|
1
|
Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, Raghu G,
Richeldi L, Selman M, Swigris JJ, Taniguchi H and Wells AU:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170742017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
George PM, Spagnolo P, Kreuter M,
Altinisik G, Bonifazi M, Martinez FJ, Molyneaux PL, Renzoni EA,
Richeldi L, Tomassetti S, et al: Progressive fibrosing interstitial
lung disease: Clinical uncertainties, consensus recommendations,
and research priorities. Lancet Respir Med. 8:925–934. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chanda D, Otoupalova E, Smith SR,
Volckaert T, De Langhe SP and Thannickal VJ: Developmental pathways
in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med. 65:56–69.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Hutchinson J, Fogarty A, Hubbard R and
McKeever T: Global incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: A systematic review. Eur Respir J. 46:795–806. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nalysnyk L, Cid-Ruzafa J, Rotella P and
Esser D: Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
Review of the literature. Eur Respir Rev. 21:355–361. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park Y, Ahn C and Kim TH: Occupational and
environmental risk factors of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A
systematic review and meta-analyses. Sci Rep. 11:43182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lv M, Liu Y, Ma S and Yu Z: Current
advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The pathogenesis,
therapeutic strategies and candidate molecules. Future Med Chem.
11:2595–2620. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hadjicharalambous MR and Lindsay MA:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Pathogenesis and the emerging role
of long non-coding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 21:5242020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Hewlett JC, Kropski JA and Blackwell TS:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions
and emerging therapeutic targets. Matrix Biol. 71-72:112–127. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
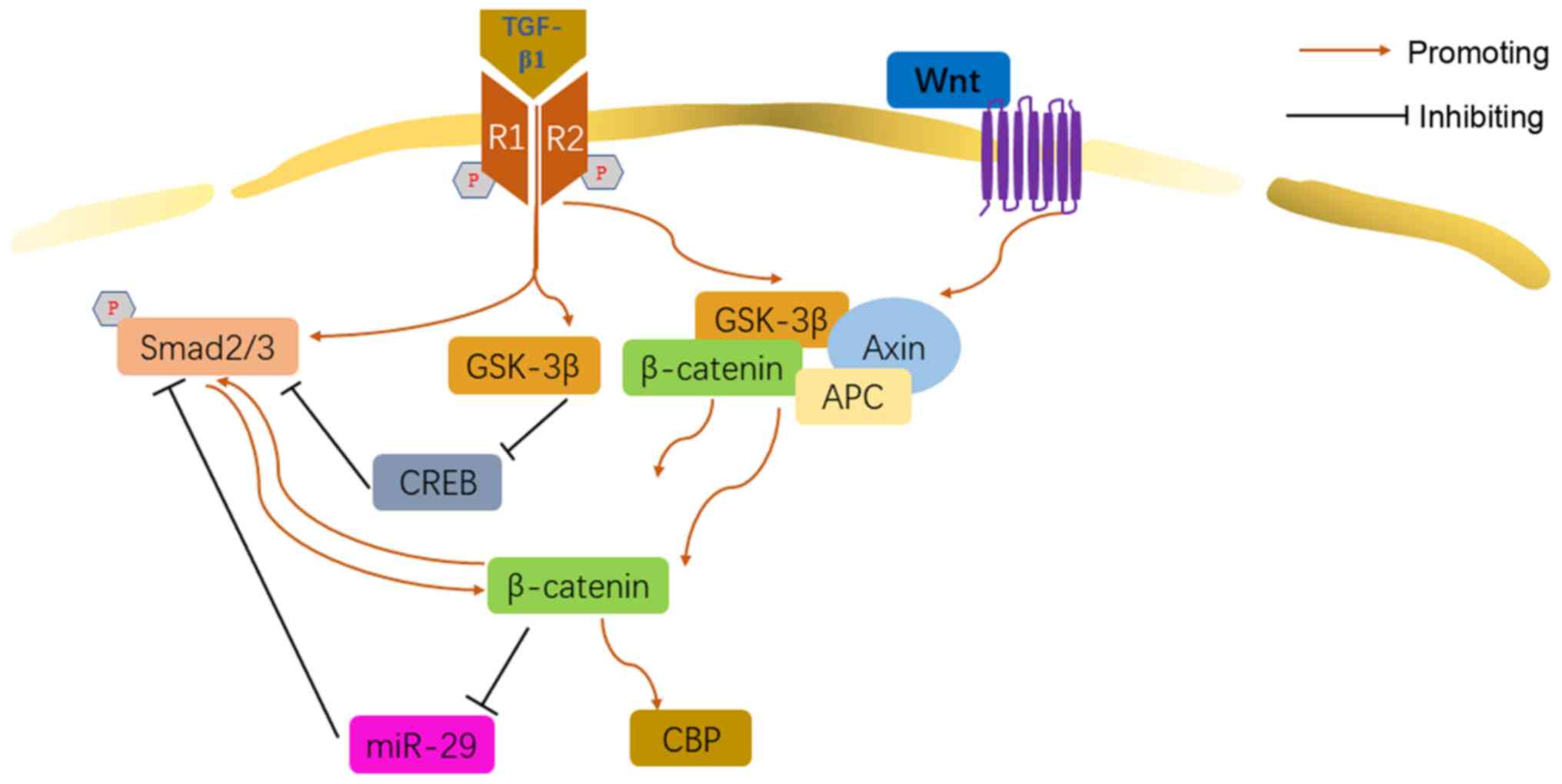
|
11
|
Prashanth Goud M, Bale S, Pulivendala G
and Godugu C: Therapeutic effects of Nimbolide, an autophagy
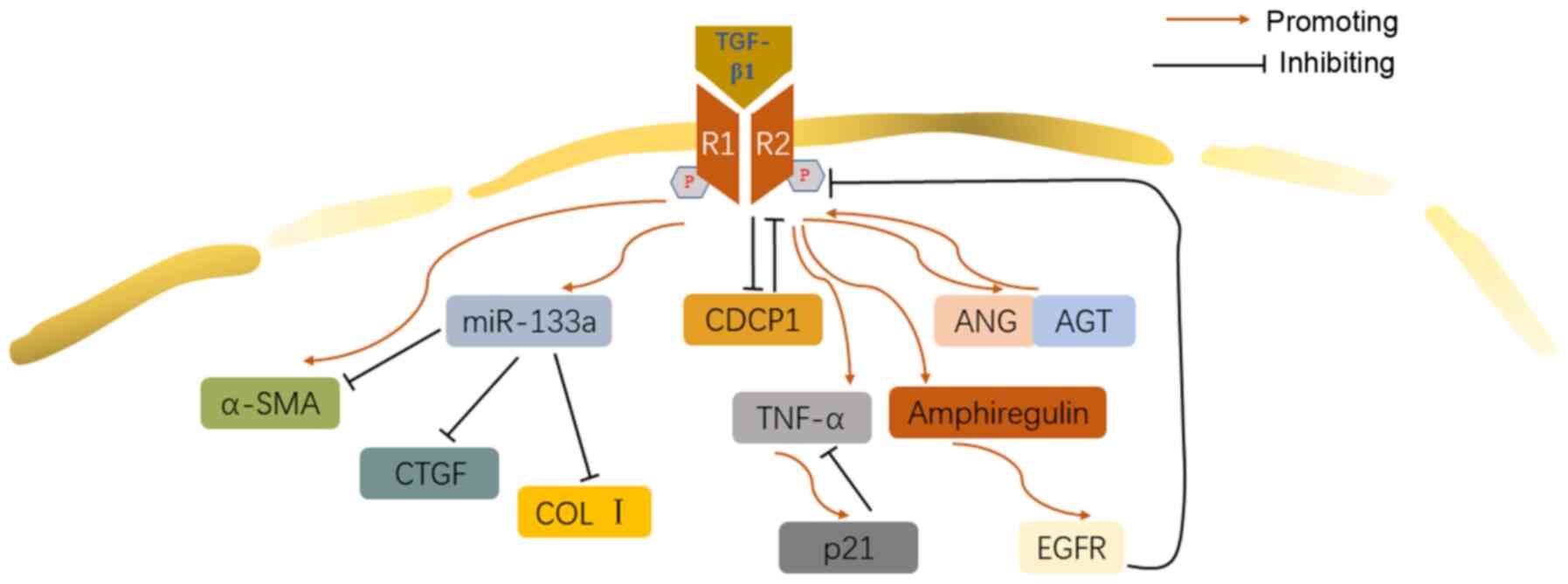
regulator, in ameliorating pulmonary fibrosis through attenuation
of TGF-β1 driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Int
Immunopharmacol. 75:1057552019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
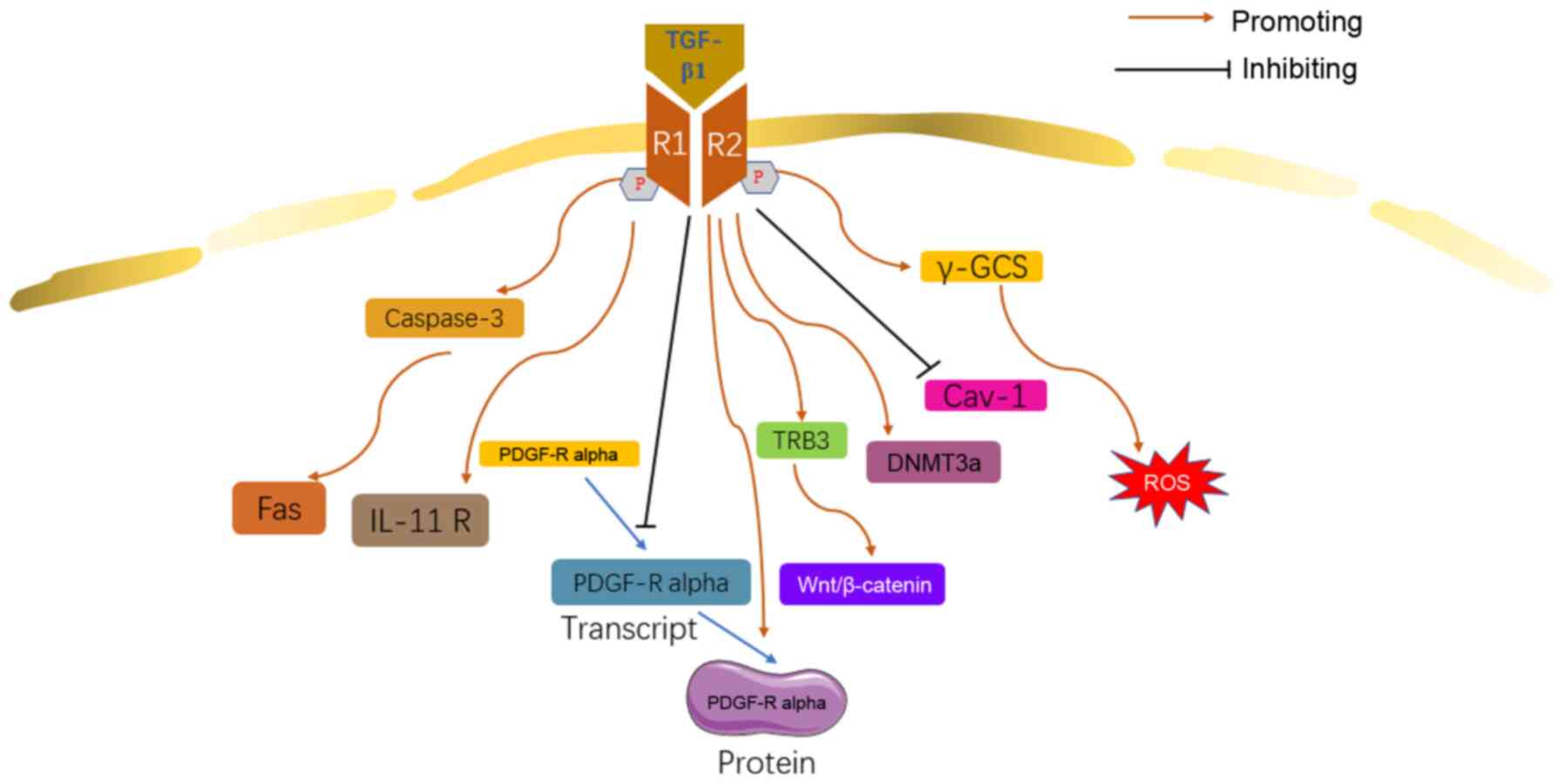
Feng F, Cheng P, Xu S, Li N, Wang H, Zhang
Y and Wang W: Tanshinone IIA attenuates silica-induced pulmonary
fibrosis via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of EMT and TGF-β1/Smad
signaling. Chem Biol Interact. 319:1090242020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Moustafa EM, Ibrahim SI and Salem FAF:
Methylsulfonylmethane inhibits lung fibrosis progression,
inflammatory response, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
the transforming growth factor-Beta 1/SMAD2/3 pathway in rats
exposed to both γ-radiation and Bisphenol-A. Toxin Rev. 1–10.
2020.
|
|
14
|
He J, Peng H, Wang M, Liu Y, Guo X, Wang
B, Dai L, Cheng X, Meng Z, Yuan L, et al: Isoliquiritigenin
inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis through activating autophagy
via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in MRC-5 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 52:810–820. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sgalla G, Iovene B, Calvello M, Ori M,
Varone F and Richeldi L: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
Pathogenesis and management. Respir Res. 19:322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim KK, Sheppard D and Chapman HA:
TGF-beta 1 signaling and tissue fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 10:a0222932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Werner F, Jain MK, Feinberg MW, Sibinga
NE, Pellacani A, Wiesel P, Chin MT, Topper JN, Perrella MA and Lee
ME: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibition of macrophage
activation is mediated via Smad3. J Biol Chem. 275:36653–36658.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flanders KC: Smad3 as a mediator of the
fibrotic response. Int J Exp Pathol. 85:47–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng R, Xiong Q, Zuo B, Jiang S, Li F,
Lei M, Deng C and Xiong Y: Using RNA interference to identify the
different roles of SMAD2 and SMAD3 in NIH/3T3 fibroblast cells.
Cell Biochem Funct. 26:548–556. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roberts AB, Piek E, Bottinger EP, Ashcroft
G, Mitchell JB and Flanders KC: Is Smad3 a major player in signal
transduction pathways leading to fibrogenesis? Chest. 120(1 Suppl):
43S–47S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Evans RA, Tian YC, Steadman R and Phillips
AO: TGF-beta1-mediated fibroblast-myofibroblast terminal
differentiation-the role of Smad proteins. Exp Cell Res.
282:90–100. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gu L, Zhu YJ, Yang X, Guo ZJ, Xu WB and
Tian XL: Effect of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway on lung
myofibroblast differentiation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:382–391.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kobayashi T, Liu X, Wen FQ, Kohyama T,
Shen L, Wang XQ, Hashimoto M, Mao L, Togo S, Kawasaki S, et al:
Smad3 mediates TGF-beta1-induced collagen gel contraction by human
lung fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 339:290–295. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Deng X, Jin K, Li Y, Gu W, Liu M and Zhou
L: Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor β1
Regulate ARDS-associated lung fibrosis through distinct signaling
pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:937–946. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lim MJ, Ahn J, Yi JY, Kim MH, Son AR, Lee
SL, Lim DS, Kim SS, Kang MA, Han Y and Song JY: Induction of
galectin-1 by TGF-β1 accelerates fibrosis through enhancing nuclear
retention of Smad2. Exp Cell Res. 326:125–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang Y, Xie Y, Abel PW, Wei P, Plowman J,
Toews ML, Strah H, Siddique A, Bailey KL and Tu Y: TGF-β1-induced
miR-424 promotes pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation by
targeting Slit2 protein expression. Biochem Pharmacol.
180:1141722020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hecker L, Vittal R, Jones T, Jagirdar R,
Luckhardt TR, Horowitz JC, Pennathur S, Martinez FJ and Thannickal
VJ: NADPH oxidase-4 mediates myofibroblast activation and
fibrogenic responses to lung injury. Nat Med. 15:1077–1081. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fierro-Fernández M, Busnadiego Ó, Sandoval
P, Espinosa-Díez C, Blanco-Ruiz E, Rodríguez M, Pian H, Ramos R,
López-Cabrera M, García-Bermejo ML and Lamas S: miR-9-5p suppresses
pro-fibrogenic transformation of fibroblasts and prevents organ
fibrosis by targeting NOX4 and TGFBR2. EMBO Rep. 16:1358–1377.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo W, Saito S, Sanchez CG, Zhuang Y,
Gongora Rosero RE, Shan B, Luo F and Lasky JA: TGF-β1
stimulates HDAC4 nucleus-to-cytoplasm translocation and NADPH
oxidase 4-derived reactive oxygen species in normal human lung
fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 312:L936–L944.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Q, Tu W, Tian K, Han L, Wang Q, Chen
P and Zhou X: Sirtuin 6 inhibits myofibroblast differentiation via
inactivating transforming growth factor-β1/Smad2 and nuclear
factor-κB signaling pathways in human fetal lung fibroblasts. J
Cell Biochem. 120:93–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, Mao J, Gao L, Liu J
and Wu T: Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2:787–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Câmara J and Jarai G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary human bronchial
epithelial cells is Smad-dependent and enhanced by fibronectin and
TNF-alpha. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 3:22010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kasai H, Allen JT, Mason RM, Kamimura T
and Zhang Z: TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to
mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir Res. 6:562005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li LC, Li DL, Xu L, Mo XT, Cui WH, Zhao P,
Zhou WC, Gao J and Li J: High-mobility group box 1 mediates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis
involving transforming growth factor-β1/Smad2/3 signaling. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 354:302–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guan S and Zhou J: CXCR7 attenuates the
TGF-β-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary
fibrosis. Mol Biosyst. 13:2116–2124. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang Y, Zhou X, Hu R and Dai A:
TGF-β1-induced SMAD2/3/4 activation promotes RELM-β transcription
to modulate the endothelium-mesenchymal transition in human
endothelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 105:52–60. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kolosionek E, Savai R, Ghofrani HA,
Weissmann N, Guenther A, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Banat GA,
Schermuly RT and Pullamsetti SS: Expression and activity of
phosphodiesterase isoforms during epithelial mesenchymal
transition: The role of phosphodiesterase 4. Mol Biol Cell.
20:4751–4765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ramirez A, Ballard EN and Roman J: TGFβ1
controls PPARγ expression, transcriptional potential, and activity,
in part, through Smad3 signaling in murine lung fibroblasts. PPAR
Res. 2012:3758762012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li HH, Cai Q, Wang YP, Liu HR and Huang M:
The role of transforming growth factor-β1/connective
tissue growth factor signaling pathway in paraquat-induced
pulmonary fibrosis. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi.
34:484–488. 2016.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng X, Qi C, Zhang S, Fang Y and Ning W:
TGF-β1 induces Fstl1 via the Smad3-c-Jun pathway in lung
fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 313:L240–L251.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Huang C, Liang Y, Zeng X, Yang X, Xu D,
Gou X, Sathiaseelan R, Senavirathna LK, Wang P and Liu L: Long
noncoding RNA FENDRR exhibits antifibrotic activity in pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 62:440–453. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Kadoya K, Togo S, Tulafu M, Namba Y, Iwai
M, Watanabe J, Okabe T, Jin J, Kodama Y, Kitamura H, et al:
Specific features of fibrotic lung fibroblasts highly sensitive to
fibrotic processes mediated via TGF-β-ERK5 interaction. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 52:822–837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cushing L, Kuang PP, Qian J, Shao F, Wu J,
Little F, Thannickal VJ, Cardoso WV and Lü J: miR-29 is a major
regulator of genes associated with pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 45:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Yang T, Liang Y, Lin Q, Liu J, Luo F, Li
X, Zhou H, Zhuang S and Zhang H: miR-29 mediates TGFβ1-induced
extracellular matrix synthesis through activation of PI3K-AKT
pathway in human lung fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 114:1336–1342.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xiao J, Meng XM, Huang XR, Chung AC, Feng
YL, Hui DS, Yu CM, Sung JJ and Lan HY: miR-29 inhibits
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Mol Ther.
20:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Yang Z and Tan M:
Inhibition of miR-182-5p attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via
TGF-β/Smad pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 39:683–695. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kang HR, Lee CG, Homer RJ and Elias JA:
Semaphorin 7A plays a critical role in TGF-beta1-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. J Exp Med. 204:1083–1093. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mukherjee D, Bercz LS, Torok MA and Mace
TA: Regulation of cellular immunity by activating transcription
factor 4. Immunol Lett. 228:24–34. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Selvarajah B, Azuelos I, Platé M,
Guillotin D, Forty EJ, Contento G, Woodcock HV, Redding M, Taylor
A, Brunori G, et al: mTORC1 amplifies the ATF4-dependent de novo
serine-glycine pathway to supply glycine during
TGF-β1-induced collagen biosynthesis. Sci Signal.
12:eaav30482019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Woodcock HV, Eley JD, Guillotin D, Platé
M, Nanthakumar CB, Martufi M, Peace S, Joberty G, Poeckel D, Good
RB, et al: The mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis represents a critical signaling
node during fibrogenesis. Nat Commun. 10:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cong LH, Li T, Wang H, Wu YN, Wang SP,
Zhao YY, Zhang GQ and Duan J: IL-17A-producing T cells exacerbate
fine particulate matter-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis by
inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated autophagy. J Cell Mol Med.
24:8532–8544. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fang L, Chen H, Kong R and Que J:
Endogenous tryptophan metabolite 5-methoxytryptophan inhibits
pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β/SMAD3 and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Life Sci. 260:1183992020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hettiarachchi SU, Li YH, Roy J, Zhang F,
Puchulu-Campanella E, Lindeman SD, Srinivasarao M, Tsoyi K, Liang
X, Ayaub EA, et al: Targeted inhibition of PI3 kinase/mTOR
specifically in fibrotic lung fibroblasts suppresses pulmonary
fibrosis in experimental models. Sci Transl Med. 12:eaay37242020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hu X, Xu Q, Wan H, Hu Y, Xing S, Yang H,
Gao Y and He Z: PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung
fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in
lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Lab Invest.
100:801–811. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Graves DT and Milovanova TN: Mucosal
immunity and the FOXO1 transcription factors. Front Immunol.
10:25302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shi L, Dong N, Fang X and Wang X:
Regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis of human
alveolar epithelial cells. J Cell Mol Med. 20:2183–2193. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wygrecka M, Zakrzewicz D, Taborski B,
Didiasova M, Kwapiszewska G, Preissner KT and Markart P: TGF-β1
induces tissue factor expression in human lung fibroblasts in a
PI3K/JNK/Akt-dependent and AP-1-dependent manner. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 47:614–627. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bengal E, Aviram S and Hayek T: p38 MAPK
in glucose metabolism of skeletal muscle: Beneficial or harmful?
Int J Mol Sci. 21:64802020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
He X and Wang C, Wang H, Li L and Wang C:
The function of MAPK cascades in response to various stresses in
horticultural plants. Front Plant Sci. 11:9522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Magnelli L, Schiavone N, Staderini F,
Biagioni A and Papucci L: MAP kinases pathways in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:28932020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Jablonska E, Markart P, Zakrzewicz D,
Preissner KT and Wygrecka M: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces
expression of human coagulation factor XII via Smad3 and JNK
signaling pathways in human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
285:11638–11651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen HH, Zhou XL, Shi YL and Yang J: Roles
of p38 MAPK and JNK in TGF-β1-induced human alveolar epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. Arch Med Res. 44:93–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Khalil N, Xu YD, O'Connor R and Duronio V:
Proliferation of pulmonary interstitial fibroblasts is mediated by
transforming growth factor-beta1-induced release of extracellular
fibroblast growth factor-2 and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK.
J Biol Chem. 280:43000–43009. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Matsumoto
K, Maruoka S and Horie T: Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces
phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast
through a c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 163:152–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cui Y, Osorio JC, Risquez C, Wang H, Shi
Y, Gochuico BR, Morse D, Rosas IO and El-Chemaly S: Transforming
growth factor-β1 downregulates vascular endothelial growth factor-D
expression in human lung fibroblasts via the Jun NH2-terminal
kinase signaling pathway. Mol Med. 20:120–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
van der Velden JL, Wagner DE, Lahue KG,
Abdalla ST, Lam YW, Weiss DJ and Janssen-Heininger YMW:
TGF-β1-induced deposition of provisional extracellular matrix by
tracheal basal cells promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in a c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-1-dependent manner. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L984–L997. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Kulasekaran P, Scavone CA, Rogers DS,
Arenberg DA, Thannickal VJ and Horowitz JC: Endothelin-1 and
transforming growth factor-beta1 independently induce fibroblast
resistance to apoptosis via AKT activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 41:484–493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
García-Alvarez J, Ramirez R, Checa M,
Nuttall RK, Sampieri CL, Edwards DR, Selman M and Pardo A: Tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 is up-regulated by transforming
growth factor-beta1 in vitro and expressed in fibroblastic foci in
vivo in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 32:201–214.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gu H, Mickler EA, Cummings OW, Sandusky
GE, Weber DJ, Gracon A, Woodruff T, Wilkes DS and Vittal R:
Crosstalk between TGF-β1 and complement activation augments
epithelial injury in pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 28:4223–4234.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Finlay GA, Thannickal VJ, Fanburg BL and
Paulson KE: Transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced activation of
the ERK pathway/activator protein-1 in human lung fibroblasts
requires the autocrine induction of basic fibroblast growth factor.
J Biol Chem. 275:27650–27656. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Caraci F, Gili E, Calafiore M, Failla M,
La Rosa C, Crimi N, Sortino MA, Nicoletti F, Copani A and Vancheri
C: TGF-beta1 targets the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway via ERK
activation in the transition of human lung fibroblasts into
myofibroblasts. Pharmacol Res. 57:274–282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ghatak S, Markwald RR, Hascall VC, Dowling
W, Lottes RG, Baatz JE, Beeson G, Beeson CC, Perrella MA,
Thannickal VJ and Misra S: Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1)
regulates CD44V6 expression and activity through extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-induced EGR1 in pulmonary fibrogenic
fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 292:10465–10489. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xiao L, Du Y, Shen Y, He Y, Zhao H and Li
Z: TGF-beta 1 induced fibroblast proliferation is mediated by the
FGF-2/ERK pathway. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:2667–2674. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lu M, Munger JS, Steadele M, Busald C,
Tellier M and Schnapp LM: Integrin alpha8beta1 mediates adhesion to
LAP-TGFbeta1. J Cell Sci. 115:4641–4648. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bugter JM, Fenderico N and Maurice MM:
Mutations and mechanisms of WNT pathway tumour suppressors in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:5–21. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Rapetti-Mauss R, Berenguier C, Allegrini B
and Soriani O: Interplay between ion channels and the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in cancers. Front Pharmacol. 11:5250202020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Söderholm S and Cantù C: The WNT/β-catenin
dependent transcription: A tissue-specific business. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. Oct 21–2020.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Lu Y, Zhang T, Shan S, Wang S, Bian W, Ren
T and Yang D: MiR-124 regulates transforming growth factor-β1
induced differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells to
myofibroblast by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Dev Biol.
449:115–121. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu L, Cui WH, Zhou WC, Li DL, Li LC, Zhao
P, Mo XT, Zhang Z and Gao J: Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling
is required for TGF-β/Smad2/3 signalling during myofibroblast
proliferation. J Cell Mol Med. 21:1545–1554. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Baarsma HA, Engelbertink LH, van Hees LJ,
Menzen MH, Meurs H, Timens W, Postma DS, Kerstjens HA and Gosens R:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) regulates TGF-β1-induced
differentiation of pulmonary fibroblasts. Br J Pharmacol.
169:590–603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Pan Q, Su Y, Zhang Z, Han
J, Zhu X, Tang C and Hu D: Wnt/β-catenin pathway forms a negative
feedback loop during TGF-β1 induced human normal skin
fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition. J Dermatol Sci. 65:38–49.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang
H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, et al: Interactions
between β-catenin and transforming growth factor-β signaling
pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are
dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response
element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem.
287:7026–7038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wang Y, Liu J, Chen J, Feng T and Guo Q:
MiR-29 mediates TGFβ 1-induced extracellular matrix synthesis
through activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human pulmonary
fibroblasts. Technol Health Care. 23(Suppl 1): S119–S125. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Noskovičová N, Heinzelmann K, Burgstaller
G, Behr J and Eickelberg O: Cub domain-containing protein 1
negatively regulates TGF-β signaling and myofibroblast
differentiation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L695–L707.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Uhal BD, Kim JK, Li X and Molina-Molina M:
Angiotensin-TGF-beta 1 crosstalk in human idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Autocrine mechanisms in myofibroblasts and macrophages.
Curr Pharm Des. 13:1247–1256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wei P, Xie Y, Abel PW, Huang Y, Ma Q, Li
L, Hao J, Wolff DW, Wei T and Tu Y: Transforming growth factor
(TGF)-β1-induced miR-133a inhibits myofibroblast differentiation
and pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 10:6702019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Yamasaki M, Kang HR, Homer RJ, Chapoval
SP, Cho SJ, Lee BJ, Elias JA and Lee CG: P21 regulates
TGF-beta1-induced pulmonary responses via a TNF-alpha-signaling
pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 38:346–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yamauchi Y, Kohyama T, Takizawa H,
Kamitani S, Desaki M, Takami K, Kawasaki S, Kato J and Nagase T:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances both epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cell contraction induced in A549 human alveolar
epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Exp Lung
Res. 36:12–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Bissonnette EY, Enciso JA and Befus AD:
TGF-beta1 inhibits the release of histamine and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha from mast cells through an autocrine pathway. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 16:275–282. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhou Y, Lee JY, Lee CM, Cho WK, Kang MJ,
Koff JL, Yoon PO, Chae J, Park HO, Elias JA and Lee CG:
Amphiregulin, an epidermal growth factor receptor ligand, plays an
essential role in the pathogenesis of transforming growth
factor-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Biol Chem. 287:41991–42000.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bonner JC, Badgett A, Lindroos PM and
Osornio-Vargas AR: Transforming growth factor beta 1 downregulates
the platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor subtype on human
lung fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 13:496–505.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ng B, Dong J, D'Agostino G, Viswanathan S,
Widjaja AA, Lim WW, Ko NSJ, Tan J, Chothani SP, Huang B, et al:
Interleukin-11 is a therapeutic target in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Sci Transl Med. 11:eaaw12372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhang Y and Yi Z:
Expression of interleukin-11 and its receptor in lung of mice with
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
43:1083–1088. 2018.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Otsuki T, Hayashi H, Nishimura Y, Hyodo F,
Maeda M, Kumagai N, Miura Y, Kusaka M and Uragami K: Dysregulation
of autoimmunity caused by silica exposure and alteration of
Fas-mediated apoptosis in T lymphocytes derived from silicosis
patients. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 24(Suppl): 11S–16S.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hagimoto N, Kuwano K, Inoshima I, Yoshimi
M, Nakamura N, Fujita M, Maeyama T and Hara N: TGF-beta 1 as an
enhancer of Fas-mediated apoptosis of lung epithelial cells. J
Immunol. 168:6470–6478. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yu W, Mi L and Wang F: Effect of the
alteration of Tribbles homologue 3 expression on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of transforming growth factor
β1-induced mouse alveolar epithelial cells through the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 21:615–622.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Andonegui G, Ni A, Leger C, Kelly MM, Wong
JF, Jalloul A and Winston BW: Sequential expression of IGF-IB
followed by active TGF-β1 induces synergistic pulmonary
fibroproliferation in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
303:L788–L798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Negreros M, Hagood JS, Espinoza CR,
Balderas-Martinez YI, Selman M and Pardo A: Transforming growth
factor beta 1 induces methylation changes in lung fibroblasts. PLoS
One. 14:e02235122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sanders YY, Liu H, Scruggs AM, Duncan SR,
Huang SK and Thannickal VJ: Epigenetic regulation of caveolin-1
gene expression in lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
56:50–61. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Arsalane K, Dubois CM, Muanza T, Bégin R,
Boudreau F, Asselin C and Cantin AM: Transforming growth
factor-beta1 is a potent inhibitor of glutathione synthesis in the
lung epithelial cell line A549: Transcriptional effect on the GSH
rate-limiting enzyme gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 17:599–607. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jardine H, MacNee W, Donaldson K and
Rahman I: Molecular mechanism of transforming growth factor
(TGF)-beta1-induced glutathione depletion in alveolar epithelial
cells. Involvement of AP-1/ARE and Fra-1. J Biol Chem.
277:21158–21166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Boustani MR, Hertig IA, Maloney EK,
Fanburg BL and White AC: Transforming growth factor B1 decreases
uptake of glutathione precursor amino acids in bovine pulmonary
artery endothelial cells. Endothelium. 5:1–10. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Cho SJ and Stout-Delgado HW: Aging and
lung disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 82:433–459. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Wakwaya Y and Brown KK: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis: Epidemiology, diagnosis and outcomes. Am J Med
Sci. 357:359–369. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Abramson MJ, Murambadoro T, Alif SM, Benke
GP, Dharmage SC, Glaspole I, Hopkins P, Hoy RF, Klebe S, Moodley Y,
et al: Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis in Australia: Case-control study. Thorax.
75:864–869. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Somogyi V, Chaudhuri N, Torrisi SE, Kahn
N, Müller V and Kreuter M: The therapy of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: What is next? Eur Respir Rev. 28:1900212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Amor MS, Rosengarten D, Shitenberg D,
Pertzov B, Shostak Y and Kramer MR: Lung transplantation in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Risk factors and outcome. Isr Med
Assoc J. 22:741–746. 2020.
|
|
109
|
Yang S, Liu P, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Dai H and
Wang C: Therapeutic applications of mesenchymal stem cells in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6396572021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Chang X, Tian M, Zhang Q, Gao J, Li S and
Sun Y: Nano nickel oxide promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through transforming growth factor β1/smads signaling pathway in
A549 cells. Environ Toxicol. 35:1308–1317. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Rosell-García T, Palomo-Álvarez O and
Rodríguez-Pascual F: A hierarchical network of hypoxia-inducible
factor and SMAD proteins governs procollagen lysyl hydroxylase 2
induction by hypoxia and transforming growth factor β1. J Biol
Chem. 294:14308–14318. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Ko J, Mills T, Huang J, Chen NY, Mertens
TCJ, Collum SD, Lee G, Xiang Y, Han L, Zhou Y, et al: Transforming
growth factor β1 alters the 3′-UTR of mRNA to promote lung
fibrosis. J Biol Chem. 294:15781–15794. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Senavirathna LK, Huang C, Pushparaj S, Xu
D and Liu L: Hypoxia and transforming growth factor β1 regulation
of long non-coding RNA transcriptomes in human pulmonary
fibroblasts. Physiol Rep. 8:e143432020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Neveu WA, Mills ST, Staitieh BS and
Sueblinvong V: TGF-β1 epigenetically modifies Thy-1 expression in
primary lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 309:C616–C626.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Kim S, Han JH, Kim S, Lee H, Kim JR, Lim
JH and Woo CH: p90RSK inhibition ameliorates TGF-β1 signaling and
pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting Smad3 transcriptional activity.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 54:195–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Yokoyama T, Chida K,
Azuma A, Suda T, Kudoh S, Sakamoto N, Okamoto K, Kobashi G, et al:
Occupational and environmental factors and idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis in Japan. Ann Occup Hyg. 49:259–265. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Kim SY, Kang DM, Lee HK, Kim KH and Choi
J: Occupational and environmental risk factors for chronic
fibrosing idiopathic interstitial pneumonia in South Korea. J Occup
Environ Med. 59:e221–e226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Baumgartner KB, Samet JM, Coultas DB,
Stidley CA, Hunt WC, Colby TV and Waldron JA: Occupational and
environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A
multicenter case-control study. Collaborating centers. Am J
Epidemiol. 152:307–315. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
García-Sancho Figueroa MC, Carrillo G,
Pérez-Padilla R, Fernández-Plata MR, Buendía-Roldán I, Vargas MH
and Selman M: Risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a
Mexican population. A case-control study. Respir Med. 104:305–309.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Awadalla NJ, Hegazy A, Elmetwally RA and
Wahby I: Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis in Egypt: A multicenter case-control study. Int
J Occup Environ Med. 3:107–116. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Koo JW, Myong JP, Yoon HK, Rhee CK, Kim Y,
Kim JS, Jo BS, Cho Y, Byun J, Choi M, et al: Occupational exposure
and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A multicentre case-control study
in Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 21:107–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Paolocci G, Folletti I, Torén K, Ekström
M, Dell'Omo M, Muzi G and Murgia N: Occupational risk factors for
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Southern Europe: A case-control
study. BMC Pulm Med. 18:752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|