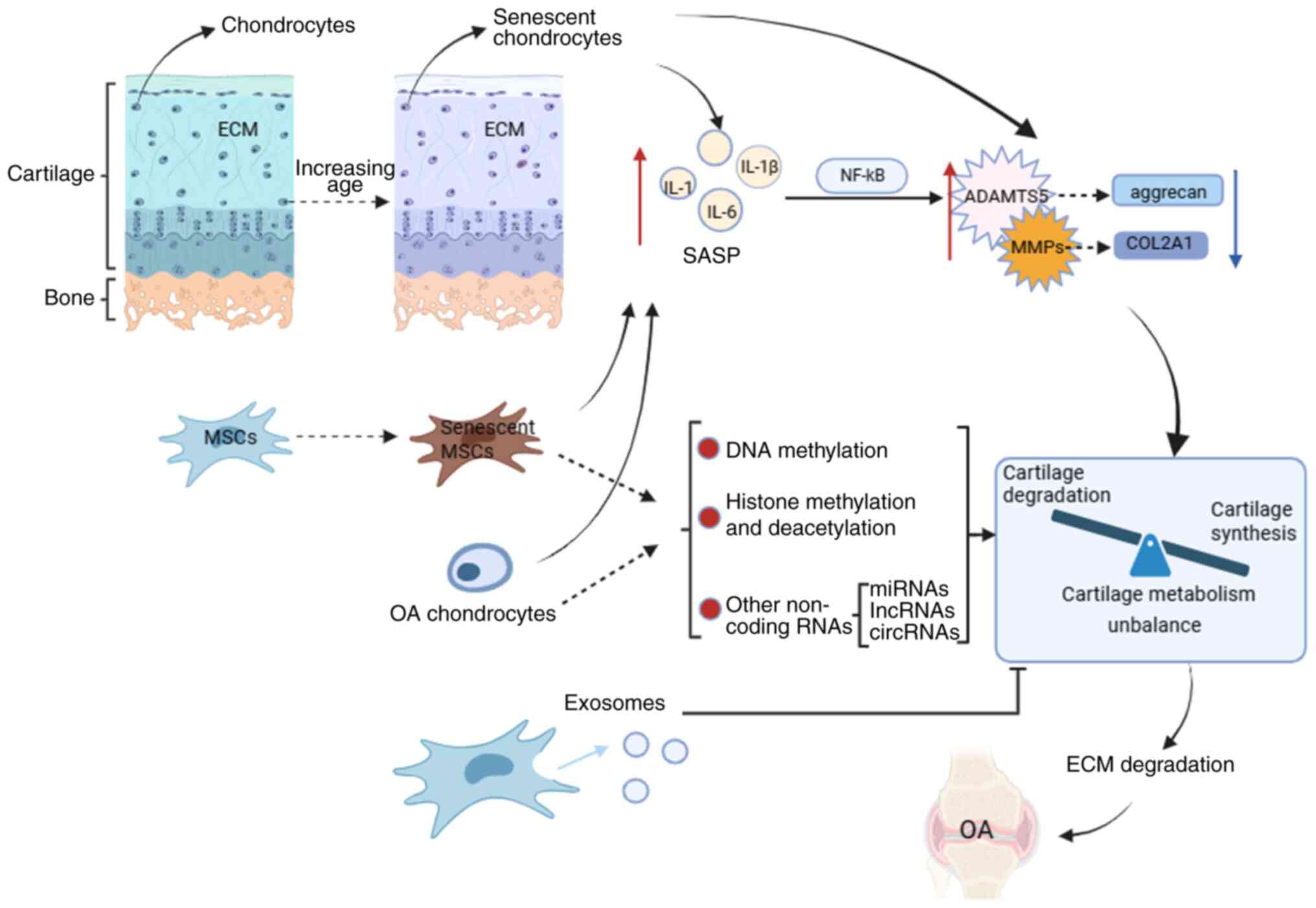
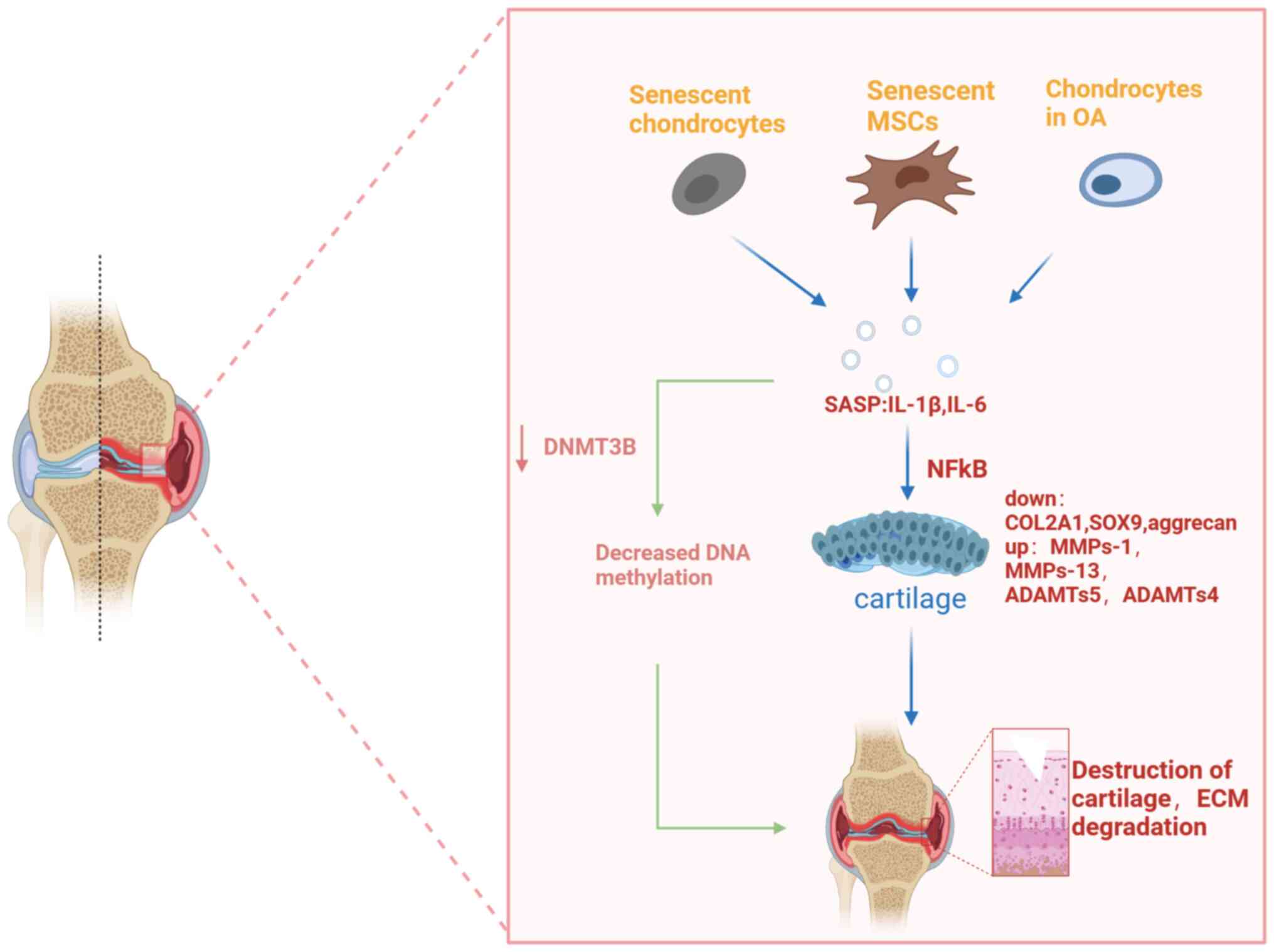
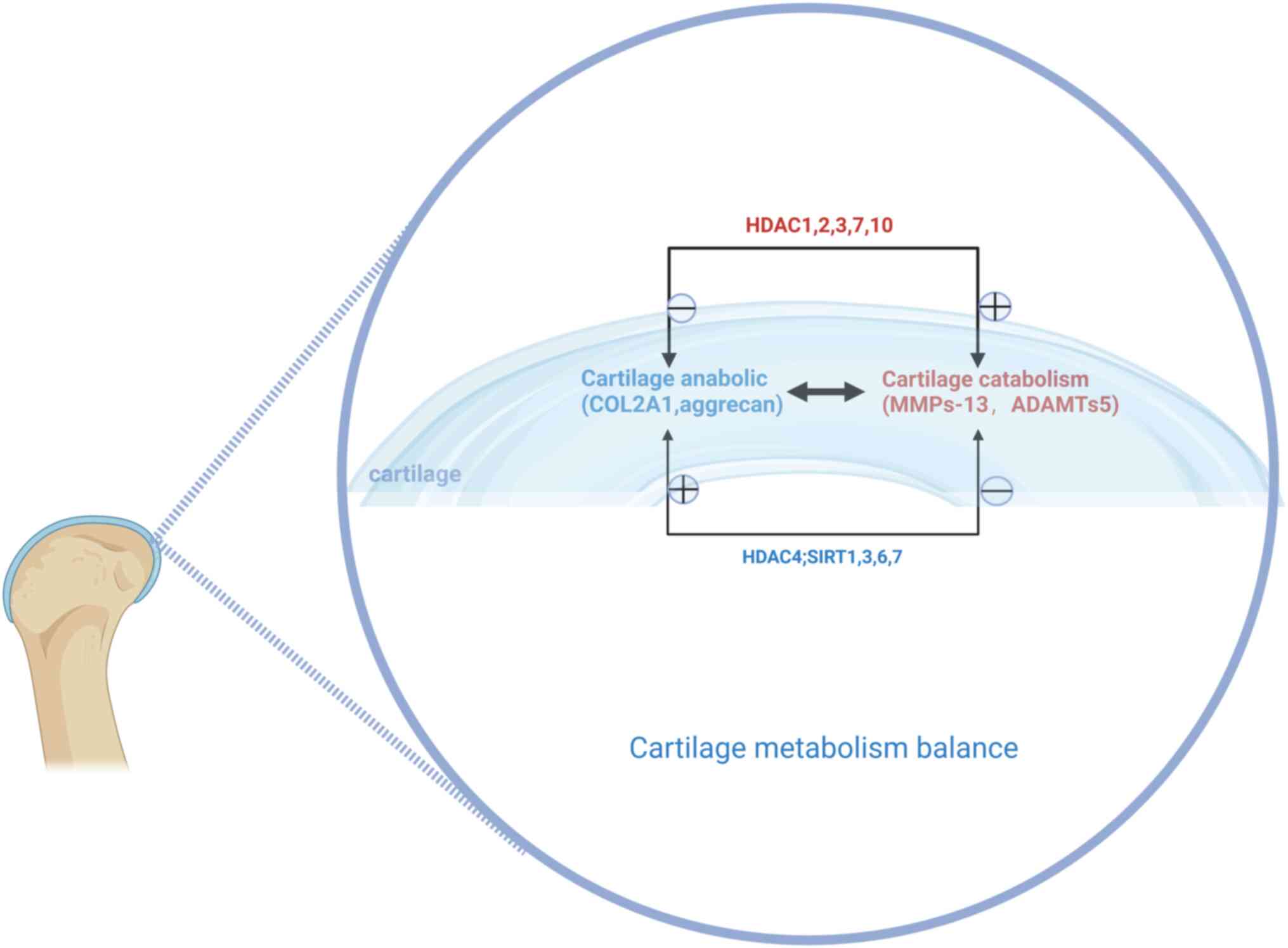
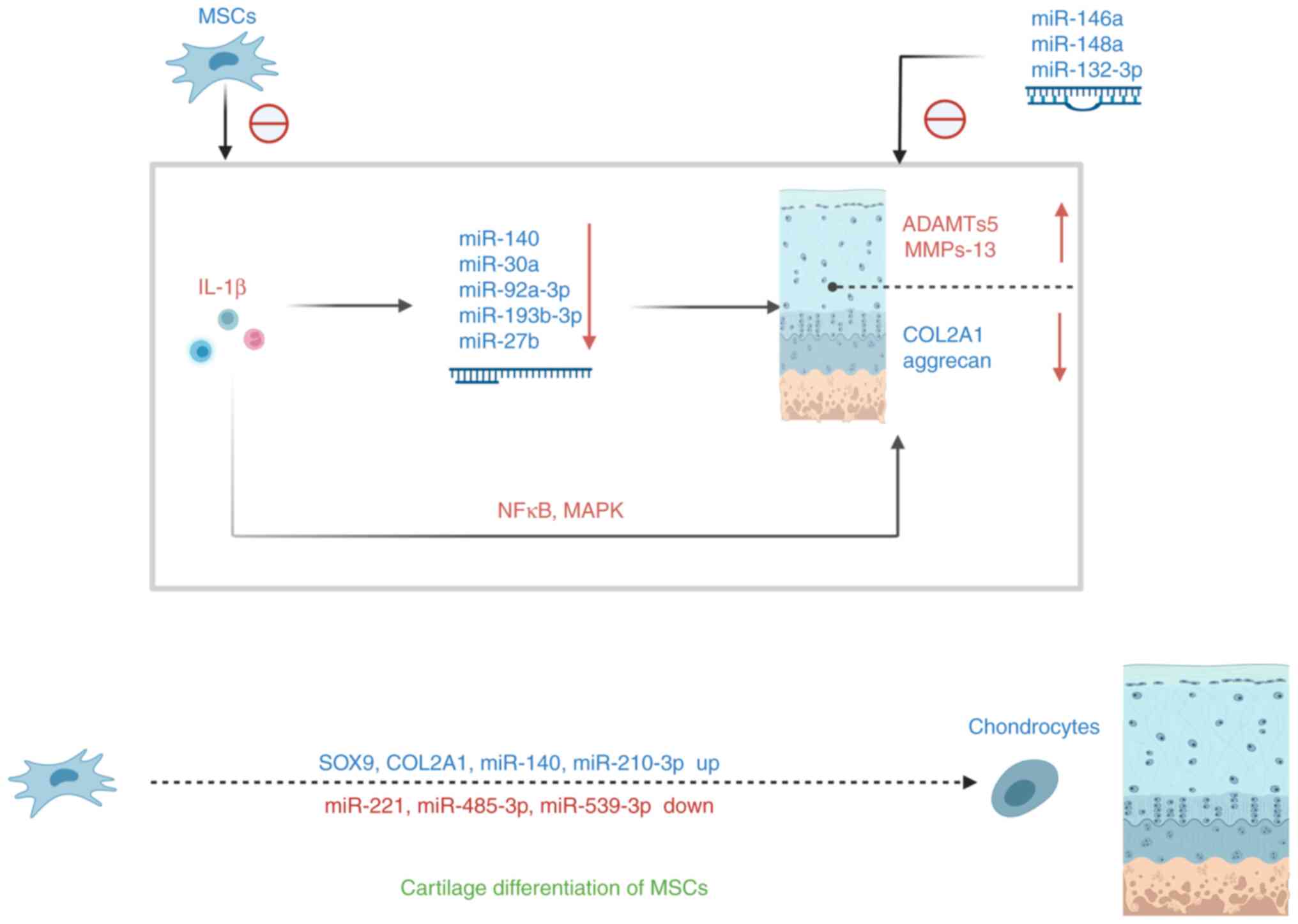
|
1
|
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR and
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:1697–1707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abramoff B and Caldera FE: Osteoarthritis:
Pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am.
104:293–311. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lan T, Luo M and Wei X: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells in cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 14:1952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J and Demaria M:
Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 28:436–453.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L,
Serrano M and Kroemer G: The hallmarks of aging. Cell.
153:1194–1217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu M, Bradley EW, Weivoda MM, Hwang SM,
Pirtskhalava T, Decklever T, Curran GL, Ogrodnik M, Jurk D, Johnson
KO, et al: Transplanted senescent cells induce an
osteoarthritis-like condition in mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med
Sci. 72:780–785. 2017.
|
|
7
|
Coppé JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, Sun Y, Muñoz
DP, Goldstein J, Nelson PS, Desprez PY and Campisi J:
Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal
cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor
suppressor. PLoS Biol. 6:2853–2868. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu M, Tchkonia T, Ding H, Ogrodnik M,
Lubbers ER, Pirtskhalava T, White TA, Johnson KO, Stout MB, Mezera
V, et al: JAK inhibition alleviates the cellular
senescence-associated secretory phenotype and frailty in old age.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E6301–E6310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greene MA and Loeser RF: Aging-related
inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
23:1966–1971. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lotz M and Loeser RF: Effects of aging on
articular cartilage homeostasis. Bone. 51:241–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeon OH, Kim C, Laberge RM, Demaria M,
Rathod S, Vasserot AP, Chung JW, Kim DH, Poon Y, David N, et al:
Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of
post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative
environment. Nat Med. 23:775–781. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding DC, Shyu WC and Lin SZ: Mesenchymal
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 20:5–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Wu Q, Wang Y, Li L, Bu H and Bao J:
Senescence of mesenchymal stem cells (Review). Int J Mol Med.
39:775–782. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alt EU, Senst C, Murthy SN, Slakey DP,
Dupin CL, Chaffin AE, Kadowitz PJ and Izadpanah R: Aging alters
tissue resident mesenchymal stem cell properties. Stem Cell Res.
8:215–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chew JRJ, Chuah SJ, Teo KYW, Zhang S, Lai
RC, Fu JH, Lim LP, Lim SK and Toh WS: Mesenchymal stem cell
exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote
periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. 89:252–264. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Loeser RF, Collins JA and Diekman BO:
Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
12:412–420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin Z, Deng Z, Liu J, Lin Z, Chen S, Deng
Z and Li W: Chloride channel and inflammation-mediated pathogenesis
of osteoarthritis. J Inflamm Res. 15:953–964. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu X, Liang Y, Li X, Ouyang K, Wang M, Cao
T, Li W, Liu J, Xiong J, Li B, et al: Exosome-mediated delivery of
kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal
stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials.
269:1205392021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
McCulloch K, Litherland GJ and Rai TS:
Cellular senescence in osteoarthritis pathology. Aging Cell.
16:210–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duan L, Liang Y, Xu X, Xiao Y and Wang D:
Recent progress on the role of miR-140 in cartilage matrix
remodelling and its implications for osteoarthritis treatment.
Arthritis Res Ther. 22:1942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fujii Y, Liu L, Yagasaki L, Inotsume M,
Chiba T and Asahara H: Cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:63162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu CF and Lefebvre V: The transcription
factors SOX9 and SOX5/SOX6 cooperate genome-wide through
super-enhancers to drive chondrogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:8183–8203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, Carito B,
Blanchet T, Ma HL, Flannery CR, Peluso D, Kanki K, Yang Z, et al:
Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a
murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature. 434:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang M, Sampson ER, Jin H, Li J, Ke QH, Im
HJ and Chen D: MMP13 is a critical target gene during the
progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R52013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Philipot D, Guérit D, Platano D, Chuchana
P, Olivotto E, Espinoza F, Dorandeu A, Pers YM, Piette J, Borzi RM,
et al: p16INK4a and its regulator miR-24 link senescence and
chondrocyte terminal differentiation-associated matrix remodeling
in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 16:R582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loeser RF: Aging and osteoarthritis: The
role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage
matrix. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse
D, Pelletier JP and Fahmi H: Role of proinflammatory cytokines in
the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:33–42.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fang H, Deng Z, Liu J, Chen S, Deng Z and
Li W: The mechanism of bone remodeling after bone aging. Clin
Interv Aging. 17:405–415. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bian Q, Wang YJ, Liu SF and Li YP:
Osteoarthritis: Genetic factors, animal models, mechanisms, and
therapies. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:74–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Molnar V, Matišić V, Kodvanj I, Bjelica R,
Jeleč Ž, Hudetz D, Rod E, Čukelj F, Vrdoljak T, Vidović D, et al:
Cytokines and chemokines involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:92082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hwang HS and Kim HA: Chondrocyte apoptosis
in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26035–2604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deng Z, Chen X, Lin Z, Alahdal M, Wang D,
Liu J and Li W: The homeostasis of cartilage matrix remodeling and
the regulation of volume-sensitive ion channel. Aging Dis.
13:787–800. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen LX, Lin L, Wang HJ, Wei XL, Fu X,
Zhang JY and Yu CL: Suppression of early experimental
osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the adenoviral
vector-mediated NF-kappaBp65-specific siRNA. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 16:174–184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fei J, Liang B, Jiang C, Ni H and Wang L:
Luteolin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in rat chondrocytes
and attenuates osteoarthritis progression in a rat model. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:1586–1592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huang X, Xi Y, Pan Q, Mao Z, Zhang R, Ma X
and You H: Caffeic acid protects against IL-1β-induced inflammatory
responses and cartilage degradation in articular chondrocytes.
Biomed Pharmacother. 107:433–439. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meszaros E and Malemud CJ: Prospects for
treating osteoarthritis: Enzyme-protein interactions regulating
matrix metalloproteinase activity. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 3:219–229.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Verma P and Dalal K: ADAMTS-4 and
ADAMTS-5: Key enzymes in osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem.
112:3507–3514. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Deng Z, Lin Z, Zhong Q, Lu M, Fang H, Liu
J, Duan L, Chen L, Wang L, Wang D and Li W: Interleukin 1
beta-induced chloride currents are important in osteoarthritis
onset: An in vitro study. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
53:400–409. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
oman-Blas JA and Jimenez SA: NF-kappaB as
a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid
arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:839–848. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lepetsos P, Papavassiliou KA and
Papavassiliou AG: Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free
Radic Biol Med. 132:90–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tang J, Cui W, Song F, Zhai C, Hu H, Zuo Q
and Fan W: Effects of mesenchymal stem cells on
interleukin-1β-treated chondrocytes and cartilage in a rat
osteoarthritic model. Mol Med Rep. 12:1753–1760. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang T and He C: Pro-inflammatory
cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 44:38–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song H and Park KH: Regulation and
function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration.
Semin Cancer Biol. 67:12–23. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lefebvre V and Dvir-Ginzberg M: SOX9 and
the many facets of its regulation in the chondrocyte lineage.
Connect Tissue Res. 58:2–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Kawakami Y, Tsuda M, Takahashi S,
Taniguchi N, Esteban CR, Zemmyo M, Furumatsu T, Lotz M, Izpisúa
Belmonte JC and Asahara H: Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha
regulates chondrogenesis via association with Sox9. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:2414–2419. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Akiyama H, Stadler HS, Martin JF, Ishii
TM, Beachy PA, Nakamura T and de Crombrugghe B: Misexpression of
Sox9 in mouse limb bud mesenchyme induces polydactyly and rescues
hypodactyly mice. Matrix Biol. 26:224–233. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Barter MJ, Gomez R, Hyatt S, Cheung K,
Skelton AJ, Xu Y, Clark IM and Young DA: The long non-coding RNA
ROCR contributes to SOX9 expression and chondrogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Development.
144:4510–4521. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nakamura Y, He X, Kato H, Wakitani S,
Kobayashi T, Watanabe S, Iida A, Tahara H, Warman ML, Watanapokasin
R and Postlethwait JH: Sox9 is upstream of microRNA-140 in
cartilage. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 166:64–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yang J, Qin S, Yi C, Ma G, Zhu H, Zhou W,
Xiong Y, Zhu X, Wang Y, He L and Guo X: MiR-140 is co-expressed
with Wwp2-C transcript and activated by Sox9 to target Sp1 in
maintaining the chondrocyte proliferation. FEBS Lett.
585:2992–2997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Si HB, Zeng Y, Liu SY, Zhou ZK, Chen YN,
Cheng JQ, Lu YR and Shen B: Intra-articular injection of
microRNA-140 (miRNA-140) alleviates osteoarthritis (OA) progression
by modulating extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in rats.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 25:1698–1707. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jiang Y, Mishima H, Sakai S, Liu YK,
Ohyabu Y and Uemura T: Gene expression analysis of major
lineage-defining factors in human bone marrow cells: Effect of
aging, gender, and age-related disorders. J Orthop Res. 26:910–917.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kearns AE, Khosla S and Kostenuik PJ:
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and
osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and
disease. Endocr Rev. 29:155–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li F and Li X, Liu G, Gao C and Li X: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells decrease the expression of RANKL in
collagen-induced arthritis rats via reducing the levels of IL-22. J
Immunol Res. 2019:84592812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin TH, Gibon E, Loi F, Pajarinen J,
Córdova LA, Nabeshima A, Lu L, Yao Z and Goodman SB: Decreased
osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells derived from the aged mouse
is associated with enhanced NF-κB activity. J Orthop Res.
35:281–288. 217
|
|
55
|
Wang X, Manner PA, Horner A, Shum L, Tuan
RS and Nuckolls GH: Regulation of MMP-13 expression by RUNX2 and
FGF2 in osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
12:963–973. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen D, Kim DJ, Shen J, Zou Z and O'Keefe
RJ: Runx2 plays a central role in osteoarthritis development. J
Orthop Translat. 23:132–139. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Li Z, Liu C, Xie Z, Song P, Zhao RC, Guo
L, Liu Z and Wu Y: Epigenetic dysregulation in mesenchymal stem
cell aging and spontaneous differentiation. PLoS One. 6:e205262011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ji Q, Xu X, Xu Y, Fan Z, Kang L, Li L,
Liang Y, Guo J, Hong T, Li Z, et al: miR-105/Runx2 axis mediates
FGF2-induced ADAMTS expression in osteoarthritis cartilage. J Mol
Med (Berl). 94:681–694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aubourg G, Rice SJ, Bruce-Wootton P and
Loughlin J: Genetics of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
30:636–649. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Tachmazidou I, Hatzikotoulas K, Southam L,
Esparza-Gordillo J, Haberland V, Zheng J, Johnson T, Koprulu M,
Zengini E, Steinberg J, et al: Identification of new therapeutic
targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK
Biobank data. Nat Genet. 51:230–236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheung KS, Sposito N, Stumpf PS, Wilson
DI, Sanchez-Elsner T and Oreffo RO: MicroRNA-146a regulates human
foetal femur derived skeletal stem cell differentiation by
down-regulating SMAD2 and SMAD3. PLoS One. 9:e980632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tardif G, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H, Hum D,
Zhang Y, Kapoor M and Martel-Pelletier J: NFAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3
regulate the expression of miR-140 in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 15:R1972013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Nishimura R, Hata K, Nakamura E, Murakami
T and Takahata Y: Transcriptional network systems in cartilage
development and disease. Histochem Cell Biol. 149:353–363. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kanaan RA and Kanaan LA: Transforming
growth factor beta1, bone connection. Med Sci Monit.
12:RA164–RA169. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dai J, Yu D, Wang Y, Chen Y, Sun H, Zhang
X, Zhu S, Pan Z, Heng BC, Zhang S and Ouyang H: Kdm6b regulates
cartilage development and homeostasis through anabolic metabolism.
Ann Rheum Dis. 76:1295–1303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Simon TC and Jeffries MA: The epigenomic
landscape in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 19:302017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Luo C, Hajkova P and Ecker JR: Dynamic DNA
methylation: In the right place at the right time. Science.
361:1336–1340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Barter MJ, Bui C, Cheung K, Falk J, Gómez
R, Skelton AJ, Elliott HR, Reynard LN and Young DA: DNA
hypomethylation during MSC chondrogenesis occurs predominantly at
enhancer regions. Sci Rep. 10:11692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Takahashi A, de Andrés MC, Hashimoto K,
Itoi E and Oreffo RO: Epigenetic regulation of interleukin-8, an
inflammatory chemokine, in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 23:1946–1954. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shen J, Wang C, Li D, Xu T, Myers J,
Ashton JM, Wang T, Zuscik MJ, McAlinden A and O'Keefe RJ: DNA
methyltransferase 3b regulates articular cartilage homeostasis by
altering metabolism. JCI Insight. 2:e936122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hashimoto K, Oreffo RO, Gibson MB,
Goldring MB and Roach HI: DNA demethylation at specific CpG sites
in the IL1B promoter in response to inflammatory cytokines in human
articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3303–3313. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Roach HI, Yamada N, Cheung KS, Tilley S,
Clarke NM, Oreffo RO, Kokubun S and Bronner F: Association between
the abnormal expression of matrix-degrading enzymes by human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes and demethylation of specific CpG sites
in the promoter regions. Arthritis Rheum. 52:3110–3124. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Goldring SR and Goldring MB: The role of
cytokines in cartilage matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 427(427 Suppl): S27–S36. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Aida Y, Maeno M, Suzuki N, Namba A,
Motohashi M, Matsumoto M, Makimura M and Matsumura H: The effect of
IL-1beta on the expression of inflammatory cytokines and their
receptors in human chondrocytes. Life Sci. 79:764–771. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Seto E and Yoshida M: Erasers of histone
acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 6:a0187132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hong S, Derfoul A, Pereira-Mouries L and
Hall DJ: A novel domain in histone deacetylase 1 and 2 mediates
repression of cartilage-specific genes in human chondrocytes. FASEB
J. 23:3539–3552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Huber LC, Brock M, Hemmatazad H, Giger OT,
Moritz F, Trenkmann M, Distler JH, Gay RE, Kolling C, Moch H, et
al: Histone deacetylase/acetylase activity in total synovial tissue
derived from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:1087–1093. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Meng F, Li Z, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Kang Y,
Zhao X, Long D, Hu S, Gu M, He S, et al: MicroRNA-193b-3p regulates
chondrogenesis and chondrocyte metabolism by targeting HDAC3.
Theranostics. 8:2862–2883. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cao K, Wei L, Zhang Z, Guo L, Zhang C, Li
Y, Sun C, Sun X, Wang S, Li P and Wei X: Decreased histone
deacetylase 4 is associated with human osteoarthritis cartilage
degeneration by releasing histone deacetylase 4 inhibition of
runt-related transcription factor-2 and increasing
osteoarthritis-related genes: A novel mechanism of human
osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther.
16:4912014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Higashiyama R, Miyaki S, Yamashita S,
Yoshitaka T, Lindman G, Ito Y, Sasho T, Takahashi K, Lotz M and
Asahara H: Correlation between MMP-13 and HDAC7 expression in human
knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 20:11–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Liao W, Sun J, Liu W, Li W, Jia J, Ou F,
Su K, Zheng Y, Zhang Z and Sun Y: HDAC10 upregulation contributes
to interleukin 1β-mediated inflammatory activation of
synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells in temporomandibular joint.
J Cell Physiol. 234:12646–12662. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Jung JW, Lee S, Seo MS, Park SB, Kurtz A,
Kang SK and Kang KS: Histone deacetylase controls adult stem cell
aging by balancing the expression of polycomb genes and jumonji
domain containing 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1165–1176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dvir-Ginzberg M, Gagarina V, Lee EJ and
Hall DJ: Regulation of cartilage-specific gene expression in human
chondrocytes by SirT1 and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. J
Biol Chem. 283:36300–36310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tsuda M, Takahashi S, Takahashi Y and
Asahara H: Transcriptional co-activators CREB-binding protein and
p300 regulate chondrocyte-specific gene expression via association
with Sox9. J Biol Chem. 278:27224–27229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fujita N, Matsushita T, Ishida K, Kubo S,
Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Kurosaka M and Kuroda R: Potential
involvement of SIRT1 in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis through
the modulation of chondrocyte gene expressions. J Orthop Res.
29:511–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen H, Liu X, Zhu W, Chen H, Hu X, Jiang
Z, Xu Y, Wang L, Zhou Y, Chen P, et al: SIRT1 ameliorates
age-related senescence of mesenchymal stem cells via modulating
telomere shelterin. Front Aging Neurosci. 6:1032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Diao Z, Ji Q, Wu Z, Zhang W, Cai Y, Wang
Z, Hu J, Liu Z, Wang Q, Bi S, et al: SIRT3 consolidates
heterochromatin and counteracts senescence. Nucleic Acids Res.
49:4203–4219. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fu Y, Kinter M, Hudson J, Humphries KM,
Lane RS, White JR, Hakim M, Pan Y, Verdin E and Griffin TM: Aging
promotes sirtuin 3-dependent cartilage superoxide dismutase 2
acetylation and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:1887–1898.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wu Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Li W, Lin Y, Yu D,
Zhang L, Li F and Pan Z: Overexpression of Sirtuin 6 suppresses
cellular senescence and NF-κB mediated inflammatory responses in
osteoarthritis development. Sci Rep. 5:176022015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Collins JA, Kim CJ, Coleman A, Little A,
Perez MM, Clarke EJ, Diekman B, Peffers MJ, Chubinskaya S,
Tomlinson RE, et al: Cartilage-specific Sirt6 deficiency represses
IGF-1 and enhances osteoarthritis severity in mice. Ann Rheum Dis.
ard-2023-2243852023.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
91
|
Zhai XY, Yan P, Zhang J, Song HF, Yin WJ,
Gong H, Li H, Wu J, Xie J and Li RK: Knockdown of SIRT6 enables
human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell senescence. Rejuvenation
Res. 19:373–384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ji ML, Jiang H, Li Z, Geng R, Hu JZ, Lin
YC and Lu J: Sirt6 attenuates chondrocyte senescence and
osteoarthritis progression. Nat Commun. 13:76582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wu SY, Du YC and Yue CF: Sirt7 protects
chondrocytes degeneration in osteoarthritis via autophagy
activation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:9246–9255.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Mohrin M, Shin J, Liu Y, Brown K, Luo H,
Xi Y, Haynes CM and Chen D: Stem cell aging. A mitochondrial
UPR-mediated metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell
aging. Science. 347:1374–1377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hsu YC, Wu YT, Tsai CL and Wei YH: Current
understanding and future perspectives of the roles of sirtuins in
the reprogramming and differentiation of pluripotent stem cells.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 243:563–575. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bi S, Liu Z, Wu Z, Wang Z, Liu X, Wang S,
Ren J, Yao Y, Zhang W, Song M, et al: SIRT7 antagonizes human stem
cell aging as a heterochromatin stabilizer. Protein Cell.
11:483–504. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hong S, Cho YW, Yu LR, Yu H, Veenstra TD
and Ge K: Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as
histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:18439–18444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ukita M, Matsushita K, Tamura M and
Yamaguchi T: Histone H3K9 methylation is involved in
temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 45:607–614.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang F, Xu L, Xu L, Xu Q, Li D, Yang Y,
Karsenty G and Chen CD: JMJD3 promotes chondrocyte proliferation
and hypertrophy during endochondral bone formation in mice. J Mol
Cell Biol. 7:23–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang P, Li Y, Meng T, Zhang J, Wei Y, Meng
Z, Lin Y, Liu D and Sui L: KDM6A promotes chondrogenic
differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells by demethylation
of SOX9. Cell Prolif. 51:e124132018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Lee HL, Yu B, Deng P, Wang CY and Hong C:
Transforming growth factor-β-induced KDM4B promotes chondrogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells.
34:711–719. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ye L, Fan Z, Yu B, Chang J, Al Hezaimi K,
Zhou X, Park NH and Wang CY: Histone demethylases KDM4B and KDM6B
promotes osteogenic differentiation of human MSCs. Cell Stem Cell.
11:50–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
He Q, Shi J, Liu W, Zhao W, Wang Z, Liu K,
Zhao D, Wang S, Guo Y, Cheng L and Gao Y: TGF-β1-induced bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) migration via histone
demethylase KDM6B mediated inhibition of methylation marker
H3K27me3. Cell Death Discov. 8:3392022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Duan L, Liang Y, Xu X, Wang J, Li X, Sun
D, Deng Z, Li W and Wang D: Noncoding RNAs in subchondral bone
osteoclast function and their therapeutic potential for
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 22:2792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
van Meurs JB, Boer CG, Lopez-Delgado L and
Riancho JA: Role of epigenomics in bone and cartilage disease. J
Bone Miner Res. 34:215–230. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Nakamura Y, Inloes JB, Katagiri T and
Kobayashi T: Chondrocyte-specific microRNA-140 regulates
endochondral bone development and targets Dnpep to modulate bone
morphogenetic protein signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 31:3019–3028. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Miyaki S, Sato T, Inoue A, Otsuki S, Ito
Y, Yokoyama S, Kato Y, Takemoto F, Nakasa T, Yamashita S, et al:
MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and
homeostasis. Genes Dev. 24:1173–1185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P and
Tsezou A: Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify
novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and
inflammatory networks. PLoS One. 3:e37402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, Grogan SP,
Higashiyama R, Inoue A, Kato Y, Sato T, Lotz MK and Asahara H:
MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular
chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2723–2730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ji Q, Xu X, Zhang Q, Kang L, Xu Y, Zhang
K, Li L, Liang Y, Hong T, Ye Q and Wang Y: The
IL-1β/AP-1/miR-30a/ADAMTS-5 axis regulates cartilage matrix
degradation in human osteoarthritis. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:771–785.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Mao G, Zhang Z, Huang Z, Chen W, Huang G,
Meng F, Zhang Z and Kang Y: MicroRNA-92a-3p regulates the
expression of cartilage-specific genes by directly targeting
histone deacetylase 2 in chondrogenesis and degradation.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 25:521–532. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Mao G, Wu P, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Liao W, Li
Y and Kang Y: MicroRNA-92a-3p regulates aggrecanase-1 and
aggrecanase-2 expression in chondrogenesis and IL-1β-induced
catabolism in human articular chondrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:38–52. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S,
Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR and Haqqi TM: MicroRNA-27b regulates the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1361–1371. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Ying D and
Dong S: MicroRNA-145 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. PLoS One. 6:e216792011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Li X, Gibson G, Kim JS, Kroin J, Xu S, van
Wijnen AJ and Im HJ: MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Gene. 480:34–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Vonk LA, Kragten AH, Dhert WJ, Saris DB
and Creemers LB: Overexpression of hsa-miR-148a promotes cartilage
production and inhibits cartilage degradation by osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:145–153. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Joung S, Yoon DS, Cho S, Ko EA, Lee KM,
Park KH, Lee JW and Kim SH: Downregulation of MicroRNA-495
alleviates IL-1β responses among chondrocytes by preventing SOX9
reduction. Yonsei Med J. 62:650–659. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Qiu M, Liu D and Fu Q: MiR-129-5p shuttled
by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves
IL-1β induced osteoarthritis via targeting HMGB1. Life Sci.
269:1189872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Zhou JX, Tian ZG, Zhu LF, Wu WD, Zhou SL,
Zhao YT and Huang S: MicroRNA-615-3p promotes the osteoarthritis
progression by inhibiting chondrogenic differentiation of bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:6212–6220. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Lv S, Xu J, Chen L, Wu H, Feng W, Zheng Y,
Li P, Zhang H, Zhang L, Chi G and Li Y: MicroRNA-27b targets CBFB
to inhibit differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells into hypertrophic chondrocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther.
11:3922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Huang T, Zhou Y, Wang J, Cao Y and Hang
DH: MiR-26b regulates cartilage differentiation of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells in rats through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:5084–5092. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Chen HO, Zhang L, Tang ZY and Gong ZM:
MiR-485-5p promotes the development of osteoarthritis by inhibiting
cartilage differentiation in BMSCs. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:3294–3302. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Qin F, Wang F, Wang XP, Chen J, Zeng FH,
Sun CL, Mao JP and Li CL: MiR-539-3p inhibited chondrogenic
differentiation in human adipose stem cells by targeting Sox9. J
Orthop Surg Res. 17:1682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Yang M, Yan X, Yuan FZ, Ye J, Du MZ, Mao
ZM, Xu BB, Chen YR, Song YF, Fan BS and Yu JK: MicroRNA-210-3p
promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic
differentiation correlated with HIF-3α signalling in bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Res Int. 2021:66999102021.
|
|
125
|
Zhang P, Gao G, Zhou Z and He X:
microRNA-130b downregulation potentiates chondrogenic
differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting
SOX9. Braz J Med Biol Res. 54:e103452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Feng L, Yang ZM, Li YC, Wang HX, Lo JHT,
Zhang XT and Li G: Linc-ROR promotes mesenchymal stem cells
chondrogenesis and cartilage formation via regulating SOX9
expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 29:568–578. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Alahdal M, Huang R, Duan L, Zhiqin D,
Hongwei O, Li W and Wang D: Indoleamine 2, 3 dioxygenase 1 impairs
chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in the joint
of osteoarthritis mice model. Front Immunol. 12:7811852021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ou F, Su K, Sun J, Liao W, Yao Y, Zheng Y
and Zhang Z: The LncRNA ZBED3-AS1 induces chondrogenesis of human
synovial fluid mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
487:457–463. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Huynh NP, Gloss CC, Lorentz J, Tang R,
Brunger JM, McAlinden A, Zhang B and Guilak F: Long non-coding RNA
GRASLND enhances chondrogenesis via suppression of the interferon
type II signaling pathway. Elife. 9:e495582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Fang P, Zhang LX, Hu Y, Zhang L and Zhou
LW: Long non-coding RNA DANCR induces chondrogenesis by regulating
the miR-1275/MMP-13 axis in synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:10459–10469. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Ji Y, Fang QY, Wang SN, Zhang ZW, Hou ZJ,
Li JN and Fu SQ: Lnc-RNA BLACAT1 regulates differentiation of bone
marrow stromal stem cells by targeting miR-142-5p in
osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:2893–2901.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Zhu Y, Li R and Wen LM: Long non-coding
RNA XIST regulates chondrogenic differentiation of synovium-derived
mesenchymal stem cells from temporomandibular joint via
miR-27b-3p/ADAMTS-5 axis. Cytokine. 137:1553522021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Chen H, Yang S and Shao R: Long non-coding
XIST raises methylation of TIMP-3 promoter to regulate collagen
degradation in osteoarthritic chondrocytes after tibial plateau
fracture. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:2712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wen C, Lin L, Zou R, Lin F and Liu Y:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome mediated long non-coding RNA
KLF3-AS1 represses autophagy and apoptosis of chondrocytes in
osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 21:289–303. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
136
|
Liu Y, Zou R, Wang Z, Wen C, Zhang F and
Lin F: Exosomal KLF3-AS1 from hMSCs promoted cartilage repair and
chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. Biochem J.
475:3629–3638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zhang H, Li J, Shao W and Shen N: LncRNA
CTBP1-AS2 is upregulated in osteoarthritis and increases the
methylation of miR-130a gene to inhibit chondrocyte proliferation.
Clin Rheumatol. 39:3473–3478. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhu J, Fu Q, Shao J, Peng J, Qian Q, Zhou
Y and Chen Y: Regulating effect of Circ_ATRNL1 on the promotion of
SOX9 expression to promote chondrogenic differentiation of hAMSCs
mediated by MiR-145-5p. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 15:487–502. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Li S, Liu J, Liu S, Jiao W and Wang X:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the
development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9
axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 19:1942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Bao C and He C: The role and therapeutic
potential of MSC-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 710:1090022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Liu Y, Lin L, Zou R, Wen C, Wang Z and Lin
F: MSC-derived exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis
of chondrocytes via lncRNA-KLF3-AS1/miR-206/GIT1 axis in
osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 17:2411–2422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Mao G, Zhang Z, Hu S, Zhang Z, Chang Z,
Huang Z, Liao W and Kang Y: Exosomes derived from
miR-92a-3p-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells enhance
chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via targeting
WNT5A. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:2472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Tao Y, Zhou J, Wang Z, Tao H, Bai J, Ge G,
Li W, Zhang W, Hao Y, Yang X and Geng D: Human bone mesenchymal
stem cells-derived exosomal miRNA-361-5p alleviates osteoarthritis
by downregulating DDX20 and inactivating the NF-κB signaling
pathway. Bioorg Chem. 113:1049782021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Cosenza S, Ruiz M, Toupet K, Jorgensen C
and Noël D: Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and
microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in
osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 7:162142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Xia Q, Wang Q, Lin F and Wang J:
miR-125a-5p-abundant exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells
suppress chondrocyte degeneration via targeting E2F2 in traumatic
osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 12:11225–11238. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Chen X, Shi Y, Xue P, Ma X, Li J and Zhang
J: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-136-5p inhibits
chondrocyte degeneration in traumatic osteoarthritis by targeting
ELF3. Arthritis Res Ther. 22:2562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Woo CH, Kim HK, Jung GY, Jung YJ, Lee KS,
Yun YE, Han J, Lee J, Kim WS, Choi JS, et al: Small extracellular
vesicles from human adipose-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage
degeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 9:17352492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wang Z, Yan K, Ge G, Zhang D, Bai J, Guo
X, Zhou J, Xu T, Xu M, Long X, et al: Exosomes derived from
miR-155-5p-overexpressing synovial mesenchymal stem cells prevent
osteoarthritis via enhancing proliferation and migration,
attenuating apoptosis, and modulating extracellular matrix
secretion in chondrocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 37:85–96. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Lu L, Wang J, Fan A, Wang P, Chen R, Lu L
and Yin F: Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular
vesicles containing microRN555A-26a-5p ameliorate cartilage damage
of osteoarthritis. J Gene Med. 23:e33792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Zeng Z, Dai Y, Deng S, Zou S, Dou T and
Wei F: Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular
vesicles alleviate chondrocyte damage during osteoarthritis through
microRNA-130b-3p-mediated inhibition of the LRP12/AKT/β-catenin
axis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 44:247–260. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Kong R, Gao J, Zhang J, Ji L, Yu Y, Zhang
L and Zhao D: Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal
miR-320c enhances chondrogenesis by targeting ADAM19. Future Med
Chem. 14:81–96. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Liu X, Liu Y, He H, Xiang W and He C:
Human adipose and synovial mesenchymal stem cells improve
osteoarthritis in rats by reducing chondrocyte reactive oxygen
species and inhibiting inflammatory response. J Clin Lab Anal.
36:e243532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wang Y, Yu D, Liu Z, Zhou F, Dai J, Wu B,
Zhou J, Heng BC, Zou XH, Ouyang H and Liu H: Exosomes from
embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through
balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular
matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:1892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Liu Y, Zeng Y, Si HB, Tang L, Xie HQ and
Shen B: Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells
overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through
downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med.
50:1088–1105. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Mao G, Hu S, Zhang Z, Wu P, Zhao X, Lin R,
Liao W and Kang Y: Exosomal miR-95-5p regulates chondrogenesis and
cartilage degradation via histone deacetylase 2/8. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5354–5366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Shema E, Bernstein BE and Buenrostro JD:
Single-cell and single-molecule epigenomics to uncover genome
regulation at unprecedented resolution. Nat Genet. 51:19–25. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Chan CKF, Gulati GS, Sinha R, Tompkins JV,
Lopez M, Carter AC, Ransom RC, Reinisch A, Wearda T, Murphy M, et
al: Identification of the human skeletal stem cell. Cell.
175:43–56.e21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Vega RB, Matsuda K, Oh J, Barbosa AC, Yang
X, Meadows E, McAnally J, Pomajzl C, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, et
al: Histone deacetylase 4 controls chondrocyte hypertrophy during
skeletogenesis. Cell. 119:555–566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Ji Q, Zheng Y, Zhang G, Hu Y, Fan X, Hou
Y, Wen L, Li L, Xu Y, Wang Y and Tang F: Single-cell RNA-seq
analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum
Dis. 78:100–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Hu X, Li Z, Ji M, Lin Y, Chen Y and Lu J:
Identification of cellular heterogeneity and immunogenicity of
chondrocytes via single-cell RNA sequencing technique in human
osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 13:10047662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Chou CH, Jain V, Gibson J, Attarian DE,
Haraden CA, Yohn CB, Laberge RM, Gregory S and Kraus VB: Synovial
cell cross-talk with cartilage plays a major role in the
pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 10:108682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Sebastian A, McCool JL, Hum NR, Murugesh
DK, Wilson SP, Christiansen BA and Loots GG: Single-cell RNA-Seq
reveals transcriptomic heterogeneity and post-traumatic
osteoarthritis-associated early molecular changes in mouse
articular chondrocytes. Cells. 10:14622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Pengas I, Eldridge S, Assiotis A,
McNicholas M, Mendes JE and Laver L: MMP-3 in the peripheral serum
as a biomarker of knee osteoarthritis, 40 years after open total
knee meniscectomy. J Exp Ortho. 5:212018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Chou CH, Lee MT, Song IW, Lu LS, Shen HC,
Lee CH, Wu JY, Chen YT, Kraus VB and Wu CC: Insights into
osteoarthritis progression revealed by analyses of both knee
tibiofemoral compartments. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:571–580.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Qu Y, Wang Y, Wang S, Yu X, He Y, Lu R,
Chen S, Meng C, Xu H, Pei W, et al: A comprehensive analysis of
single-cell RNA transcriptome reveals unique SPP1+ chondrocytes in
human osteoarthritis. Comput Biol Med. 160:1069262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Gao C, Pu H, Zhou Q, Tao T, Liu H, Sun X,
He X and Xiao J: Two reactive behaviors of chondrocytes in an
IL-1β-induced inflammatory environment revealed by the single-cell
RNA sequencing. Aging (Albany NY). 13:11646–11664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Yoshimoto M, Sadamori K, Tokumura K,
Tanaka Y, Fukasawa K and Hinoi E: Bioinformatic analysis reveals
potential relationship between chondrocyte senescence and protein
glycosylation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 14:11536892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|