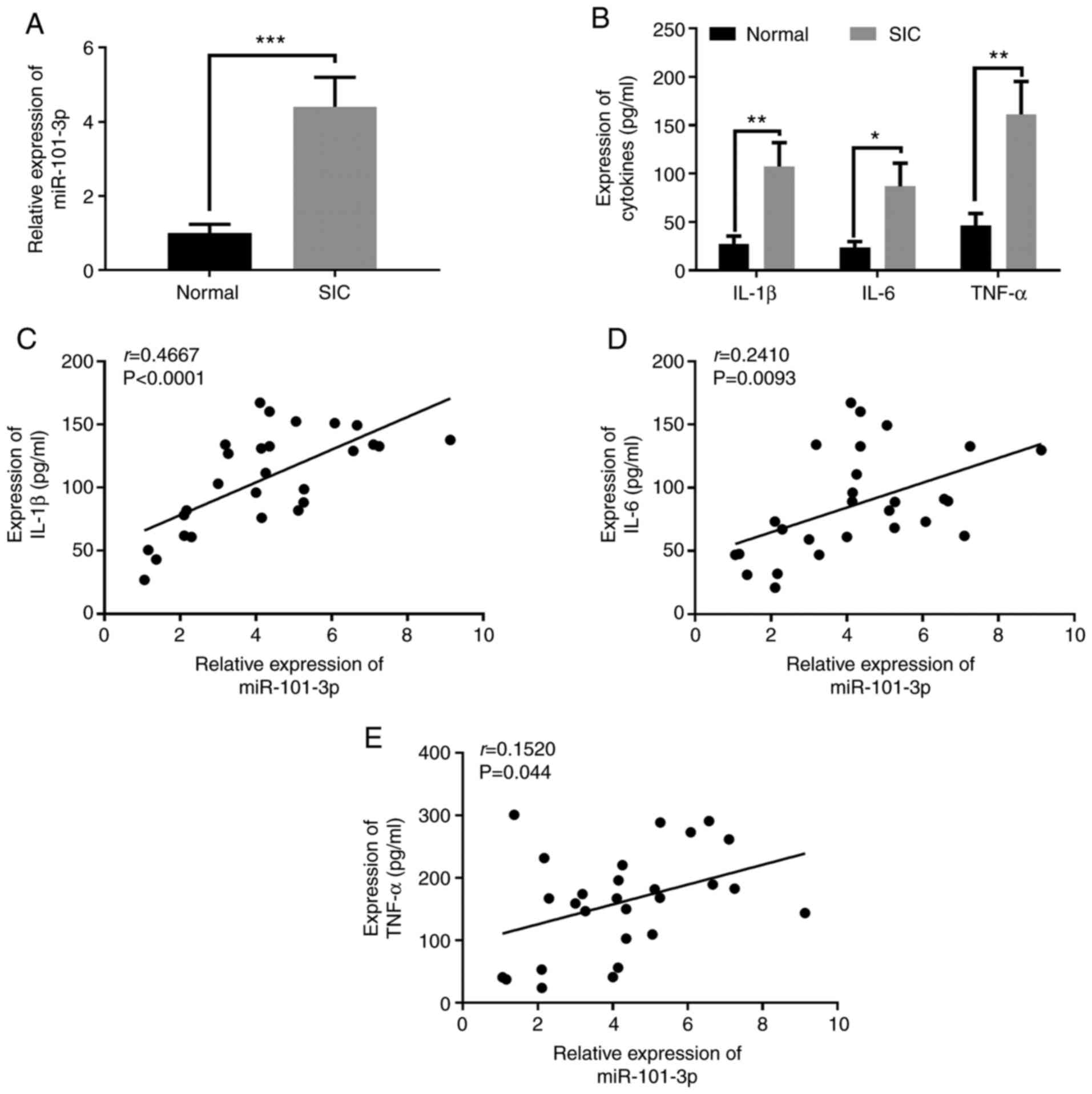
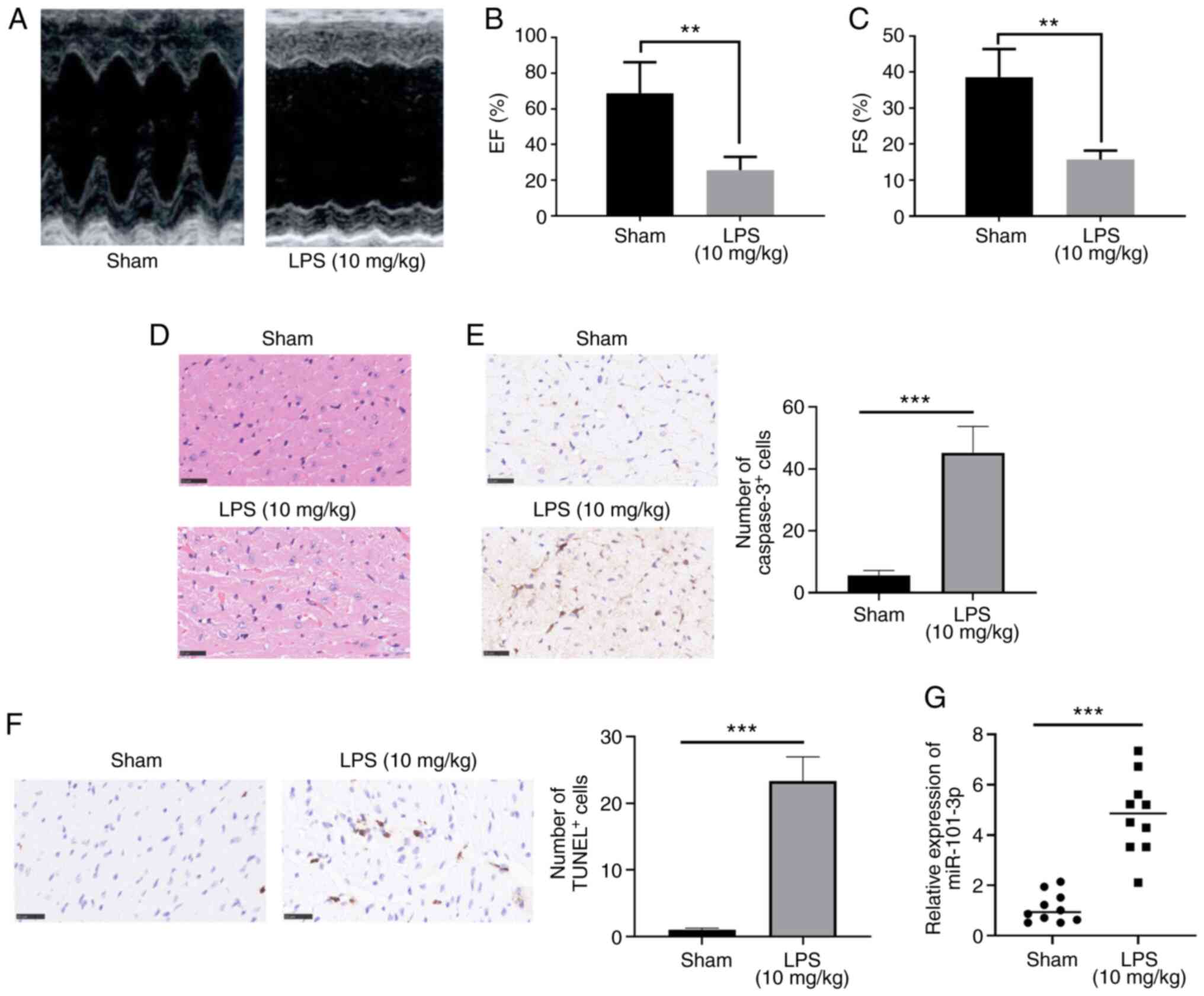
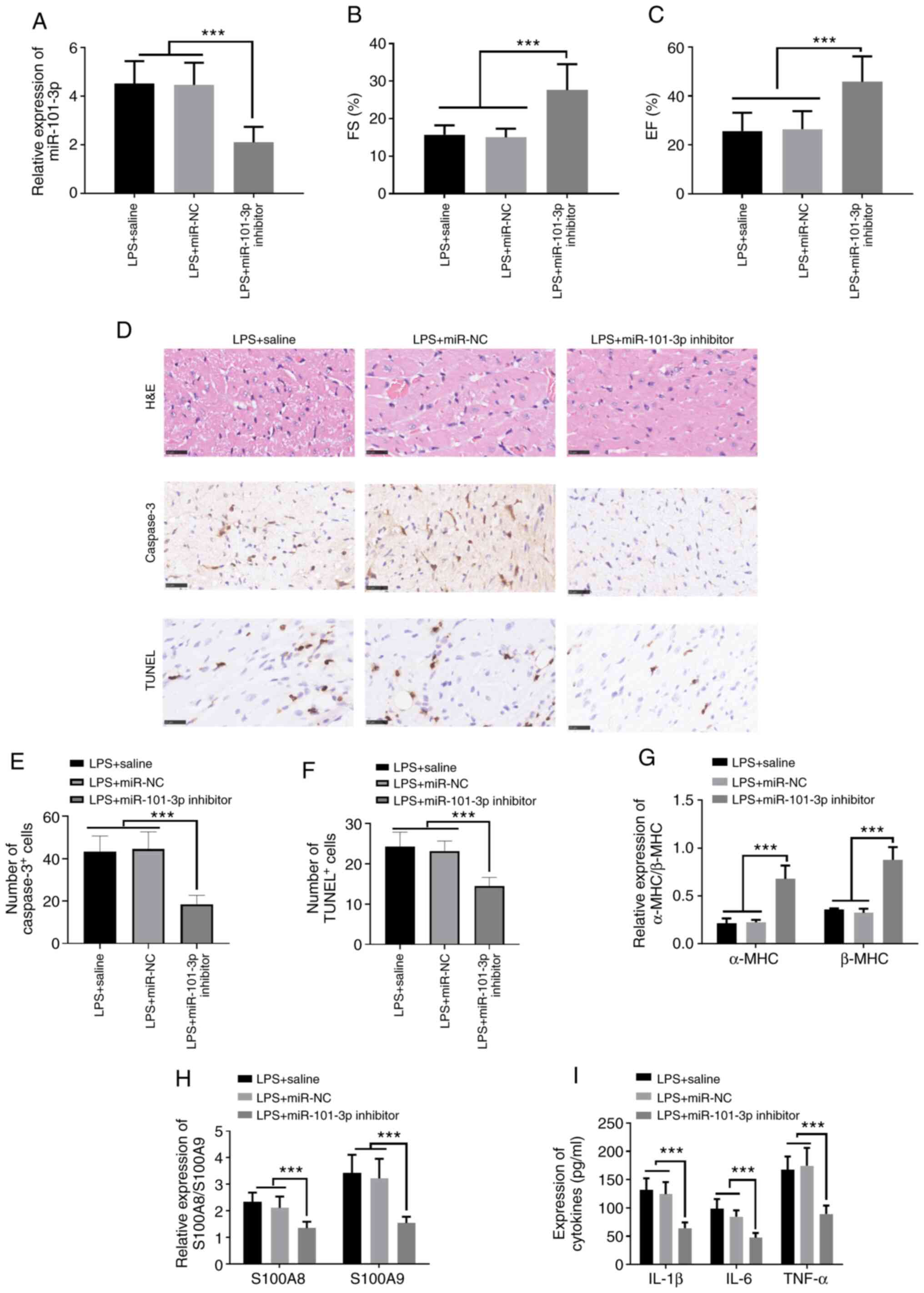
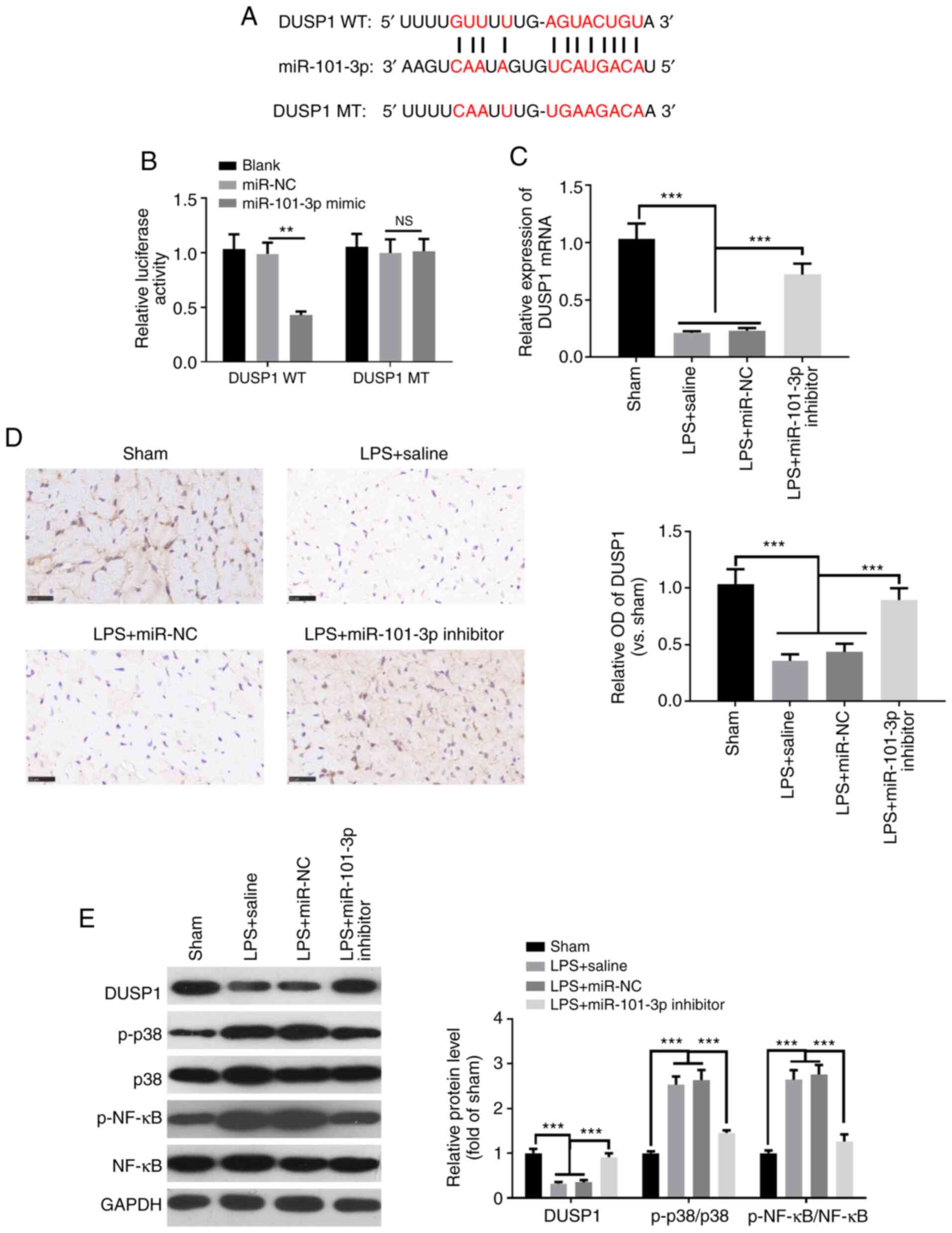
|
1
|
Frencken JF, Donker DW, Spitoni C,
Koster-Brouwer ME, Soliman IW, Ong DSY, Horn J, van der Poll T, van
Klei WA, Bonten MJM and Cremer OL: Myocardial injury in patients
with sepsis and its association with long-term outcome. Circ
Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 11:e0040402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lv X and Wang H: Pathophysiology of
sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Mil Med Res.
3:302016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao C, Zhang Y, Chai Y, Wang L, Yin C,
Shou S and Jin H: Attenuation of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by
regulation of microRNA-23b is mediated through targeting of
MyD88-mediated NF-κB activation. Inflammation. 42:973–986. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ouyang MZ, Zhou D, Zhu Y, Zhang M and Li
L: The inhibition of MyD88 and TRIF signaling serve equivalent
roles in attenuating myocardial deterioration due to acute severe
inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 41:399–408. 2018.
|
|
6
|
Zeng M, Zhang B, Li B, Kan Y, Wang S, Feng
W and Zheng X: Adenosine attenuates LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction
by inhibition of mitochondrial function via the ER pathway. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019:18320252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen S and Fan B: Myricetin protects
cardiomyocytes from LPS-induced injury. Myricetin schützt
Kardiomyozyten vor LPS-induzierten Verletzungen. Herz. 43:265–274.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zheng Z, Ma H, Zhang X, Tu F, Wang X, Ha
T, Fan M, Liu L, Xu J, Yu K, et al: Enhanced glycolytic metabolism
contributes to cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis. J
Infect Dis. 215:1396–1406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qiu Z, He Y, Ming H, Lei S, Leng Y and Xia
ZY: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) aggravates high glucose- and
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury through activating
ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in H9C2
cardiomyocytes. J Diabetes Res. 2019:81518362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wancket LM, Frazier WJ and Liu Y:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1 in immunology,
physiology, and disease. Life Sci. 90:237–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boutros T, Chevet E and Metrakos P:
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase
regulation: Roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev.
60:261–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Low HB and Zhang Y: Regulatory roles of
MAPK phosphatases in cancer. Immune Netw. 16:85–98. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoppstädter J and Ammit AJ: Role of
dual-specificity phosphatase 1 in glucocorticoid-driven
anti-inflammatory responses. Front Immunol. 10:14462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kristiansen M, Hughes R, Patel P, Jacques
TS, Clark AR and Ham J: Mkp1 is a c-Jun target gene that
antagonizes JNK-dependent apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J
Neurosci. 30:10820–10832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rastogi R, Jiang Z, Ahmad N, Rosati R, Liu
Y, Beuret L, Monks R, Charron J, Birnbaum MJ and Samavati L:
Rapamycin induces mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase
phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) expression through activation of protein
kinase B and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase pathways. J
Biol Chem. 288:33966–33977. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C and Zardo G:
MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear
functions. Int J Mol Sci. 17:17122016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Wang X and Yu Y: MiR-146b protect against
sepsis induced mice myocardial injury through inhibition of Notch1.
J Mol Histol. 49:411–417. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Zhou J, Wu Z, Chen C, Liu J, Wu G,
Zhai J, Liu F and Li G: miR-101-3p suppresses HOX transcript
antisense RNA (HOTAIR)-induced proliferation and invasion through
directly targeting SRF in gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Res.
25:1383–1390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li CY, Xiong DD, Huang CQ, He RQ, Liang
HW, Pan DH, Wang HL, Wang YW, Zhu HW and Chen G: Clinical value of
miR-101-3p and biological analysis of its prospective targets in
breast cancer: A study based on the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) and
bioinformatics. Med Sci Monit Med Sci Monit. 23:1857–1871. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu Q, Gong W, Gu J, Geng G, Li T, Tian R,
Yang Z, Zhang H, Shao L, Liu T, et al: Plasma microRNA profiles as
a potential biomarker in differentiating adult-onset still's
disease from sepsis. Front Immunol. 9:30992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei Q, Lv F, Zhang H, Wang X, Geng Q,
Zhang X, Li T, Wang S, Wang Y and Cui Y: MicroRNA-101-3p inhibits
fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation and inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis by targeting PTGS2. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR201911362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sukma Dewi I, Hollander Z, Lam KK, McManus
JW, Tebbutt SJ, Ng RT, Keown PA, McMaster RW, McManus BM, Gidlöf O
and Öhman J: Association of serum MiR-142-3p and MiR-101-3p levels
with acute cellular rejection after heart transplantation. PLoS
One. 12:e01708422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen L, Liu P, Feng X and Ma C:
Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:3178–3189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang Q, Chen J, Long X, Yao X, Zou X,
Yang Y, Huang G and Zhang H: Phillyrin protects mice from traumatic
brain injury by inhibiting the inflammation of microglia via PPARγ
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 79:1060832020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K
and Yasuda T: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction:
Pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care. 4:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan Y, Chen S, Zhong J, Ren J and Dong M:
Mitochondrial injury and targeted intervention in septic
cardiomyopathy. Curr Pharm Des. 25:2060–2070. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
De Kock I, Van Daele C and Poelaert J:
Sepsis and septic shock: Pathophysiological and cardiovascular
background as basis for therapy. Acta Clin Belg. 65:323–329. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li HM, Li KY, Xing Y, Tang XX, Yang DM,
Dai XM, Lu DX and Wang HD: Phenylephrine attenuated sepsis-induced
cardiac inflammation and mitochondrial injury through an effect on
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 73:186–194.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J,
Zhang J, Sun Q, Chen Y, Yang Y, Xu T, et al: miR-21-3p controls
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 94:43–53. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Qin Z, Zhu K, Xue J, Cao P, Xu L, Xu Z,
Liang K, Zhu J and Jia R: Zinc-induced protective effect for
testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting antioxidation
via microRNA-101-3p/Nrf2 pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 11:9295–9309.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Hyer JM, Yu H, D'Silva NJ and
Kirkwood KL: DUSP1 phosphatase regulates the proinflammatory milieu
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 74:7191–7197.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ying H, Kang Y, Zhang H, Zhao D, Xia J, Lu
Z, Wang H, Xu F and Shi L: MiR-127 modulates macrophage
polarization and promotes lung inflammation and injury by
activating the JNK pathway. J Immunol. 194:1239–1251. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Brudecki L, Ferguson DA, McCall CE and El
Gazzar M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 disrupts
proinflammatory protein synthesis in endotoxin-adapted monocytes.
Clin Vaccine Immunol. 20:1396–1404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kawai M, Karam TS, Michael JJ, Wang L and
Chandra M: Comparison of elementary steps of the cross-bridge cycle
in rat papillary muscle fibers expressing α- and β-myosin heavy
chain with sinusoidal analysis. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.
37:203–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, Jakoniuk
I, Anderson SM, Li B, Pickel J, McKay R, Nadal-Ginard B, Bodine DM,
et al: Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature.
410:701–705. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu Q, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang W, Yang Z, Li T,
Tian Y, Chen P, Ma K, Jia Z and Zhou C: Rapamycin efficiently
promotes cardiac differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells.
Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201605522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li P, Chen XR, Xu F, Liu C, Li C, Liu H,
Wang H, Sun W, Sheng YH and Kong XQ: Alamandine attenuates
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via inhibiting MAPKs
signaling pathways. Life Sci. 206:106–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiao X, Yang C, Qu SL, Shao YD, Zhou CY,
Chao R, Huang L and Zhang C: S100 proteins in atherosclerosis. Clin
Chim Acta. 502:293–304. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Huang H and Tu L: Expression of S100
family proteins in neonatal rats with sepsis and its significance.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1631–1639. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tosson AMS, Glaser K, Weinhage T, Foell D,
Aboualam MS, Edris AA, El Ansary M, Lotfy S and Speer CP:
Evaluation of the S100 protein A12 as a biomarker of neonatal
sepsis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 33:2768–2774. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang L, Zhang L, Liu Z, Zhao S, Xu D, Li
L, Peng Q and Ai Y: Pentamidine protects mice from cecal ligation
and puncture-induced brain damage via inhibiting S100B/RAGE/NF-κB.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 517:221–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|