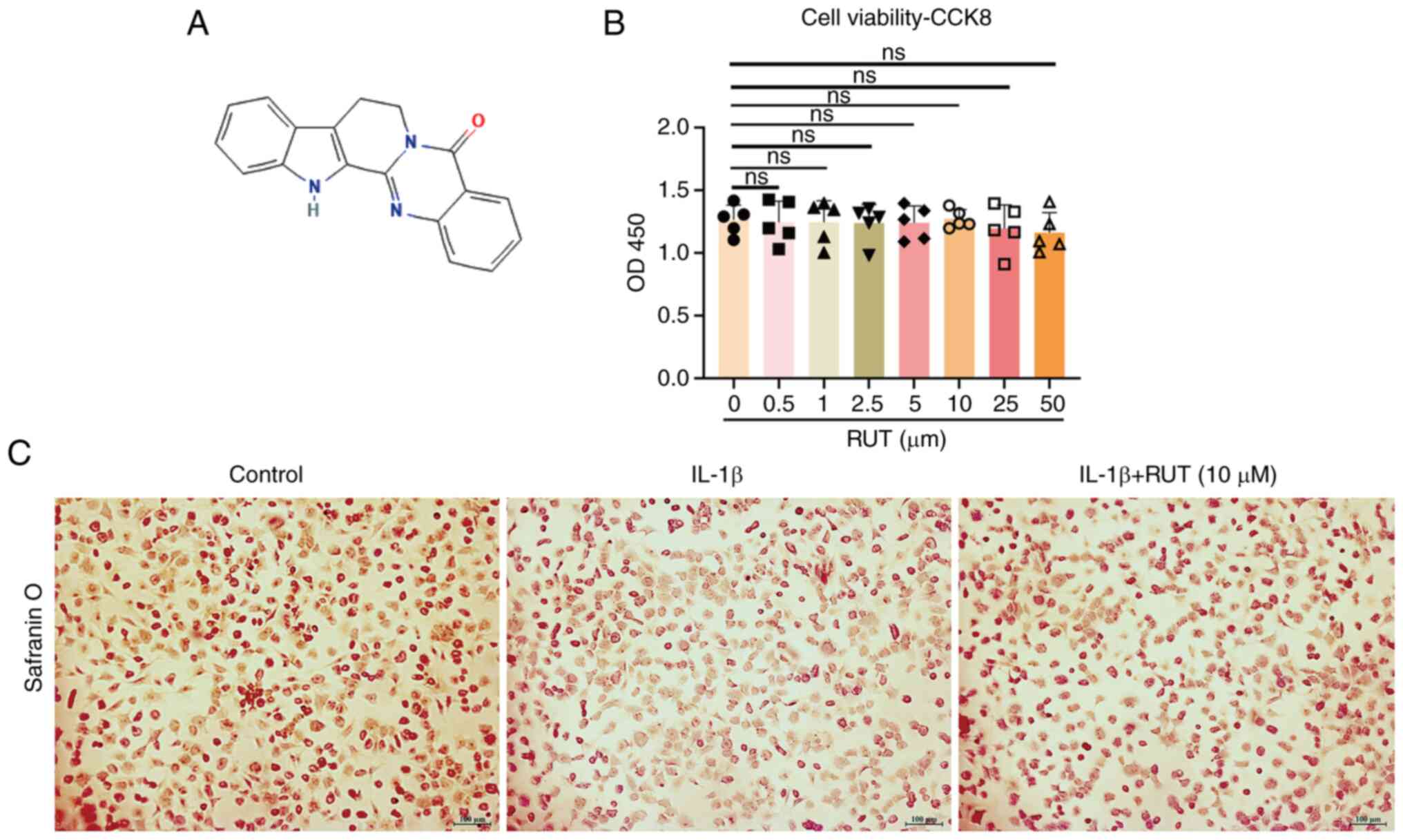
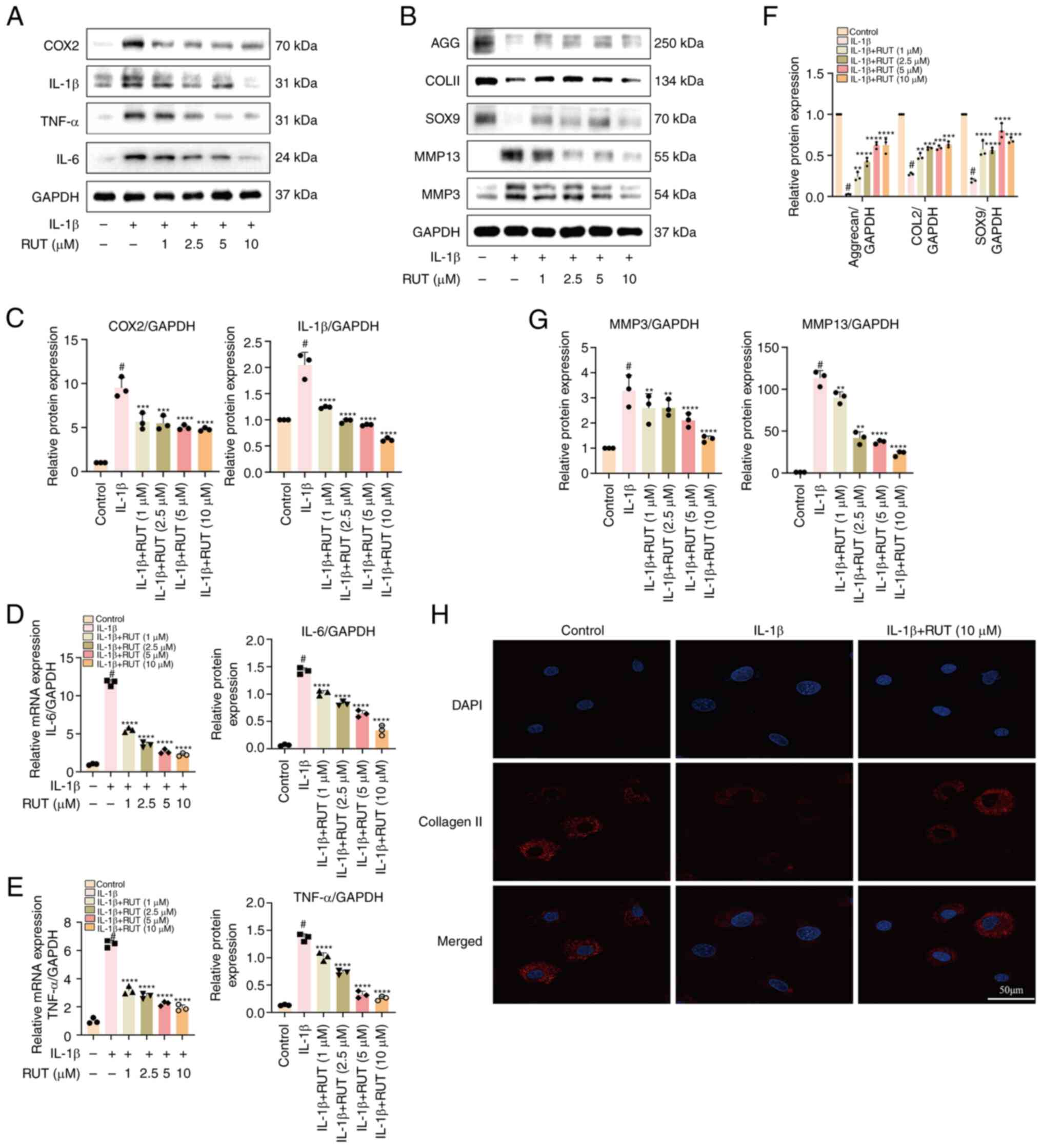
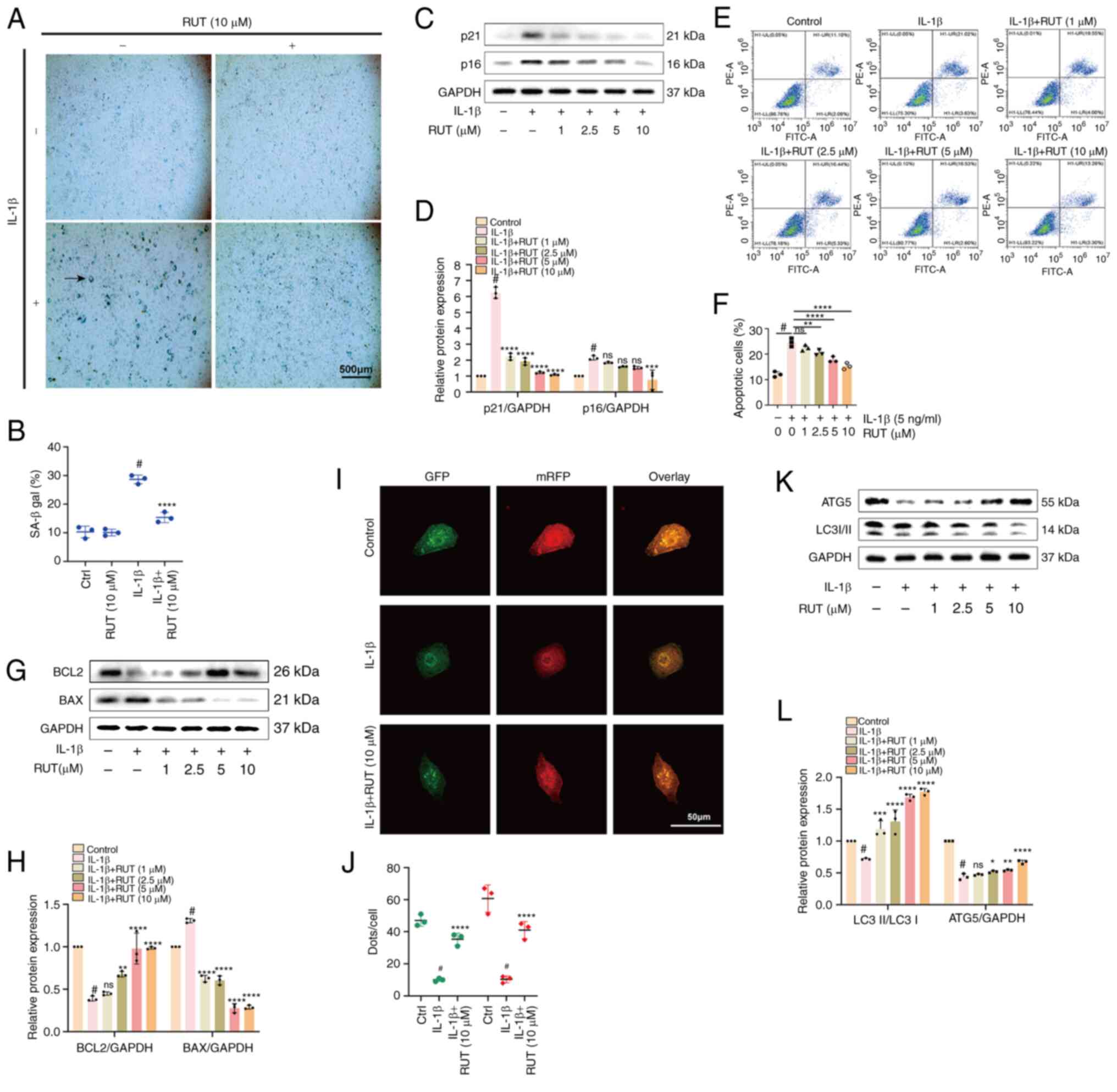
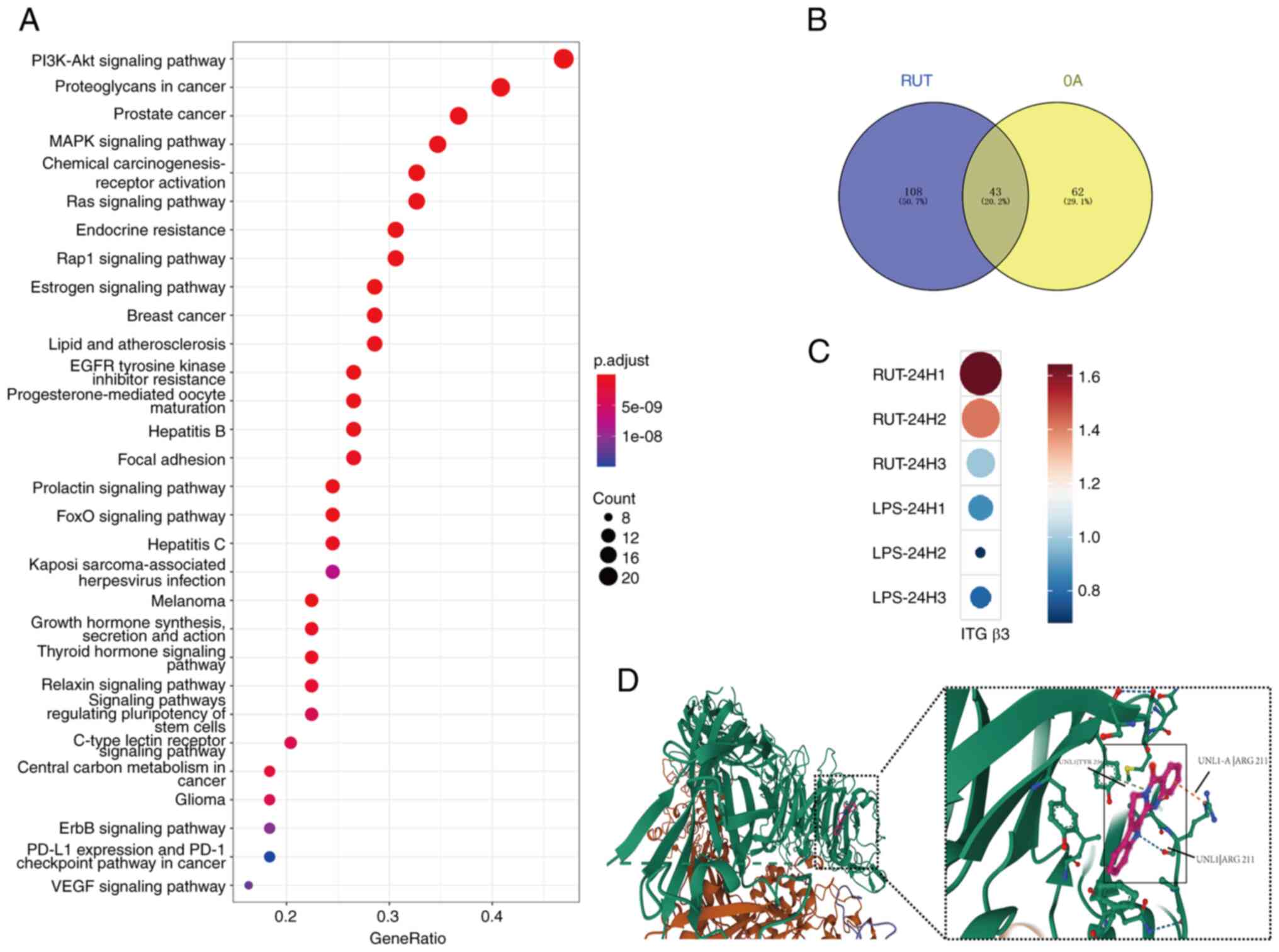
|
1
|
Wang BW, Jiang Y, Yao ZL, Chen PS, Yu B
and Wang SN: Aucubin protects chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced
apoptosis in vitro and inhibits osteoarthritis in mice model. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 13:3529–3538. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Cui J, Shibata Y, Zhu T, Zhou J and Zhang
J: Osteocytes in bone aging: Advances, challenges, and future
perspectives. Ageing Res Rev. 77:1016082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu Y, Wang Z, Fu X, Lin Z and Yu K:
Geraniol-mediated osteoarthritis improvement by down-regulating
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and MAPK signals: In vivo and in vitro studies. Int
Immunopharmacol. 86:1067132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rannou F, Pelletier JP and
Martel-Pelletier J: Efficacy and safety of topical NSAIDs in the
management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting
trials and surveys. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 45:S18–21. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schurman DJ and Smith RL: Osteoarthritis:
Current treatment and future prospects for surgical, medical, and
biologic intervention. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (427 Suppl):
S183–S189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho Y, Jeong S, Kim H, Kang D, Lee J, Kang
SB and Kim JH: Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in
osteoarthritis: Current status and future directions. Exp Mol Med.
53:1689–1696. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zou K, Wong J, Abdullah N, Chen X, Smith
T, Doherty M and Zhang W: Examination of overall treatment effect
and the proportion attributable to contextual effect in
osteoarthritis: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann
Rheum Dis. 75:1964–1970. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ni B, Pei W, Qu Y, Zhang R, Chu X, Wang Y,
Huang X and You H: MCC950, the NLRP3 inhibitor, protects against
cartilage degradation in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2021:41390482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang H, Li J, Xiang X, Zhou B, Zhao C,
Wei Q, Sun Y, Chen J, Lai B, Luo Z and Li A: Tert-butylhydroquinone
attenuates osteoarthritis by protecting chondrocytes and inhibiting
macrophage polarization. Bone Joint Res. 10:704–713. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou S, Shi J, Wen H, Xie W, Han X and Li
H: A chondroprotective effect of moracin on IL-1β-induced primary
rat chondrocytes and an osteoarthritis rat model through Nrf2/HO-1
and NF-κB axes. Food Funct. 11:7935–7945. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu L, Wu Z, He Y, Chen Z, Xu K, Yu W, Fang
W, Ma C, Moqbel SAA, Ran J, et al: MFN2 contributes to metabolic
disorders and inflammation in the aging of rat chondrocytes and
osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 28:1079–1091. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao Y, Tang S, Nie X, Zhou Z, Ruan G, Han
W, Zhu Z and Ding C: Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway
and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine.
65:1032832021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang SH, Mori D, Kobayashi H, Mori Y,
Nakamoto H, Okada K, Taniguchi Y, Sugita S, Yano F, Chung UI, et
al: Excessive mechanical loading promotes osteoarthritis through
the gremlin-1-NF-κB pathway. Nat Commun. 10:14422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Shao Z, Hu X, Chen Z, Li B, Jiang
R, Bsoul N, Chen J, Xu C and Gao W: Inhibition of
PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling by Aloin for ameliorating the
progression of osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int
Immunopharmacol. 89:1070792020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang X, Xi Y, Mao Z, Chu X, Zhang R, Ma
X, Ni B, Cheng H and You H: Vanillic acid attenuates cartilage
degeneration by regulating the MAPK and PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathways.
Eur J Pharmacol. 859:1724812019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nieminen R, Korhonen R, Moilanen T, Clark
AR and Moilanen E: Aurothiomalate inhibits cyclooxygenase 2, matrix
metalloproteinase 3, and interleukin-6 expression in chondrocytes
by increasing MAPK phosphatase 1 expression and decreasing p38
phosphorylation: MAPK phosphatase 1 as a novel target for
antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1650–1659. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moon TC, Murakami M, Kudo I, Son KH, Kim
HP, Kang SS and Chang HW: A new class of COX-2 inhibitor,
rutaecarpine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Inflamm Res. 48:621–625. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Yan T, Sun D, Xie C, Wang T, Liu
X, Wang J, Wang Q, Luo Y, Wang P, et al: Rutaecarpine inhibits
KEAP1-NRF2 interaction to activate NRF2 and ameliorate dextran
sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 148:33–41.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Woo HG, Lee CH, Noh MS, Lee JJ, Jung YS,
Baik EJ, Moon CH and Lee SH: Rutaecarpine, a quinazolinocarboline
alkaloid, inhibits prostaglandin production in RAW264.7
macrophages. Planta Med. 67:505–509. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jayakumar T, Lin KC, Chang CC, Hsia CW,
Manubolu M, Huang WC, Sheu JR and Hsia CH: Targeting MAPK/NF-κB
Pathways in Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Rutaecarpine: Impact on
Src/FAK-Mediated Macrophage Migration. Int J Mol Sci. 23:2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Guo B, Zhao C, Zhang C, Xiao Y, Yan G, Liu
L and Pan H: Elucidation of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Er
Miao San by integrative approach of network pharmacology and
experimental verification. Pharmacol Res. 175:1060002022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han M, Hu L and Chen Y: Rutaecarpine may
improve neuronal injury, inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and
oxidative stress by regulating the expression of ERK1/2 and
Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:2923–2931. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fukuma Y, Sakai E, Komaki S, Nishishita K,
Okamoto K and Tsukuba T: Rutaecarpine attenuates osteoclastogenesis
by impairing macrophage colony stimulating factor and receptor
activator of nuclear factor κ-B ligand-stimulated signalling
pathways. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 45:863–865. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jing S, Wan J, Wang T, He Z, Ding Q, Sheng
G, Wang S, Zhao H, Zhu Z, Wu H and Li W: Flavokawain A alleviates
the progression of mouse osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo
study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 10:10717762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
John SP, Singh A, Sun J, Pierre MJ,
Alsalih L and Lipsey C: Small-molecule screening identifies Syk
kinase inhibition and rutaecarpine as modulators of macrophage
training and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. 41:1114412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McAlindon T: Osteoarthritis research
society international (OARSI) Classification and Guidelines. HSS J.
8:66–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Sun K, Luo J, Jing X, Xiang W, Guo J, Yao
X, Liang S, Guo F and Xu T: Hyperoside ameliorates the progression
of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine.
80:1533872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lepetsos P, Papavassiliou KA and
Papavassiliou AG: Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free
Radic Biol Med. 132:90–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Maki K, Nava MM, Villeneuve C, Chang M,
Furukawa KS, Ushida T and Wickstrom SA: Hydrostatic pressure
prevents chondrocyte differentiation through heterochromatin
remodeling. J Cell Sci. 134:jcs2476432021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Attur MG, Dave MN, Clancy RM, Patel IR,
Abramson SB and Amin AR: Functional genomic analysis in
arthritis-affected cartilage: Yin-yang regulation of inflammatory
mediators by alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha V beta 3 integrins. J
Immunol. 164:2684–2691. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Haugh MG, Vaughan TJ and Mcnamara LM: The
role of integrin α(V)β(3) in Osteocyte mechanotransduction. J Mech
Behav Biomed Mater. 42:67–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Onuma K, Liu C, Wong H, Bloom MS,
Elliott EE, Cao RR, Hu N, Lingampalli N, Sharpe O, et al:
Dysregulated integrin alphaVbeta3 and CD47 signaling promotes joint
inflammation, cartilage breakdown, and progression of
osteoarthritis. JCI Insight. 4:e1286162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang Z, Boyko T, Tran MC, LaRussa M,
Bhatia N, Rashidi V, Longaker MT and Yang GP: DEL1 protects against
chondrocyte apoptosis through integrin binding. J Surg Res.
231:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu R, Yu X, Liang S, Cheng P, Wang Z, He
ZY, Lv ZT, Wan JL, Mo H, Zhu WT and Chen AM: Physalin A Inhibits
MAPK and NF-κB signal transduction through integrin αVβ3 and exerts
chondroprotective effect. Front Pharmacol. 12:7619222021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cheng C, Tian J, Zhang F, Deng Z, Tu M, Li
L, Yang H, Xiao K, Guo W, Yang RQ, et al: WISP1 protects against
chondrocyte senescence and apoptosis by regulating αvβ3 and
PI3K/Akt pathway in osteoarthritis. DNA Cel Biol. 40:629–637. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Emami A, Tepper J, Short B, Yaksh TL,
Bendele AM, Ramani T, Cisternas AF, Chang GH and Mellon RD:
Toxicology evaluation of drugs administered via uncommon routes:
Intranasal, intraocular, intrathecal/intraspinal, and
intra-articular. Int J Toxicol. 37:4–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|