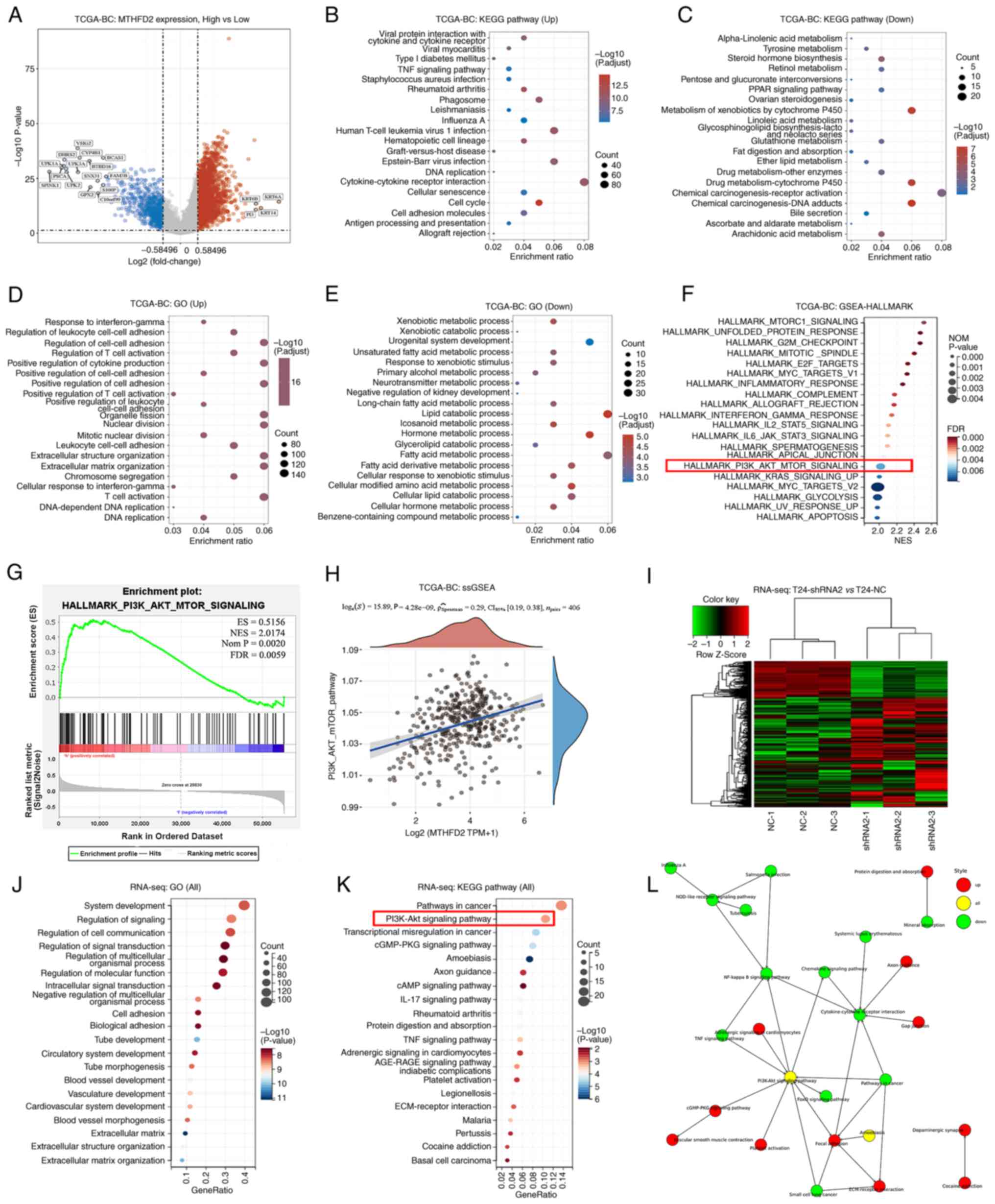
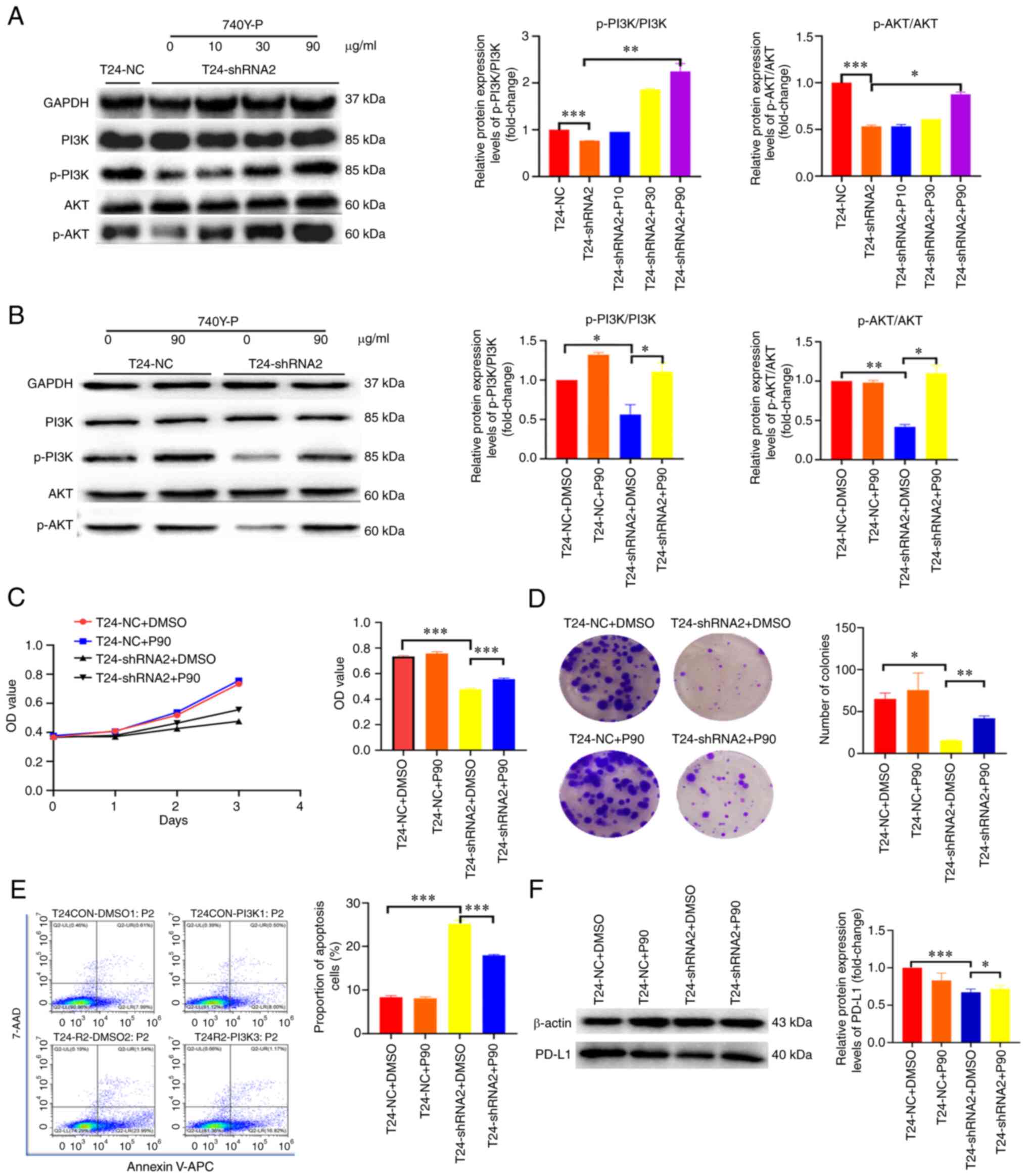
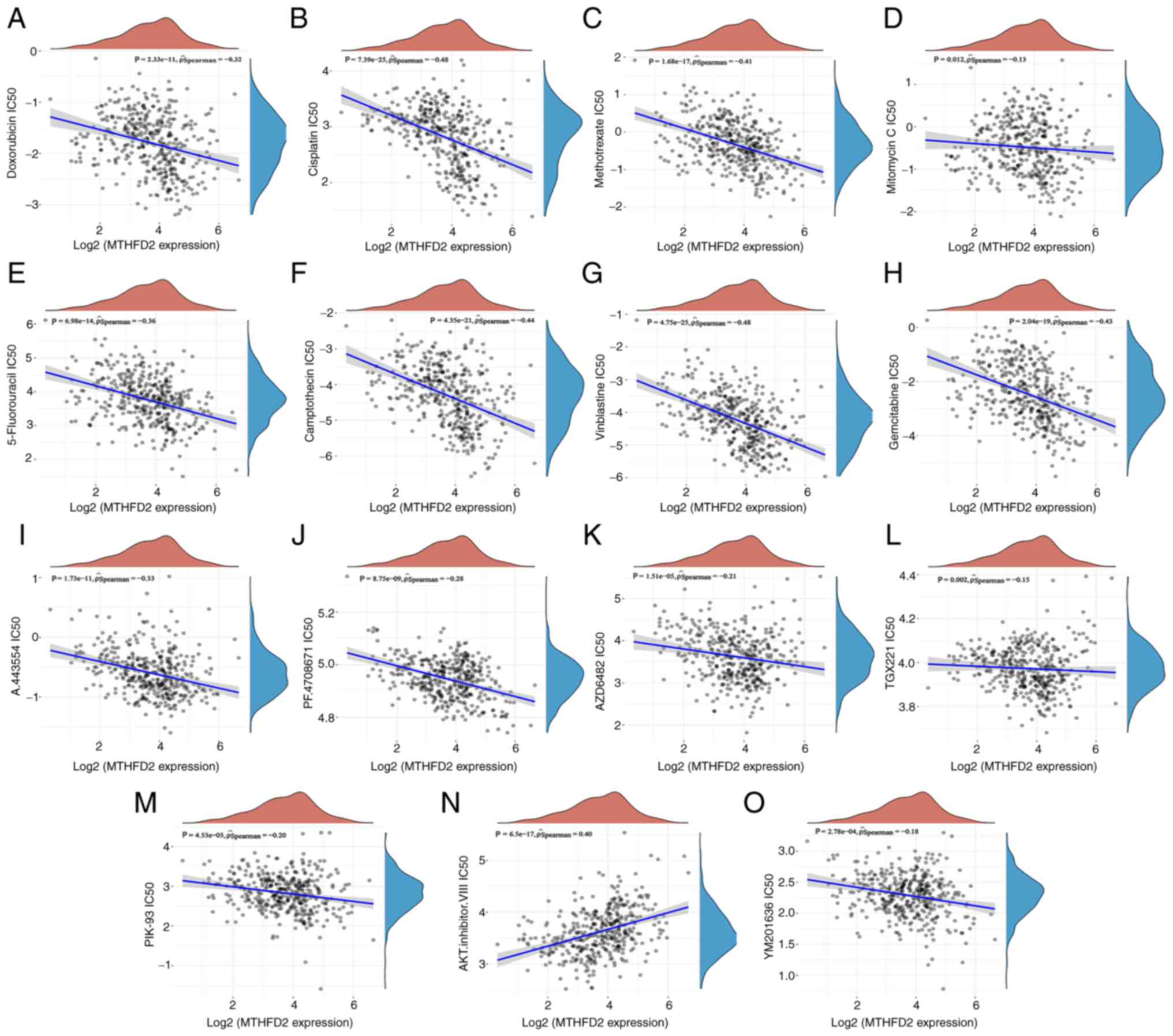
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schmitz-Drager BJ, Droller M, Lokeshwar
VB, Lotan Y, Hudson MA, van Rhijn BW, Marberger MJ, Fradet Y,
Hemstreet GP, Malmstrom PU, et al: Molecular markers for bladder
cancer screening, early diagnosis, and surveillance: The WHO/ICUD
consensus. Urol Int. 94:1–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, Compérat
EM, Cowan NC, Gakis G, Hernández V, Espinós EL, Lorch A, Neuzillet
Y, et al: European association of urology guidelines on
muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2020
guidelines. Eur Urol. 79:82–104. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lopez-Beltran A, Cimadamore A, Blanca A,
Massari F, Vau N, Scarpelli M, Cheng L and Montironi R: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of bladder cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 13:1312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balar AV, Galsky MD, Rosenberg JE, Powles
T, Petrylak DP, Bellmunt J, Loriot Y, Necchi A, Hoffman-Censits J,
Perez-Gracia JL, et al: Atezolizumab as first-line treatment in
cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and metastatic
urothelial carcinoma: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial.
Lancet. 389:67–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Stenehjem DD, Tran D, Nkrumah MA and Gupta
S: PD1/PDL1 inhibitors for the treatment of advanced urothelial
bladder cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 11:5973–5989. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mejia NR and MacKenzie RE: NAD-dependent
methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase is expressed by immortal
cells. J Biol Chem. 260:14616–14620. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nilsson R, Jain M, Madhusudhan N, Sheppard
NG, Strittmatter L, Kampf C, Huang J, Asplund A and Mootha VK:
Metabolic enzyme expression highlights a key role for MTHFD2 and
the mitochondrial folate pathway in cancer. Nat Commun. 5:31282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cui X, Su H, Yang J, Wu X, Huo K, Jing X
and Zhang S: Up-regulation of MTHFD2 is associated with
clinicopathological characteristics and poor survival in ovarian
cancer, possibly by regulating MOB1A signaling. J Ovarian Res.
15:232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ju HQ, Lu YX, Chen DL, Zuo ZX, Liu ZX, Wu
QN, Mo HY, Wang ZX, Wang DS, Pu HY, et al: Modulation of redox
homeostasis by inhibition of MTHFD2 in colorectal cancer:
Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Natl Cancer Inst.
111:584–596. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Lin H, Huang B, Wang H, Liu X, Hong Y, Qiu
S and Zheng J: MTHFD2 overexpression predicts poor prognosis in
renal cell carcinoma and is associated with cell proliferation and
vimentin-modulated migration and invasion. Cell Physiol Biochem.
51:991–1000. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu F, Liu Y, He C, Tao L, He X, Song H
and Zhang G: Increased MTHFD2 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:8685–8690. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Huang Y, Jiang C, Ou H, Guo B, Liao
H, Li X and Yang D: Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2
overexpression is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 48:953–960.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang J, Qin Y, Lin C, Huang X and Zhang
F: MTHFD2 facilitates breast cancer cell proliferation via the AKT
signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 22:7032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei Y, Liu P, Li Q, Du J, Chen Y, Wang Y,
Shi H, Wang Y, Zhang H, Xue W, et al: The effect of MTHFD2 on the
proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cell lines. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:6361–6370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi Y, Xu Y, Yao J, Yan C, Su H, Zhang X,
Chen E and Ying K: MTHFD2 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in
lung adenocarcinoma by regulating AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signalling.
J Cell Mol Med. 25:7013–7027. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Liu S, Piao C, Zhang Z, Zhang X,
Jiang Y and Kong C: Non-metabolic function of MTHFD2 activates CDK2
in bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 112:4909–4919. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu L, Liu X, Zhang W, Hu H, Wang Q and Xu
K: MTHFD2 is a potential oncogene for its strong association with
poor prognosis and high level of immune infiltrates in urothelial
carcinomas of bladder. BMC Cancer. 22:5562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dillies MA, Rau A, Aubert J,
Hennequet-Antier C, Jeanmougin M, Servant N, Keime C, Marot G,
Castel D, Estelle J, et al: A comprehensive evaluation of
normalization methods for Illumina high-throughput RNA sequencing
data analysis. Brief Bioinform. 14:671–683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu
JS, Li B and Liu XS: TIMER: A web server for comprehensive analysis
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 77:e108–e110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Xu X, Deng W, Huang M, Wu Y, Zhou
Z, Zhu K, Wang Y, Cheng X, Zhou X, et al: CCL18 enhances migration,
invasion and EMT by binding CCR8 in bladder cancer cells. Mol Med
Rep. 19:1678–1686. 2019.
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anders S, Pyl PT and Huber W: HTSeq-a
python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data.
Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Ma Y, Wu Z, Zeng F, Song B, Zhang Y,
Li J, Lui S and Wu M: Tumor mutational burden predicting the
efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 12:7514072021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grayson M: Bladder cancer. Nature.
551:S332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hurst CD, Alder O, Platt FM, Droop A,
Stead LF, Burns JE, Burghel GJ, Jain S, Klimczak LJ, Lindsay H, et
al: Genomic subtypes of non-invasive bladder cancer with distinct
metabolic profile and female gender bias in KDM6A mutation
frequency. Cancer Cell. 32:701–715.e707. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kobayashi T, Owczarek TB, McKiernan JM and
Abate-Shen C: Modelling bladder cancer in mice: Opportunities and
challenges. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:42–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Mariathasan S, Turley SJ, Nickles D,
Castiglioni A, Yuen K, Wang Y, Kadel EE III, Koeppen H, Astarita
JL, Cubas R, et al: TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1
blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature.
554:544–548. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ducker GS, Chen L, Morscher RJ,
Ghergurovich JM, Esposito M, Teng X, Kang Y and Rabinowitz JD:
Reversal of cytosolic one-carbon flux compensates for loss of the
mitochondrial folate pathway. Cell Metab. 23:1140–1153. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singer K, Cheng WC, Kreutz M, Ho PC and
Siska PJ: Immunometabolism in cancer at a glance. Dis Model Mech.
11:dmm0342722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sugiura A, Andrejeva G, Voss K, Heintzman
DR, Xu X, Madden MZ, Ye X, Beier KL, Chowdhury NU, Wolf MM, et al:
MTHFD2 is a metabolic checkpoint controlling effector and
regulatory T cell fate and function. Immunity. 55:65–81.e69. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Shang M, Yang H, Yang R, Chen T, Fu Y, Li
Y, Fang X, Zhang K, Zhang J, Li H, et al: The folate cycle enzyme
MTHFD2 induces cancer immune evasion through PD-L1 up-regulation.
Nat Commun. 12:19402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|