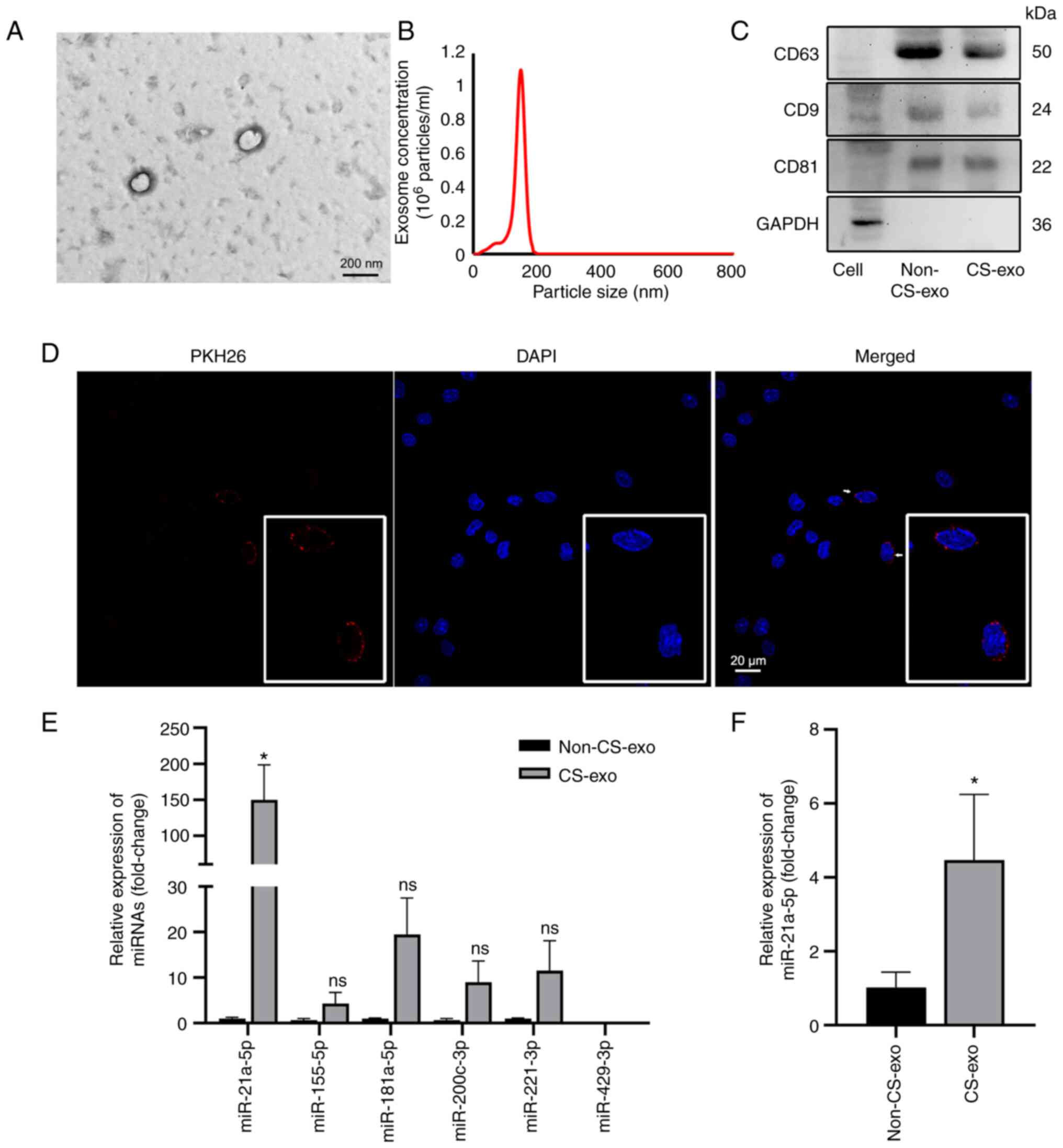
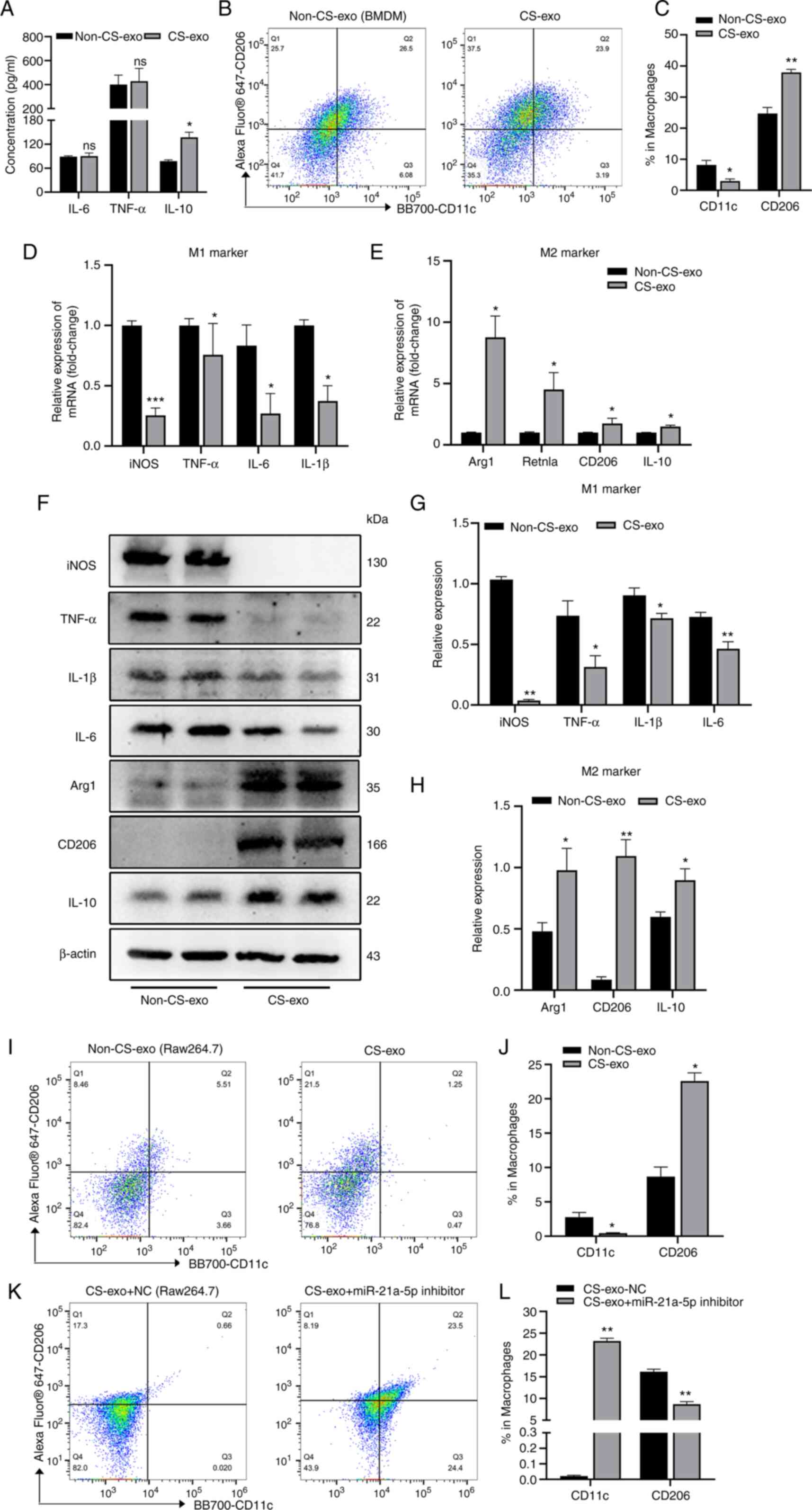
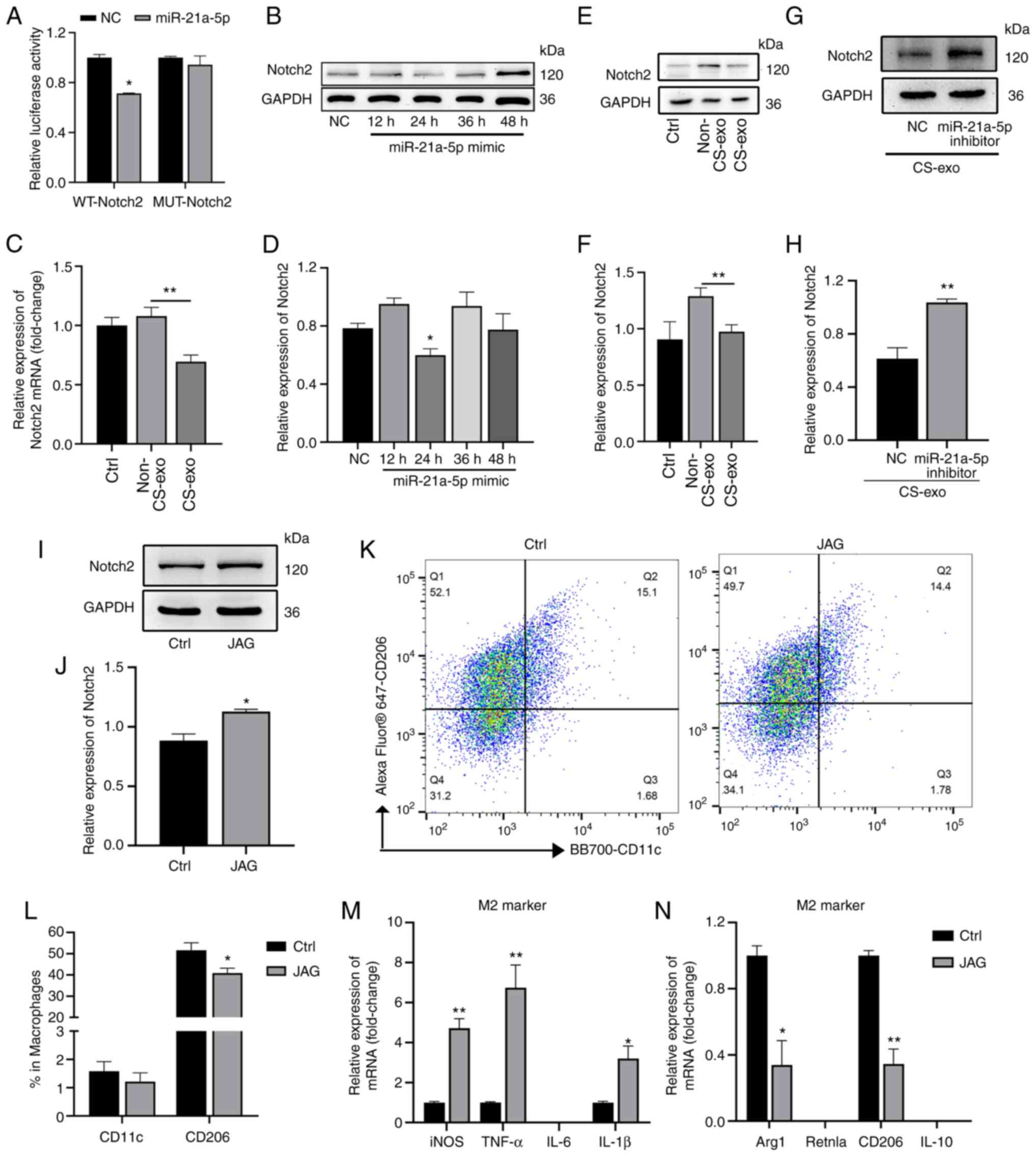
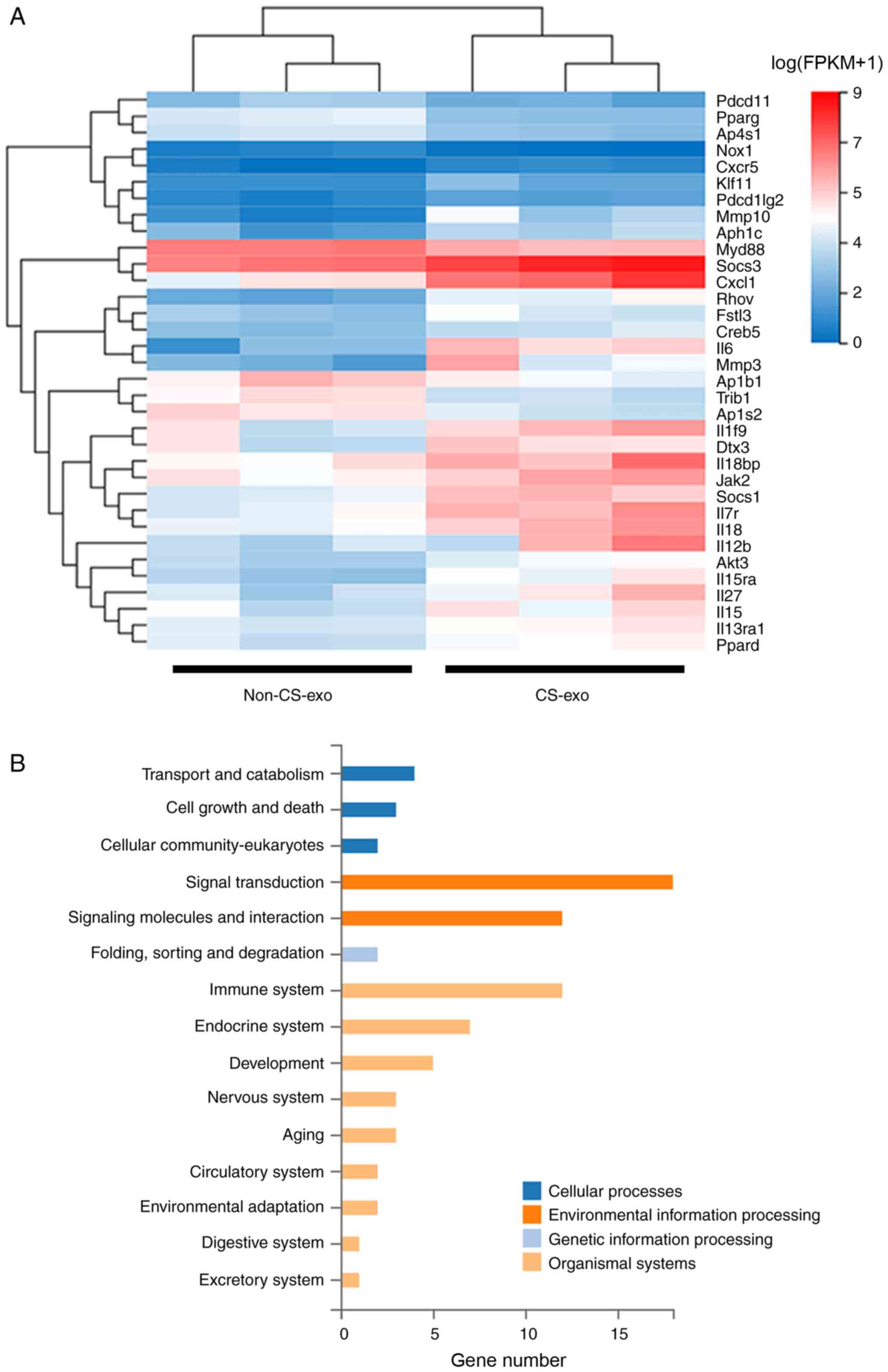
|
1
|
Tremblay L, Valenza F, Ribeiro SP, Li J
and Slutsky AS: Injurious ventilatory strategies increase cytokines
and c-fos m-RNA expression in an isolated rat lung model. J Clin
Invest. 99:944–952. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ranieri VM, Suter PM, Tortorella C, De
Tullio R, Dayer JM, Brienza A, Bruno F and Slutsky AS: Effect of
mechanical ventilation on inflammatory mediators in patients with
acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 282:54–61. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Imai Y, Parodo J, Kajikawa O, de Perrot M,
Fischer S, Edwards V, Cutz E, Liu M, Keshavjee S, Martin TR, et al:
Injurious mechanical ventilation and end-organ epithelial cell
apoptosis and organ dysfunction in an experimental model of acute
respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 289:2104–2112. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silva PL, Negrini D and Macêdo Rocco PR:
Mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury in healthy lungs. Best
Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 29:301–313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Imanaka H, Shimaoka M, Matsuura N,
Nishimura M, Ohta N and Kiyono H: Ventilator-induced lung injury is
associated with neutrophil infiltration, macrophage activation, and
TGF-beta 1 mRNA upregulation in rat lungs. Anesth Analg.
92:428–436. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bissonnette EY, Lauzon-Joset JF, Debley JS
and Ziegler SF: Cross-talk between alveolar macrophages and lung
epithelial cells is essential to maintain lung homeostasis. Front
Immunol. 11:5830422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guillot L, Nathan N, Tabary O, Thouvenin
G, Le Rouzic P, Corvol H, Amselem S and Clement A: Alveolar
epithelial cells: Master regulators of lung homeostasis. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2568–2573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Opitz B, van Laak V, Eitel J and Suttorp
N: Innate immune recognition in infectious and noninfectious
diseases of the lung. Am J Resp Crit Care. 181:1294–1309. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cheng P, Li S and Chen H: Macrophages in
lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells. 10:4362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laskin DL, Malaviya R and Laskin JD: Role
of macrophages in acute lung injury and chronic fibrosis induced by
pulmonary toxicants. Toxicol Sci. 168:287–301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Bhattacharya J and Westphalen K:
Macrophage-epithelial interactions in pulmonary alveoli. Semin
Immunopathol. 38:461–469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Corvol H, Flamein F, Epaud R, Clement A
and Guillot L: Lung alveolar epithelium and interstitial lung
disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1643–1651. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Skerrett SJ, Liggitt HD, Hajjar AM, Ernst
RK, Miller SI and Wilson CB: Respiratory epithelial cells regulate
lung inflammation in response to inhaled endotoxin. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 287:L143–L152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cohen TS, Cavanaugh KJ and Margulies SS:
Frequency and peak stretch magnitude affect alveolar epithelial
permeability. Eur Respir J. 32:854–861. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heise RL, Stober V, Cheluvaraju C,
Hollingsworth JW and Garantziotis S: Mechanical stretch induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelia via
hyaluronan activation of innate immunity. J Biol Chem.
286:17435–17444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beckmann A, Grissmer A, Meier C and
Tschernig T: Intercellular communication between alveolar
epithelial cells and macrophages. Ann Anat. 227:151417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mayer AK, Bartz H, Fey F, Schmidt LM and
Dalpke AH: Airway epithelial cells modify immune responses by
inducing an anti-inflammatory microenvironment. Eur J Immunol.
38:1689–1699. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iraci N, Leonardi T, Gessler F, Vega B and
Pluchino S: Focus on extracellular vesicles: Physiological role and
signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:1712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tomankova T, Petrek M and Kriegova E:
Involvement of microRNAs in physiological and pathological
processes in the lung. Respir Res. 11:1592010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang T, Jiang L, Wei X, Dong Z, Liu B,
Zhao J, Wang L, Xie P, Wang Y and Zhou S: Inhibition of miR-221
alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inactivation of
SOCS1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 18:1893–1907. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Q, Ge YL, Li M, Fang XZ, Yuan YP, Liang
L and Huang SQ: miR-127 contributes to ventilator-induced lung
injury. Mol Med Rep. 16:4119–4126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J and Wang ZX:
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and
chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:35–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
da Costa Martins PA and De Windt LJ:
miR-21: A miRaculous socratic paradox. Cardiovasc Res. 87:397–400.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu WD, Xu J, Zhang M, Zhu TM, Zhang YH
and Sun K: MicroRNA-21 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury by targeting nuclear factor-κB. Exp Ther Med.
16:4616–4622. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding Y, Hou Y, Liu Y, Xie X, Cui Y and Nie
H: Prospects for miR-21 as a target in the treatment of lung
diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 27:415–422. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Alipoor SD, Mortaz E, Garssen J,
Movassaghi M, Mirsaeidi M and Adcock IM: Exosomes and exosomal
miRNA in respiratory diseases. Mediat Inflamm. 216:56284042016.
|
|
28
|
Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X,
Xia R, Wang W, Ma Z and Shi X: Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils
induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis
in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. 25:3562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu F, Peng W, Chen J, Xu Z, Jiang R, Shao
Q, Zhao N and Qian K: Exosomes derived from alveolar epithelial
cells promote alveolar macrophage activation mediated by miR-92a-3p
in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
11:6465462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Q, Xie W, Wang Y, Chen S, Han J, Wang
L, Gui P and Wu Q: JAK2/STAT1-mediated HMGB1 translocation
increases inflammation and cell death in a ventilator-induced lung
injury model. Lab Invest. 99:1810–1821. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu H, Ling M, Xue J, Dai X, Sun Q, Chen C,
Liu Y, Zhou L, Liu J, Luo F, et al: Exosomal microRNA-21 derived
from bronchial epithelial cells is involved in aberrant
epithelium-fibroblast cross-talk in COPD induced by cigarette
smoking. Theranostics. 8:5419–5433. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang K, Yang J, Guo S, Zhao G, Wu H and
Deng G: Peripheral circulating exosome-mediated delivery of miR-155
as a novel mechanism for acute lung inflammation. Mol Ther.
27:1758–1771. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li W, Qiu X, Jiang H, Han Y, Wei D and Liu
J: Downregulation of miR-181a protects mice from LPS-induced acute
lung injury by targeting Bcl-2. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1375–1382.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Q, Du J, Yu X, Xu J, Huang F, Li X,
Zhang C, Li X, Chang J, Shang D, et al: miRNA-200c-3p is crucial in
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cell Discov. 3:170212017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao J, Tang J, Chen Q, Tang D, Liu M, Luo
M, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao Z, Tang C, et al: miR-429 regulates
alveolar macrophage inflammatory cytokine production and is
involved in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Biochem J. 471:281–291.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wynn TA, Chawla A and Pollard JW:
Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature.
496:445–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ivashkiv LB: Epigenetic regulation of
macrophage polarization and function. Trends Immunol. 34:216–223.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Hu G and Christman JW: Editorial: Alveolar
macrophages in lung inflammation and resolution. Front Immunol.
10:22752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fortini ME: Notch signaling: The core
pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev Cell. 16:633–647.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Greenbaum D, Colangelo C, Williams K and
Gerstein M: Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels
on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 4:1172003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian J, Cui X, Sun J and Zhang J: Exosomal
microRNA-16-5p from adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes
TLR4-mediated M2 macrophage polarization in septic lung injury. Int
Immunopharmacol. 98:1078352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen Z, Wu H, Shi R, Fan W, Zhang J, Su W,
Wang Y and Li P: miRNAomics analysis reveals the promoting effects
of cigarette smoke extract-treated Beas-2B-derived exosomes on
macrophage polarization. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 572:157–163. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y and Wang B: Exosome
theranostics: Biology and translational medicine. Theranostics.
8:237–255. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yao M, Cui B, Zhang W, Ma W, Zhao G and
Xing L: Exosomal miR-21 secreted by IL-1β-primed-mesenchymal stem
cells induces macrophage M2 polarization and ameliorates sepsis.
Life Sci. 264:1186582021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lee HY, Hur J, Kang JY, Rhee CK and Lee
SY: MicroRNA-21 inhibition suppresses Alveolar M2 macrophages in an
ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mice model. Allergy Asthma
Immunol Res. 13:312–329. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kovall RA: Structures of CSL, notch and
mastermind proteins: Piecing together an active transcription
complex. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 17:117–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fiúza UM and Arias AM: Cell and molecular
biology of notch. J Endocrinol. 194:459–474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang Y, He F, Feng F, Liu XW, Dong GY, Qin
HY, Hu XB, Zheng MH, Liang L, Feng L, et al: Notch signaling
determines the M1 versus M2 polarization of macrophages in
antitumor immune responses. Cancer Res. 70:4840–4849. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Q, Wang C, Liu Z, Liu X, Han C, Cao
X and Li N: Notch signal suppresses toll-like receptor-triggered
inflammatory responses in macrophages by inhibiting extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated nuclear factor κB activation.
J Biol Chem. 287:6208–6217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liu Y, Stewart KN, Bishop E, Marek CJ,
Kluth DC, Rees AJ and Wilson HM: Unique expression of suppressor of
cytokine signaling 3 is essential for classical macrophage
activation in rodents in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol.
180:6270–6278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pascal LE, True LD, Campbell DS, Deutsch
EW, Risk M, Coleman IM, Eichner LJ, Nelson PS and Liu AY:
Correlation of mRNA and protein levels: Cell type-specific gene
expression of cluster designation antigens in the prostate. BMC
Genomics. 9:2462008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gygi SP, Rochon Y, Franza BR and Aebersold
R: Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol
Cell Biol. 19:1720–1730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|