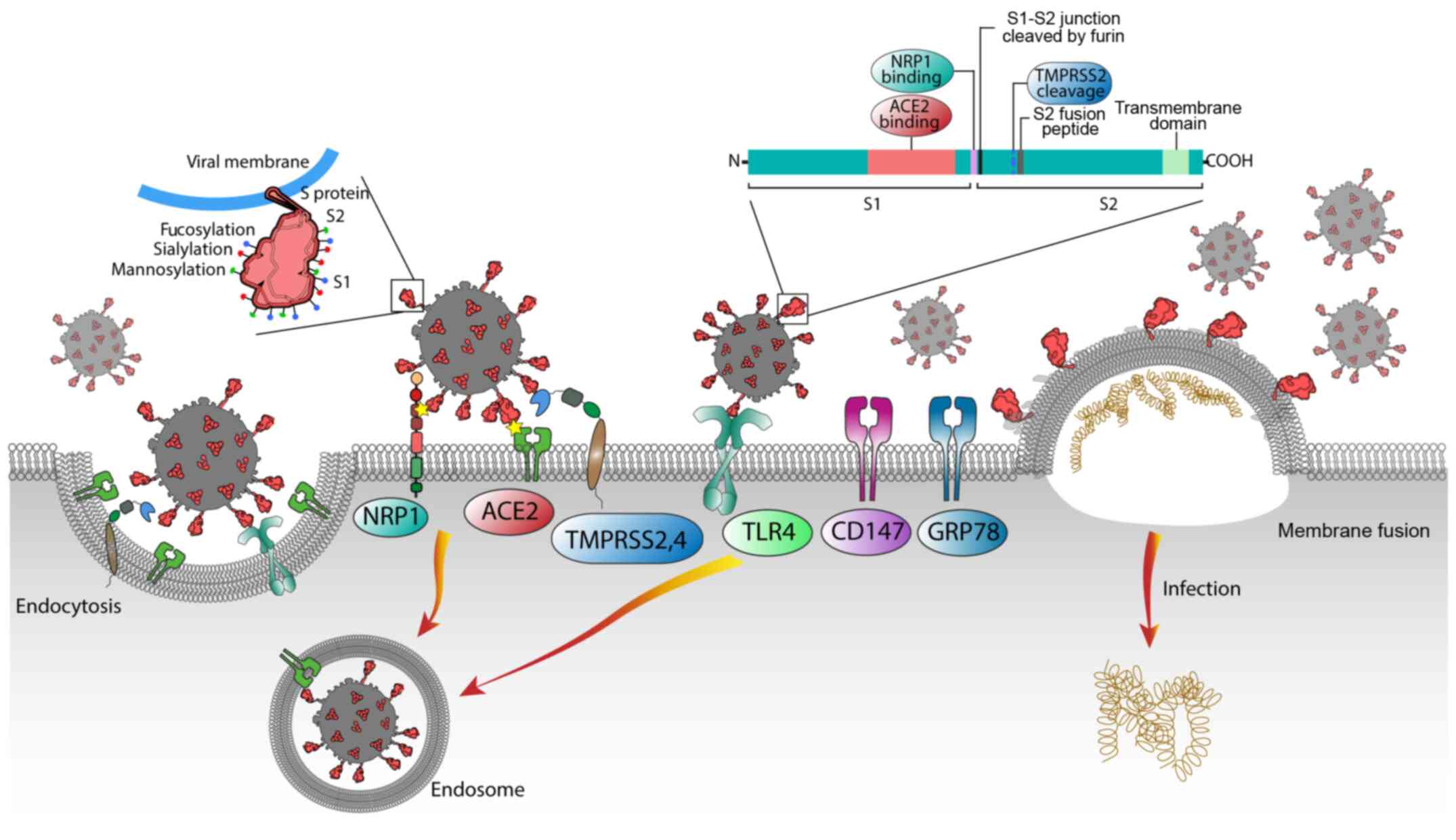
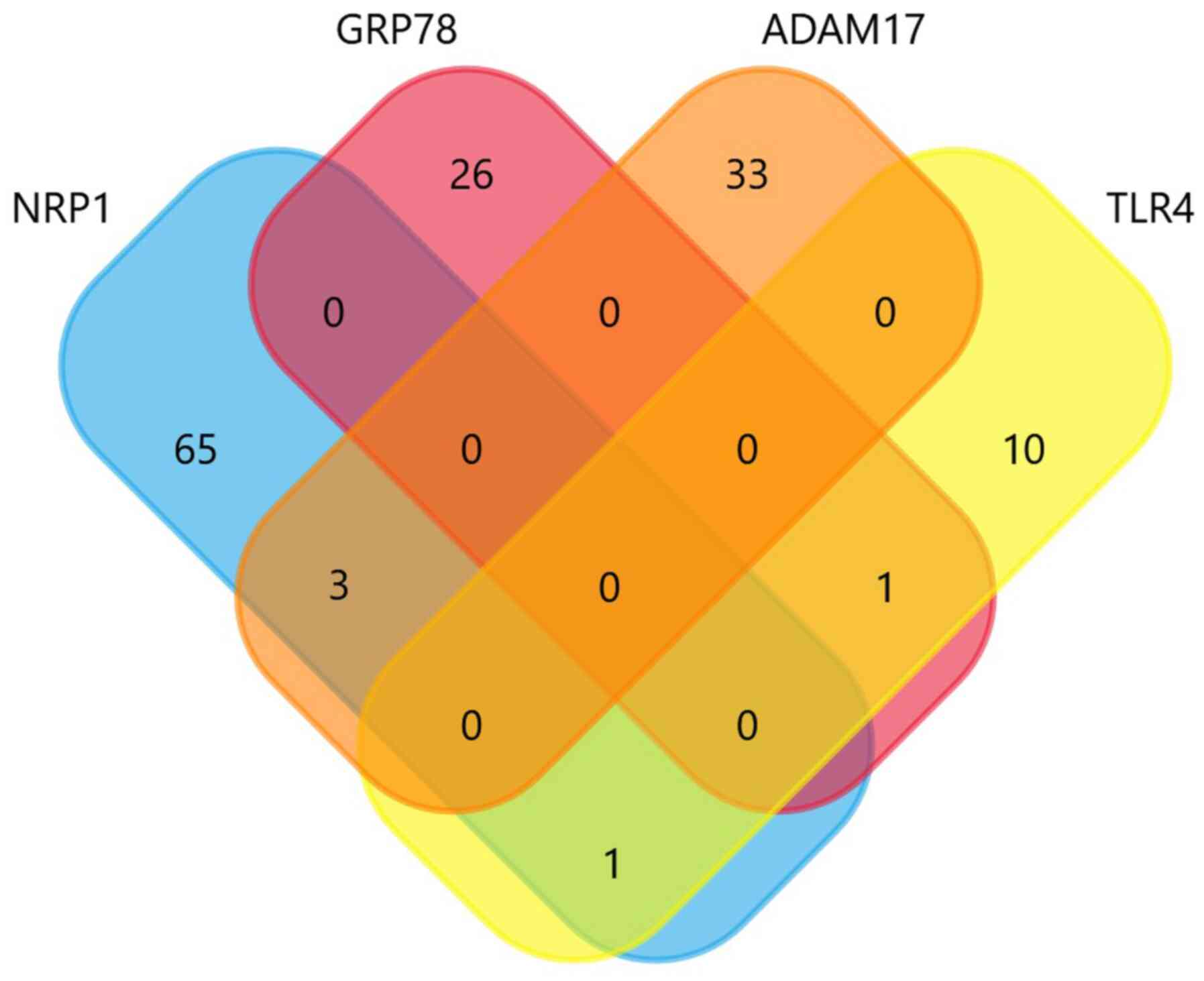
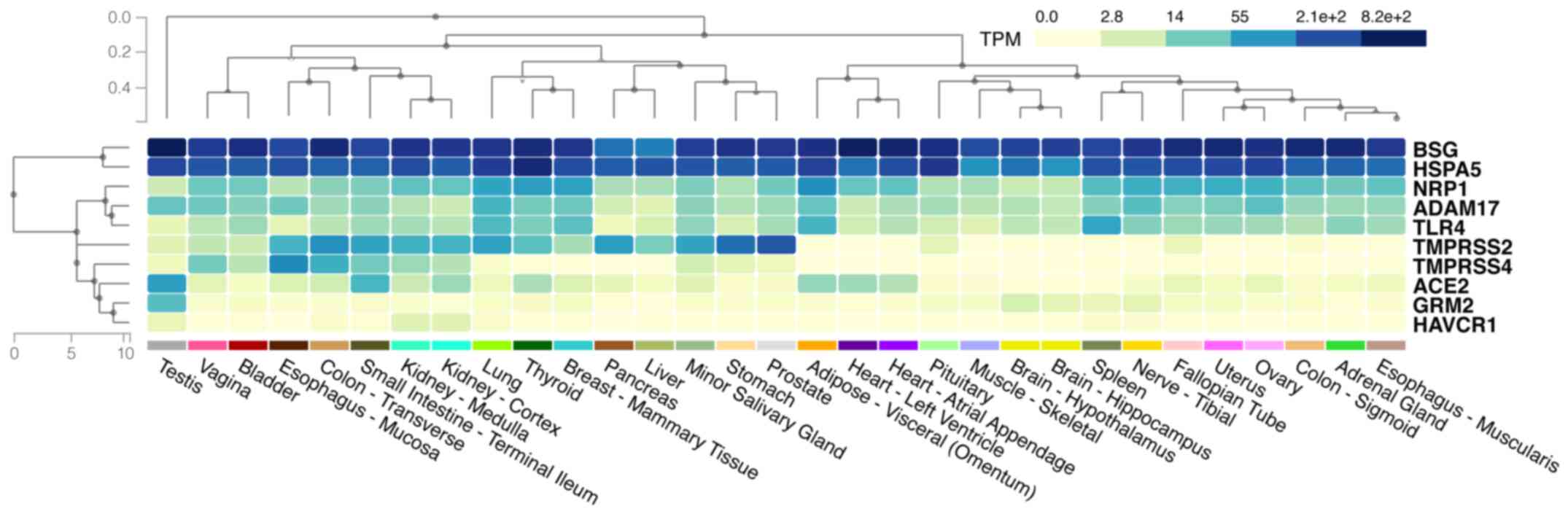
|
1
|
Osuchowski MF, Winkler MS, Skirecki T,
Cajander S, Shankar-Hari M, Lachmann G, Monneret G, Venet F, Bauer
M, Brunkhorst FM, et al: The COVID-19 puzzle: Deciphering
pathophysiology and phenotypes of a new disease entity. Lancet
Respir Med. 9:622–642. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singh S, Pandey R, Tomar S, Varshney R,
Sharma D and Gangenahalli G: A brief molecular insight of COVID-19:
Epidemiology, clinical manifestation, molecular mechanism, cellular
tropism and immuno-pathogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:3987–4002.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murgolo N, Therien AG, Howell B, Klein D,
Koeplinger K, Lieberman LA, Adam GC, Flynn J, McKenna P,
Swaminathan G, et al: SARS-CoV-2 tropism, entry, replication, and
propagation: Considerations for drug discovery and development.
PLoS Pathog. 17:e10092252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gao S and Zhang L: ACE2 partially dictates
the host range and tropism of SARS-CoV-2. Comput Struct Biotechnol
J. 18:4040–4047. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cai L, Guo X, Cao Y, Ying P, Hong L, Zhang
Y, Yi G and Fu M: Determining available strategies for prevention
and therapy: Exploring COVID-19 from the perspective of ACE2
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:432021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Glowacka I, Bertram S, Müller MA, Allen P,
Soilleux E, Pfefferle S, Steffen I, Tsegaye TS, He Y, Gnirss K, et
al: Evidence that TMPRSS2 activates the severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus spike protein for membrane fusion and reduces
viral control by the humoral immune response. J Virol.
85:4122–4134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Piva F, Sabanovic B, Cecati M and
Giulietti M: Expression and Co-expression analyses of TMPRSS2, a
key element in COVID-19. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.
40:451–455. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hou Y, Zhao J, Martin W, Kallianpur A,
Chung MK, Jehi L, Sharifi N, Erzurum S, Eng C and Cheng F: New
insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: An ACE2 and
TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis. BMC Med. 18:2162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zipeto D, Palmeira JDF, Argañaraz GA and
Argañaraz ER: ACE2/ADAM17/TMPRSS2 interplay may be the main risk
factor for COVID-19. Front Immunol. 11:5767452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shang J, Wan Y, Luo C, Ye G, Geng Q,
Auerbach A and Li F: Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 117:11727–11734. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Magrone T, Magrone M and Jirillo E: Focus
on receptors for coronaviruses with special reference to
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2 as a potential drug Target-A
perspective. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 20:807–811.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jia H, Neptune E and Cui H: Targeting ACE2
for COVID-19 therapy: Opportunities and challenges. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 64:416–425. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, Huan Y, Guo F, Guan
B, Yang P, Sarao R, Wada T, Leong-Poi H, et al:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung
failure. Nature. 436:112–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schuler BA, Habermann AC, Plosa EJ, Taylor
CJ, Jetter C, Negretti NM, Kapp ME, Benjamin JT, Gulleman P,
Nichols DS, et al: Age-determined expression of priming protease
TMPRSS2 and localization of SARS-CoV-2 in lung epithelium. J Clin
Invest. 131:e1407662021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Musso N, Falzone L, Stracquadanio S,
Bongiorno D, Salerno M, Esposito M, Sessa F, Libra M, Stefani S and
Pomara C: Post-mortem detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Long-buried
lung samples. Diagnostics (Basel). 11:11582021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Deinhardt-Emmer S, Wittschieber D, Sanft
J, Kleemann S, Elschner S, Haupt KF, Vau V, Häring C, Rödel J,
Henke A, et al: Early postmortem mapping of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in
patients with COVID-19 and the correlation with tissue damage.
Elife. 10:e603612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao XH, Luo T, Shi Y, He ZC, Tang R, Zhang
PP, Cai J, Zhou XD, Jiang DP, Fei XC, et al: A cohort autopsy study
defines COVID-19 systemic pathogenesis. Cell Res. 31:836–846. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zang R, Gomez Castro MF, McCune BT, Zeng
Q, Rothlauf PW, Sonnek NM, Liu Z, Brulois KF, Wang X, Greenberg HB,
et al: TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human
small intestinal enterocytes. Sci Immunol. 5:eabc35822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kyrou I, Randeva HS, Spandidos DA and
Karteris E: Not only ACE2-the quest for additional host cell
mediators of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a novel
SARS-CoV-2 host cell entry mediator implicated in COVID-19. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 6:212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Katopodis P, Kerslake R, Davies J, Randeva
HS, Chatha K, Hall M, Spandidos DA, Anikin V, Polychronis A,
Robertus JL, et al: COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 host cell entry
mediators: Expression profiling of TMRSS4 in health and disease.
Int J Mol Med. 47:642021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Cuervo NZ and Grandvaux N: ACE2: Evidence
of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications in
comorbidities. Elife. 9:e613902020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Davies J, Randeva HS, Chatha K, Hall M,
Spandidos DA, Karteris E and Kyrou I: Neuropilin-1 as a new
potential SARS-CoV-2 infection mediator implicated in the
neurologic features and central nervous system involvement of
COVID-19. Mol Med Rep. 22:4221–4226. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Daly JL, Simonetti B, Antón-Plágaro C,
Williamson MK, Shoemark DK, Simón-Gracia L, Klein K, Bauer M,
Hollandi R, Greber UF, et al: Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for
SARS-CoV-2 infection. Science. 370:861–865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro LD,
Djannatian M, Franz J, Kuivanen S, van der Meer F, Kallio K, Kaya
T, Anastasina M, et al: Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell
entry and infectivity. Science. 370:856–860. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kielian M: Enhancing host cell infection
by SARS-CoV-2. Science. 370:765–766. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro LD,
Djannatian M, Franz J, Kuivanen S, Kallio K, Kaya T, Anastasina M,
Smura T, et al: Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and
provides a possible pathway into the central nervous system.
bioRxiv. Jul 15–2020.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Elfiky AA: SARS-CoV-2 Spike-heat shock
protein A5 (GRP78) recognition may be related to the immersed human
coronaviruses. Front Pharmacol. 11:5774672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, Elshahat ME and
Elfiky AA: COVID-19 spike-host cell receptor GRP78 binding site
prediction. J Infect. 80:554–562. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang K, Chen W, Zhang Z, Deng Y, Lian JQ,
Du P, Wei D, Zhang Y, Sun XX, Gong L, et al: CD147-spike protein is
a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5:2832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shilts J, Crozier TWM, Greenwood EJD,
Lehner PJ and Wright GJ: No evidence for basigin/CD147 as a direct
SARS-CoV-2 spike binding receptor. Sci Rep. 11:4132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Minami T, Iwata Y and Wada T: Renal
complications in coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review.
Inflamm Regen. 40:312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang C, Zhang Y, Zeng X, Chen H, Chen Y,
Yang D, Shen Z, Wang X, Liu X, Xiong M, et al: Kidney injury
molecule-1 is a potential receptor for SARS-CoV-2. J Mol Cell Biol.
13:185–196. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wan C and Zhang C: Kidney injury
molecule-1: A novel entry factor for SARS-CoV-2. J Mol Cell Biol.
13:159–160. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bu Z, Wang J, Yang G, Wang X, Wen Z, Shuai
L, Luo J, Wang C, Sun Z, Liu R, et al: Metabotropic glutamate
receptor subtype 2 is a receptor of SARS-CoV-2. Res Sq. April
21–2021.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cui C, Huang C, Zhou W, Ji X, Zhang F,
Wang L, Zhou Y and Cui Q: AGTR2, one possible novel key gene for
the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into human cells. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput
Biol Bioinforma. 18:1230–1233. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang Q, Chen CZ, Swaroop M, Xu M, Wang L,
Lee J, Wang AQ, Pradhan M, Hagen N, Chen L, et al: Heparan sulfate
assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved
drugs in vitro. Cell Discov. 6:802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lambert DW, Yarski M, Warner FJ, Thornhill
P, Parkin ET, Smith AI, Hooper NM and Turner AJ: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain
shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus
(SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J Biol
Chem. 280:30113–30119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Palau V, Riera M and Soler MJ: ADAM17
inhibition may exert a protective effect on COVID-19. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 35:1071–1072. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Heurich A, Hofmann-Winkler H, Gierer S,
Liepold T, Jahn O and Pöhlmann S: TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2
differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry
driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike
protein. J Virol. 88:1293–1307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Kumar J, Murugaiah V, Sotiriadis G, Kaur
A, Jeyaneethi J, Sturniolo I, Alhamlan FS, Chatterjee J, Hall M,
Kishore U and Karteris E: Surfactant Protein D as a potential
biomarker and therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol.
9:5422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsieh MH, Beirag N, Murugaiah V, Chou YC,
Kuo WS, Kao HF, Madan T, Kishore U and Wang JY: Human surfactant
Protein D binds spike protein and acts as an entry inhibitor of
SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped viral particles. Front Immunol.
12:6413602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Madan T, Biswas B, Varghese PM, Subedi R,
Pandit H, Idicula-Thomas S, Kundu I, Rooge S, Agarwal R, Tripathi
DM, et al: A recombinant fragment of human surfactant Protein D
binds spike protein and inhibits infectivity and replication of
SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
65:41–53. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tong M, Xiong Y, Zhu C, Xu H, Zheng Q,
Jiang Y, Zou L, Xiao X, Chen F, Yan X, et al: Serum surfactant
protein D in COVID-19 is elevated and correlated with disease
severity. BMC Infect Dis. 21:7372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Aboudounya MM and Heads RJ: COVID-19 and
toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 may bind and activate TLR4
to increase ACE2 expression, facilitating entry and causing
hyper-inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2021:88743392021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gadanec LK, McSweeney KR, Qaradakhi T, Ali
B, Zulli A and Apostolopoulos V: Can SARS-CoV-2 virus use multiple
receptors to enter host cells? Int J Mol Sci. 22:9922021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao Y, Kuang M, Li J, Zhu L, Jia Z, Guo
X, Hu Y, Kong J, Yin H, Wang X and You F: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
interacts with and activates TLR41. Cell Res. 31:818–820. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zamorano Cuervo N and Grandvaux N: ACE2:
Evidence of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications
in comorbidities. Elife. 9:e613902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou H, Fan S,
Zhang Q, Shi X, Wang Q, Zhang L and Wang X: Structure of the
SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2
receptor. Nature. 581:215–220. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shrimp JH, Kales SC, Sanderson PE,
Simeonov A, Shen M and Hall MD: An enzymatic TMPRSS2 assay for
assessment of clinical candidates and discovery of inhibitors as
potential treatment of COVID-19. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci.
3:997–1007. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee JJ, Kopetz S, Vilar E, Shen JP, Chen K
and Maitra A: Relative abundance of SARS-CoV-2 entry genes in the
enterocytes of the lower gastrointestinal tract. Genes (Basel).
11:6452020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Choudhury A and Mukherjee S: In silico
studies on the comparative characterization of the interactions of
SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein with ACE-2 receptor homologs and
human TLRs. J Med Virol. 92:2105–2113. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dexheimer PJ and Cochella L: MicroRNAs:
From mechanism to organism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:4092020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Peng Y and Croce CM: The role of MicroRNAs
in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 1:150042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: The evolution of
gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev
Genet. 8:93–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka
D, Sobolewski C and Foti M: Deciphering miRNAs' Action through
miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci. 20:62492019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cai Y, Yu X, Hu S and Yu J: A brief review
on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 7:147–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Ge Y, Xu Y, Guo M, Mi K, Xu
R, Pei Y, Zhang Q, Luan X, et al: SARS-CoV-2 encoded microRNAs are
involved in the process of virus infection and host immune
response. J Biomed Res. 35:216–227. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chauhan N, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC and Yallapu
MM: COVID-19: Fighting the invisible enemy with microRNAs. Expert
Rev Anti Infect Ther. 19:137–145. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Fani M, Zandi M, Ebrahimi S, Soltani S and
Abbasi S: The role of miRNAs in COVID-19 disease. Future Virol.
16:301–306. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Bugnon LA, Raad J, Merino GA, Yones C,
Ariel F, Milone DH and Stegmayer G: Deep Learning for the discovery
of new pre-miRNAs: Helping the fight against COVID-19. Mach Learn
with Appl. 6:1001502021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Abedi F, Rezaee R, Hayes AW, Nasiripour S
and Karimi G: MicroRNAs and SARS-CoV-2 life cycle, pathogenesis,
and mutations: Biomarkers or therapeutic agents? Cell Cycle.
20:143–153. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Haddad H and Al-Zyoud W: miRNA target
prediction might explain the reduced transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in
Jordan, Middle East. Noncoding RNA Res. 5:135–143. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sardar R, Satish D, Birla S and Gupta D:
Integrative analyses of SARS-CoV-2 genomes from different
geographical locations reveal unique features potentially
consequential to host-virus interaction, pathogenesis and clues for
novel therapies. Heliyon. 6:e046582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Matarese A, Gambardella J, Sardu C and
Santulli G: miR-98 regulates TMPRSS2 expression in human
endothelial cells: Key implications for COVID-19. Biomedicines.
8:4622020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Nersisyan S, Shkurnikov M, Turchinovich A,
Knyazev E and Tonevitsky A: Integrative analysis of miRNA and mRNA
sequencing data reveals potential regulatory mechanisms of ACE2 and
TMPRSS2. PLoS One. 15:e02359872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lu D, Chatterjee S, Xiao K, Riedel I, Wang
Y, Foo R, Bär C and Thum T: MicroRNAs targeting the SARS-CoV-2
entry receptor ACE2 in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
148:46–49. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Khan MA, Sany MRU, Islam MS and Islam
ABMMK: Epigenetic regulator miRNA pattern differences among
SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and SARS-CoV-2 World-Wide isolates delineated
the mystery behind the epic pathogenicity and distinct clinical
characteristics of pandemic COVID-19. Front Genet. 11:7652020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Paul S, Bravo Vázquez LA, Reyes-Pérez PR,
Estrada-Meza C, Aponte Alburquerque RA, Pathak S, Banerjee A,
Bandyopadhyay A, Chakraborty S and Srivastava A: The role of
microRNAs in solving COVID-19 puzzle from infection to
therapeutics: A mini-review. Virus Res. 308:1986312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dash S, Dash C and Pandhare J: Therapeutic
significance of microRNA-mediated regulation of PARP-1 in
SARS-CoV-2 infection. Noncoding RNA. 7:602021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mukhopadhyay D and Mussa BM:
Identification of novel hypothalamic MicroRNAs as promising
therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 by regulating ACE2 and TMPRSS2
expression: An in silico analysis. Brain Sci. 10:6662020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Wang X: miRDB: A microRNA target
prediction and functional annotation database with a wiki
interface. RNA. 14:1012–1017. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Wicik Z, Eyileten C, Jakubik D, Simões SN,
Martins DC Jr, Pavão R, Siller-Matula JM and Postula M: ACE2
interaction networks in COVID-19: A physiological framework for
prediction of outcome in patients with cardiovascular risk factors.
J Clin Med. 9:37432020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|