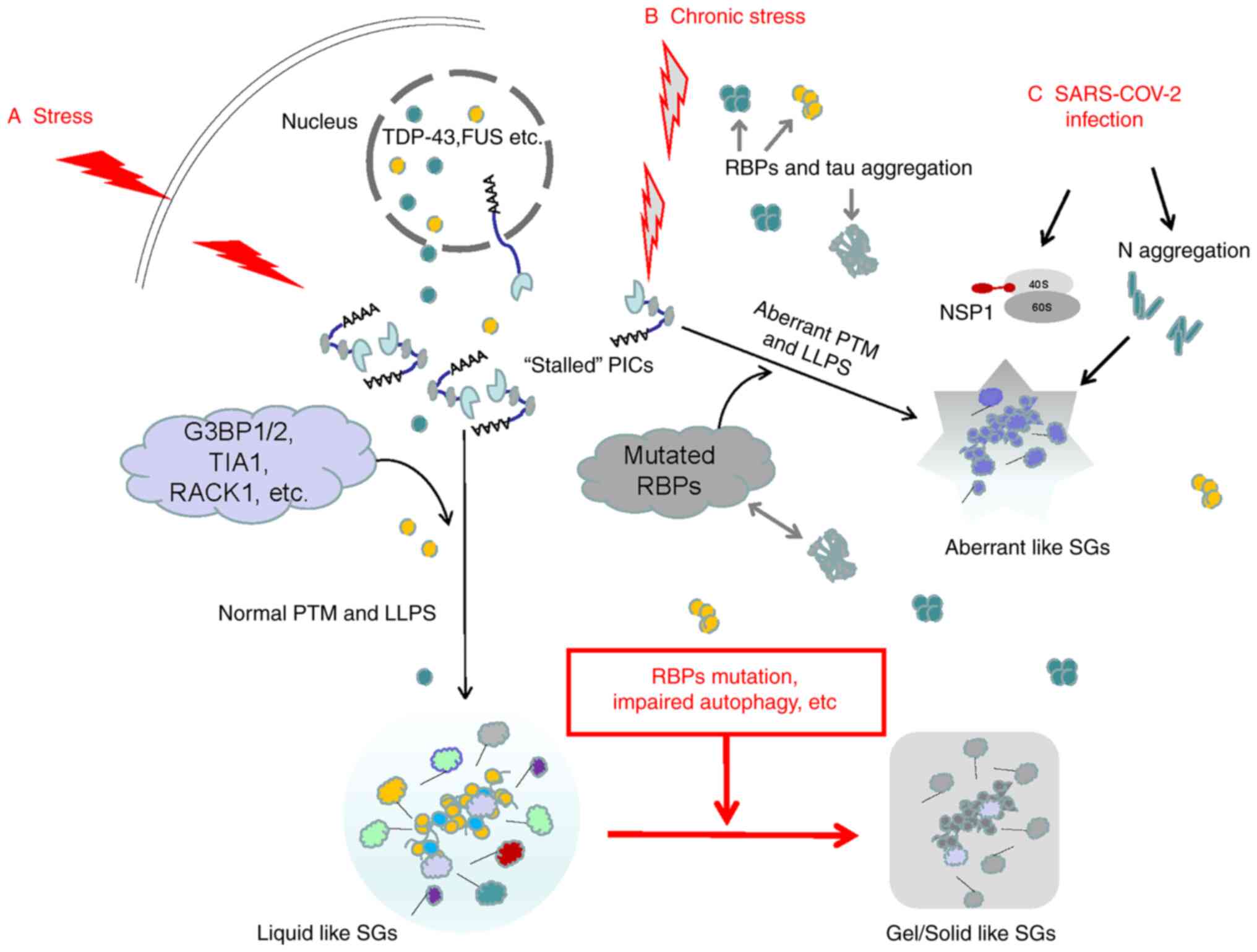
|
1
|
Ivanov P, Kedersha N and Anderson P:
Stress granules and processing bodies in translational control.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 11:a0328132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hentze MW, Castello A, Schwarzl T and
Preiss T: A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 19:327–341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shin Y and Brangwynne CP: Liquid phase
condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science.
357:eaaf43822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Riggs CL, Kedersha N, Ivanov P and
Anderson P: Mammalian stress granules and P bodies at a glance. J
Cell Sci. 133:jcs2424872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heberle AM, Razquin Navas P,
Langelaar-Makkinje M, Kasack K, Sadik A, Faessler E, Hahn U,
Marx-Stoelting P, Opitz CA, Sers C, et al: The PI3K and MAPK/p38
pathways control stress granule assembly in a hierarchical manner.
Life Sci Alliance. 2:e2018002572019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Golob-Schwarzl N, Krassnig S, Toeglhofer
AM, Park YN, Gogg-Kamerer M, Vierlinger K, Schröder F, Rhee H,
Schicho R, Fickert P and Haybaeck J: New liver cancer biomarkers:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway members and eukaryotic translation initiation
factors. Eur J Cancer. 83:56–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sfakianos AP, Mellor LE, Pang YF,
Kritsiligkou P, Needs H, Abou-Hamdan H, Désaubry L, Poulin GB, Ashe
MP and Whitmarsh AJ: The mTOR-S6 kinase pathway promotes stress
granule assembly. Cell Death Differ. 25:1766–1780. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Onomoto K, Yoneyama M, Fung G, Kato H and
Fujita T: Antiviral innate immunity and stress granule responses.
Trends Immunol. 35:420–428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McCormick C and Khaperskyy DA: Translation
inhibition and stress granules in the antiviral immune response.
Nat Rev Immunol. 17:647–660. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Q, Leng K, Liu Y, Sun H, Gao J, Ren Q,
Zhou T, Dong J and Xia J: The impact of hyperglycaemia on
PKM2-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome/stress granule signalling in
macrophages and its correlation with plaque vulnerability: An in
vivo and in vitro study. Metabolism. 107:1542312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Herman AB, Silva Afonso M, Kelemen SE, Ray
M, Vrakas CN, Burke AC, Scalia RG, Moore K and Autieri MV:
Regulation of stress granule formation by inflammation, vascular
injury, and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
39:2014–2027. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Patel A, Lee HO, Jawerth L, Maharana S,
Jahnel M, Hein MY, Stoynov S, Mahamid J, Saha S, Franzmann TM, et
al: A Liquid-to-Solid phase transition of the ALS Protein FUS
accelerated by disease mutation. Cell. 162:1066–1077. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ramaswami M, Taylor JP and Parker R:
Altered ribostasis: RNA-protein granules in degenerative disorders.
Cell. 154:727–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ambadipudi S, Biernat J, Riedel D,
Mandelkow E and Zweckstetter M: Liquid-liquid phase separation of
the microtubule-binding repeats of the Alzheimer-related protein
Tau. Nat Commu. 8:2752017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wegmann S, Eftekharzadeh B, Tepper K,
Zoltowska KM, Bennett RE, Dujardin S, Laskowski PR, MacKenzie D,
Kamath T, Commins C, et al: Tau protein liquid-liquid phase
separation can initiate tau aggregation. EMBO J. 37:e980492018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kedersha N, Chen S, Gilks N, Li W, Miller
IJ, Stahl J and Anderson P: Evidence that ternary complex
(eIF2-GTP-tRNA(i) (Met))-deficient preinitiation complexes are core
constituents of mammalian stress granules. Mol Biol Cell.
13:195–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: Visibly
stressed: The role of eIF2, TIA-1, and stress granules in protein
translation. Cell Stress Chaperones. 7:213–221. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hofmann S, Kedersha N, Anderson P and
Ivanov P: Molecular mechanisms of stress granule assembly and
disassembly. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1868:1188762021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wolozin B and Ivanov P: Stress granules
and neurodegeneration. Na Rev Neurosci. 20:649–666. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jain S, Wheeler JR, Walters RW, Agrawal A,
Barsic A and Parker R: ATPase-modulated stress granules contain a
diverse proteome and substructure. Cell. 164:487–498. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Protter DSW and Parker R: Principles and
properties of stress granules. Trends Cell Biol. 26:668–679. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Markmiller S, Soltanieh S, Server KL, Mak
R, Jin W, Fang MY, Luo EC, Krach F, Yang D, Sen A, et al:
Context-dependent and disease-specific diversity in protein
interactions within stress granules. Cell. 172:590–604.e13. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Kedersha N, Panas MD, Achorn CA, Lyons S,
Tisdale S, Hickman T, Thomas M, Lieberman J, McInerney GM, Ivanov P
and Anderson P: G3BP-Caprin1-USP10 complexes mediate stress granule
condensation and associate with 40S subunits. J Cell Biol.
212:845–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: Stress
granules: The Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci. 33:141–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaehler C, Isensee J, Hucho T, Lehrach H
and Krobitsch S: 5-fluorouracil affects assembly of stress granules
based on RNA incorporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:6436–6447. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujimura K, Sasaki AT and Anderson P:
Selenite targets eIF4E-binding protein-1 to inhibit translation
initiation and induce the assembly of non-canonical stress
granules. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:8099–8110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohn T, Kedersha N, Hickman T, Tisdale S
and Anderson P: A functional RNAi screen links O-GlcNAc
modification of ribosomal proteins to stress granule and processing
body assembly. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1224–1231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aulas A, Lyons SM, Fay MM, Anderson P and
Ivanov P: Nitric oxide triggers the assembly of 'type II' stress
granules linked to decreased cell viability. Cell Death Dis.
9:11292018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: RNA granules. J
Cell Biol. 172:803–808. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang C, Chen Y, Dai H, Zhang H, Xie M,
Zhang H, Chen F, Kang X, Bai X and Chen Z: UBAP2L arginine
methylation by PRMT1 modulates stress granule assembly. Cell Death
Differ. 27:227–241. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tsai WC, Gayatri S, Reineke LC, Sbardella
G, Bedford MT and Lloyd RE: Arginine demethylation of G3BP1
promotes stress granule assembly. J Biol Chemistry.
291:22671–22685. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kedersha N and Anderson P: Stress
granules: Sites of mRNA triage that regulate mRNA stability and
translatability. Biochem Soc Trans. 30:963–969. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mateju D, Eichenberger B, Voigt F,
Eglinger J, Roth G and Chao JA: Single-molecule imaging reveals
translation of mRNAs localized to stress granules. Cell.
183:1801–1812.e13. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arimoto K, Fukuda H, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Saito
H and Takekawa M: Formation of stress granules inhibits apoptosis
by suppressing stress-responsive MAPK pathways. Nat Cell Biol.
10:1324–1332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park YJ, Choi DW, Cho SW, Han J, Yang S
and Choi CY: Stress granule formation attenuates RACK1-mediated
apoptotic cell death induced by morusin. Int J Mol Sci.
21:53602020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Panas MD, Ivanov P and Anderson P:
Mechanistic insights into mammalian stress granule dynamics. J Cell
Biol. 215:313–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Tourrière H, Chebli K, Zekri L, Courselaud
B, Blanchard JM, Bertrand E and Tazi J: The RasGAP-associated
endoribonuclease G3BP assembles stress granules. J Cell Biol.
160:823–831. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Omer A, Patel D, Moran JL, Lian XJ, Di
Marco S and Gallouzi IE: Autophagy and heat-shock response impair
stress granule assembly during cellular senescence. Mech Ageing
Dev. 192:1113822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Omer A, Barrera MC, Moran JL, Lian XJ, Di
Marco S, Beausejour C and Gallouzi IE: G3BP1 controls the
senescence-associated secretome and its impact on cancer
progression. Nat Commun. 11:49792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Coppé JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A and
Campisi J: The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark
side of tumor suppression. Annu Rev Pathol. 5:99–118. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Anderson P, Kedersha N and Ivanov P:
Stress granules, P-bodies and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1849:861–870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
El-Naggar AM and Sorensen PH:
Translational control of aberrant stress responses as a hallmark of
cancer. J Pathol. 244:650–666. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vilas-Boas Fde A, da Silva AM, de Sousa
LP, Lima KM, Vago JP, Bittencourt LF, Dantas AE, Gomes DA, Vilela
MC, Teixeira MM and Barcelos LS: Impairment of stress granule
assembly via inhibition of the eIF2alpha phosphorylation sensitizes
glioma cells to chemotherapeutic agents. J Neurooncol. 127:253–260.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fournier MJ, Gareau C and Mazroui R: The
chemotherapeutic agent bortezomib induces the formation of stress
granules. Cancer Cell Int. 10:122010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Gao X, Jiang L, Gong Y, Chen X, Ying M,
Zhu H, He Q, Yang B and Cao J: Stress granule: A promising target
for cancer treatment. Br J Pharmacol. 176:4421–4433. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Khan FH, Dervan E, Bhattacharyya DD,
McAuliffe JD, Miranda KM and Glynn SA: The role of nitric oxide in
cancer: Master regulator or NOt? Int J Mol Sci. 21:93932020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Alam U and Kennedy D: G3BP1 and G3BP2
regulate translation of interferon-stimulated genes: IFITM1, IFITM2
and IFITM3 in the cancer cell line MCF7. Mol Cell Biochem.
459:189–204. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gupta N, Badeaux M, Liu Y, Naxerova K,
Sgroi D, Munn LL, Jain RK and Garkavtsev I: Stress
granule-associated protein G3BP2 regulates breast tumor initiation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:1033–1038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Somasekharan SP, El-Naggar A, Leprivier G,
Cheng H, Hajee S, Grunewald TG, Zhang F, Ng T, Delattre O,
Evdokimova V, et al: YB-1 regulates stress granule formation and
tumor progression by translationally activating G3BP1. J Cell Biol.
208:913–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Ramachandran B, Stabley JN, Cheng SL,
Behrmann AS, Gay A, Li L, Mead M, Kozlitina J, Lemoff A, Mirzaei H,
et al: A GTPase-activating protein-binding protein
(G3BP1)/antiviral protein relay conveys arteriosclerotic Wnt
signals in aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 293:7942–7968.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Schneider JW, Oommen S, Qureshi MY,
Goetsch SC, Pease DR, Sundsbak RS, Guo W, Sun M, Sun H, Kuroyanagi
H, et al: Dysregulated ribonucleoprotein granules promote
cardiomyopathy in RBM20 gene-edited pigs. Nat Med. 26:1788–1800.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Smit M, Coetzee AR and Lochner A: The
pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia and perioperative myocardial
infarction. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 34:2501–2512. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Garikipati VNS, Verma SK, Cheng Z, Liang
D, Truongcao MM, Cimini M, Yue Y, Huang G, Wang C, Benedict C, et
al: Circular RNA CircFndc3b modulates cardiac repair after
myocardial infarction via FUS/VEGF-A axis. Nat Commun. 10:43172019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mahboubi H and Stochaj U: Cytoplasmic
stress granules: Dynamic modulators of cell signaling and disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:884–895. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yoneyama M, Jogi M and Onomoto K:
Regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling by stress-induced
RNA granules. J Biochem. 159:279–286. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu S, Chen D, Chen D, Hu Q, Zhou L, Ge X,
Han J, Guo X and Yang H: Pseudorabies virus infection inhibits
stress granules formation via dephosphorylating eIF2α. Vet
Microbiol. 247:1087862020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Khong A, Kerr CH, Yeung CHL, Keatings K,
Nayak A, Allan DW and Jan E: Disruption of stress granule formation
by the multifunctional cricket paralysis virus 1A protein. J Virol.
91:e01779–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Visser LJ, Medina GN, Rabouw HH, de Groot
RJ, Langereis MA, de Los Santos T and van Kuppeveld FJM:
Foot-and-Mouth disease virus leader protease cleaves G3BP1 and
G3BP2 and inhibits stress granule formation. J Virol. 93:e00922–18.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Dougherty JD, Tsai WC and Lloyd RE:
Multiple poliovirus proteins repress cytoplasmic RNA granules.
Viruses. 7:6127–6140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yang X, Hu Z, Fan S, Zhang Q, Zhong Y, Guo
D, Qin Y and Chen M: Picornavirus 2A protease regulates stress
granule formation to facilitate viral translation. PLoS Pathog.
14:e10069012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Le Sage V, Cinti A, McCarthy S, Amorim R,
Rao S, Daino GL, Tramontano E, Branch DR and Mouland AJ: Ebola
virus VP35 blocks stress granule assembly. Virology. 502:73–83.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Savastano A, Ibáñez de Opakua A, Rankovic
M and Zweckstetter M: Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase
separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates. Nat
Commun. 11:60412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang J, Shi C, Xu Q and Yin H: SARS-CoV-2
nucleocapsid protein undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation into
stress granules through its N-terminal intrinsically disordered
region. Cell Discov. 7:52021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lu S, Ye Q, Singh D, Cao Y, Diedrich JK,
Yates JR III, Villa E, Cleveland DW and Corbett KD: The SARS-CoV-2
nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates
with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein. Nat Commun.
12:5022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Prasad K, Alasmari AF, Ali N, Khan R,
Alghamdi A and Kumar V: Insights into the SARS-CoV-2-Mediated
alteration in the stress granule protein regulatory networks in
humans. Pathogens. 10:14592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Thoms M, Buschauer R, Ameismeier M, Koepke
L, Denk T, Hirschenberger M, Kratzat H, Hayn M, Mackens-Kiani T,
Cheng J, et al: Structural basis for translational shutdown and
immune evasion by the Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science.
369:1249–1255. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shi M, Wang L, Fontana P, Vora S, Zhang Y,
Fu TM, Lieberman J and Wu H: SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 suppresses host but
not viral translation through a bipartite mechanism. bioRxiv.
2020:3029012020.
|
|
68
|
Schubert K, Karousis ED, Jomaa A, Scaiola
A, Echeverria B, Gurzeler LA, Leibundgut M, Thiel V, Mühlemann O
and Ban N: SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRNA channel to
inhibit translation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 27:959–966. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nakagawa K, Narayanan K, Wada M and Makino
S: Inhibition of stress granule formation by middle east
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 4a accessory protein facilitates
viral translation, leading to efficient virus replication. J Virol.
92:e00902–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Callaway E: Heavily mutated omicron
variant puts scientists on alert. Nature. 600:212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Dudman J and Qi X: Stress granule
dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Cell
Neurosci. 14:5985172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Anderson EN, Gochenaur L, Singh A, Grant
R, Patel K, Watkins S, Wu JY and Pandey UB: Traumatic injury
induces stress granule formation and enhances motor dysfunctions in
ALS/FTD models. Hum Mol Genet. 27:1366–1381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ayuso MI, Martínez-Alonso E, Regidor I and
Alcázar A: Stress granule induction after brain ischemia is
independent of eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF) 2α
phosphorylation and is correlated with a decrease in eIF4B and
eIF4E proteins. J Biol Chemistry. 291:27252–27264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Correia AS, Patel P, Dutta K and Julien
JP: Inflammation induces TDP-43 mislocalization and aggregation.
PLoS One. 10:e01402482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cao X, Jin X and Liu B: The involvement of
stress granules in aging and aging-associated diseases. Aging Cell.
19:e131362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cruz A, Verma M and Wolozin B: The
Pathophysiology of tau and stress granules in disease. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1184:359–372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Webber CJ, Lei SE and Wolozin B: The
pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease: Disturbing the
balance between phase separation and irreversible aggregation. Prog
Mol Biol Transl Sci. 174:187–223. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Rozpędek-Kamińska W, Siwecka N,
Wawrzynkiewicz A, Wojtczak R, Pytel D, Diehl JA and Majsterek I:
The PERK-dependent molecular mechanisms as a novel therapeutic
target for neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 21:21082020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ma T, Trinh MA, Wexler AJ, Bourbon C,
Gatti E, Pierre P, Cavener DR and Klann E: Suppression of eIF2α
kinases alleviates Alzheimer's disease-related plasticity and
memory deficits. Nat Neurosci. 16:1299–1305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kim HJ, Raphael AR, LaDow ES, McGurk L,
Weber RA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Finkbeiner S, Gitler AD and
Bonini NM: Therapeutic modulation of eIF2α phosphorylation rescues
TDP-43 toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease models.
Nat Genet. 46:152–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Banani SF, Lee HO, Hyman AA and Rosen MK:
Biomolecular condensates: Organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 18:285–298. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Flores BN, Li X, Malik AM, Martinez J, Beg
AA and Barmada SJ: An intramolecular salt bridge linking TDP43 RNA
binding, protein stability, and TDP43-dependent neurodegeneration.
Cell Rep. 27:1133–1150.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Archbold HC, Jackson KL, Arora A, Weskamp
K, Tank EM, Li X, Miguez R, Dayton RD, Tamir S, Klein RL and
Barmada SJ: TDP43 nuclear export and neurodegeneration in models of
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Sci Rep.
8:46062018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Suk TR and Rousseaux MWC: The role of
TDP-43 mislocalization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol
Neurodegener. 15:452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tomé SO, Vandenberghe R, Ospitalieri S,
Van Schoor E, Tousseyn T, Otto M, von Arnim CAF and Thal DR:
Distinct molecular patterns of TDP-43 pathology in Alzheimer's
disease: Relationship with clinical phenotypes. Acta Neuropathol
Commun. 8:612020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Vanderweyde T, Apicco DJ, Youmans-Kidder
K, Ash PEA, Cook C, Lummertz da Rocha E, Jansen-West K, Frame AA,
Citro A, Leszyk JD, et al: Interaction of tau with the RNA-binding
Protein TIA1 regulates tau pathophysiology and toxicity. Cell Rep.
15:1455–1466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Apicco DJ, Ash PEA, Maziuk B, LeBlang C,
Medalla M, Al Abdullatif A, Ferragud A, Botelho E, Ballance HI,
Dhawan U, et al: Reducing the RNA binding protein TIA1 protects
against tau-mediated neurodegeneration in vivo. Nat Neurosci.
21:72–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Gal J, Kuang L, Barnett KR, Zhu BZ,
Shissler SC, Korotkov KV, Hayward LJ, Kasarskis EJ and Zhu H: ALS
mutant SOD1 interacts with G3BP1 and affects stress granule
dynamics. Acta Neuropathol. 132:563–576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sidibé H, Dubinski A and Vande Velde C:
The multi-functional RNA-binding protein G3BP1 and its potential
implication in neurodegenerative disease. J Neurochem. 157:944–962.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Gogia N, Sarkar A, Mehta AS, Ramesh N,
Deshpande P, Kango-Singh M, Pandey UB and Singh A: Inactivation of
Hippo and cJun-N-terminal Kinase (JNK) signaling mitigate FUS
mediated neurodegeneration in vivo. Neurobio Dis. 140:1048372020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Picchiarelli G, Demestre M, Zuko A, Been
M, Higelin J, Dieterlé S, Goy MA, Mallik M, Sellier C,
Scekic-Zahirovic J, et al: FUS-mediated regulation of acetylcholine
receptor transcription at neuromuscular junctions is compromised in
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci. 22:1793–1805. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fifita JA, Zhang KY, Galper J, Williams
KL, McCann EP, Hogan AL, Saunders N, Bauer D, Tarr IS, Pamphlett R,
et al: Genetic and pathological assessment of hnRNPA1, hnRNPA2/B1,
and hnRNPA3 in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Neurodegener Dis. 17:304–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kim HJ, Kim NC, Wang YD, Scarborough EA,
Moore J, Diaz Z, MacLea KS, Freibaum B, Li S, Molliex A, et al:
Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause
multi-system proteinopathy and ALS. Nature. 495:467–473. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Montalbano M, McAllen S, Cascio FL,
Sengupta U, Garcia S, Bhatt N, Ellsworth A, Heidelman EA, Johnson
OD, Doskocil S and Kayed R: TDP-43 and tau oligomers in Alzheimer's
disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and frontotemporal
dementia. Neurobiol Dis. 146:1051302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhao M, Kim JR, van Bruggen R and Park J:
RNA-binding proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Cells.
41:818–829. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Mackenzie IR, Nicholson AM, Sarkar M,
Messing J, Purice MD, Pottier C, Annu K, Baker M, Perkerson RB,
Kurti A, et al: TIA1 mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and
frontotemporal dementia promote phase separation and alter stress
granule dynamics. Neuron. 95:808–816.e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chew J, Gendron TF, Prudencio M, Sasaguri
H, Zhang YJ, Castanedes-Casey M, Lee CW, Jansen-West K, Kurti A,
Murray ME, et al: Neurodegeneration. C9ORF72 repeat expansions in
mice cause TDP-43 pathology, neuronal loss, and behavioral
deficits. Science. 348:1151–1154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Chew J, Cook C, Gendron TF, Jansen-West K,
Del Rosso G, Daughrity LM, Castanedes-Casey M, Kurti A, Stankowski
JN, Disney MD, et al: Aberrant deposition of stress
granule-resident proteins linked to C9orf72-associated TDP-43
proteinopathy. Mol Neurodegener. 14:92019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Chitiprolu M, Jagow C, Tremblay V,
Bondy-Chorney E, Paris G, Savard A, Palidwor G, Barry FA, Zinman L,
Keith J, et al: A complex of C9ORF72 and p62 uses arginine
methylation to eliminate stress granules by autophagy. Nat Commun.
9:27942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Deng Z, Lim J, Wang Q, Purtell K, Wu S,
Palomo GM, Tan H, Manfredi G, Zhao Y, Peng J, et al:
ALS-FTLD-linked mutations of SQSTM1/p62 disrupt selective autophagy
and NFE2L2/NRF2 anti-oxidative stress pathway. Autophagy.
16:917–931. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Jiang Z, Belforte JE, Lu Y, Yabe Y, Pickel
J, Smith CB, Je HS, Lu B and Nakazawa K: eIF2alpha
Phosphorylation-dependent translation in CA1 pyramidal cells
impairs hippocampal memory consolidation without affecting general
translation. J Neurosci. 30:2582–2594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Trinh MA, Ma T, Kaphzan H, Bhattacharya A,
Antion MD, Cavener DR, Hoeffer CA and Klann E: The eIF2α kinase
PERK limits the expression of hippocampal metabotropic glutamate
receptor-dependent long-term depression. Learn Mem. 21:298–304.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Hijioka M, Inden M, Yanagisawa D and
Kitamura Y: DJ-1/PARK7: A new therapeutic target for
neurodegenerative disorders. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:548–552. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Repici M, Hassanjani M, Maddison DC,
Garção P, Cimini S, Patel B, Szegö ÉM, Straatman KR, Lilley KS,
Borsello T, et al: The Parkinson's disease-linked protein DJ-1
associates with cytoplasmic mRNP granules during stress and
neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 56:61–77. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Ma J, Wu R, Zhang Q, Wu JB, Lou J, Zheng
Z, Ding JQ and Yuan Z: DJ-1 interacts with RACK1 and protects
neurons from oxidative-stress-induced apoptosis. Biochem J.
462:489–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|