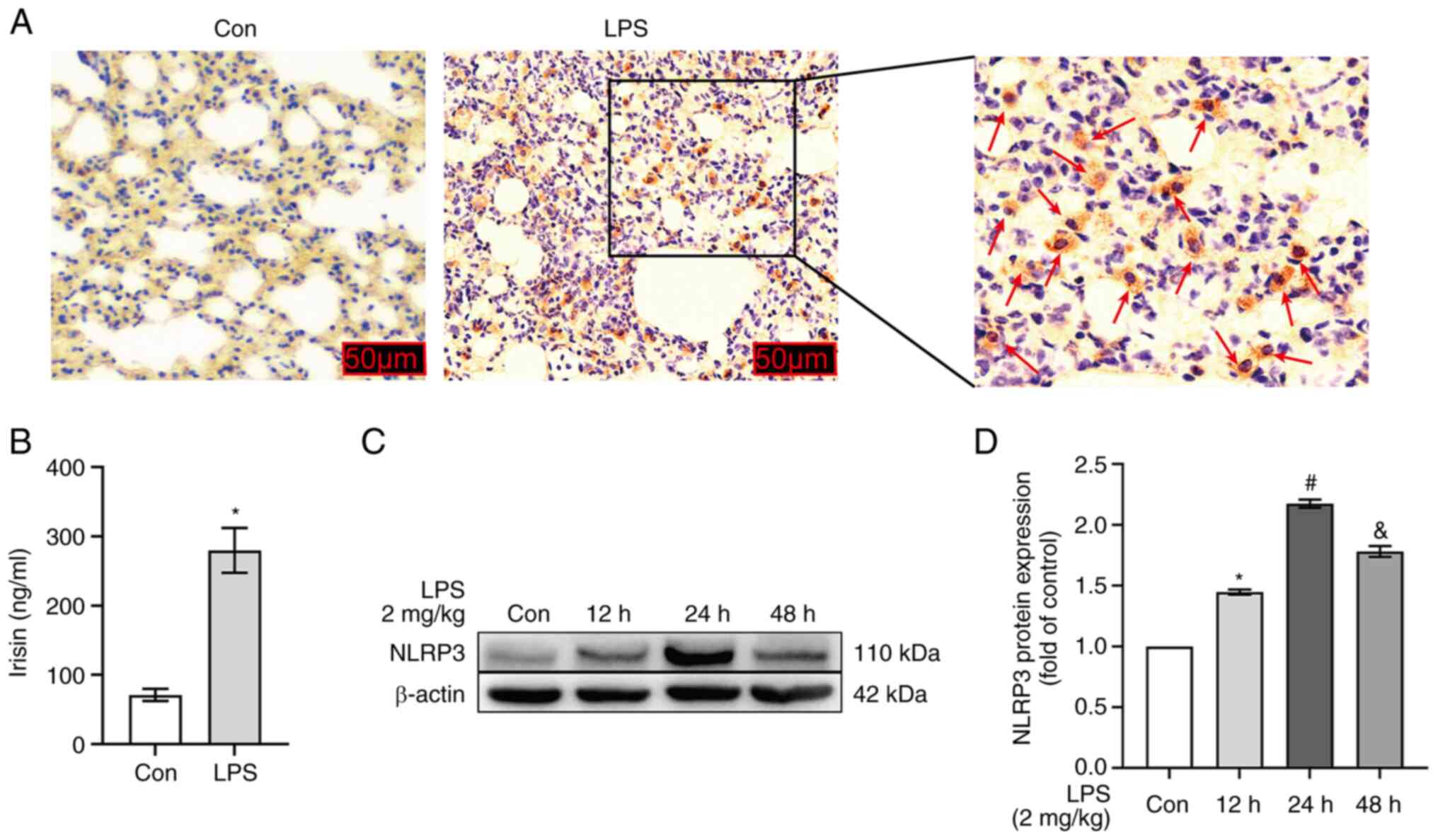
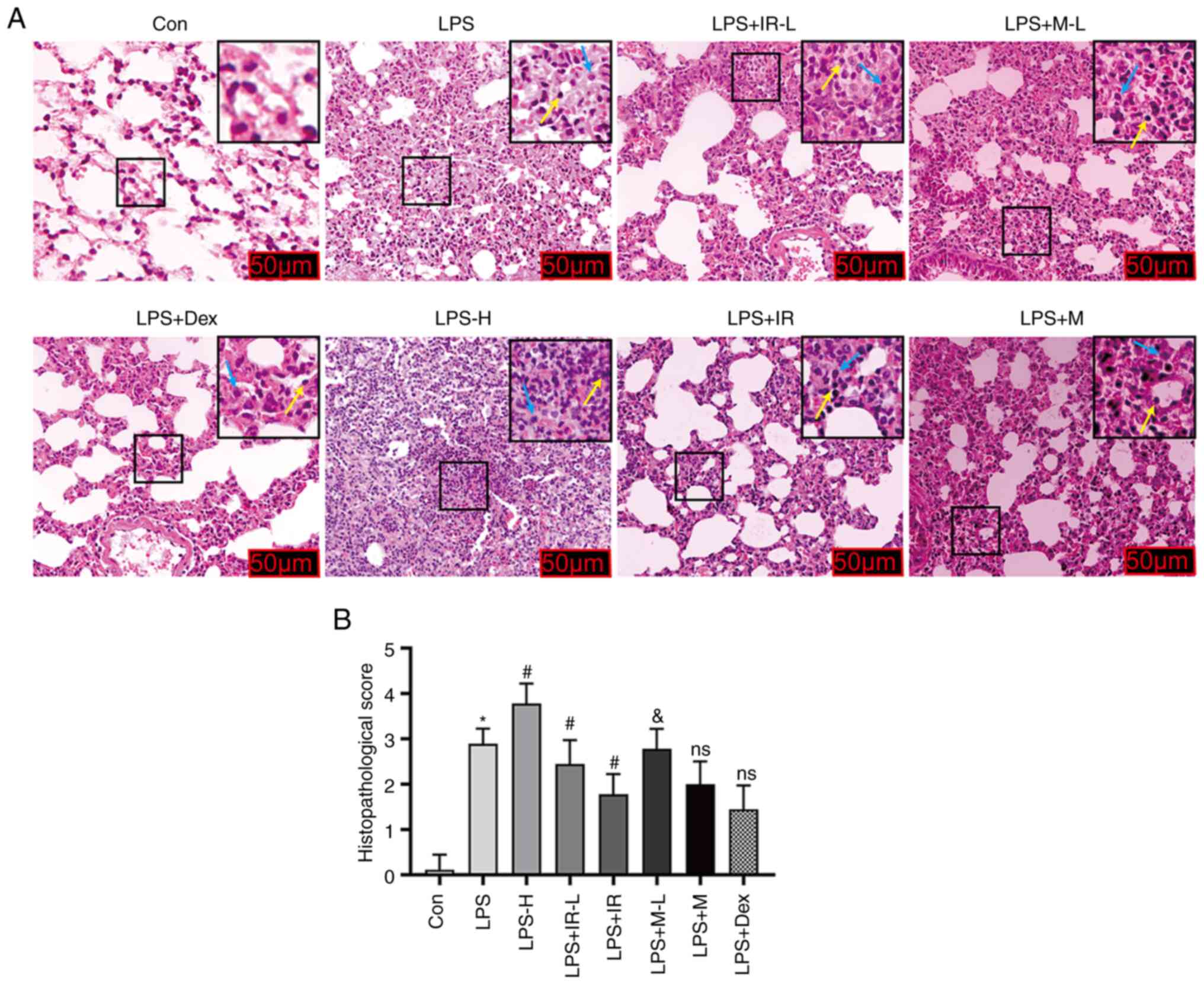
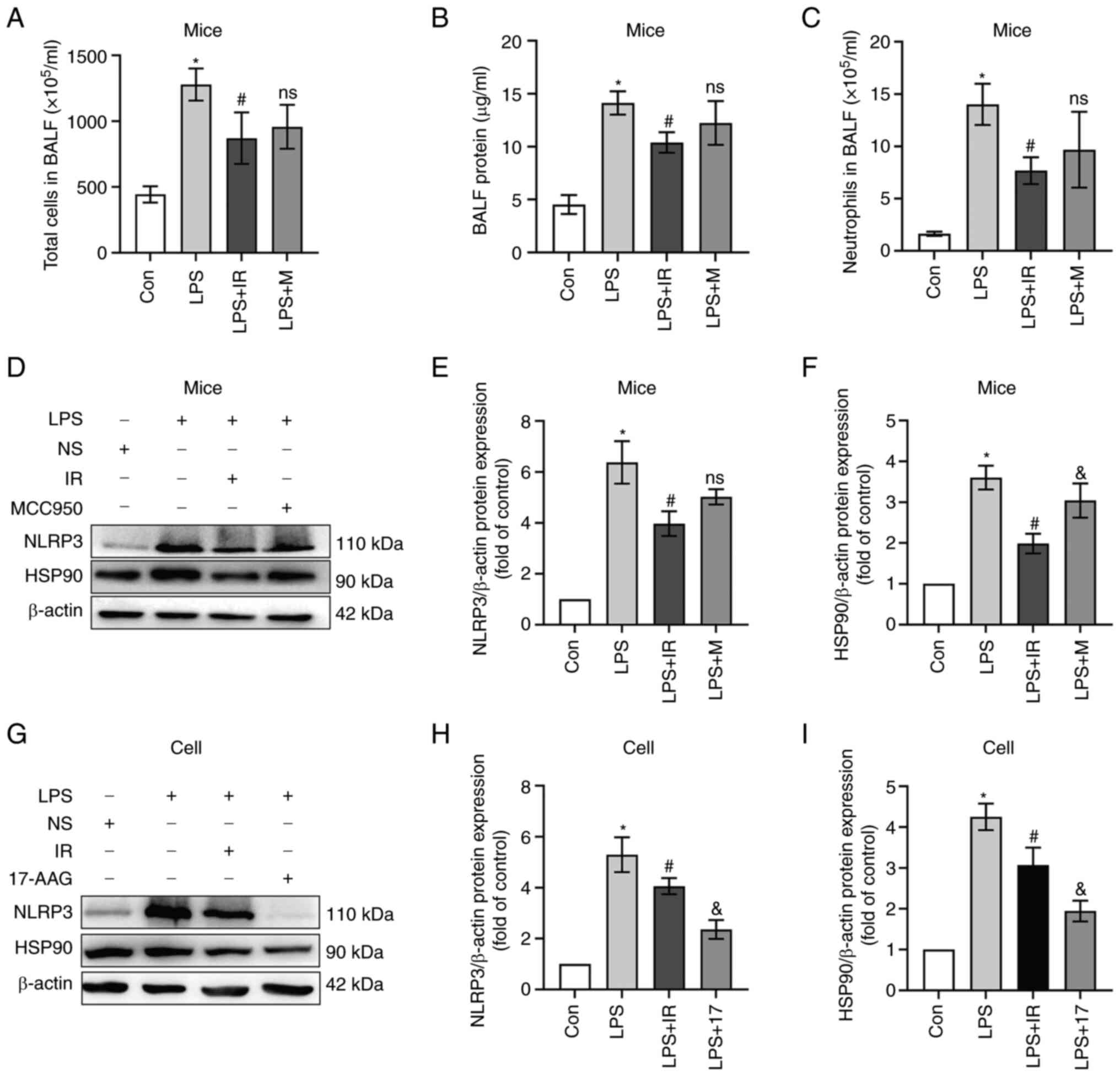
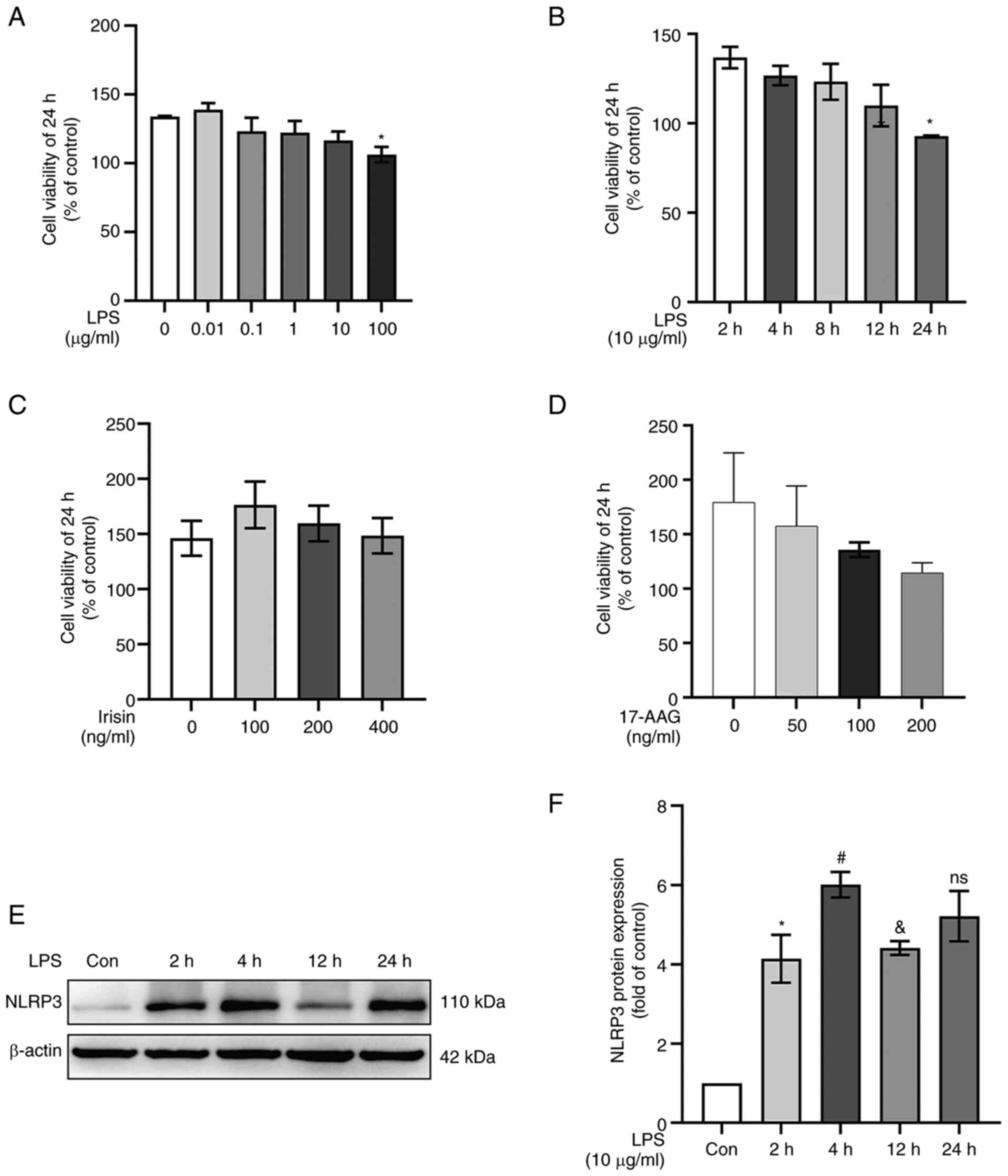
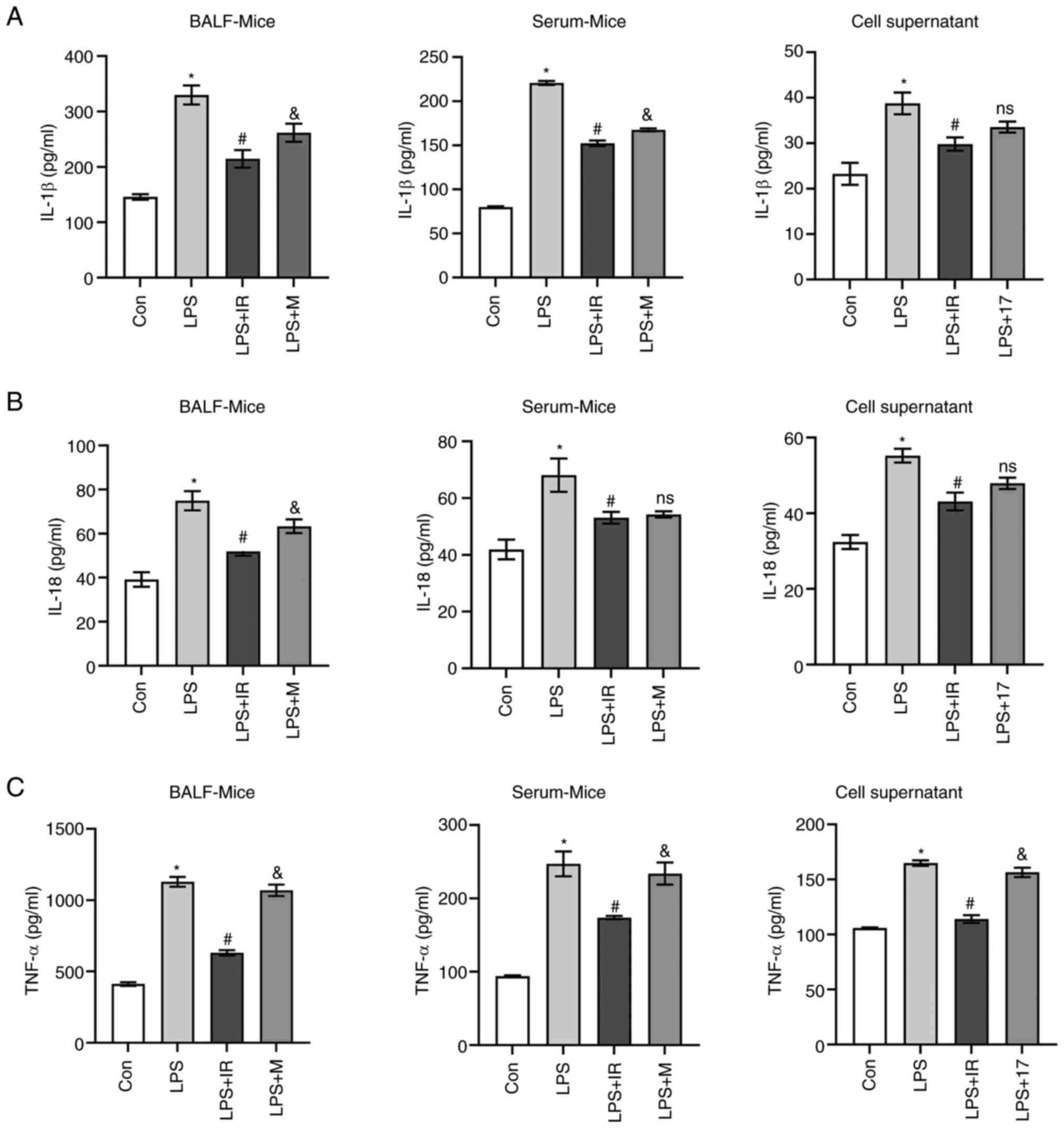
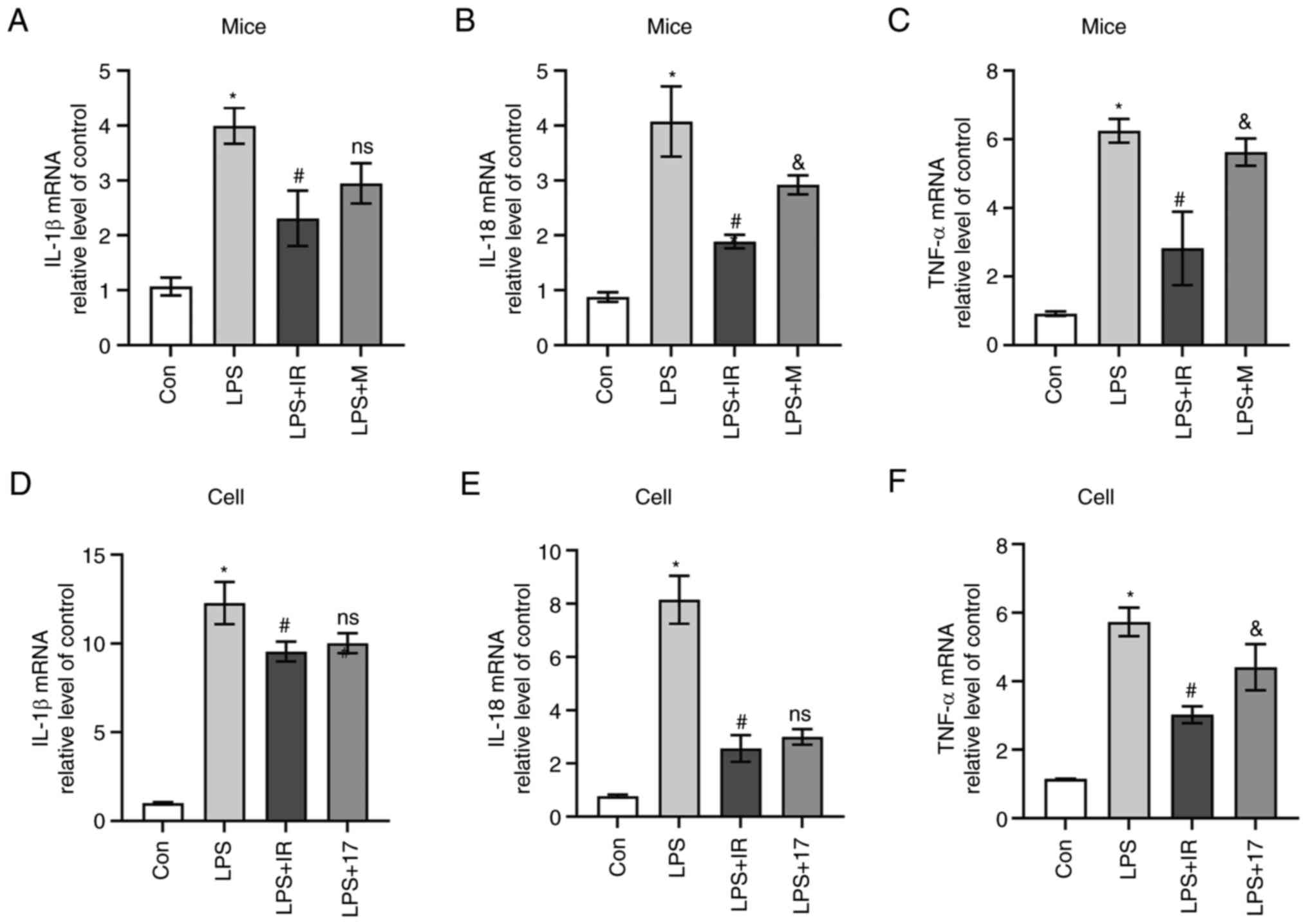
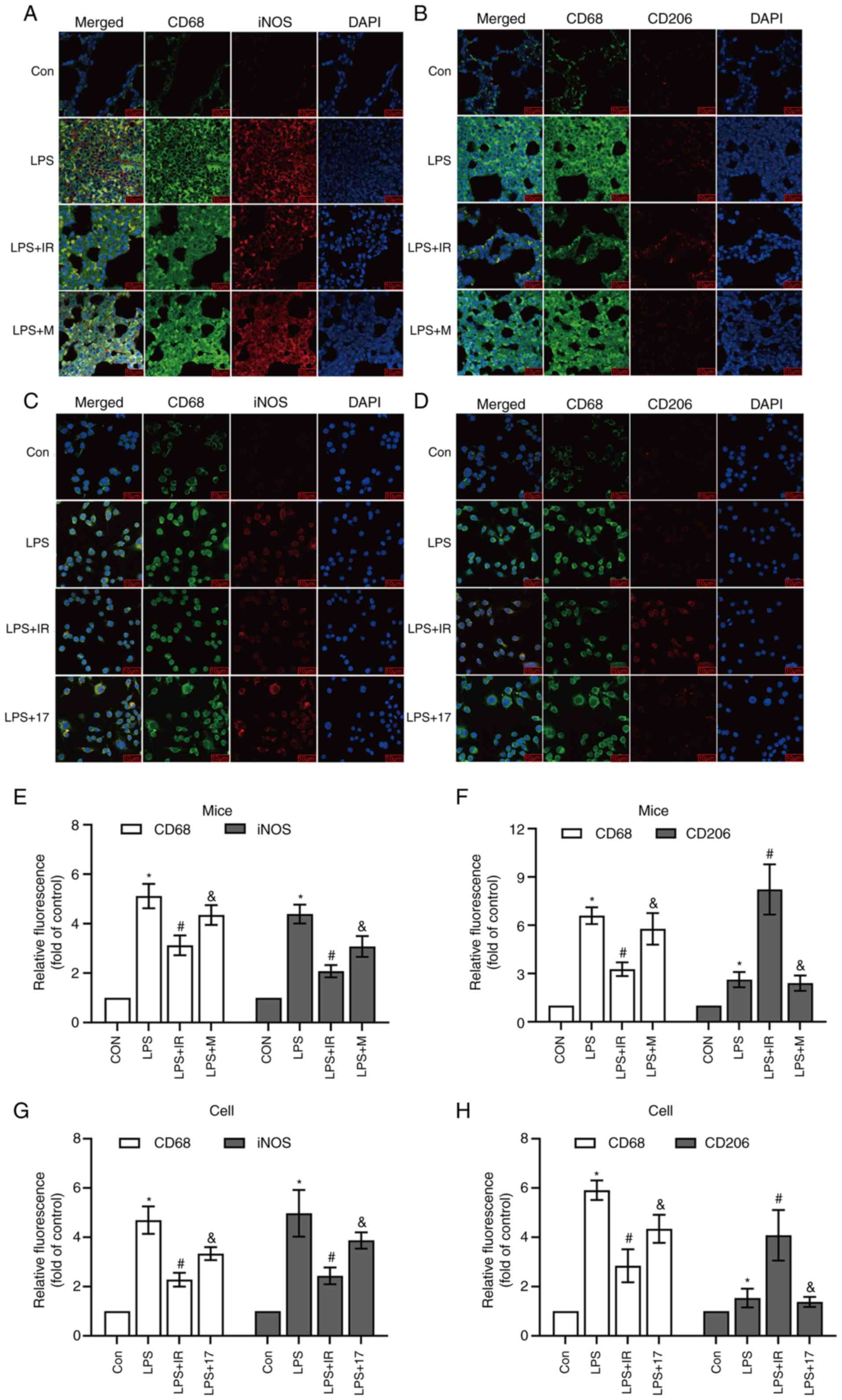
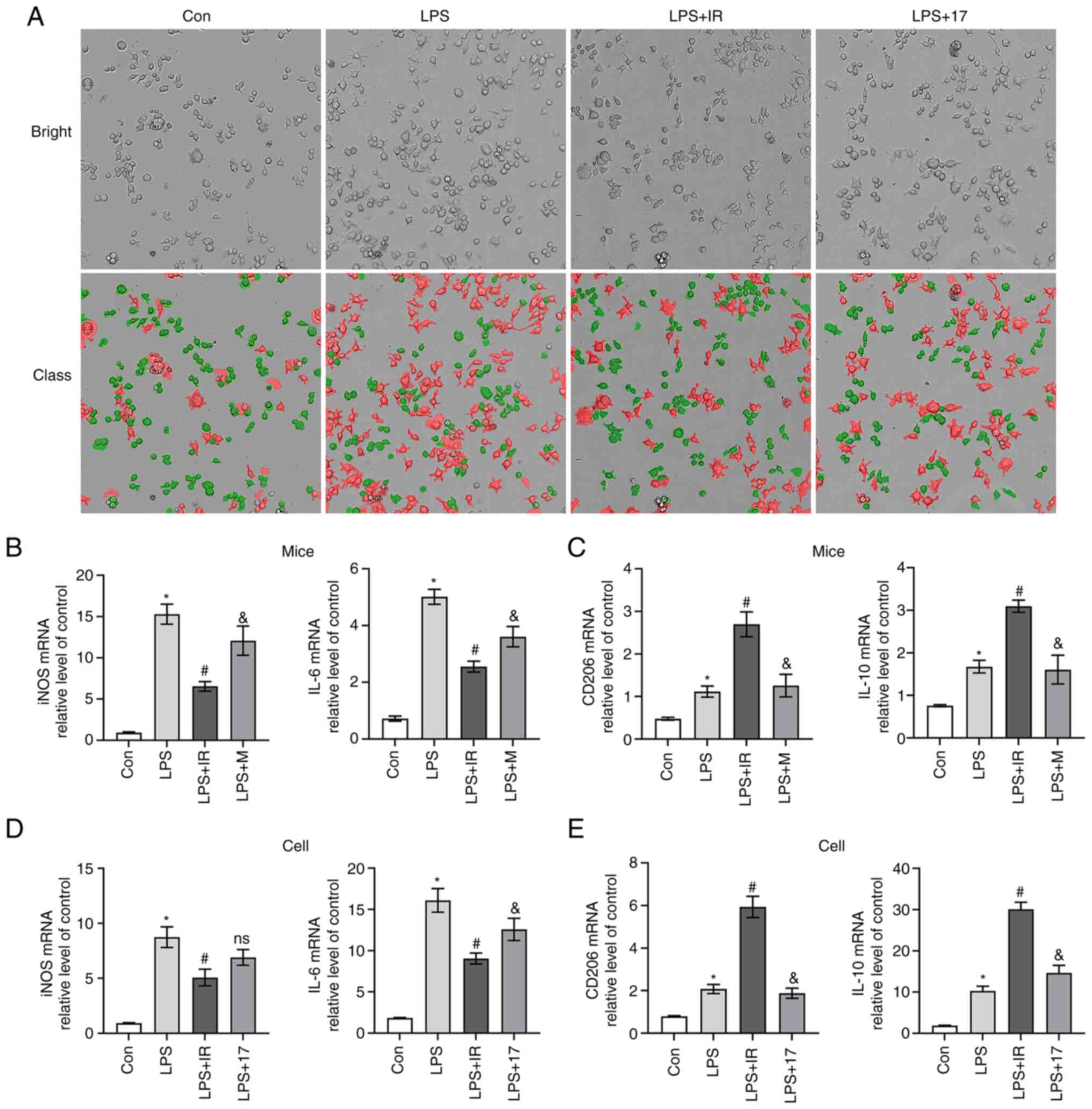
|
1
|
Wheeler AP and Bernard GR: Acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: A clinical
review. Lancet. 369:1553–1564. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou Z, Li X, Qian Y, Liu C, Huang X and
Fu M: Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors suppress pyroptosis in THP-1
cells. Biochem J. 477:3923–3934. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kovacs SB and Miao EA: Gasdermins:
Effectors of pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 27:673–684. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan EK and Fan J: Regulation of alveolar
macrophage death in acute lung inflammation. Respir Res. 19:502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martin WJ II, Wu M and Pasula R: A novel
approach to restore lung immunity during systemic
immunosuppression. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 116:221–227.
2005.
|
|
7
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gordon S, Plüddemann A and Martinez
Estrada F: Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic
diversity and functions. Immunol Rev. 262:36–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu J, Jiang Y, Wang J, Shi X, Liu Q, Liu
Z, Li Y, Scott MJ, Xiao G, Li S, et al: Macrophage endocytosis of
high-mobility group box 1 triggers pyroptosis. Cell Death Differ.
21:1229–1239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Z, Scott MJ, Fan EK, Li Y, Liu J, Xiao
G, Li S, Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Jiang Y and Fan J: Tissue damage
negatively regulates LPS-induced macrophage necroptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 23:1428–1447. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Zhao Y, Zhang P, Li Y, Yang Y,
Yang Y, Zhu J, Song X, Jiang G and Fan J: Hemorrhagic shock primes
for lung vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis: Role in pulmonary
inflammation following LPS. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He X, Qian Y, Li Z, Fan EK, Li Y, Wu L,
Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Shi X and Fan J: TLR4-upregulated IL-1β and
IL-1RI promote alveolar macrophage pyroptosis and lung inflammation
through an autocrine mechanism. Sci Rep. 6:316632016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mayor A, Martinon F, De Smedt T, Pétrilli
V and Tschopp J: A crucial function of SGT1 and HSP90 in
inflammasome activity links mammalian and plant innate immune
responses. Nat Immunol. 8:497–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Davis BK, Wen H and Ting JP: The
inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated
diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:707–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Piippo N, Korhonen E, Hytti M, Skottman H,
Kinnunen K, Josifovska N, Petrovski G, Kaarniranta K and Kauppinen
A: Hsp90 inhibition as a means to inhibit activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome. Sci Rep. 8:67202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang M, Liu L, Lin X, Wang Y, Li Y, Guo
Q, Li S, Sun Y, Tao X, Zhang D, et al: A translocation pathway for
vesicle-mediated unconventional protein secretion. Cell.
181:637–652.e615. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X and Rapoport TA: Mechanistic insights
into ER-associated protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
53:22–28. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruggiano A, Foresti O and Carvalho P:
Quality control: ER-associated degradation: Protein quality control
and beyond. J Cell Biol. 204:869–879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V,
Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE and Mantzoros CS: FNDC5 and
irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in
serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating
concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism.
61:1725–1738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rabiee F, Lachinani L, Ghaedi S,
Nasr-Esfahani MH, Megraw TL and Ghaedi K: New insights into the
cellular activities of Fndc5/Irisin and its signaling pathways.
Cell Biosci. 10:512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong XQ, Geng Z, Zhou B, Zhang F, Han Y,
Zhou YB, Wang JJ, Gao XY, Chen Q, Li YH, et al: FNDC5 attenuates
adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance via
AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization in obesity. Metabolism.
83:31–41. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mazur-Bialy AI, Pocheć E and Zarawski M:
Anti-inflammatory properties of irisin, mediator of physical
activity, are connected with TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
activation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:7012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shao L, Meng D, Yang F, Song H and Tang D:
Irisin-mediated protective effect on LPS-induced acute lung injury
via suppressing inflammation and apoptosis of alveolar epithelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:194–200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (NRC): Institute
for laboratory animal research: Guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals. 8th edition. National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Griffin RJ, Williams BW, Bischof JC, Olin
M, Johnson GL and Lee BW: Use of a fluorescently labeled
poly-caspase inhibitor for in vivo detection of apoptosis related
to vascular-targeting agent arsenic trioxide for cancer therapy.
Technol Cancer Res Treat. 6:651–654. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cursio R, Colosetti P, Auberger P and
Gugenheim J: Liver apoptosis following normothermic
ischemia-reperfusion: In vivo evaluation of caspase activity by
FLIVO assay in rats. Transplant Proc. 40:2038–2041. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gill SE, Rohan M and Mehta S: Role of
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in murine
sepsis-induced lung injury in vivo. Respir Res. 16:1092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Lei W, Zhang S and Yao L: MCC950,
a NLRP3 inhibitor, ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
inflammation in mice. Bioorg Med Chem. 30:1159542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yokoyama S, Cai Y, Murata M, Tomita T,
Yoneda M, Xu L, Pilon AL, Cachau RE and Kimura S: A novel pathway
of LPS uptake through syndecan-1 leading to pyroptotic cell death.
Elife. 7:e378542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, He WT, Hu L, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X,
Xu X, Wang Z, Huang K and Han J: Pyroptosis is driven by
non-selective gasdermin-D pore and its morphology is different from
MLKL channel-mediated necroptosis. Cell Res. 26:1007–1020. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT:
Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to
osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages. Cell Microbiol.
8:1812–1825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lv H, Liu Q, Wen Z, Feng H, Deng X and Ci
X: Xanthohumol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute
lung injury via induction of AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signal axis. Redox
Biol. 12:311–324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hughes KT and Beasley MB: Pulmonary
manifestations of acute lung injury: More than just diffuse
alveolar damage. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 141:916–922. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nahrendorf M and Swirski FK: Abandoning
M1/M2 for a network model of macrophage function. Circ Res.
119:414–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Jiang R, Xu J, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Liu J and
Tan Y: Ligustrazine alleviate acute lung injury through suppressing
pyroptosis and apoptosis of alveolar macrophages. Front Pharmacol.
12:6805122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benoit M, Desnues B and Mege JL:
Macrophage polarization in bacterial infections. J Immunol.
181:3733–3739. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Man SM, Karki R and Kanneganti TD:
Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory
caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev.
277:61–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Frank D and Vince JE: Pyroptosis versus
necroptosis: Similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death
Differ. 26:99–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sun X, Sun J, Dong B, Huang G, Zhang L,
Zhou W, Lv J, Zhang X, Liu M, Xu L, et al: Noninvasive temperature
monitoring for dual-modal tumor therapy based on lanthanide-doped
up-conversion nanocomposites. Biomaterials. 201:42–52. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Aggarwal NR, King LS and D'Alessio FR:
Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and
resolution. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 306:L709–L725.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He WT, Wan H, Hu L, Chen P, Wang X, Huang
Z, Yang ZH, Zhong CQ and Han J: Gasdermin D is an executor of
pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Res.
25:1285–1298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo D, Dai W, Feng X, Ding C, Shao Q, Xiao
R, Zhao N, Peng W, Yang Y, Cui Y, et al: Suppression of lncRNA
NLRP3 inhibits NLRP3-triggered inflammatory responses in early
acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis. 12:8982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins
SC, Muñoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, Vetter I, Dungan LS, Monks BG,
Stutz A, et al: A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3
inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med.
21:248–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|