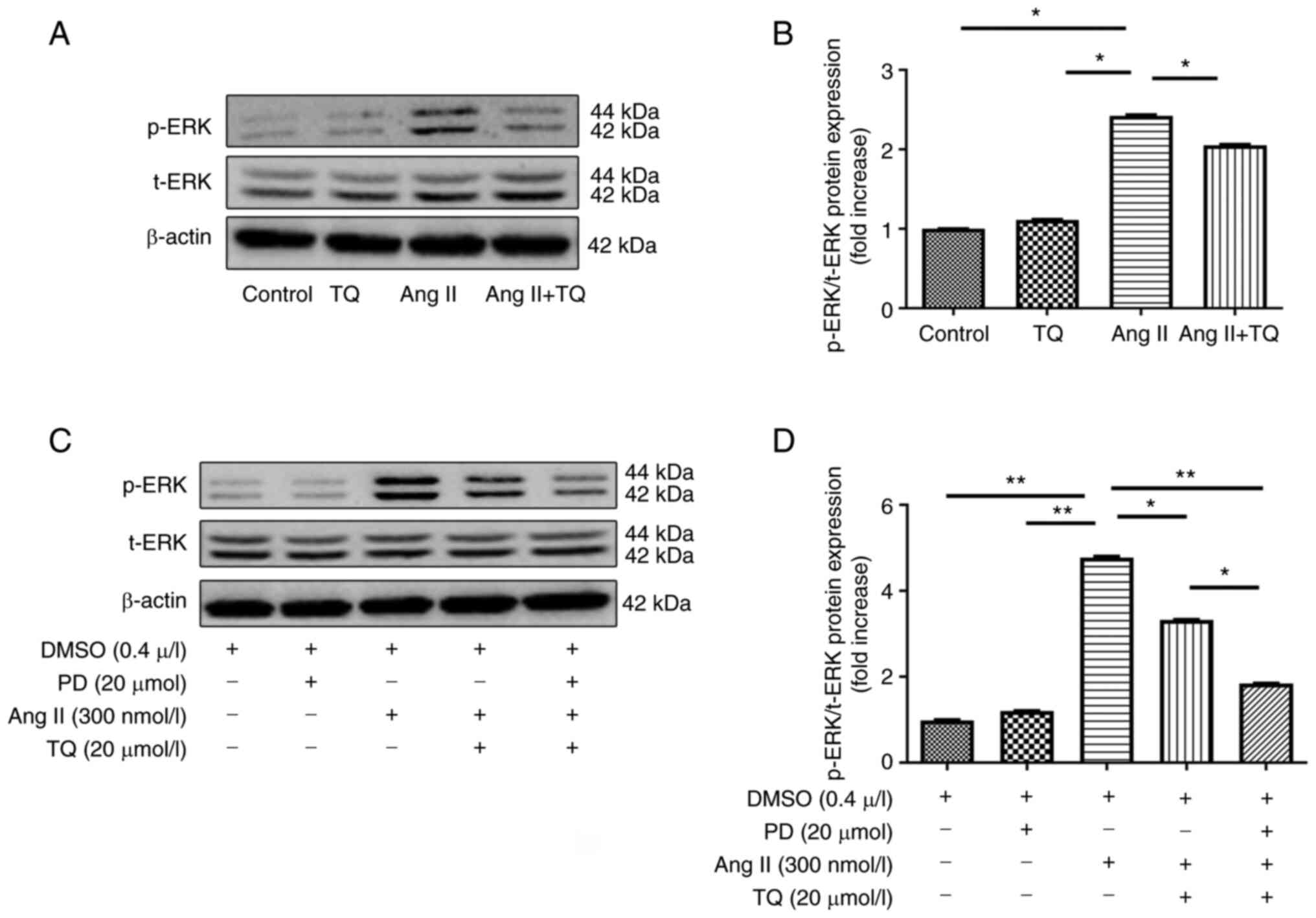
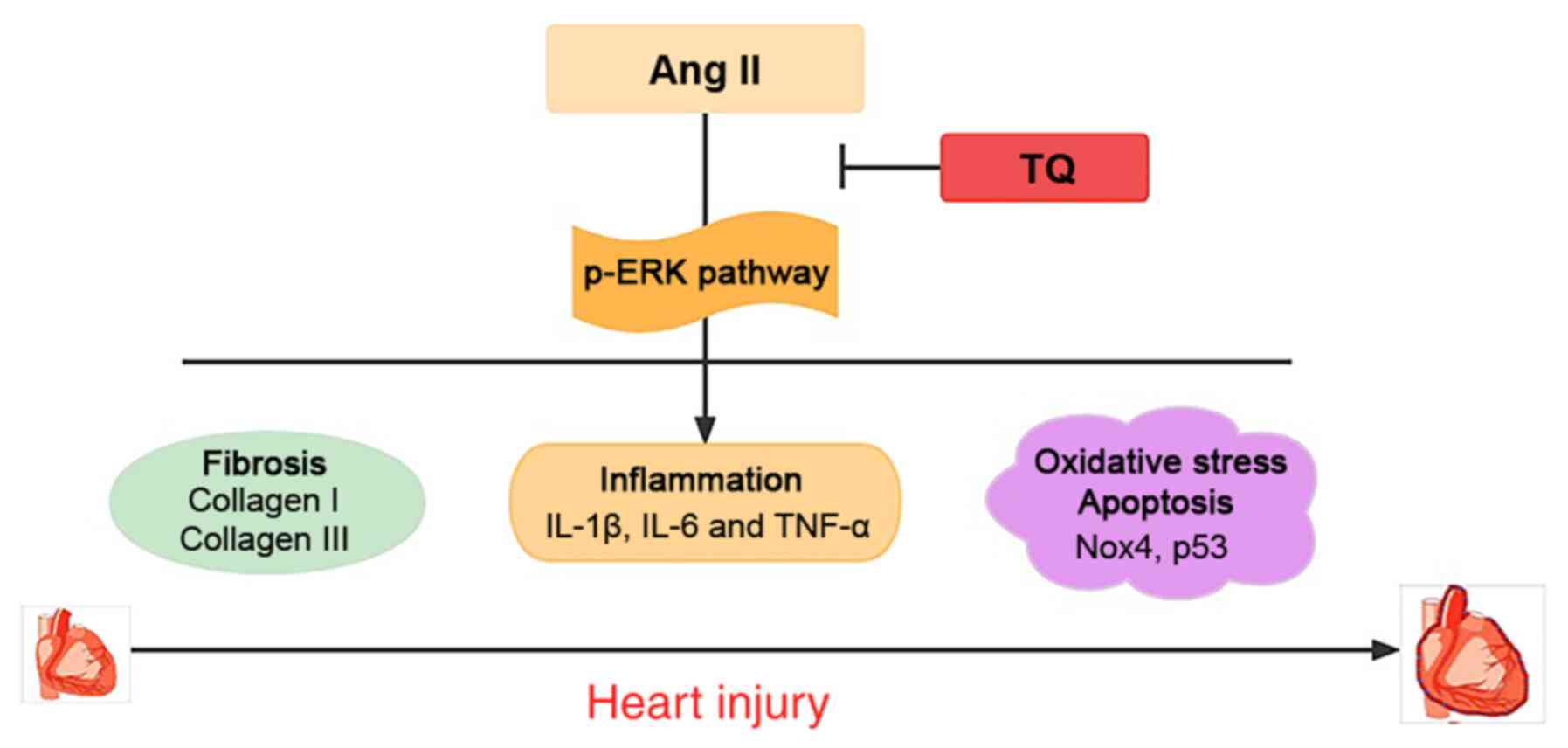
|
1
|
Kim JA, Berliner JA and Nadler JL:
Angiotensin II increases monocyte binding to endothelial cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 226:862–868. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lonn EM, Yusuf S, Jha P, Montague TJ, Teo
KK, Benedict CR and Pitt B: Emerging role of angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitors in cardiac and vascular protection. Circulation.
90:2056–2069. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alderman MH, Madhavan S, Ooi WL, Cohen H,
Sealey JE and Laragh JH: Association of the renin-sodium profile
with the risk of myocardial infarction in patients with
hypertension. N Engl J Med. 324:1098–1104. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Daugherty A, Manning MW and Cassis LA:
Angiotensin II promotes atherosclerotic lesions and aneurysms in
apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 105:1605–162. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cassis LA, Gupte M, Thayer S, Zhang X,
Charnigo R, Howatt DA, Rateri DL and Daugherty A: ANG II infusion
promotes abdominal aortic aneurysms independent of increased blood
pressure in hypercholesterolemic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 296:H1660–H1665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guan XH, Hong X, Zhao N, Liu XH, Xiao YF,
Chen TT, Deng LB, Wang XL, Wang JB, Ji GJ, et al: CD38 promotes
angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Cell Mol Med.
21:1492–1502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chobanian AV and Alexander RW:
Exacerbation of atherosclerosis by hypertension. Potential
mechanisms and clinical implications. Arch Intern Med.
156:1952–1956. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jia L, Li Y, Xiao C and Du J: Angiotensin
II induces inflammation leading to cardiac remodeling. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 17:221–231. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
She G, Ren YJ, Wang Y, Hou MC, Wang HF,
Gou W, Lai BC, Lei T, Du XJ and Deng XL: KCa 3.1
channels promote cardiac fibrosis through mediating inflammation
and differentiation of monocytes into myofibroblasts in angiotensin
II-treated rats. J Am Heart Assoc. 8:e0104182019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Touyz RM, Anagnostopoulou A, Camargo LL,
Rios FJ and Montezano AC: Vascular biology of superoxide-generating
NADPH oxidase 5-implications in hypertension and cardiovascular
disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 30:1027–1040. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Roessner A and
Schneider-Stock R: Thymoquinone: A promising anti-cancer drug from
natural sources. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1249–1253. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
el Tahir KE, Ashour MM and al-Harbi MM:
The cardiovascular actions of the volatile oil of the black seed
(Nigella sativa) in rats: Elucidation of the mechanism of action.
Gen Pharmacol. 24:1123–1131. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Woo CC, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Tan KH:
Thymoquinone: Potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:443–451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hosseinzadeh H, Taiari S and Nassiri-Asl
M: Effect of thymoquinone, a constituent of Nigella sativa L., on
ischemia-reperfusion in rat skeletal muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol. 385:503–508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao J, Ke ZP, Shi Y, Zeng Q and Cao Z:
The cardioprotective effect of thymoquinone on ischemia-reperfusion
injury in isolated rat heart via regulation of apoptosis and
autophagy. J Cell Biochem. 119:7212–7217. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adalı F, Gonul Y, Kocak A, Yuksel Y,
Ozkececi G, Ozdemir C, Tunay K, Bozkurt MF and Sen OG: Effects of
thymoquinone against cisplatin-induced cardiac injury in rats. Acta
Cir Bras. 31:271–277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jalili C, Sohrabi M, Jalili F and
Salahshoor MR: Assessment of thymoquinone effects on apoptotic and
oxidative damage induced by morphine in mice heart. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 64:33–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ortega R, Collado A, Selles F,
Gonzalez-Navarro H, Sanz MJ, Real JT and Piqueras L: SGLT-2
(Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) Inhibition reduces Ang II
(Angiotensin II)-induced dissecting abdominal aortic aneurysm in
ApoE (Apolipoprotein E) knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 39:1614–1628. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stegbauer J, Thatcher SE, Yang G,
Bottermann K, Rump LC, Daugherty A and Cassis LA: Mas receptor
deficiency augments angiotensin II-induced atherosclerosis and
aortic aneurysm ruptures in hypercholesterolemic male mice. J Vasc
Surg. 70:1658–68.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Atta MS, El-Far AH, Farrag FA, Abdel-Daim
MM, Al Jaouni SK and Mousa SA: Thymoquinone attenuates
cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2018:78456812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Satoh K, Nigro P, Zeidan A, Soe NN, Jaffré
F, Oikawa M, O'Dell MR, Cui Z, Menon P, Lu Y, et al: Cyclophilin A
promotes cardiac hypertrophy in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1116–1123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koutnikova H, Laakso M, Lu L, Combe R,
Paananen J, Kuulasmaa T, Kuusisto J, Häring HU, Hansen T, Pedersen
O, et al: Identification of the UBP1 locus as a critical blood
pressure determinant using a combination of mouse and human
genetics. PLoS Genet. 5:e10005912009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen P, Yang F, Wang W, Li X, Liu D, Zhang
Y, Yin G, Lv F, Guo Z, Mehta JL and Wang X: Liraglutide attenuates
myocardial fibrosis via inhibition of AT1R-mediated ROS production
in hypertensive mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 26:179–188.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Madeddu P, Emanueli C, Maestri R, Salis
MB, Minasi A, Capogrossi MC and Olivetti G: Angiotensin II type 1
receptor blockade prevents cardiac remodeling in bradykinin B(2)
receptor knockout mice. Hypertension. 35:391–396. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE and
Rifai N: C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in
the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med.
342:836–843. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matsushita K, Yatsuya H, Tamakoshi K, Yang
PO, Otsuka R, Wada K, Mitsuhashi H, Hotta Y, Kondo T, Murohara T
and Toyoshima H: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is quite low
in Japanese men at high coronary risk. Circ J. 71:820–825. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shimada K, Fujita M, Tanaka A, Yoshida K,
Jisso S, Tanaka H, Yoshikawa J, Kohro T, Hayashi D, Okada Y, et al:
Elevated serum C-reactive protein levels predict cardiovascular
events in the Japanese coronary artery disease (JCAD) study. Circ
J. 73:78–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Touyz RM: Intracellular mechanisms
involved in vascular remodelling of resistance arteries in
hypertension: Role of angiotensin II. Exp Physiol. 90:449–455.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ojha S, Azimullah S, Mohanraj R, Sharma C,
Yasin J, Arya DS and Adem A: Thymoquinone protects against
myocardial ischemic injury by mitigating oxidative stress and
inflammation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:1436292015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ninh VK, El Hajj EC, Ronis MJ and Gardner
JD: N-Acetylcysteine prevents the decreases in cardiac collagen
I/III ratio and systolic function in neonatal mice with prenatal
alcohol exposure. Toxicol Lett. 315:87–95. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Husse B, Briest W, Homagk L, Isenberg G
and Gekle M: Cyclical mechanical stretch modulates expression of
collagen I and III by PKC and tyrosine kinase in cardiac
fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
293:R1898–R1907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cowling RT, Kupsky D, Kahn AM, Daniels LB
and Greenberg BH: Mechanisms of cardiac collagen deposition in
experimental models and human disease. Transl Res. 209:138–155.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wynn TA and Ramalingam TR: Mechanisms of
fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med.
18:1028–1040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Villarreal FJ, Kim NN, Ungab GD, Printz MP
and Dillmann WH: Identification of functional angiotensin II
receptors on rat cardiac fibroblasts. Circulation. 88:2849–2861.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schnee JM and Hsueh WA: Angiotensin II,
adhesion, and cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 46:264–268. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Leask A: Getting to the heart of the
matter: New insights into cardiac fibrosis. Circ Res.
116:1269–1276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brandes RP, Weissmann N and Schröder K:
NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular disease. Free Radic Biol Med.
49:687–706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nabeebaccus A, Zhang M and Shah AM: NADPH
oxidases and cardiac remodelling. Heart Fail Rev. 16:5–12. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li DX, Chen W, Jiang YL, Ni JQ and Lu L:
Antioxidant protein peroxiredoxin 6 suppresses the vascular
inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in
angiotensin II-induced endotheliocyte. Gen Physiol Biophys.
39:545–555. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Heymes C, Bendall JK, Ratajczak P, Cave
AC, Samuel JL, Hasenfuss G and Shah AM: Increased myocardial NADPH
oxidase activity in human heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol.
41:2164–2171. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schröder K, Zhang M, Benkhoff S, Mieth A,
Pliquett R, Kosowski J, Kruse C, Luedike P, Michaelis UR, Weissmann
N, et al: Nox4 is a protective reactive oxygen species generating
vascular NADPH oxidase. Circ Res. 110:1217–1225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Farina F, Sancini G, Mantecca P,
Gallinotti D, Camatini M and Palestini P: The acute toxic effects
of particulate matter in mouse lung are related to size and season
of collection. Toxicol Lett. 202:209–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Qin F, Patel R, Yan C and Liu W: NADPH
oxidase is involved in angiotensin II-induced apoptosis in H9C2
cardiac muscle cells: Effects of apocynin. Free Radic Biol Med.
40:236–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tian HP, Sun YH, He L, Yi YF, Gao X and Xu
DL: Single-stranded DNA-binding protein 1 abrogates cardiac
fibroblast proliferation and collagen expression induced by
angiotensin II. Int Heart J. 59:1398–1408. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Purcell NH, Wilkins BJ, York A,
Saba-El-Leil MK, Meloche S, Robbins J and Molkentin JD: Genetic
inhibition of cardiac ERK1/2 promotes stress-induced apoptosis and
heart failure but has no effect on hypertrophy in vivo. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:14074–14079. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cipolletta E, Rusciano MR, Maione AS,
Santulli G, Sorriento D, Del Giudice C, Ciccarelli M, Franco A,
Crola C, Campiglia P, et al: Targeting the CaMKII/ERK interaction
in the heart prevents cardiac hypertrophy. PLoS One.
10:e01304772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jagavelu K, Tietge UJ, Gaestel M, Drexler
H, Schieffer B and Bavendiek U: Systemic deficiency of the MAP
kinase-activated protein kinase 2 reduces atherosclerosis in
hypercholesterolemic mice. Circ Res. 101:1104–1112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Matsuzawa A and Ichijo H: Molecular
mechanisms of the decision between life and death: Regulation of
apoptosis by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. J Biochem.
130:1–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Y, Song J, Bian H, Bo J, Lv S, Pan W
and Lv X: Apelin promotes hepatic fibrosis through ERK signaling in
LX-2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 460:205–215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ning ZW, Luo XY, Wang GZ, Li Y, Pan MX,
Yang RQ, Ling XG, Huang S, Ma XX, Jin SY, et al: MicroRNA-21
mediates angiotensin II-induced liver fibrosis by activating NLRP3
inflammasome/IL-1β axis via targeting Smad7 and Spry1. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 27:1–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Xu Z, Sun J, Tong Q, Lin Q, Qian L, Park Y
and Zheng Y: The role of ERK1/2 in the development of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 17:20012016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhao J, Miao G, Wang T, Li J and Xie L:
Urantide attenuates myocardial damage in atherosclerotic rats by
regulating the MAPK signalling pathway. Life Sci. 262:1185512020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cheng M, Wu G, Song Y, Wang L, Tu L, Zhang
L and Zhang C: Celastrol-induced suppression of the miR-21/ERK
signalling pathway attenuates cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1928–1938. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li P, Chen XR, Xu F, Liu C, Li C, Liu H,
Wang H, Sun W, Sheng YH and Kong XQ: Alamandine attenuates
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via inhibiting MAPKs
signaling pathways. Life Sci. 206:106–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu M, Qin J, Hao Y, Liu M, Luo J, Luo T
and Wei L: Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses skeletal muscle
myostatin expression in diabetes: Involvement of ROS-ERK and NF-κB
pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:7824972013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rao RK and Clayton LW: Regulation of
protein phosphatase 2A by hydrogen peroxide and glutathionylation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 293:610–616. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|