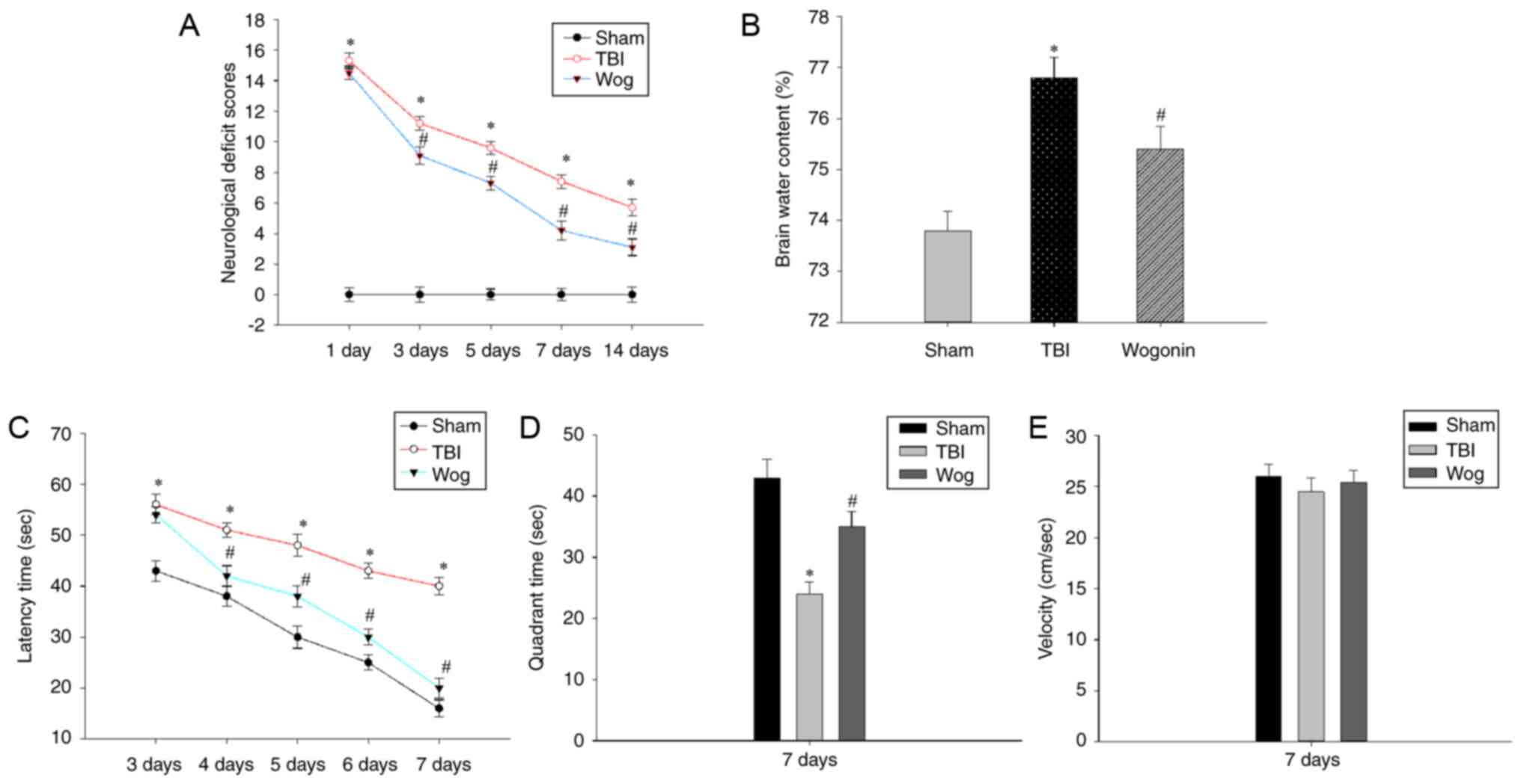
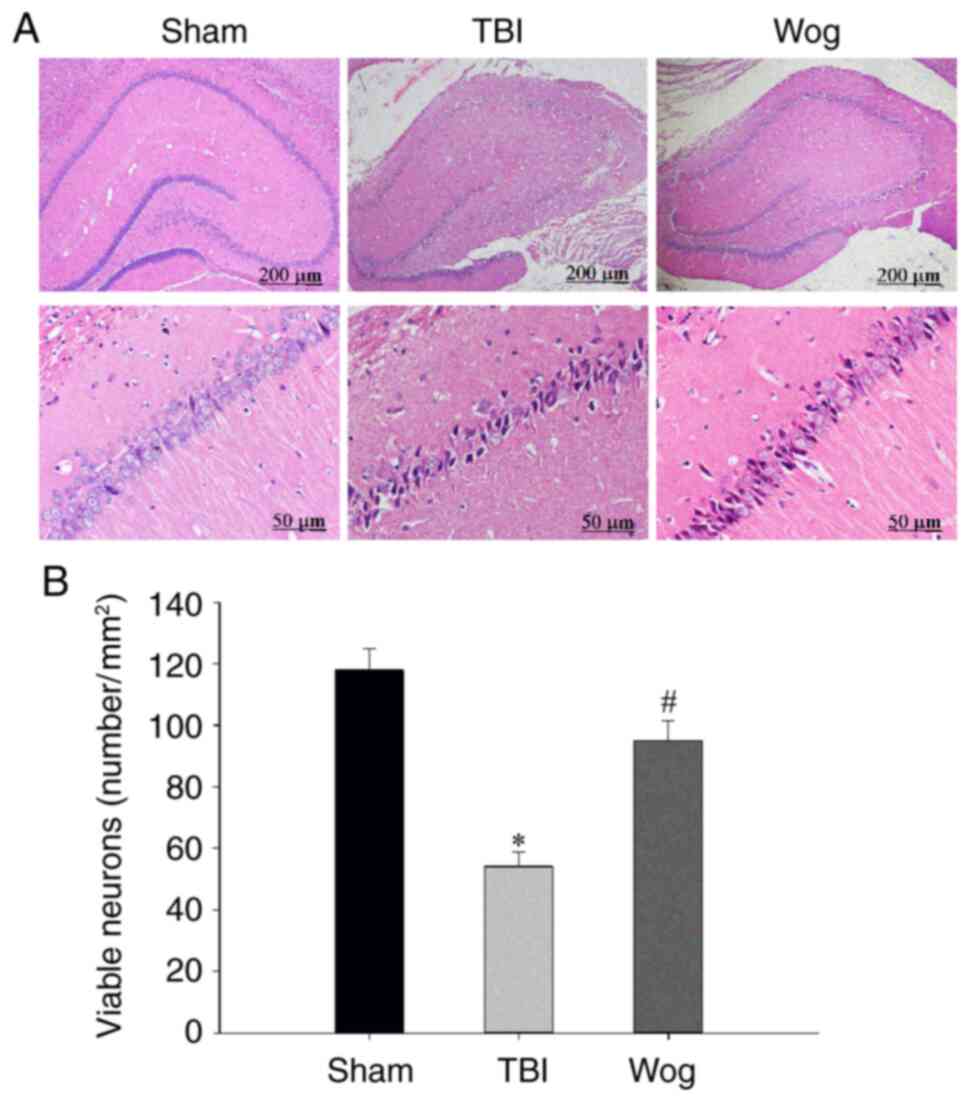
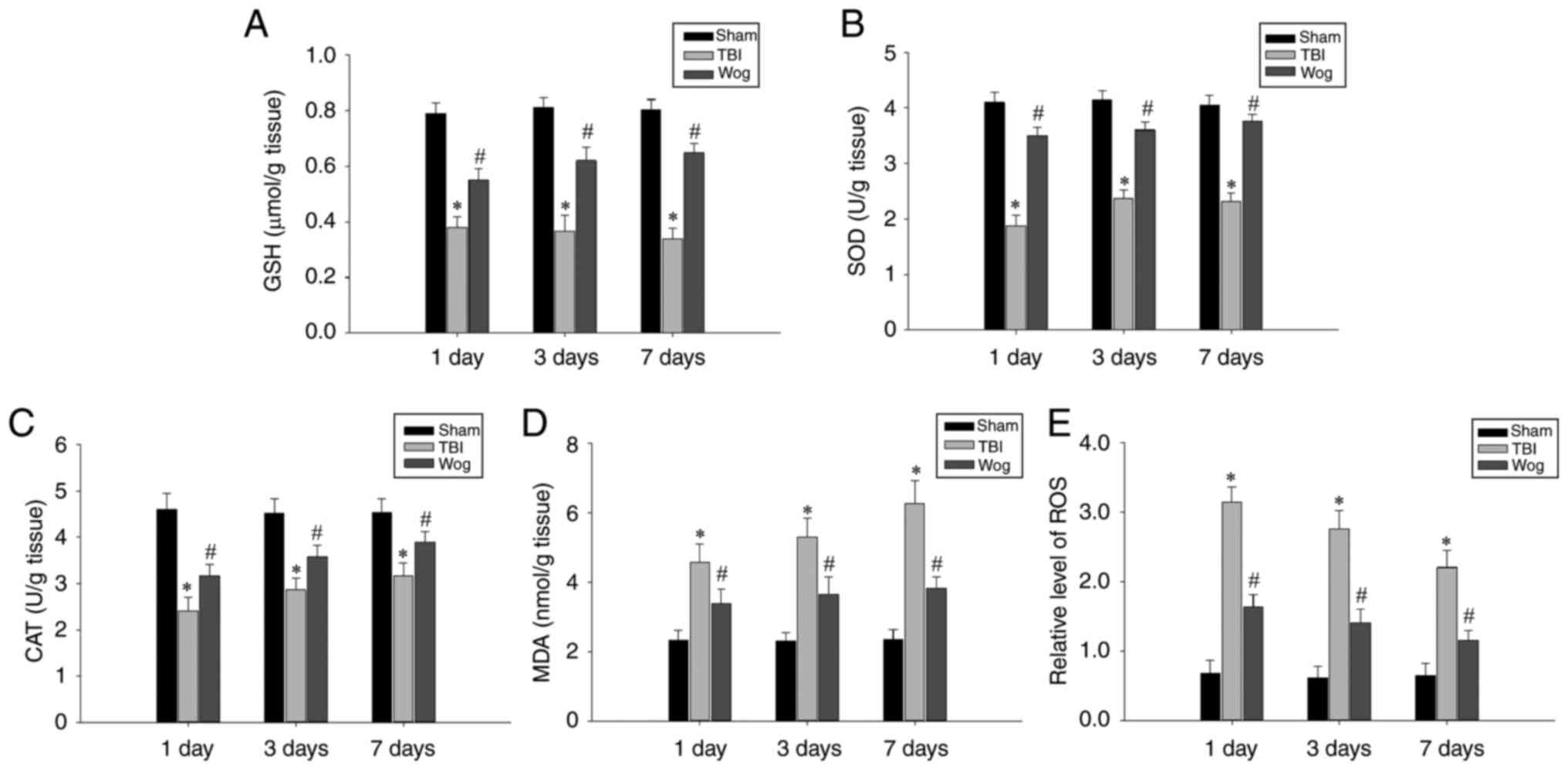
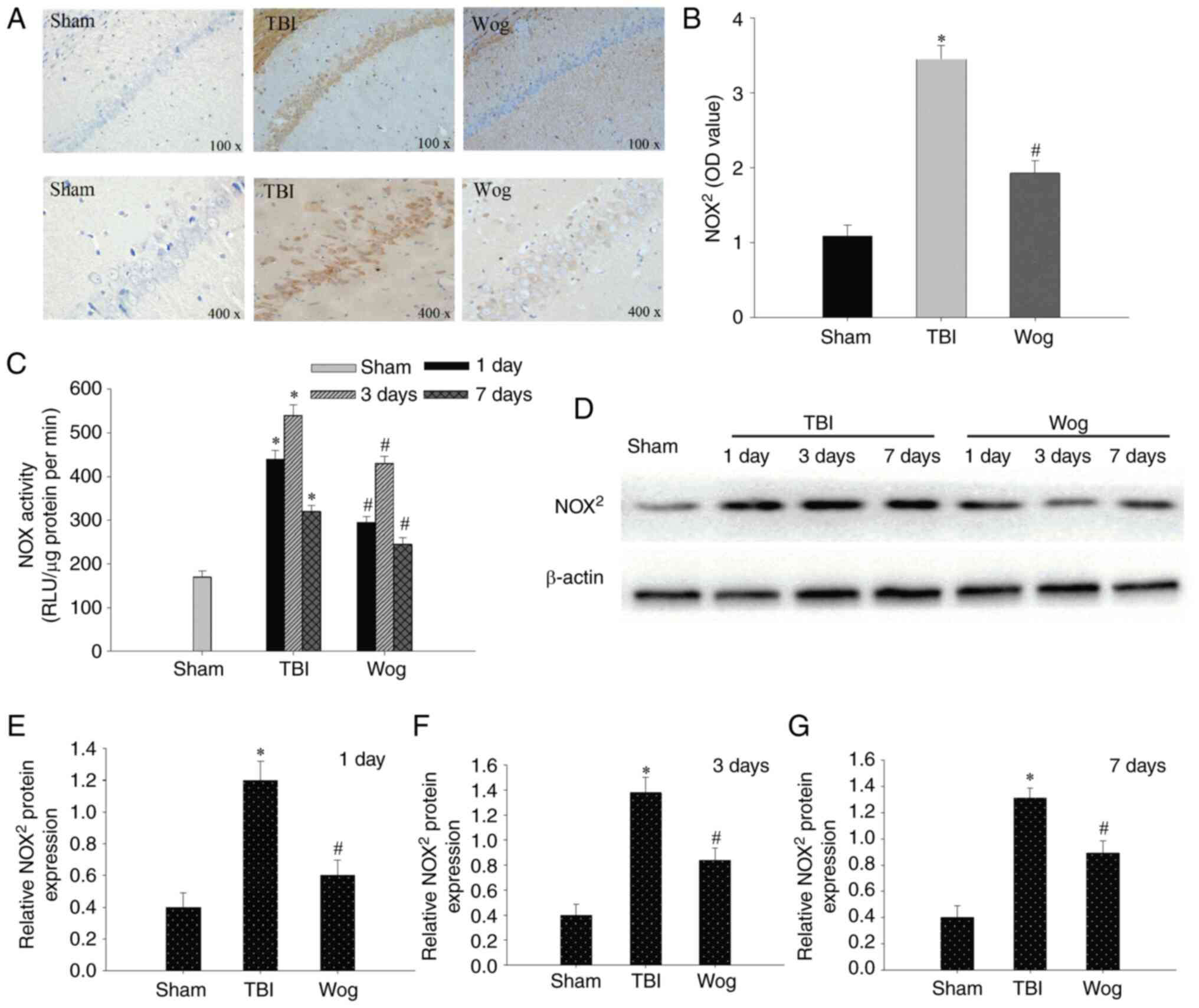
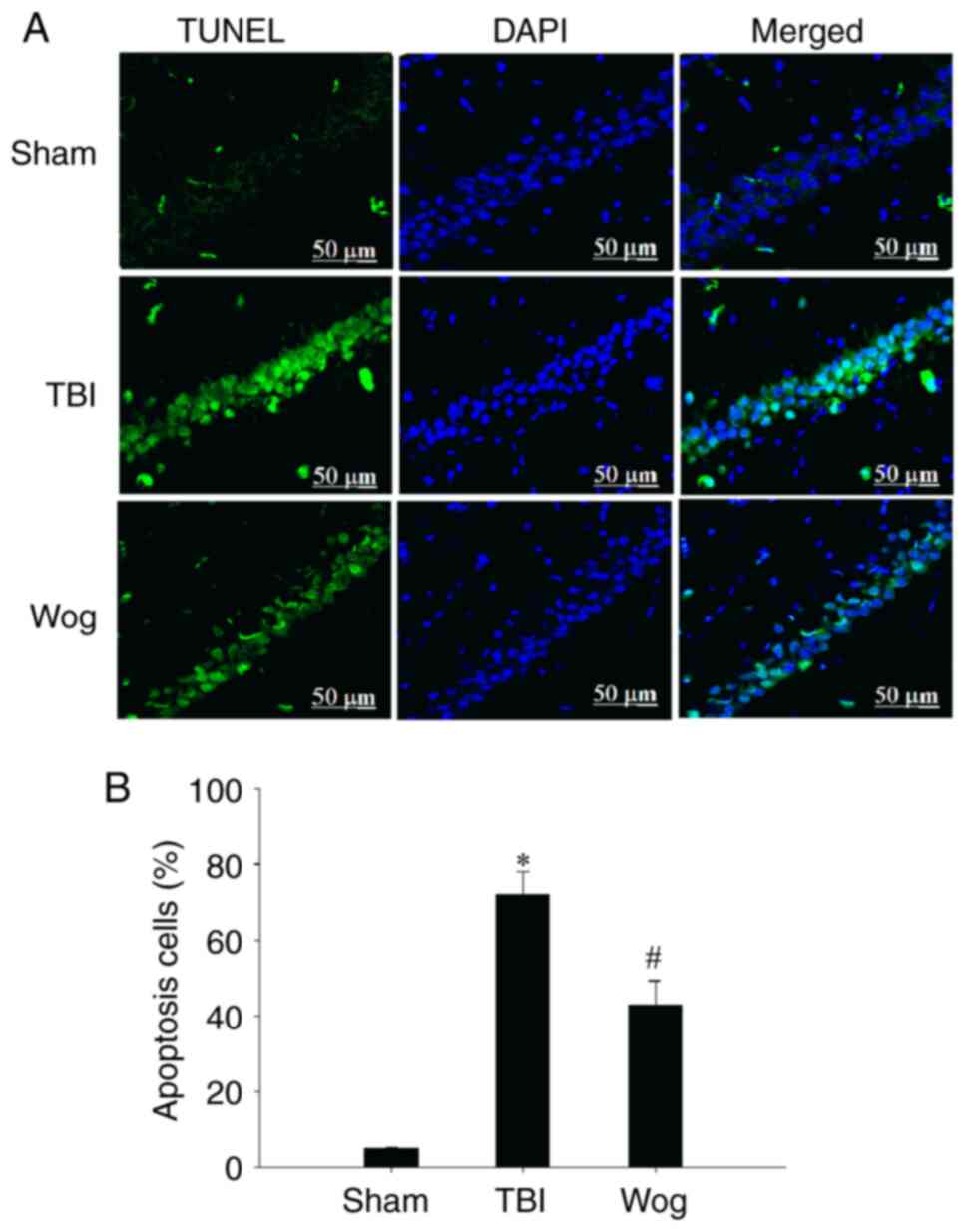
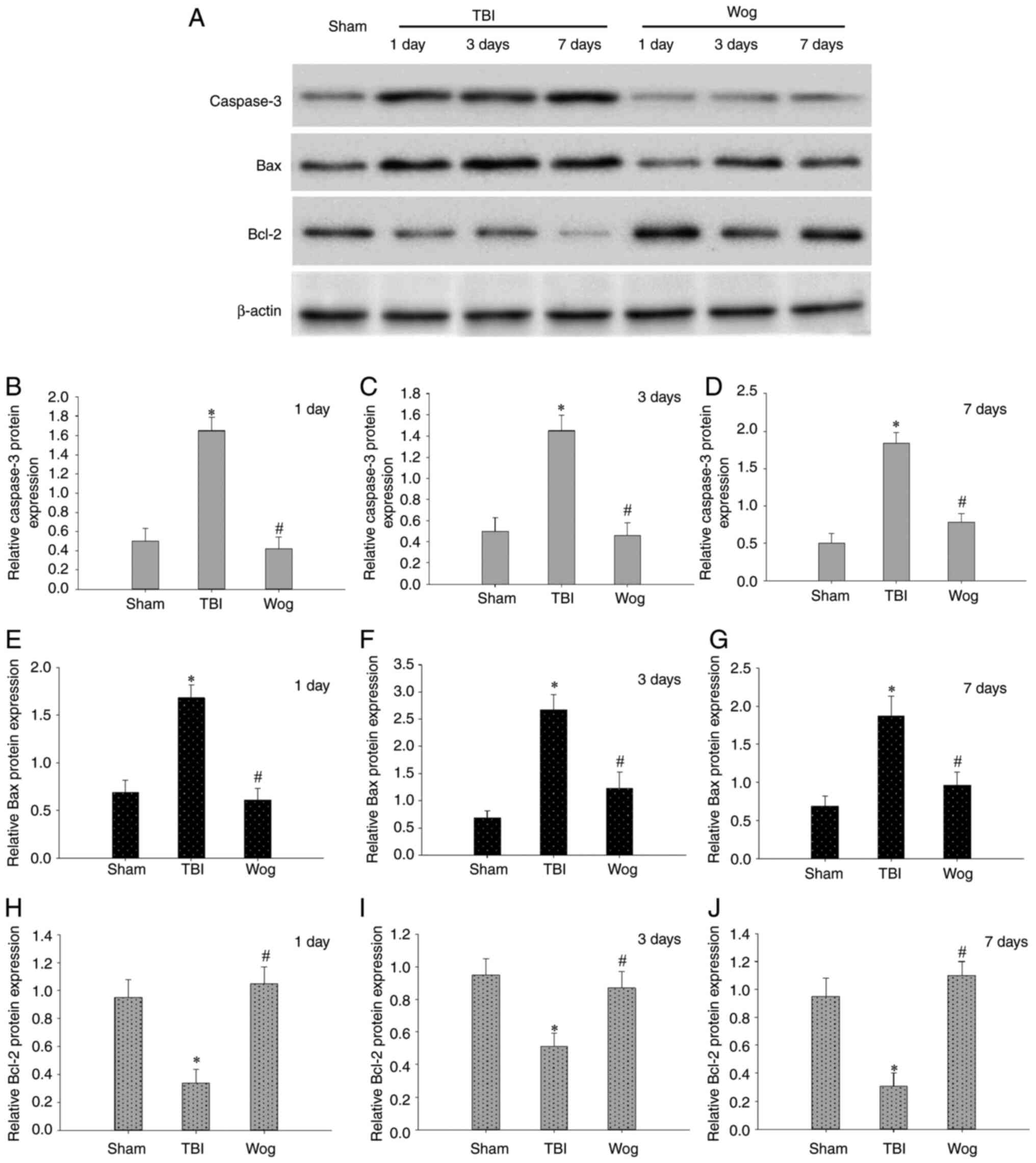
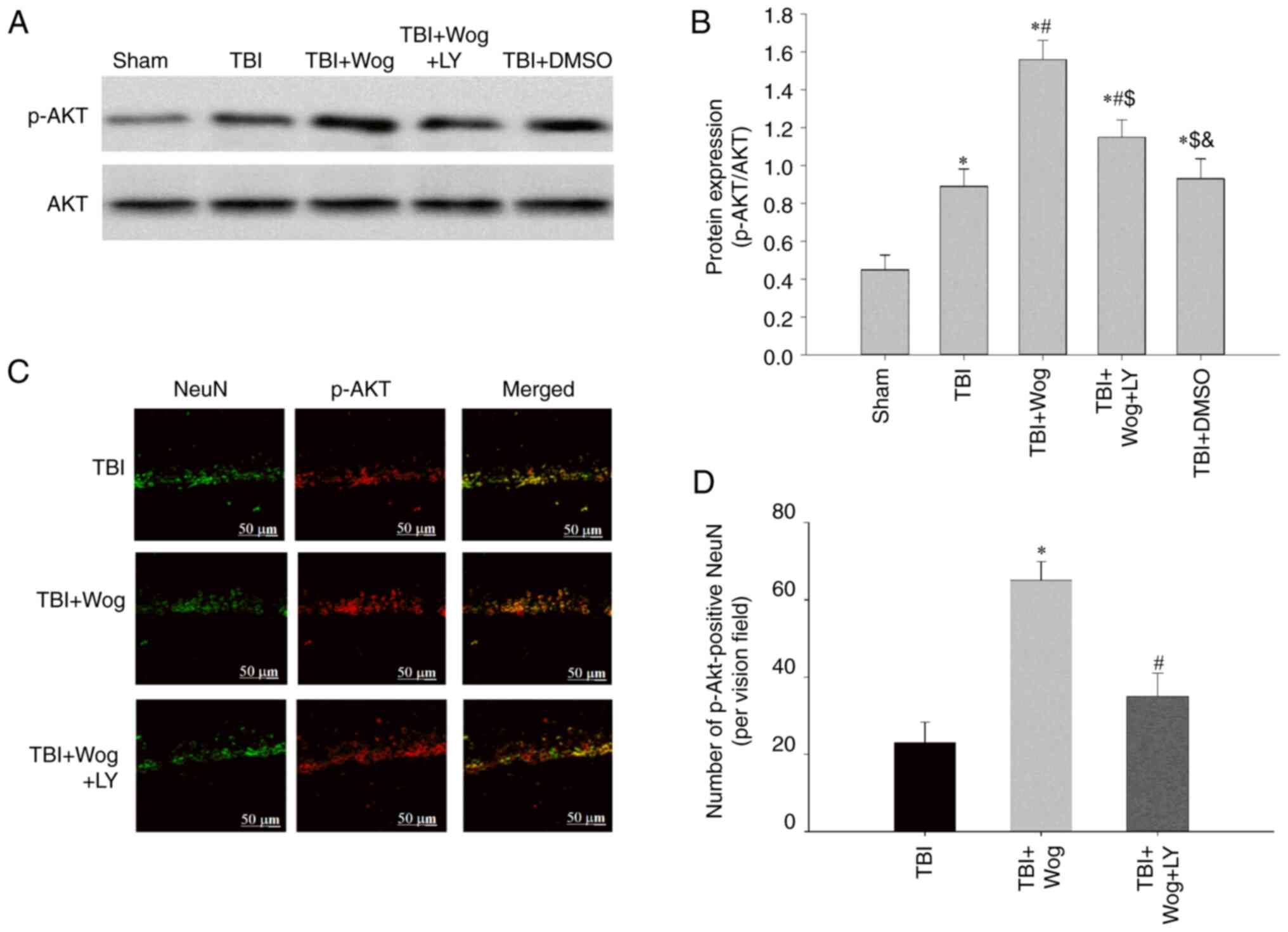
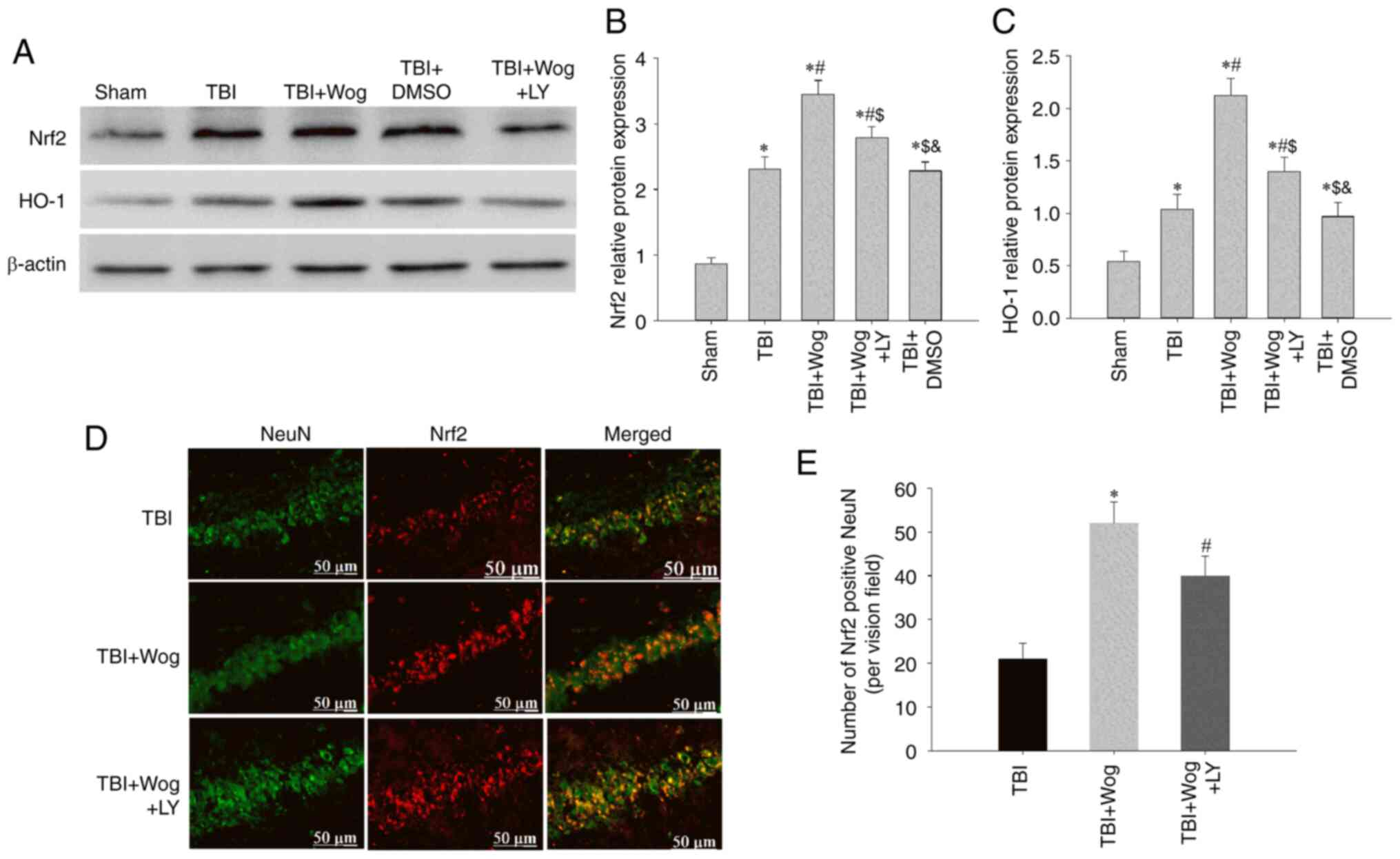
|
1
|
Chowdhury T, Kowalski S, Arabi Y and Dash
HH: Specific intensive care management of patients with traumatic
brain injury: Present and future. Saudi J Anaesth. 8:268–275. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vidhya V, Gudigar A, Raghavendra U, Hegde
A, Menon GR, Molinari F, Ciaccio EJ and Acharya UR: Automated
detection and screening of traumatic brain injury (TBI) using
computed tomography images: A comprehensive review and future
perspectives. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18:64992021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schweitzer AD, Niogi SN, Whitlow CJ and
Tsiouris AJ: Traumatic brain injury: Imaging patterns and
complications. Radiographics. 39:1571–1595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu LM, Dong X, Xue XD, Zhang J, Li Z, Wu
HJ, Yang ZL, Yang Y and Wang HS: Naringenin improves mitochondrial
function and reduces cardiac damage following ischemia-reperfusion
injury: The role of the AMPK-SIRT3 signaling pathway. Food Funct.
10:2752–2765. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Qian F, Han Y, Han Z, Zhang D, Zhang L,
Zhao G, Li S, Jin G, Yu R and Liu H: In situ implantable,
post-trauma microenvironment-responsive, ROS depletion hydrogels
for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Biomaterials.
270:1206752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slavoaca D, Muresanu D, Birle C, Rosu OV,
Chirila I, Dobra I, Jemna N, Strilciuc S and Vos P: Biomarkers in
traumatic brain injury: New concepts. Neurolog Sci. 41:2033–2044.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bedard K and Krause KH: The NOX family of
ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology.
Physiol Rev. 87:245–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chandran R, Kim T, Mehta SL, Udho E,
Chanana V, Cengiz P, Kim H, Kim C and Vemuganti R: A combination
antioxidant therapy to inhibit NOX2 and activate Nrf2
decreases secondary brain damage and improves functional recovery
after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
38:1818–1827. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Salman M, Tabassum H and Parvez S:
Nrf2/HO-1 mediates the neuroprotective effects of pramipexole by
attenuating oxidative damage and mitochondrial perturbation after
traumatic brain injury in rats. Dis Model Mech. 13:dmm0450212020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Hassanin M, Mai T, Tadros M, Elmazar M and
Singab AN: Wogonin a promising component of scutellaria
baicalensis: A review on its chemistry, pharmacokinetics and
biological activities. Archives of Pharmaceutical Sciences Ain
Shams University. 3:170–179. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huynh DL, Ngau TH, Nguyen NH, Tran BG and
Nguyen CT: Potential therapeutic and pharmacological effects of
Wogonin: An updated review. Mol Biol Rep. 47:9779–9789. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chun W, Lee HJ, Kong PJ, Lee GH, Cheongsu
LY, Park H and Kim SS: Synthetic wogonin derivatives suppress
lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production and hydrogen
peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Arch Pharm Res. 28:216–219. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei L, Zhao J, Liu XQ, Chen J, Qi XM, Xia
LL and Wu YG: Wogonin alleviates kidney tubular epithelial injury
in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling
pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther. 15:3131–3150. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Zhu G, Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang H, Jin W, Su
F, Liang J, Wang K, Zhang J and Chen C: The key target and
molecular mechanism of the volatile component of scutellaria
baicalensis georgi in acute lung injury based on network
pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 12:6507802021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Umemoto Y, Patel A, Huynh T and
Chitravanshi VC: Wogonin attenuates the deleterious effects of
traumatic brain injury in anesthetized Wistar rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 848:121–130. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CC, Hung TH, Wang YH, Lin CW, Wang
PY, Lee CY and Chen SF: Wogonin improves histological and
functional outcomes, and reduces activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling
after experimental traumatic brain injury. PLoS One. 7:e302942012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feng Y, Gao J, Cui Y, Li M, Li R, Cui C
and Cui J: Neuroprotective effects of resatorvid against traumatic
brain injury in rat: Involvement of neuronal autophagy and TLR4
signaling pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:155–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ates O, Cayli S, Altinoz E, Gurses I,
Yucel N, Sener M, Kocak A and Yologlu S: Neuroprotection by
resveratrol against traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 294:137–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen SF, Hsu CW, Huang WH and Wang JY:
Post-injury baicalein improves histological and functional outcomes
and reduces inflammatory cytokines after experimental traumatic
brain injury. Br J Pharmacol. 155:1279–1296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng Y, Cui Y, Gao JL, Li MH, Li R, Jiang
XH, Tian YX, Wang KJ, Cui CM and Cui JZ: Resveratrol attenuates
neuronal autophagy and inflammatory injury by inhibiting the
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in experimental traumatic brain
injury. Int J Mol Med. 37:921–930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Changmeng C, Sixin S, Jianzhong C, Yan F,
Junling G and Pei J: Vitamin D receptor activation influences NADPH
oxidase (NOX2) activity and protects against
neurological deficits and apoptosis in a rat model of traumatic
brain injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:92457022017.
|
|
22
|
Wang P, Wu Q, Wu W, Li H, Guo Y, Yu P, Gao
G, Shi Z, Zhao B and Chang YZ: Mitochondrial ferritin deletion
exacerbates β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017:10203572017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Song SX, Gao JL, Wang KJ, Li R, Tian YX,
Wei JQ and Cui JZ: Attenuation of brain edema and spatial learning
deficits by the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity using apocynin
following diffuse traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Med Rep.
7:327–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Du G, Zhao Z, Chen Y, Li Z, Tian Y, Liu Z,
Liu B and Song J: Quercetin attenuates neuronal autophagy and
apoptosis in rat traumatic brain injury model via activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurol Res. 38:1012–1019. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Netteland DF, Mejlnder-Evjensvold M, Skaga
NO, Sandset EC, Aarhus M and Helseth E: Cerebral venous thrombosis
in traumatic brain injury: A cause of secondary insults and added
mortality. J Neurosurg. 134:1–9. 2020.
|
|
26
|
Robicsek SA, Bhattacharya A, Rabai F,
Shukla K and Doré S: Blood-related toxicity after traumatic brain
injury: Potential targets for neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol.
57:159–178. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Khellaf A, Khan DZ and Helmy A: Recent
advances in traumatic brain injury. J Neurol. 266:2878–2889. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gennai S, Monsel A, Hao Q, Liu J, Gudapati
V, Barbier EL and Lee JW: Cell-based therapy for traumatic brain
injury. Br J Anaesth. 115:203–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huynh DL, Sharma N, Singh AK, Sodhi SS,
Zhang JJ, Mongre RK, Ghosh M, Kim N, Park YH and Jeong DK:
Anti-tumor activity of wogonin, an extract from Scutellaria
baicalensis, through regulating different signaling pathways. Chin
J Nat Med. 15:15–40. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Du D, Tang W, Zhou C, Sun X, Wei Z, Zhong
J and Huang Z: Fecal microbiota transplantation is a promising
method to restore gut microbiota dysbiosis and relieve neurological
deficits after traumatic brain injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021:58168372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji X, Tian Y, Xie K, Liu W, Qu Y and Fei
Z: Protective effects of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat model of
traumatic brain injury via reducing oxidative stress. J Surg Res.
178:e9–e16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu C, He D and Zhao Q: Licoricidin
improves neurological dysfunction after traumatic brain injury in
mice via regulating FoxO3/wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Nat Med.
74:767–776. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen J, Chen W, Han K, Qi E, Chen R, Yu M,
Hou L and Lv L: Effect of oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral
medulla on sympathetic hyperactivity after traumatic brain injury.
Eur J Neurosci. 50:1972–1980. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Masomi-Bornwasser J, Kurz E, Frenz C,
Schmitt J, Wesp DMA, König J, Lotz J, Ringel F, Kerz T, Krenzlin H
and Keric N: The influence of oxidative stress on neurological
outcomes in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomolecules.
11:16152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carteri RB, Kopczynski A, Rodolphi MS,
Strogulski NR, Sartor M, Feldmann M, Bastiani MAD, Wannmacher CMD,
de Franceschi ID, Hansel G, et al: Testosterone administration
after traumatic brain injury reduces mitochondrial dysfunction and
neurodegeneration. J Neurotrauma. 36:2246–2259. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong MY, Gao JL, Cui JZ, Wang KJ, Tian YX,
Li R, Wang HT and Wang H: Effect of c-Jun NH-terminal
kinase-mediated p53 expression on neuron autophagy following
traumatic brain injury in rats. Chinese Med J (Engl).
125:2019–2024. 2012.
|
|
37
|
Deng H, Yue JK, Zusman BE, Nwachuku EL,
Abou-Al-Shaar H, Upadhyayula PS, Okonkwo DO and Puccio AM: B-cell
lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and regulation of apoptosis after traumatic
brain injury: A clinical perspective. Medicina (Kaunas).
56:3002020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schober ME, Requena DF, Block B, Davis LJ,
Rodesch C, Casper TC, Juul SE, Kesner RP and Lane RH:
Erythropoietin improved cognitive function and decreased
hippocampal caspase activity in rat pups after traumatic brain
injury. J Neurotrauma. 31:358–369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Jackman KA, Miller AA, de Silva TM, Crack
PJ, Drummond GR and Sobey CG: Reduction of cerebral infarct volume
by apocynin requires pretreatment and is absent in Nox2-defificient
mice. Br J Pharmacol. 156:680–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dohi K, Ohtaki H, Nakamachi T, Yofu S,
Satoh K, Miyamoto K, Song D, Tsunawaki S, Shioda S and Aruga T:
Gp91phox (NOX2) in classically activated microglia exacerbates
traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflflammation. 7:412010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang M, Zhang J and Gong N: Role of the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: A
narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 27:apm-21-32862021.
|
|
42
|
Li Q, Cheng K, Wang AY, Xu QG, Fu ZF, He
SY and Xu PX: microRNA-126 inhibits tube formation of HUVECs by
interacting with EGFL7 and down-regulating PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 116:1090072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang G, Shi Y, Jiang X, Leak RK, Hu X, Wu
Y, Pu H, Li WW, Tang B, Wang Y, et al: HDAC inhibition prevents
white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization
through the GSK3β/PTEN/Akt axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:2853–2858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shen M, Wang S, Wen X, Han XR, Wang YJ,
Zhou XM, Zhang MH, Wu DM, Lu J and Zheng YL: Dexmedetomidine exerts
neuroprotective effect via the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway in rats with traumatic brain injury. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:885–893. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang L, Zhang J, Shan G, Liang J, Jin W,
Li Y, Su F, Ba Y, Tian X, Sun X, et al: Establishment of a lung
cancer discriminative model based on an optimized support vector
machine algorithm and study of key targets of Wogonin in lung
cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12:7289372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Parajuli P, Joshee N, Chinni SR, Rimando
AM, Mittal S, Sethi S and Yadav AK: Delayed growth of glioma by
Scutellaria flavonoids involve inhibition of Akt, GSK-3 and NF-κB
signaling. J Neurooncol. 101:15–24. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Huang KF, Zhang GD, Huang YQ and Diao Y:
Wogonin induces apoptosis and down-regulates survivin in human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:334–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang ZG, Cheng Y, Yu XC, Ye LB, Xia QH,
Johnson NR, Wei X, Chen DQ, Cao G, Fu XB, et al: bFGF protects
against blood-brain barrier damage through junction protein
regulation via PI3K-Akt-Rac1 pathway following traumatic brain
injury. Mol Neurobiol. 53:7298–7311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wu F, Chen Z, Tang C, Zhang J, Cheng L,
Zuo H, Zhang H, Chen D, Xiang L, Xiao J, et al: Acid fibroblast
growth factor preserves blood-brain barrier integrity by activating
the PI3K-Akt-Rac1 pathway and inhibiting RhoA following traumatic
brain injury. Am J Transl Res. 9:910–925. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liao K, Su X, Lei K, Liu Z, Lu L, Wu Q,
Pan H, Huang Q, Zhao Y, Wang M, et al: Sinomenine protects bone
from destruction to ameliorate arthritis via activating
p62Thr269/Ser272-Keap1-Nrf2 feedback loop. Biomed Pharmacother.
135:1111952021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Motohashi H, Katsuoka F, Engel JD and
Yamamoto M: Small maf proteins are obligate transcriptional
cofactors for normal keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1-Nrf2
regulatory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:6379–6384. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ndisang JF: Synergistic interaction
between heme oxygenase (HO) and nuclear-factor E2-related factor-2
(Nrf2) against oxidative stress in cardiovascular related diseases.
Curr Pharm Des. 23:1465–1470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bhowmick S, D'Mello V, Caruso D and
Abdul-Muneer PM: Traumatic brain injury-induced downregulation of
Nrf2 activates inflammatory response and apoptotic cell death. J
Mol Med (Berl). 97:1627–1641. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Salman M, Tabassum H and Parvez S: Tannic
acid provides neuroprotective effects against traumatic brain
injury through the PGC-1α/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Mol Neurobiol.
57:2870–2885. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao F, Wu X, Mao X, Niu F, Zhang B, Dong J
and Liu B: Astaxanthin provides neuroprotection in an experimental
model of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Am J
Transl Res. 13:1483–1493. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li F, Wang X, Zhang Z, Gao P and Zhang X:
Breviscapine provides a neuroprotective effect after traumatic
brain injury by modulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 120:14899–14907. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhuang Y, Wu H, Wang X, He J, He S and Yin
Y: Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress-induced intestinal
barrier injury through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:75918402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li ST, Dai Q, Zhang SX, Liu YJ, Yu QQ, Tan
F, Lu SH, Wang Q, Chen JW, Huang HQ, et al: Ulinastatin attenuates
LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by
inhibiting the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:1294–1304. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wen Z, Hou W, Wu W, Zhao Y, Dong X, Bai X,
Peng L and Song L: 6′-O-Galloylpaeoniflorin attenuates cerebral
ischemia reperfusion-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress
via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 activation. Oxid Med Cell Long.
2018:86782672018.
|