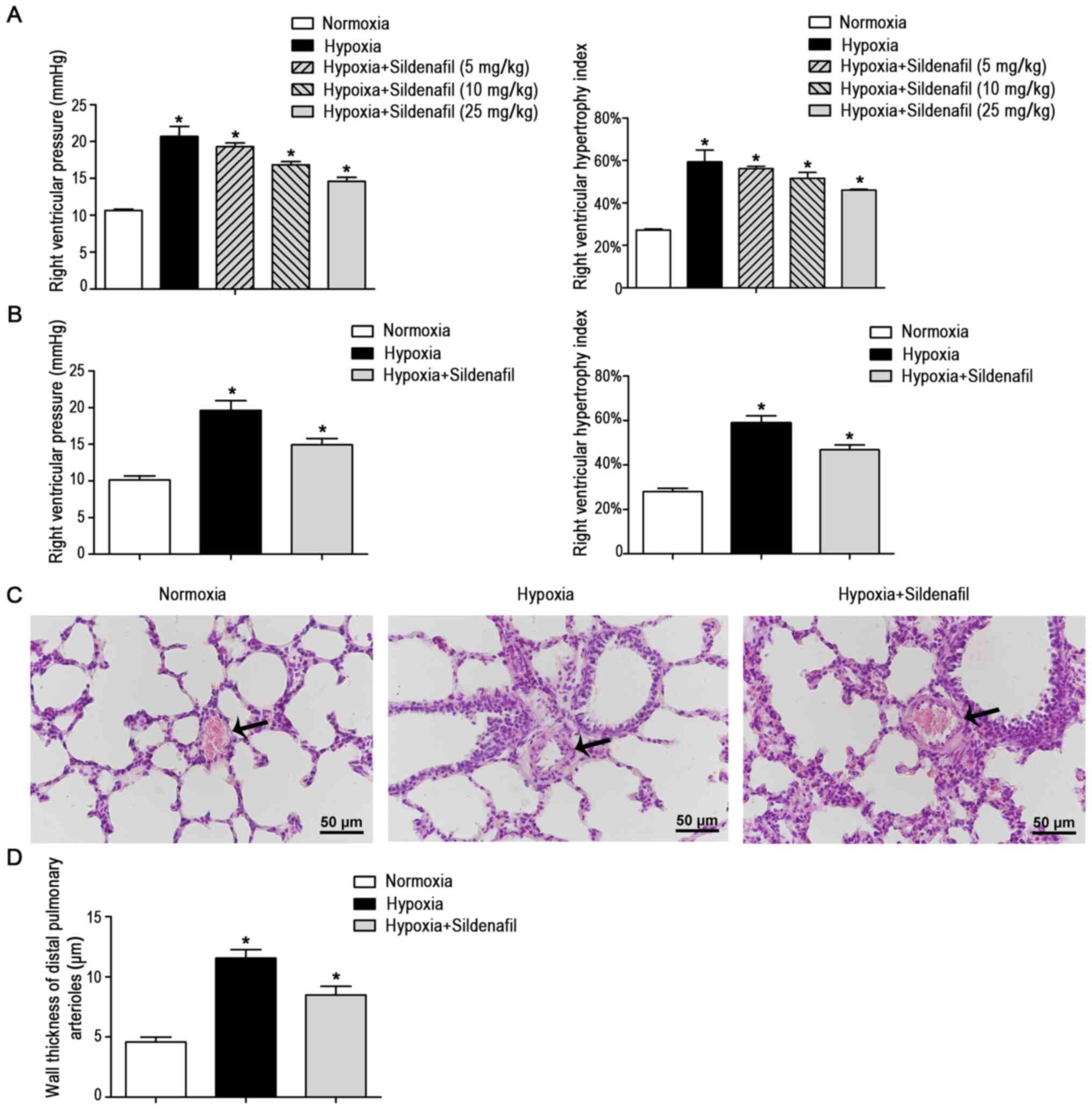
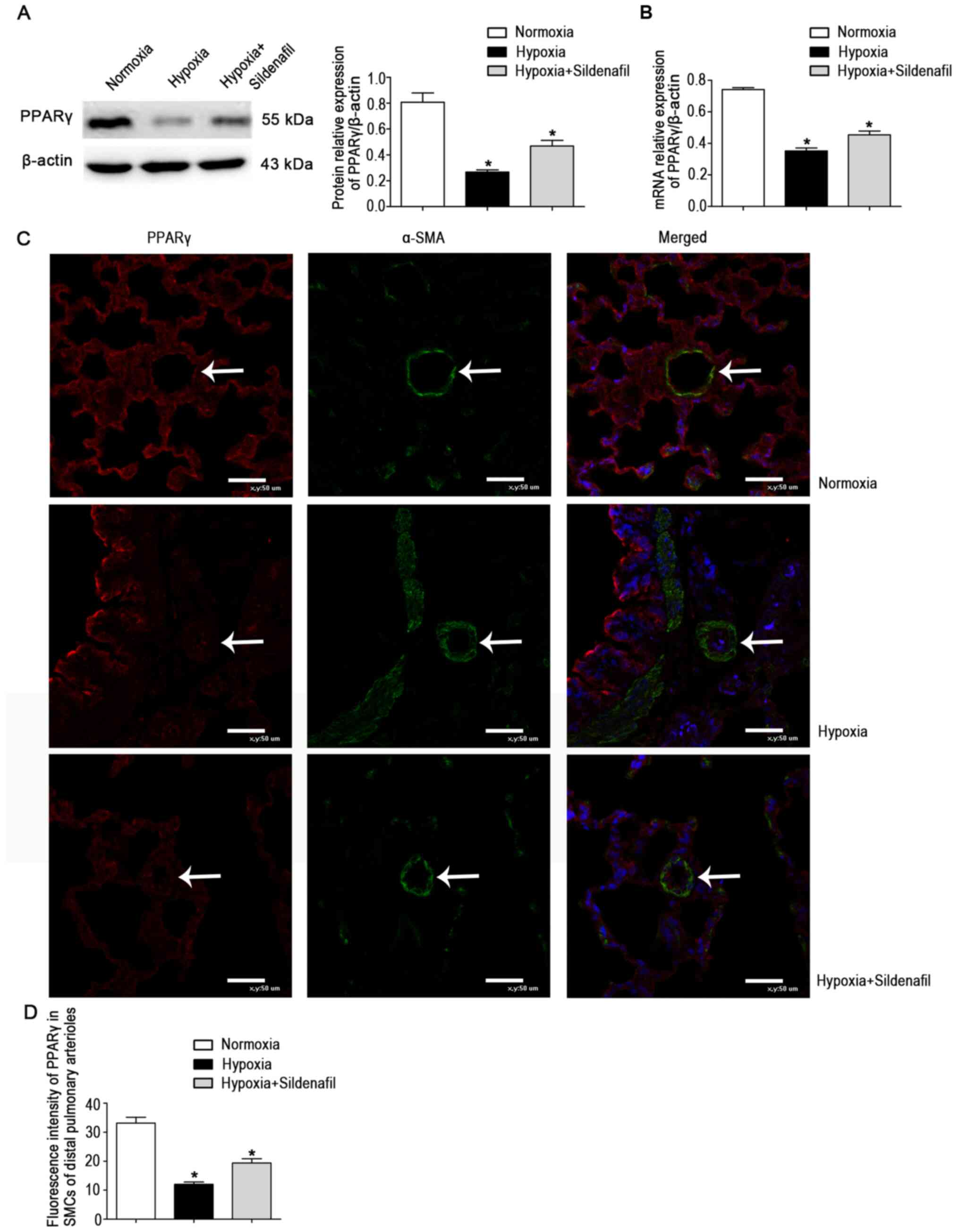
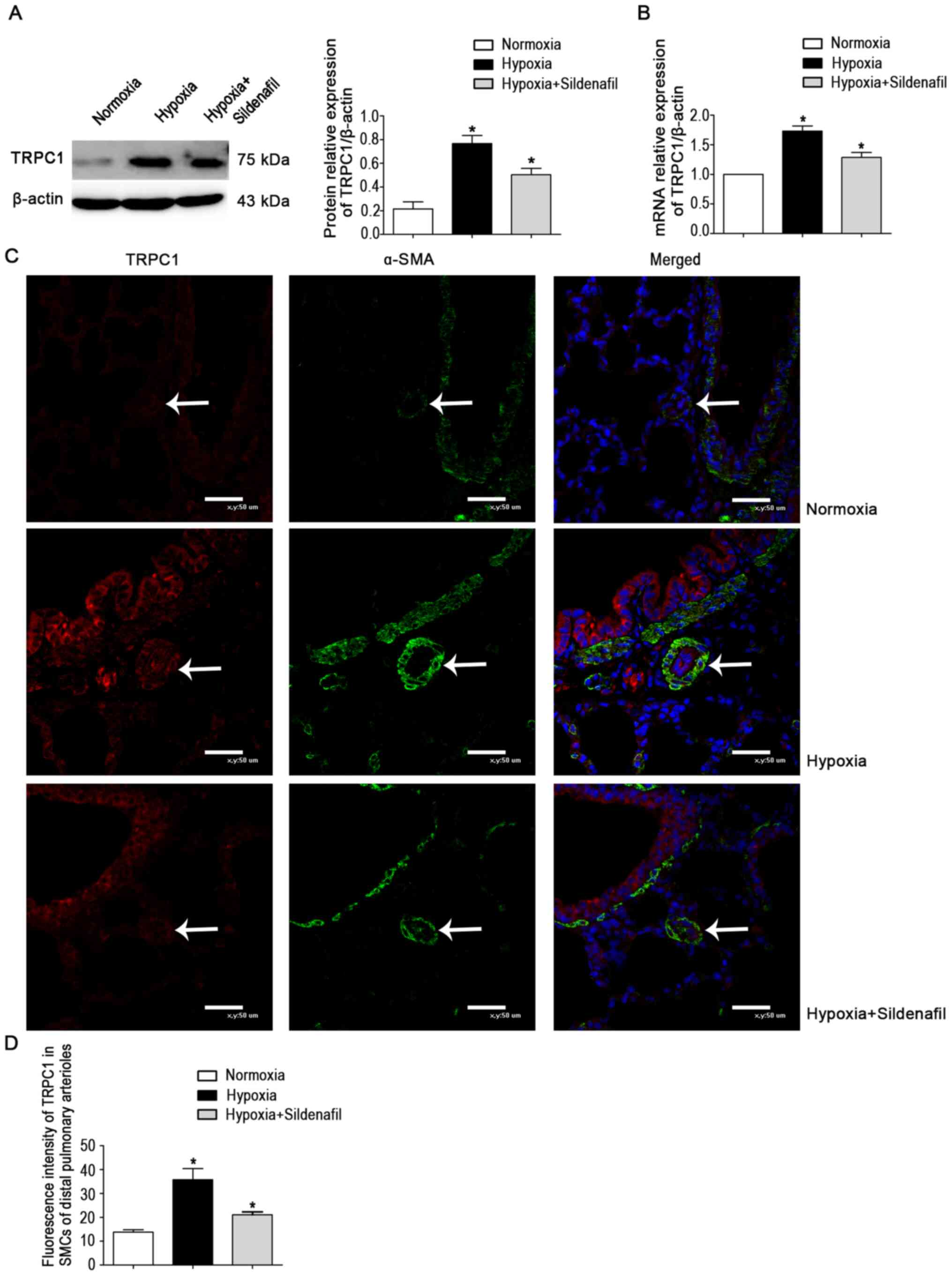
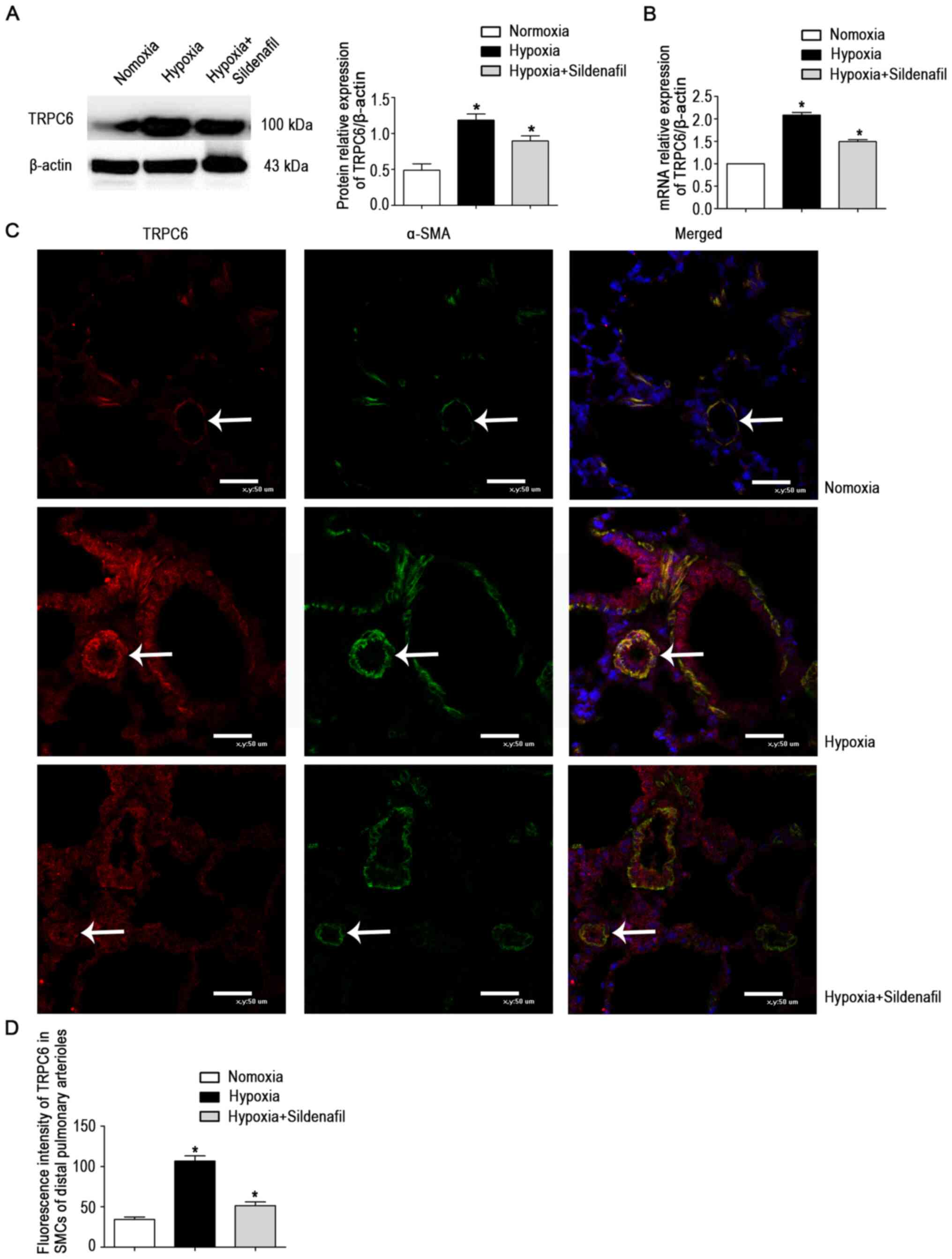
|
1
|
Kelly LE, Ohlsson A and Shah PS:
Sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension in neonates. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 8:CD0054942017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Behringer A, Trappiel M, Berghausen EM,
Ten Freyhaus H, Wellnhofer E, Odenthal M, Blaschke F, Er F,
Gassanov N, Rosenkranz S, et al: Pioglitazone alleviates cardiac
and vascular remodelling and improves survival in monocrotaline
induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 389:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tajsic T and Morrell NW: Smooth muscle
cell hypertrophy, proliferation, migration and apoptosis in
pulmonary hypertension. Compr Physiol. 1:295–317. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y, Cui Y, Deng W, Wang H, Qin W,
Huang C, Li C, Zhang J, Guo Y, Wu D, et al: Isoquercitrin protects
against pulmonary hypertension via inhibiting PASMCs proliferation.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 44:362–370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Afdal P and AbdelMassih AF: Is pulmonary
vascular disease reversible with PPAR γ agonists? Microcirculation.
25:e124442018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kahveci H, Yilmaz O, Avsar UZ, Ciftel M,
Kilic O, Laloglu F and Ozturk K: Oral sildenafil and inhaled
iloprost in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 49:1205–1213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kraemer U, Cochius-den Otter S, Snoek KG
and Tibboel D: Pharmacodynamic considerations in the treatment of
pulmonary hypertension in infants: Challenges and future
perspectives. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 12:1–19. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamamura A, Fujitomi E, Ohara N, Tsukamoto
K, Sato M and Yamamura H: Tadalafil induces antiproliferation,
apoptosis, and phosphodiesterase type 5 downregulation in
idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension in vitro. Eur J
Pharmacol. 810:44–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barst RJ, Beghetti M, Pulido T, Layton G,
Konourina I, Zhang M and Ivy DD; STARTS-2 Investigators: STARTS-2:
Long-term survival with oral sildenafil monotherapy in
treatment-naive pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Circulation. 129:1914–1923. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iacovidou N, Syggelou A, Fanos V and
Xanthos T: The use of sildenafil in the treatment of persistent
pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: A review of the literature.
Curr Pharm Des. 18:3034–3045. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang RC, Jiang FM, Zheng QL, Li CT, Peng
XY, He CY, Luo J and Liang ZA: Efficacy and safety of sildenafil
treatment in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review.
Respir Med. 108:531–537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD and Sibley
D: cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in
nitric oxide and cGMP action. Pharmacol Rev. 62:525–563. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu W, Ran P, Zhang D, Peng G, Li B, Zhong
N and Wang J: Sildenafil inhibits chronically hypoxic upregulation
of canonical transient receptor potential expression in rat
pulmonary arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C114–C123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Sonneveld R, Hoenderop JG, Isidori AM,
Henique C, Dijkman HB, Berden JH, Tharaux PL, van der Vlag J and
Nijenhuis T: Sildenafil prevents podocyte injury via
PPAR-γ-mediated TRPC6 inhibition. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:1491–1505.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chandra M, Miriyala S and Panchatcharam M:
PPARγ and its role in cardiovascular diseases. PPAR Res.
2017:64046382017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Martinho S, Adão R, Leite-Moreira AF and
Brás-Silva C: Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn:
Pathophysiological mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches.
Front Pediatr. 8:3422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mohey V, Singh M, Puri N, Kaur T, Pathak D
and Singh AP: Sildenafil obviates ischemia-reperfusion
injury-induced acute kidney injury through peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ agonism in rats. J Surg Res.
201:69–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia Y, Yang XR, Fu Z, Paudel O, Abramowitz
J, Birnbaumer L and Sham JS: Classical transient receptor potential
1 and 6 contribute to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension through
differential regulation of pulmonary vascular functions.
Hypertension. 63:173–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang K, Lu W, Jiang Q, Yun X, Zhao M,
Jiang H and Wang J: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
γ-mediated inhibition on hypoxia-triggered store-operated calcium
entry. A Caveolin-1-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
53:882–892. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du Y, Fu J, Yao L, Qiao L, Liu N, Xing Y
and Xue X: Altered expression of PPAR γ and TRPC in neonatal rats
with persistent pulmonary hypertension. Mol Med Rep. 16:1117–1124.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu YP, Zhu JJ, Cheng F, Jiang KW, Gu WZ,
Shen Z, Wu YD, Liang L and Du LZ: Ghrelin ameliorates
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via phospho-GSK3 β/β-catenin
signaling in neonatal rats. J Mol Endocrinol. 47:33–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du Y, Fu J, Yao L, Zhang D, Liu N and Xue
X: Effects of FHL1 and P21 on hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular
remodeling in neonatal rats. Exp Ther Med. 14:4245–4253.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jasińska-Stroschein M, Owczarek J, Łuczak
A and Orszulak-Michalak D: The beneficial impact of fasudil and
sildenafil on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats:
A hemodynamic and biochemical study. Pharmacology. 91:178–184.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Liu G, Cai D, Pan B, Lin Y, Li X, Li
S, Zhu L, Liao X and Wang H: H2S inhibition of chemical
hypoxia-induced proliferation of HPASMCs is mediated by the
upregulation of COX-2/PGI2. Int J Mol Med. 33:359–366. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lin C, Li X, Luo Q, Yang H, Li L, Zhou Q,
Li Y, Tang H and Wu L: RELM-β promotes human pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cell proliferation via FAK-stimulated surviving. Exp
Cell Res. 351:43–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hilgendorff A, Apitz C, Bonnet D and
Hansmann G: Pulmonary hypertension associated with acute or chronic
lung diseases in the preterm and term neonate and infant. The
European Paediatric Pulmonary Vascular Disease Network, endorsed by
ISHLT and DGPK. Heart. 102(Suppl 2): ii49–ii56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu YP, He Q, Shen Z, Shu XL, Wang CH, Zhu
JJ, Shi LP and Du LZ: miR-126a-5p is involved in the
hypoxia-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition of neonatal
pulmonary hypertension. Hypertens Res. 40:552–561. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gong J, Feng Z, Peterson AL, Carr JF, Vang
A, Braza J, Choudhary G, Dennery PA and Yao H: Endothelial to
mesenchymal transition during neonatal hyperoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension. J Pathol. 252:411–422. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Menon RT, Shrestha AK, Reynolds CL,
Barrios R, Caron KM and Shivanna B: Adrenomedullin is necessary to
resolve hyperoxia-induced experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia
and pulmonary hypertension in mice. Am J Pathol. 190:711–722. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Makker K, Afolayan AJ, Teng RJ and Konduri
GG: Altered hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) signaling
contributes to impaired angiogenesis in fetal lambs with persistent
pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). Physiol Rep.
7:e139862019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cohen SS, Powers BR, Lerch-Gaggl A, Teng
RJ and Konduri GG: Impaired cerebral angiogenesis in the fetal lamb
model of persistent pulmonary hypertension. Int J Dev Neurosci.
38:113–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amer R, Elsayed YN, Graham MR, Sikarwar
AS, Hinton M and Dakshinamurti S: Effect of vasopressin on a
porcine model of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 54:319–332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Blasina F, Vaamonde L, Silvera F, Solla G,
Abin-Carriquiry JA, Gutiérrez C, Beltramo P, Garcia-Gabay I and
Martell M: Efficacy and safety of a novel nitric oxide generator
for the treatment of neonatal pulmonary hypertension: Experimental
and clinical studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 54:68–76. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fernandez RA, Wan J, Song S, Smith KA, Gu
Y, Tauseef M, Tang H, Makino A, Mehta D and Yuan JX: Upregulated
expression of STIM2, TRPC6, and Orai2 contributes to the transition
of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells from a contractile to
proliferative phenotype. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C581–C593.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tseng V, Sutliff RL and Hart CM: Redox
biology of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in
pulmonary hypertension. Antioxid Redox Signal. 31:874–897. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Grygiel-Górniak B: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and
clinical implications - a review. Nutr J. 13:172014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang L, Waltenberger B, Pferschy-Wenzig
EM, Blunder M, Liu X, Malainer C, Blazevic T, Schwaiger S,
Rollinger JM, Heiss EH, et al: Natural product agonists of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ): A review.
Biochem Pharmacol. 92:73–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ajith TA and Jayakumar TG: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors in cardiac energy metabolism and
cardiovascular disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:649–658.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Lu W, Yang K, Wang Y, Zhang J, Jia
J, Yun X, Tian L, Chen Y, Jiang Q, et al: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ inhibits pulmonary hypertension
targeting store-operated calcium entry. J Mol Med (Berl).
93:327–342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Malczyk M, Veith C, Fuchs B, Hofmann K,
Storch U, Schermuly RT, Witzenrath M, Ahlbrecht K, Fecher-Trost C,
Flockerzi V, et al: Classical transient receptor potential channel
1 in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 188:1451–1459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|