) inhibits proliferation and tumorigenesis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncol Res. 25:1001–1008. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mi Y, Zhang D, Jiang W, Weng J, Zhou C,
Huang K, Tang H, Yu Y, Liu X, Cui W, et al: miR-181a-5p promotes
the progression of gastric cancer via RASSF6-mediated MAPK
signalling activation. Cancer Lett. 389:11–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang H, Yan B, Zhang P, Liu S, Li Q, Yang
J, Yang F and Chen E: MiR-496-promotes migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting RASSF6 in colorectal
cancer. J Cell Physiol. 235:1469–1479. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|