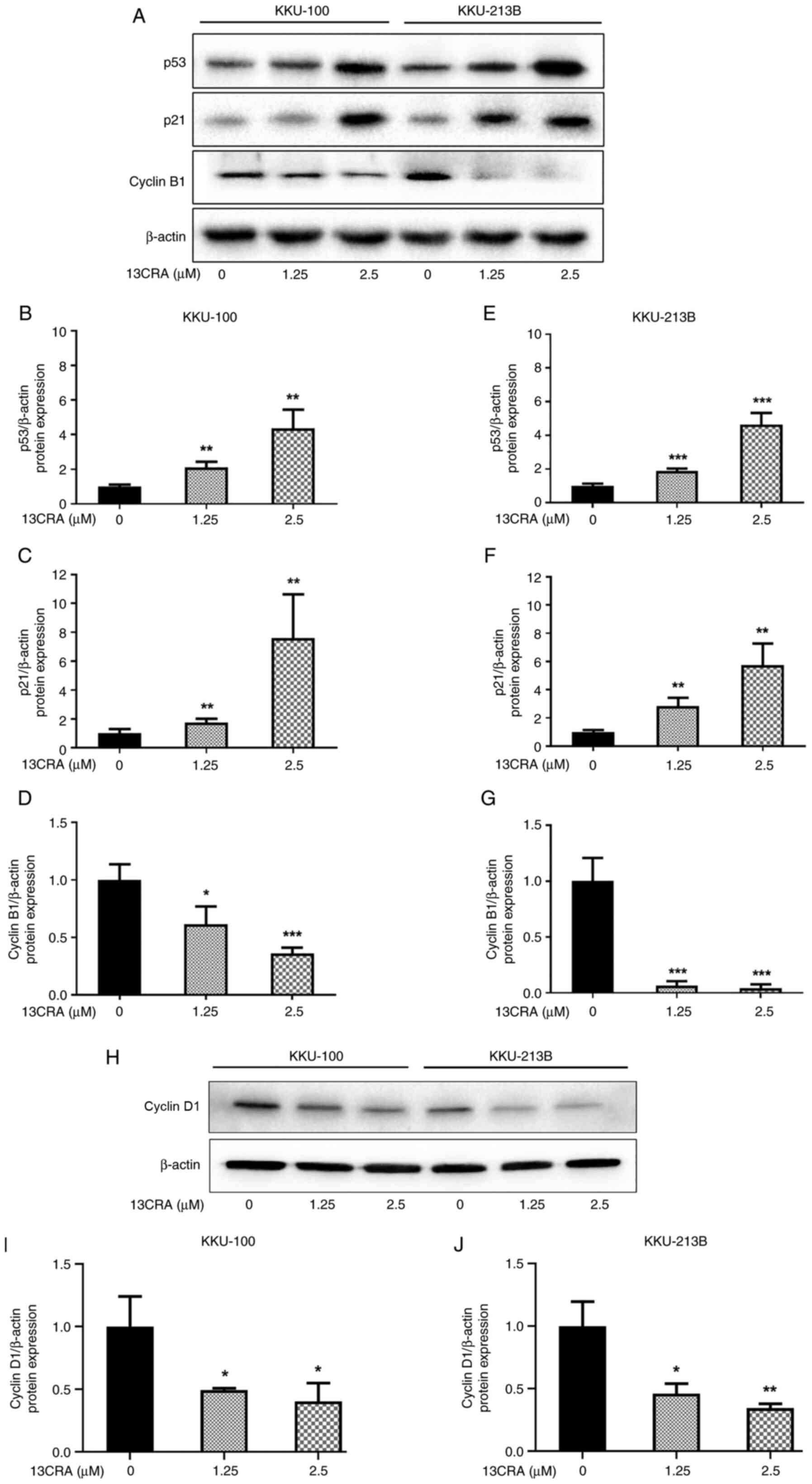
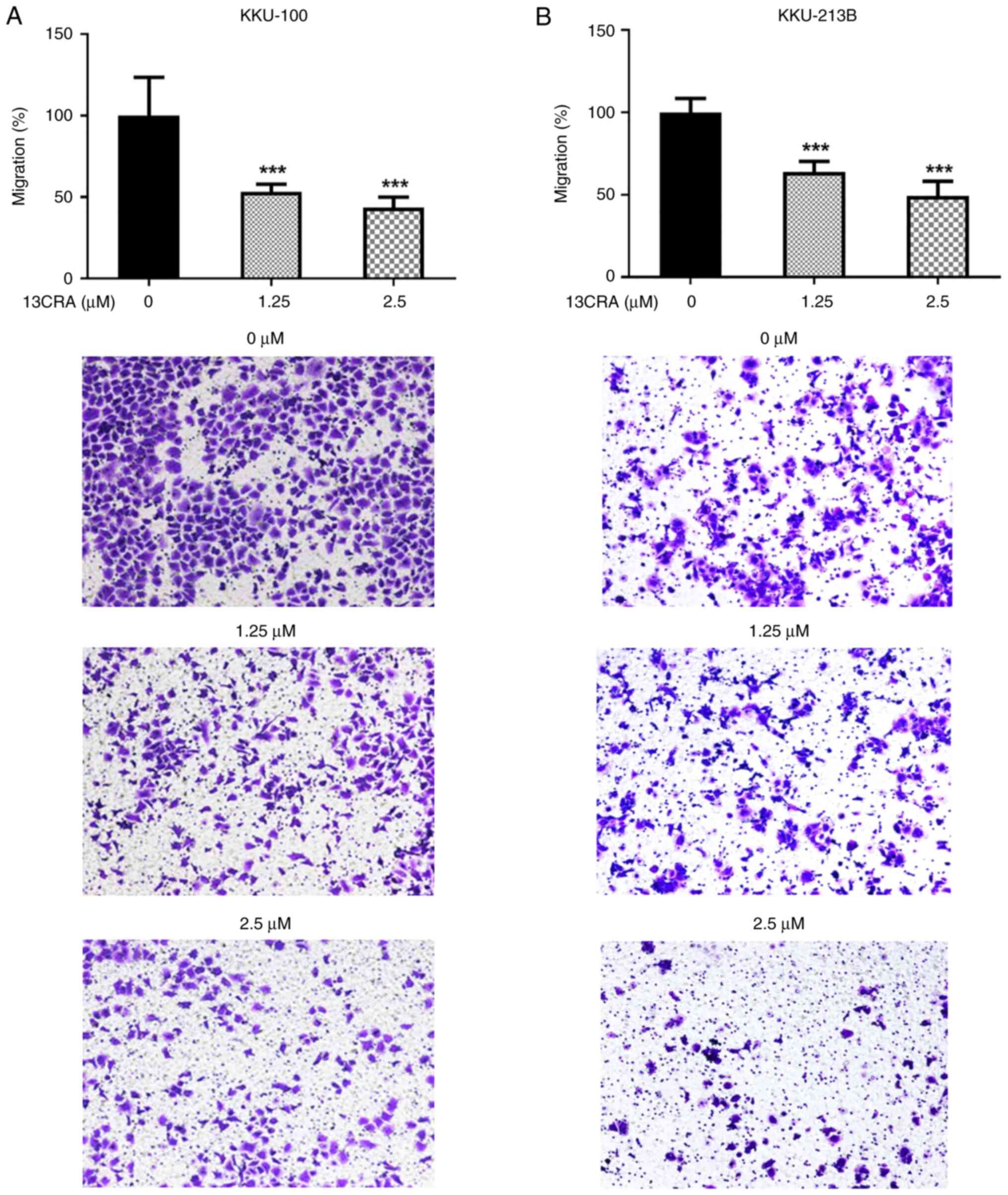
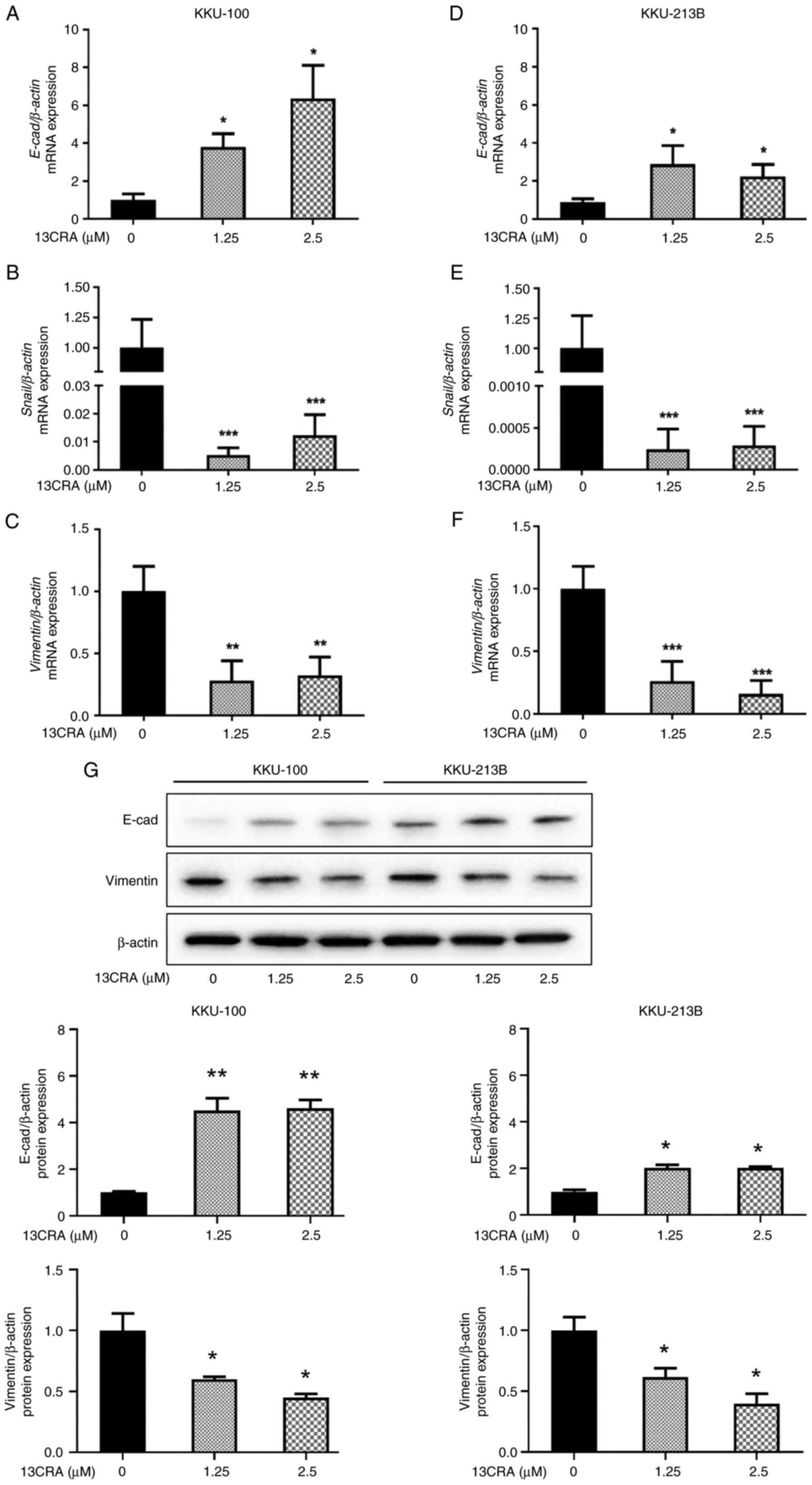
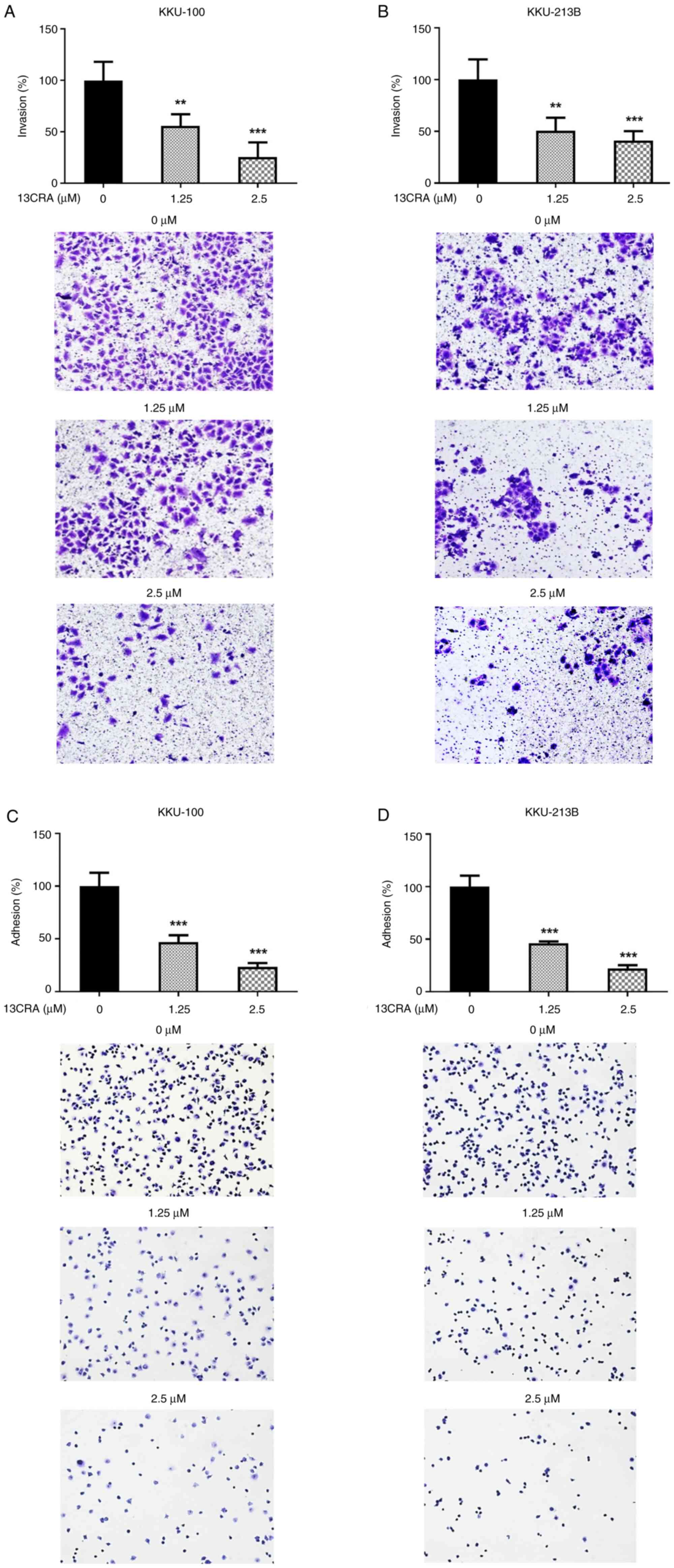
|
1
|
Meyskens FL Jr, Goodman GE and Alberts DS:
13-Cis-retinoic acid: Pharmacology, toxicology, and clinical
applications for the prevention and treatment of human cancer. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 3:75–101. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blaner WS: Cellular metabolism and actions
of 13-cis-retinoic acid. J Am Acad Dermatol. 45:S129–S135. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Layton A: The use of isotretinoin in acne.
Dermatoendocrinol. 1:162–169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Avis I, Mathias A, Unsworth EJ, Miller MJ,
Cuttitta F, Mulshine JL and Jakowlew SB: Analysis of small cell
lung cancer cell growth inhibition by 13-cis-retinoic acid:
Importance of bioavailability. Cell Growth Differ. 6:485–492.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang SY, Shyu RY, Chen HY, Lee MM, Wu KL
and Yeh MY: In vitro and in vivo growth inhibition of SC-M1 gastric
cancer cells by retinoic acid. Oncology. 53:334–340. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toma S, Isnardi L, Raffo P, Dastoli G, De
Francisci E, Riccardi L, Palumbo R and Bollag W: Effects of
all-trans-retinoic acid and 13-cis-retinoic acid on breast-cancer
cell lines: Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction. Int J
Cancer. 70:619–627. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Adachi Y, Itoh F, Yamamoto H, Iku S,
Matsuno K, Arimura Y and Imai K: Retinoic acids reduce matrilysin
(matrix metalloproteinase 7) and inhibit tumor cell invasion in
human colon cancer. Tumour Biol. 22:247–253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Guruvayoorappan C, Pradeep CR and Kuttan
G: 13-cis-retinoic acid induces apoptosis by modulating caspase-3,
bcl-2, and p53 gene expression and regulates the activation of
transcription factors in B16F-10 melanoma cells. J Environ Pathol
Toxicol Oncol. 27:197–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A,
Rodrigues PM, Khan SA, Roberts LR, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Andersen
JB, Braconi C, et al: Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in
mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:557–588. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Blechacz B: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current
knowledge and new developments. Gut Liver. 11:13–26. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Shin HR, Oh JK, Masuyer E, Curado MP,
Bouvard V, Fang YY, Wiangnon S, Sripa B and Hong ST: Epidemiology
of cholangio-carcinoma: An update focusing on risk factors. Cancer
Sci. 101:579–585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Valle JW, Furuse J, Jitlal M, Beare S,
Mizuno N, Wasan H, Bridgewater J and Okusaka T: Cisplatin and
gemcitabine for advanced biliary tract cancer: A meta-analysis of
two randomised trials. Ann Oncol. 25:391–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ,
Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML,
Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, et al: Sustained proliferation in
cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35(Suppl): S25–S54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Miller DM, Thomas SD, Islam A, Muench D
and Sedoris K: c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5546–5553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nelson AM, Gilliland KL, Cong Z and
Thiboutot DM: 13-cis Retinoic acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle
arrest in human SEB-1 sebocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 126:2178–2189.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vaquero J, Guedj N, Clapéron A, Nguyen
Ho-Bouldoires TH, Paradis V and Fouassier L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to
regulatory networks. J Hepatol. 66:424–441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cadamuro M, Nardo G, Indraccolo S,
Dall'olmo L, Sambado L, Moserle L, Franceschet I, Colledan M,
Massani M, Stecca T, et al: Platelet-derived growth factor-D and
Rho GTPases regulate recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts
in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 58:1042–1053. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, Khuntikeo
N, Puapairoj A, Jearanaikoon P, Saya H and Yongvanit P: Loss of
E-cadherin promotes migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma
cells and serves as a potential marker of metastasis. Tumour Biol.
35:8645–8652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fares J, Fares MY, Khachfe HH, Salhab HA
and Fares Y: Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of
cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:282020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dustin ML, Rothlein R, Bhan AK, Dinarello
CA and Springer TA: Induction by IL 1 and interferon-γ: Tissue
distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence
molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986.137:245–254. View Article : Google Scholar
J Immunol. 186:5024–5033. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Fosslien E: Review: Molecular pathology of
cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer-induced angiogenesis. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
31:325–348. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wagenaar-Miller RA, Hanley G,
Shattuck-Brandt R, DuBois RN, Bell RL, Matrisian LM and Morgan DW:
Cooperative effects of matrix metalloproteinase and
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on intestinal adenoma reduction. Br J
Cancer. 88:1445–1452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Itatsu K, Sasaki M, Yamaguchi J, Ohira S,
Ishikawa A, Ikeda H, Sato Y, Harada K, Zen Y, Sato H, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is involved in the up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in cholangiocarcinoma induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Am J Pathol. 174:829–841. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tuponchai P, Kukongviriyapan V, Prawan A,
Kongpetch S and Senggunprai L: Myricetin ameliorates
cytokine-induced migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells
via suppression of STAT3 pathway. J Cancer Res Ther. 15:157–163.
2019.
|
|
27
|
Kaewmeesri P, Kukongviriyapan V, Prawan A,
Kongpetch S and Senggunprai L: Cucurbitacin B diminishes metastatic
behavior of cholangiocarcinoma cells by suppressing focal adhesion
kinase. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 22:219–225. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sripa B, Leungwattanawanit S, Nitta T,
Wongkham C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Sripa C and Miwa M:
Establishment and characterization of an opisthorchiasis-associated
cholangiocarcinoma cell line (KKU-100). World J Gastroenterol.
11:3392–3397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sripa B, Seubwai W, Vaeteewoottacharn K,
Sawanyawisuth K, Silsirivanit A, Kaewkong W, Muisuk K, Dana P,
Phoomak C, Lert-Itthiporn W, et al: Functional and genetic
characterization of three cell lines derived from a single tumor of
an Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma patient.
Hum Cell. 33:695–708. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Butsri S, Kukongviriyapan V, Senggunprai
L, Kongpetch S and Prawan A: All-trans-retinoic acid induces
RARB-dependent apoptosis via ROS induction and enhances cisplatin
sensitivity by NRF2 downregulation in cholangiocarcinoma cells.
Oncol Lett. 23:1792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Guruvayoorappan C and Kuttan G: 13
cis-retinoic acid regulates cytokine production and inhibits
angiogenesis by disrupting endothelial cell migration and tube
formation. J Exp Ther Oncol. 7:173–182. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chung KD, Jeong YI, Chung CW, Kim DH and
Kang DH: Anti-tumor activity of all-trans retinoic
acid-incorporated glycol chitosan nanoparticles against HuCC-T1
human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int J Pharm. 422:454–461. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Veal GJ, Cole M, Errington J, Pearson AD,
Foot AB, Whyman G and Boddy AV; UKCCSG Pharmacology Working Group:
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of 13-cis-retinoic acid
(isotretinoin) in children with high-risk neuroblastoma-a study of
the United Kingdom children's cancer study group. Br J Cancer.
96:424–431. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nguyen PH, Giraud J, Staedel C,
Chambonnier L, Dubus P, Chevret E, Boeuf H, Gauthereau X, Rousseau
B, Fevre M, et al: All-trans retinoic acid targets gastric cancer
stem cells and inhibits patient-derived gastric carcinoma tumor
growth. Oncogene. 35:5619–5628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ozeki M and Shively JE: Differential cell
fates induced by all-trans retinoic acid-treated HL-60 human
leukemia cells. J Leukoc Biol. 84:769–779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang H, Satyamoorthy K, Herlyn M and
Rosdahl I: All-trans retinoic acid (atRA) differentially induces
apoptosis in matched primary and metastatic melanoma cells-a
speculation on damage effect of atRA via mitochondrial dysfunction
and cell cycle redistribution. Carcinogenesis. 24:185–191. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang H and Rosdahl I: Expression of p27
and MAPK proteins involved in all-trans retinoic acid-induced
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in matched primary and metastatic
melanoma cells. Int J Oncol. 25:1241–1248. 2004.
|
|
39
|
Dimberg A, Bahram F, Karlberg I, Larsson
LG, Nilsson K and Oberg F: Retinoic acid-induced cell cycle arrest
of human myeloid cell lines is associated with sequential
down-regulation of c-Myc and cyclin E and posttranscriptional
up-regulation of p27(Kip1). Blood. 99:2199–2206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cui J, Gong M, He Y, Li Q, He T and Bi Y:
All-trans retinoic acid inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion
and induces differentiation of hepa1-6 cells through reversing EMT
in vitro. Int J Oncol. 48:349–357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shi G, Zheng X, Wu X, Wang S, Wang Y and
Xing F: All-trans retinoic acid reverses epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in paclitaxel-resistant cells by inhibiting nuclear
factor kappa B and upregulating gap junctions. Cancer Sci.
110:379–388. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Speyer MT, Jackson JA and Burkey BB: The
effects of 13-cis retinoic acid on squamous cell carcinoma
proliferation and adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins.
Laryngoscope. 107:44–48. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang C, Wang Q, Xu Z, Li WS, Chen C, Yao
XQ and Liu FK: Cyclooxygenase-2 knockdown using retinoic acid
chalcone (RAC), a promising therapeutic strategy for colon cancer.
Am J Cancer Res. 5:2012–2021. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Saensa-Ard S, Leuangwattanawanit S,
Senggunprai L, Namwat N, Kongpetch S, Chamgramol Y, Loilome W,
Khansaard W, Jusakul A, Prawan A, et al: Establishment of
cholangiocarcinoma cell lines from patients in the endemic area of
liver fluke infection in Thailand. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177259252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Madzharova E, Kastl P, Sabino F and Auf
dem Keller U: Post-translational modification-dependent activity of
matrix metalloproteinases. Int J Mol Sci. 20:30772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|