|
1
|
Yunna C, Mengru H, Lei W and Weidong C:
Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 877:1730902020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TAJ: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Juhas U, Ryba-Stanisławowska M, Szargiej P
and Myśliwska J: Different pathways of macrophage activation and
polarization. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 69:496–502. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang T and He C: Pro-inflammatory
cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 44:38–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ploeger DT, Hosper NA, Schipper M, Koerts
JA, de Rond S and Bank RA: Cell plasticity in wound healing:
paracrine factors of M1/M2 polarized macrophages influence the
phenotypical state of dermal fibroblasts. Cell Commun Signal.
11:292013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tu Z, Chen M, Wang M, Shao Z, Jiang X,
Wang K, Yao Z, Yang S, Zhang X, Gao W, et al: Engineering bioactive
M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and
antibacterial scaffolds for rapid angiogenesis and diabetic wound
repair. Adv Funct Mater. 31:21009242021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yin C, Zhao Q, Li W, Zhao Z, Wang J, Deng
T, Zhang P, Shen K, Li Z and Zhang Y: Biomimetic anti-inflammatory
nano-capsule serves as a cytokine blocker and M2 polarization
inducer for bone tissue repair. Acta Biomater. 102:416–426. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim J: Regulation of immune cell functions
by metabolic reprogramming. J Immunol Res. 2018:86054712018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang M, Chen F, Tang Y, Wang J, Chen X, Li
X and Zhang X: Regulation of macrophage polarization and functional
status by modulating hydroxyapatite ceramic micro/nano-topography.
Mater Des. 213:1103022022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
O'Neill LAJ and Hardie DG: Metabolism of
inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature.
493:346–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
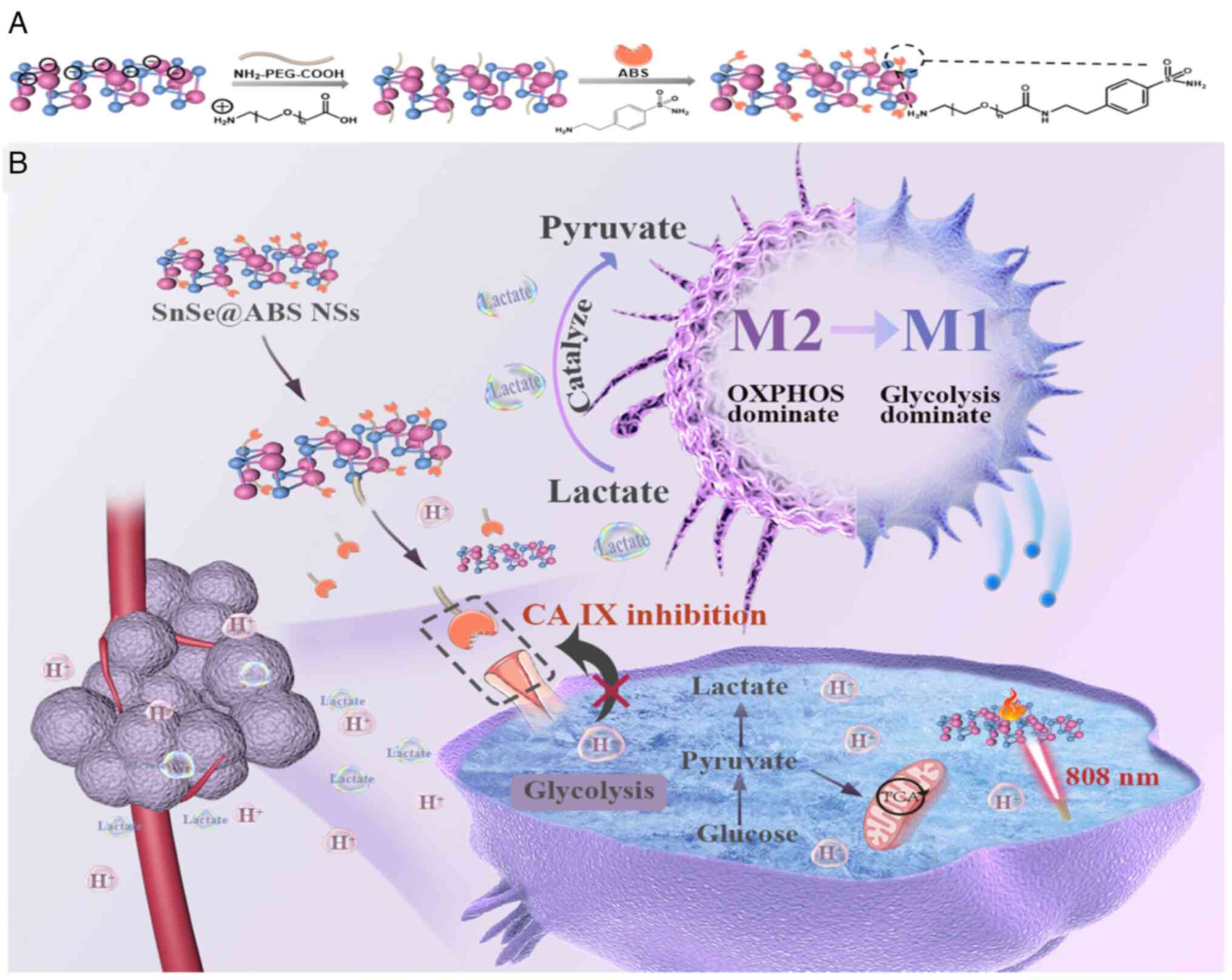
13
|
Tu B, Gao Y, Sun F, Shi M and Huang Y:
Lipid metabolism regulation based on nanotechnology for enhancement
of tumor immunity. Front Pharmacol. 13:8404402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin L, Chen H, Zhao R, Zhu M and Nie G:
Nanomedicine targets iron metabolism for cancer therapy. Cancer
Sci. 113:828–837. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Lin X, Xiao Z, Chen T, Liang SH and Guo H:
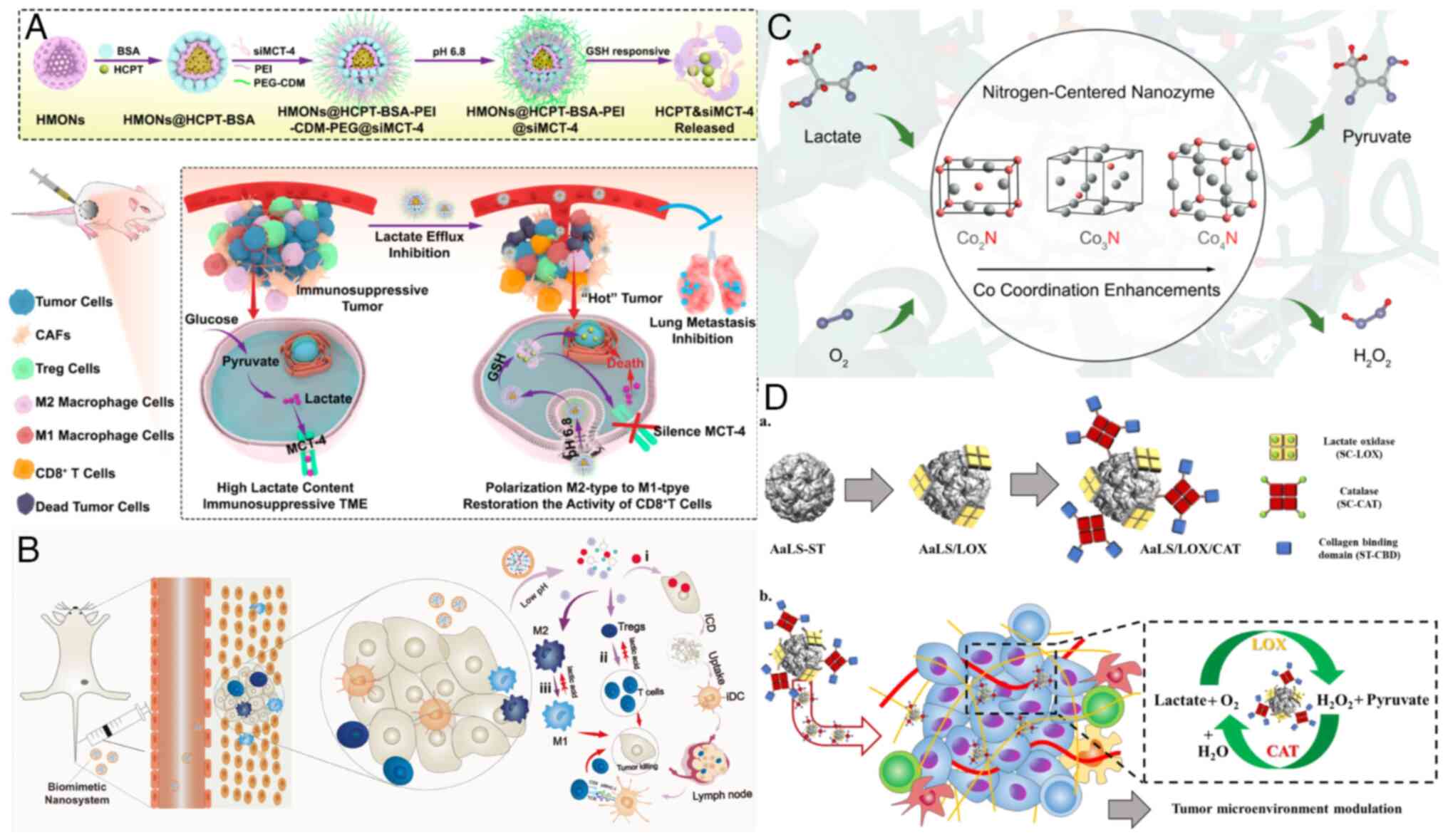
Glucose metabolism on tumor plasticity diagnosis, and treatment.
Front Oncol. 10:3172020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
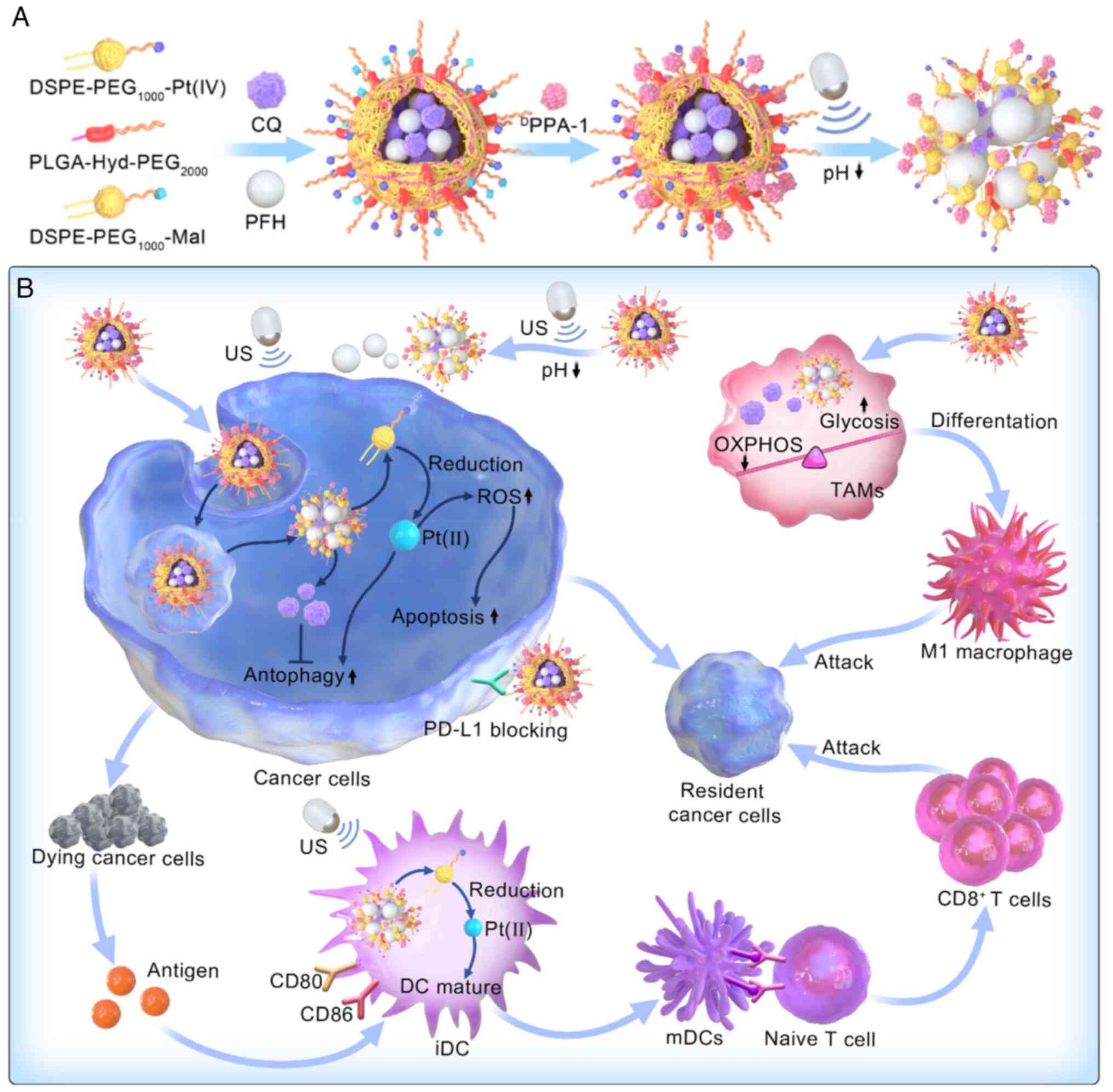
16
|
Prasad CP, Gogia A and Batra AJC:
Essential role of aerobic glycolysis in epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition during carcinogenesis. Clin Transl Oncol. 24:1844–1855.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang B and Shi J: Chemistry of advanced
nanomedicines in cancer cell metabolism regulation. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 7:20013882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garedew A, Henderson SO and Moncada S:
Activated macrophages utilize glycolytic ATP to maintain
mitochondrial membrane potential and prevent apoptotic cell death.
Cell Death Differ. 17:1540–1550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galván-Peña S and O'Neill LAJ: Metabolic
reprograming in macrophage polarization. Front Immunol.
5:4202014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Yu G, Chu H, Wang X, Xiong L, Cai
G, Liu R, Gao H, Tao B, Li W, et al: Macrophage-associated PGK1
phosphorylation promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis. Mol
Cell. 71:201–215.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
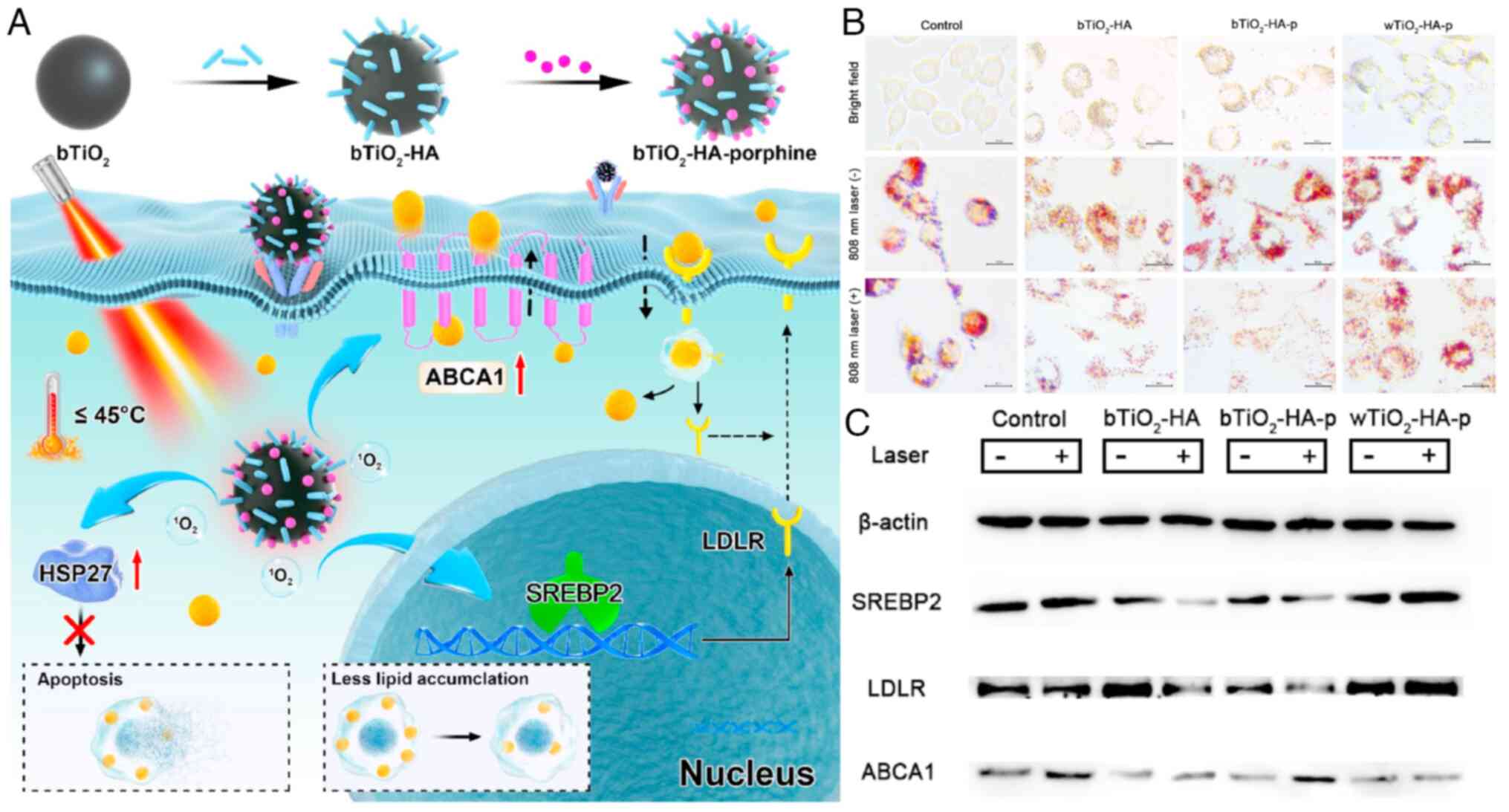
|
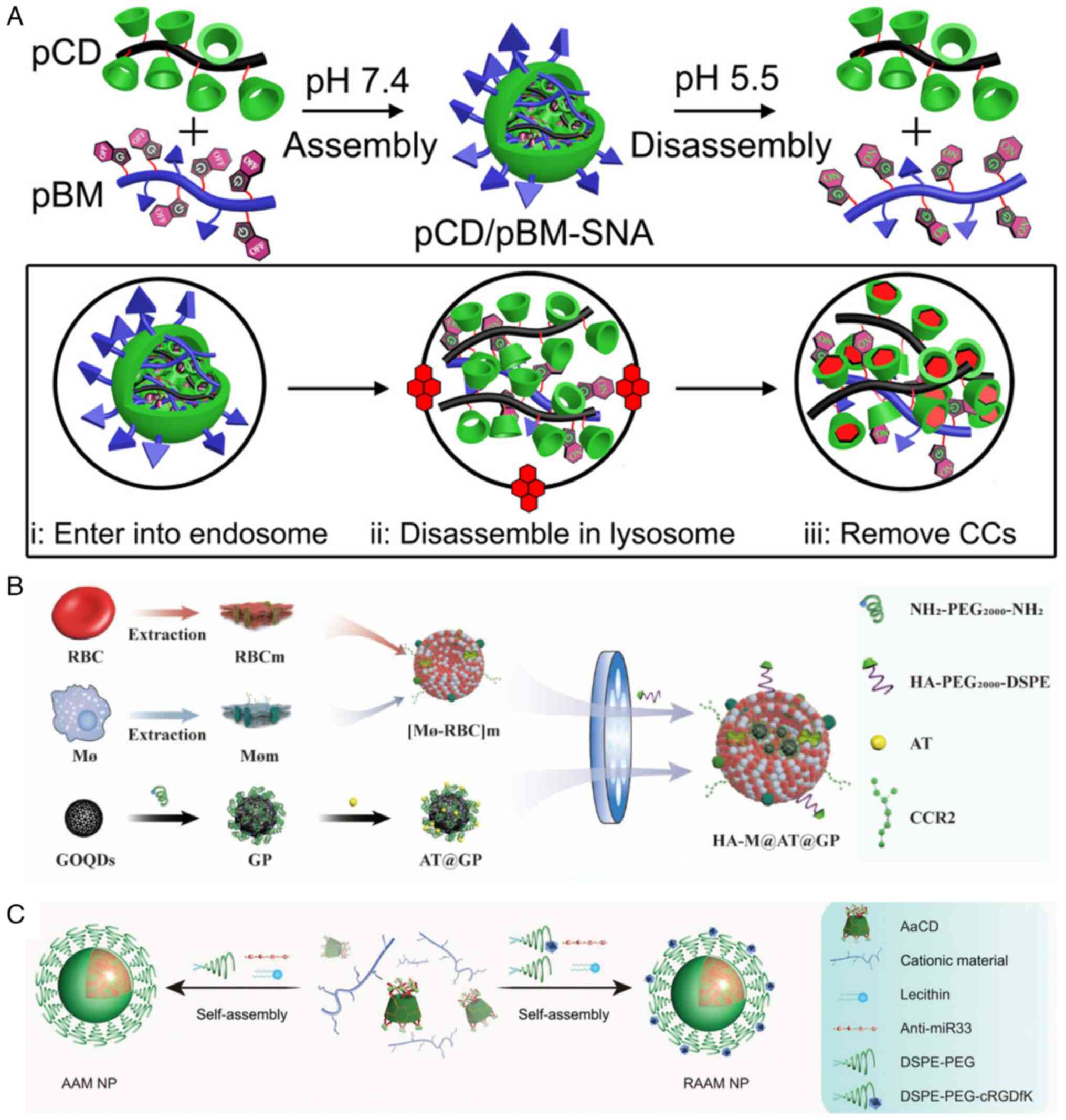
Bailey JD, Diotallevi M, Nicol T, McNeill
E, Shaw A, Chuaiphichai S, Hale A, Starr A, Nandi M, Stylianou E,
et al: Nitric oxide modulates metabolic remodeling in inflammatory
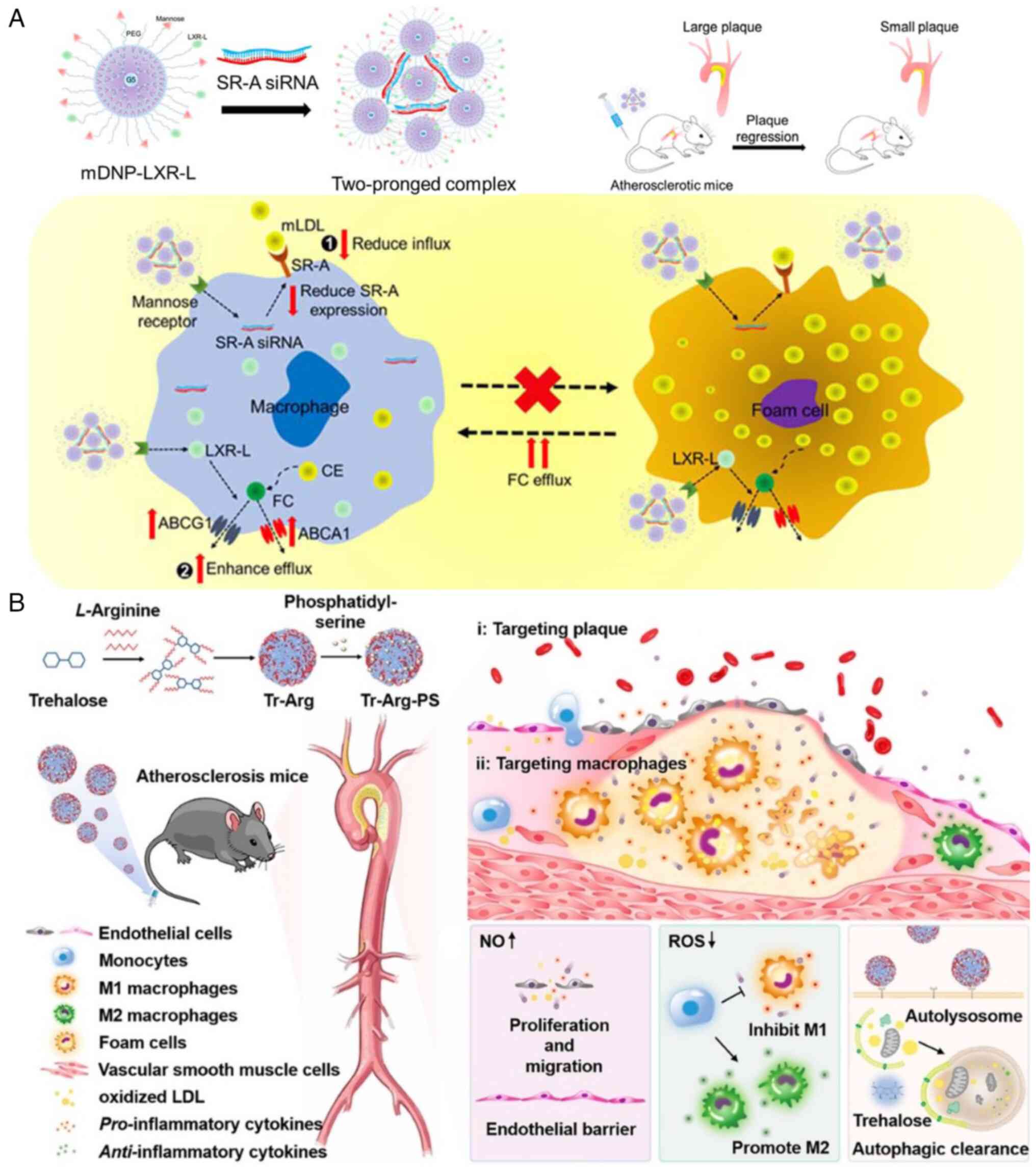
macrophages through TCA cycle regulation and itaconate
accumulation. Cell Rep. 28:218–230.e7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Na YR, Je S and Seok SH: Metabolic
features of macrophages in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cancer
Lett. 413:46–58. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Yang P, Yu T, Gao M, Liu D, Zhang
J, Lu C, Chen X, Zhang X and Liu Y: Lactylation of PKM2 suppresses
inflammatory metabolic adaptation in pro-inflammatory macrophages.
Int J Biol Sci. 18:6210–6225. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang K, Xu J, Fan M, Tu F, Wang X, Ha T,
Williams DL and Li C: Lactate suppresses macrophage
pro-inflammatory response to LPS stimulation by inhibition of YAP
and NF-κB activation via GPR81-mediated signaling. Front Immunol.
11:5879132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang F, Zhang S, Vuckovic I, Jeon R,
Lerman A, Folmes CD, Dzeja PP and Herrmann J: Glycolytic
stimulation is not a requirement for M2 macrophage differentiation.
Cell Metab. 28:463–475.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang T, Liu H, Lian G, Zhang SY, Wang X
and Jiang C: HIF1α-induced glycolysis metabolism is essential to
the activation of inflammatory macrophages. Mediators Inflamm.
2017:90293272017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhihua Y, Yulin T, Yibo W, Wei D, Yin C,
Jiahao X, Runqiu J and Xuezhong X: Hypoxia decreases macrophage
glycolysis and M1 percentage by targeting microRNA-30c and mTOR in
human gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 110:2368–2377. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Everts B, Amiel E, Huang SCC, Smith AM,
Chang CH, Lam WY, Redmann V, Freitas TC, Blagih J, van der Windt
GJ, et al: TLR-driven early glycolytic reprogramming via the
kinases TBK1-IKKε supports the anabolic demands of dendritic cell
activation. Nat Immunol. 15:323–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Im SS, Yousef L, Blaschitz C, Liu JZ,
Edwards RA, Young SG, Raffatellu M and Osborne TF: Linking lipid
metabolism to the innate immune response in macrophages through
sterol regulatory element binding protein-1a. Cell Metab.
13:540–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gordon S: Phagocytosis: An immunobiologic
process. Immunity. 44:463–475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cader MZ, Boroviak K, Zhang Q, Assadi G,
Kempster SL, Sewell GW, Saveljeva S, Ashcroft JW, Clare S,
Mukhopadhyay S, et al: C13orf31 (FAMIN) is a central regulator of
immunometabolic function. Nat Immunol. 17:1046–1056. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nomura M, Liu J, Rovira II,
Gonzalez-Hurtado E, Lee J, Wolfgang MJ and Finkel T: Fatty acid
oxidation in macrophage polarization. Nat Immunol. 17:216–217.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schönfeld P and Wojtczak L: Short- and
medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: The cellular
perspective. J Lipid Res. 57:943–954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Coniglio S, Shumskaya M and Vassiliou E:
Unsaturated fatty acids and their immunomodulatory properties.
Biology (Basel). 12:2792023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deng Y, Li W, Zhang Y, Li J, He F, Dong K,
Hong Z, Luo R and Pei X: α-Linolenic acid inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis in vitro and prevents inflammation in vivo.
Foods. 12:6822023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Laval T, Chaumont L and Demangel C: Not
too fat to fight: The emerging role of macrophage fatty acid
metabolism in immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunol Rev.
301:84–97. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Suzuki M, Takaishi S, Nagasaki M, Onozawa
Y, Iino I, Maeda H, Komai T and Oda T: Medium-chain fatty
acid-sensing receptor, GPR84, is a proinflammatory receptor. J Biol
Chem. 288:10684–10691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang J, Wu X, Simonavicius N, Tian H and
Ling L: Medium-chain fatty acids as ligands for orphan G
protein-coupled receptor GPR84. J Biol Chem. 281:34457–34464. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hidalgo MA, Carretta MD and Burgos RA:
Long chain fatty acids as modulators of immune cells function:
Contribution of FFA1 and FFA4 receptors. Front Physiol.
12:6683302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Forsman H, Dahlgren C, Mårtensson J,
Björkman L and Sundqvist M: Function and regulation of GPR84 in
human neutrophils. Br J Pharmacol. Mar 4–2023.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Danielski LG, Giustina AD, Bonfante S,
Barichello T and Petronilho F: The NLRP3 inflammasome and its role
in sepsis development. Inflammation. 43:24–31. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kuhajda FP: Fatty-acid synthase and human
cancer: New perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition.
16:202–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moon JS, Lee S, Park MA, Siempos II,
Haslip M, Lee PJ, Yun M, Kim CK, Howrylak J, Ryter SW, et al:
UCP2-induced fatty acid synthase promotes NLRP3 inflammasome
activation during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 125:665–680. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Namgaladze D and Brüne B: Fatty acid
oxidation is dispensable for human macrophage IL-4-induced
polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:1329–1335. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu L, Zhao Q, Yang T, Ding W and Zhao Y:
Cellular metabolism and macrophage functional polarization. Int Rev
Immunol. 34:82–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hohensinner PJ, Lenz M, Haider P, Mayer J,
Richter M, Kaun C, Goederle L, Brekalo M, Salzmann M, Sharma S, et
al: Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid oxidation reduces
atherosclerosis progression by suppression of macrophage NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 190:1146342021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sola-García A, Cáliz-Molina MÁ, Espadas I,
Petr M, Panadero-Morón C, González-Morán D, Martín-Vázquez ME,
Narbona-Pérez ÁJ, López-Noriega L, Martínez-Corrales G, et al:
Metabolic reprogramming by Acly inhibition using SB-204990 alters
glucoregulation and modulates molecular mechanisms associated with
aging. Commun Biol. 6:2502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Luo J, Yang H and Song BL: Mechanisms and
regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:225–245. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Guo H, Callaway JB and Ting JP:
Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and
therapeutics. Nat Med. 21:677–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhou QD, Chi X, Lee MS, Hsieh WY,
Mkrtchyan JJ, Feng AC, He C, York AG, Bui VL, Kronenberger EB, et
al: Interferon-mediated reprogramming of membrane cholesterol to
evade bacterial toxins. Nat Immunol. 21:746–755. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao J, Chen J, Li M, Chen M and Sun C:
Multifaceted functions of CH25H and 25HC to modulate the lipid
metabolism, immune responses, and broadly antiviral activities.
Viruses. 12:7272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Platanias LC: Mechanisms of type-I- and
type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:375–386.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hsieh WY, Zhou QD, York AG, Williams KJ,
Scumpia PO, Kronenberger EB, Hoi XP, Su B, Chi X, Bui VL, et al:
Toll-like receptors induce signal-specific reprogramming of the
macrophage lipidome. Cell Metab. 32:128–143.e5. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
York AG, Williams KJ, Argus JP, Zhou QD,
Brar G, Vergnes L, Gray EE, Zhen A, Wu NC, Yamada DH, et al:
Limiting cholesterol biosynthetic flux spontaneously engages type I
IFN signaling. Cell. 163:1716–1729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kieler M, Hofmann M and Schabbauer G: More
than just protein building blocks: How amino acids and related
metabolic pathways fuel macrophage polarization. FEBS J.
288:3694–3714. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yuan P, Hu X and Zhou Q: The
nanomaterial-induced bystander effects reprogrammed macrophage
immune function and metabolic profile. Nanotoxicology.
14:1137–1155. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Puchalska P, Huang X, Martin SE, Han X,
Patti GJ and Crawford PA: Isotope tracing untargeted metabolomics
reveals macrophage polarization-state-specific metabolic
coordination across intracellular compartments. Science. 9:298–313.
2018.
|
|
58
|
O'Neill LA, Kishton RJ and Rathmell J: A
guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat Rev Immunol.
16:553–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Qualls JE, Subramanian C, Rafi W, Smith
AM, Balouzian L, DeFreitas AA, Shirey KA, Reutterer B, Kernbauer E,
Stockinger S, et al: Sustained generation of nitric oxide and
control of mycobacterial infection requires argininosuccinate
synthase 1. Cell Host Microbe. 12:313–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yue Y, Huang W, Liang J, Guo J, Ji J, Yao
Y, Zheng M, Cai Z, Lu L and Wang J: IL4I1 is a novel regulator of
M2 macrophage polarization that can inhibit T cell activation via
L-tryptophan and arginine depletion and IL-10 production. PLoS One.
10:e01429792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M,
Tritschler I, Trump S, Schumacher T, Jestaedt L, Schrenk D, Weller
M, et al: An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl
hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 478:197–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Huang SCC, Smith AM, Everts B, Colonna M,
Pearce EL, Schilling JD and Pearce EJ: Metabolic reprogramming
mediated by the mTORC2-IRF4 signaling axis is essential for
macrophage alternative activation. Immunity. 45:817–830. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Covarrubias AJ, Aksoylar HI, Yu J, Snyder
NW, Worth AJ, Iyer SS, Wang J, Ben-Sahra I, Byles V,
Polynne-Stapornkul T, et al: Akt-mTORC1 signaling regulates Acly to
integrate metabolic input to control of macrophage activation.
Elife. 5:e116122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu PS, Wang H, Li X, Chao T, Teav T,
Christen S, Di Conza G, Cheng WC, Chou CH, Vavakova M, et al:
α-ketoglutarate orchestrates macrophage activation through
metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming. Nat Immunol. 18:985–994.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhou W, Hu G, He J, Wang T, Zuo Y, Cao Y,
Zheng Q, Tu J, Ma J, Cai R, et al: SENP1-Sirt3 signaling promotes
α-ketoglutarate production during M2 macrophage polarization. Cell
Rep. 39:1106602022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Palmieri EM, Menga A, Martín-Pérez R,
Quinto A, Riera-Domingo C, De Tullio G, Hooper DC, Lamers WH,
Ghesquière B, McVicar DW, et al: Pharmacologic or genetic targeting
of glutamine synthetase skews macrophages toward an M1-like
phenotype and inhibits tumor metastasis. Cell Rep. 20:1654–1666.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mazzone M, Menga A and Castegna A:
Metabolism and TAM functions-it takes two to tango. FEBS J.
285:700–716. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ryan DG and O'Neill LAJ: Krebs cycle
reborn in macrophage immunometabolism. Annu Rev Immunol.
38:289–313. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
McGettrick AF and O'Neill LAJ: How
metabolism generates signals during innate immunity and
inflammation. J Biol Chem. 288:22893–22898. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
O'Neill LAJ: A broken krebs cycle in
macrophages. Immunity. 42:393–394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jha AK, Huang SCC, Sergushichev A,
Lampropoulou V, Ivanova Y, Loginicheva E, Chmielewski K, Stewart
KM, Ashall J, Everts B, et al: Network integration of parallel
metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that
regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity. 42:419–430. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Infantino V, Pierri CL and Iacobazzi V:
Metabolic routes in inflammation: The citrate pathway and its
potential as therapeutic target. Curr Med Chem. 26:7104–7116. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Infantino V, Iacobazzi V, Palmieri F and
Menga A: ATP-citrate lyase is essential for macrophage inflammatory
response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 440:105–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tannahill G, Curtis A, Adamik J,
Palsson-McDermott EM, McGettrick AF, Goel G, Frezza C, Bernard NJ,
Kelly B, Foley NH, et al: Succinate is an inflammatory signal that
induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature. 496:238–242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
He W, Miao FJ, Lin DC, Schwandner RT, Wang
Z, Gao J, Chen JL, Tian H and Ling L: Citric acid cycle
intermediates as ligands for orphan G-protein-coupled receptors.
Nature. 429:188–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Toma I, Kang JJ, Sipos A, Vargas S, Bansal
E, Hanner F, Meer E and Peti-Peterdi J: Succinate receptor GPR91
provides a direct link between high glucose levels and renin
release in murine and rabbit kidney. J Clin Invest. 118:2526–2534.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Peti-Peterdi J, Kang JJ and Toma I:
Activation of the renal renin-angiotensin system in diabetes-new
concepts. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 23:3047–3049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sadagopan N, Li W, Roberds SL, Major T,
Preston GM, Yu Y and Tones MA: Circulating succinate is elevated in
rodent models of hypertension and metabolic disease. Am J
Hypertens. 20:1209–1215. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Macaulay IC, Tijssen MR, Thijssen-Timmer
DC, Gusnanto A, Steward M, Burns P, Langford CF, Ellis PD,
Dudbridge F, Zwaginga JJ, et al: Comparative gene expression
profiling of in vitro differentiated megakaryocytes and
erythroblasts identifies novel activatory and inhibitory platelet
membrane proteins. Blood. 109:3260–3269. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Wu JY, Huang TW, Hsieh YT, Wang YF, Yen
CC, Lee GL, Yeh CC, Peng YJ, Kuo YY, Wen HT, et al: Cancer-derived
succinate promotes macrophage polarization and cancer metastasis
via succinate receptor. Mol Cell. 77:213–227.e5. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wunderer F, Traeger L, Sigurslid HH,
Meybohm P, Bloch DB and Malhotra R: The role of hepcidin and iron
homeostasis in atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res. 153:1046642020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xia Y, Li Y, Wu X, Zhang Q, Chen S, Ma X
and Yu M: Ironing out the details: How iron orchestrates macrophage
polarization. Front Immunol. 12:6695662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liang G, Sakamoto A, Cornelissen A, Hong
CC and Finn AV: Ironing-out the role of hepcidin in
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:303–305. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Marques L, Negre-Salvayre A, Costa L and
Canonne-Hergaux F: Iron gene expression profile in atherogenic Mox
macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:1137–1146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Handa P, Thomas S, Morgan-Stevenson V,
Maliken BD, Gochanour E, Boukhar S, Yeh MM and Kowdley KV: Iron
alters macrophage polarization status and leads to steatohepatitis
and fibrogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 105:1015–1026. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hu X, Cai X, Ma R, Fu W, Zhang C and Du X:
Iron-load exacerbates the severity of atherosclerosis via inducing
inflammation and enhancing the glycolysis in macrophages. J Cell
Physiol. 234:18792–18800. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhou Y, Que KT, Zhang Z, Yi ZJ, Zhao PX,
You Y, Gong JP and Liu ZJ: Iron overloaded polarizes macrophage to
proinflammation phenotype through ROS/acetyl-p53 pathway. Cancer
Med. 7:4012–4022. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang CY and Babitt JL: Hepcidin regulation
in the anemia of inflammation. Curr Opin Hematol. 23:189–197. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kanamori Y, Murakami M, Matsui T and
Funaba M: JNK facilitates IL-1β-induced hepcidin transcription via
JunB activation. Cytokine. 111:295–302. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kanamori Y, Murakami M, Sugiyama M,
Hashimoto O, Matsui T and Funaba M: Hepcidin and IL-1β. Vitam Horm.
110:143–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhang Z, Zhang F, An P, Guo X, Shen Y, Tao
Y, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Ning B, et al: Ferroportin1 deficiency in
mouse macrophages impairs iron homeostasis and inflammatory
responses. Blood. 118:1912–1922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Jiang L, Zheng H, Lyu Q, Hayashi S, Sato
K, Sekido Y, Nakamura K, Tanaka H, Ishikawa K, Kajiyama H, et al:
Lysosomal nitric oxide determines transition from autophagy to
ferroptosis after exposure to plasma-activated Ringer's lactate.
Redox Biol. 43:1019892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Krümmel B, Plötz T, Jörns A, Lenzen S and
Mehmeti I: The central role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in the
regulation of ferroptosis and its implications for pro-inflammatory
cytokine-mediated beta-cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1867:1661142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
de Goede KE, Driessen AJM and Van den
Bossche J: Metabolic cancer-macrophage crosstalk in the tumor
microenvironment. Biology (Basel). 9:3802020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ling J, Chang Y, Yuan Z, Chen Q, He L and
Chen T: Designing lactate dehydrogenase-mimicking SnSe nanosheets
to reprogram tumor-associated macrophages for potentiation of
photothermal immunotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
14:27651–27665. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jeong H, Kim S, Hong BJ, Lee CJ, Kim YE,
Bok S, Oh JM, Gwak SH, Yoo MY, Lee MS, et al: Tumor-associated
macrophages enhance tumor hypoxia and aerobic glycolysis. Cancer
Res. 79:795–806. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lin Y, Xu J and Lan H: Tumor-associated
macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical
therapeutic applications. J Hematol Oncol. 12:762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu D, Chang C, Lu N, Wang X, Lu Q, Ren X,
Ren P, Zhao D, Wang L, Zhu Y, et al: Comprehensive proteomics
analysis reveals metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated
macrophages stimulated by the tumor microenvironment. J Proteome
Res. 16:288–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Faubert B, Li KY, Cai L, Hensley CT, Kim
J, Zacharias LG, Yang C, Do QN, Doucette S, Burguete D, et al:
Lactate metabolism in human lung tumors. Cell. 171:358–371.e9.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Goswami KK, Banerjee S, Bose A and Baral
R: Lactic acid in alternative polarization and function of
macrophages in tumor microenvironment. Hum Immunoll. 83:409–417.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Colegio OR, Chu NQ, Szabo AL, Chu T,
Rhebergen AM, Jairam V, Cyrus N, Brokowski CE, Eisenbarth SC,
Phillips GM, et al: Functional polarization of tumour-associated
macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature. 513:559–563.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chiu DKC, Xu IMJ, Lai RKH, Tse AP, Wei LL,
Koh HY, Li LL, Lee D, Lo RC, Wong CM, et al: Hypoxia induces
myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment to hepatocellular
carcinoma through chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 26. Hepatology.
64:797–813. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Xu Y, Lu J, Tang Y, Xie W, Zhang H, Wang
B, Zhang S, Hou W, Zou C, Jiang P and Zhang W: PINK1 deficiency in
gastric cancer compromises mitophagy, promotes the Warburg effect,
and facilitates M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Lett.
529:19–36. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C,
Weng Y, Liu W, Kim S, Lee S, Perez-Neut M, et al: Metabolic
regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature.
574:575–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Locatelli SL, Careddu G, Serio S, Consonni
FM, Maeda A, Viswanadha S, Vakkalanka S, Castagna L, Santoro A,
Allavena P, et al: Targeting cancer cells and tumor
microenvironment in preclinical and clinical models of hodgkin
lymphoma using the dual PI3Kδ/γ inhibitor RP6530. Clin Cancer Res.
25:1098–1112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Ohashi T, Aoki M, Tomita H, Akazawa T,
Sato K, Kuze B, Mizuta K, Hara A, Nagaoka H, Inoue N and Ito Y:
M2-like macrophage polarization in high lactic acid-producing head
and neck cancer. Cancer Sci. 108:1128–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Kumar V: Targeting macrophage
immunometabolism: Dawn in the darkness of sepsis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 58:173–185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kanmani P and Kim H: Protective effects of
lactic acid bacteria against TLR4 induced inflammatory response in
hepatoma HepG2 cells through modulation of toll-like receptor
negative regulators of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB
signaling. Front Immunol. 9:15372018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Feng R, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Imura S,
Iwahashi S, Saito Y and Shimada M: Nrf2 activation drive
macrophages polarization and cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal
transition during interaction. Cell Commun Signal. 16:542018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams
JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews
DW, et al: Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of
the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ.
25:486–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Carmona-Fontaine C, Deforet M, Akkari L,
Thompson CB, Joyce JA and Xavier JB: Metabolic origins of spatial
organization in the tumor microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:2934–2939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Li K, Lin C, He Y, Lu L, Xu K, Tao B, Xia
Z, Zeng R, Mao Y, Luo Z and Cai K: Engineering of
cascade-responsive nanoplatform to inhibit lactate efflux for
enhanced tumor chemo-immunotherapy. ACS Nano. 14:14164–14180. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Choi H, Yeo M, Kang Y, Kim HJ, Park SG,
Jang E, Park SH, Kim E and Kang S: Lactate
oxidase/catalase-displaying nanoparticles efficiently consume
lactate in the tumor microenvironment to effectively suppress tumor
growth. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:52023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wang H, Wu C, Tong X and Chen S: A
biomimetic metal-organic framework nanosystem modulates
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment metabolism to amplify
immunotherapy. J Control Release. 353:727–737. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Zhao S, Li H, Liu R, Tao N, Deng L, Xu Q,
Hou J, Sheng J, Zheng J, Wang L, et al: Nitrogen-centered lactate
oxidase nanozyme for tumor lactate modulation and microenvironment
remodeling. J Am Chem Soc. 145:10322–10332. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yang X, Zhao M, Wu Z, Chen C, Zhang Y,
Wang L, Guo Q, Wang Q, Liang S, Hu S, et al: Nano-ultrasonic
contrast agent for chemoimmunotherapy of breast cancer by immune
metabolism reprogramming and tumor autophagy. ACS Nano.
16:3417–3431. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wu H, Han Y, Rodriguez Sillke Y, Deng H,
Siddiqui S, Treese C, Schmidt F, Friedrich M, Keye J, Wan J, et al:
Lipid droplet-dependent fatty acid metabolism controls the immune
suppressive phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages. EMBO Mol
Med. 11:e106982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wu L, Zhang X, Zheng L, Zhao H, Yan G,
Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Lei J, Zhang J, Wang J, et al: RIPK3 orchestrates
fatty acid metabolism in tumor-associated macrophages and
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Immunol Res. 8:710–721. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Niu Z, Shi Q, Zhang W, Shu Y, Yang N, Chen
B, Wang Q, Zhao X, Chen J, Cheng N, et al: Caspase-1 cleaves PPARγ
for potentiating the pro-tumor action of TAMs. Nat Commun.
8:7662017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Di Conza G, Tsai CH, Gallart-Ayala H, Yu
YR, Franco F, Zaffalon L, Xie X, Li X, Xiao Z, Raines LN, et al:
Tumor-induced reshuffling of lipid composition on the endoplasmic
reticulum membrane sustains macrophage survival and pro-tumorigenic
activity. Nat Immunol. 22:1403–1415. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Bidault G, Virtue S, Petkevicius K, Jolin
HE, Dugourd A, Guénantin AC, Leggat J, Mahler-Araujo B, Lam BYH, Ma
MK, et al: SREBP1-induced fatty acid synthesis depletes macrophages
antioxidant defences to promote their alternative activation. Nat
Metab. 3:1150–1162. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhao Q, Lin X and Wang G: Targeting
SREBP-1-mediated lipogenesis as potential strategies for cancer.
Front Oncol. 12:9523712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang T, Guo Z, Huo X, Gong Y, Li C, Huang
J, Wang Y, Feng H, Ma X, Jiang C, et al: Dysregulated lipid
metabolism blunts the sensitivity of cancer cells to EZH2
inhibitor. EBioMedicine. 77:1038722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Chen M and Huang J: The expanded role of
fatty acid metabolism in cancer: New aspects and targets. Precis
Clin Med. 2:183–191. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Xiang W, Shi R, Kang X, Zhang X, Chen P,
Zhang L, Hou A, Wang R, Zhao Y, Zhao K, et al: Monoacylglycerol
lipase regulates cannabinoid receptor 2-dependent macrophage
activation and cancer progression. Nat Commun. 9:25742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Jiang M, Li X, Zhang J, Lu Y, Shi Y, Zhu
C, Liu Y, Qin B, Luo Z, Du Y, et al: Dual inhibition of endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidation stress manipulates the polarization
of macrophages under hypoxia to sensitize immunotherapy. ACS Nano.
15:14522–14534. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Hou L, Gong X, Yang J, Zhang H, Yang W and
Chen X: Hybrid-membrane-decorated prussian blue for effective
cancer immunotherapy via tumor-associated macrophages polarization
and hypoxia relief. Adv Mater. 34:22003892022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Yang Z, Luo Y, Yu H, Liang K, Wang M, Wang
Q, Yin B and Chen H: Reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment
based on a light-activated nanoplatform for efficient cancer
therapy. Adv Mater. 34:21089082022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Costa da Silva M, Breckwoldt MO, Vinchi F,
Correia MP, Stojanovic A, Thielmann CM, Meister M, Muley T, Warth
A, Platten M, et al: Iron induces anti-tumor activity in
tumor-associated macrophages. Front Immunol. 8:14792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zhang F, Li F, Lu GH, Nie W, Zhang L, Lv
Y, Bao W, Gao X, Wei W, Pu K and Xie HY: Engineering magnetosomes
for ferroptosis/immunomodulation synergism in cancer. ACS Nano.
13:5662–5673. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gu Z, Liu T, Liu C, Yang Y, Tang J, Song
H, Wang Y, Yang Y and Yu C: Ferroptosis-strengthened metabolic and
inflammatory regulation of tumor-associated macrophages provokes
potent tumoricidal activities. Nano Lett. 21:6471–6479. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Altman BJ, Stine ZE and Dang CV: From
Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:619–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Zhu Y, Zhang S, Sun J, Wang T, Liu Q, Wu
G, Qian Y, Yang W, Wang Y and Wang W: Cigarette smoke promotes oral
leukoplakia via regulating glutamine metabolism and M2 polarization
of macrophage. Int J Oral Sci. 13:252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Oh MH, Sun IH, Zhao L, Leone RD, Sun IM,
Xu W, Collins SL, Tam AJ, Blosser RL, Patel CH, et al: Targeting
glutamine metabolism enhances tumor-specific immunity by modulating
suppressive myeloid cells. J Clin Invest. 130:3865–3884. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Du B, Jiao Q, Bai Y, Yu M, Pang M, Zhao M,
Ma H and Yao H: Glutamine metabolism-regulated nanoparticles to
enhance chemoimmunotherapy by increasing antigen presentation
efficiency. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 14:8753–8765. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Hoves S, Ooi CH, Wolter C, Sade H,
Bissinger S, Schmittnaegel M, Ast O, Giusti AM, Wartha K, Runza V,
et al: Rapid activation of tumor-associated macrophages boosts
preexisting tumor immunity. J Exp Med. 215:859–876. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kashyap AS, Schmittnaegel M, Rigamonti N,
Pais-Ferreira D, Mueller P, Buchi M, Ooi CH, Kreuzaler M,
Hirschmann P, Guichard A, et al: Optimized antiangiogenic
reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment potentiates CD40
immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:541–551. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Beatty GL, Chiorean EG, Fishman MP,
Saboury B, Teitelbaum UR, Sun W, Huhn RD, Song W, Li D, Sharp LL,
et al: CD40 agonists alter tumor stroma and show efficacy against
pancreatic carcinoma in mice and humans. Science. 331:1612–1616.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Liu PS, Chen YT, Li X, Hsueh PC, Tzeng SF,
Chen H, Shi PZ, Xie X, Parik S, Planque M, et al: CD40 signal
rewires fatty acid and glutamine metabolism for stimulating
macrophage anti-tumorigenic functions. Nat Immunol. 24:452–462.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Mai Z, Zhong J, Zhang J, Chen G, Tang Y,
Ma W, Li G, Feng Z, Li F, Liang XJ, et al: Carrier-free
immunotherapeutic nano-booster with dual synergistic effects based
on glutaminase inhibition combined with photodynamic therapy. ACS
Nano. 17:1583–1596. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Tabas I and Bornfeldt KE: Intracellular
and intercellular aspects of macrophage immunometabolism in
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 126:1209–1227. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhu X, Owen JS, Wilson MD, Li H, Griffiths
GL, Thomas MJ, Hiltbold EM, Fessler MB and Parks JS: Macrophage
ABCA1 reduces MyD88-dependent Toll-like receptor trafficking to
lipid rafts by reduction of lipid raft cholesterol. J Lipid Res.
51:3196–3206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Stewart CR, Stuart LM, Wilkinson K, van
Gils JM, Deng J, Halle A, Rayner KJ, Boyer L, Zhong R, Frazier WA,
et al: CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly
of a Toll-like receptor 4 and 6 heterodimer. Nat Immunol.
11:155–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
144
|
Miller YI, Viriyakosol S, Worrall DS,
Boullier A, Butler S and Witztum JL: Toll-like receptor 4-dependent
and -independent cytokine secretion induced by minimally oxidized
low-density lipoprotein in macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 25:1213–1219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM,
Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nuñez G, Schnurr
M, et al: NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and
activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 464:1357–1361. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Chen J, Su Y, Pi S, Hu B and Mao L: The
dual role of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 in
atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 8:6823892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Tomas L, Edsfeldt A, Mollet IG, Perisic
Matic L, Prehn C, Adamski J, Paulsson-Berne G, Hedin U, Nilsson J,
Bengtsson E, et al: Altered metabolism distinguishes high-risk from
stable carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Eur Heart J. 39:2301–2310.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Mügge A: The role of reactive oxygen
species in atherosclerosis. Z Kardiol. 87:851–864. 1998.
|
|
149
|
Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D and
Mehta J: Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
19:422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
He J, Zhang W, Zhou X, Xu F, Zou J, Zhang
Q, Zhao Y, He H, Yang H and Liu J: Reactive oxygen species
(ROS)-responsive size-reducible nanoassemblies for deeper
atherosclerotic plaque penetration and enhanced macrophage-targeted
drug delivery. Bioact Mater. 19:115–126. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Wang Y, Li L, Zhao W, Dou Y, An H, Tao H,
Xu X, Jia Y, Lu S, Zhang J and Hu H: Targeted therapy of
atherosclerosis by a broad-spectrum reactive oxygen species
scavenging nanoparticle with intrinsic anti-inflammatory activity.
ACS Nano. 12:8943–8960. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Hu R, Dai C, Dong C, Ding L, Huang H, Chen
Y and Zhang B: Living macrophage-delivered tetrapod PdH nanoenzyme
for targeted atherosclerosis management by ROS scavenging, hydrogen
anti-inflammation, and autophagy activation. ACS Nano.
16:15959–15976. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Sun W, Xu Y, Yao Y, Yue J, Wu Z, Li H,
Shen G, Liao Y, Wang H and Zhou W: Self-oxygenation mesoporous
MnO2 nanoparticles with ultra-high drug loading capacity
for targeted arteriosclerosis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology.
20:882022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Han XB, Li HX, Jiang YQ, Wang H, Li XS,
Kou JY, Zheng YH, Liu ZN, Li H, Li J, et al: Upconversion
nanoparticle-mediated photodynamic therapy induces autophagy and
cholesterol efflux of macrophage-derived foam cells via ROS
generation. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Dai T, He W, Tu S, Han J, Yuan B, Yao C,
Ren W and Wu A: Black TiO2 nanoprobe-mediated mild
phototherapy reduces intracellular lipid levels in atherosclerotic
foam cells via cholesterol regulation pathways instead of
apoptosis. Bioact Mater. 17:18–28. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Zhang Y, Gong F, Wu Y, Hou S, Xue L, Su Z
and Zhang C: Poly-β-cyclodextrin supramolecular nanoassembly with a
pH-sensitive switch removing lysosomal cholesterol crystals for
antiatherosclerosis. Nano Lett. 21:9736–9745. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
You P, Mayier A, Zhou H, Yang A, Fan J, Ma
S, Liu B and Jiang Y: Targeting and promoting atherosclerosis
regression using hybrid membrane coated nanomaterials via
alleviated inflammation and enhanced autophagy. Appl Mater Today.
26:1013862022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Li C, Dou Y, Chen Y, Qi Y, Li L, Han S,
Jin T, Guo J, Chen J and Zhang J: Site-specific microRNA-33
antagonism by pH-responsive nanotherapies for treatment of
atherosclerosis via regulating cholesterol efflux and adaptive
immunity. Adv Funct Mater. 30:20021312020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
He H, Wang J, Yannie PJ, Korzun WJ, Yang H
and Ghosh S: Nanoparticle-based 'two-pronged' approach to regress
atherosclerosis by simultaneous modulation of cholesterol influx
and efflux. Biomaterials. 260:1203332020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Wu Z, Zhou M, Tang X, Zeng J, Li Y, Sun Y,
Huang J, Chen L, Wan M and Mao C: Carrier-free trehalose-based
nanomotors targeting macrophages in inflammatory plaque for
treatment of atherosclerosis. ACS Nano. 16:3808–3820. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|