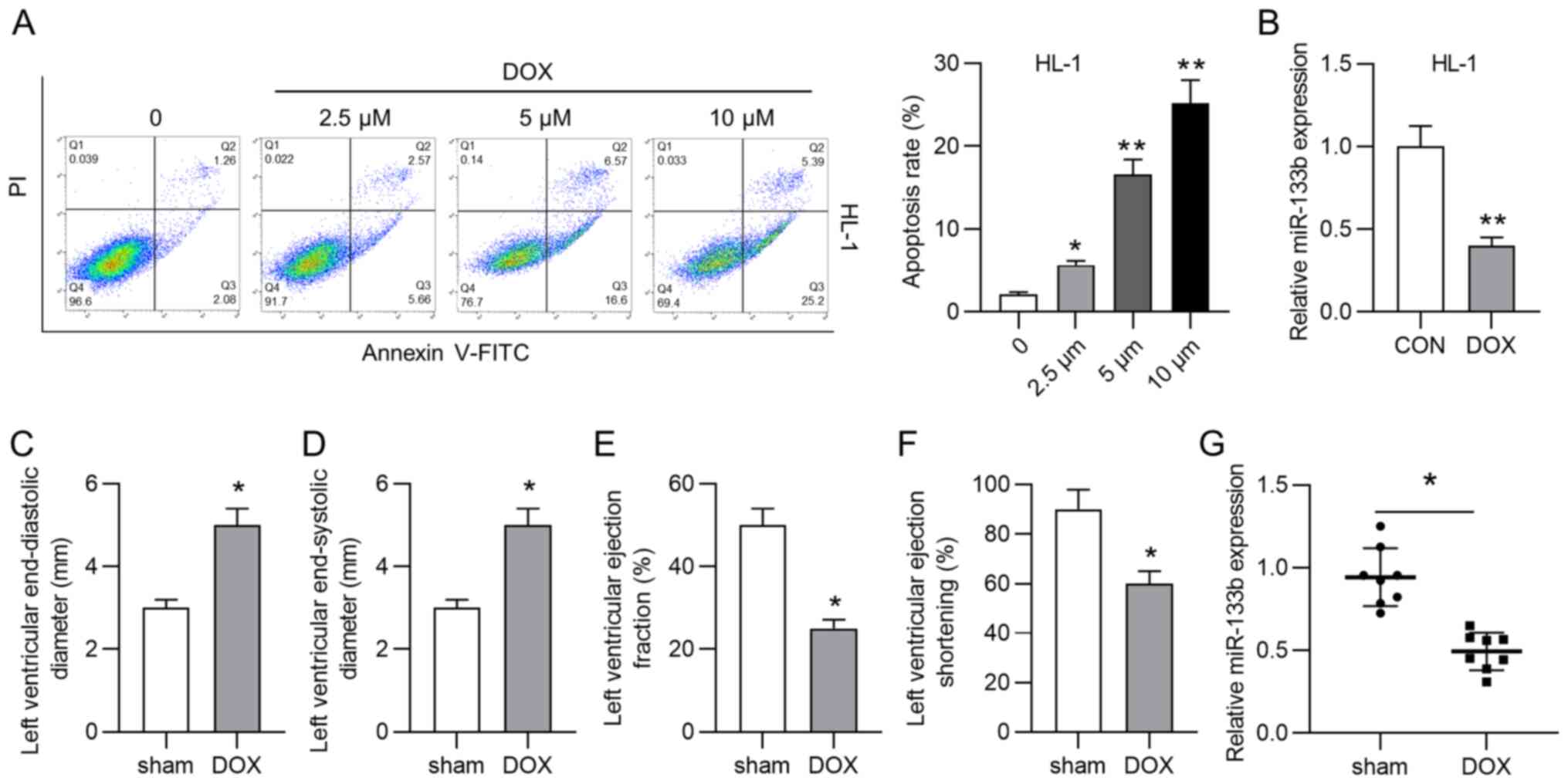
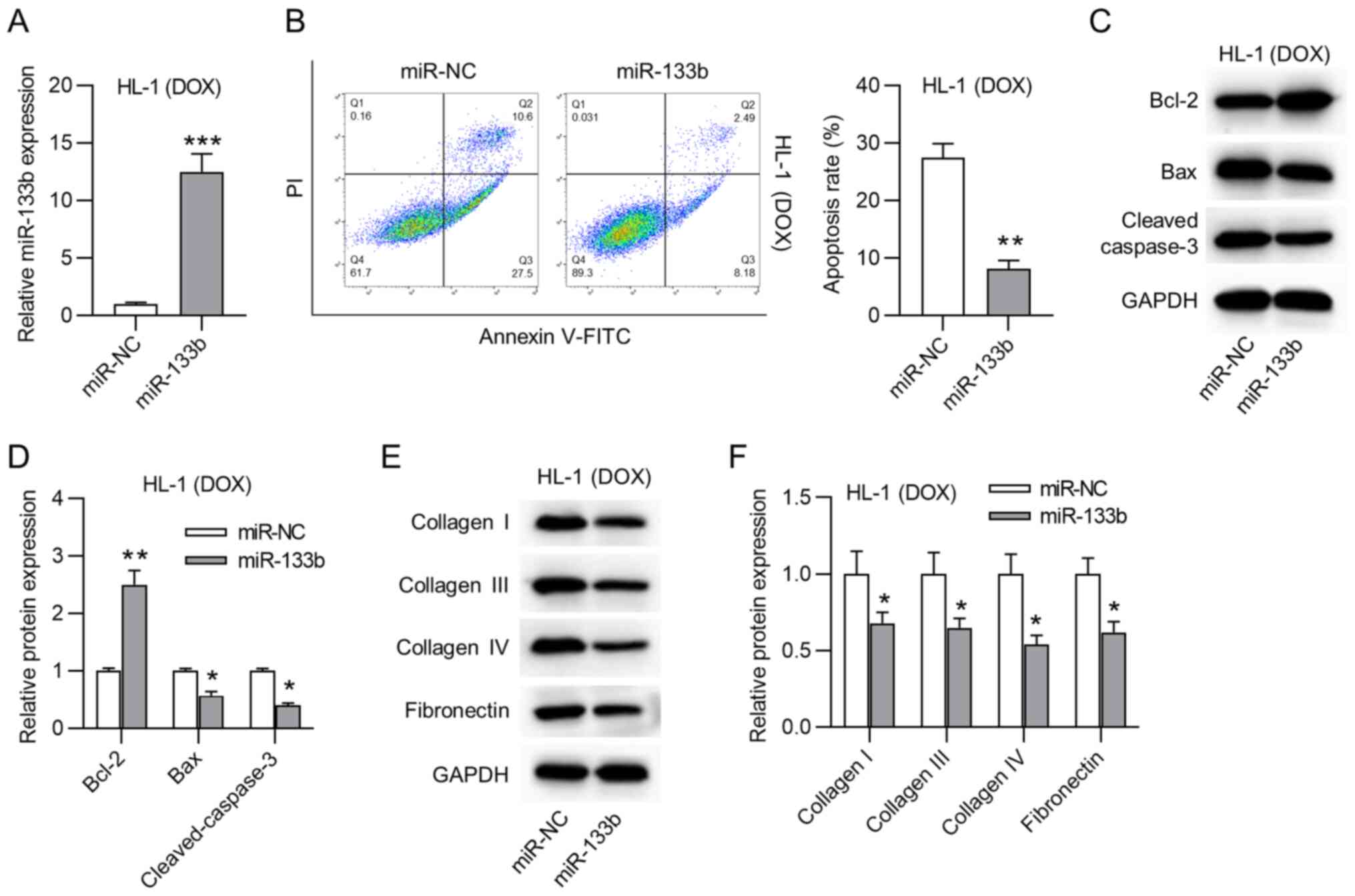
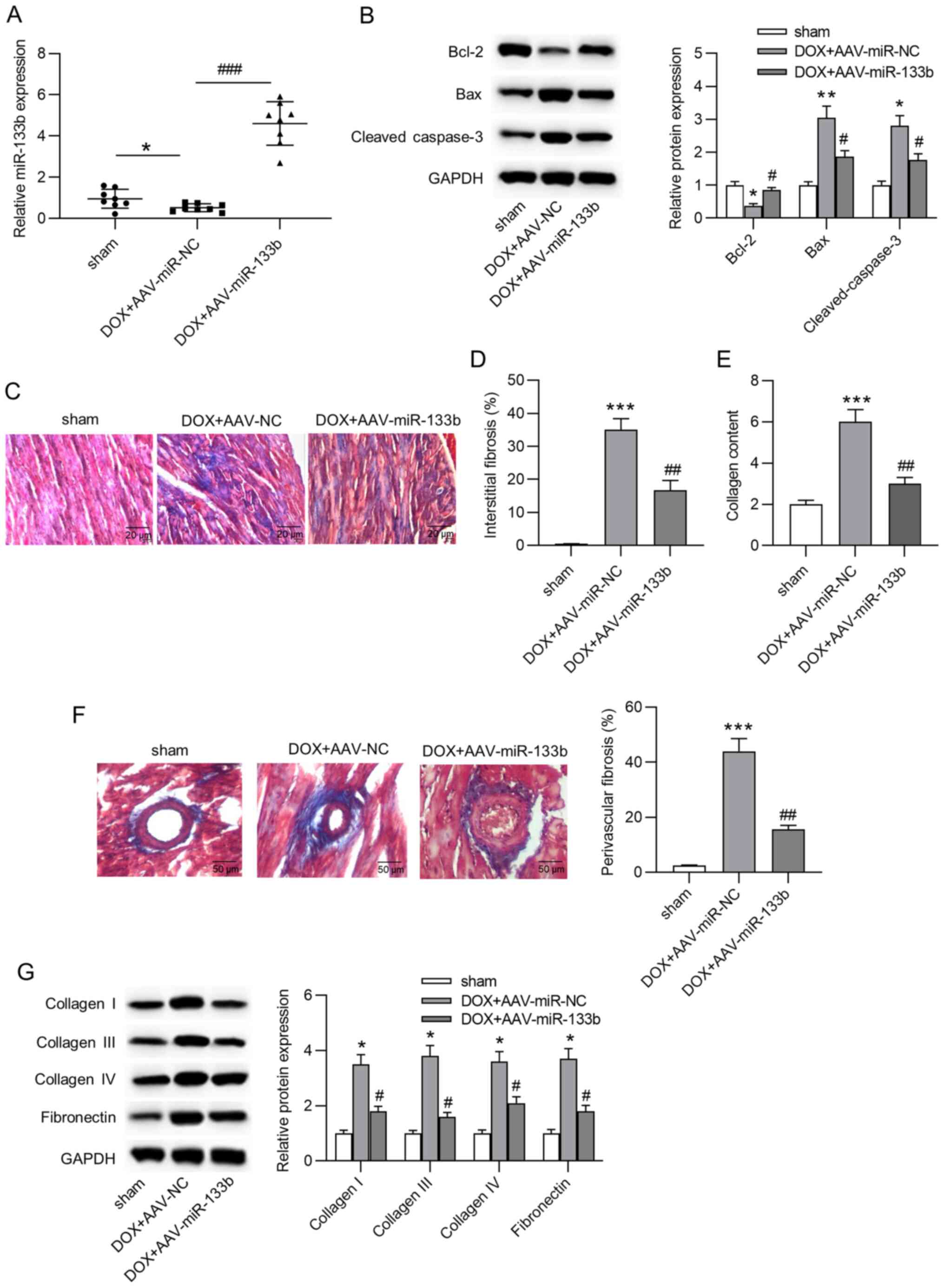
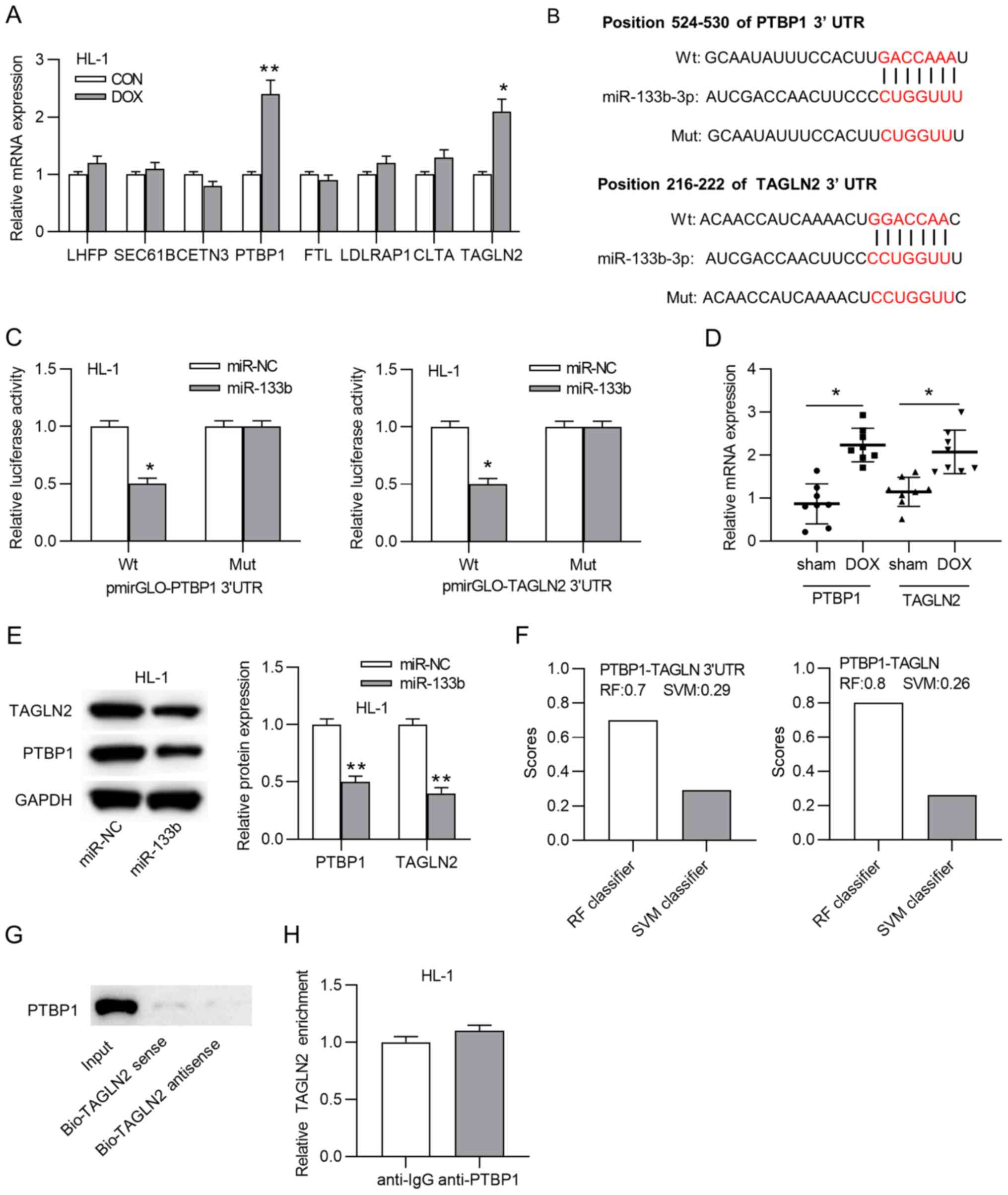
|
1
|
Rivankar S: An overview of doxorubicin
formulations in cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:853–858.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Genovese I, Fiorillo A, Ilari A,
Masciarelli S, Fazi F and Colotti G: Binding of doxorubicin to
Sorcin impairs cell death and increases drug resistance in cancer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 8:e29502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Borlle L, Dergham A, Wund Z, Zumbo B,
Southard T and Hume KR: Salinomycin decreases feline sarcoma and
carcinoma cell viability when combined with doxorubicin. BMC Vet
Res. 15:362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis HL
Jr, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M and Muggia FM: Risk factors for
doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med.
91:710–717. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
du Pré BC, Dierickx P, Crnko S, Doevendans
PA, Vos MA, Geijsen N, Neutel D, van Veen TAB and van Laake LW:
Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes as an in vitro model for circadian
rhythms in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 112:58–63. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hole LD, Larsen TH, Fossan KO, Limé F and
Schjøtt J: Diazoxide protects against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity in the rat. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 15:282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Beer EL, Bottone AE and Voest EE:
Doxorubicin and mechanical performance of cardiac trabeculae after
acute and chronic treatment: A review. Eur J Pharmacol. 415:1–11.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Unverferth DV, Magorien RD, Leier CV and
Balcerzak SP: Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cancer Treat Rev.
9:149–164. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cecen E, Dost T, Culhaci N, Karul A, Ergur
B and Birincioglu M: Protective effects of silymarin against
doxorubicin-induced toxicity. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
12:2697–2704. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Burlacu A, Siriopol D, Voroneanu L, Nistor
I, Hogas S, Nicolae A, Nedelciuc I, Tinica G and Covic A:
Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis prevalence and correlations
in acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary
percutaneous coronary interventions: Data from Nonrandomized
Single-Center Study (REN-ACS)-A single center, prospective,
observational study. J Am Heart Assoc. 4:e0023792015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Lin RC and McMullen
JR: MiRNA therapeutics: A new class of drugs with potential
therapeutic applications in the heart. Future Med Chem.
7:1771–1792. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao L, Qi Y, Xu L, Tao X, Han X, Yin L
and Peng J: MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via
targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Redox Biol. 15:284–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gupta SK, Garg A, Avramopoulos P,
Engelhardt S, Streckfuss-Bömeke K, Batkai S and Thum T: MiR-212/132
cluster modulation prevents Doxorubicin-Mediated atrophy and
cardiotoxicity. Mol Ther. 27:17–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Li N, Zhou H and Tang Q: MiR-133: A
suppressor of cardiac remodeling? Front Pharmacol. 9:9032018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Li M, Xu L, Liu J, Wang D, Li Q,
Wang L, Li P, Chen S and Liu T: Expression of Bcl-2 and microRNAs
in cardiac tissues of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Mol Med
Rep. 15:359–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cortez-Dias N, Costa MC, Carrilho-Ferreira
P, Silva D, Jorge C, Calisto C, Pessoa T, Robalo Martins S, de
Sousa JC, da Silva PC, et al: Circulating miR-122-5p/miR-133b Ratio
is a specific early prognostic biomarker in acute myocardial
infarction. Circ J. 80:2183–2191. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L and Wang H: Long Non-coding RNA in
CNS injuries: A new target for therapeutic intervention. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 17:754–766. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Atef MM, Amer AI, Hafez YM, Elsebaey MA,
Saber SA and Abd El-Khalik SR: Long non-coding RNA EGFR-AS1 in
colorectal cancer: A potential factor in tumorigenesis and survival
via miRNA-133b sponge and EGFR/STAT3 axis regulation. Br J Biomed
Sci. 2020.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
21
|
Zhao N, Liu H, Zhang A and Wang M:
Expression levels and clinical significance of miR-203 and miR-133b
in laryngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 20:2132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Li Y, Li Z and Cao L: LncRNA
MST1P2/miR-133b axis affects the chemoresistance of bladder cancer
to cisplatin-based therapy via Sirt1/p53 signaling. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 34:e224522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sandhu H, Cooper S, Hussain A, Mee C and
Maddock H: Attenuation of Sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity through
the A3 adenosine receptor activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 814:95–105.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cooper SL, Sandhu H, Hussain A, Mee C and
Maddock H: Involvement of mitogen activated kinase kinase 7
intracellular signalling pathway in Sunitinib-induced
cardiotoxicity. Toxicology. 394:72–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hanousková B, Skála M, Brynychová V,
Zárybnický T, Skarková V, Kazimírová P, Vernerová A, Souček P,
Skálová L, Pudil R and Matoušková P: Imatinib-induced changes in
the expression profile of microRNA in the plasma and heart of
mice-A comparison with doxorubicin. Biomed Pharmacother.
115:1088832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He SF, Zhu HJ, Han ZY, Wu H, Jin SY, Irwin
MG and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-133b-5p is involved in cardioprotection of
morphine preconditioning in rat cardiomyocytes by targeting fas.
Can J Cardiol. 32:996–1007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Panizo S, Carrillo-López N, Naves-Díaz M,
Solache-Berrocal G, Martínez-Arias L, Rodrigues-Díez RR,
Fernández-Vázquez A, Martínez-Salgado C, Ruiz-Ortega M, Dusso A, et
al: Regulation of miR-29b and miR-30c by vitamin D receptor
activators contributes to attenuate uraemia-induced cardiac
fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 32:1831–1840. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roca-Alonso L, Castellano L, Mills A,
Dabrowska AF, Sikkel MB, Pellegrino L, Jacob J, Frampton AE, Krell
J, Coombes RC, et al: Myocardial MiR-30 downregulation triggered by
doxorubicin drives alterations in β-adrenergic signaling and
enhances apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17542015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tao L, Bei Y, Chen P, Lei Z, Fu S, Zhang
H, Xu J, Che L, Chen X, Sluijter JP, et al: Crucial role of miR-433
in regulating cardiac fibrosis. Theranostics. 6:2068–2083. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Sun L, Sun H, Liu X, Luo X, Li C,
Sun D and Li T: Overexpression of microRNA-133b reduces myocardial
injuries in children with viral myocarditis by targeting Rab27B
gene. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 63:80–86. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Balli E, Mete UO, Tuli A, Tap O and Kaya
M: Effect of melatonin on the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin. Histol
Histopathol. 19:1101–1108. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ganey PE, Carter LS, Mueller RA and
Thurman RG: Doxorubicin toxicity in perfused rat heart. Decreased
cell death at low oxygen tension. Circ Res. 68:1610–1613. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saltiel E and McGuire W: Doxorubicin
(adriamycin) cardiomyopathy. West J Med. 139:332–341.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mitani I, Jain D, Joska TM, Burtness B and
Zaret BL: Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: Prevention of congestive
heart failure with serial cardiac function monitoring with
equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography in the current era. J
Nucl Cardiol. 10:132–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li J, Zhang S, Zou Y, Wu L, Pei M and
Jiang Y: MiR-145 promotes miR-133b expression through c-myc and
DNMT3A-mediated methylation in ovarian cancer cells. J Cell
Physiol. 235:4291–4301. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ruggeri C, Gioffré S, Achilli F, Colombo
GI and D'Alessandra Y: Role of microRNAs in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity: An overview of preclinical models and cancer
patients. Heart Fail Rev. 23:109–122. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Lu Q, Huo J, Liu P, Bai L and Ma A: lncRNA
HOXB-AS3 protects doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting
miRNA-875-3p. Exp Ther Med. 19:1388–1392. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zeng W, Zhu JF, Liu JY, Li YL, Dong X,
Huang H and Shan L: MiR-133b inhibits cell proliferation, migration
and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting
EGFR. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:476–484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sugiyama T, Taniguchi K, Matsuhashi N,
Tajirika T, Futamura M, Takai T, Akao Y and Yoshida K: MiR-133b
inhibits growth of human gastric cancer cells by silencing pyruvate
kinase muscle-splicer polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1.
Cancer Sci. 107:1767–1775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao F, Zhou LH, Ge YZ, Ping WW, Wu X, Xu
ZL, Wang M, Sha ZL and Jia RP: MicroRNA-133b suppresses bladder
cancer malignancy by targeting TAGLN2-mediated cell cycle. J Cell
Physiol. 234:4910–4923. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Coelho MB, Ascher DB, Gooding C, Lang E,
Maude H, Turner D, Llorian M, Pires DE, Attig J and Smith CW:
Functional interactions between polypyrimidine tract binding
protein and PRI peptide ligand containing proteins. Biochem Soc
Trans. 44:1058–1065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang H, Wang D, Li M, Plecitá-Hlavatá L,
D'Alessandro A, Tauber J, Riddle S, Kumar S, Flockton A, McKeon BA,
et al: Metabolic and proliferative state of vascular adventitial
fibroblasts in pulmonary hypertension is regulated through a
MicroRNA-124/PTBP1 (polypyrimidine tract binding protein
1)/pyruvate kinase muscle axis. Circulation. 136:2468–2485. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pina JM, Reynaga JM, Truong AAM and
Keppetipola NM: Post-Translational modifications in polypyrimidine
tract binding proteins PTBP1 and PTBP2. Biochemistry. 57:3873–3882.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang J, Bahi N, Llovera M, Comella JX and
Sanchis D: Polypyrimidine tract binding proteins (PTB) regulate the
expression of apoptotic genes and susceptibility to
caspase-dependent apoptosis in differentiating cardiomyocytes. Cell
Death Differ. 16:1460–1468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Caruso P, Dunmore BJ, Schlosser K, Schoors
S, Dos Santos C, Perez-Iratxeta C, Lavoie JR, Zhang H, Long L,
Flockton AR, et al: Identification of MicroRNA-124 as a major
regulator of enhanced endothelial cell glycolysis in pulmonary
arterial hypertension via PTBP1 (Polypyrimidine Tract Binding
Protein) and Pyruvate Kinase M2. Circulation. 136:2451–2467. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Belanger K, Nutter CA, Li J, Yu P and
Kuyumcu-Martinez MN: A developmentally regulated spliced variant of
PTBP1 is upregulated in type 1 diabetic hearts. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 509:384–389. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Li AY, Yang Q and Yang K: MiR-133a
mediates the hypoxia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting TAGLN2
expression in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|