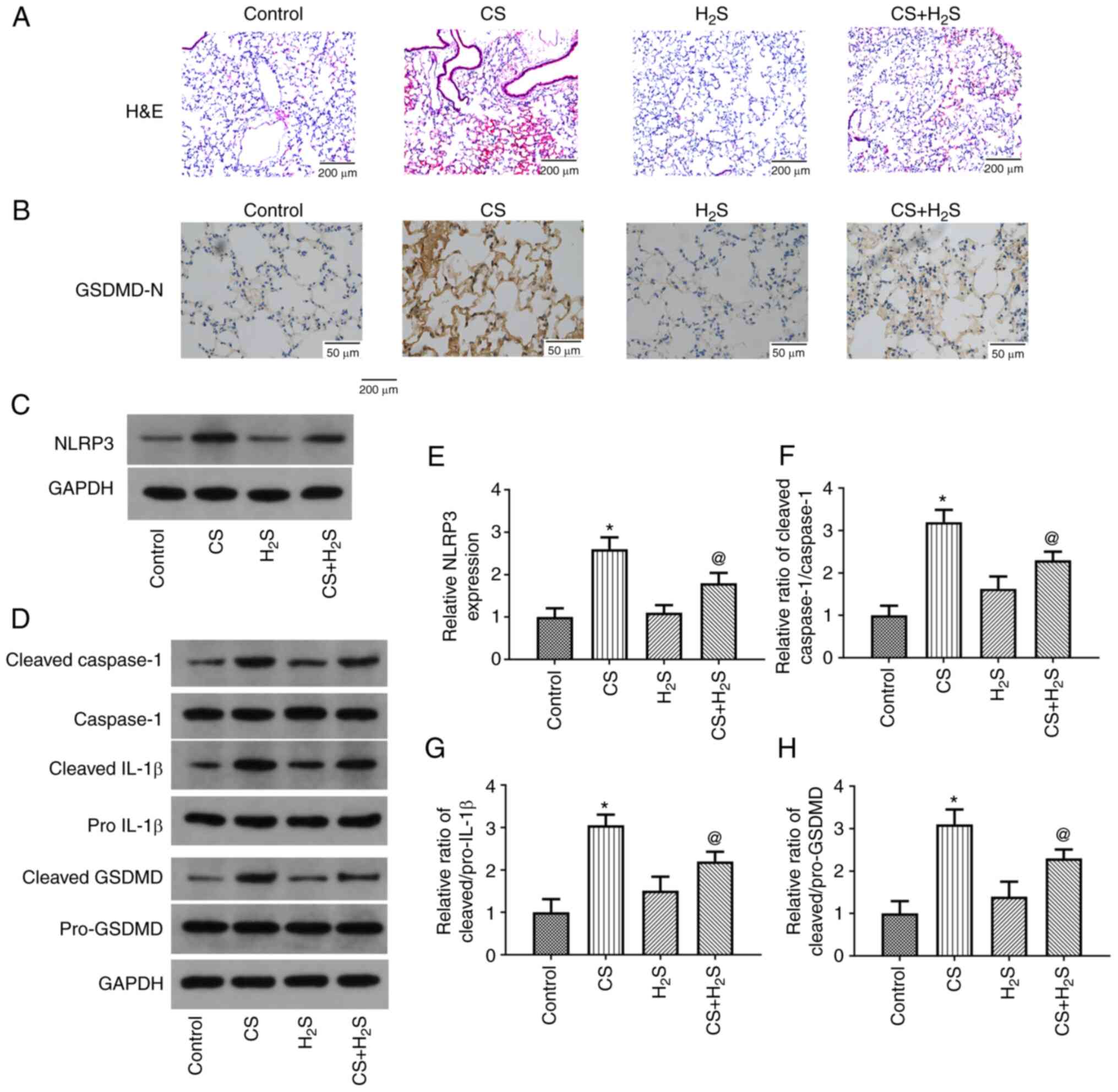
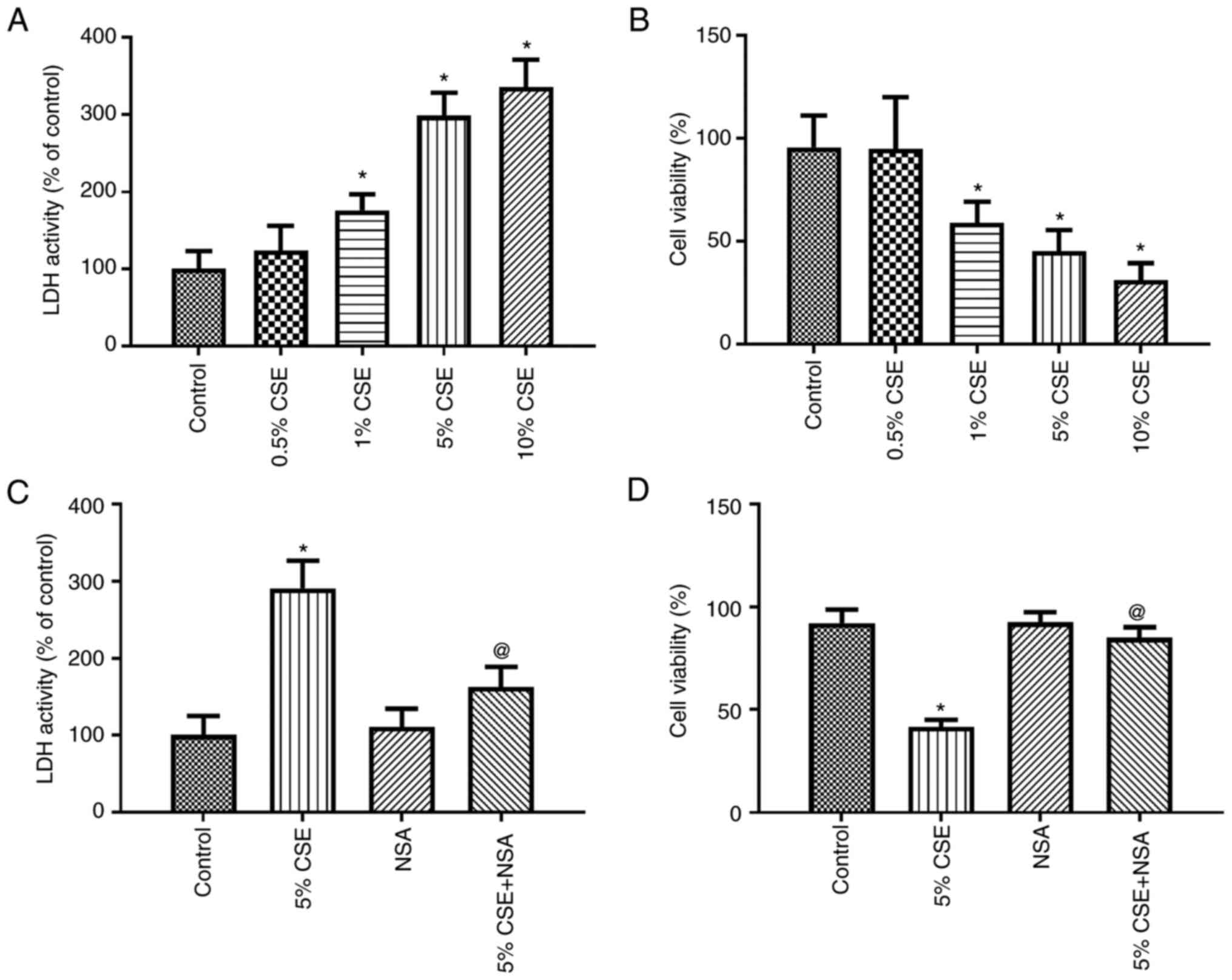
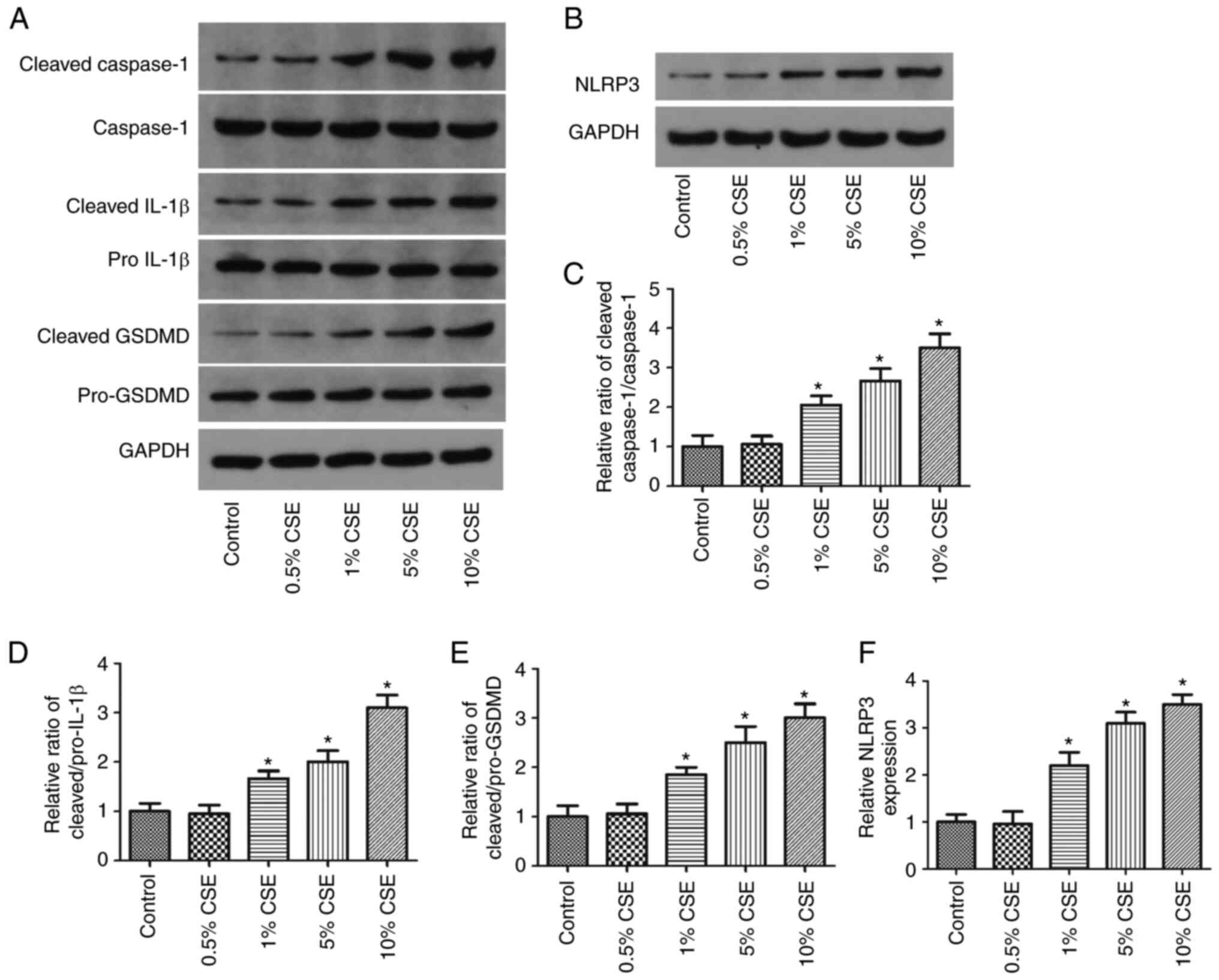
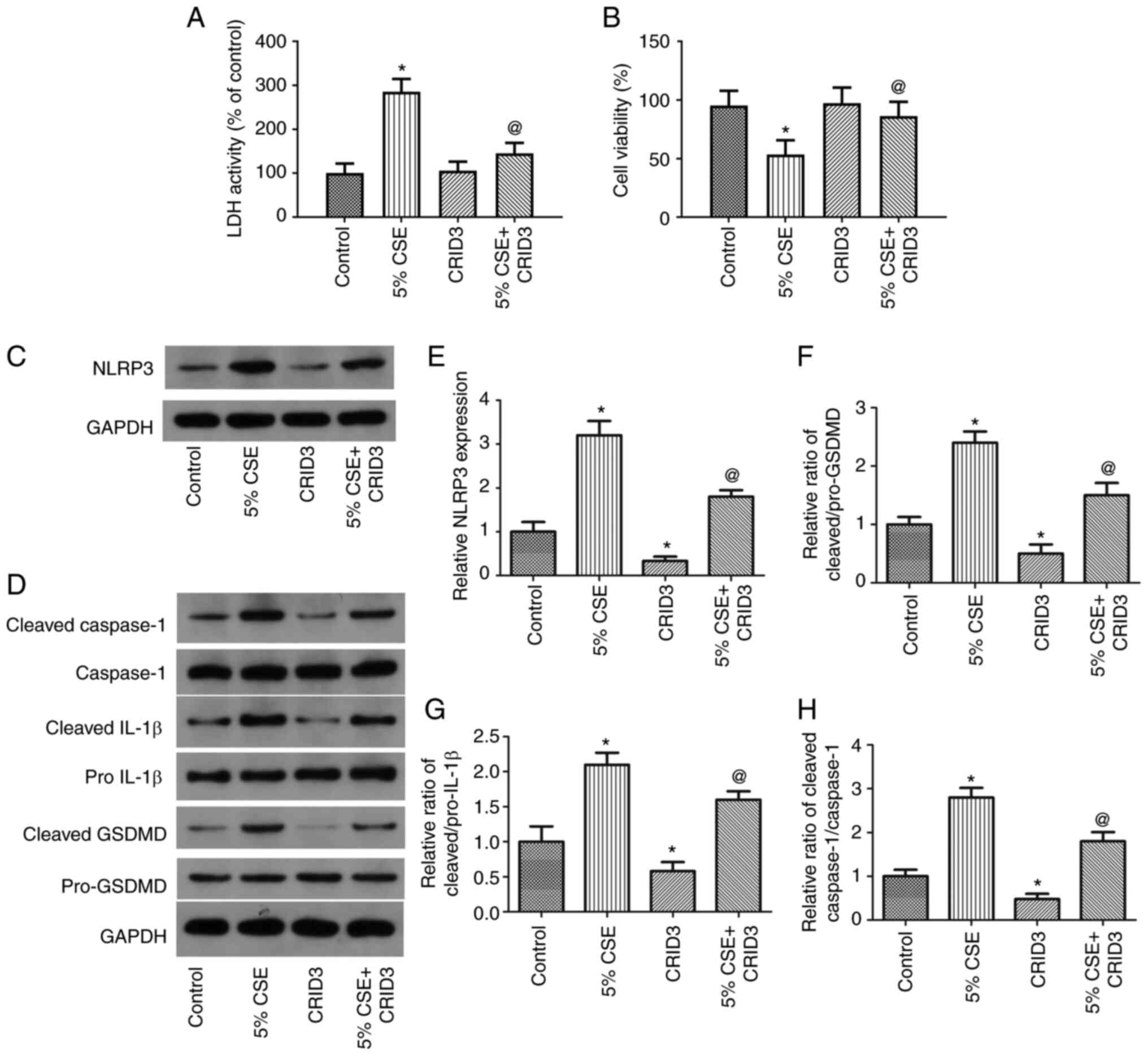
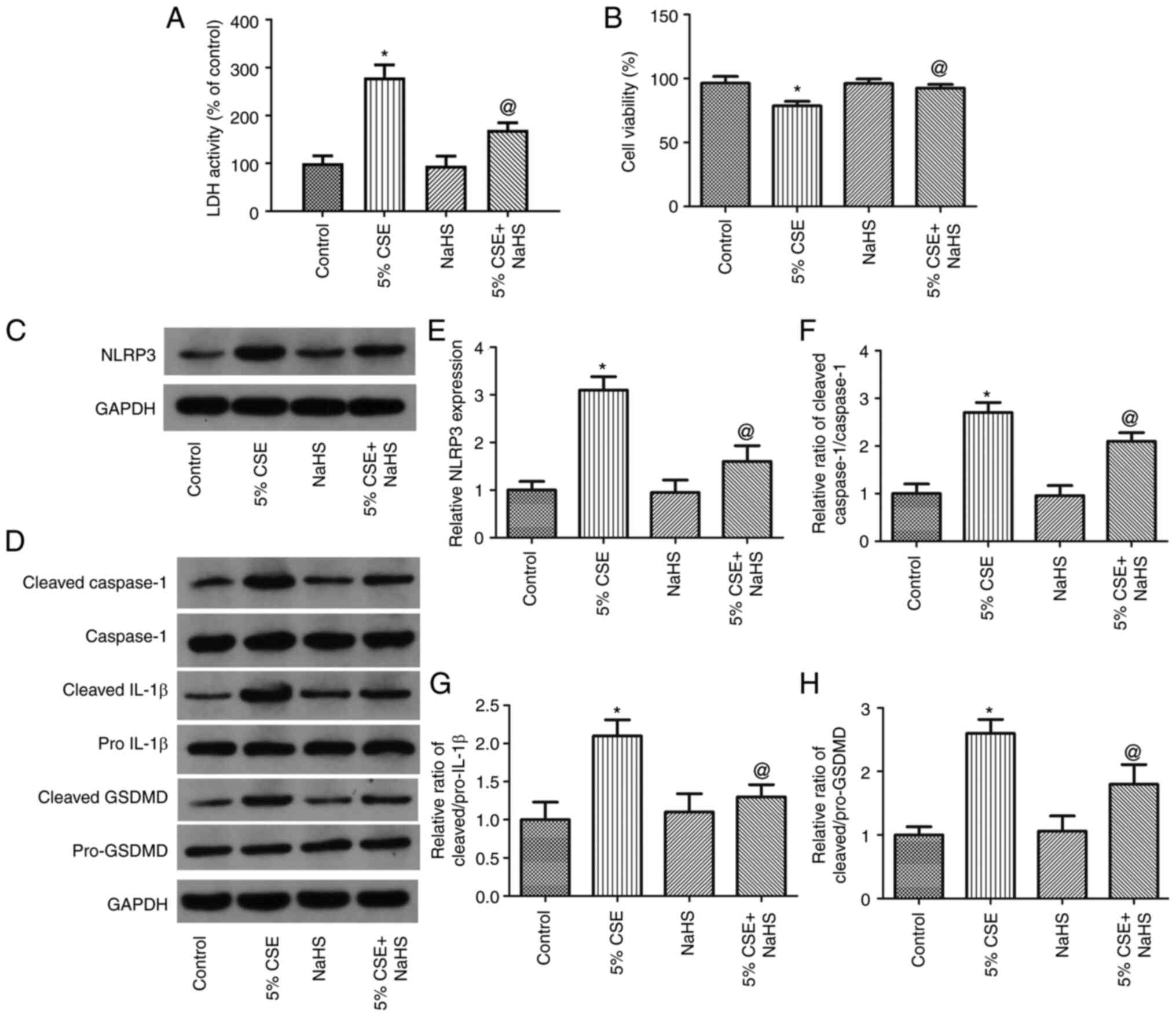
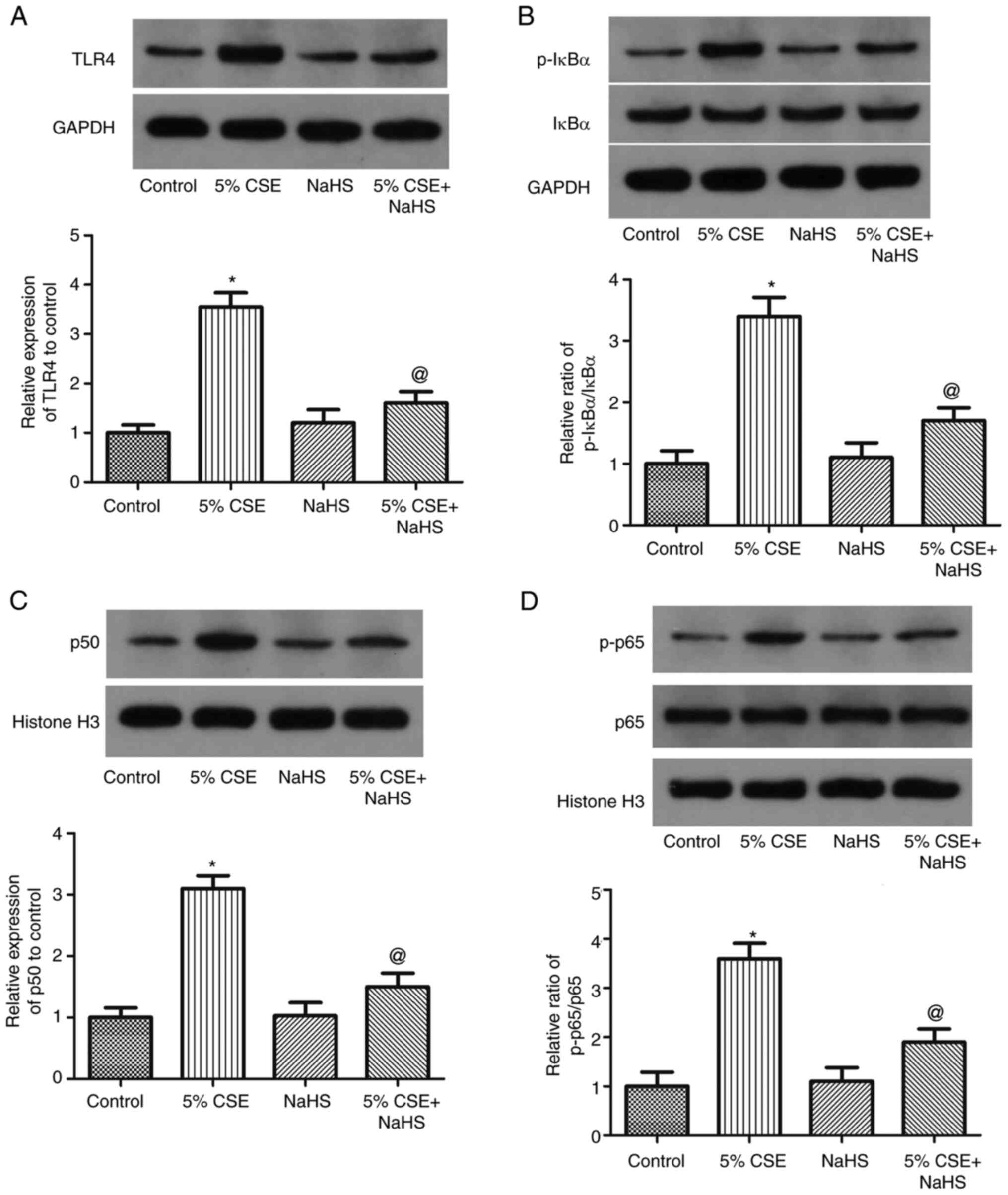
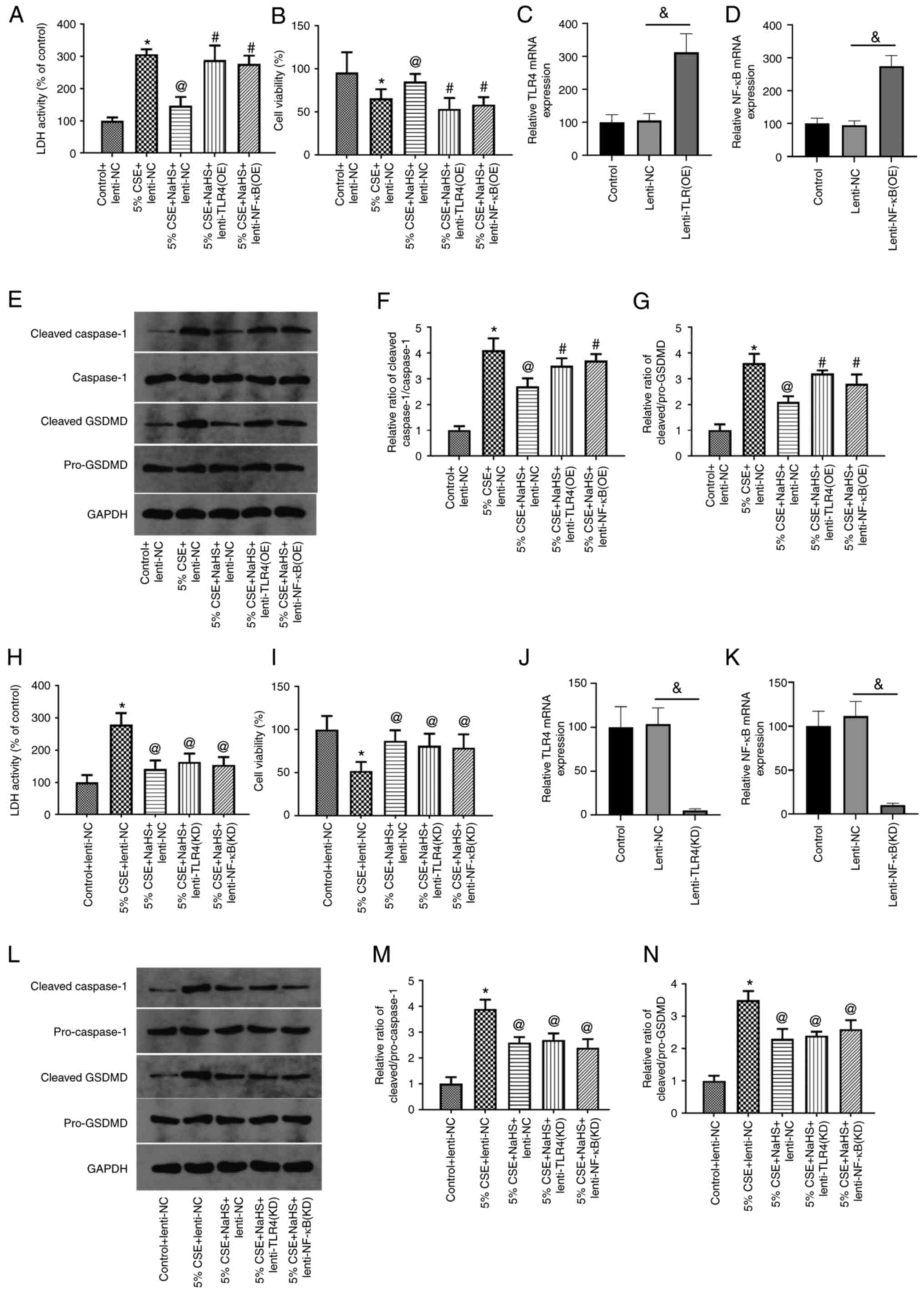
|
1
|
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, Chen W, Wang L, Liu
S, Li Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Yin P, et al: Cause-specific mortality for
240 causes in China during 1990–2013: A systematic subnational
analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet.
387:251–272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
López-Campos JL, Tan W and Soriano JB:
Global burden of COPD. Respirology. 21:14–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saetta M, Turato G, Maestrelli P, Mapp CE
and Fabbri LM: Cellular and structural bases of chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 163:1304–1309. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Churg A, Wang RD, Tai H, Wang X, Xie C,
Dai J, Shapiro SD and Wright JL: Macrophage metalloelastase
mediates acute cigarette smoke-induced inflammation via tumor
necrosis factor-alpha release. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
167:1083–1089. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, Xu Y, Zhang X, Bai
C, Kang J, Ran P, Shen H, Wen F, et al: Prevalence and risk factors
of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China
Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): A national cross-sectional study.
Lancet. 391:1706–1717. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
US Preventive Services Task Force
(USPSTF), . Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Davidson KW,
Epling JW Jr, García FA, Gillman M, Kemper AR, Krist AH, et al:
Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: US preventive
services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 315:1372–1377.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M: Pyroptosis.
Curr Biol. 26:R568–R572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong ZW and Yuan YF: Juglanin suppresses
fibrosis and inflammation response caused by LPS in acute lung
injury. Int J Mol Med. 41:3353–3365. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Song D, Bo F, Deng M and Tang X:
Diazepam inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pyroptotic cell
death and alleviated pulmonary fibrosis in mice by specifically
activating GABAA receptor α4-subunit. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1092392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pinkerton JW, Kim RY, Robertson AAB,
Hirota JA, Wood LG, Knight DA, Cooper MA, O'Neill LAJ, Horvat JC
and Hansbro PM: Inflammasomes in the lung. Mol Immunol. 86:44–55.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YC, Liu QX, Zheng Q, Liu T, Xu XE,
Liu XH, Gao W, Bai XJ and Li ZF: Dihydromyricetin alleviates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis in mice model. Inflammation.
42:1301–1310. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu WJ, Wang XX, Jin JJ, Zou Q, Wu L, Lv
TF, Wan B, Zhan P, Zhu SH, Liu HB, et al: Inhibition of GGPPS1
attenuated LPS-induced acute lung injury and was associated with
NLRP3 inflammasome suppression. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
316:L567–L577. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsai YM, Chiang KH, Hung JY, Chang WA, Lin
HP, Shieh JM, Chong IW and Hsu YL: Der f1 induces pyroptosis in
human bronchial epithelia via the NLRP3 inflammasome. Int J Mol
Med. 41:757–764. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang MY, Jiang YX, Yang YC, Liu JY, Huo
C, Ji XL and Qu YQ: Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in
human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1
pathway. Life Sci. 269:1190902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Z, Lian X, Su X, Wu W, Zeng Y and Chen
X: Exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate
cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and injury by inhibiting
alveolar macrophages pyroptosis. Respir Res. 23:52022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang R: Hydrogen sulfide: The third
gasotransmitter in biology and medicine. Antioxid Redox Signal.
12:1061–1064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oláh G, Módis K, Törö G, Hellmich MR,
Szczesny B and Szabo C: Role of endogenous and exogenous nitric
oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide in HCT116 colon cancer
cell proliferation. Biochem Pharmacol. 149:186–204. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu X, Li H, Gong Y, Zheng H and Zhao D:
Hydrogen sulfide ameliorated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting autophagy through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in
mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 507:514–518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu M, Li Z, Liang B, Li L, Liu S, Tan W,
Long J, Tang F, Chu C and Yang J: Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates rat
myocardial fibrosis induced by thyroxine through PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Endocr J. 65:769–781. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
George AK, Singh M, Homme RP, Majumder A,
Sandhu HS and Tyagi SC: A hypothesis for treating inflammation and
oxidative stress with hydrogen sulfide during age-related macular
degeneration. Int J Ophthalmol. 11:881–887. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Meng J, Wang C, Yang C, Wang Y and
Li Y and Li Y: Hydrogen sulfide alleviates cigarette smoke-induced
COPD through inhibition of the TGF-β1/smad pathway. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 245:190–200. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press; Washington, DC:
1996
|
|
24
|
Ke Q, Yang L, Cui Q, Diao W, Zhang Y, Xu M
and He B: Ciprofibrate attenuates airway remodeling in cigarette
smoke-exposed rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 271:1032902020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hosseini A, Rasaie D, Soleymani Asl S,
Nili Ahmadabadi A and Ranjbar A: Evaluation of the protective
effects of curcumin and nanocurcumin against lung injury induced by
sub-acute exposure to paraquat in rats. Toxin Rev. 40:1233–1241.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Song B, Ye L, Wu S and Jing Z: Long
non-coding RNA MEG3 regulates CSE-induced apoptosis and
inflammation via regulating miR-218 in 16HBE cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 521:368–374. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding Y, Liu P, Chen ZL, Zhang SJ, Wang YQ,
Cai X, Luo L, Zhou X and Zhao L: Emodin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury via inhibiting the
TLR4 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol.
9:9622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Xia G, Zhang Y, Liu J, Liu X, Li
W, Lv Y, Wei S, Liu J and Quan J: Palmitate induces VSMC apoptosis
via toll like receptor (TLR)4/ROS/p53 pathway. Atherosclerosis.
263:74–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang W, Ni H, Wang H and Gu H: NLRP3
inflammasome is essential for the development of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:13209–13216. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee S, Suh GY, Ryter SW and Choi AM:
Regulation and function of the nucleotide binding domain
leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor, pyrin domain-containing-3
inflammasome in lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
54:151–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eltom S, Belvisi MG, Stevenson CS, Maher
SA, Dubuis E, Fitzgerald KA and Birrell MA: Role of the
inflammasome-caspase1/11-IL-1/18 axis in cigarette smoke driven
airway inflammation: An insight into the pathogenesis of COPD. PLoS
One. 9:e1128292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barnes PJ: Inflammatory mechanisms in
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 138:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Heo MJ, Kim TH, You JS, Blaya D,
Sancho-Bru P and Kim SG: Alcohol dysregulates miR-148a in
hepatocytes through FoxO1, facilitating pyroptosis via TXNIP
overexpression. Gut. 68:708–720. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi
J, Sun H, Wang DC and Shao F: Pore-forming activity and structural
autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 535:111–116. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang H and Liu Y: Gasdermins pore cell
membrane to pyroptosis. Sci China Life Sci. 59:1090–1092. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yue LM, Gao YM and Han BH: Evaluation on
the effect of hydrogen sulfide on the NLRP3 signaling pathway and
its involvement in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Cell
Biochem. 120:481–492. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Y, Jin S, Teng X, Hu Z, Zhang Z, Qiu
X, Tian D and Wu Y: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates LPS-induced acute
kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018:67172122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tan Z, Shi Y, Yan Y, Liu W, Li G and Li R:
Impact of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on toll-like receptor pathway
in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail. 37:727–733.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han SJ, Kim JI, Park JW and Park KM:
Hydrogen sulfide accelerates the recovery of kidney tubules after
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
30:1497–1506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Xu W, Wang Y, Luo H, Quan S, Zhou
J, Yang N, Zhang T, Wu L, Liu J, et al: Hydrogen sulfide reduces
kidney injury due to urinary-derived sepsis by inhibiting NF-κB
expression, decreasing TNF-α levels and increasing IL-10 levels.
Exp Ther Med. 8:464–470. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fu Y, Liu B, Zhang N, Liu Z, Liang D, Li
F, Cao Y, Feng X, Zhang X and Yang Z: Magnolol inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by interfering
with TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. J
Ethnopharmacol. 145:193–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Varshney D, Singh S, Sinha E, Mohanty KK,
Kumar S, Kumar Barik S, Patil SA and Katara P: Systematic review
and meta-analysis of human Toll-like receptors genetic
polymorphisms for susceptibility to tuberculosis infection.
Cytokine. 152:1557912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou P, Weng R, Chen Z, Wang R, Zou J, Liu
X, Liao J, Wang Y, Xia Y and Wang Q: TLR4 signaling in MPP+-induced
activation of BV-2 cells. Neural Plast. 2016:50767402016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang H, Park PH, McMullen MR and Nagy LE:
Mechanisms for the anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin in
macrophages. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23 (Suppl 1):S50–S53. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Säfholm J, Lövdahl C, Swedin L, Boels PJ,
Dahlén SE, Arner A and Adner M: Inflammation-induced airway smooth
muscle responsiveness is strain dependent in mice. Pulm Pharmacol
Ther. 24:361–366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Soleimani A, Rahmani F, Ferns GA, Ryzhikov
M, Avan A and Hassanian SM: Role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in
the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Gene. 726:1441322020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu Z, Gan L, Xu Y, Luo D, Ren Q, Wu S and
Sun C: Melatonin alleviates inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through
inhibiting NF-κB/GSDMD signal in mice adipose tissue. J Pineal Res.
63:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chen X, Liu G, Yuan Y, Wu G, Wang S and
Yuan L: NEK7 interacts with NLRP3 to modulate the pyroptosis in
inflammatory bowel disease via NF-κB signaling. Cell Death Dis.
10:9062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shao XF, Li B, Shen J, Wang QF, Chen SS,
Jiang XC and Qiang D: Ghrelin alleviates traumatic brain
injury-induced acute lung injury through pyroptosis/NF-κB pathway.
Int Immunopharmacol. 79:1061752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tian L, Yan J, Li K, Zhang W, Lin B, Lai
W, Bian L, Liu H, Xi Z and Liu X: Ozone exposure promotes
pyroptosis in rat lungs via the TLR2/4-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling
pathway. Toxicology. 450:1526682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu Z, Wang C, Rathkey JK, Yang J, Dubyak
GR, Abbott DW and Xiao TS: Structures of the gasdermin D C-terminal
domains reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition. Structure.
26:778–784.e3. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ayala-Cuellar AP, Cho J and Choi KC:
Toll-like receptors: A pathway alluding to cancer control. J Cell
Physiol. 234:21707–21715. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lei J, Fu Y, Zhuang Y, Zhang K and Lu D:
miR-382-3p suppressed IL-1β induced inflammatory response of
chondrocytes via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway by directly
targeting CX43. J Cell Physiol. 234:23160–23168. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen Z, Liu Q, Zhu Z, Xiang F, Wu R and
Kang X: Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to uterine activation by
upregulating pro-inflammatory cytokine and CAP expression via the
NF-κB/P38MAPK signaling pathway during pregnancy. J Cell Physiol.
235:513–525. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|