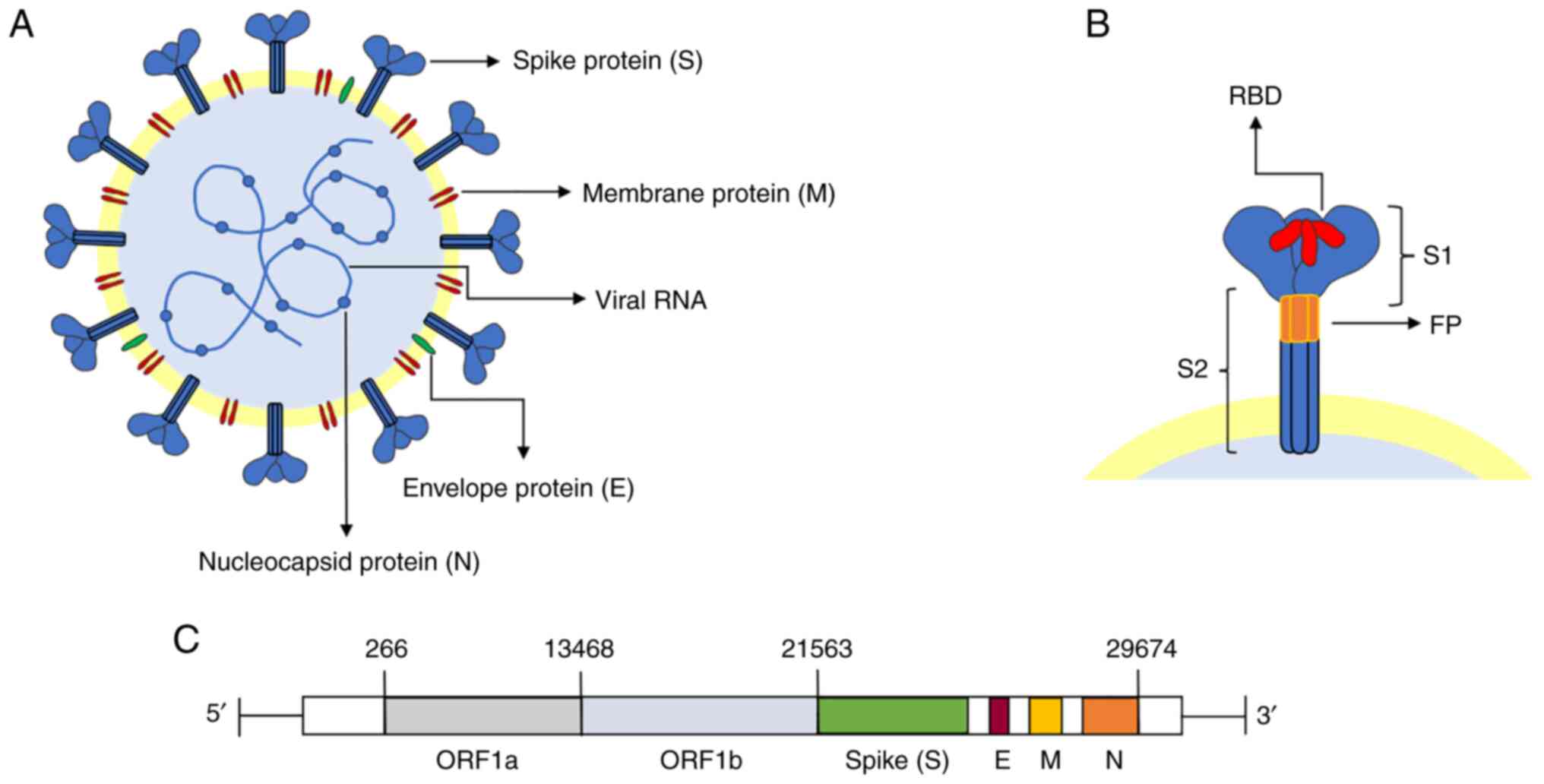
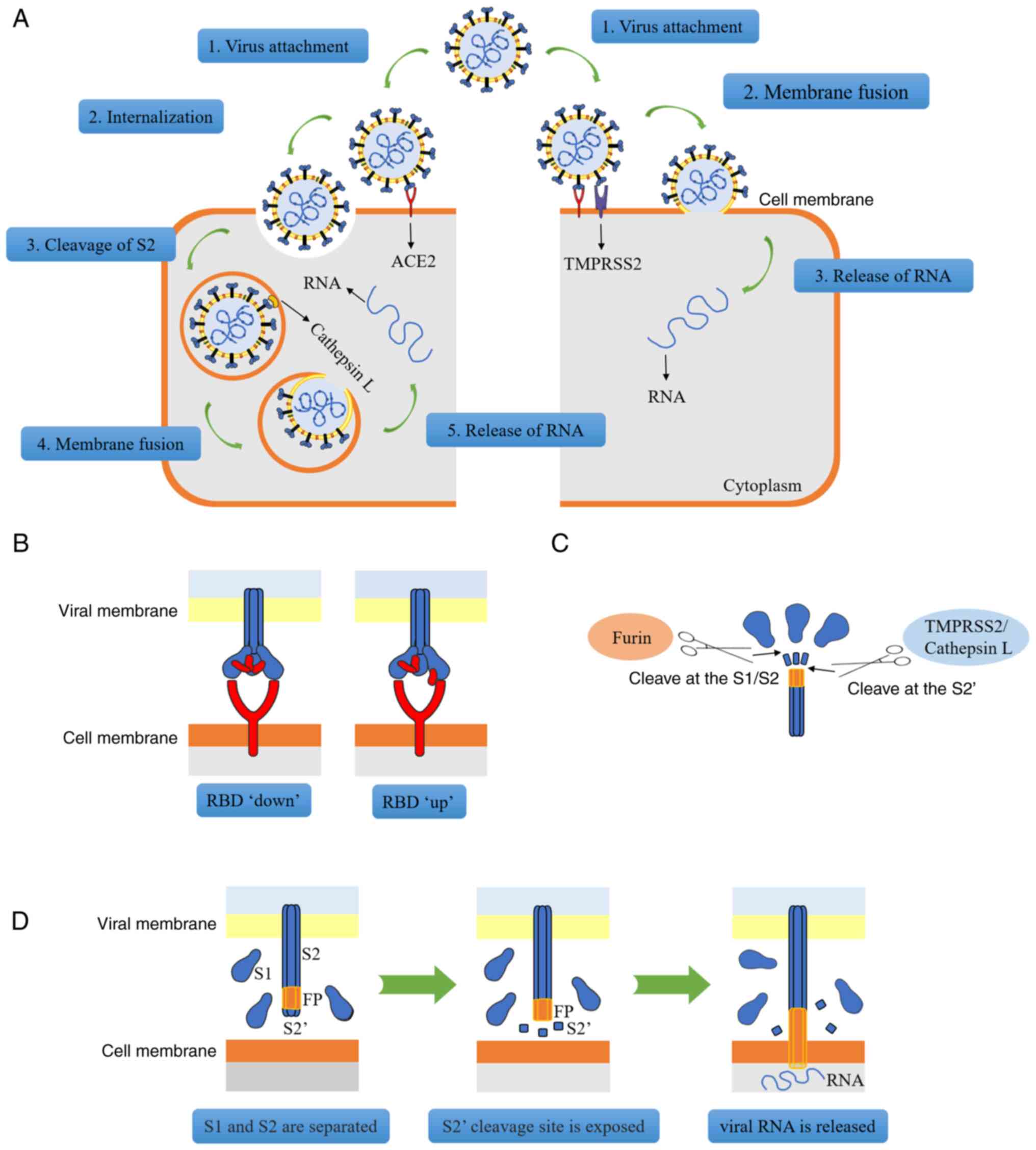
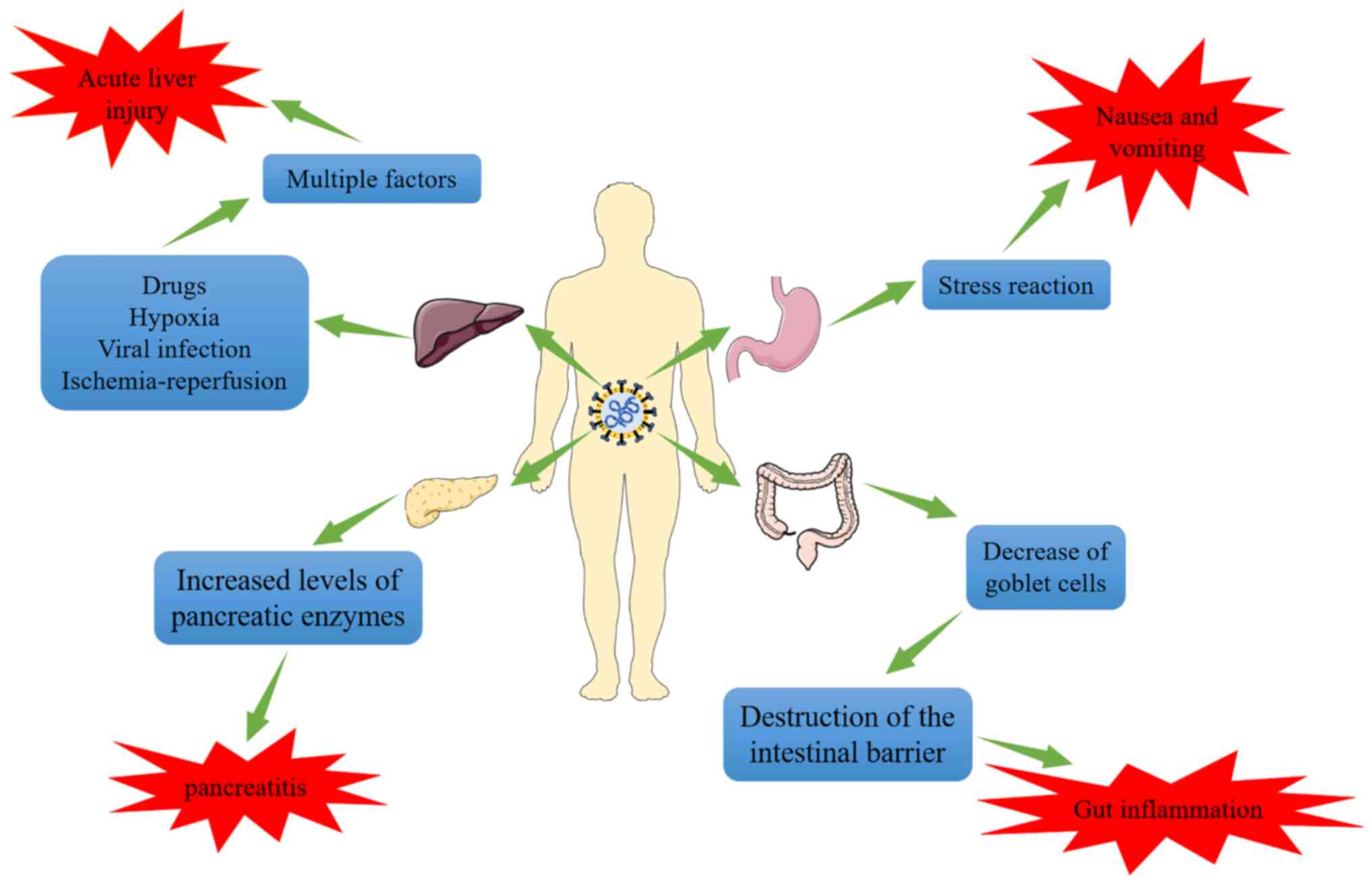
|
1
|
Li J, Li C, Wang X, Wang Y and Zhou Y:
Considerations and perspectives on digestive diseases during the
COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. Ann Palliat Med.
10:4858–4867. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Delgado-Gonzalez P, Gonzalez-Villarreal
CA, Roacho-Perez JA, Quiroz-Reyes AG, Islas JF, Delgado-Gallegos
JL, Arellanos-Soto D, Galan-Huerta KA and Garza-Treviño EN:
Inflammatory effect on the gastrointestinal system associated with
COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol. 27:4160–4171. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rizvi A, Patel Z, Liu Y, Satapathy SK,
Sultan K and Trindade AJ; Northwell Health COVID-19 Research
Consortium: Gastrointestinal sequelae 3 and 6 months after
hospitalization for coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 19:2438–2440.e1. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Fang LG and Zhou Q: Remarkable
gastrointestinal and liver manifestations of COVID-19: A clinical
and radiologic overview. World J Clin Cases. 9:4969–4979. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Gkogkou E, Barnasas G, Vougas K and
Trougakos IP: Expression profiling meta-analysis of ACE2 and
TMPRSS2, the putative anti-inflammatory receptor and priming
protease of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells, and identification of
putative modulators. Redox Biol. 36:1016152020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jackson CB, Farzan M, Chen B and Choe H:
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
23:3–20. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Parmar MS: TMPRSS2: An equally important
protease as ACE2 in the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Mayo
Clin Proc. 96:2748–2752. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang X, He C, Hua X, Kan A, Sun S, Wang J
and Li S: Bioinformatic Analysis of correlation between immune
infiltration and COVID-19 in cancer patients. Int J Biol Sci.
16:2464–2476. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Hoang T, Nguyen TQ and Tran TTA: Genetic
Susceptibility of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in six common cancers and
possible impacts on COVID-19. Cancer Res Treat. 53:650–656. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Viveiros A, Gheblawi M, Aujla PK,
Sosnowski DK, Seubert JM, Kassiri Z and Oudit GY: Sex- and
age-specific regulation of ACE2: Insights into severe COVID-19
susceptibility. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 164:13–16. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Da Eira D, Jani S and Ceddia RB:
Obesogenic and ketogenic diets distinctly regulate the SARS-CoV-2
Entry Proteins ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and the Renin-angiotensin system in
rat lung and heart tissues. Nutrients. 13:33572021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rando HM, MacLean AL, Lee AJ, Lordan R,
Ray S, Bansal V, Skelly AN, Sell E, Dziak JJ, Shinholster L, et al:
Pathogenesis, symptomatology, and transmission of SARS-CoV-2
through analysis of viral genomics and structure. mSystems.
6:e00095212021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saied EM, El-Maradny YA, Osman AA, Darwish
AMG, Abo Nahas HH, Niedbala G, Piekutowska M, Abdel-Rahman MA,
Balbool BA and Abdel-Azeem AM: A comprehensive review about the
molecular structure of severe acute respiratory syndrome
coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Insights into natural products against
COVID-19. Pharmaceutics. 13:17592021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Salem R, El-Kholy AA, Waly FR, Ayman D,
Sakr A and Hussein M: Generation and utility of a single-chain
fragment variable monoclonal antibody platform against a
baculovirus expressed recombinant receptor binding domain of
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Mol Immunol. 141:287–296. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tai L, Zhu G, Yang M, Cao L, Xing X, Yin
G, Chan C, Qin C, Rao Z, Wang X, et al: Nanometer-resolution in
situ structure of the SARS-CoV-2 postfusion spike protein. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21127031182021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Grishin AM, Dolgova NV, Landreth S,
Fisette O, Pickering IJ, George GN, Falzarano D and Cygler M:
Disulfide bonds play a critical role in the structure and function
of the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen. J
Mol Biol. 434:1673572022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen Y, Guo Y, Pan Y and Zhao ZJ:
Structure analysis of the receptor binding of 2019-nCoV. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 525:135–140. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Xiao T, Cai Y and Chen B:
Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Curr Opin Virol. 50:173–182.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Edenfield RC and Easley CA IV:
Implications of testicular ACE2 and the renin-angiotensin system
for SARS-CoV-2 on testis function. Nat Rev Urol. 19:116–127. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li D, Liu X, Zhang L, He J, Chen X, Liu S,
Fu J, Fu S, Chen H, Fu J and Cheng J: COVID-19 disease and
malignant cancers: The impact for the furin gene expression in
susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2. Int J Biol Sci. 17:3954–3967. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peacock TP, Goldhill DH, Zhou J, Baillon
L, Frise R, Swann OC, Kugathasan R, Penn R, Brown JC, Sanchez-David
RY, et al: The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
is required for transmission in ferrets. Nat Microbiol. 6:899–909.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wu CT, Lidsky PV, Xiao Y, Lee IT, Cheng R,
Nakayama T, Jiang S, Demeter J, Bevacqua RJ, Chang CA, et al:
SARS-CoV-2 infects human pancreatic β cells and elicits β cell
impairment. Cell Metab. 33:1565–1576.e5. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yele V, Sanapalli BKR and Mohammed AA:
Imidazoles and benzimidazoles as putative inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2
B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and 1 (Gamma) variant spike glycoproteins: A
computational approach. Chem Zvesti. 76:1107–1117. 2022.
|
|
24
|
Liu C, Zhou D, Nutalai R, Duyvesteyn HME,
Tuekprakhon A, Ginn HM, Dejnirattisai W, Supasa P, Mentzer AJ, Wang
B, et al: The antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 Beta underscores the
antigenic distance to other variants. Cell Host Microbe.
30:53–68.e12. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Moss DL and Rappaport J: SARS-CoV-2 beta
variant substitutions alter spike glycoprotein receptor binding
domain structure and stability. J Biol Chem. 297:1013712021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sanches PRS, Charlie-Silva I, Braz HLB,
Bittar C, Freitas Calmon M, Rahal P and Cilli EM: Recent advances
in SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and RBD mutations comparison between
new variants Alpha (B.1.1.7, United Kingdom), Beta (B.1.351, South
Africa), Gamma (1Brazil) and Delta (B.1.617.2, India). J Virus
Erad. 7:1000542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Storti B, Quaranta P, Di Primio C,
Clementi N, Mancini N, Criscuolo E, Spezia PG, Carnicelli V,
Lottini G, Paolini E, et al: A spatial multi-scale fluorescence
microscopy toolbox discloses entry checkpoints of SARS-CoV-2
variants in Vero E6 cells. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
19:6140–6156. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Alaofi AL and Shahid M: Mutations of
SARS-CoV-2 RBD may alter its molecular structure to improve its
infection efficiency. Biomolecules. 11:12732021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Bhattacharya M, Chatterjee S, Sharma AR,
Agoramoorthy G and Chakraborty C: D614G mutation and SARS-CoV-2:
Impact on S-protein structure, function, infectivity, and immunity.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 105:9035–9045. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy
KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, Spitters C, Ericson K, Wilkerson S, Tural
A, et al: First Case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United
States. N Engl J Med. 382:929–936. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, Lu R, Han K, Wu G and
Tan W: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical
specimens. JAMA. 323:1843–1844. 2020.
|
|
32
|
Xu Y, Li X, Zhu B, Liang H, Fang C, Gong
Y, Guo Q, Sun X, Zhao D, Shen J, et al: Characteristics of
pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for
persistent fecal viral shedding. Nat Med. 26:502–505. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen L, Lou J, Bai Y and Wang M: COVID-19
disease with positive fecal and negative pharyngeal and sputum
viral tests. Am J Gastroenterol. 115:7902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Burgueño JF, Reich A, Hazime H, Quintero
MA, Fernandez I, Fritsch J, Santander AM, Brito N, Damas OM,
Deshpande A, et al: Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Molecules ACE2
and TMPRSS2 in the Gut of Patients With IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
26:797–808. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xiao F, Tang M, Zheng X, Liu Y, Li X and
Shan H: Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2.
Gastroenterology. 158:1831–1833.e3. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, Nair N,
Mahajan S, Sehrawat TS, Bikdeli B, Ahluwalia N, Ausiello JC, Wan
EY, et al: Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat Med.
26:1017–1032. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mohamed DZ, Ghoneim ME, Abu-Risha SE,
Abdelsalam RA and Farag MA: Gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases
during the COVID-19 pandemic: Manifestations, mechanism and
management. World J Gastroenterol. 27:4504–4535. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin L, Jiang X, Zhang Z, Huang S, Zhang Z,
Fang Z, Gu Z, Gao L, Shi H, Mai L, et al: Gastrointestinal symptoms
of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gut. 69:997–1001. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Elmunzer BJ, Spitzer RL, Foster LD,
Merchant AA, Howard EF, Patel VA, West MK, Qayed E, Nustas R,
Zakaria A, et al: Digestive manifestations in patients hospitalized
with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
19:1355–1365.e4. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ferm S, Fisher C, Pakala T, Tong M, Shah
D, Schwarzbaum D, Cooley V, Hussain S and Kim SH: Analysis of
gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection
in 892 patients in queens, NY. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:2378–2379.e1. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang MK, Yue HY, Cai J, Zhai YJ, Peng JH,
Hui JF, Hou DY, Li WP and Yang JS: COVID-19 and the digestive
system: A comprehensive review. World J Clin Cases. 9:3796–3813.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Andrews PLR, Cai W, Rudd JA and Sanger GJ:
COVID-19, nausea, and vomiting. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
36:646–656. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Boraschi P, Giugliano L, Mercogliano G,
Donati F, Romano S and Neri E: Abdominal and gastrointestinal
manifestations in COVID-19 patients: Is imaging useful? World J
Gastroenterol. 27:4143–4159. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Carvalho A, Alqusairi R, Adams A, Paul M,
Kothari N, Peters S and DeBenedet AT: SARS-CoV-2 gastrointestinal
infection causing hemorrhagic colitis: Implications for detection
and transmission of COVID-19 disease. Am J Gastroenterol.
115:942–946. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li X, Huang S, Lu J, Lai R, Zhang Z, Lin
X, Zheng X and Shan H: Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Caused by
SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 115:1541–1542. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xu Z, Tang M, Chen P, Cai H and Xiao F:
SARS-CoV-2 gastro-intestinal infection prolongs the time to recover
from COVID-19. Front Med (Lausanne). 8:6835512021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hu F, Chen F, Ou Z, Fan Q, Tan X, Wang Y,
Pan Y, Ke B, Li L, Guan Y, et al: A compromised specific humoral
immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain is
related to viral persistence and periodic shedding in the
gastrointestinal tract. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:1119–1125. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Noviello D, Costantino A, Muscatello A,
Bandera A, Consonni D, Vecchi M and Basilisco G: Functional
gastrointestinal and somatoform symptoms five months after
SARS-CoV-2 infection: A controlled cohort study. Neurogastroenterol
Motil. 34:e141872022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu YL, Ren J, Yuan JP, Zhang ZJ, Guo WY,
Guan Y, Moeckel G, Ahuja N and Fu T: Postoperative onset and
detection of SARS-CoV-2 in surgically resected specimens from
gastrointestinal cancer patients with pre/asymptomatic COVID-19.
Ann Surg. 272:e321–e328. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Nabil A, Elshemy MM, Uto K, Soliman R,
Hassan AA, Shiha G and Ebara M: Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in
gastroenterology and its current epidemiological situation: An
updated review until January 2021. EXCLI J. 20:366–385.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McAllister MJ, Kirkwood K, Chuah SC,
Thompson EJ, Cartwright JA, Russell CD, Dorward DA, Lucas CD and Ho
GT: Intestinal protein characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 entry
molecules ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and
Fatal COVID-19 Infection. Inflammation. 45:567–572. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Suárez-Fariñas M, Tokuyama M, Wei G, Huang
R, Livanos A, Jha D, Levescot A, Irizar H, Kosoy R, Cording S, et
al: Intestinal inflammation modulates the expression of ACE2 and
TMPRSS2 and potentially overlaps with the pathogenesis of
SARS-CoV-2-related disease. Gastroenterology. 160:287–301.e20.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tao SS, Wang XY, Yang XK, Liu YC, Fu ZY,
Zhang LZ, Wang ZX, Ni J, Shuai ZW and Pan HF: COVID-19 and
inflammatory bowel disease crosstalk: From emerging association to
clinical proposal. J Med Virol. 94:5640–5652. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Shen S, Gong M, Wang G, Dua K, Xu J, Xu X
and Liu G: COVID-19 and gut injury. Nutrients. 14:44092022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Viganò C, Massironi S, Pirola L,
Cristoferi L, Fichera M, Bravo M, Mauri M, Redaelli AE, Dinelli ME
and Invernizzi P: COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory bowel
disease: A single-center observational study in Northern Italy.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 26:e138–e139. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Derikx LAAP, Lantinga MA, de Jong DJ, van
Dop WA, Creemers RH, Römkens TEH, Jansen JM, Mahmmod N, West RL,
Tan ACITL, et al: Clinical Outcomes of Covid-19 in patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: A nationwide cohort study. J Crohns
Colitis. 15:529–539. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhou L, Niu Z, Jiang X, Zhang Z, Zheng Y,
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Gao L, Huang H, Wang X and Sun Q: SARS-CoV-2 Targets
by the pscRNA Profiling of ACE2, TMPRSS2 and Furin Proteases.
iScience. 23:1017442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Qi F, Qian S, Zhang S and Zhang Z: Single
cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and
receptors of human coronaviruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
526:135–140. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee JJ, Kopetz S, Vilar E, Shen JP, Chen K
and Maitra A: Relative Abundance of SARS-CoV-2 entry genes in the
enterocytes of the lower gastrointestinal tract. Genes (Basel).
11:6452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
An X, Lin W, Liu H, Zhong W, Zhang X, Zhu
Y, Wang X, Li J and Sheng Q: SARS-CoV-2 Host Receptor ACE2 protein
expression atlas in human gastrointestinal tract. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6598092021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang M, Feng C, Zhang X, Hu S, Zhang Y,
Min M, Liu B, Ying X and Liu Y: Susceptibility factors of stomach
for SARS-CoV-2 and treatment implication of mucosal protective
agent in COVID-19. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:5979672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sun SH, Chen Q, Gu HJ, Yang G, Wang YX,
Huang XY, Liu SS, Zhang NN, Li XF, Xiong R, et al: A Mouse Model of
SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe.
28:124–133.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hartman AL, Nambulli S, McMillen CM, White
AG, Tilston-Lunel NL, Albe JR, Cottle E, Dunn MD, Frye LJ,
Gilliland TH, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection of African green monkeys
results in mild respiratory disease discernible by PET/CT imaging
and shedding of infectious virus from both respiratory and
gastrointestinal tracts. PLoS Pathog. 16:e10089032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jiao L, Li H, Xu J, Yang M, Ma C, Li J,
Zhao S, Wang H, Yang Y, Yu W, et al: The gastrointestinal tract is
an alternative route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a nonhuman primate
model. Gastroenterology. 160:1647–1661. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Livanos AE, Jha D, Cossarini F,
Gonzalez-Reiche AS, Tokuyama M, Aydillo T, Parigi TL, Ladinsky MS,
Ramos I, Dunleavy K, et al: Intestinal host response to SARS-CoV-2
Infection and COVID-19 outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal
symptoms. Gastroenterology. 160:2435–2450.e34. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Qi J, Zhou Y, Hua J, Zhang L, Bian J, Liu
B, Zhao Z and Jin S: The scRNA-seq Expression Profiling of the
Receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 reveals human
organs susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 18:2842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang M, Yan W, Qi W, Wu D, Zhu L, Li W,
Wang X, Ma K, Ni M, Xu D, et al: Clinical characteristics and risk
factors of liver injury in COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study
from Wuhan, China. Hepatol Int. 14:723–732. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhang H, Liao YS, Gong J, Liu J and Zhang
H: Clinical characteristics and risk factors for liver injury in
COVID-19 patients in Wuhan. World J Gastroenterol. 26:4694–4702.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wisniewska H, Skowron M, Bander D, Hornung
M, Jurczyk K, Karpinska E, Laurans Ł, Socha Ł, Czajkowski Z and
Wawrzynowicz-Syczewska M: Nosocomial COVID-19 Infection and Severe
COVID-19 pneumonia in patients hospitalized for alcoholic liver
disease: A case report. Am J Case Rep. 21:e9274522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang SJ, Wei TC, Hsu CH, Ho SN, Lai CY,
Huang SF, Chen YY, Liu SJ, Yu GY and Dou HY: Characterization of
virus replication, pathogenesis, and cytokine responses in syrian
hamsters inoculated with SARS-CoV-2. J Inflamm Res. 14:3781–3795.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wong GL, Yip TC, Wong VW, Tse YK, Hui DS,
Lee SS, Yeoh EK, Chan HL and Lui GC: SARS-CoV-2 viral persistence
based on cycle threshold value and liver injury in patients with
COVID-19. Open Forum Infect Dis. 8:ofab2052021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lei HY, Ding YH, Nie K, Dong YM, Xu JH,
Yang ML, Liu MQ, Wei L, Nasser MI, Xu LY, et al: Potential effects
of SARS-CoV-2 on the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Biomed
Pharmacother. 133:1110642021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zhong P, Xu J, Yang D, Shen Y, Wang L,
Feng Y, Du C, Song Y, Wu C, Hu X and Sun Y: COVID-19-associated
gastrointestinal and liver injury: Clinical features and potential
mechanisms. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2562020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Siddiqui MA, Suresh S, Simmer S,
Abu-Ghanimeh M, Karrick M, Nimri F, Musleh M, Mediratta V,
Al-Shammari M, Russell S, et al: Increased morbidity and mortality
in COVID-19 patients with liver injury. Dig Dis Sci. 67:2577–2583.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wijarnpreecha K, Ungprasert P,
Panjawatanan P, Harnois DM, Zaver HB, Ahmed A and Kim D: COVID-19
and liver injury: A meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
33:990–995. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wang Q, Zhao H, Liu LG, Wang YB, Zhang T,
Li MH, Xu YL, Gao GJ, Xiong HF, Fan Y, et al: Pattern of liver
injury in adult patients with COVID-19: A retrospective analysis of
105 patients. Mil Med Res. 7:282020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Del Nonno F, Nardacci R, Colombo D,
Visco-Comandini U, Cicalini S, Antinori A, Marchioni L, D'Offizi G,
Piacentini M and Falasca L: Hepatic failure in COVID-19: Is iron
overload the dangerous trigger? Cells. 10:11032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gomi K, Ito T, Yamaguchi F, Kamio Y, Sato
Y, Mori H, Endo K, Abe T, Sakakura S, Kobayashi K, et al: Clinical
features and mechanism of liver injury in patients with mild or
moderate coronavirus disease 2019. JGH Open. 5:888–895. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ma C, Cong Y and Zhang H: COVID-19 and the
digestive system. Am J Gastroenterol. 115:1003–1006. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhang Q, Li J, Zhang Y, Gao J, Wang P, Ai
M, Ding W and Tan X: Differences in clinical characteristics and
liver injury between suspected and confirmed COVID-19 patients in
Jingzhou, Hubei Province of China. Medicine (Baltimore).
100:e259132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M,
Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, Vanstapel A, Werlein C, Stark H,
Tzankov A, et al: Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis,
and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 383:120–128. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
82
|
Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker
M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS, Mehra MR, Schuepbach RA, Ruschitzka
F and Moch H: Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in
COVID-19. Lancet. 395:1417–1418. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L,
Zhang C, Liu S, Zhao P, Liu H, Zhu L, et al: Pathological findings
of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Lancet Respir Med. 8:420–422. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Paizis G, Tikellis C, Cooper ME, Schembri
JM, Lew RA, Smith AI, Shaw T, Warner FJ, Zuilli A, Burrell LM and
Angus PW: Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the
novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2. Gut. 54:1790–1796.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Bender JM and Worman HJ: Coronavirus
Disease 2019 and liver injury: A retrospective analysis of
hospitalized patients in New York City. J Clin Transl Hepatol.
9:551–558. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chew M, Tang Z, Radcliffe C, Caruana D,
Doilicho N, Ciarleglio MM, Deng Y and Garcia-Tsao G: Significant
liver injury during hospitalization for COVID-19 is not associated
with liver insufficiency or death. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
19:2182–2191.e7. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Vishwajeet V, Purohit A, Kumar D, Parag V,
Tripathi S, Kanchan T, Kothari N, Dutt N, Elhence PA, Bhatia PK, et
al: Evaluation of pathological findings of COVID-19 by minimally
invasive autopsies: A single tertiary care center experience from
India. J Lab Physicians. 13:97–106. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Tollard C, Champenois V, Delemer B,
Carsin-Vu A and Barraud S: An inaugural diabetic ketoacidosis with
acute pancreatitis during COVID-19. Acta Diabetol. 58:389–391.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kumaran NK, Karmakar BK and Taylor OM:
Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) associated with acute necrotising
pancreatitis (ANP). BMJ Case Rep. 13:e2379032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Alves AM, Yvamoto EY, Marzinotto MAN,
Teixeira ACS and Carrilho FJ: SARS-CoV-2 leading to acute
pancreatitis: An unusual presentation. Braz J Infect Dis.
24:561–564. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hadi A, Werge M, Kristiansen KT, Pedersen
UG, Karstensen JG, Novovic S and Gluud LL: Coronavirus Disease-19
(COVID-19) associated with severe acute pancreatitis: Case report
on three family members. Pancreatology. 20:665–667. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Barlass U, Wiliams B, Dhana K, Adnan D,
Khan SR, Mahdavinia M and Bishehsari F: Marked elevation of lipase
in COVID-19 Disease: A cohort study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol.
11:e002152020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Inamdar S, Benias PC, Liu Y, Sejpal DV,
Satapathy SK and Trindade AJ; Northwell COVID-19 Research
Consortium: Prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes of hospitalized
patients with coronavirus disease 2019 presenting as acute
pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 159:2226–2228.e2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Samies NL, Yarbrough A and Boppana S:
Pancreatitis in pediatric patients with COVID-19. J Pediatric
Infect Dis Soc. 10:57–59. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Pandanaboyana S, Moir J, Leeds JS, Oppong
K, Kanwar A, Marzouk A, Belgaumkar A, Gupta A, Siriwardena AK,
Haque AR, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection in acute pancreatitis
increases disease severity and 30-day mortality: COVID PAN
collaborative study. Gut. 70:1061–1069. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Liu F, Long X, Zhang B, Zhang W, Chen X
and Zhang Z: ACE2 expression in pancreas may cause pancreatic
damage after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:2128–2130.e2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Qadir MMF, Bhondeley M, Beatty W, Gaupp
DD, Doyle-Meyers LA, Fischer T, Bandyopadhyay I, Blair RV, Bohm R,
Rappaport J, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection of the pancreas promotes
thrombofibrosis and is associated with new-onset diabetes. JCI
Insight. 6:e1515512021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
98
|
Jablonska B, Olakowski M and Mrowiec S:
Association between acute pancreatitis and COVID-19 infection: What
do we know? World J Gastrointest Surg. 13:548–562. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Cao W, Feng Q and Wang X: Computational
analysis of TMPRSS2 expression in normal and SARS-CoV-2-infected
human tissues. Chem Biol Interact. 346:1095832021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
100
|
Kusmartseva I, Wu W, Syed F, Van Der Heide
V, Jorgensen M, Joseph P, Tang X, Candelario-Jalil E, Yang C, Nick
H, et al: Expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors in the pancreas of
normal organ donors and individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab.
32:1041–1051.e6. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Coate KC, Cha J, Shrestha S, Wang W,
Goncalves LM, Almaca J, Kapp ME, Fasolino M, Morgan A, Dai C, et
al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are expressed in
the microvasculature and ducts of human pancreas but are not
enriched in β cells. Cell Metab. 32:1028–1040.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Steenblock C, Richter S, Berger I, Barovic
M, Schmid J, Schubert U, Jarzebska N, von Mässenhausen A,
Linkermann A, Schürmann A, et al: Viral infiltration of pancreatic
islets in patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun. 12:35342021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Shaharuddin SH, Wang V, Santos RS, Gross
A, Wang Y, Jawanda H, Zhang Y, Hasan W, Garcia G Jr, Arumugaswami V
and Sareen D: Deleterious Effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on human
pancreatic cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 11:6784822021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|