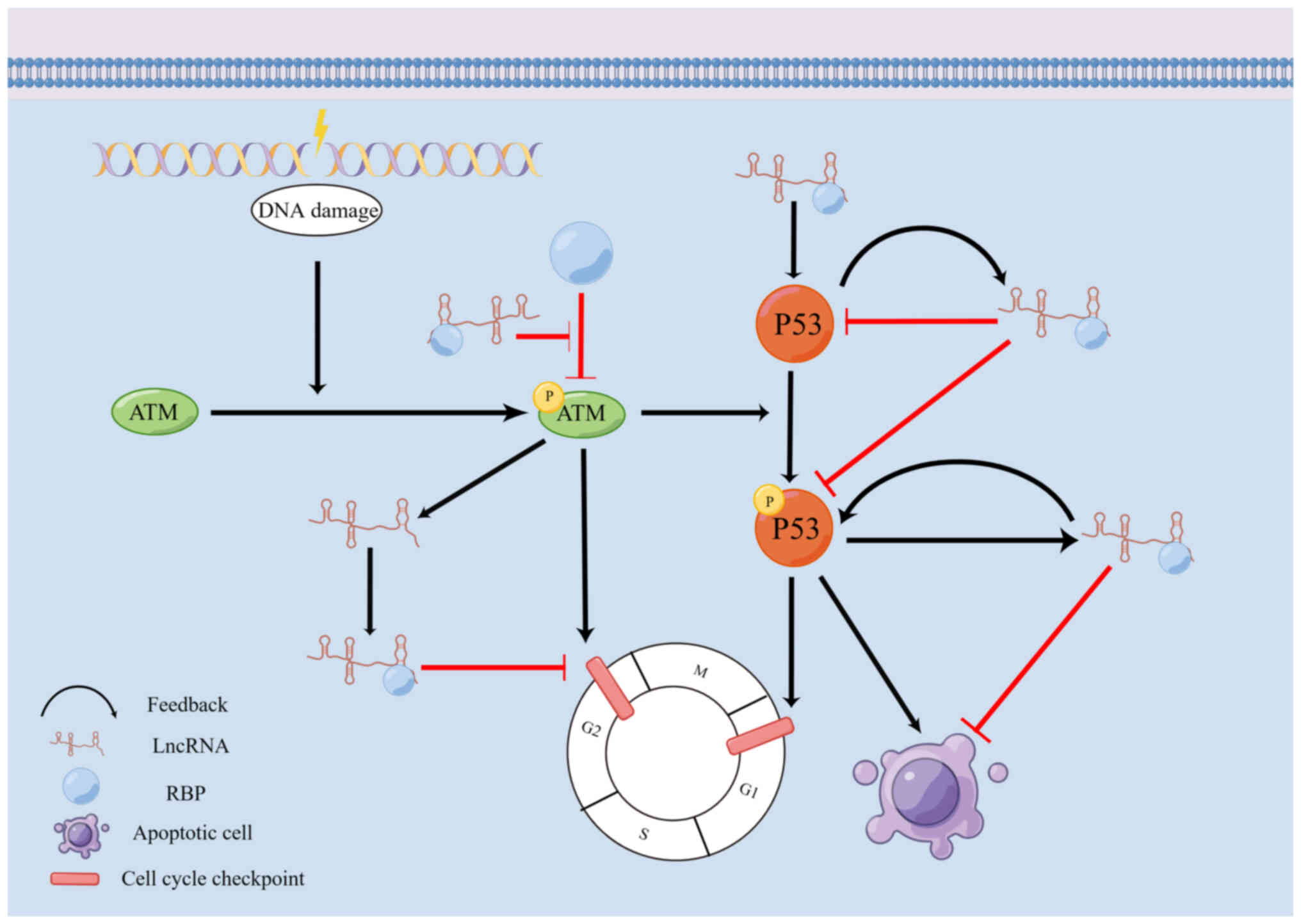
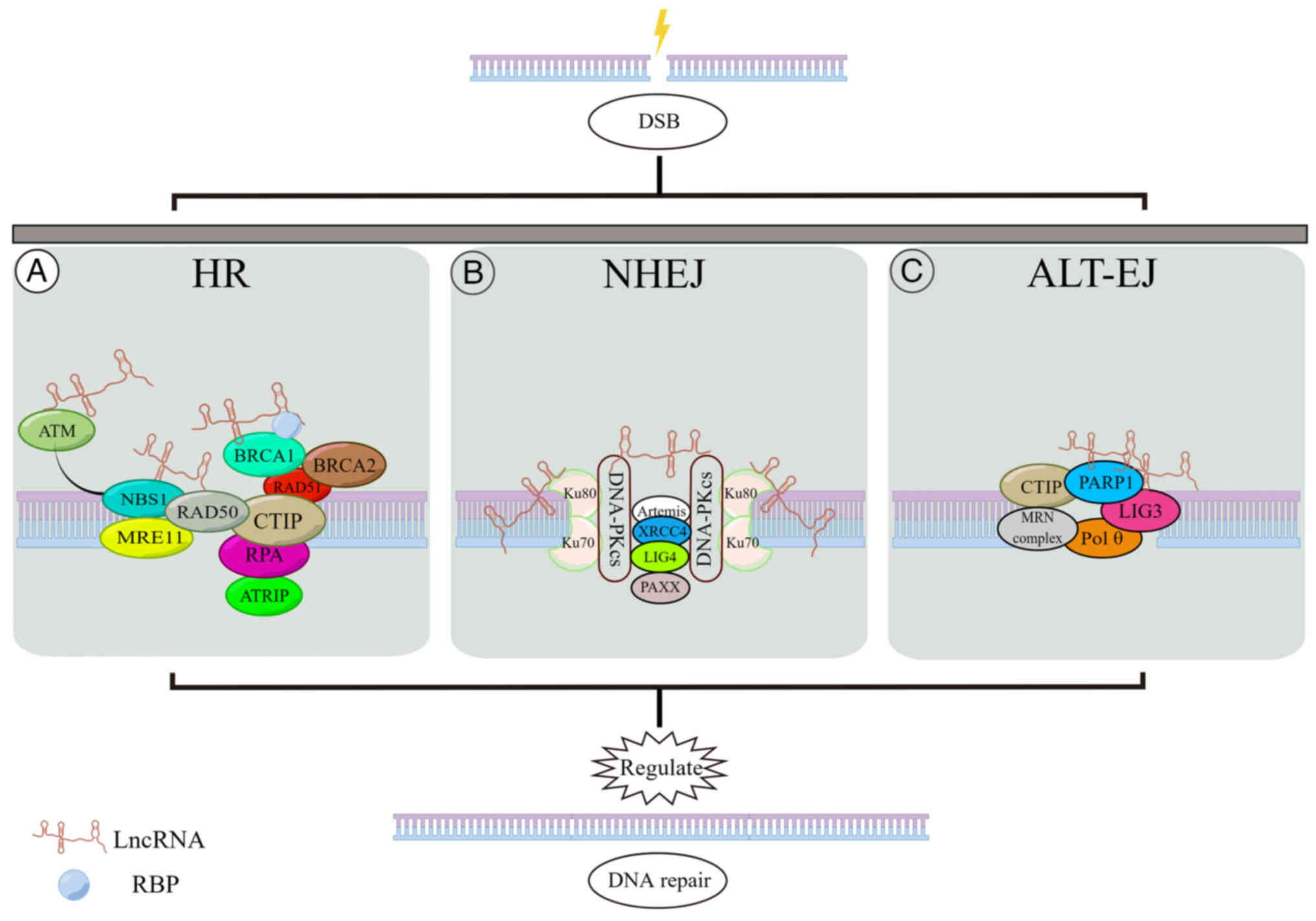
|
1
|
Ragunathan K, Upfold NLE and Oksenych V:
Interaction between fibroblasts and immune cells following DNA
Damage induced by ionizing radiation. Int J Mol Sci. 21:86352020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marshall CJ and Santangelo TJ: Archaeal
DNA repair mechanisms. Biomolecules. 10:14722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maremonti E, Brede DA, Olsen AK, Eide DM
and Berg ES: Ionizing radiation, genotoxic stress, and
mitochondrial DNA copy-number variation in Caenorhabditis elegans:
Droplet digital PCR analysis. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ
Mutagen. 858-860:5032772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pariset E, Malkani S, Cekanaviciute E and
Costes SV: Ionizing radiation-induced risks to the central nervous
system and countermeasures in cellular and rodent models. Int J
Radiat Biol. 97(Suppl): S132–S150. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu R, Hogberg J, Adner M, Ramos-Ramirez P,
Stenius U and Zheng H: Crystalline silica particles cause rapid
NLRP3-dependent mitochondrial depolarization and DNA damage in
airway epithelial cells. Part Fibre Toxicol. 17:392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dussert F, Arthaud PA, Arnal ME, Dalzon B,
Torres A, Douki T, Herlin N, Rabilloud T and Carriere M: Toxicity
to RAW264.7 macrophages of silica nanoparticles and the E551 food
additive, in combination with genotoxic agents. Nanomaterials
(Basel). 10:14182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang R, Yu T, Li Y and Hu J: Upregulated
has-miR-4516 as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of
dust-induced pulmonary fibrosis in patients with pneumoconiosis.
Toxicol Res (Camb). 7:415–422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gupta N, Khetan D, Chaudhary R and Shukla
JS: Prospective cohort study to assess the effect of storage
duration, Leuko-filtration, and gamma irradiation on cell-free DNA
in red cell components. Transfus Med Hemother. 47:409–419. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lindahl T and Barnes DE: Repair of
endogenous DNA damage. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol.
65:127–133. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jackson SP and Bartek J: The DNA-damage
response in human biology and disease. Nature. 461:1071–1078. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aguilera A and Garcia-Muse T: Causes of
genome instability. Annu Rev Genet. 47:1–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aguilera A and Gomez-Gonzalez B: Genome
instability: A mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat
Rev Genet. 9:204–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Sun H, Huang Y, Wang Y, Liu Y and
Chen X: Pathways and assays for DNA double-strand break repair by
homologous recombination. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
51:879–889. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O'Connor MJ: Targeting the DNA damage
response in cancer. Mol Cell. 60:547–560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: The DNA damage
response and cancer therapy. Nature. 481:287–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pilie PG, Tang C, Mills GB and Yap TA:
State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response
in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:81–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Marchese FP, Raimondi I and Huarte M: The
multidimensional mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function. Genome
Biol. 18:2062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fanale D, Castiglia M, Bazan V and Russo
A: Involvement of Non-coding RNAs in Chemo- and Radioresistance of
colorectal Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 937:207–228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou XL, Wang WW, Zhu WG, Yu CH, Tao GZ,
Wu QQ, Song YQ, Pan P and Tong YS: High expression of long
non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 predicts chemoradioresistance and poor
prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Mol Carcinog.
55:2095–2105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haemmig S, Yang D, Sun X, Das D, Ghaffari
S, Molinaro R, Chen L, Deng Y, Freeman D, Moullan N, et al: Long
noncoding RNA SNHG12 integrates a DNA-PK-mediated DNA damage
response and vascular senescence. Sci Transl Med. 12:eaaw18682020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Tao Y, Li Y, Zhao J, Zhang L,
Zhang X, Dong C, Xie Y, Dai X, Zhang X and Liao Q: The regulatory
network analysis of long noncoding RNAs in human colorectal cancer.
Funct Integr Genomics. 18:261–275. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y and Wang Y, Luo W, Song X, Huang L,
Xiao J, Jin F, Ren Z and Wang Y: Roles of long non-coding RNAs and
emerging RNA-binding proteins in innate antiviral responses.
Theranostics. 10:9407–9424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ciccia A and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 40:179–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Michelini F, Pitchiaya S, Vitelli V,
Sharma S, Gioia U, Pessina F, Cabrini M, Wang Y, Capozzo I,
Iannelli F, et al: Damage-induced lncRNAs control the DNA damage
response through interaction with DDRNAs at individual
double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol. 19:1400–1411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Surova O and Zhivotovsky B: Various modes
of cell death induced by DNA damage. Oncogene. 32:3789–3797. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Roos WP, Thomas AD and Kaina B: DNA damage
and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:20–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun X, Wang Y, Ji K, Liu Y, Kong Y, Nie S,
Li N, Hao J, Xie Y, Xu C, et al: NRF2 preserves genomic integrity
by facilitating ATR activation and G2 cell cycle arrest. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48:9109–9123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu R, Hu Y, Zhang S, Li X, Tang M, Yang M,
Wu X, Li Z, Liao X, Xu Y, et al: LncRNA CTBP1-DT-encoded
microprotein DDUP sustains DNA damage response signalling to
trigger dual DNA repair mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res.
50:8060–8079. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu CH, Chen CY, Yeh CT and Lin KH:
Radiosensitization of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting
radio-associated MicroRNA. Int J Mol Sci. 21:18592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kitagawa R and Kastan MB: The
ATM-dependent DNA damage signaling pathway. Cold Spring Harb Symp
Quant Biol. 70:99–109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A,
McDonald ER III, Hurov KE, Luo J, Bakalarski CE, Zhao Z, Solimini
N, Lerenthal Y, et al: ATM and ATR substrate analysis reveals
extensive protein networks responsive to DNA damage. Science.
316:1160–1166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bartek J and Lukas J: DNA damage
checkpoints: From initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 19:238–245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shiloh Y: ATM and related protein kinases:
Safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:155–168. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wan G, Mathur R, Hu X, Liu Y, Zhang X,
Peng G and Lu X: Long non-coding RNA ANRIL (CDKN2B-AS) is induced
by the ATM-E2F1 signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 25:1086–1095. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wan G, Hu X, Liu Y, Han C, Sood AK, Calin
GA, Zhang X and Lu X: A novel non-coding RNA lncRNA-JADE connects
DNA damage signalling to histone H4 acetylation. EMBO J.
32:2833–2847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schoeftner S and Blasco MA:
Developmentally regulated transcription of mammalian telomeres by
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Nat Cell Biol. 10:228–236. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu Y and Komiyama M: Structure, function
and targeting of human telomere RNA. Methods. 57:100–105. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Dai Y, Hardy S
and de Lange T: p53- and ATM-dependent apoptosis induced by
telomeres lacking TRF2. Science. 283:1321–1325. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Okamoto K, Bartocci C, Ouzounov I,
Diedrich JK, Yates JR III and Denchi EL: A two-step mechanism for
TRF2-mediated chromosome-end protection. Nature. 494:502–505. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Zeng D, Cao J, Wang M, Shu B,
Kuang G, Ou TM, Tan JH, Gu LQ, Huang ZS and Li D: Interaction of
Quindoline derivative with telomeric repeat-containing RNA induces
telomeric DNA-damage response in cancer cells through inhibition of
telomeric repeat factor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj.
1861:3246–3256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang A, Zhou N, Huang J, Liu Q, Fukuda K,
Ma D, Lu Z, Bai C, Watabe K and Mo YY: The human long non-coding
RNA-RoR is a p53 repressor in response to DNA damage. Cell Res.
23:340–350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Meek DW and Anderson CW: Posttranslational
modification of p53: Cooperative integrators of function. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0009502009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zilfou JT and Lowe SW: Tumor suppressive
functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0018832009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Vousden KH and Prives C: Blinded by the
light: The growing complexity of p53. Cell. 137:413–431. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang A, Xu M and Mo YY: Role of the
lncRNA-p53 regulatory network in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol.
6:181–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shihabudeen Haider Ali MS, Cheng X, Moran
M, Haemmig S, Naldrett MJ, Alvarez S, Feinberg MW and Sun X: LncRNA
Meg3 protects endothelial function by regulating the DNA damage
response. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:1505–1522. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Wen D, Huang Z, Li Z, Tang X, Wen X, Liu J
and Li M: LINC02535 co-functions with PCBP2 to regulate DNA damage
repair in cervical cancer by stabilizing RRM1 mRNA. J Cell Physiol.
235:7592–7603. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li N and Richard S: Sam68 functions as a
transcriptional coactivator of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44:8726–8741. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M,
Raj A, Rivea Morales D, Thomas K, Presser A, Bernstein BE, van
Oudenaarden A, et al: Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs
associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:11667–11672. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, Garber M,
Koziol MJ, Kenzelmann-Broz D, Khalil AM, Zuk O, Amit I, Rabani M,
et al: A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates
global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell. 142:409–419.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hung T, Wang Y, Lin MF, Koegel AK, Kotake
Y, Grant GD, Horlings HM, Shah N, Umbricht C, Wang P, et al:
Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding RNAs within
cell-cycle promoters. Nat Genet. 43:621–629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
van Gent DC, Hoeijmakers JH and Kanaar R:
Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection.
Nat Rev Genet. 2:196–206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sharma V, Khurana S, Kubben N, Abdelmohsen
K, Oberdoerffer P, Gorospe M and Misteli T: A BRCA1-interacting
lncRNA regulates homologous recombination. EMBO Rep. 16:1520–1534.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Deng B, Xu W, Wang Z, Liu C, Lin P, Li B,
Huang Q, Yang J, Zhou H and Qu L: An LTR retrotransposon-derived
lncRNA interacts with RNF169 to promote homologous recombination.
EMBO Rep. 20:e476502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Branzei D and Foiani M: Regulation of DNA
repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:297–308.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lieber MR: The mechanism of human
nonhomologous DNA end joining. J Biol Chem. 283:1–5. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
San Filippo J, Sung P and Klein H:
Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Annu Rev Biochem.
77:229–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kumar A, Purohit S and Sharma NK: Aberrant
DNA Double-strand break repair threads in breast carcinoma:
Orchestrating genomic insult survival. J Cancer Prev. 21:227–234.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yao Y, Li X, Chen W, Liu H, Mi L, Ren D,
Mo A and Lu P: ATM promotes RAD51-mediated meiotic DSB repair by
inter-sister-chromatid recombination in Arabidopsis. Front Plant
Sci. 11:8392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Trenner A and Sartori AA: Harnessing DNA
Double-strand break repair for cancer treatment. Front Oncol.
9:13882019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Gomez-Mejiba SE and Ramirez DC: Trapping
of DNA radicals with the nitrone spin trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline
N-oxide and genotoxic damage: Recent advances using the immuno-spin
trapping technology. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 782:1082832019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dasika GK, Lin SC, Zhao S, Sung P,
Tomkinson A and Lee EY: DNA damage-induced cell cycle checkpoints
and DNA strand break repair in development and tumorigenesis.
Oncogene. 18:7883–7899. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhao Y, Li H, Fang S, Kang Y, Wu W, Hao Y,
Li Z, Bu D, Sun N, Zhang MQ and Chen R: NONCODE 2016: An
informative and valuable data source of long non-coding RNAs.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D203–D208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Dimitrova N, Zamudio JR, Jong RM, Soukup
D, Resnick R, Sarma K, Ward AJ, Raj A, Lee JT, Sharp PA and Jacks
T: LincRNA-p21 activates p21 in cis to promote Polycomb target gene
expression and to enforce the G1/S checkpoint. Mol Cell.
54:777–790. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Schmitt AM, Garcia JT, Hung T, Flynn RA,
Shen Y, Qu K, Payumo AY, Peres-da-Silva A, Broz DK, Baum R, et al:
An inducible long noncoding RNA amplifies DNA damage signaling. Nat
Genet. 48:1370–1376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu X, Li D, Zhang W, Guo M and Zhan Q:
Long non-coding RNA gadd7 interacts with TDP-43 and regulates Cdk6
mRNA decay. EMBO J. 31:4415–4427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shen L, Wang Q, Liu R, Chen Z, Zhang X,
Zhou P and Wang Z: LncRNA lnc-RI regulates homologous recombination
repair of DNA double-strand breaks by stabilizing RAD51 mRNA as a
competitive endogenous RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:717–729. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Huang R and Zhou PK: DNA damage repair:
Historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical
translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 6:2542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Thapar R, Wang JL, Hammel M, Ye R, Liang
K, Sun C, Hnizda A, Liang S, Maw SS, Lee L, et al: Mechanism of
efficient double-strand break repair by a long non-coding RNA.
Nucleic Acids Res. 48:10953–10972. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang Y, He Q, Hu Z, Feng Y, Fan L, Tang
Z, Yuan J, Shan W, Li C, Hu X, et al: Long noncoding RNA LINP1
regulates repair of DNA double-strand breaks in triple-negative
breast cancer. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 23:522–530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang X, Liu H, Shi L, Yu X, Gu Y and Sun
X: LINP1 facilitates DNA damage repair through non-homologous end
joining (NHEJ) pathway and subsequently decreases the sensitivity
of cervical cancer cells to ionizing radiation. Cell Cycle.
17:439–447. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Soutoglou E and Misteli T: Activation of
the cellular DNA damage response in the absence of DNA lesions.
Science. 320:1507–1510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Downs JA and Jackson SP: A means to a DNA
end: The many roles of Ku. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:367–378. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang D, Zhou Z, Wu E, Ouyang C, Wei G,
Wang Y, He D, Cui Y, Zhang D, Chen X, et al: LRIK interacts with
the Ku70-Ku80 heterodimer enhancing the efficiency of NHEJ repair.
Cell Death Differ. 27:3337–3353. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Guo Z, Wang YH, Xu H, Yuan CS, Zhou HH,
Huang WH, Wang H and Zhang W: LncRNA linc00312 suppresses
radiotherapy resistance by targeting DNA-PKcs and impairing DNA
damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis.
12:692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Uziel T, Lerenthal Y, Moyal L, Andegeko Y,
Mittelman L and Shiloh Y: Requirement of the MRN complex for ATM
activation by DNA damage. EMBO J. 22:5612–5621. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Prakash R, Zhang Y, Feng W and Jasin M:
Homologous recombination and human health: The roles of BRCA1,
BRCA2, and associated proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
7:a0166002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gorgoulis VG, Pefani DE, Pateras IS and
Trougakos IP: Integrating the DNA damage and protein stress
responses during cancer development and treatment. J Pathol.
246:12–40. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Heyer WD, Ehmsen KT and Liu J: Regulation
of homologous recombination in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet.
44:113–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Maréchal A and Zou L: DNA damage sensing
by the ATM and ATR kinases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0127162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Renkawitz J, Lademann CA and Jentsch S:
Mechanisms and principles of homology search during recombination.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:369–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ranjha L, Howard SM and Cejka P: Main
steps in DNA double-strand break repair: An introduction to
homologous recombination and related processes. Chromosoma.
127:187–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yu N, Qin H, Zhang F, Liu T, Cao K, Yang
Y, Chen Y and Cai J: The role and mechanism of long non-coding RNAs
in homologous recombination repair of radiation-induced DNA damage.
J Gene Med. 25:e34702023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ohta T, Sato K and Wu W: The BRCA1
ubiquitin ligase and homologous recombination repair. FEBS Lett.
585:2836–2844. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim H, Chen J and Yu X: Ubiquitin-binding
protein RAP80 mediates BRCA1-dependent DNA damage response.
Science. 316:1202–1205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hu Y, Scully R, Sobhian B, Xie A,
Shestakova E and Livingston DM: RAP80-directed tuning of BRCA1
homologous recombination function at ionizing radiation-induced
nuclear foci. Genes Dev. 25:685–700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Coleman KA and Greenberg RA: The
BRCA1-RAP80 complex regulates DNA repair mechanism utilization by
restricting end resection. J Biol Chem. 286:13669–13680. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hu Y, Petit SA, Ficarro SB, Toomire KJ,
Xie A, Lim E, Cao SA, Park E, Eck MJ, Scully R, et al: PARP1-driven
poly-ADP-ribosylation regulates BRCA1 function in homologous
recombination-mediated DNA repair. Cancer Discov. 4:1430–1447.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hu Z, Mi S, Zhao T, Peng C, Peng Y, Chen
L, Zhu W, Yao Y, Song Q, Li X, et al: BGL3 lncRNA mediates
retention of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex at DNA damage sites. EMBO J.
39:e1041332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang ZW, Pan JJ, Hu JF, Zhang JQ, Huang L,
Huang Y, Liao CY, Yang C, Chen ZW, Wang YD, et al: SRSF3-mediated
regulation of N6-methyladenosine modification-related lncRNA ANRIL
splicing promotes resistance of pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine.
Cell Rep. 39:1108132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Syed A and Tainer JA: The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1
complex conducts the orchestration of damage signaling and outcomes
to stress in DNA replication and repair. Annu Rev Biochem.
87:263–294. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Stracker TH and Petrini JH: The MRE11
complex: Starting from the ends. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:90–103.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Xu A, Huang MF, Zhu D, Gingold JA, Bazer
DA, Chang B, Wang D, Lai CC, Lemischka IR, Zhao R and Lee DF:
LncRNA H19 suppresses Osteosarcomagenesis by regulating snoRNAs and
DNA repair protein complexes. Front Genet. 11:6118232020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Wu C, Chen W, Yu F, Yuan Y, Chen Y, Hurst
DR, Li Y, Li L and Liu Z: Long noncoding RNA HITTERS protects oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells from endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis via promoting MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex
formation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 7:20027472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Paull TT: Mechanisms of ATM Activation.
Annu Rev Biochem. 84:711–738. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhao K, Wang X, Xue X, Li L and Hu Y: A
long noncoding RNA sensitizes genotoxic treatment by attenuating
ATM activation and homologous recombination repair in cancers. PLoS
Biol. 18:e30006662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bunting SF, Callén E, Wong N, Chen HT,
Polato F, Gunn A, Bothmer A, Feldhahn N, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Cao
L, et al: 53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in
Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks. Cell.
141:243–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Escribano-Díaz C, Orthwein A,
Fradet-Turcotte A, Xing M, Young JT, Tkáč J, Cook MA, Rosebrock AP,
Munro M, Canny MD, et al: A cell cycle-dependent regulatory circuit
composed of 53BP1-RIF1 and BRCA1-CtIP controls DNA repair pathway
choice. Mol Cell. 49:872–883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zimmermann M, Lottersberger F, Buonomo SB,
Sfeir A and de Lange T: 53BP1 regulates DSB repair using Rif1 to
control 5' end resection. Science. 339:700–704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Poulsen M, Lukas C, Lukas J, Bekker-Jensen
S and Mailand N: Human RNF169 is a negative regulator of the
ubiquitin-dependent response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell
Biol. 197:189–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hu Q, Botuyan MV, Cui G, Zhao D and Mer G:
Mechanisms of Ubiquitin-nucleosome recognition and regulation of
53BP1 chromatin recruitment by RNF168/169 and RAD18. Mol Cell.
66:473–487.e479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Muvarak N, Kelley S, Robert C, Baer MR,
Perrotti D, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Civin C, Scheibner K and
Rassool FV: c-MYC generates repair errors via increased
transcription of Alternative-NHEJ Factors, LIG3 and PARP1, in
tyrosine kinase-activated leukemias. Mol Cancer Res. 13:699–712.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ahrabi S, Sarkar S, Pfister SX, Pirovano
G, Higgins GS, Porter AC and Humphrey TC: A role for human
homologous recombination factors in suppressing
microhomology-mediated end joining. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:5743–5757. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Leppard JB, Dong Z, Mackey ZB and
Tomkinson AE: Physical and functional interaction between DNA
ligase IIIalpha and poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase 1 in DNA
single-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol. 23:5919–5927. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Chiruvella KK, Liang Z and Wilson TE:
Repair of double-strand breaks by end joining. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0127572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Hu Y, Lin J, Fang H, Fang J, Li C, Chen W,
Liu S, Ondrejka S, Gong Z, Reu F, et al: Targeting the
MALAT1/PARP1/LIG3 complex induces DNA damage and apoptosis in
multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 32:2250–2262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Langelier MF, Ruhl DD, Planck JL, Kraus WL
and Pascal JM: The Zn3 domain of human poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 (PARP-1) functions in both DNA-dependent
poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis activity and chromatin compaction. J
Biol Chem. 285:18877–18887. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Huang J, Lin C, Dong H, Piao Z, Jin C, Han
H and Jin D: Targeting MALAT1 induces DNA damage and sensitize
non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin by repressing BRCA1.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 86:663–672. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Goldstein M and Kastan MB: The DNA damage
response: Implications for tumor responses to radiation and
chemotherapy. Annu Rev Med. 66:129–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Yao RW, Wang Y and Chen LL: Cellular
functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 21:542–551. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Kang M, Ren M, Li Y, Fu Y, Deng M and Li
C: Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA PART1 induces gefitinib
resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via functioning as
a competing endogenous RNA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1712018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Xiong XD, Ren X, Cai MY, Yang JW, Liu X
and Yang JM: Long non-coding RNAs: An emerging powerhouse in the
battle between life and death of tumor cells. Drug Resist Updat.
26:28–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Li Z, Zhou Y, Tu B, Bu Y, Liu A and Kong
J: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 affects the efficacy of radiotherapy
for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating Cks1
expression. J Oral Pathol Med. 46:583–590. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Sun M, Jin FY, Xia R, Kong R, Li JH, Xu
TP, Liu YW, Zhang EB, Liu XH and De W: Decreased expression of long
noncoding RNA GAS5 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell
proliferation in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:3192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Liu J, Ben Q, Lu E, He X, Yang X, Ma J,
Zhang W, Wang Z, Liu T, Zhang J and Wang H: Long noncoding RNA
PANDAR blocks CDKN1A gene transcription by competitive interaction
with p53 protein in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:1682018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Shao L, Zuo X, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Yang N,
Shen B, Wang J, Wang X, Li R, Jin G, et al: The inherited
variations of a p53-responsive enhancer in 13q12.12 confer lung
cancer risk by attenuating TNFRSF19 expression. Genome Biol.
20:1032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhen Y, Ye Y, Wang H, Xia Z, Wang B, Yi W
and Deng X: Knockdown of SNHG8 repressed the growth, migration, and
invasion of colorectal cancer cells by directly sponging with
miR-663. Biomed Pharmacother. 116:1090002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Liu J, Yang C, Gu Y, Li C, Zhang H, Zhang
W, Wang X, Wu N and Zheng C: Knockdown of the lncRNA SNHG8 inhibits
cell growth in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma.
Cell Mol Biol Lett. 23:172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Tian X, Liu Y, Wang Z and Wu S: lncRNA
SNHG8 promotes aggressive behaviors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via
regulating miR-656-3p/SATB1 axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
131:1105642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Miao W, Lu T, Liu X, Yin W and Zhang H:
LncRNA SNHG8 induces ovarian carcinoma cells cellular process and
stemness through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Biomark. 28:459–471.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Fan D, Qiu B, Yang XJ, Tang HL, Peng SJ,
Yang P, Dong YM, Yang L, Bao GQ and Zhao HD: LncRNA SNHG8 promotes
cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cell through
miR-634/ZBTB20 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:11639–11649.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhu W, Tan L, Ma T, Yin Z and Gao J: Long
noncoding RNA SNHG8 promotes chemoresistance in gastric cancer via
binding with hnRNPA1 and stabilizing TROY expression. Dig Liver
Dis. 54:1573–1582. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Wang Z, Wang X, Rong Z, Dai L, Qin C, Wang
S and Geng W: LncRNA LINC01134 contributes to radioresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating DNA damage response via MAPK
signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:7918892021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Sun Y, Wang J, Ma Y, Li J, Sun X, Zhao X,
Shi X, Hu Y, Qu F and Zhang X: Radiation induces NORAD expression
to promote ESCC radiotherapy resistance via EEPD1/ATR/Chk1
signalling and by inhibiting pri-miR-199a1 processing and the
exosomal transfer of miR-199a-5p. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
40:3062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Yao P, Li Y, Shen W, Xu X, Zhu W, Yang X,
Cao J and Xing C: ANKHD1 silencing suppresses the proliferation,
migration and invasion of CRC cells by inhibiting YAP1-induced
activation of EMT. Am J Cancer Res. 8:2311–2324. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Yao PA, Wu Y, Zhao K, Li Y, Cao J and Xing
C: The feedback loop of ANKHD1/lncRNA MALAT1/YAP1 strengthens the
radioresistance of CRC by activating YAP1/AKT signaling. Cell Death
Dis. 13:1032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Kagawa Y, Kano
Y, Takahashi Y, Wu X, Hiraki M, Hamabe A, Konno M, Haraguchi N, et
al: Significance of Polypyrimidine Tract-binding Protein 1
expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1705–1716.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Huan L, Guo T, Wu Y, Xu L, Huang S, Xu Y,
Liang L and He X: Hypoxia induced LUCAT1/PTBP1 axis modulates
cancer cell viability and chemotherapy response. Mol Cancer.
19:112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Jin MH and Oh DY: ATM in DNA repair in
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 203:1073912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cimprich KA and Cortez D: ATR: An
essential regulator of genome integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:616–627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Panzarino NJ, Krais JJ, Cong K, Peng M,
Mosqueda M, Nayak SU, Bond SM, Calvo JA, Doshi MB, Bere M, et al:
Replication gaps underlie BRCA deficiency and therapy response.
Cancer Res. 81:1388–1397. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Zhang B, Bao W, Zhang S, Chen B, Zhou X,
Zhao J, Shi Z, Zhang T, Chen Z, Wang L, et al: LncRNA HEPFAL
accelerates ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
SLC7A11 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 13:7342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Jiang Y, Guo H, Tong T, Xie F, Qin X, Wang
X, Chen W and Zhang J: lncRNA lnc-POP1-1 upregulated by VN1R5
promotes cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma through interaction with MCM5. Mol Ther. 30:448–467.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
136
|
Choi PS and Thomas-Tikhonenko A:
RNA-binding proteins of COSMIC importance in cancer. J Clin Invest.
131:e1516272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Fabbri L, Chakraborty A, Robert C and
Vagner S: The plasticity of mRNA translation during cancer
progression and therapy resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:558–577.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Duffy AG, Makarova-Rusher OV, Ulahannan
SV, Rahma OE, Fioravanti S, Walker M, Abdullah S, Raffeld M,
Anderson V, Abi-Jaoudeh N, et al: Modulation of tumor eIF4E by
antisense inhibition: A phase I/II translational clinical trial of
ISIS 183750-an antisense oligonucleotide against eIF4E-in
combination with irinotecan in solid tumors and
irinotecan-refractory colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
139:1648–1657. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Shen L and Pelletier J: Selective
targeting of the DEAD-box RNA helicase eukaryotic initiation factor
(eIF) 4A by natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 37:609–616. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Zhu H, Chen K, Chen Y, Liu J, Zhang X,
Zhou Y, Liu Q, Wang B, Chen T and Cao X: RNA-binding protein ZCCHC4
promotes human cancer chemoresistance by disrupting
DNA-damage-induced apoptosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7:2402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|