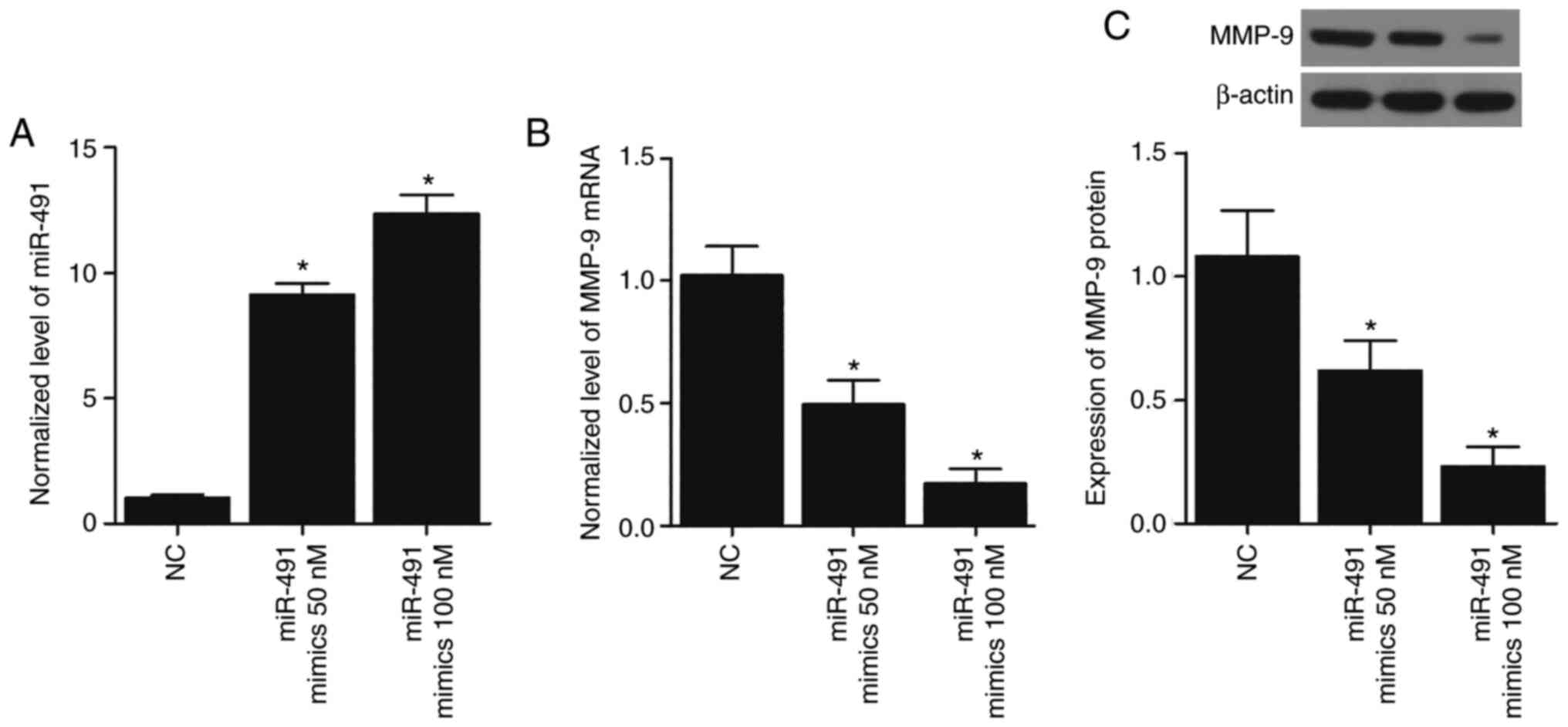
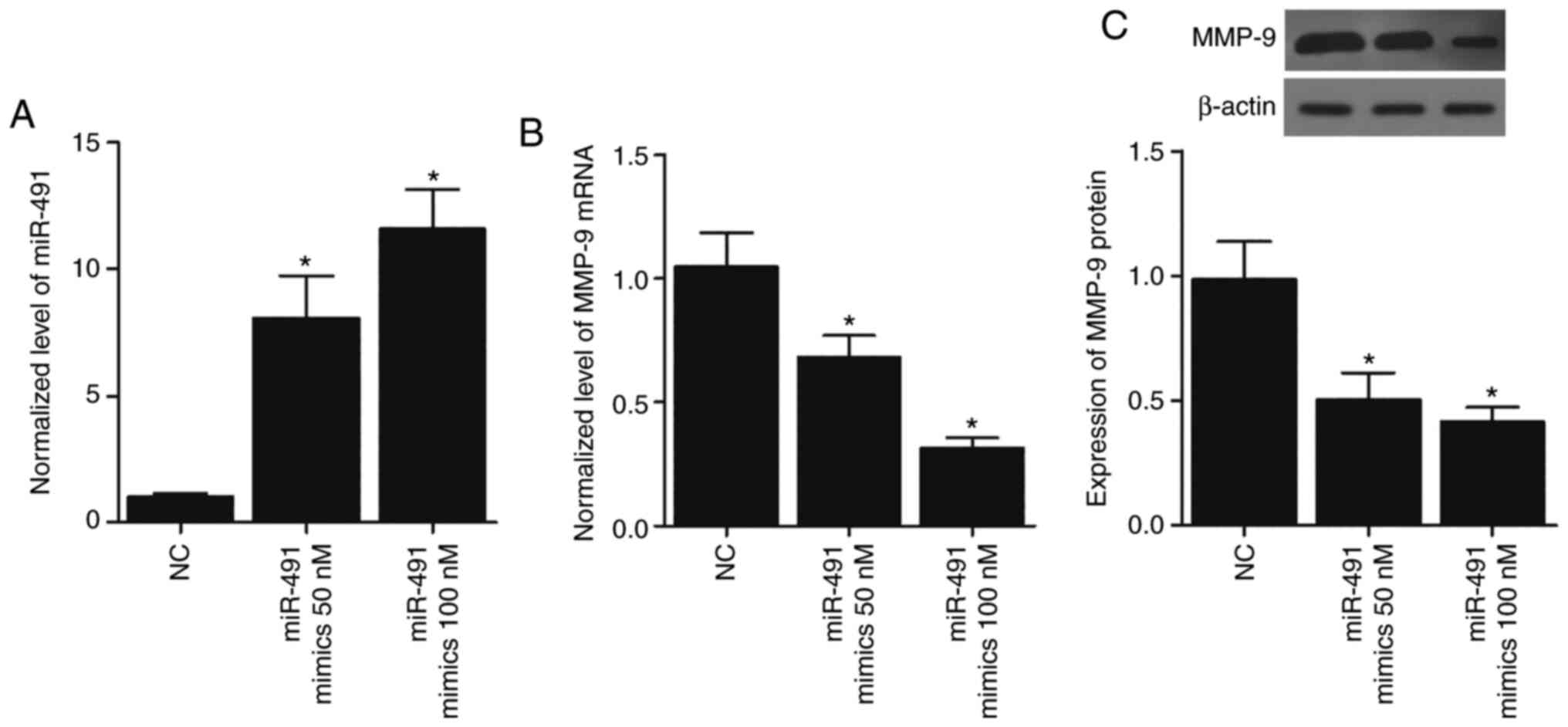
|
1
|
Hunter J, Annadurai S and Rothwell M:
Diagnosis, management and prevention of ventilator-associated
pneumonia in the UK. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 24:971–977. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vincent JL: Ventilator-associated
pneumonia. J Hosp Infect. 57:272–280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Namath A and Patterson AJ: Genetic
polymorphisms in sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 25835–856. (x)2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S, Esau
CC, Burchard J, Linsley PS and Krichevsky AM: MicroRNA 21 promotes
glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:5369–5380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan G, He Z, Cao L, Shi X, Wu S and Zhou
G: miR-139 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting ROCK1. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 24:1167–1177. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deveci M, Catalyürek UV and Toland AE:
mrSNP: Software to detect SNP effects on microRNA binding. BMC
Bioinformatics. 15:732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian X and Zhang X: A Single nucleotide
polymorphism (rs1056629) in 3′-UTR of MMP-9 is responsible for a
decreased risk of metastatic osteosarcoma by compromising its
interaction with microRNA-491-5p. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:1415–1424. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan M, Zhan Q, Duan X, Song B, Zeng S,
Chen X, Yang Q and Xia J: A functional polymorphism at miR-491-5p
binding site in the 3′-UTR of MMP-9 gene confers increased risk for
atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in a Chinese population.
Atherosclerosis. 226:447–452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li YT, Wang YC, Lee HL, Lu MC and Yang SF:
Elevated plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its correlations
with severity of disease in patients with ventilator-associated
pneumonia. Int J Med Sci. 13:638–645. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vandooren J, Van den Steen PE and
Opdenakker G: Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 48:222–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Atkinson JJ and Senior RM: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
28:12–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiang TY, Tsao SM, Yeh CB and Yang SF:
Matrix metalloproteinases in pneumonia. Clin Chim Acta.
433:272–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brown GM, Brown DM, Donaldson K, Drost E
and MacNee W: Neutrophil sequestration in rat lungs. Thorax.
50:661–667. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Shao X, Dou X, Zhang X, Wang Y,
Zhu C, Hao C, Fan M, Ji W and Yan Y: Role of the mycoplasma
pneumoniae/interleukin-8/neutrophil axis in the pathogenesis of
pneumonia. PLoS One. 11:e01463772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou XY, Ben SQ, Chen HL and Ni SS: A
comparison of APACHE II and CPIS scores for the prediction of
30-day mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Int J Infect Dis. 30:144–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fan Y, Gao F, Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhu M and
Xiong L: Does ventilator-associated event surveillance detect
ventilator-associated pneumonia in intensive care units? A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 20:3382016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Craven DE, Hudcova J and Lei Y: Diagnosis
of ventilator-associated respiratory infections (VARI):
Microbiologic clues for tracheobronchitis (VAT) and pneumonia
(VAP). Clin Chest Med. 32:547–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A,
Hernández-Guillamon M, Lo EH and Montaner J: MMP-9-positive
neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier
breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during
hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke.
39:1121–1126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Tepper D and
Leonard A: Matrix metalloproteinases and blood-brain barrier
disruption in acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 4:322013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boroujerdi A, Welser-Alves JV and Milner
R: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates post-hypoxic vascular
pruning of cerebral blood vessels by degrading laminin and
claudin-5. Angiogenesis. 18:255–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Eriksson P, Hansson GK, Herzfeld
I, Klein M, Hansson LO and Valen G: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 and its regulators in the unstable coronary
atherosclerotic plaque. Int J Mol Med. 15:57–65. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu J, Van den Steen PE, Sang QX and
Opdenakker G: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as therapy for
inflammatory and vascular diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:480–498.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ram M, Sherer Y and Shoenfeld Y: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and autoimmune diseases. J Clin Immunol.
26:299–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahrens D, Koch AE, Pope RM,
Stein-Picarella M and Niedbala MJ: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (96-kd gelatinase B) in human rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 39:1576–1587. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang YH, Lin IL, Tsay GJ, Yang SC, Yang
TP, Ho KT, Hsu TC and Shiau MY: Elevated circulatory MMP-2 and
MMP-9 levels and activities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Biochem. 41:955–959. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lakatos G, Sipos F, Miheller P, Hritz I,
Varga MZ, Juhasz M, Molnar B, Tulassay Z and Herszenyi L: The
behavior of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lymphocytic colitis,
collagenous colitis and ulcerative colitis. Pathol Oncol Res.
18:85–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peterson JT: The importance of estimating
the therapeutic index in the development of matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitors. Cardiovasc Res. 69:677–687. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ben David D, Reznick AZ, Srouji S and
Livne E: Exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines upregulates MMP-9
synthesis by mesenchymal stem cells-derived osteoprogenitors.
Histochem Cell Biol. 129:589–597. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ben-David D, Livne E and Reznick AZ: The
involvement of oxidants and NF-kB in cytokine-induced MMP-9
synthesis by bone marrow-derived osteoprogenitor cells. Inflamm
Res. 61:673–688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ordas I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart
DC and Sandborn WJ: Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 380:1606–1619.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schaaf B, Liebau C, Kurowski V, Droemann D
and Dalhoff K: Hospital acquired pneumonia with high-risk bacteria
is associated with increased pulmonary matrix metalloproteinase
activity. BMC Pulm Med. 8:122008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
El Solh AA, Akinnusi ME, Wiener-Kronish
JP, Lynch SV, Pineda LA and Szarpa K: Persistent infection with
pseudomonas aeruginosa in ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 178:513–519. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
El-Solh AA, Amsterdam D, Alhajhusain A,
Akinnusi ME, Saliba RG, Lynch SV and Wiener-Kronish JP: Matrix
metalloproteases in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with
type III Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. J Infect. 59:49–55.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ito A, Mukaiyama A, Itoh Y, Nagase H,
Thogersen IB, Enghild JJ, Sasaguri Y and Mori Y: Degradation of
interleukin 1beta by matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem.
271:14657–14660. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schönbeck U, Mach F and Libby P:
Generation of biologically active IL-1 beta by matrix
metalloproteinases: A novel caspase-1-independent pathway of IL-1
beta processing. J Immunol. 161:3340–3346. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Amantea D, Russo R, Certo M, Rombola L,
Adornetto A, Morrone LA, Corasaniti MT and Bagetta G:
Caspase-1-independent maturation of IL-1β in ischemic brain injury:
Is there a role for gelatinases? Mini Rev Med Chem. 16:729–737.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wittmann M, Kingsbury SR and McDermott MF:
Is caspase 1 central to activation of interleukin-1? Joint Bone
Spine. 78:327–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Saren P, Welgus HG and Kovanen PT:
TNF-alpha and IL-1beta selectively induce expression of 92-kDa
gelatinase by human macrophages. J Immunol. 157:4159–4165.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gearing AJ, Beckett P, Christodoulou M,
Churchill M, Clements J, Davidson AH, Drummond AH, Galloway WA,
Gilbert R, Gordon JL, et al: Processing of tumour necrosis
factor-alpha precursor by metalloproteinases. Nature. 370:555–557.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu Q and Stamenkovic I: Cell
surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically
activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis.
Genes Dev. 14:163–176. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rainer PP, Hao S, Vanhoutte D, Lee DI,
Koitabashi N, Molkentin JD and Kass DA: Cardiomyocyte-specific
transforming growth factor β suppression blocks neutrophil
infiltration, augments multiple cytoprotective cascades, and
reduces early mortality after myocardial infarction. Circ Res.
114:1246–1257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dayer C and Stamenkovic I: Recruitment of
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) to the fibroblast cell surface
by lysyl hydroxylase 3 (LH3) triggers transforming growth factor-β
(TGF-β) activation and fibroblast differentiation. J Biol Chem.
290:13763–13778. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|