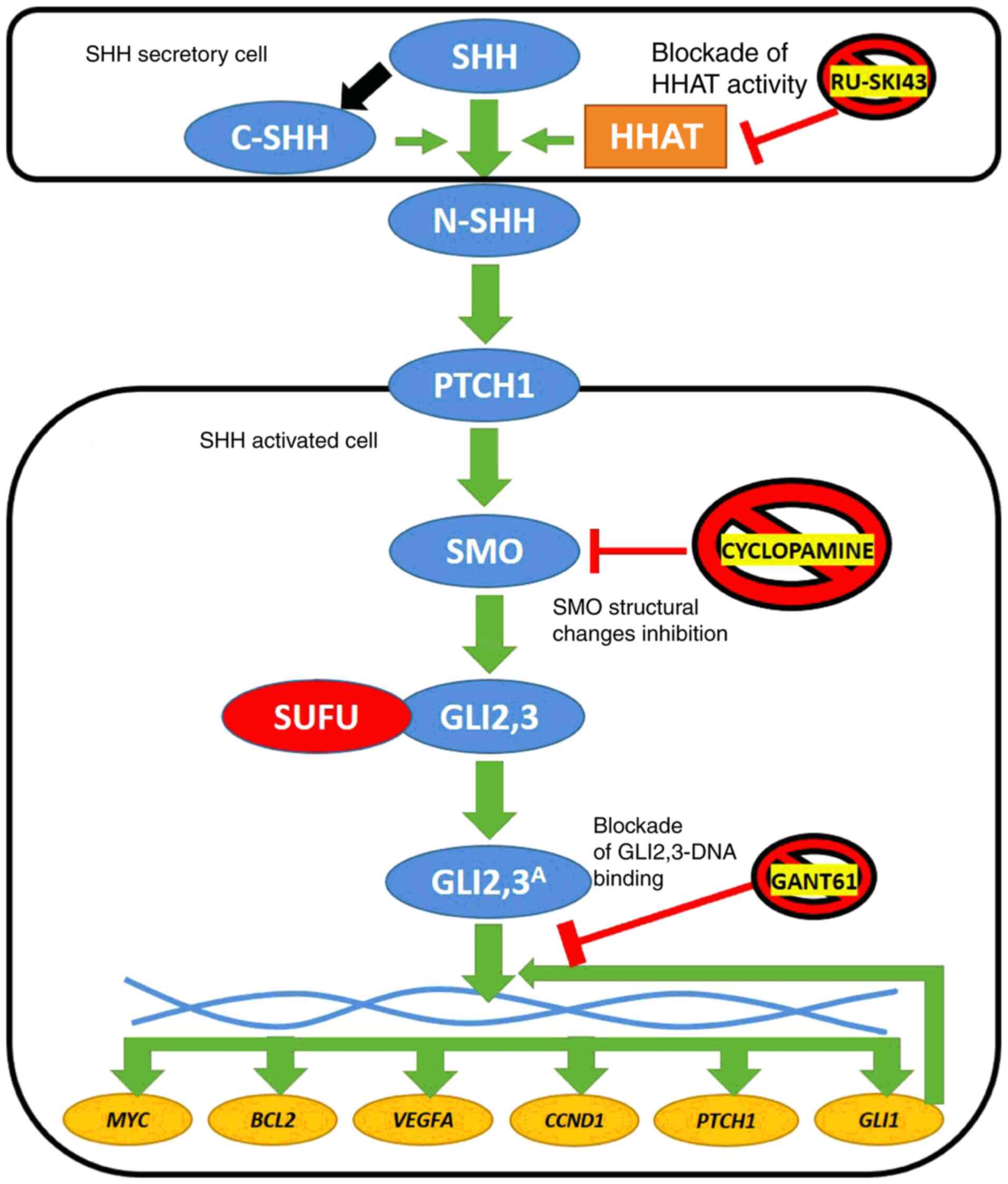
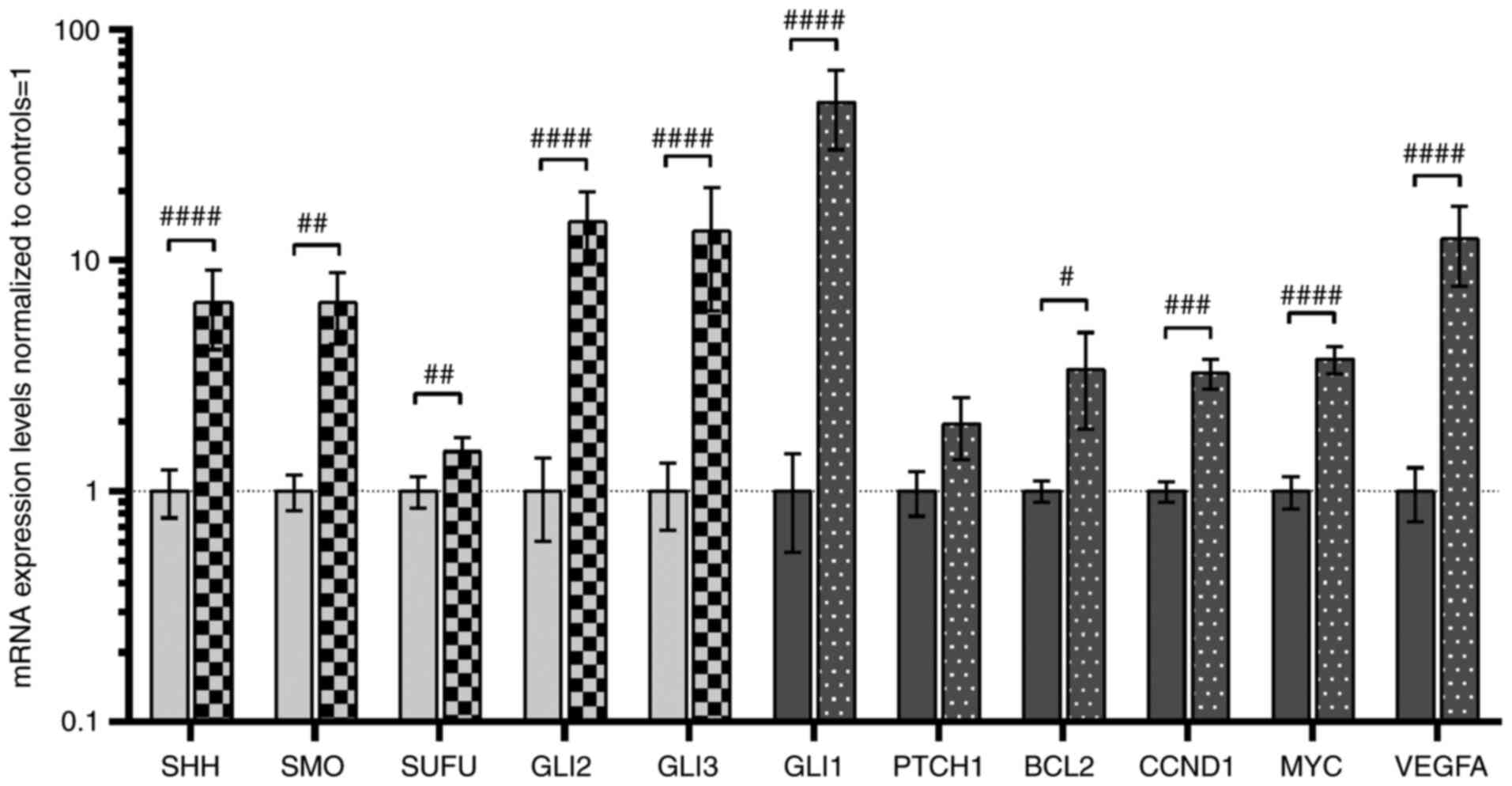
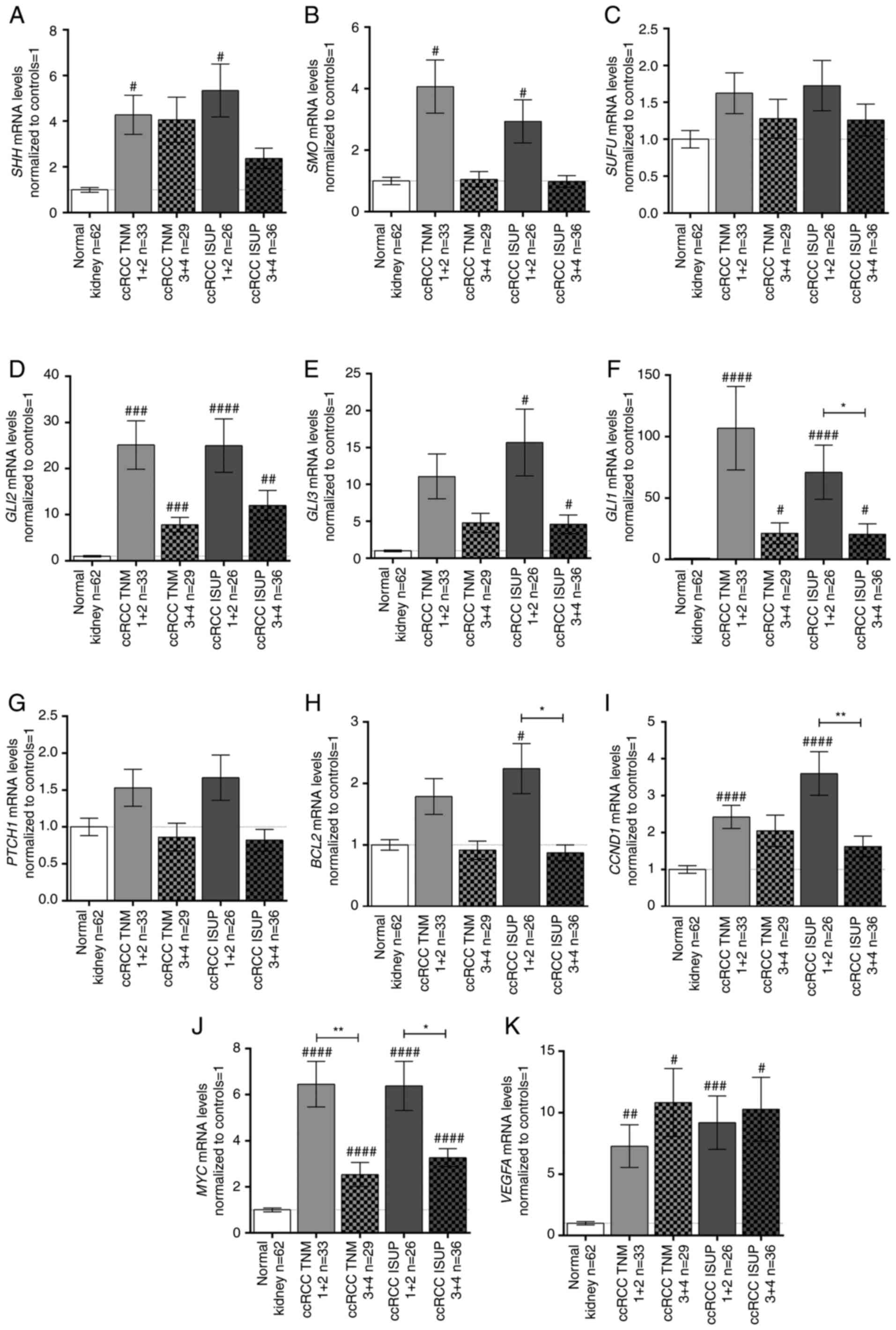
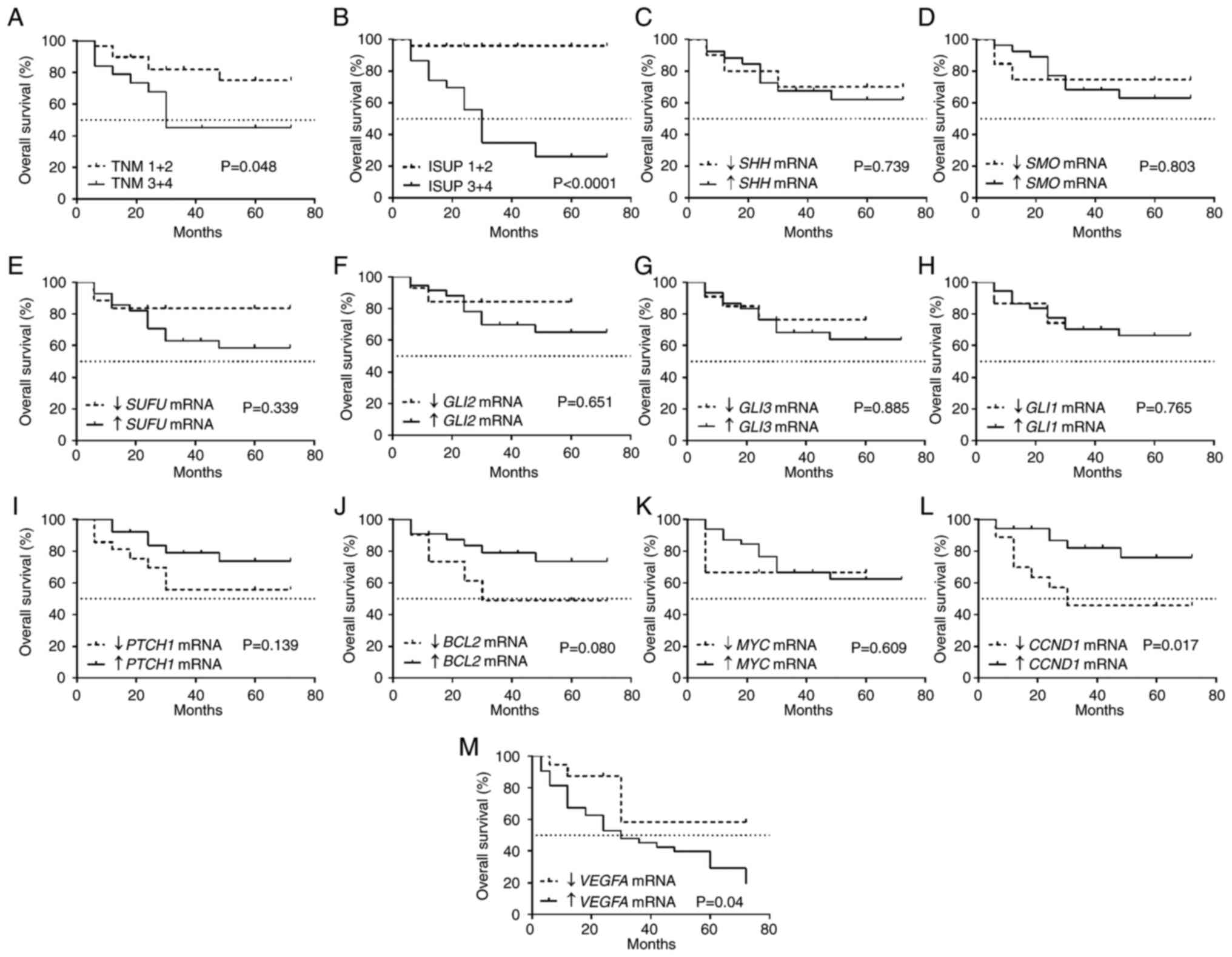
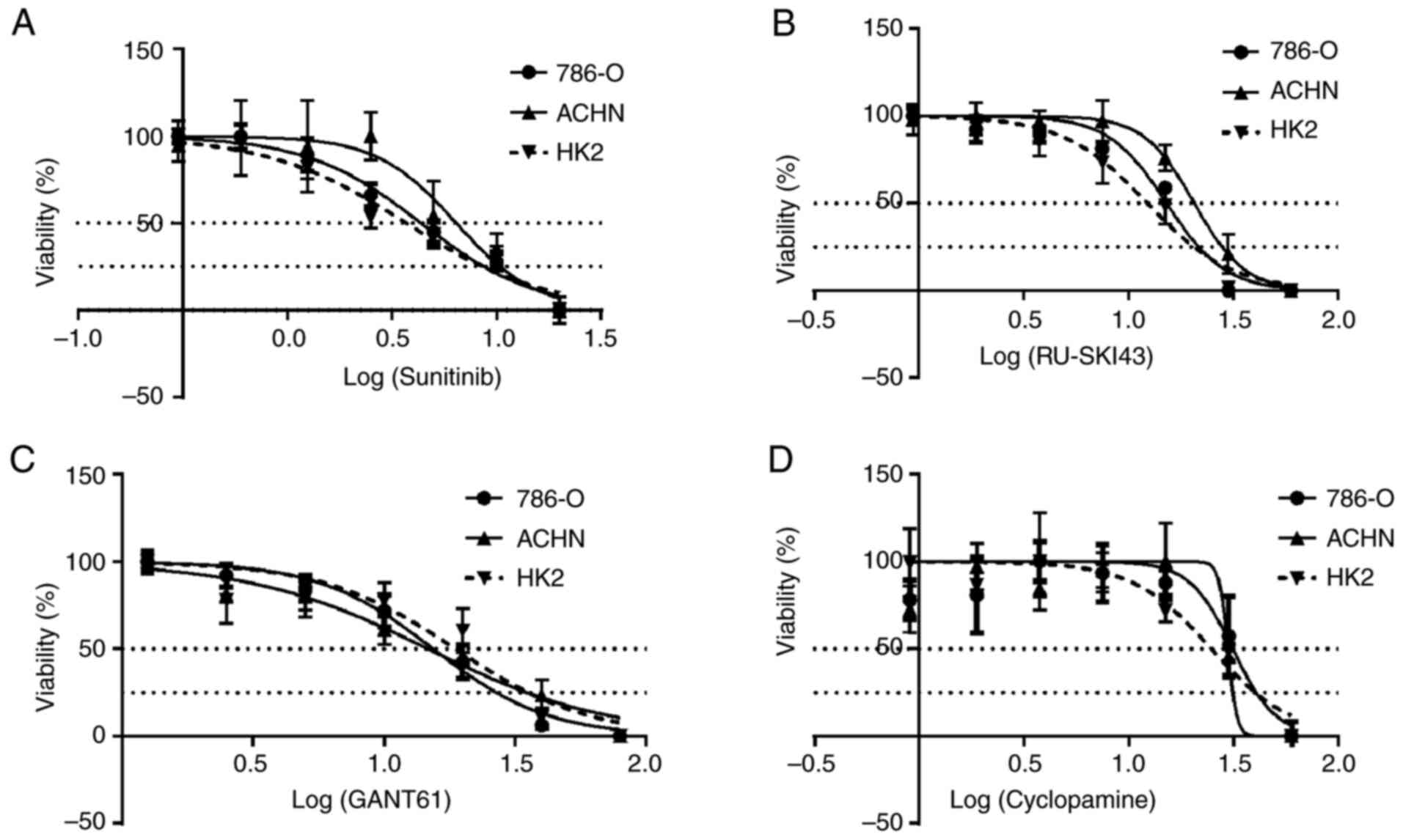
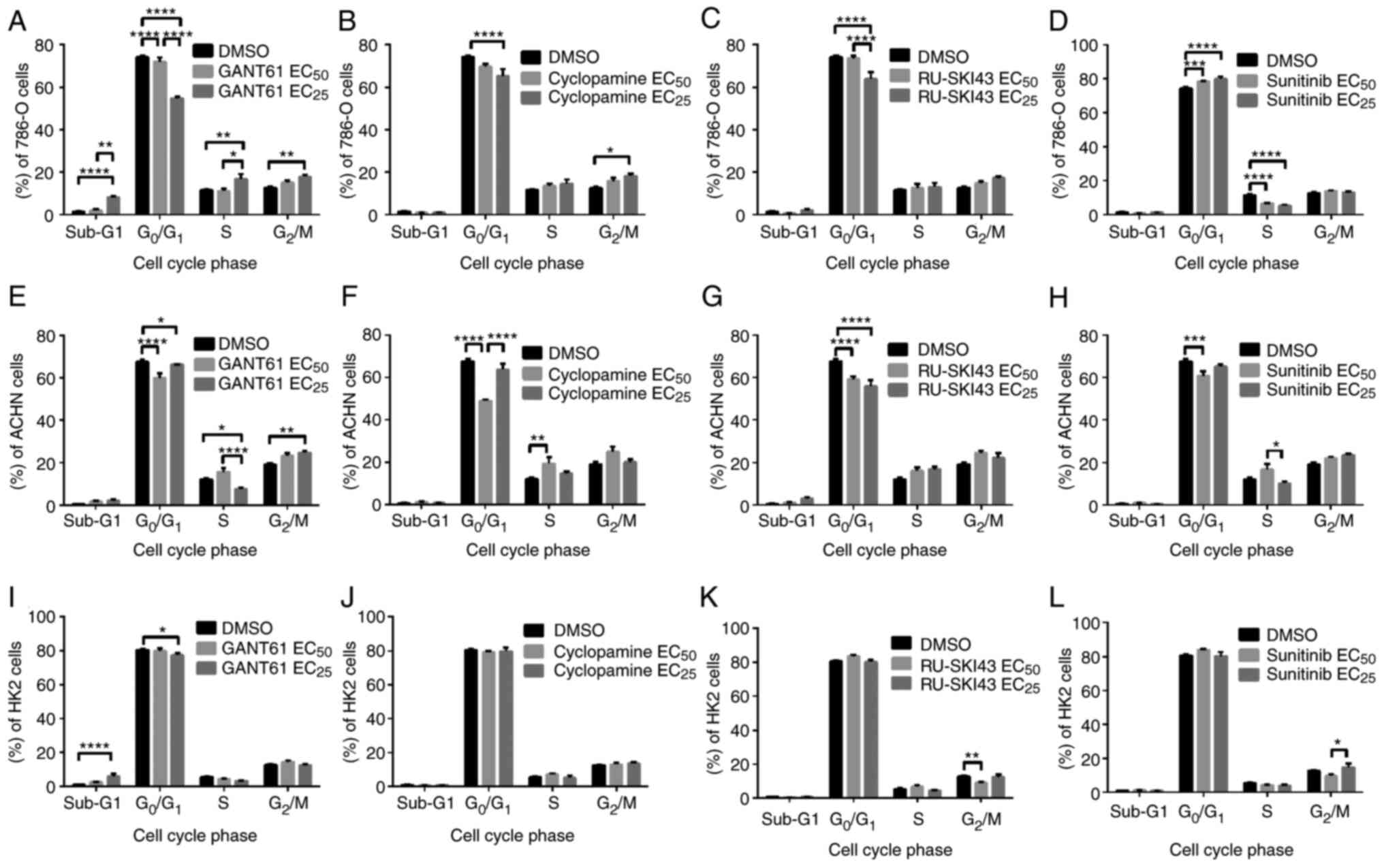
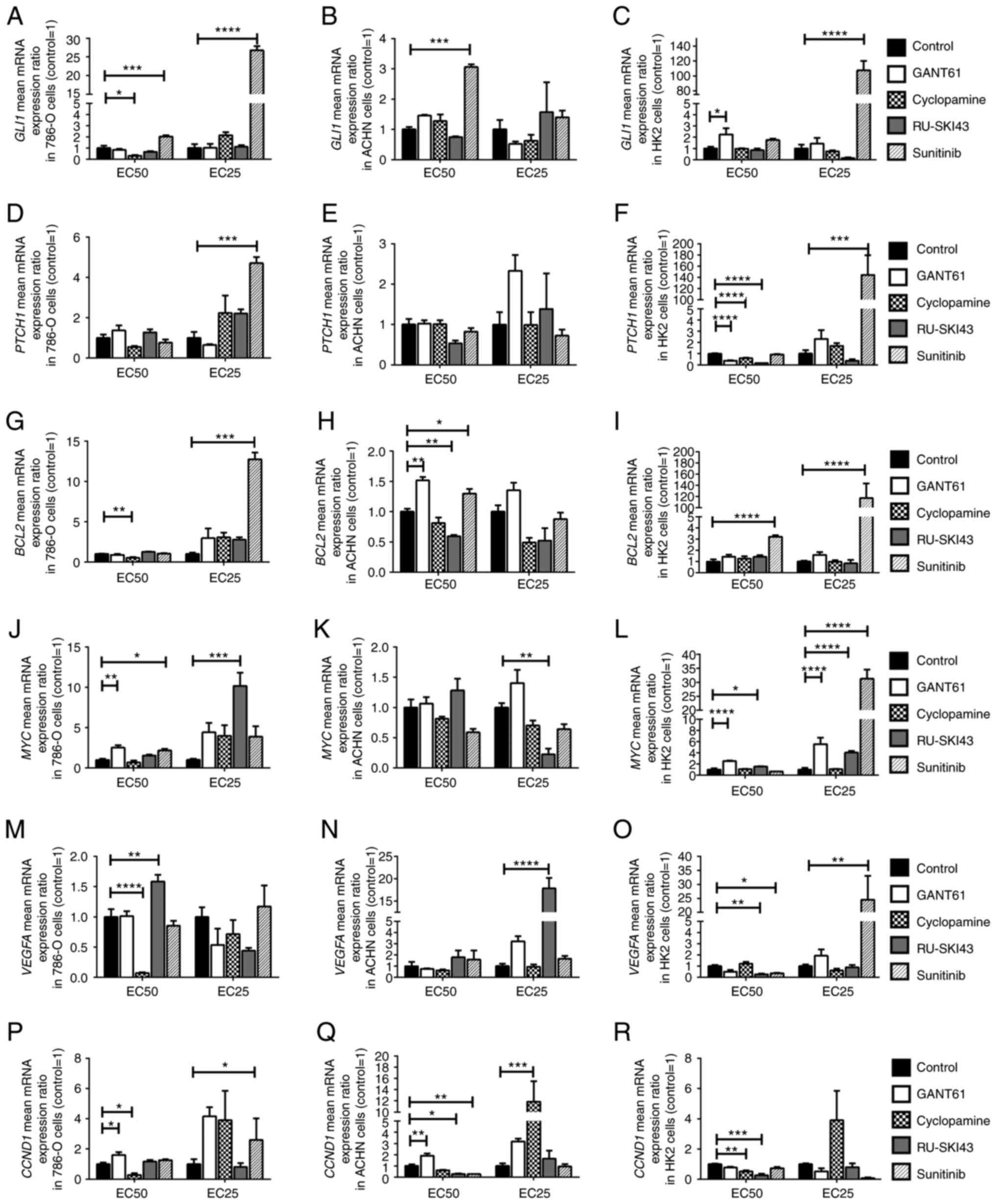
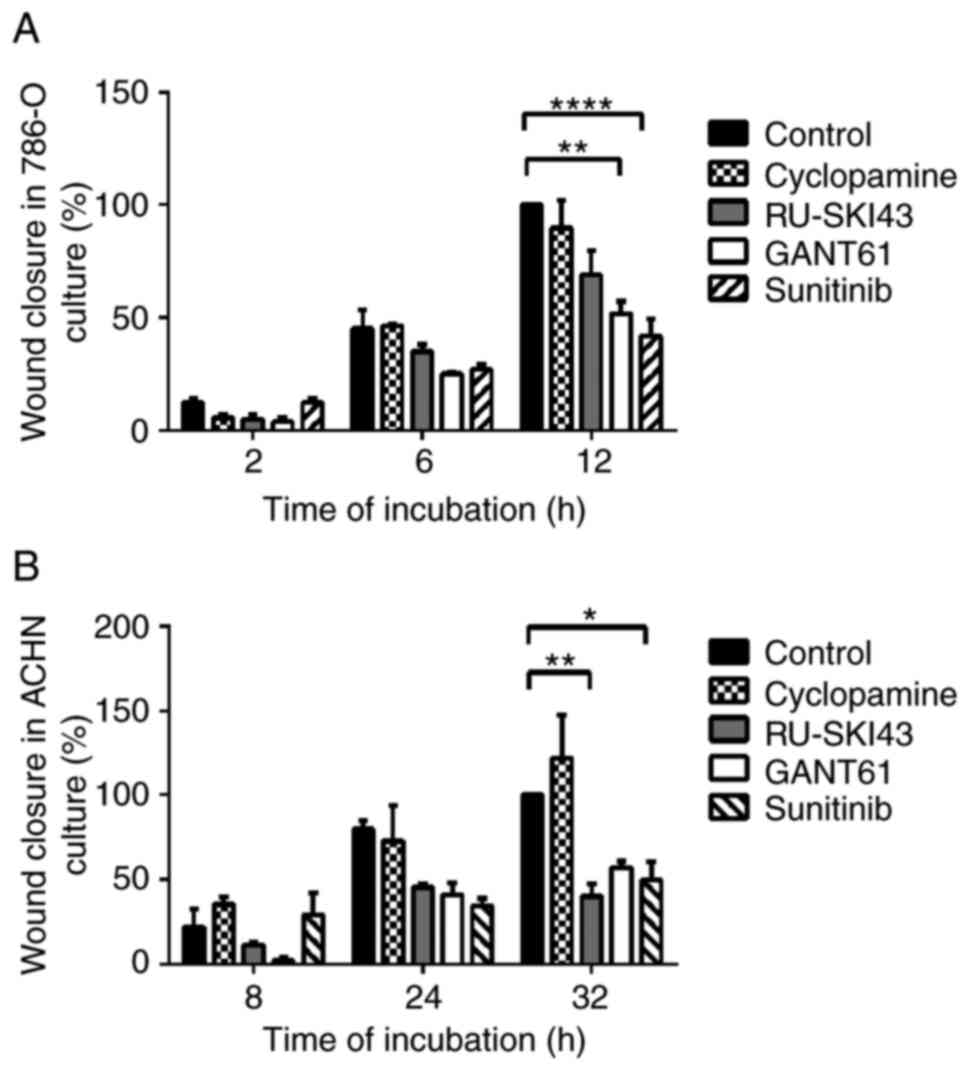
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality Worldwide for 36
Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Padala SA and Barsouk A, Thandra KC,
Saginala K, Mohammed A, Vakiti A, Rawla P and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. World J Oncol. 11:79–87.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton
C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J and Ficarra V: Renal
cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M,
Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V, Grünwald V and Gillessen S;
clinicalguidelines@esmo.org: Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical
Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann
Oncol. 30:706–720. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carballo GB, Honorato JR, de Lopes GPF and
Spohr TCLSE: A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Commun
Signal. 16:112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kotulak-Chrząszcz A, Kmieć Z and
Wierzbicki P: Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway in gynecological and
genitourinary cancer (Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:1062021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Liu H and Qing G: Targeting
oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Sig Transduct
Target Ther. 3:52018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Warren CFA, Wong-Brown MW and Bowden NA:
BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis.
10:1772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Claesson-Welsh L and Welsh M: VEGFA and
tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med. 273:114–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Qie S and Diehl JA: Cyclin D1, cancer
progression, and opportunities in cancer treatment. J Mol Med
(Berl). 94:1313–1326. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang J, Jiang D, Zhu T, Wang Y, Wang H,
Wang Q, Tan L, Zhu H and Yao J: Prognostic significance of c-MYC
amplification in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 107:436–443. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang S, Nong L, Wang W, Liang L, Zheng Y,
Liu J, Li D, Li X, Zhang B and Li T: Prognostic impact of diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma with extra copies of MYC, BCL2 and/or BCL6:
Comparison with double/triple hit lymphoma and double expressor
lymphoma. Diagn Pathol. 14:812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang SD, Mccrudden CM and Kwok HF:
Prognostic significance of combining VEGFA, FLT1 and KDR mRNA
expression in lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:1893–1901. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shan YS, Hsu HP, Lai MD, Hung YH, Wang CY,
Yen MC and Chen YL: Cyclin D1 overexpression correlates with poor
tumor differentiation and prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett.
14:4517–4526. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Behnsawy HM, Shigemura K, Meligy FY,
Yamamichi F, Yamashita M, Haung WC, Li X, Miyake H, Tanaka K,
Kawabata M, et al: Possible role of sonic hedgehog and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell cancer progression.
Korean J Urol. 54:5472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kotulak-Chrzaszcz A, Klacz J, Matuszewski
M, Kmiec Z and Wierzbicki P: Expression of the Sonic Hedgehog
pathway components in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
18:5801–5810. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou J, Zhu G, Huang J, Li L, Du Y, Gao Y,
Wu D, Wang X, Hsieh JT, He D and Wu K: Non-canonical GLI1/2
activation by PI3K/AKT signaling in renal cell carcinoma: A novel
potential therapeutic target. Cancer Lett. 370:313–323. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Furukawa J, Miyake H and Fujisawa M: GLI2
expression levels in radical nephrectomy specimens as a predictor
of disease progression in patients with metastatic clear cell renal
cell carcinoma following treatment with sunitinib. Mol Clin Oncol.
5:186–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Wu K, Gao D, Zhu G, Wu D, Wang X,
Chen Y, Du Y, Song W, Ma Z, et al: Reciprocal regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 2α and GLI1 expression associated with the
radioresistance of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 90:942–951. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xin M, Ji X, De La Cruz LK, Thareja S and
Wang B: Strategies to target the Hedgehog signaling pathway for
cancer therapy. Med Res Rev. 38:870–913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lanyon-Hogg T, Masumoto N, Bodakh G,
Konitsiotis AD, Thinon E, Rodgers UR, Owens RJ, Magee AI and Tate
EW: Synthesis and characterisation of
5-acyl-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine inhibitors of Hedgehog
acyltransferase. Data Brief. 7:257–281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gong X, Qian H, Cao P, Zhao X, Zhou Q, Lei
J and Yan N: Structural basis for the recognition of Sonic Hedgehog
by human Patched1. Science. 361:eaas89352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M
and Lo HW: Targeting the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway: Review
of smoothened and GLI inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 8:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T and
Toftgard R: Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell
growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:8455–8460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gonnissen A, Isebaert S and Haustermans K:
Targeting the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: Beyond
smoothened. Oncotarget. 6:13899–13913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI and
Sesterhenn IA: Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary
system and male genital organs. World Health Organization
Classification of Tumours. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004, https://www.patologi.com/WHO%20kidney%20testis.pdf.
|
|
27
|
The Cancer Genome and Atlas Research
Network: Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 499:43–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wierzbicki PM, Klacz J, Rybarczyk A,
Slebioda T, Stanislawowski M, Wronska A, Kowalczyk A, Matuszewski M
and Kmiec Z: Identification of a suitable qPCR reference gene in
metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol.
35:12473–12487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vichai V and Kirtikara K: Sulforhodamine B
colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc.
1:1112–1116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kang CW, Han YE, Kim J, Oh JH, Cho YH and
Lee EJ: 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde accelerates acute wound healing
through activation of focal adhesion signalling in keratinocytes.
Sci Rep. 7:141922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan YJ, Wei LL, Wu XJ, Huo FC, Mou J and
Pei DS: MiR-106a-5p inhibits the cell migration and invasion of
renal cell carcinoma through targeting PAK5. Cell Death Dis.
8:e31552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pinto BI, Cruz ND, Lujan OR, Propper CR
and Kellar RS: In vitro scratch assay to demonstrate effects of
arsenic on skin cell migration. J Vis Exp. 3791:588382019.
|
|
34
|
Zhao JJ, Chen PJ, Duan RQ, Li KJ, Wang YZ
and Li Y: MiR-630 functions as a tumor oncogene in renal cell
carcinoma. Arch Med Sci. 12:473–478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rybarczyk A, Klacz J, Wronska A,
Matuszewski M, Kmiec Z and Wierzbicki PM: Overexpression of the
YAP1 oncogene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with
poor outcome. Oncol Rep. 38:427–439. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wierzbicki PM, Klacz J, Kotulak-Chrzaszcz
A, Wronska A, Stanislawowski M, Rybarczyk A, Ludziejewska A, Kmiec
Z and Matuszewski M: Prognostic significance of VHL, HIF1A, HIF2A,
VEGFA and p53 expression in patients with clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma treated with sunitinib as first-line treatment. Int J
Oncol. 55:371–390. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE
and Ulbright TM: The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the
urinary system and male genital organs-part A: Renal, penile, and
testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 70:93–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng L, Rui C, Zhang H, Chen J, Jia X and
Xiao Y: Sonic hedgehog signaling in epithelial tissue development.
Regen Med Res. 7:32019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fernandes-Silva H, Correia-Pinto J and
Moura R: Canonical Sonic Hedgehog signaling in early lung
development. J Dev Biol. 5:32017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Memi F, Zecevic N and Radonjić N: Multiple
roles of Sonic Hedgehog in the developing human cortex are
suggested by its widespread distribution. Brain Struct Funct.
223:2361–2375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Park SM, Jang HJ and Lee JH: Roles of
primary cilia in the developing brain. Front Cell Neurosci.
13:2182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Martinez-Chavez E, Scheerer C, Wizenmann A
and Blaess S: The zinc finger transcription factor GLI3 is a
regulator of precerebellar neuronal migration. Development.
145:dev1660332018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lopez-Rios J: The many lives of SHH in
limb development and evolution. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 49:116–124.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tickle C and Towers M: Sonic Hedgehog
signaling in limb development. Front Cell Dev Biol. 5:142017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rivell A, Petralia RS, Wang YX, Clawson E,
Moehl K, Mattson MP and Yao PJ: Sonic hedgehog expression in the
postnatal brain. Biol Open. 8:bio.0405922019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang C, Cassandras M and Peng T: The role
of Hedgehog signaling in adult lung regeneration and maintenance. J
Dev Biol. 7:142019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Fattahi S, Pilehchian Langroudi M and
Akhavan-Niaki H: Hedgehog signaling pathway: Epigenetic regulation
and role in disease and cancer development. J Cell Physiol.
233:5726–5735. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Le H, Kleinerman R, Lerman OZ, Brown D,
Galiano R, Gurtner GC, Warren SM, Levine JP and Saadeh PB: Hedgehog
signaling is essential for normal wound healing: Hedgehog signaling
is essential for normal wound healing. Wound Repair Regen.
16:768–773. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Takebe H, Shalehin N, Hosoya A, Shimo T
and Irie K: Sonic Hedgehog regulates bone fracture healing. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:6772020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Saze Z, Terashima M, Kogure M, Ohsuka F,
Suzuki H and Gotoh M: Activation of the Sonic Hedgehog pathway and
its prognostic impact in patients with gastric cancer. Dig Surg.
29:115–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choe JY, Yun JY, Jeon YK, Kim SH, Choung
HK, Oh S, Park M and Kim JE: Sonic hedgehog signalling proteins are
frequently expressed in retinoblastoma and are associated with
aggressive clinicopathological features. J Clin Pathol. 68:6–11.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhan H, Yuan Z, Lu P, Zhan
L and Xu W: The Hedgehog signalling pathway and its prognostic
impact in human gliomas: Role of Hedgehog pathway in gliomas. ANZ J
Surg. 81:440–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Dierks C, Beigi R, Guo GR, Zirlik K,
Stegert MR, Manley P, Trussell C, Schmitt-Graeff A, Landwerlin K,
Veelken H and Warmuth M: Expansion of Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic
stem cells is dependent on Hedgehog pathway activation. Cancer
Cell. 14:238–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Al Ghamdi D, Gomaa W, Abulaban A, Al-Ahwal
M, Buhmeida A, Al-Qahtani M and Al-Maghrabi J: The significance of
sonic hedgehog immunohistochemical expression in colorectal
carcinoma. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 3:169–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kurebayashi J, Kanomata N, Koike Y, Ohta
Y, Saitoh W and Kishino E: Comprehensive immunohistochemical
analyses on expression levels of Hedgehog signaling molecules in
breast cancers. Breast Cancer. 25:759–767. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pestell RG: New roles of Cyclin D1. Am J
Pathol. 183:3–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Skoda AM, Simovic D, Karin V, Kardum V,
Vranic S and Serman L: The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway
in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 18:8–20.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Delahunt B, Cheville JC, Martignoni G,
Humphrey PA, Magi-Galluzzi C, McKenney J, Egevad L, Algaba F, Moch
H, Grignon DJ, et al: The International society of urological
pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other
prognostic parameters. Am J Surg Pathol. 37:1490–1504. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jäger W, Thomas C, Fazli L, Hurtado-Coll
A, Li E, Janssen C, Gust KM, So AI, Hainz M, Schmidtmann I, et al:
DHH is an independent prognosticator of oncologic outcome of clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 192:1842–1848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Niewiadomski P, Niedziółka SM, Markiewicz
Ł, Uśpieński T, Baran B and Chojnowska K: Gli Proteins: Regulation
in development and cancer. Cells. 8:1472019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Radha G and Raghavan SC: BCL2: A promising
cancer therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:309–314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Itoi T, Yamana K, Bilim V, Takahashi K and
Tomita F: Impact of frequent Bcl-2 expression on better prognosis
in renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 90:200–205. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yang JF, Shi SN, Xu WH, Qiu YH, Zheng JZ,
Yu K, Song XY, Li F, Wang Y, Wang R, et al: Screening,
identification and validation of CCND1 and PECAM1/CD31 for
predicting prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients. Aging
(Albany NY). 11:12057–12079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wang QS, Li F, Liao ZQ, Li K, Yang XL, Lin
YY, Zhao YL, Weng SY, Xia Y, Ye Y, et al: Low level of Cyclin-D1
correlates with worse prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
patients. Cancer Med. 8:4100–4109. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang XN, Su XX, Cheng SQ, Sun ZY, Huang ZS
and Ou TM: MYC modulators in cancer: A patent review. Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 29:353–367. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tang SW, Chang WH, Su YC, Chen YC, Lai YH,
Wu PT, Hsu CI, Lin WC, Lai MK and Lin JY: MYC pathway is activated
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and essential for proliferation
of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 273:35–43.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Tchakarska G and Sola B: The double
dealing of cyclin D1. Cell Cycle. 19:163–178. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Moradi Binabaj M, Bahrami A, Khazaei M,
Ryzhikov M, Ferns GA, Avan A and Mahdi Hassanian S: The prognostic
value of cyclin D1 expression in the survival of cancer patients: A
meta-analysis. Gene. 728:1442832020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kumari S, Puneet, Prasad SB, Yadav SS,
Kumar M, Khanna A, Dixit VK, Nath G, Singh S and Narayan G: Cyclin
D1 and cyclin E2 are differentially expressed in gastric cancer.
Med Oncol. 33:402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lehn S, Tobin NP, Berglund P, Nilsson K,
Sims AH, Jirström K, Härkönen P, Lamb R and Landberg G:
Down-regulation of the oncogene cyclin D1 increases migratory
capacity in breast cancer and is linked to unfavorable prognostic
features. Am J Pathol. 177:2886–2897. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mylona E, Tzelepis K, Theohari I,
Giannopoulou I, Papadimitriou C and Nakopoulou L: Cyclin D1 in
invasive breast carcinoma: Favourable prognostic significance in
unselected patients and within subgroups with an aggressive
phenotype. Histopathology. 62:472–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Ortiz AB, Garcia D, Vicente Y, Palka M,
Bellas C and Martin P: Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 protein
expression and gene amplification in invasive breast carcinoma.
PLoS One. 12:e01880682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ebru T, Fulya OP, Hakan A, Vuslat YC,
Necdet S, Nuray C and Filiz O: Analysis of various potential
prognostic markers and survival data in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Int Braz J Urol. 43:440–454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Wang X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tu M, Wang Y and
Shi G: Upregulated VEGFA and DLL4 act as potential prognostic genes
for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther.
11:1697–1706. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Zhang J and Zhang Q: VHL and hypoxia
signaling: Beyond HIF in cancer. Biomedicines. 6:352018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Aziz SA, Sznol J, Adeniran A, Colberg JW,
Camp RL and Kluger HM: Vascularity of primary and metastatic renal
cell carcinoma specimens. J Transl Med. 11:152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Turner KJ, Moore JW, Jones A, Taylor CF,
Cuthbert-Heavens D, Han C, Leek RD, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH,
Ratcliffe PJ, et al: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors in
human renal cancer: Relationship to angiogenesis and to the von
Hippel-Lindau gene mutation. Cancer Res. 62:2957–2961.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Brodaczewska KK, Szczylik C, Fiedorowicz
M, Porta C and Czarnecka AM: Choosing the right cell line for renal
cell cancer research. Mol Cancer. 15:832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Petrova E, Matevossian A and Resh MD:
Hedgehog acyltransferase as a target in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 34:263–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Matevossian A and Resh MD: Hedgehog
Acyltransferase as a target in estrogen receptor positive, HER2
amplified, and tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
14:722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu HY and Dong Z: Gli3 silencing enhances
cyclopamine suppressive effects on ovarian cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 7:2007–2011. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mukherjee S, Frolova N, Sadlonova A, Novak
Z, Steg A, Page GP, Welch DR, Lobo-Ruppert SM, Ruppert JM, Johnson
MR and Frost AR: Hedgehog signaling and response to cyclopamine
differ in epithelial and stromal cells in benign breast and breast
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:674–683. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Steg A, Amm HM, Novak Z, Frost AR and
Johnson MR: Gli3 mediates cell survival and sensitivity to
cyclopamine in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:893–902.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Peer E, Tesanovic S and Aberger F:
Next-generation Hedgehog/GLI pathway inhibitors for cancer therapy.
Cancers (Basel). 11:5382019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Dormoy V, Danilin S, Lindner V, Thomas L,
Rothhut S, Coquard C, Helwig JJ, Jacqmin D, Lang H and Massfelder
T: The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is reactivated in human
renal cell carcinoma and plays orchestral role in tumor growth. Mol
Cancer. 8:1232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
D'Amato C, Rosa R, Marciano R, D'Amato V,
Formisano L, Nappi L, Raimondo L, Di Mauro C, Servetto A, Fulciniti
F, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signalling by NVP-LDE225
(Erismodegib) interferes with growth and invasion of human renal
cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 111:1168–1179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Carpenter RL and Ray H: Safety and
tolerability of Sonic Hedgehog pathway inhibitors in Cancer. Drug
Saf. 42:263–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Chang Y, Chen H, Duan J, Wu W, Le F and
Mou F: The inhibitory effect and safety of GANT61 on HeLa cells in
nude mice. Exp Mol Pathol. 113:1043522020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Carballo GB, Ribeiro JH, Lopes GPF, Ferrer
VP, Dezonne RS, Pereira CM and Spohr TCLS: GANT-61 induces
autophagy and apoptosis in glioblastoma cells despite their
heterogeneity. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 41:1227–1244. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Brown LC, Desai K, Zhang T and Ornstein
MC: The immunotherapy landscape in renal cell carcinoma. BioDrugs.
34:733–748. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|