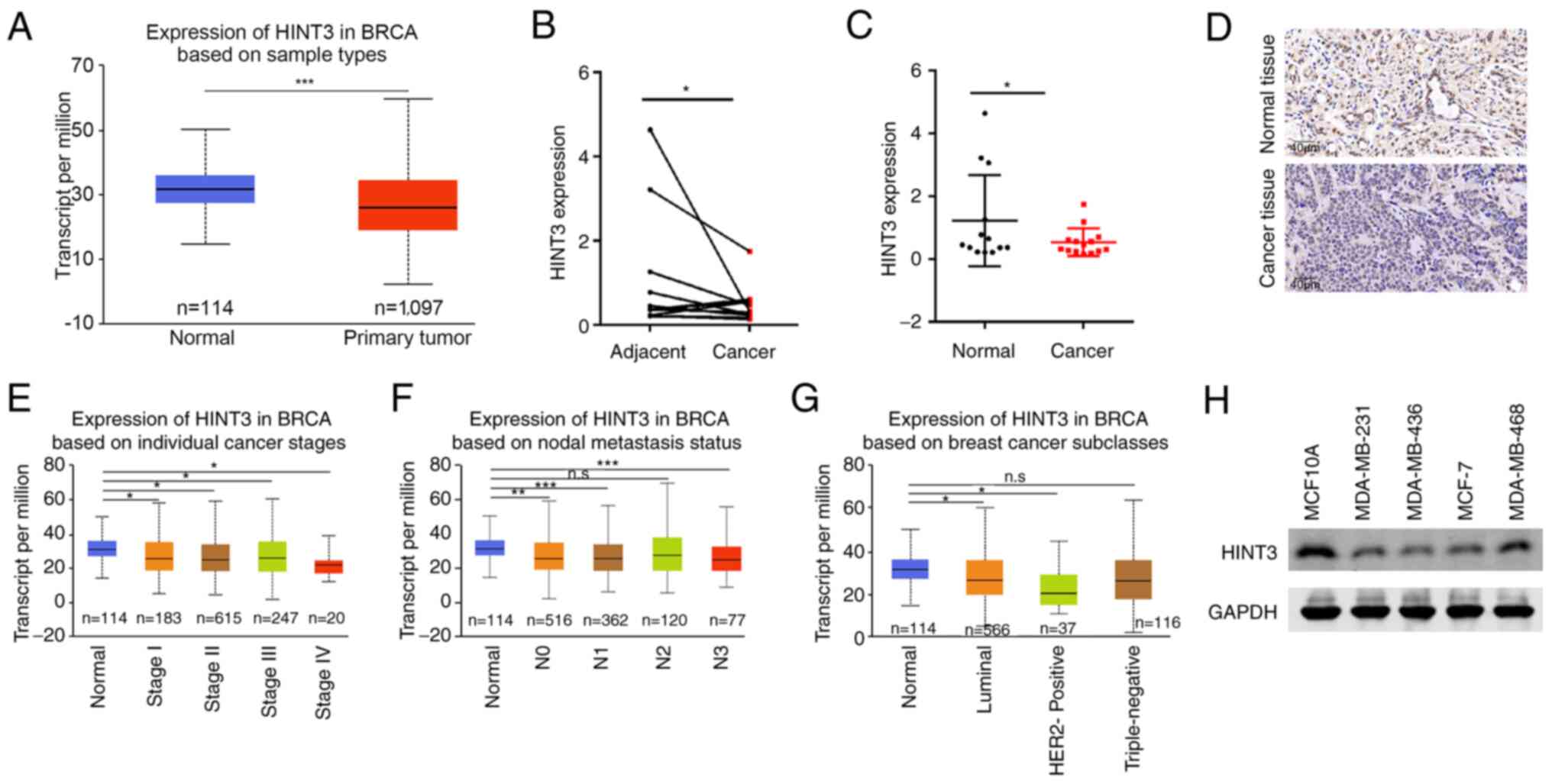
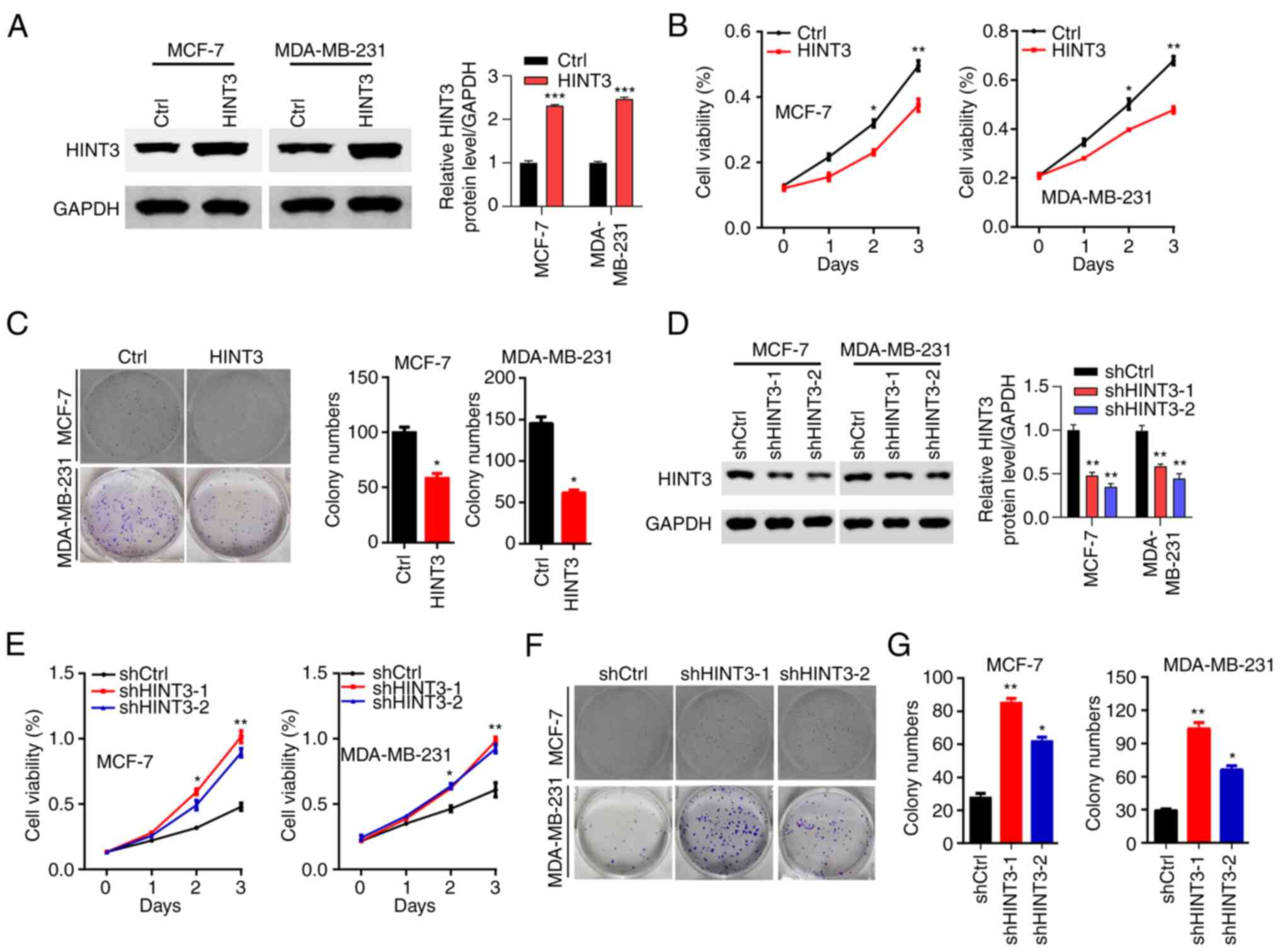
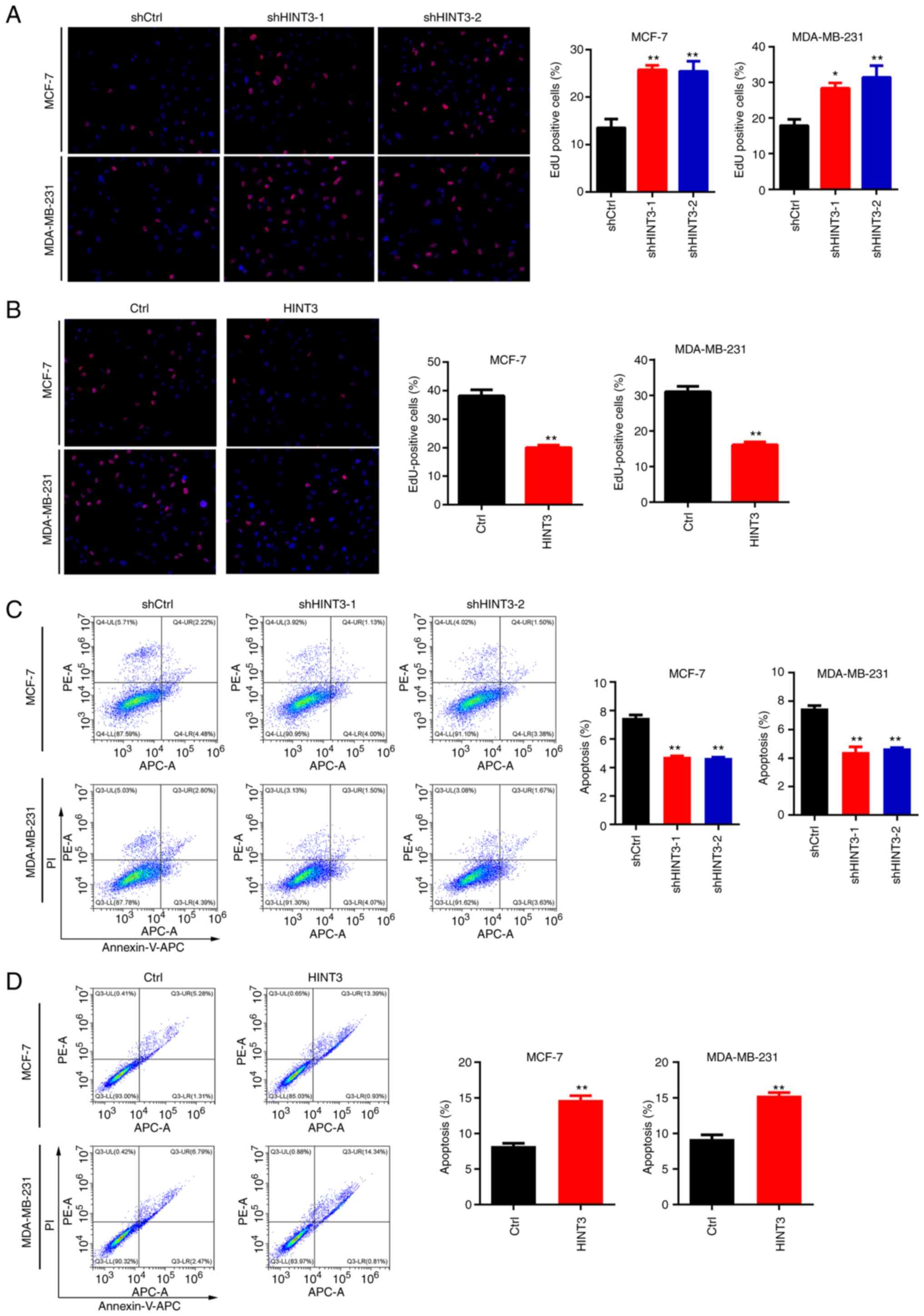
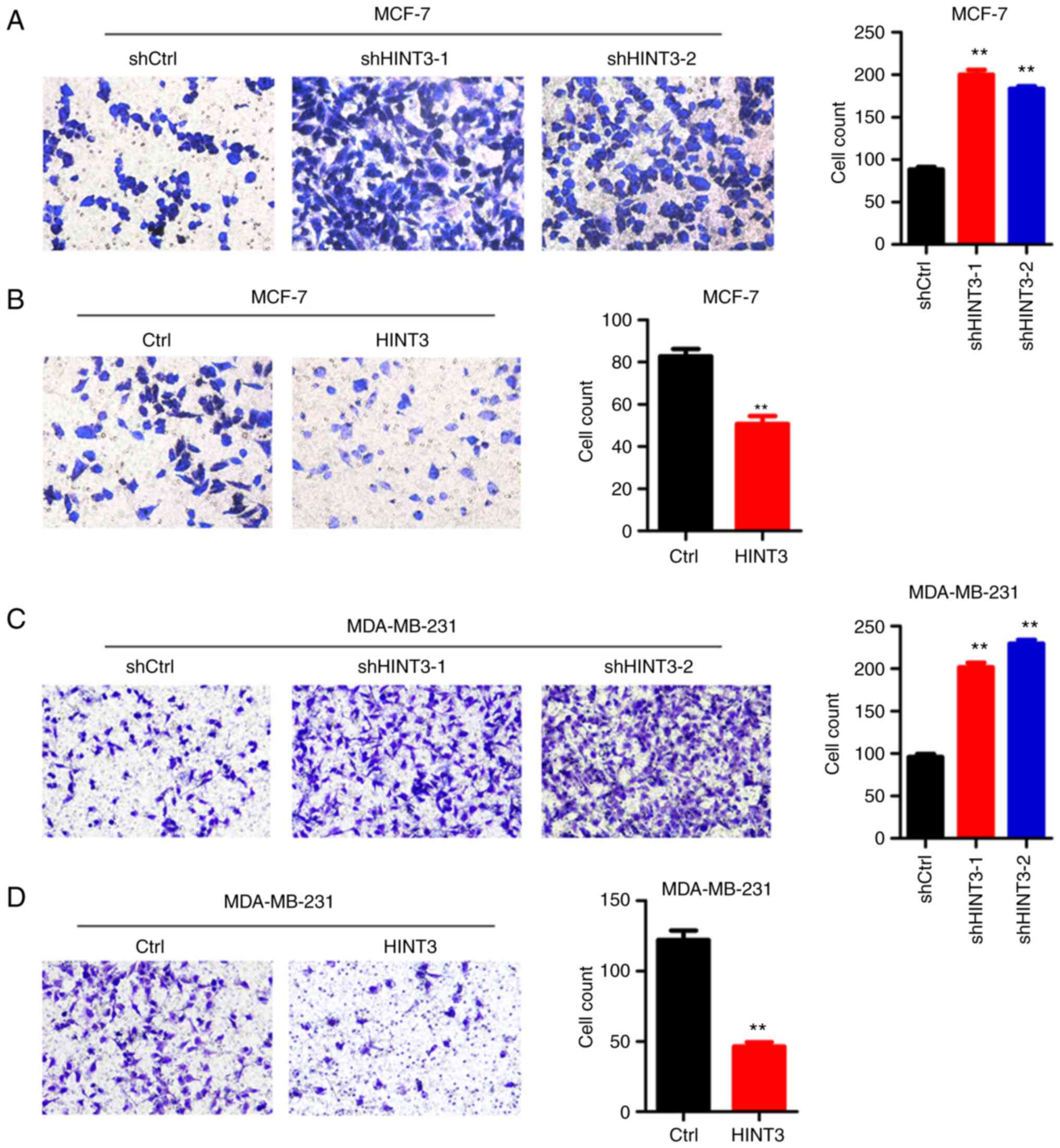
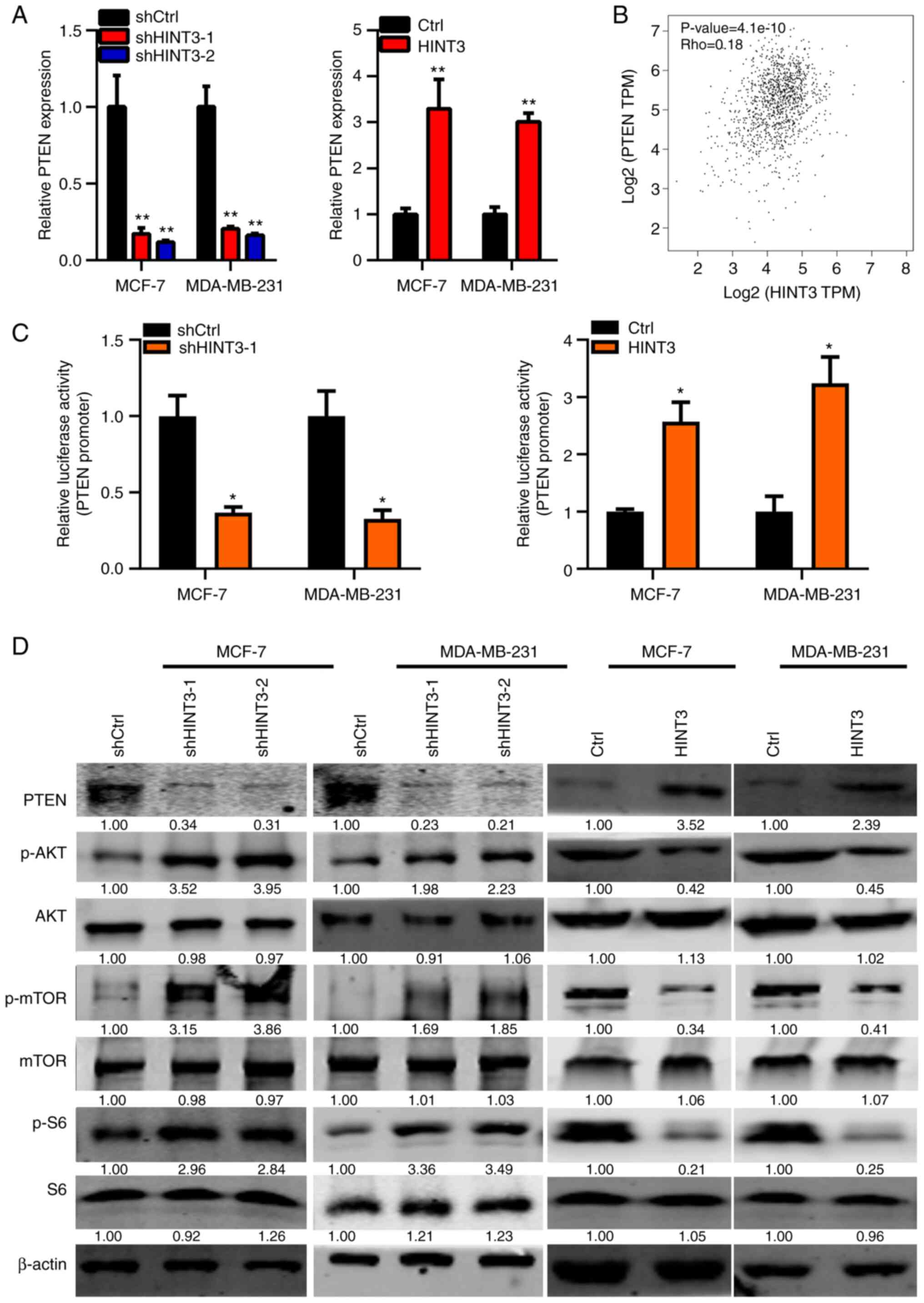
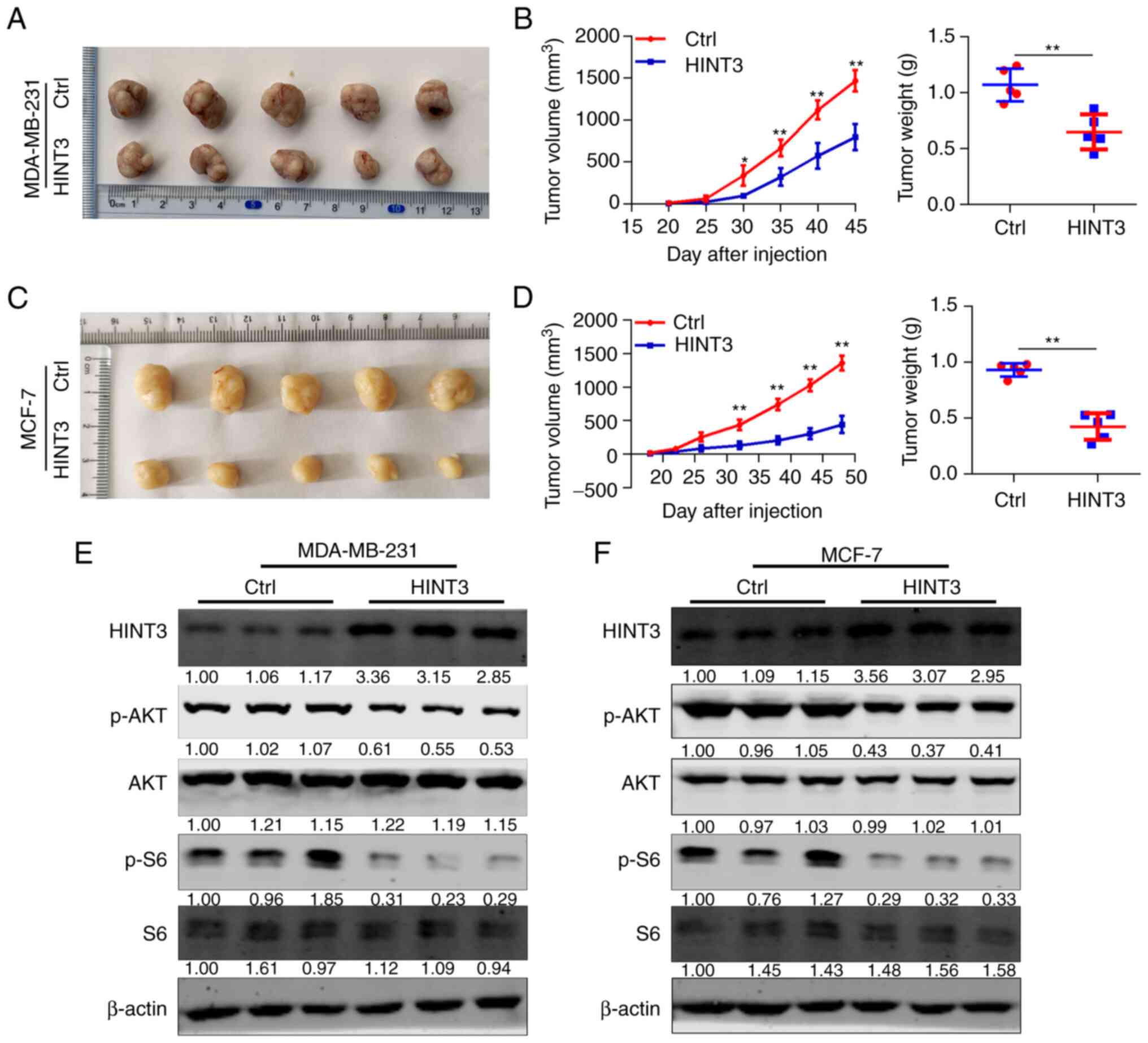
|
1
|
Harbeck N, Penault-Llorca F, Cortes J,
Gnant M, Houssami N, Poortmans P, Ruddy K, Tsang J and Cardoso F:
Breast cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brenner C: Hint, Fhit, and GalT: Function,
structure, evolution, and mechanism of three branches of the
histidine triad superfamily of nucleotide hydrolases and
transferases. Biochemistry. 41:9003–9014. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su T, Suzui M, Wang L, Lin CS, Xing WQ and
Weinstein IB: Deletion of histidine triad nucleotide-binding
protein 1/PKC-interacting protein in mice enhances cell growth and
carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7824–7829. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li H, Zhang Y, Su T, Santella RM and
Weinstein IB: Hint1 is a haplo-insufficient tumor suppressor in
mice. Oncogene. 25:713–721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang H, Wei X, Su X, Qiao F, Xu Z, Gu D,
Fan H and Chen J: Clinical significance of expression of Hint1 and
potential epigenetic mechanism in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
38:1557–1564. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang YJ, Li H, Wu HC, Shen J, Wang L, Yu
MW, Lee PH, Bernard Weinstein I and Santella RM: Silencing of
Hint1, a novel tumor suppressor gene, by promoter hypermethylation
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 275:277–284. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li W, Cai S, Wang L, Yang C, Zhou B and
Wang H: HINT2 downregulation promotes colorectal carcinoma
migration and metastasis. Oncotarget. 8:13521–13531. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou DK, Qian XH, Cheng J, Chen LH and
Wang WL: Clinical significance of down-regulated HINT2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e178152019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martin J, Magnino F, Schmidt K, Piguet AC,
Lee JS, Semela D, St-Pierre MV, Ziemiecki A, Cassio D, Brenner C,
et al: Hint2, a mitochondrial apoptotic sensitizer down-regulated
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 130:2179–2188. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du L, Li X, Zhen L, Chen W, Mu L, Zhang Y
and Song A: Everolimus inhibits breast cancer cell growth through
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:7163–7169.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li F, Shi Y, Yang X, Luo Z, Zhang G, Yu K,
Li F, Chen L, Zhao Y, Xie Y, et al: Anhydroicaritin inhibits EMT in
breast cancer by enhancing GPX1 expression: A research based on
sequencing technologies and bioinformatics analysis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7644812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Wu N, Zhang J, Wang H and Men X:
MiR-153-5p enhances the sensitivity of triple-negative breast
cancer cells to paclitaxel by inducing G2M phase arrest. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:4089–4097. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao C, Xiao G, Piersigilli A, Gou J,
Ogunwobi O and Bargonetti J: Context-dependent roles of MDMX (MDM4)
and MDM2 in breast cancer proliferation and circulating tumor
cells. Breast Cancer Res. 21:52019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bachmeier B, Fichtner I, Killian PH,
Kronski E, Pfeffer U and Efferth T: Development of resistance
towards artesunate in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. PLoS
One. 6:e205502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salic A and Mitchison TJ: A chemical
method for fast and sensitive detection of DNA synthesis in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2415–2420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chou TF, Cheng J, Tikh IB and Wagner CR:
Evidence that human histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 3
(Hint3) is a distinct branch of the histidine triad (HIT)
superfamily. J Mol Biol. 373:978–989. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huen MSY, Sy SMH and Chen J: BRCA1 and its
toolbox for the maintenance of genome integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 11:138–148. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR,
Phillips KA, Mooij TM, Roos-Blom MJ, Jervis S, van Leeuwen FE,
Milne RL, Andrieu N, et al: Risks of breast, ovarian, and
contralateral breast cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers.
JAMA. 317:2402–2416. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Balmaña J, Diez O, Rubio IT and Cardoso F;
ESMO Guidelines Working Group, : BRCA in breast cancer: ESMO
clinical practice guidelines. Ann Oncol. 22 (Suppl 6):vi31–vi34.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paluch-Shimon S, Cardoso F, Sessa C,
Balmana J, Cardoso MJ, Gilbert F and Senkus E; ESMO Guidelines
Committee, : Prevention and screening in BRCA mutation carriers and
other breast/ovarian hereditary cancer syndromes: ESMO clinical
practice guidelines for cancer prevention and screening. Ann Oncol.
27 (Suppl 5):v103–v110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nik-Zainal S, Davies H, Staaf J,
Ramakrishna M, Glodzik D, Zou X, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB,
Martin S, Wedge DC, et al: Landscape of somatic mutations in 560
breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature. 534:47–54. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Litton JK, Rugo HS, Ettl J, Hurvitz SA,
Gonçalves A, Lee KH, Fehrenbacher L, Yerushalmi R, Mina LA, Martin
M, et al: Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a
germline BRCA mutation. N Engl J Med. 379:753–763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ozga M: HINT1-a novel tumor suppressor
protein of the HIT superfamily. Postepy Biochem. 56:55–60. 2010.(In
Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martin J, St-Pierre MV and Dufour JF: Hit
proteins, mitochondria and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1807:626–632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Worby CA and Dixon JE: Pten. Annu Rev
Biochem. 83:641–669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan H, Wu Y, Yu S, Li X, Wang A, Wang S,
Chen W and Lu Y: Critical role of mTOR in regulating aerobic
glycolysis in carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 58:9–19. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Liang D, Zhang XP, He CF, Cao L,
Zhang SQ, Xiao X, Li SJ and Cao YX: Novel PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
inhibitor, W922, prevents colorectal cancer growth via the
regulation of autophagy. Int J Oncol. 58:70–82. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Costa C, Wang Y, Ly A, Hosono Y, Murchie
E, Walmsley CS, Huynh T, Healy C, Peterson R, Yanase S, et al: PTEN
loss mediates clinical cross-resistance to CDK4/6 and PI3Kα
inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 10:72–85. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pandolfi PP: Breast cancer-loss of PTEN
predicts resistance to treatment. N Engl J Med. 351:2337–2338.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose
S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al:
PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human
brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 275:1943–1947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Donia M, McCubrey JA, Bendtzen K and
Nicoletti F: Potential use of rapamycin in HIV infection. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 70:784–793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Basile MS, Cavalli E, McCubrey J,
Hernández-Bello J, Muñoz-Valle JF, Fagone P and Nicoletti F: The
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: A potential pharmacological target in
COVID-19. Drug Discov Today. 27:848–856. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mammana S, Bramanti P, Mazzon E, Cavalli
E, Basile MS, Fagone P, Petralia MC, McCubrey JA, Nicoletti F and
Mangano K: Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in
animal models of multiple sclerosis. Oncotarget. 9:8263–8277. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ji L, Xie W and Zhang Z: Efficacy and
safety of sirolimus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum.
50:1073–1080. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|