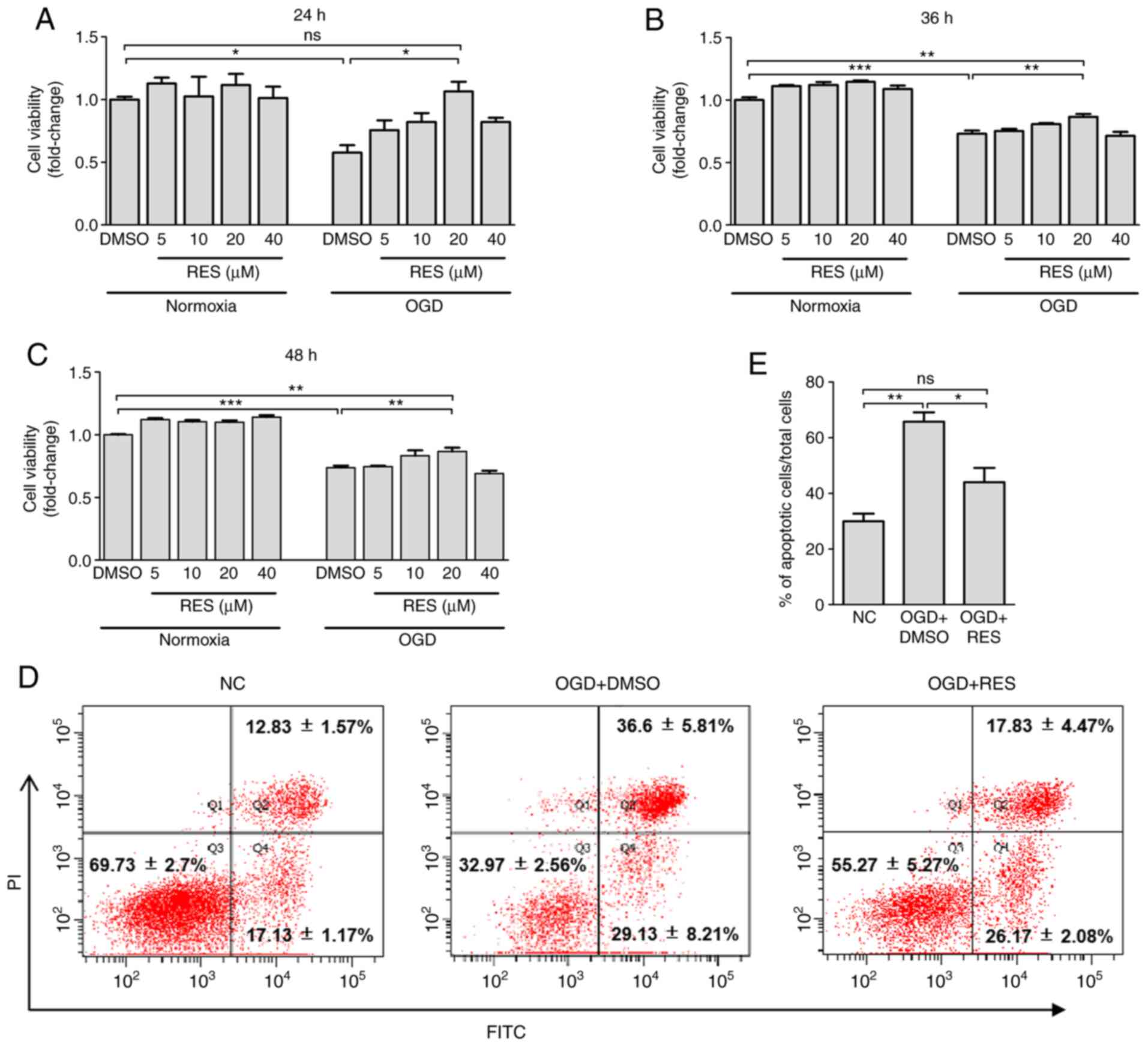
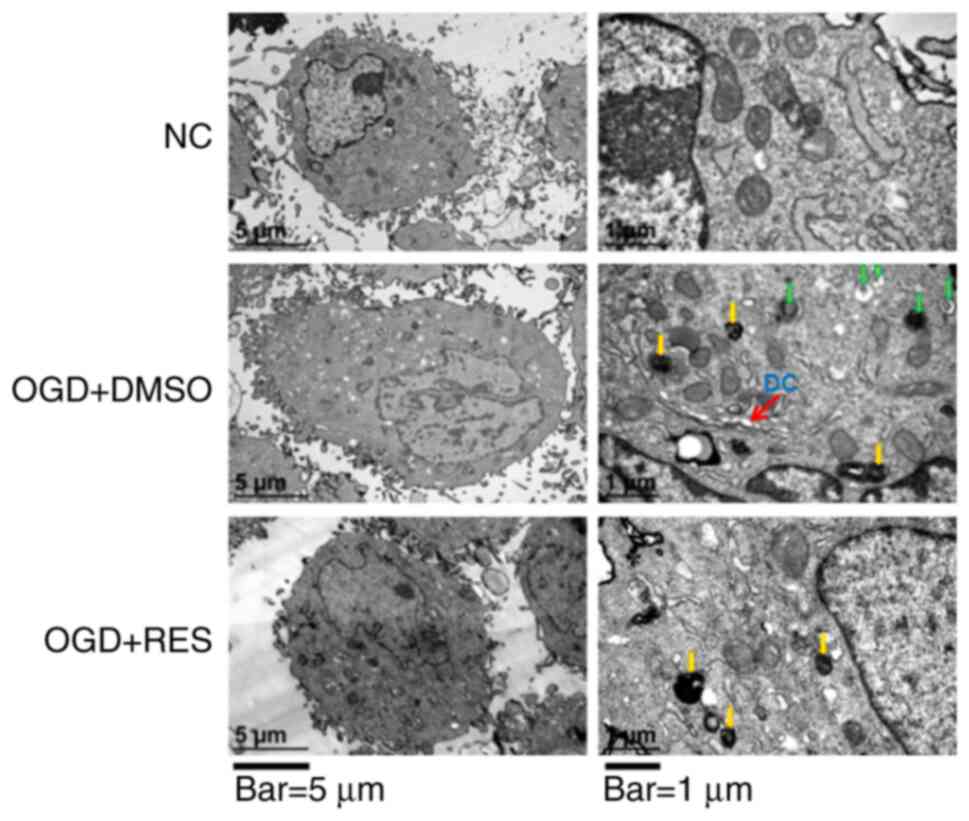
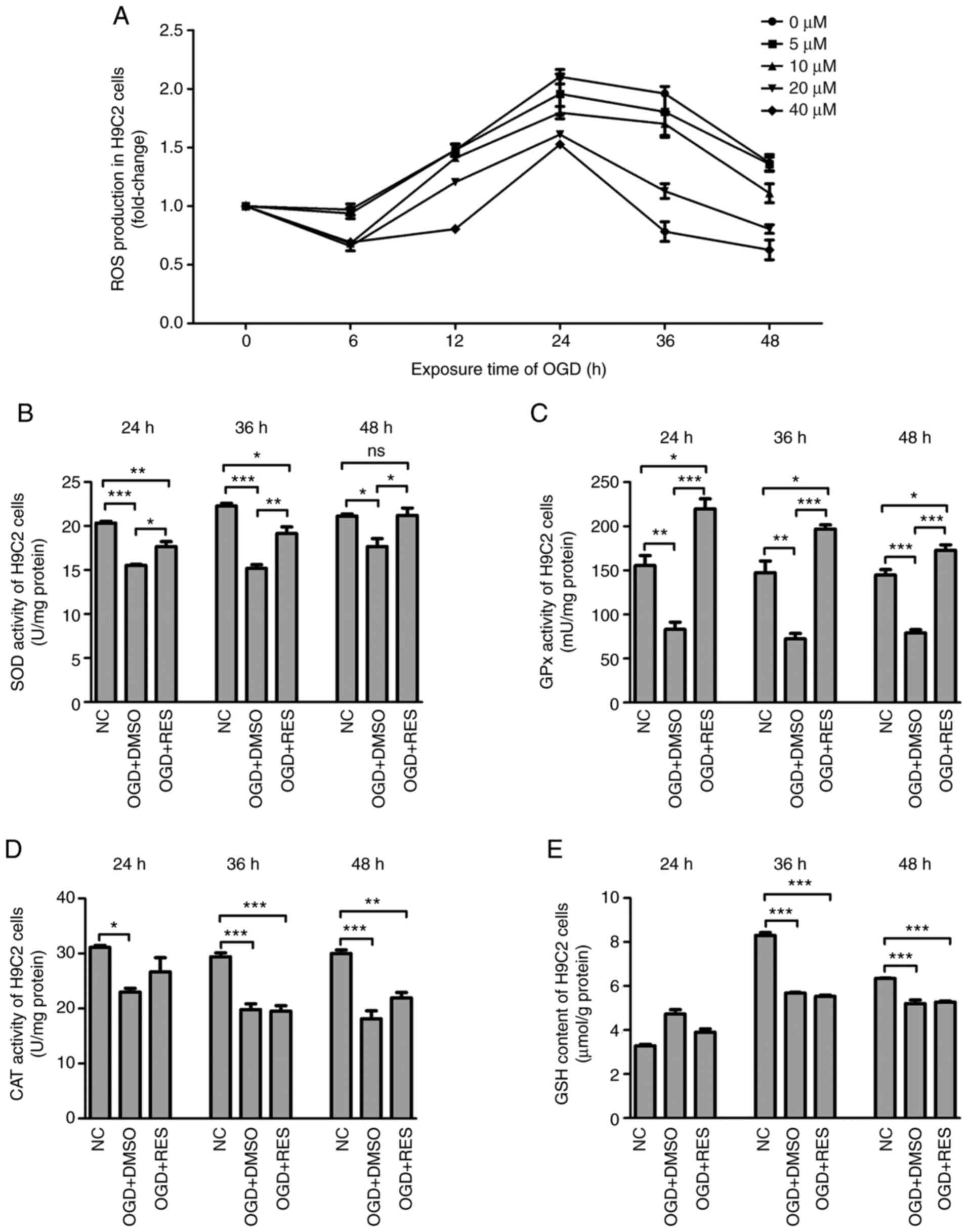
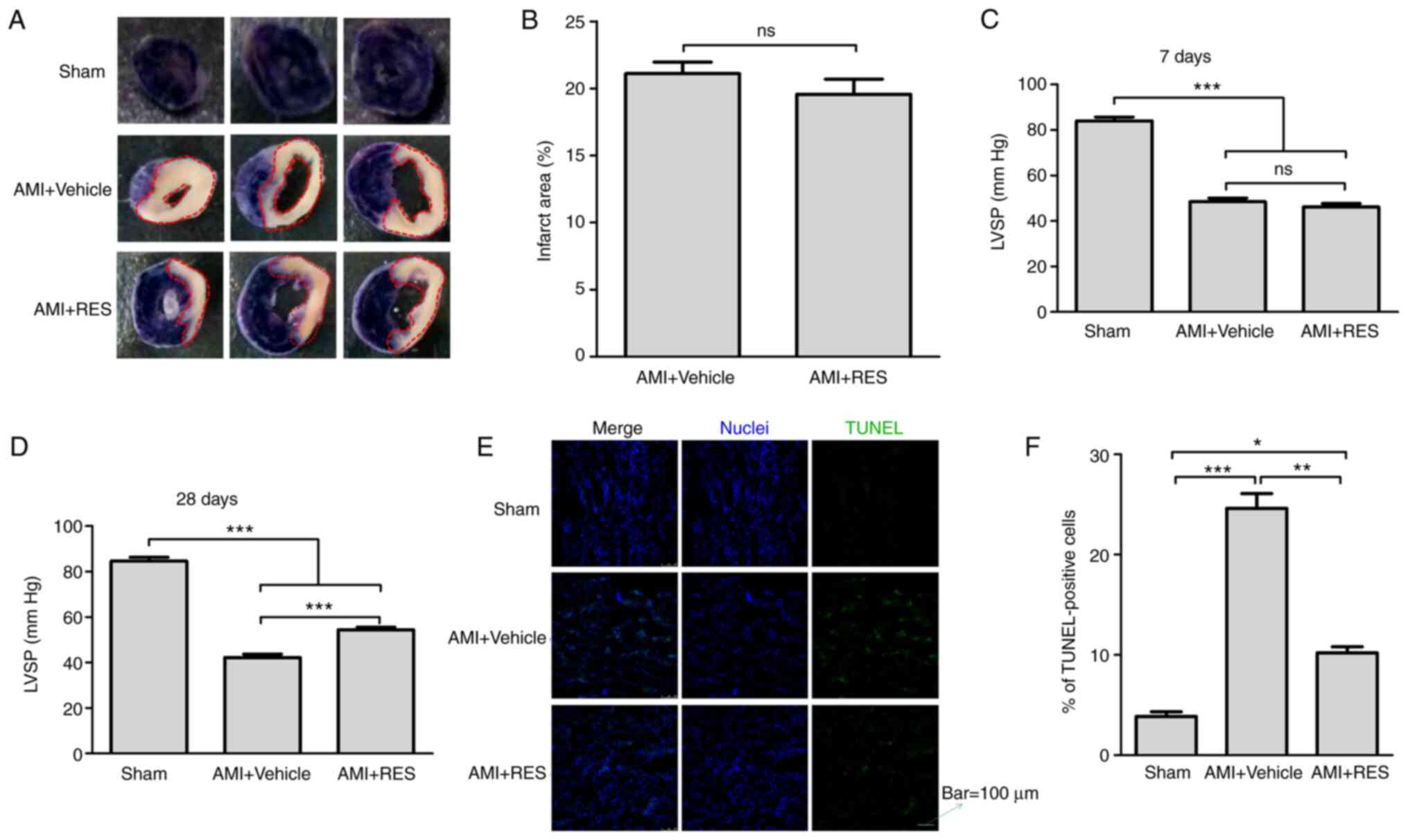
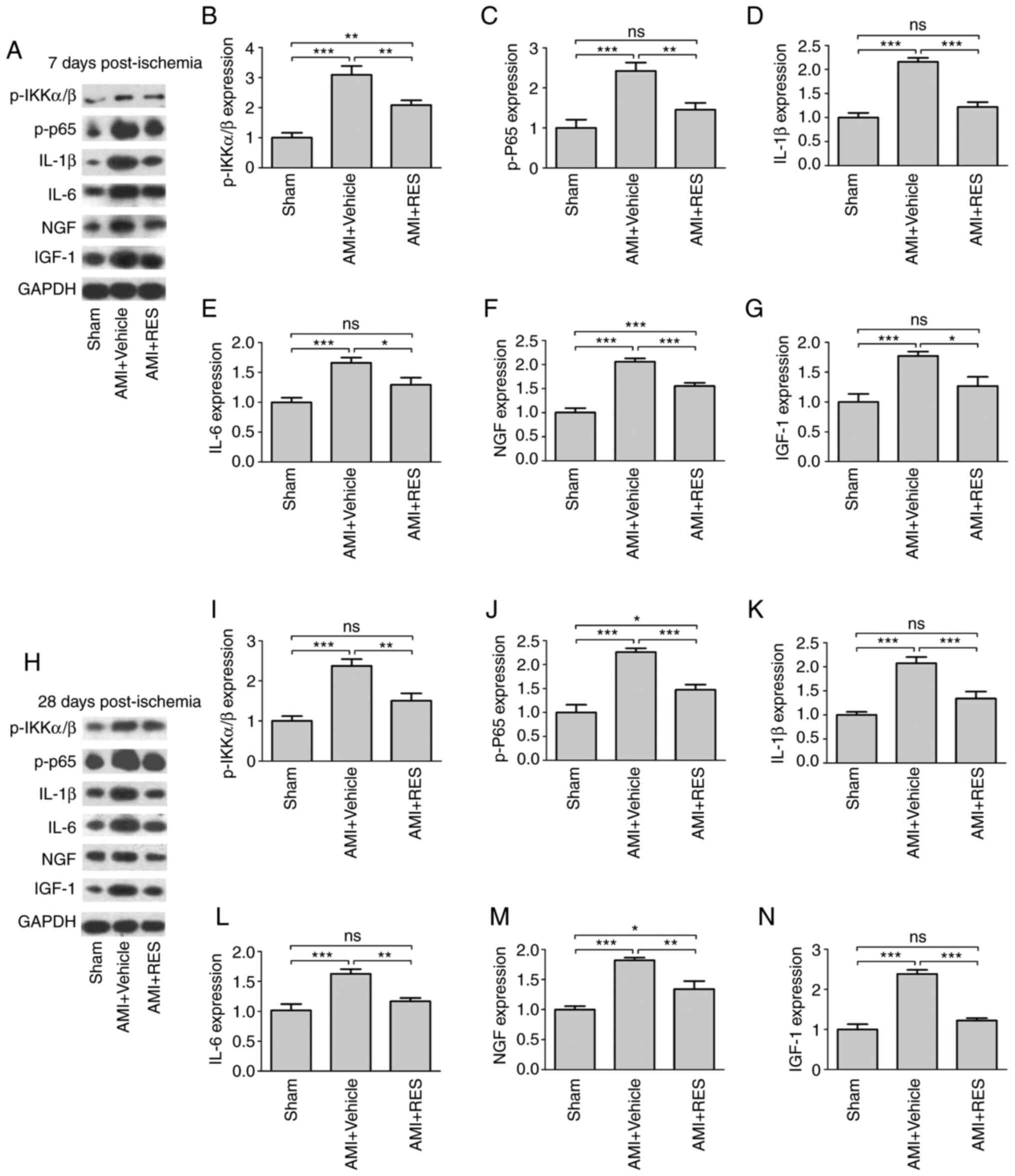
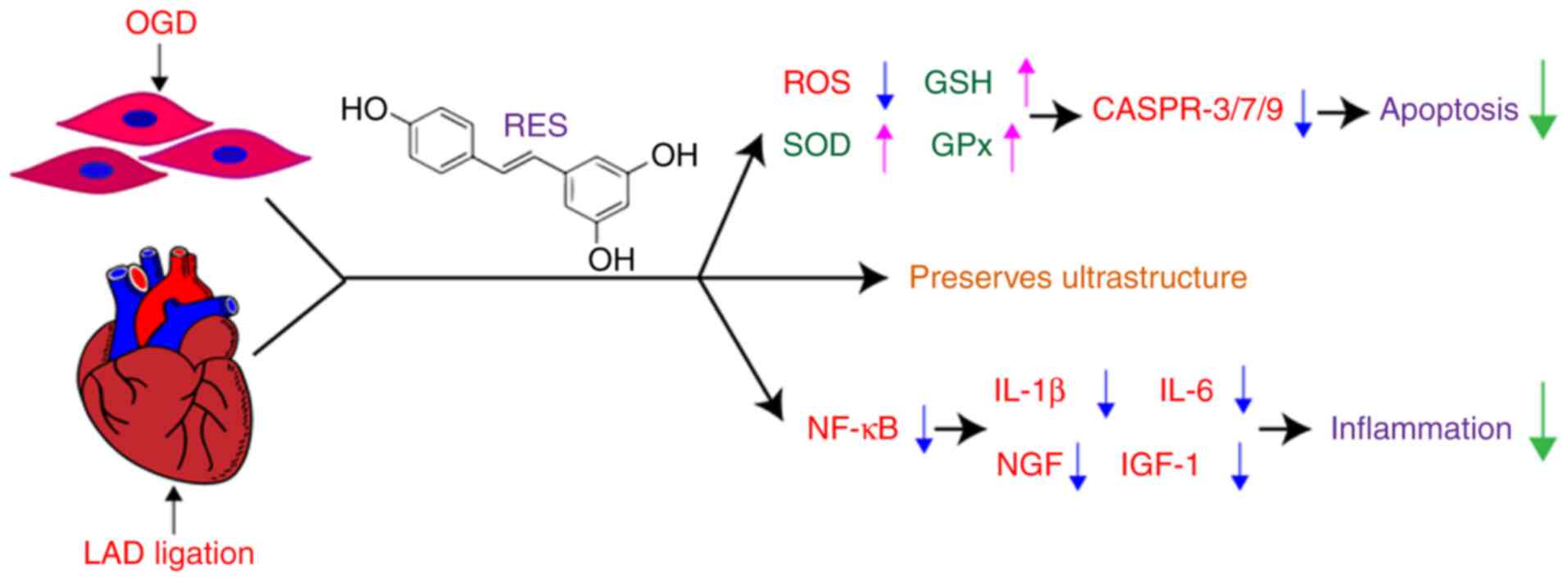
|
1
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C,
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E and Cerretani D: Cardiac oxidative stress
and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:26–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pagliaro P and Penna C: Redox signalling
and cardioprotection: Translatability and mechanism. Br J
Pharmacol. 172:1974–1995. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Hansen JM, Jones DP and Harris C: The
redox theory of development. Antioxid Redox Signal. 32:715–740.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blaser H, Dostert C, Mak TW and Brenner D:
TNF and ROS crosstalk in inflammation. Trends Cell Biol.
26:249–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choudhury S, Ghosh S, Gupta P, Mukherjee S
and Chattopadhyay S: Inflammation-induced ROS generation causes
pancreatic cell death through modulation of Nrf2/NF-κB and SAPK/JNK
pathway. Free Radic Res. 49:1371–1383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wan J, Shan Y, Fan Y, Fan C, Chen S, Sun
J, Zhu L, Qin L, Yu M and Lin Z: NF-κB inhibition attenuates
LPS-induced TLR4 activation in monocyte cells. Mol Med Rep.
14:4505–4510. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hinz M and Scheidereit C: The IκB kinase
complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 15:46–61. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Xie C, Zhuang J, Li H, Yao Y, Shao C
and Wang H: Resveratrol attenuates inflammation in the rat heart
subjected to ischemia-reperfusion: Role of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 11:1120–1126. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Ahmad R, Javed S and Bhandari U:
Antiapoptotic potential of herbal drugs in cardiovascular
disorders: An overview. Pharm Biol. 48:358–374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bonnefont-Rousselot D: Resveratrol and
cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients. 8:2502016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Stephan LS, Almeida ED, Markoski MM,
Garavaglia J and Marcadenti A: Red wine, resveratrol and atrial
fibrillation. Nutrients. 9:11902017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Annunziata G, Sanduzzi Zamparelli M,
Santoro C, Ciampaglia R, Stornaiuolo M, Tenore GC, Sanduzzi A and
Novellino E: May polyphenols have a role against coronavirus
infection? An overview of in vitro evidence. Front Med (Lausanne).
7:2402020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mao ZJ, Lin H, Hou JW, Zhou Q, Wang Q and
Chen YH: A meta-analysis of resveratrol protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: Evidence from small animal studies and
insight into molecular mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:57938672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen X, Wang M, Bi X, Zhang J, Wen S, Fu G
and Xia L: Resveratrol prevents endothelial progenitor cells from
senescence and reduces the oxidative reaction via PPAR-γ/HO-1
pathways. Mol Med Rep. 14:5528–5534. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun ZM, Guan P, Luo LF, Qin LY, Wang N,
Zhao YS and Ji ES: Resveratrol protects against CIH-induced
myocardial injury by targeting Nrf2 and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Life Sci. 245:1173622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma L, Chuang CC, Weng W, Zhao L, Zheng Y,
Zhang J and Zuo L: Paeonol protects rat heart by improving regional
blood perfusion during no-reflow. Front Physiol. 7:2982016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shinomol GK and Muralidhara: Differential
induction of oxidative impairments in brain regions of male mice
following subchronic consumption of Khesari dhal (Lathyrus sativus)
and detoxified Khesari dhal. Neurotoxicology. 28:798–806. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Boos DD and Stefanski LA: P-value
precision and reproducibility. Am Stat. 65:213–221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Misra MK, Sarwat M, Bhakuni P, Tuteja R
and Tuteja N: Oxidative stress and ischemic myocardial syndromes.
Med Sci Monit. 15:RA209–RA219. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bienert GP, Møller AL, Kristiansen KA,
Schulz A, Møller IM, Schjoerring JK and Jahn TP: Specific
aquaporins facilitate the diffusion of hydrogen peroxide across
membranes. J Biol Chem. 282:1183–1192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luna CM, Pastori GM, Driscoll S, Groten K,
Bernard S and Foyer CH: Drought controls on
H2O2 accumulation, catalase (CAT) activity
and CAT gene expression in wheat. J Exp Bot. 56:417–423. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bagulho A, Vilas-Boas F, Pena A, Peneda C,
Santos FC, Jerónimo A, de Almeida RFM and Real C: The extracellular
matrix modulates H2O2 degradation and redox
signaling in endothelial cells. Redox Biol. 6:454–460. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rhee SG, Woo HA and Kang D: The role of
peroxiredoxins in the transduction of H2O2
signals. Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:537–557. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Aguilar-Alonso P, Vera-López O,
Brambila-Colombres E, Segura-Badilla O, Avalos-López R,
Lazcano-Hernández M and Navarro-Cruz AR: Evaluation of oxidative
stress in cardiomyocytes during the aging process in rats treated
with resveratrol. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:13904832018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Frangogiannis NG: Targeting the
inflammatory response in healing myocardial infarcts. Curr Med
Chem. 13:1877–1893. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frangogiannis NG: The inflammatory
response in myocardial injury, repair, and remodelling. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 11:255–265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Christia P and Frangogiannis NG: Targeting
inflammatory pathways in myocardial infarction. Eur J Clin Invest.
43:986–995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Anzai T: Inflammatory mechanisms of
cardiovascular remodeling. Circ J. 82:629–635. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Chen Y, Yue Z, He Y, Zou J, Chen
S, Liu M, Chen X, Liu Z, Liu X, et al: The p65 subunit of NF-κB
involves in RIP140-mediated inflammatory and metabolic
dysregulation in cardiomyocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 554:22–27.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mahmoud AI, O'Meara CC, Gemberling M, Zhao
L, Bryant DM, Zheng R, Gannon JB, Cai L, Choi WY, Egnaczyk GF, et
al: Nerves regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart
regeneration. Dev Cell. 34:387–399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y and Wu JH: GW26-e0203 effects of
nerve growth factor on late reperfusion after myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 66(16 Suppl): C28–C29. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jackson R, Tilokee EL, Latham N, Mount S,
Rafatian G, Strydhorst J, Ye B, Boodhwani M, Chan V, Ruel M, et al:
Paracrine engineering of human cardiac stem cells with insulin-like
growth factor 1 enhances myocardial repair. J Am Heart Assoc.
4:e0021042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xin P, Pan Y, Zhu W, Huang S, Wei M and
Chen C: Favorable effects of resveratrol on sympathetic neural
remodeling in rats following myocardial infarction. Eur J
Pharmacol. 649:293–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ahmet I, Tae HJ, Lakatta EG and Talan M:
Long-term low dose dietary resveratrol supplement reduces
cardiovascular structural and functional deterioration in chronic
heart failure in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 95:268–274. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chekalina NI: Resveratrol has a positive
effect on parameters of central hemodynamics and myocardial
ischemia in patients with stable coronary heart disease. Wiad Lek.
70:286–291. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|