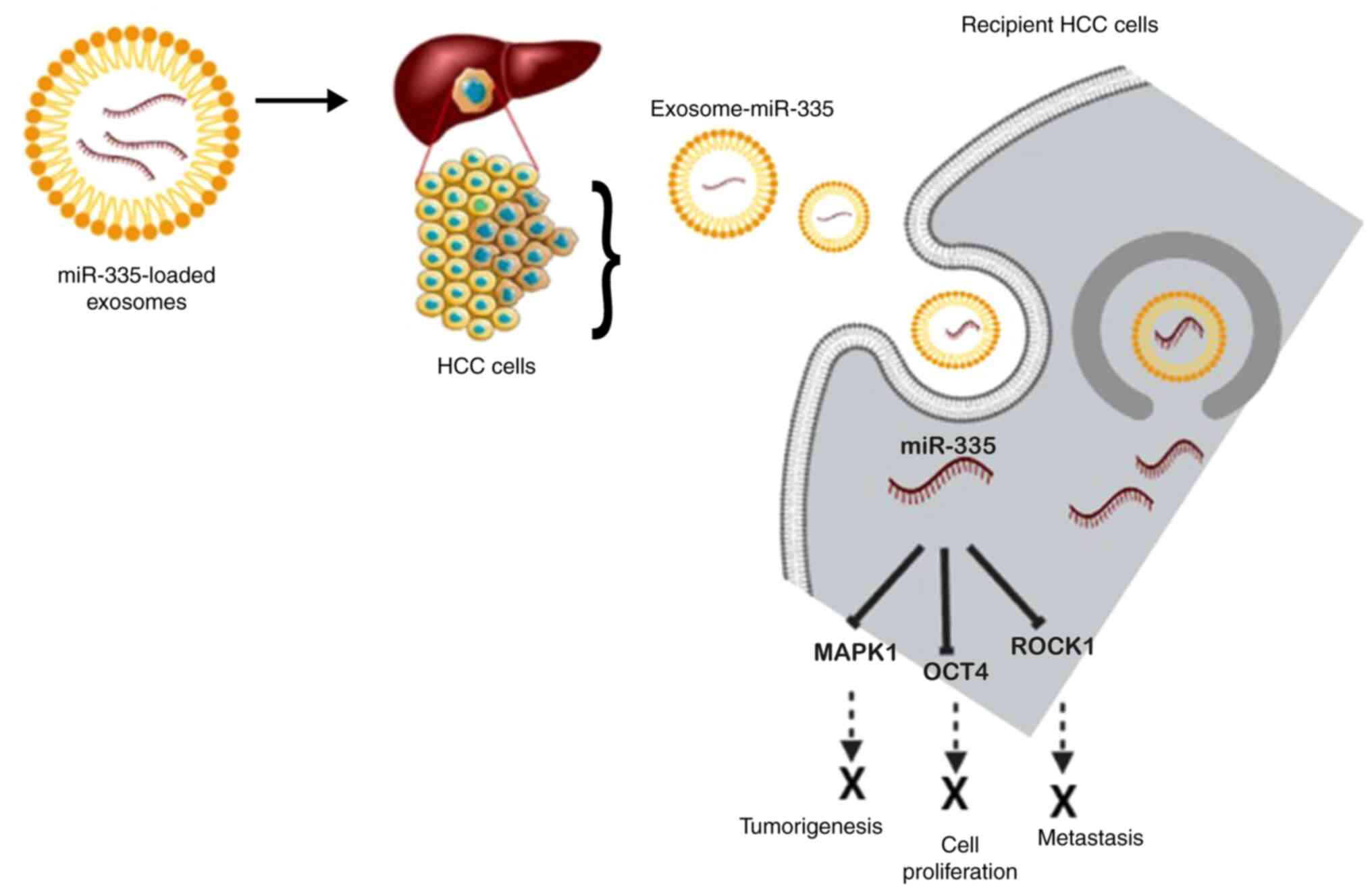
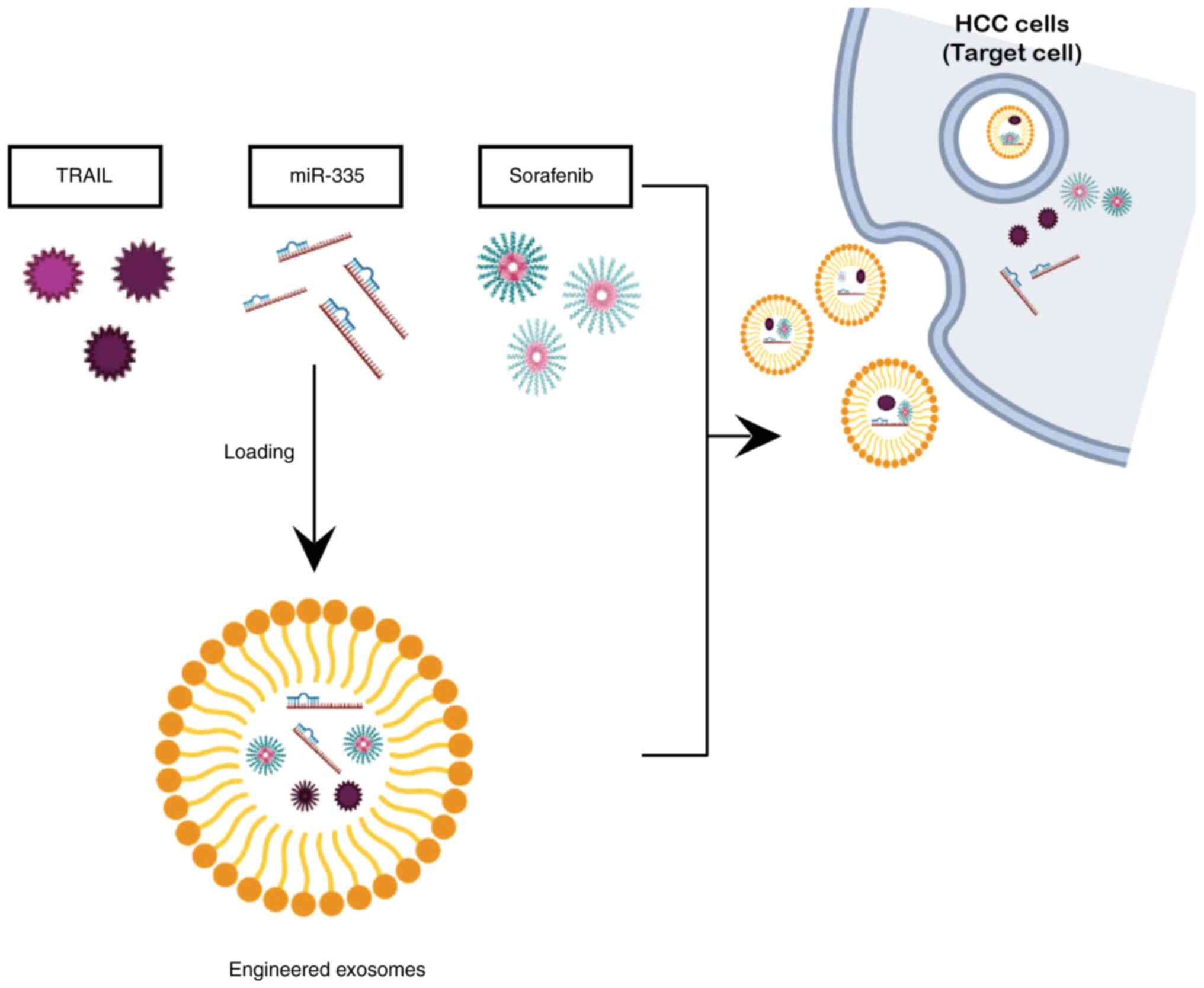
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singal AG and El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular
carcinoma from epidemiology to prevention: Translating knowledge
into practice. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:2140–2151. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dasgupta P, Henshaw C, Youlden DR, Clark
PJ, Aitken JF and Baade PD: Global trends in incidence rates of
primary adult liver cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Front Oncol. 10:1712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gomes MA, Priolli DG, Tralhão JG and
Botelho MF: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, biology,
diagnosis, and therapies. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 59:514–524.
2013.In English, Portuguese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Center MM and Jemal A: International
trends in liver cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 20:2362–2368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farinati F, Sergio A, Baldan A, Giacomin
A, Di Nolfo MA, Del Poggio P, Benvegnu L, Rapaccini G, Zoli M,
Borzio F, et al: Early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma:
When and how much do staging and choice of treatment really matter?
A multi-center study. BMC Cancer. 9:332009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kakushadze Z, Raghubanshi R and Yu W:
Estimating cost savings from early cancer diagnosis. Data.
2:302017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Finn RS: Emerging targeted strategies in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 33(Suppl 1):
S11–S19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
WHO's International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC): World Cancer Report 2014. Stewart BW and Kleihues P:
IARC Press; Lyon: 2014
|
|
10
|
Dimitroulis D, Damaskos C, Valsami S,
Davakis S, Garmpis N, Spartalis E, Athanasiou A, Moris D,
Sakellariou S, Kykalos S, et al: From diagnosis to treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An epidemic problem for both developed
and developing world. World J Gastroenterol. 23:5282–5294. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arruebo M, Vilaboa N, Saez-Gutierrez B,
Lambea J, Tres A, Valladares M and González-Fernández A: Assessment
of the evolution of cancer treatment therapies. Cancers (Basel).
3:3279–3330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Madabushi R, Booth B,
Chattopadhyay S, Sridhara R, Justice R and Pazdur R: Sorafenib for
the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist.
14:95–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux
M, Kim TY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, et al: Atezolizumab
plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 382:1894–1905. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ikeda K, Kudo M, Kawazoe S, Osaki Y, Ikeda
M, Okusaka T, Tamai T, Suzuki T, Hisai T, Hayato S, et al: Phase 2
study of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 52:512–519. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin C, Wang A, Liu L, Wang G, Li G and Han
Z: miR-145-5p inhibits tumor occurrence and metastasis through the
NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting TLR4 in malignant melanoma. J
Cell Biochem. Jan 30–2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget.
6:8474–8490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hydbring P, Wang Y, Fassl A, Li X, Matia
V, Otto T, Choi YJ, Sweeney KE, Suski JM, Yin H, et al:
Cell-cycle-targeting MicroRNAs as therapeutic tools against
refractory cancers. Cancer Cell. 31:576–590.e8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nagy Á, Lánczky A, Menyhárt O and Győrffy
B: Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma
using expression data of independent datasets. Sci Rep. 8:92272018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Xu M, Zhou F and Yan J:
Serum miR-1301-3p, miR-335-5p, miR-28-5p and their target B7-H3 may
serve as novel biomarkers for colorectal cancer. J BUON.
24:1120–1127. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Du W, Tang H, Lei Z, Zhu J, Zeng Y, Liu Z
and Huang JA: miR-335-5p inhibits TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer via
ROCK1. Respir Res. 20:2252019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xu X, Tao Y, Shan L, Chen R, Jiang H, Qian
Z, Cai F, Ma L and Yu Y: The role of MicroRNAs in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cancer. 9:3557–3569. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang G, Dong F, Xu Z, Sharma S, Hu X, Chen
D, Zhang L, Zhang J and Dong Q: MicroRNA profile in HBV-induced
infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 17:8052017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gougelet A: Exosomal microRNAs as a
potential therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 10:785–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ye L, Wang F, Wu H, Yang H, Yang Y, Ma Y,
Xue A, Zhu J, Chen M, Wang J and Zhang QA: Functions and targets of
miR-335 in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 14:3335–3349. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Scarola M, Schoeftner S, Schneider C and
Benetti R: miR-335 directly targets Rb1 (pRb/p105) in a proximal
connection to p53-dependent stress response. Cancer Res.
70:6925–6933. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Bian T, Feng J, Qian L, Zhang J,
Jiang D, Zhang Q, Li X, Liu Y and Shi J: miR-335 inhibited cell
proliferation of lung cancer cells by target Tra2β. Cancer Sci.
109:289–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tang H, Zhu J, Du W, Liu S, Zeng Y, Ding
Z, Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu Z and Huang J: CPNE1 is a target of
miR-335-5p and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of
non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1312018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li HW and Liu J: Circ_0009910 promotes
proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through miR-335-5p/ROCK1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:1725–1735. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Li W, Chen C, Pei Y and Long X:
MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via
downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 36:6313–6319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen K and Zhang L: LINC00339 regulates
ROCK1 by miR-152 to promote cell proliferation and migration in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 120:14431–14443. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen C, Wu CQ, Zhang ZQ, Yao DK and Zhu L:
Loss of expression of miR-335 is implicated in hepatic stellate
cell migration and activation. Exp Cell Res. 317:1714–1725. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang X, Song H, Zi Z, Kou J, Chen S, Dai
Y, Wang J, Yuan L and Gao K: Circ_0005075 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by suppression of microRNA-335. J Cell
Physiol. 234:21937–21946. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Li X, Yao Z, Wei C, Ning N and Li
J: GABAergic signaling facilitates breast cancer metastasis by
promoting ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation. Cancer Lett.
348:100–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji YY, Song Y and Wang AN: MiR-335-5p
inhibits proliferation of Huh-7 liver cancer cells via targeting
the Oct4/Akt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:1853–1860.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang BJ, Gong HY, Zheng F, Liu DJ and Liu
HX: Up-regulation of miR-335 predicts a favorable prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:6213–6218. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim Y, Kim H, Park D and Jeoung D: miR-335
targets SIAH2 and confers sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs by
increasing the expression of HDAC3. Mol Cells. 38:562–572. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng Y and Shen P: miR-335 acts as a
tumor suppressor and enhances ionizing radiation-induced tumor
regression by targeting ROCK1. Front Oncol. 10:2782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cui L, Hu Y, Bai B and Zhang S: Serum
miR-335 level is associated with the treatment response to
trans-arterial chemoembolization and prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:276–283. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen S and Xia X: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1
suppresses sorafenib sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
via regulating miR-335-c-Met. J Cell Physiol. Apr 1–2019.Epub ahead
of print.
|
|
47
|
Dohi O, Yasui K, Gen Y, Takada H, Endo M,
Tsuji K, Konishi C, Yamada N, Mitsuyoshi H, Yagi N, et al:
Epigenetic silencing of miR-335 and its host gene MEST in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:411–418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Shang X, Li G, Liu H, Li T, Liu J, Zhao Q
and Wang C: Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals that hsa_
circ_0005075, a new circular RNA biomarker, is involved in
hepatocellular crcinoma development. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e38112016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nie Y, Zhu X, Bu N, Jiang Y, Su Y, Pan K
and Li S: Circ_0064288 acts as an oncogene of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by inhibiting miR-335-5p expression and promoting
ROCK1 expression. BMC Cancer. 22:2652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Apoptosis
control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
11:255–260. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wajant H: Molecular mode of action of
TRAIL receptor agonists-common principles and their translational
exploitation. Cancers (Basel). 11:9542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Amarante-Mendes GP and Griffith TS:
Therapeutic applications of TRAIL receptor agonists in cancer and
beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 155:117–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Willms A, Schittek H, Rahn S, Sosna J,
Mert U, Adam D and Trauzold A: Impact of p53 status on
TRAIL-mediated apoptotic and non-apoptotic signaling in cancer
cells. PLoS One. 14:e02148472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Micheau O, Shirley S and Dufour F: Death
receptors as targets in cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 169:1723–1744.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lim B, Allen JE, Prabhu VV, Talekar MK,
Finnberg NK and El-Deiry WS: Targeting TRAIL in the treatment of
cancer: New developments. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:1171–1185.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Graves JD, Kordich JJ, Huang TH, Piasecki
J, Bush TL, Sullivan T, Foltz IN, Chang W, Douangpanya H, Dang T,
et al: Apo2L/TRAIL and the death receptor 5 agonist antibody AMG
655 cooperate to promote receptor clustering and antitumor
activity. Cancer Cell. 26:177–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zamai L, Ahmad M, Bennett IM, Azzoni L,
Alnemri ES and Perussia B: Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated
cytotoxicity: Differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature
and mature primary human NK cells. J Exp Med. 188:2375–2380. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang Y, Yang X, Xu T, Kong Q, Zhang Y,
Shen Y, Wei Y, Wang G and Chang KJ: Overcoming resistance to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in solid tumor cells by simultaneously
targeting death receptors, c-FLIP and IAPs. Int J Oncol.
49:153–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Galal El-Shemi A, Mohammed Ashshi A, Oh E,
Jung BK, Basalamah M, Alsaegh A and Yun CO: Efficacy of combining
ING4 and TRAIL genes in cancer-targeting gene virotherapy strategy:
First evidence in preclinical hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Ther.
25:54–65. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG, Kurzrock R,
Ebbinghaus S, O'Dwyer PJ, Gordon MS, Novotny W, Goldwasser MA,
Tohnya TM, Lum BL, et al: Phase I dose-escalation study of
recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor
agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:2839–2846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS,
Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA,
et al: Identification and characterization of a new member of the
TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue
CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A: Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2
ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family.
J Biol Chem. 271:12687–12690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu CH, Chern GJ, Hsu FF, Huang KW, Sung
YC, Huang HC, Qiu JT, Wang SK, Lin CC, Wu CH, et al: A
multifunctional nanocarrier for efficient TRAIL-based gene therapy
against hepatocellular carcinoma with desmoplasia in mice.
Hepatology. 67:899–913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kim CY, Jeong M, Mushiake H, Kim BM, Kim
WB, Ko JP, Kim MH, Kim M, Kim TH, Robbins PD, et al: Cancer gene
therapy using a novel secretable trimeric TRAIL. Gene Ther.
13:330–338. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Grisendi G, Bussolari R, Cafarelli L,
Petak I, Rasini V, Veronesi E, De Santis G, Spano C, Tagliazzucchi
M, Barti-Juhasz H, et al: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells as
stable source of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand delivery for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 70:3718–3729. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu S, Qiu J, He G, He W, Liu C, Cai D and
Pan H: TRAIL promotes hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis and
inhibits proliferation and migration via interacting with IER3.
Cancer Cell Int. 21:632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lemke J, von Karstedt S, Zinngrebe J and
Walczak H: Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Cell
Death Differ. 21:1350–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Holland PM: Death receptor agonist
therapies for cancer, which is the right TRAIL? Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 25:185–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang L, Gu J, Lin T, Huang X, Roth JA and
Fang B: Mechanisms involved in development of resistance to
adenovirus-mediated proapoptotic gene therapy in DLD1 human colon
cancer cell line. Gene Ther. 9:1262–1270. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hinz S, Trauzold A, Boenicke L, Sandberg
C, Beckmann S, Bayer E, Walczak H, Kalthoff H and Ungefroren H:
Bcl-XL protects pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells against CD95- and
TRAIL-receptor-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene. 19:5477–5486. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Zuzak TJ, Wiewrodt
BR, Ho R, Ikegaki N and Brodeur GM: Resistance to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis
in neuroblastoma cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8
expression. Cancer Res. 61:1314–1319. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Marini P, Denzinger S, Schiller D, Kauder
S, Welz S, Humphreys R, Daniel PT, Jendrossek V, Budach W and Belka
C: Combined treatment of colorectal tumours with agonistic TRAIL
receptor antibodies HGS-ETR1 and HGS-ETR2 and radiotherapy:
Enhanced effects in vitro and dose-dependent growth delay in vivo.
Oncogene. 25:5145–5154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R,
Alderson R, Bloom M, Sung C, Riccobene T, Johnson R, Fiscella M,
Mahoney A, et al: HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1
monoclonal antibody, induces cell death in multiple tumour types in
vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer. 92:1430–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kelley SK, Harris LA, Xie D, Deforge L,
Totpal K, Bussiere J and Fox JA: Preclinical studies to predict the
disposition of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in humans: characterization of in vivo
efcacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
299:31–38. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hymowitz SG, O'Connell MP, Ultsch MH,
Hurst A, Totpal K, Ashkenazi A, de Vos AM and Kelley RF: A unique
zinc-binding site revealed by a high-resolution X-ray structure of
homotrimeric Apo2L/TRAIL. Biochemistry. 39:633–640. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Mérino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Solary E
and Micheau O: TRAIL in cancer therapy: Present and future
challenges. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:1299–1314. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lawrence D, Shahrokh Z, Marsters S,
Achilles K, Shih D, Mounho B, Hillan K, Totpal K, DeForge L, Schow
P, et al: Differential hepatocyte toxicity of recombinant
Apo2L/TRAIL versions. Nat Med. 7:383–385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ashley DM, Riffkin CD, Lovric MM, Mikeska
T, Dobrovic A, Maxwell JA, Friedman HS, Drummond KJ, Kaye AH, Gan
HK, et al: In vitro sensitivity testing of minimally passaged and
uncultured gliomas with TRAIL and/or chemotherapy drugs. Br J
Cancer. 99:294–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bae S, Ma K, Kim TH, Lee ES, Oh KT, Park
ES, Lee KC and Youn YS: Doxorubicin-loaded human serum albumin
nanoparticles surface-modified with TNF-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand and transferrin for targeting multiple tumor types.
Biomaterials. 33:1536–1546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Mitchell MJ, Wayne E, Rana K, Schaffer CB
and King MR: TRAIL-coated leukocytes that kill cancer cells in the
circulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:930–935. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Naval J, de Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A,
Anel A and Martinez-Lostao L: Importance of TRAIL molecular anatomy
in receptor oligomerization and signaling Implications for cancer
therapy. Cancers (Basel). 11:4442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Griffith T, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger LM,
Maliszewski CR and Fanger NA: Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal
activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J
Exp Med. 189:1343–1354. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama M,
Kawasaki A, Akiba H, Okumura K and Yagita H: Involvement of
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in human CD4+ T cell-mediated
cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 162:2639–2647. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Monleón I, Martínez-Lorenzo MJ, Anel A,
Lasierra P, Larrad L, Pineiro A, Naval J and Alava MA: CD59
cross-linking induces secretion of APO2 ligand in overactivated
human T cells. Eur J Immunol. 30:1078–1087. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Monleón I, Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Monteagudo
L, Lasierra P, Taulés M, Iturralde M, Piñeiro A, Larrad L, Alava
MA, Naval J and Anel A: Differential secretion of Fas ligand- or
APO2 ligand/TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-carrying
microvesicles during activation-induced death of human T cells. J
Immunol. 167:6736–6744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wajant H, Moosmayer D, Wüest T, Bartke T,
Gerlach E, Schönherr U, Peters N, Scheurich P and Pfizenmaier K:
Differential activation of TRAIL-R1 and -2 by soluble and membrane
TRAIL allows selective surface antigen-directed activation of
TRAIL-R2 by a soluble TRAIL derivative. Oncogene. 20:4101–4106.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
De Miguel D, Basáñez G, Sánchez D, Malo
PG, Marzo I, Larrad L, Naval J, Pardo J, Anel A and Martinez-Lostao
L: Liposomes decorated with Apo2L/TRAIL overcome chemoresistance of
human hematologic tumor cells. Mol Pharm. 10:893–904. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
De Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A, Anel A and
Martinez-Lostao L: Liposome-bound TRAIL induces superior DR5
clustering and enhanced DISC recruitment in histiocytic lymphoma
U937 cells. Leuk Res. 39:657–666. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
De Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A, Ayuso JM,
Erviti-Ardanaz S, Pazo-Cid R, del Agua C, Fernández LJ, Ochoa I,
Anel A and Martinez-Lostao L: TRAIL-coated lipid-nanoparticles
overcome resistance to soluble recombinant TRAIL in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Nanotechnology. 27:1851012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
De Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A, Ayuso JM,
Pejenaute-Ochoa D, Jarauta V, Marzo I, Fernández LJ, Ochoa I, Conde
B, Anel A and Martinez-Lostao L: High-order TRAIL oligomer
formation in TRAIL-coated lipid nanoparticles enhances DR5
cross-linking and increases antitumour effect against colon cancer.
Cancer Lett. 383:250–260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kim TH, Jiang HH, Park CW, Youn YS, Lee S,
Chen X and Lee KC: PEGylated TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
(TRAIL)-loaded sustained release PLGA microspheres for enhanced
stability and antitumor activity. J Control Release. 150:63–69.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chinnappan M, Srivastava A, Amreddy N,
Razaq M, Pareek V, Ahmed R, Mehta M, Peterson JE, Munshi A and
Ramesh R: Exosomes as drug delivery vehicle and contributor of
resistance to anticancer drugs. Cancer Lett. 486:18–28. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang J, Yeung BZ, Cui M, Peer CJ, Lu Z,
Figg WD, Guillaume Wientjes M, Woo S and Au JL: Exosome is a
mechanism of inter-cellular drug transfer: Application of
quantitative pharmacology. J Control Release. 268:147–158. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lee Y, El Andaloussi S and Wood MJ:
Exosomes and microvesicles: Extracellular vesicles for genetic
information transfer and gene therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 21:R125–R134.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lee JK, Park SR, Jung BK, Jeon YK, Lee YS,
Kim MK, Kim YG, Jang JY and Kim CW: Exosomes derived from
mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating
VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e842562013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Syn NL, Wang L, Chow EK, Lim CT and Goh
BC: Exosomes in cancer nanomedicine and immunotherapy: Prospects
and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 35:665–676. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ha D, Yang N and Nadithe V: Exosomes as
therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological
membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm
Sin B. 6:287–296. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Farooqi AA, Desai NN, Qureshi MZ,
Librelotto DRN, Gasparri ML, Bishayee A, Nabavi SM, Curti V and
Daglia M: Exosome biogenesis, bioactivities and functions as new
delivery systems of natural compounds. Biotechnol Adv. 36:328–334.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Maia J, Caja S, Strano Moraes MC, Couto N
and Costa-Silva B: Exosome-based cell-cell communication in the
tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Yeo RW, Lai RC, Zhang B, Tan SS, Yin Y,
The BJ and Lim SK: Mesenchymal stem cell: An efficient mass
producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
65:336–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Lou G, Chen Z, Zheng M and Liu Y:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic
strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 49:e3462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Cho BS, Kim JO, Ha DH and Yi YW: Exosomes
derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells
alleviate atopic dermatitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:1872018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
El-Andaloussi S, Lee Y, Lakhal-Littleton
S, Li J, Seow Y, Gardiner C, Alvarez-Erviti L, Sargent IL and Wood
MJ: Exosome-mediated delivery of siRNA in vitro and in vivo. Nat
Protoc. 7:2112–2126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, Rotan O,
Horn PA, Epple M and Giebel B: Characterisation of exosomes derived
from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning
electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 87:146–150.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kalra H, Adda CG, Liem M, Ang CS, Mechler
A, Simpson RJ, Hulett MD and Mathivanan S: Comparative proteomics
evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of
the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics.
13:3354–3364. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Rani S, Ryan AE, Griffin MD and Ritter T:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward
cell-free therapeutic applications. Mol Ther. 23:812–823. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sun L, Xu R, Sun X, Duan Y, Han Y, Zhao Y,
Qian H, Zhu W and Xu W: Safety evaluation of exosomes derived from
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell. Cytotherapy.
18:413–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C,
Lakhal S and Wood MJ: Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by
systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol.
29:341–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
El Andaloussi S, Lakhal S, Mäger I and
Wood MJ: Exosomes for targeted siRNA delivery across biological
barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 65:391–397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Escudier B, Dorval T, Chaput N, André F,
Caby MP, Novault S, Flament C, Leboulaire C, Borg C, Amigorena S,
et al: Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous
dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: Results of thefirst phase I
clinical trial. J Transl Med. 3:102005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Morse MA, Garst J, Osada T, Khan S,
Hobeika A, Clay TM, Valente N, Shreeniwas R, Sutton MA, Delcayre A,
et al: A phase I study of dexosome immunotherapy in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. 3:92005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Dai S, Wei D, Wu Z, Zhou X, Wei X, Huang H
and Li G: Phase I clinical trial of autologous ascites-derived
exosomes combined with GM-CSF for colorectal cancer. Mol Ther.
16:782–790. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Iranifar E, Seresht BM, Momeni F, Fadaei
E, Mehr MH, Ebrahimi Z, Rahmati M, Kharazinejad E and Mirzaei H:
Exosomes and microRNAs: New potential therapeutic candidates in
Alzheimer disease therapy. J Cell Physiol. 234:2296–2305. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Qu M, Lin Q, Huang L, Fu Y, Wang L, He S,
Fu Y, Yang S, Zhang Z, Zhang L and Sun X: Dopamine-loaded blood
exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson's
disease. J Control Release. 287:156–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang H, Sui H, Zheng Y, Jiang Y, Shi Y,
Liang J and Zhao L: Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate
cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of
the Tau protein through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Nanoscale.
11:7481–7496. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Yuan D, Deygen
I, Klyachko NL, Kabanov AV and Batrakova EV: Engineering
macro-phage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to
pulmonary metastases: In vitro and in vivo evaluations.
Nanomedicine. 14:195–204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Azmi AS, Bao B and Sarkar FH: Exosomes in
cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: A
comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:623–642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Mendt M, Kamerkar S, Sugimoto H, McAndrews
KM, Wu CC, Gagea M, Yang S, Blanko EVR, Peng Q, Ma X, et al:
Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic
cancer. JCI Insight. 3:e992632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wang Y, Balaji V, Kaniyappan S, Krüger L,
Irsen S, Tepper K, Chandupatla R, Maetzler W, Schneider A,
Mandelkow E and Mandelkow EM: The release and trans-synaptic
transmission of Tau via exosomes. Mol Neurodegener. 12:52017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Jiang XC and Gao JQ: Exosomes as novel
bio-carriers for gene and drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 521:167–175.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hadla M, Palazzolo S, Corona G, Caligiuri
I, Canzonieri V, Toffoli G and Rizzolio F: Exosomes increase the
therapeutic index of doxorubicin in breast and ovarian cancer mouse
models. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:2431–2441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Smyth TJ, Redzic JS, Graner MW and
Anchordoquy TJ: Examination of the specificity of tumor cell
derived exosomes with tumor cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1838:2954–2965. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Mahajan V,
Deygen I, Klyachko NL, Inskoe E, Piroyan A, Sokolsky M, Okolie O,
et al: Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome
MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 12:655–664. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S,
Audet J, Dvorak HF and Chan WCW: Analysis of nanoparticle delivery
to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 1:160142016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Faivre S, Rimassa L and Finn RS: Molecular
therapies for HCC: Looking outside the box. J Hepatol. 72:342–352.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Trivedi R and Mishra DP: Trailing TRAIL
resistance: Novel targets for TRAIL sensitization in cancer cells.
Front Oncol. 5:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Sterzenbach U, Putz U, Low LH, Silke J,
Tan SS and Howitt J: Engineered exosomes as vehicles for
biologically active proteins. Mol Ther. 25:1269–1278. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Rivoltini L, Chiodoni C, Squarcina P,
Tortoreto M, Villa A, Vergani B, Bürdek M, Botti L, Arioli I, Cova
A, et al: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-armed
exosomes deliver proapoptotic signals to tumor site. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:3499–3512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Yuan Z, Kolluri KK, Gowers KH and Janes
SM: TRAIL delivery by MSC-derived extracellular vesicles is an
effective anticancer therapy. J Extracell Vesicles. 6:12652912017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Shamili FH, Bayegi HR, Salmasi Z, Sadri K,
Mahmoudi M, Kalantari M, Ramezani M and Abnous K: Exosomes derived
from TRAIL-engineered mesenchymal stem cells with effective
anti-tumor activity in a mouse melanoma model. Int J Pharm.
549:218–229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Nojiri K, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K, Tameda M,
Inagaki Y, Ogura S, Kasai C, Kusagawa S, Yoneda M, Yamamoto N, et
al: Sorafenib and TRAIL have synergistic effect on hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:101–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Chen KF, Tai WT, Liu TH, Huang HP, Lin YC,
Shiau CW, Li PK, Chen PJ and Cheng AL: Sorafenib overcomes TRAIL
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the inhibition
of STAT3. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5189–5199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Munir J, Yoon JK and Ryu S: Therapeutic
miRNA-enriched extracellular vesicles: Current approaches and
future prospects. Cells. 9:22712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Almanza G, Rodvold JJ, Tsui B, Jepsen K,
Carter H and Zanetti M: Extracellular vesicles produced in B cells
deliver tumor suppressor miR-335 to breast cancer cells disrupting
oncogenic programming in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 8:175812018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Li L, Piontek K, Ishida M, Fausther M,
Dranoff JA, Fu R, Mezey E, Gould SJ, Fordjour FK, Meltzer SJ, et
al: Extracellular vesicles carry microRNA-195 to intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma and improve survival in a rat model. Hepatology.
65:501–514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Wang F, Li L, Piontek K, Sakaguchi M and
Selaru FM: Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 67:940–954. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Andriolo G, Provasi E, Lo Cicero V,
Brambilla A, Soncin S, Torre T, Milano G, Biemmi V, Vassalli G,
Turchetto L, et al: Exosomes from human cardiac progenitor cells
for therapeutic applications: Development of a GMP-grade
manufacturing method. Front Physiol. 9:11692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Yoo KH, Thapa N, Kim BJ, Lee JO, Jang YN,
Chwae YJ and Kim J: Possibility of exosome-based coronavirus
disease 2019 vaccine (review). Mol Med Rep. 25:262022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Cooke JN, Ellis JA, Hossain S, Nguyen J,
Bruce JN and Joshi S: Computational pharmacokinetic rationale for
intra-arterial delivery to the brain. Drug Deliv Transl Res.
6:622–629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Ciuleanu T, Bazin I, Lungulescu D, Miron
L, Bondarenko I, Deptala A, Rodriguez-Torres M, Giantonio B, Fox
NL, Wissel P, et al: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
phase II study to assess the efficacy and safety of mapatumumab
with sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Ann Oncol. 27:680–687. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
von Pawel J, Harvey JH, Spigel DR, Dediu
M, Reck M, Cebotaru CL, Humphreys RC, Gribbin MJ, Fox NL and
Camidge DR: Phase II trial of mapatumumab, a fully human agonist
monoclonal anti-body to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 1 (TRAIL-R1), in combination
with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 15:188–196.e2. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Davies A, Sage B, Kolluri K, Alrifai D,
Graham R, Weil B, Rego R, Bain O, Patrick PS, Champion K, et al:
TACTICAL: A phase I/II trial to assess the safety and efficacy of
MSCTRAIL in the treatment of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 37:TPS91162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Forero A, Bendell JC, Kumar P, Janisch L,
Rosen M, Wang Q, Copigneaux C, Desai M, Senaldi G and Maitland ML:
First-in-human study of the antibody DR5 agonist DS-8273a in
patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 35:298–306.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Xie Y, Bai O, Zhang H, Yuan J, Zong S,
Chibbar R, Slattery K, Qureshi M, Wei Y, Deng Y and Xiang J:
Membrane-bound HSP70-engineered myeloma cell-derived exosomes
stimulate more efficient CD8(+) CTL- and NK-mediated antitumour
immunity than exosomes released from heat-shocked tumour cells
expressing cytoplasmic HSP70. J Cell Mol Med. 14:2655–2666. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Ke C, Hou H, Li J, Su K, Huang C, Lin Y,
Lu Z, Du Z, Tan W and Yuan Z: Extracellular vesicle delivery of
TRAIL eradicates resistant tumor growth in combination with CDK
inhibition by dinaciclib. Cancers (Basel). 12:11572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Yuan Q, Su K, Li S, Long X, Liu L, Yang M,
Yuan X, Sun J, Hu J, Li Q, et al: Pulmonary delivery of
extracellular vesicle-encapsulated dinaciclib as an effective lung
cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 14:35502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Jiang L, Gu Y, Du Y, Tang X, Wu X and Liu
J: Engineering exosomes endowed with targeted delivery of
triptolide for malignant melanoma therapy. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 13:42411–42428. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|