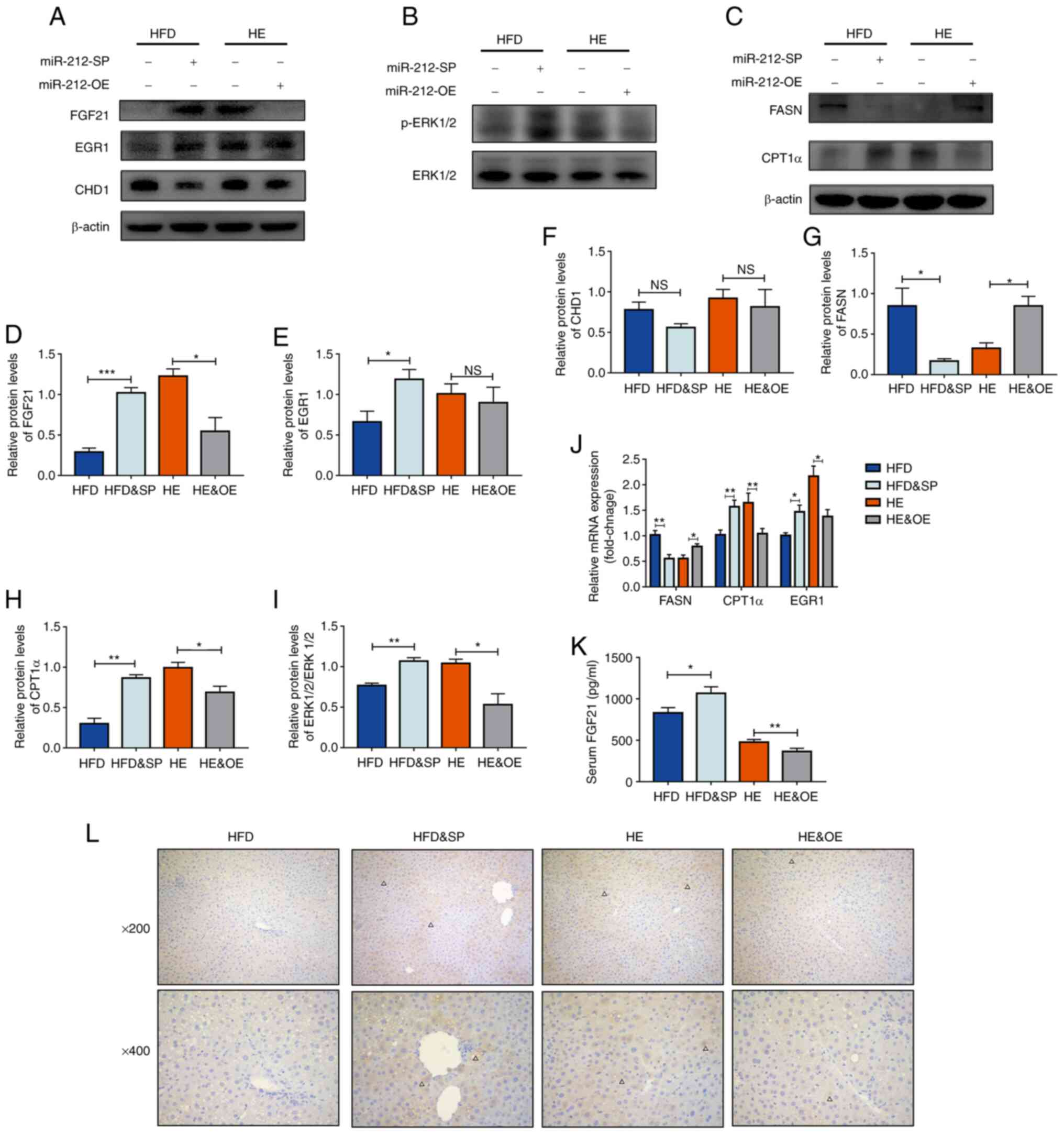
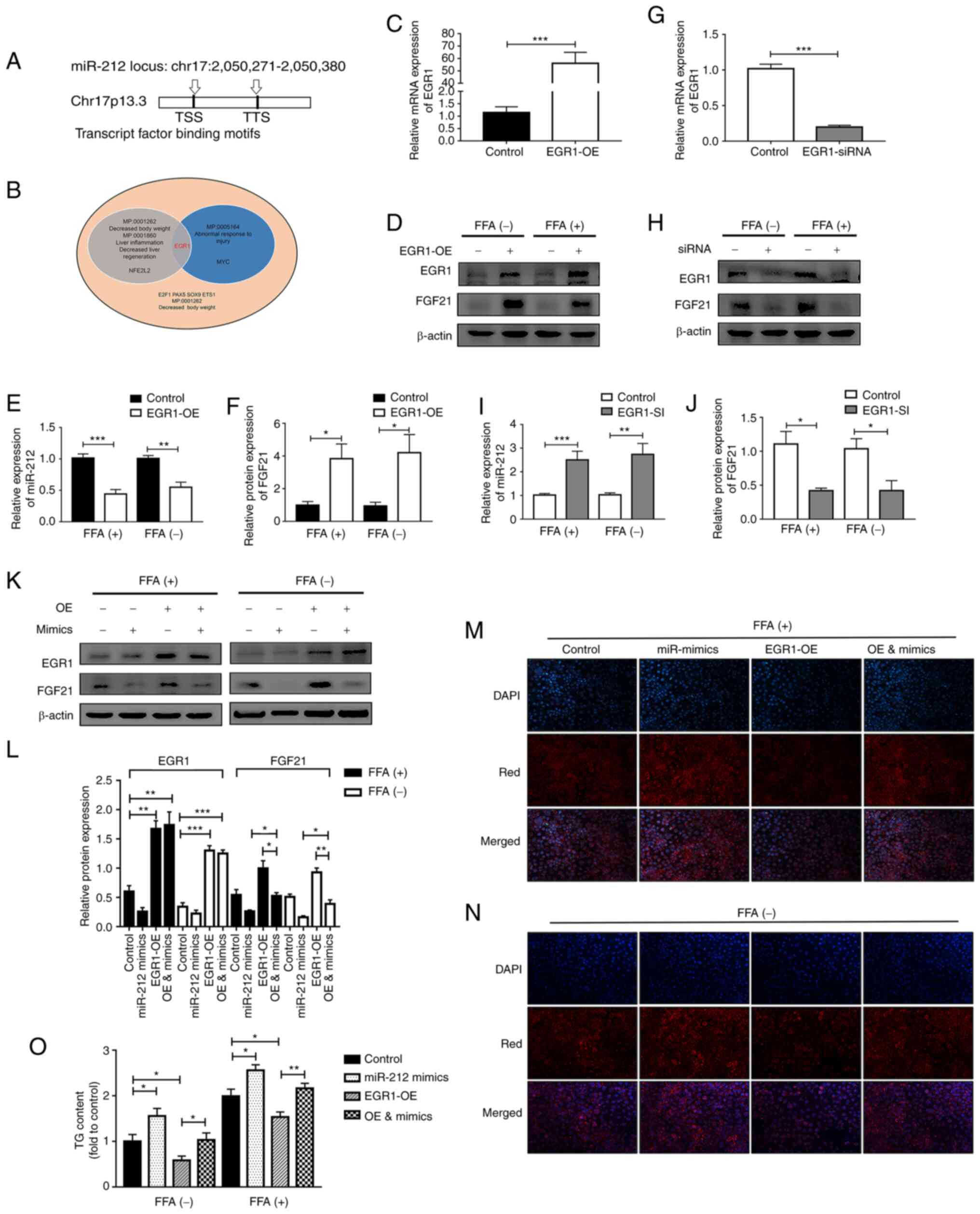
|
1
|
Simon TG, Roelstraete B, Khalili H,
Hagström H and Ludvigsson JF: Mortality in biopsy-confirmed
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from a nationwide cohort.
Gut. 70:1375–1382. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cotter TG and Rinella M: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease 2020: The state of the disease.
Gastroenterology. 158:1851–11864. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Younossi ZM: Patient-reported outcomes and
the economic effects of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The value proposition. Hepatology.
68:2405–2412. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rohilla S, Awasthi A, Kaur S and Puria R:
Evolutionary conservation of long non-coding RNAs in non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Life Sci. 264:1185602021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
El-Agroudy NN, Kurzbach A, Rodionov RN,
O'Sullivan J, Roden M, Birkenfeld AL and Pesta DH: Are lifestyle
therapies effective for NAFLD treatment? Trends Endocrinol Metab.
30:701–709. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takahashi H, Kotani K, Tanaka K, Egucih Y
and Anzai K: Therapeutic approaches to nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Exercise intervention and related mechanisms. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:5882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Keating SE, Hackett DA, Parker HM,
O'Connor HT, Gerofi JA, Sainsbury A, Baker MK, Chuter VH, Caterson
ID, George J and Johnson NA: Effect of aerobic exercise training
dose on liver fat and visceral adiposity. J Hepatol. 63:174–182.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Glass O, Filozof C, Noureddin M,
Berner-Hansen M, Schabel E, Omokaro SO, Schattenberg JM, Barradas
K, Miller V, Francque S, et al: Standardisation of diet and
exercise in clinical trials of NAFLD-NASH: Recommendations from the
liver forum. J Hepatol. 73:680–693. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fabian MR and Sonenberg N: The mechanics
of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: A look under the hood of miRISC.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:586–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao J, Bei Y, Liu J, Dimitrova-Shumkovska
J, Kuang D, Zhou Q, Li J, Yang Y, Xiang Y, Wang F, et al: MiR-212
downregulation contributes to the protective effect of exercise
against non-alcoholic fatty liver via targeting FGF-21. J Cell Mol
Med. 20:204–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liang X, Zeng J, Wang L, Fang M, Wang Q,
Zhao M, Xu X, Liu Z, Li W, Liu S, et al: Histone demethylase
retinoblastoma binding protein 2 is overexpressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma and negatively regulated by hsa-miR-212. PLoS One.
8:e697842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Beermann J, Napp
LC, Jabs O, Bhayadia R, Melk A, Ucar A, Chowdhury K, Lorenzen JM,
et al: Vascular importance of the miR-212/132 cluster. Eur Heart J.
35:3224–3231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang Y, Banan A, Forsyth CB, Fields JZ,
Lau CK, Zhang LJ and Keshavarzian A: Effect of alcohol on miR-212
expression in intestinal epithelial cells and its potential role in
alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 32:355–364. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mollet IG, Malm HA, Wendt A, Orho-Melander
M and Eliasson L: Integrator of stress responses calmodulin binding
transcription activator 1 (Camta1) regulates miR-212/miR-132
expression and insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 291:18440–18452.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ucar A, Gupta SK, Fiedler J, Erikci E,
Kardasinski M, Batkai S, Dangwal S, Kumarswamy R, Bang C, Holzmann
A, et al: The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac
hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy. Nat Commun. 3:10782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo Y, Yu J, Wang C, Li K, Liu B, Du Y,
Xiao F, Chen S and Guo F: miR-212-5p suppresses lipid accumulation
by targeting FAS and SCD1. J Mol Endocrinol. 59:205–217. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, de la
Fuente JR and Grant M: Development of the alcohol use disorders
identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early
detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II.
Addiction. 88:791–804. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park SE, Lee SW, Hossain MA, Kim MY, Kim
MN, Ahn EY, Park YC, Suh H, Kim GY, Choi YH and Kim ND: A
chenodeoxycholic derivative, HS-1200, induces apoptosis and cell
cycle modulation via Egr-1 gene expression control on human
hepatoma cells. Cancer Lett. 270:77–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM,
Bisaria N, Kelley GM and Bartel DP: The biochemical basis of
microRNA targeting efficacy. Science. 366:eaav17412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
ELife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW,
Grimson A and Bartel DP: Weak seed-pairing stability and high
target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other
microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1139–1146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK,
Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP and Bartel DP: MicroRNA targeting
specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell.
27:91–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: MiRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Green CD, Huang Y, Dou X, Yang L, Liu Y
and Han JDJ: Impact of dietary interventions on noncoding RNA
networks and mRNAs encoding chromatin-related factors. Cell Rep.
18:2957–2968. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gonzalez JN, Zweig AS, Speir ML, Schmelter
D, Rosenbloom KR, Raney BJ, Powell CC, Nassar LR, Maulding ND, Lee
CM, et al: The UCSC genome browser database: 2021 update. Nucleic
Acids Res. 49:D1046–D1057. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A, van
der Lee R, Zhang X, Richmond PA, Modi BP, Correard S, Gheorghe M,
Baranašić D, et al: JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database
of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.
48:D87–D92. 2020.
|
|
30
|
Chang TH, Huang HY, Hsu JB, Weng SL, Horng
JT and Huang HD: An enhanced computational platform for
investigating the roles of regulatory RNA and for identifying
functional RNA motifs. BMC Bioinformatics. 14(Suppl 2): S42013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Smith CL and Eppig JT: The mammalian
phenotype ontology: Enabling robust annotation and comparative
analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 1:390–399. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McLean CS, Mielke C, Cordova JM, Langlais
PR, Bowen B, Miranda D, Coletta DK and Mandarino LJ: Gene and
microRNA expression responses to exercise; relationship with
insulin sensitivity. PLoS One. 10:e01270892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Orci LA, Gariani K, Oldani G, Delaune V,
Morel P and Toso C: Exercise-based interventions for nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:1398–1411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hayamizu TF, Baldock RA and Ringwald M:
Mouse anatomy ontologies: Enhancements and tools for exploring and
integrating biomedical data. Mamm Genome. 26:422–430. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han MS, Perry RJ, Camporez JP, Scherer PE,
Shulman GI, Gao G and Davis RJ: A feed-forward regulatory loop in
adipose tissue promotes signaling by the hepatokine FGF21. Genes
Dev. 35:133–146. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Zhou Y, Jia X, Zhou M and Liu J: Egr-1 is
involved in the inhibitory effect of leptin on PPARgamma expression
in hepatic stellate cell in vitro. Life Sci. 84:544–551. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li J, Xu C, Liu Y, Li Y, Du S, Zhang R,
Sun Y, Zhang R, Wang Y, Xue H, et al: Fibroblast growth factor 21
inhibited ischemic arrhythmias via targeting miR-143/EGR1 axis.
Basic Res Cardiol. 115:92020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Adams AC, Yang C, Coskun T, Cheng CC,
Gimeno RE, Luo Y and Kharitonenkov A: The breadth of FGF21's
metabolic actions are governed by FGFR1 in adipose tissue. Mol
Metab. 2:31–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Samms RJ, Murphy M, Fowler MJ, Cooper S,
Emmerson P, Coskun T, Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A, Ebling FJP and
Tsintzas K: Dual effects of fibroblast growth factor 21 on hepatic
energy metabolism. J Endocrinol. 227:37–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang WF, Li SM, Ren GP, Zheng W, Lu YJ, Yu
YH, Xu WJ, Li TH, Zhou LH, Liu Y and Li DS: Recombinant murine
fibroblast growth factor 21 ameliorates obesity-related
inflammation in monosodium glutamate-induced obesity rats.
Endocrine. 49:119–129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Maratos-Flier E: Fatty liver and FGF21
physiology. Exp Cell Res. 360:2–5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Byun S, Seok S, Kim YC, Zhang Y, Yau P,
Iwamori N, Xu HE, Ma J, Kemper B and Kemper JK: Fasting-induced
FGF21 signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation
via JMJD3 histone demethylase. Nat Commun. 11:8072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|