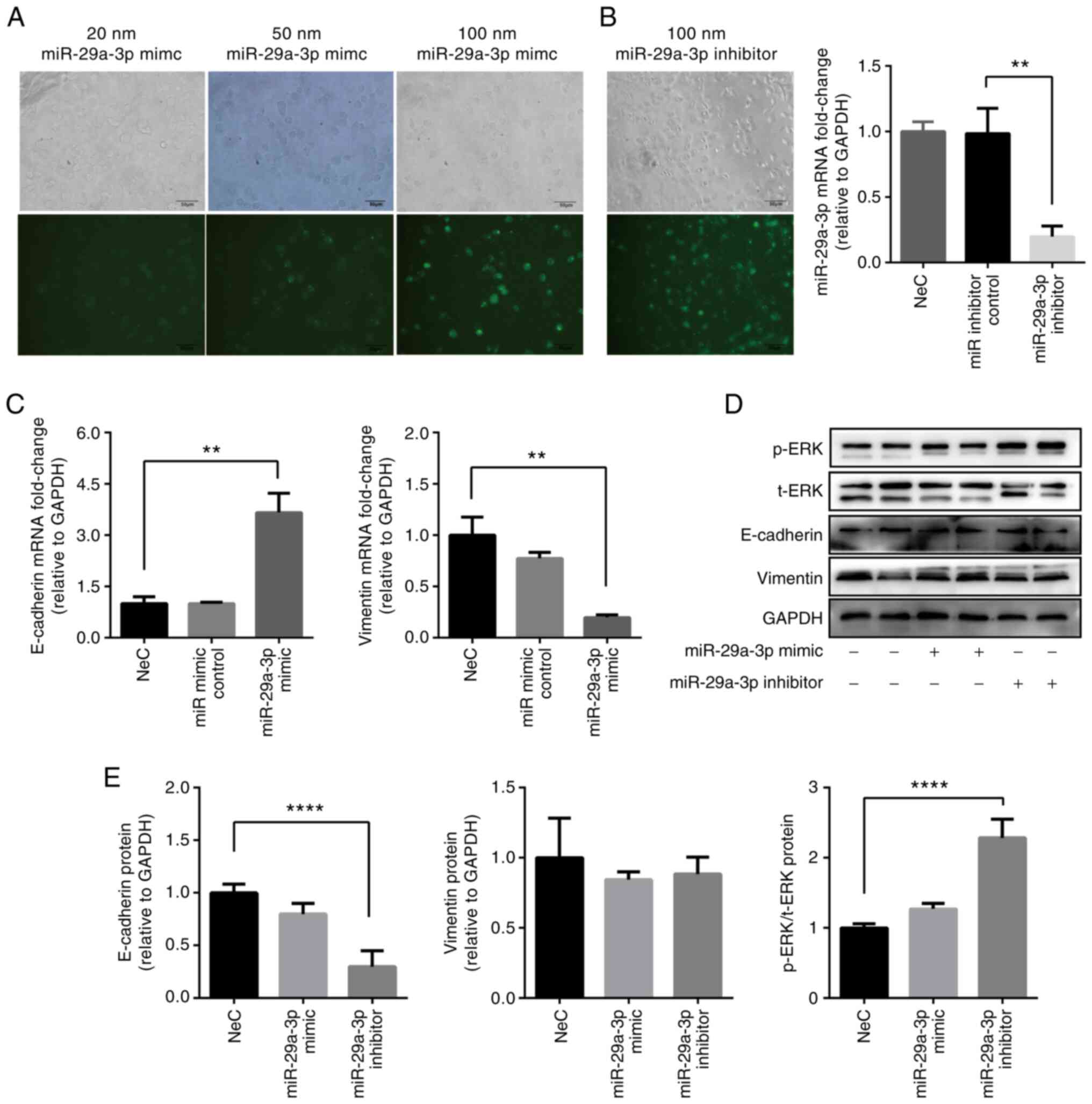
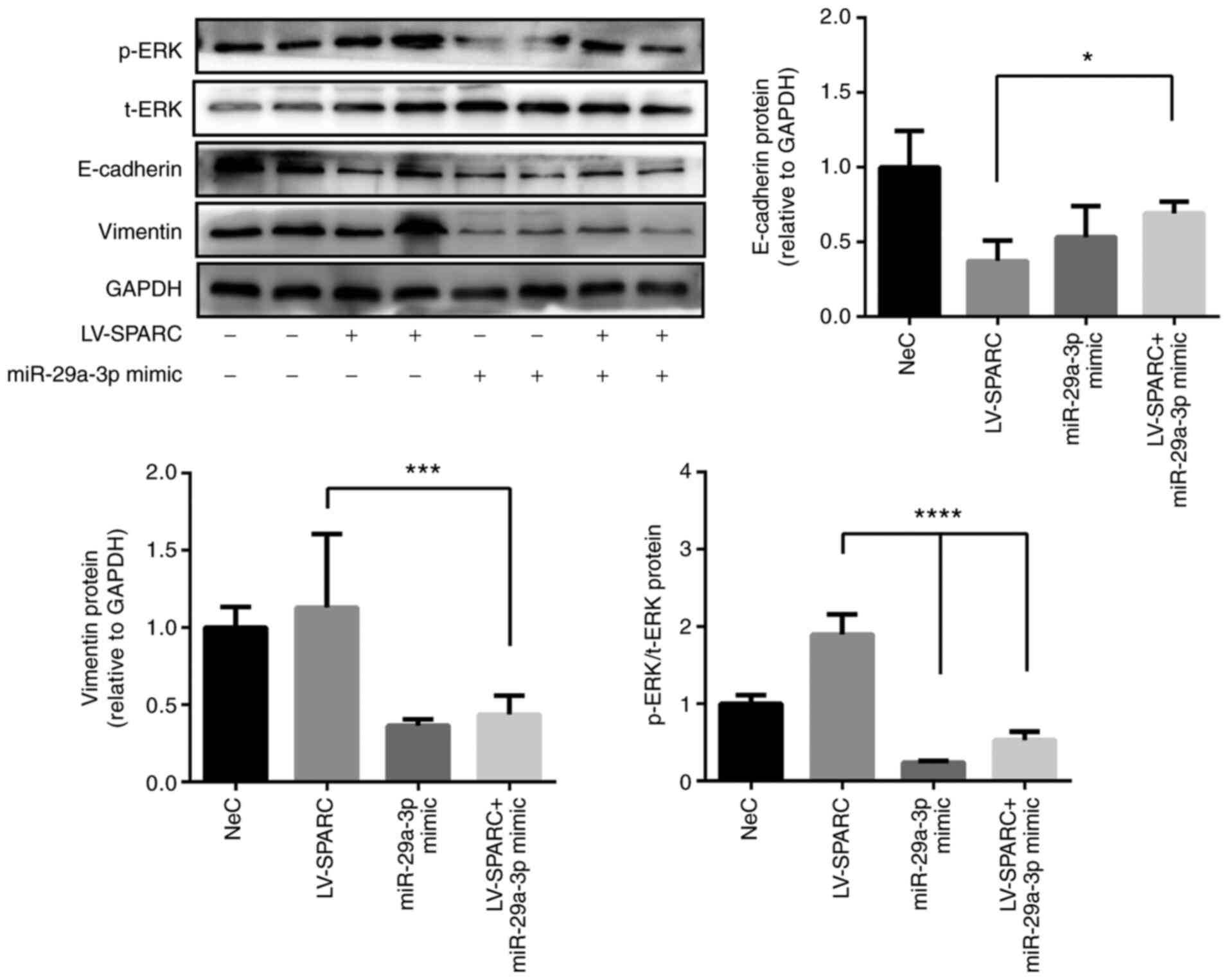
|
1
|
Szefler SJ, Fitzgerald DA, Adachi Y, Doull
IJ, Fischer GB, Fletcher M, Hong J, García-Marcos L, Pedersen S,
Østrem A, et al: A worldwide charter for all children with asthma.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 55:1282–1292. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seys SF, Lokwani R, Simpson JL and Bullens
DMA: New insights in neutrophilic asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med.
25:113–120. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gibson PG and Foster PS: Neutrophilic
asthma: Welcome back! Eur Respir J. 54:19018462019.
|
|
4
|
Postma DS and Rabe KF: The asthma-COPD
overlap syndrome. N Engl J Med. 373:1241–1249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jonas S and Izaurralde E: Towards a
molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat
Rev Genet. 16:421–433. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwon JJ, Factora TD, Dey S and Kota J: A
systematic review of miR-29 in cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
12:173–194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gao Y, Qiao H, Lu Z and Hou Y: miR-29
promotes the proliferation of cultured rat neural stem/progenitor
cells via the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
20:2111–2118. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sohal SS, Ward C and Walters EH:
Importance of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in COPD and
asthma. Thorax. 69:7682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haddad A, Gaudet M, Plesa M, Allakhverdi
Z, Mogas AK, Audusseau S, Baglole CJ, Eidelman DH, Olivenstein R,
Ludwig MS and Hamid Q: Neutrophils from severe asthmatic patients
induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition in healthy bronchial
epithelial cells. Respir Res. 20:2342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilson RH, Whitehead GS, Nakano H, Free
ME, Kolls JK and Cook DN: Allergic sensitization through the airway
primes Th17-dependent neutrophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 180:720–730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Zhang M, Jiang M and Nong G:
Effect of IL-7 on Th17 cell responses in a mouse model of
neutrophilic asthma. Mol Med Rep. 22:1205–1112. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hou C, Kong J, Liang Y, Huang H, Wen H,
Zheng X, Wu L and Chen Y: HMGB1 contributes to allergen-induced
airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma by modulating
airway inflammation and activating lung fibroblasts. Cell Mol
Immunol. 12:409–423. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xiao J, Meng XM, Huang XR, Chung AC, Feng
YL, Hui DS, Yu CM, Sung JJ and Lan HY: miR-29 inhibits
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Mol Ther.
20:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pavlek LR, Vudatala S, Bartlet CW,
Buhimschi IA, Buhimschi CS and Rogers LK: miR-29b is associated
with perinatal inflammation in extremely preterm infants. Pediatr
Res. 89:889–893. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chi Y, Di Q, Han G, Li M and Sun B:
Mir-29b mediates the regulation of Nrf2 on airway epithelial
remodeling and Th1/Th2 differentiation in COPD rats. Saudi J Biol
Sci. 26:1915–1921. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Shen B, Zhang D, Wang Y, Tang Z,
Ni N, Jin X, Luo M, Sun H and Gu P: miR-29a regulates the
proliferation and differentiation of retinal progenitors by
targeting Rbm8a. Oncotarget. 8:31993–32008. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pereira PA, Tomás JF, Queiroz JA,
Figueiras AR and Sousa F: Recombinant pre-miR-29b for Alzheimer s
disease therapeutics. Sci Rep. 6:199462016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fukata T, Mizushima T, Nishimura J,
Okuzaki D, Wu X, Hirose H, Yokoyama Y, Kubota Y, Nagata K,
Tsujimura N, et al: The supercarbonate apatite-MicroRNA complex
inhibits dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 12:658–671. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He Y, Huang C, Lin X and Li J: MicroRNA-29
family, a crucial therapeutic target for fibrosis diseases.
Biochimie. 95:1355–1359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cushing L, Kuang P and Lü J: The role of
miR-29 in pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem Cell Biol. 93:109–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li J, Cen B, Chen S and He Y: MicroRNA-29b
inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrosis via regulation of the TGF-β1/Smad
pathway in primary human endometrial stromal cells. Mol Med Rep.
13:4229–4237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pain M, Bermudez O, Lacoste P, Royer PJ,
Botturi K, Tissot A, Brouard S, Eickelberg O and Magnan A: Tissue
remodelling in chronic bronchial diseases: From the epithelial to
mesenchymal phenotype. Eur Respir Rev. 23:118–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Srivastava SP, Hedayat AF, Kanasaki K and
Goodwin JE: microRNA crosstalk influences
epithelial-to-mesenchymal, endothelial-to-mesenchymal, and
macrophage-to-mesenchymal transitions in the kidney. Front
Pharmacol. 10:9042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong SL and Sukkar MB: The SPARC protein:
An overview of its role in lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis and
its potential role in chronic airways disease. Br J Pharmacol.
174:3–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Trombetta-Esilva J and Bradshaw AD: The
function of SPARC as a mediator of fibrosis. Open Rheumatol J.
6:146–155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bradshaw AD: The role of secreted protein
acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) in cardiac repair and fibrosis:
Does expression of SPARC by macrophages influence outcomes? J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 93:156–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang JC, Lai S, Guo X, Zhang X, de
Crombrugghe B, Sonnylal S, Arnett FC and Zhou X: Attenuation of
fibrosis in vitro and in vivo with SPARC siRNA. Arthritis Res Ther.
12:R602010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang F, Zhang Y, Da J, Jia Z, Wu H and Gu
K: Downregulation of SPARC expression decreases cell migration and
invasion involving epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the
p-FAK/p-ERK pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Cancer. 11:414–420. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun W, Feng J, Yi Q, Xu X, Chen Y and Tang
L: SPARC acts as a mediator of TGF-β1 in promoting
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in A549 and H1299 lung cancer
cells. Biofactors. 44:453–464. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu J, Wang LY, Li CY, Wu JY, Zhang YT,
Pang KP, Wei Y, Du LQ, Liu M and Wu XY: SPARC promotes self-renewal
of limbal epithelial stem cells and ocular surface restoration
through JNK and p38-MAPK signaling pathways. Stem Cells.
38:134–145. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|