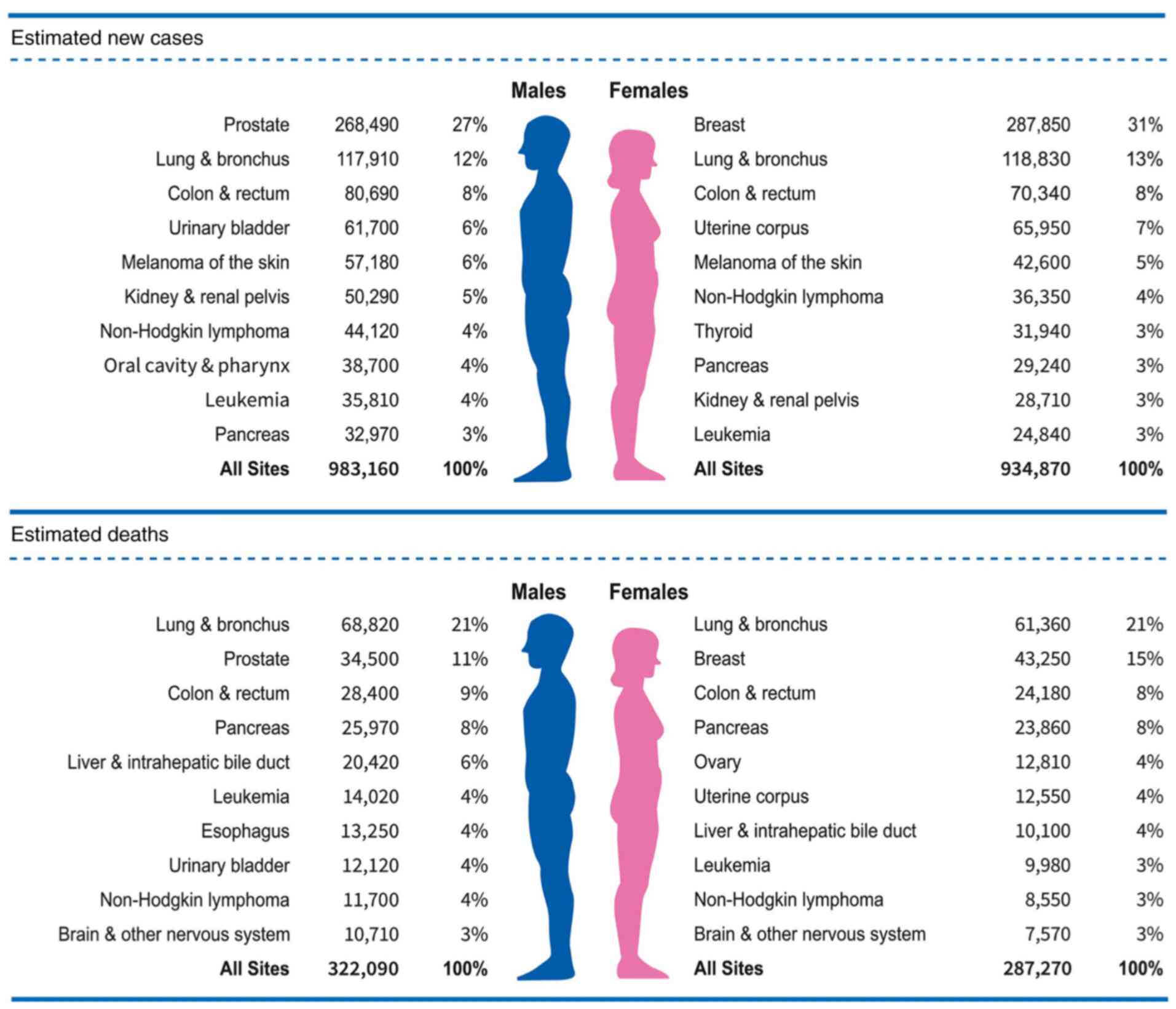
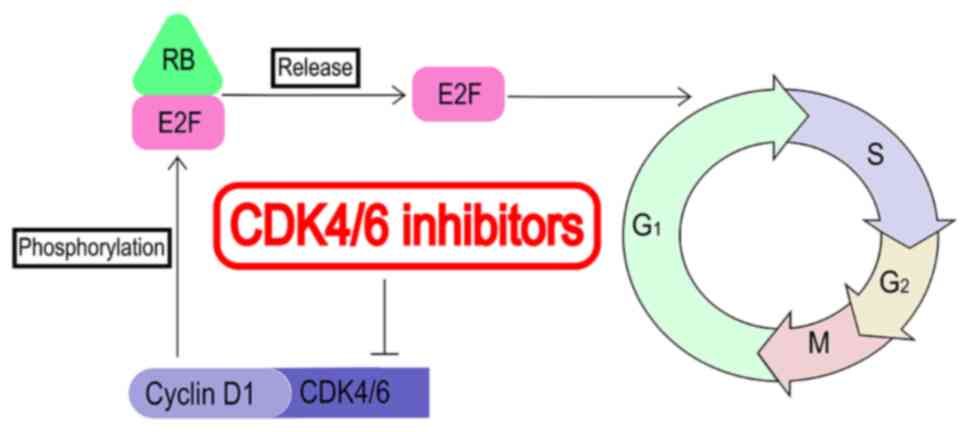
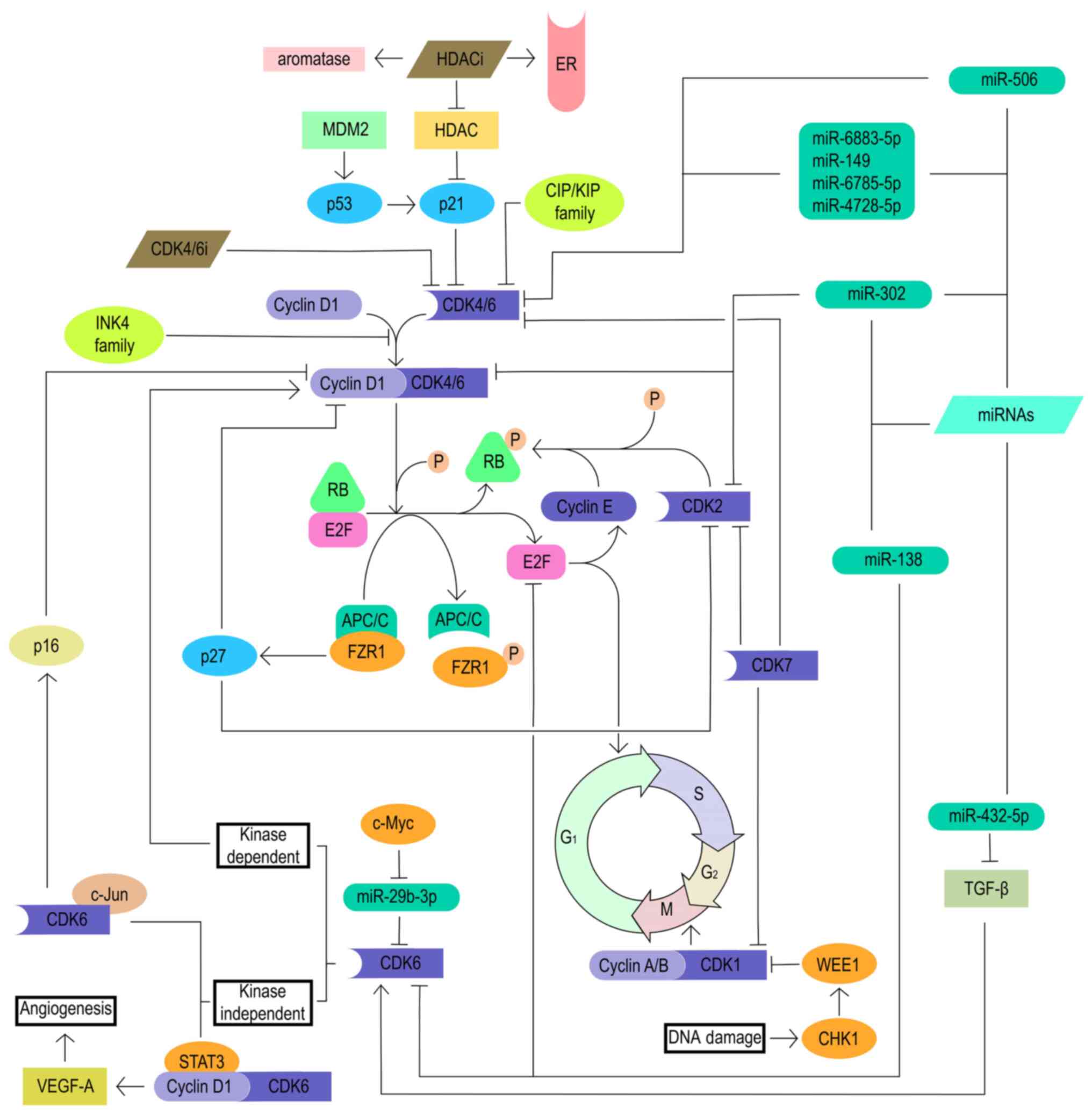
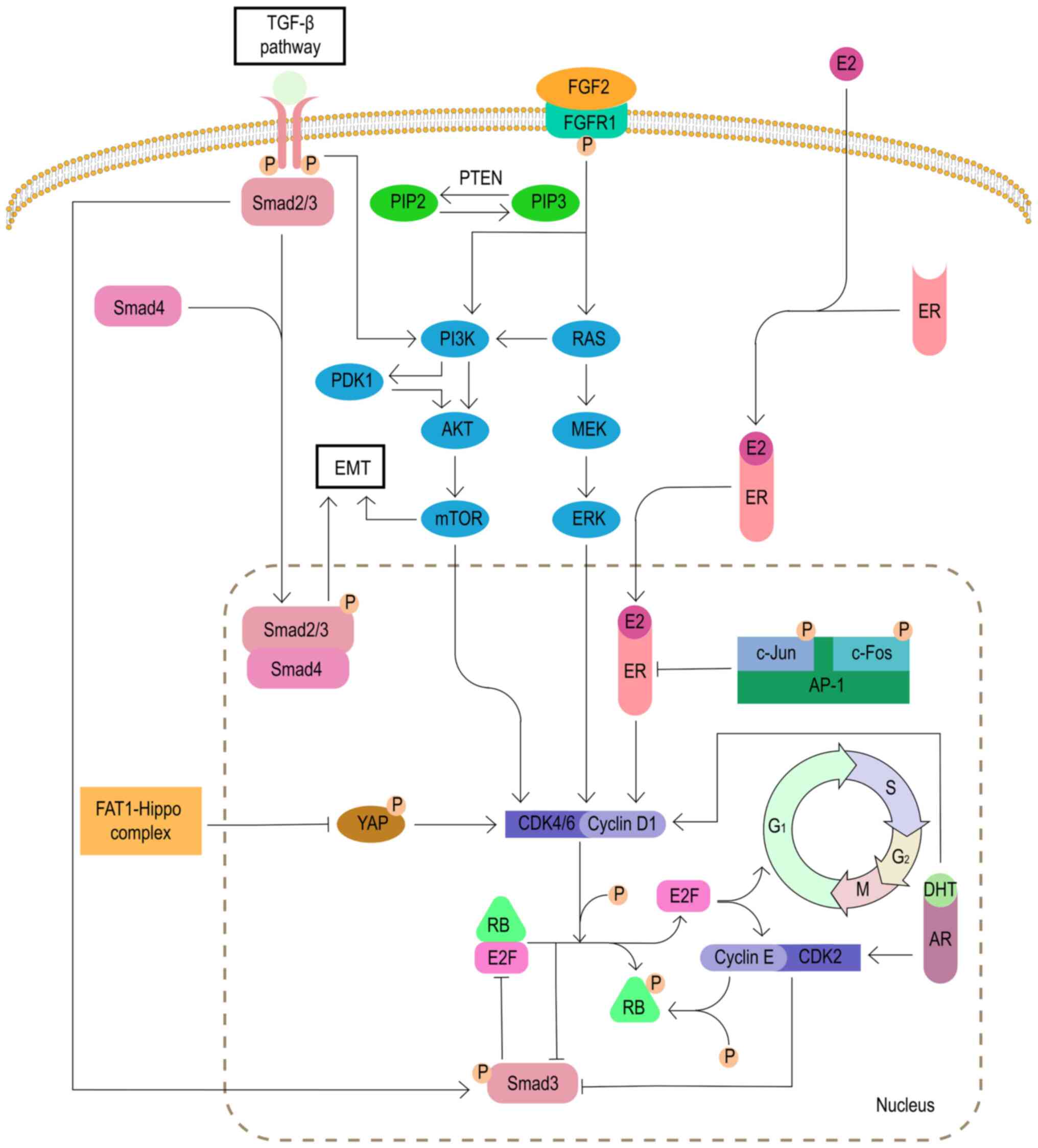
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dai X, Li T, Bai Z, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhan J
and Shi B: Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical
use and future trends. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2929–2943.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E, Aapro M,
André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya G, Biganzoli L, Cardoso
MJ, et al: 3rd ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for
advanced breast cancer (ABC 3). Ann Oncol. 28:31112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Milani A, Geuna E, Mittica G and Valabrega
G: Overcoming endocrine resistance in metastatic breast cancer:
Current evidence and future directions. World J Clin Oncol.
5:990–1001. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clarke R, Tyson JJ and Dixon JM: Endocrine
resistance in breast cancer-an overview and update. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 418:220–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Brufsky AM and Dickler MN: Estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer: Exploiting signaling pathways
implicated in endocrine resistance. Oncologist. 23:528–539. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu W and Xu B: Overcoming resistance to
endocrine therapy in hormone receptor-positive human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+/HER2−)
advanced breast cancer: A meta-analysis and systemic review of
randomized clinical trials. Front Med. 15:208–220. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nair BC and Vadlamudi RK: Regulation of
hormonal therapy resistance by cell cycle machinery. Gene Ther Mol
Biol. 12:3952008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spring LM, Wander SA, Andre F, Moy B,
Turner NC and Bardia A: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors
for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Past, present, and
future. Lancet. 395:817–827. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Altucci L, Addeo R, Cicatiello L, Germano
D, Pacilio C, Battista T, Cancemi M, Petrizzi VB, Bresciani F and
Weisz A: Estrogen induces early and timed activation of
cyclin-dependent kinases 4, 5, and 6 and increases cyclin messenger
ribonucleic acid expression in rat uterus. Endocrinology.
138:978–984. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Geum D, Sun W, Paik SK, Lee CC and Kim K:
Estrogen-induced cyclin D1 and D3 gene expressions during mouse
uterine cell proliferation in vivo: Differential induction
mechanism of cyclin D1 and D3. Mol Reprod Dev. 46:450–458. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K,
Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, Ettl J, Patel R, Pinter T, Schmidt M, et
al: The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in
combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line
treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced
breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2 study.
Lancet Oncol. 16:25–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Finn RS, Boer K, Bondarenko I, Patel R,
Pinter T, Schmidt M, Shparyk YV, Thummala A, Voitko N, Bananis E,
et al: Overall survival results from the randomized phase 2 study
of palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone
for first-line treatment of ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer
(PALOMA-1, TRIO-18). Breast Cancer Res Treat. 183:419–428. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I,
Im SA, Masuda N, Colleoni M, DeMichele A, Loi S, Verma S, et al:
Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 379:1926–1936. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap
YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Petrakova K, Blackwell
KL, Winer EP, et al: Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III
trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus
letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced
breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 30:18422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Jerusalem G,
De Laurentiis M, Im S, Petrakova K, Valeria Bianchi G, Martín M,
Nusch A, et al: Ribociclib plus fulvestrant for postmenopausal
women with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in the phase III
randomized MONALEESA-3 trial: Updated overall survival. Ann Oncol.
32:1015–1024. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J,
Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, et al:
The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in
hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that
progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: A randomized clinical
trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:116–124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu B, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Hu X, Li W, Tong
Z, Sun T, Teng Y, Wu X, Ouyang Q, et al: Dalpiciclib versus placebo
plus fulvestrant in HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer that relapsed
or progressed on previous endocrine therapy (DAWNA-1): A
multi-center, randomized, phase 3 study. J Clin Oncol. 39(15
Suppl): S1002. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu B, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Hu X, Li W, Tong
Z, Sun T, Teng Y, Wu X, Ouyang Q, et al: Dalpiciclib or placebo
plus fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative
advanced breast cancer: A randomized, phase 3 trial. Nat Med.
27:1904–1909. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang P, Xu B, Gui L, Wang W, Xiu M, Zhang
X, Sun G, Zhu X and Zou J: A phase 1 study of dalpiciclib, a
cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor in Chinese patients with
advanced breast cancer. Biomark Res. 9:242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Malumbres M, Sotillo R, Santamaria D,
Galán J, Cerezo A, Ortega S, Dubus P and Barbacid M: Mammalian
cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and
Cdk6. Cell. 118:493–504. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guarducci C, Bonechi M, Boccalini G,
Benelli M, Risi E, Di Leo A, Malorni L and Migliaccio I: Mechanisms
of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer and potential
biomarkers of response. Breast Care (Basel). 12:304–308. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Siebert R, Willers CP and Opalka B: Role
of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor gene family p15,
p16, p18 and p19 in leukemia and lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma.
23:505–520. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Green JL, Okerberg ES, Sejd J, Palafox M,
Monserrat L, Alemayehu S, Wu J, Sykes M, Aban A, Serra V and
Nomanbhoy T: Direct CDKN2 modulation of CDK4 alters target
engagement of CDK4 inhibitor drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:771–779.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Finn RS, Crown JP, Ettl J, Schmidt M,
Bondarenko IM, Lang I, Pinter T, Boer K, Patel R, Randolph S, et
al: Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in combination with
letrozole as first-line treatment of ER-positive, HER2-negative,
advanced breast cancer: Expanded analyses of subgroups from the
randomized pivotal trial PALOMA-1/TRIO-18. Breast Cancer Res.
18:672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Turner NC, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Loi S, Colleoni
M, Loibl S, DeMichele A, Harbeck N, André F, Bayar MA, et al:
Cyclin E1 expression and palbociclib efficacy in previously treated
hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
37:1169–1178. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Finn RS, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Martin M, Rugo HS,
Diéras V, Im SA, Gelmon KA, Harbeck N, Lu DR, et al: Biomarker
analyses of response to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition and
endocrine therapy in women with treatment-Naïve metastatic breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 26:110–121. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu A, Wu B, Guo J, Luo W, Wu D, Yang H,
Zhen Y, Yu X, Wang H, Zhou Y, et al: Elevated expression of CDK4 in
lung cancer. J Transl Med. 9:382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Olanich ME, Sun W, Hewitt SM, Abdullaev Z,
Pack SD and Barr FG: CDK4 amplification reduces sensitivity to
CDK4/6 inhibition in fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:4947–4959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang C, Li Z, Bhatt T, Dickler M, Giri D,
Scaltriti M, Baselga J, Rosen N and Chandarlapaty S: Acquired CDK6
amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6
inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene.
36:2255–2264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Tigan AS, Bellutti F, Kollmann K, Tebb G
and Sexl V: CDK6-a review of the past and a glimpse into the
future: From cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation.
Oncogene. 35:3083–3091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C,
Warsch W, Scheicher R, Ott RG, Schäfer M, Fajmann S, Schlederer M,
Schiefer AI, et al: A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the
cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 30:359–360. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gacche RN and Assaraf YG: Redundant
angiogenic signaling and tumor drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
36:47–76. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ji W, Zhang W, Wang X, Shi Y, Yang F, Xie
H, Zhou W, Wang S and Guan X: c-myc regulates the sensitivity of
breast cancer cells to palbociclib via c-myc/miR-29b-3p/CDK6 axis.
Cell Death Dis. 11:7602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Etemadmoghadam D, Au-Yeung G, Wall M,
Mitchell C, Kansara M, Loehrer E, Batzios C, George J, Ftouni S,
Weir BA, et al: Resistance to CDK2 inhibitors is associated with
selection of polyploid cells in CCNE1-amplified ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:5960–5971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schachter MM, Merrick KA, Larochelle S,
Hirschi A, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Rubin SM and Fisher RP: A Cdk7-Cdk4
T-loop phosphorylation cascade promotes G1 progression. Mol Cell.
50:250–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Martin LA, Pancholi S, Ribas R, Gao Q,
Simigdala N, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Johnston SR and Dowsett M:
Abstract P3-03-09: Resistance to palbociclib depends on multiple
targetable mechanisms highlighting the potential of drug holidays
and drug switching to improve therapeutic outcome. Cancer Res. 77(4
Suppl): P3-03-092017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Howell SJ, Krebs MG, Lord S, Kenny L, Bahl
A, Clack G, Ainscow E, Arkenau HT, Mansi JL, Palmieri C, et al:
265P Study of samuraciclib (CT7001), a first-in-class, oral,
selective inhibitor of CDK7, in combination with fulvestrant in
patients with advanced hormone receptor positive HER2 negative
breast cancer (HR+BC). Ann Oncol. 32(Suppl 5): S477–S478. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Orlando S, Gallastegui E, Besson A, Abril
G, Aligué R, Pujol MJ and Bachs O: p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 collaborate
in the regulation of transcription by recruiting cyclin-Cdk
complexes on the promoters of target genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:6860–6873. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Álvarez-Fernández M and Malumbres M:
Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition.
Cancer Cell. 37:514–529. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva O, Chumsri S, Nguyen
N, Sukumar S and Brodie AM: Functional activation of the estrogen
receptor-α and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat
sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole. Cancer Res.
71:1893–1903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yardley DA, Ismail-Khan RR, Melichar B,
Lichinitser M, Munster PN, Klein PM, Cruickshank S, Miller KD, Lee
MJ and Trepel JB: Randomized phase II, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study of exemestane with or without entinostat
in postmenopausal women with locally recurrent or metastatic
estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer progressing on treatment
with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. J Clin Oncol.
31:2128–2135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang Z, Li W, Hu X, Zhang Q, Sun T, Cui
S, Wang S, Ouyang Q, Yin Y, Geng C, et al: Tucidinostat plus
exemestane for postmenopausal patients with advanced, hormone
receptor-positive breast cancer (ACE): A randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:806–815. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matheson CJ, Backos DS and Reigan P:
Targeting WEE1 kinase in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 37:872–881.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pandey K, An HJ, Kim SK, Lee SA, Kim S,
Lim SM, Kim GM, Sohn J and Moon YW: Molecular mechanisms of
resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review. Int J
Cancer. 145:1179–1188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Ramanujan A and Tiwari S: APC/C and
retinoblastoma interaction: Cross-talk of retinoblastoma protein
with the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Biosci Rep. 36:e003772016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H and Wan Y:
Regulation of Skp2-p27 axis by the Cdh1/anaphase-promoting complex
pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol. 173:217–228.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Laroche-Clary A, Chaire V, Algeo MP,
Derieppe MA, Loarer FL and Italiano A: Combined targeting of MDM2
and CDK4 is synergistic in dedifferentiated liposarcomas. J Hematol
Oncol. 10:1232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cox LS: Multiple pathways control cell
growth and transformation: Overlapping and independent activities
of p53 and p21Cip1/WAF1/Sdi1. J Pathol. 183:134–140. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin SL, Chang DC, Ying SY, Leu D and Wu
DT: MicroRNA miR-302 inhibits the tumorigenecity of human
pluripotent stem cells by coordinate suppression of the CDK2 and
CDK4/6 cell cycle pathways. Cancer Res. 70:9473–9482. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qiu S, Huang D, Yin D, Li F, Li X, Kung HF
and Peng Y: Suppression of tumorigenicity by microRNA-138 through
inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma
multiforme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1697–1707. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu G, Sun Y, Ji P, Li X, Cogdell D, Yang
D, Parker Kerrigan BC, Shmulevich I, Chen K, Sood AK, et al:
MiR-506 suppresses proliferation and induces senescence by directly
targeting the CDK4/6-FOXM1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Pathol.
233:308–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lulla AR, Slifker MJ, Zhou Y, Lev A,
Einarson MB, Dicker DT and El-Deiry WS: miR-6883 family miRNAs
target CDK4/6 to induce G1 phase cell-cycle arrest in
colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 77:6902–6913. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cornell L, Wander SA, Visal T, Wagle N and
Shapiro GI: MicroRNA-mediated suppression of the TGF-β pathway
confers transmissible and reversible CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance.
Cell Rep. 26:2667–2680.e7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Turner N and Grose R: Fibroblast growth
factor signalling: From development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:116–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Turner N, Pearson A, Sharpe R, Lambros M,
Geyer F, Lopez-Garcia MA, Natrajan R, Marchio C, Iorns E, Mackay A,
et al: FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and
is a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 70:2085–2094.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Formisano L, Lu Y, Servetto A, Hanker AB,
Jansen VM, Bauer JA, Sudhan DR, Guerrero-Zotano AL, Croessmann S,
Guo Y, et al: Aberrant FGFR signaling mediates resistance to CDK4/6
inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. Nat Commun. 10:13732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kilker RL and Planas-Silva MD: Cyclin D1
is necessary for tamoxifen-induced cell cycle progression in human
breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:11478–11484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Costa C, Wang Y, Ly A, Hosono Y, Murchie
E, Walmsley CS, Huynh T, Healy C, Peterson R, Yanase S, et al: PTEN
loss mediates clinical cross-resistance to CDK4/6 and PI3Kα
inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 10:72–85. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Bencivenga D, Caldarelli I, Stampone E,
Mancini FP, Balestrieri ML, Della Ragione F and Borriello A:
p27Kip1 and human cancers: A reappraisal of a still
enigmatic protein. Cancer Lett. 403:354–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Finn RS, Aleshin A and Slamon DJ:
Targeting the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4/6 in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 18:172016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 in cell
proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 20:2390–2400. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shen Q, Uray IP, Li Y, Zhang Y, Hill J, Xu
XC, Young MR, Gunther EJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Colburn NH, et al:
Targeting the activator protein 1 transcription factor for the
prevention of estrogen receptor-negative mammary tumors. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 1:45–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Tewari D, Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Sureda A,
Farooqi AA, Atanasov AG, Vacca RA, Sethi G and Bishayee A:
Targeting activator protein 1 signaling pathway by bioactive
natural agents: Possible therapeutic strategy for cancer prevention
and intervention. Pharmacol Res. 128:366–375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
McNamara KM, Yoda T, Takagi K, Miki Y,
Suzuki T and Sasano H: Androgen receptor in triple negative breast
cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 133:66–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ji W, Shi Y, Wang X, He W, Tang L, Tian S,
Jiang H, Shu Y and Guan X: Combined androgen receptor blockade
overcomes the resistance of breast cancer cells to palbociclib. Int
J Biol Sci. 15:522–532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Z, Razavi P, Li Q, Toy W, Liu B, Ping
C, Hsieh W, Sanchez-Vega F, Brown DN, Da Cruz Paula AF, et al: Loss
of the FAT1 tumor suppressor promotes resistance to CDK4/6
inhibitors via the Hippo pathway. Cancer Cell. 34:893–905.e8. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu F and Korc M: Cdk4/6 inhibition
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances invasiveness
in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2138–2148. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Non-Smad
TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 118:3573–3584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zelivianski S, Cooley A, Kall R and Jeruss
JS: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4-mediated phosphorylation inhibits
Smad3 activity in cyclin D-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 8:1375–1387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang J, Song K, Krebs TL, Jackson MW and
Danielpour D: Rb/E2F4 and Smad2/3 link survivin to TGF-beta-induced
apoptosis and tumor progression. Oncogene. 27:5326–5338. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Decker JT, Wan L, Shea LD and Jeruss JS:
Abstract P4-03-16: Cyclin E affects Smad3 pathway in trastuzumab
resistant HER2+ breast cancer. Cancer Res. 78(4 Suppl): pp.
P4-03-162018, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Jiang Z, Song E, Wang X, Wang H, Wang X,
Wu J, Yin Y, Zhang Q, Chen J, Che W, et al: Guidelines of Chinese
society of clinical oncology (CSCO) on diagnosis and treatment of
breast cancer (2020 version). 2020. Transl Breast Cancer Res.
1:272020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Johnston SRD, Harbeck N, Hegg R, Toi M,
Martin M, Shao ZM, Zhang QY, Martinez Rodriguez JL, Campone M,
Hamilton E, et al: Abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy for
the adjuvant treatment of HR+, HER2-, node-positive, high-risk,
early breast cancer (monarchE). J Clin Oncol. 38:3987–3998. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hamilton E, Cortes J, Ozyilkan O, Chen SC,
Petrakova K, Manikhas A, Jerusalem G, Hegg R, Huober J, Chapman SC,
et al: nextMONARCH: Abemaciclib monotherapy or combined with
tamoxifen for metastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer.
21:181–190.e2. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wander SA, Zangardi M, Niemierko A,
Kambadakone A, Kim LSL, Xi J, Pandey AK, Spring L, Stein C, Juric
D, et al: A multicenter analysis of abemaciclib after progression
on palbociclib in patients (pts) with hormone receptor-positive
(HR+)/HER2-metastatic breast cancer (MBC). J Clin Oncol. 37(15
Suppl): S10572019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Kalinsky K, Accordino MK, Chiuzan C, Mundi
PS, Trivedi MS, Novik Y, Tiersten A, Raptis G, Baer LN, Oh SY, et
al: A randomized, phase II trial of fulvestrant or exemestane with
or without ribociclib after progression on anti-estrogen therapy
plus cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition (CDK 4/6i) in patients
(pts) with unresectable or hormone receptor-positive (HR+),
HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC): MAINTAIN trial. J
Clin Oncol. 40(17 Suppl): LBA1004. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Mayer EL, Wander SA, Regan MM, DeMichele
A, Forero-Torres A, Rimawi MF, Ma CX, Cristofanilli M, Anders CK,
Bartlett CH, et al: Palbociclib after CDK and endocrine therapy
(PACE): A randomized phase II study of fulvestrant, palbociclib,
and avelumab for endocrine pre-treated ER+/HER2-metastatic breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36(15 Suppl): TPS11042018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Bardia A, Aftimos P, Bihani T,
Anderson-Villaluz AT, Jung J, Conlan MG and Kaklamani VG: EMERALD:
Phase III trial of elacestrant (RAD1901) vs endocrine therapy for
previously treated ER+ advanced breast cancer. Future Oncol.
15:3209–3218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bidard FC, Kaklamani VG, Neven P, Streich
G, Montero AJ, Forget F, Mouret-Reynier MA, Sohn JH, Taylor D,
Harnden KK, et al: Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor
degrader) versus standard endocrine therapy for estrogen
receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-negative advanced breast cancer: Results from the randomized
phase III EMERALD trial. J Clin Oncol. JCO22003382022.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mosele F, Stefanovska B, Lusque A, Tran
Dien A, Garberis I, Droin N, Le Tourneau C, Sablin MP, Lacroix L,
Enrico D, et al: Outcome and molecular landscape of patients with
PIK3CA-mutated metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 31:377–386.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
André F, Ciruelos EM, Juric D, Loibl S,
Campone M, Mayer IA, Rubovszky G, Yamashita T, Kaufman B, Lu YS, et
al: Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone
receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor
receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival
results from SOLAR-1. Ann Oncol. 32:208–217. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Rugo HS, Lerebours F, Ciruelos E,
Drullinsky P, Borrego MR, Neven P, Park YH, Prat A, Bachelot T,
Juric D, et al: Alpelisib (ALP) + fulvestrant (FUL) in patients
(pts) with PIK3CA-mutated (mut) hormone receptor-positive (HR+),
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced
breast cancer (ABC) previously treated with cyclin-dependent kinase
4/6 inhibitor (CDKi) + aromatase inhibitor (AI): BYLieve study
results. J Clin Oncol. 38(15 Suppl): S10062020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Bartsch R: ASCO 2020: Highlights in breast
cancer. Memo. 14:58–61. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
André F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone
M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, Iwata H, Conte P, Mayer IA, Kaufman B, et al:
Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 380:1929–1940. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Suppan C: Post San Antonio update-my top
three abstracts! Memo-Mag Eur Med Oncol. 14:244–246. 2021.
|
|
88
|
Piccart M, Hortobagyi GN, Campone M,
Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Ito Y, Noguchi S, Perez A, Rugo HS, Deleu
I, et al: Everolimus plus exemestane for hormone-receptor-positive,
human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast
cancer: Overall survival results from BOLERO-2†. Ann Oncol.
25:2357–2362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, DeMichele A, Clark
AS, Zelnak AB, Yardley DA, Karuturi MS, Sanft TB, Blau S, Hart LL,
et al: Triplet therapy (continuous ribociclib, everolimus,
exemestane) in HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer postprogression on a
CDK4/6 inhibitor (TRINITI-1): Efficacy, safety, and biomarker
results. J Clin Oncol. 37(15 Suppl): S10162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, DeMichele A, Clark
AS, Zelnak A, Yardley DA, Karuturi M, Sanft T, Blau S, Hart L, et
al: Phase I/II trial of exemestane, ribociclib, and everolimus in
women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer
after progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors (TRINITI-1). Clin Cancer
Res. 27:4177–4185. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wander SA, Juric D, Supko JG, Micalizzi
DS, Spring L, Vidula N, Beeler M, Habin KR, Viscosi E, Fitzgerald
DM, et al: Phase Ib trial to evaluate safety and anti-tumor
activity of the AKT inhibitor, ipatasertib, in combination with
endocrine therapy and a CDK4/6 inhibitor for patients with hormone
receptor positive (HR+)/HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer
(MBC) (TAKTIC). J Clin Oncol. 38(15 Suppl): S10662020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Martin LA and Dowsett M: BCL-2: A new
therapeutic target in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer?
Cancer Cell. 24:7–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lok SW, Whittle JR, Vaillant F, The CE, Lo
LL, Policheni AN, Bergin ART, Desai J, Ftouni S, Gandolfo LC, et
al: A phase Ib dose-escalation and expansion study of the BCL2
inhibitor venetoclax combined with tamoxifen in ER and
BCL2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 9:354–369.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
A phase II study comparing the efficacy of
venetoclax + fulvestrant vs fulvestrant in women with estrogen
receptor-positive, Her2-negative locally advanced or metastatic
breast cancer who experienced disease recurrence or progression
during or after CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy (Veronica).
|
|
95
|
Lindeman GJ, Bowen R, Jerzak KJ, Song X,
Decker T, Boyle FM, McCune SL, Armstrong A, Shannon CM, Bertelli G,
et al: Results from VERONICA: A randomized, phase II study of
second-/third-line venetoclax (VEN) + fulvestrant (F) versus F
alone in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-negative, locally
advanced, or metastatic breast cancer (LA/MBC). J Clin Oncol. 39(15
Suppl): pp. S10042021, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Goel S, DeCristo MJ, Watt AC, BrinJones H,
Sceneay J, Li BB, Khan N, Ubellacker JM, Xie S, Metzger-Filho O, et
al: CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity. Nature.
548:471–475. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ogata R, Kishino E, Saitoh W, Koike Y and
Kurebayashi J: Resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6
inhibitors confers cross-resistance to other CDK inhibitors but not
to chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer.
28:206–215. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Rugo HS, Cristofanilli M, Loibl S, Harbeck
N, DeMichele A, Iwata H, Park YH, Brufsky A, Theall KP, Huang X, et
al: Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with
hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: Analyses from
PALOMA-3. Oncologist. 26:e1339–e1346. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Princic N, Aizer A, Tang DH, Smith DM,
Johnson W and Bardia A: Predictors of systemic therapy sequences
following a CDK 4/6 inhibitor-based regimen in post-menopausal
women with hormone receptor positive, HEGFR-2 negative metastatic
breast cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 35:73–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Kolyadina IV, Bolotina L, Zhukova L,
Vladimirova LU, Sultanbaev A, Karabina E, Ganshina I, Ovchinnikova
E, Kolyadina IV, Antonova G, et al: The effectiveness and safety of
eribulin therapy in HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast
cancer post-CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy in Russian clinical practice.
J Clin Oncol. 39(15 Suppl): e130352021. View Article : Google Scholar
|