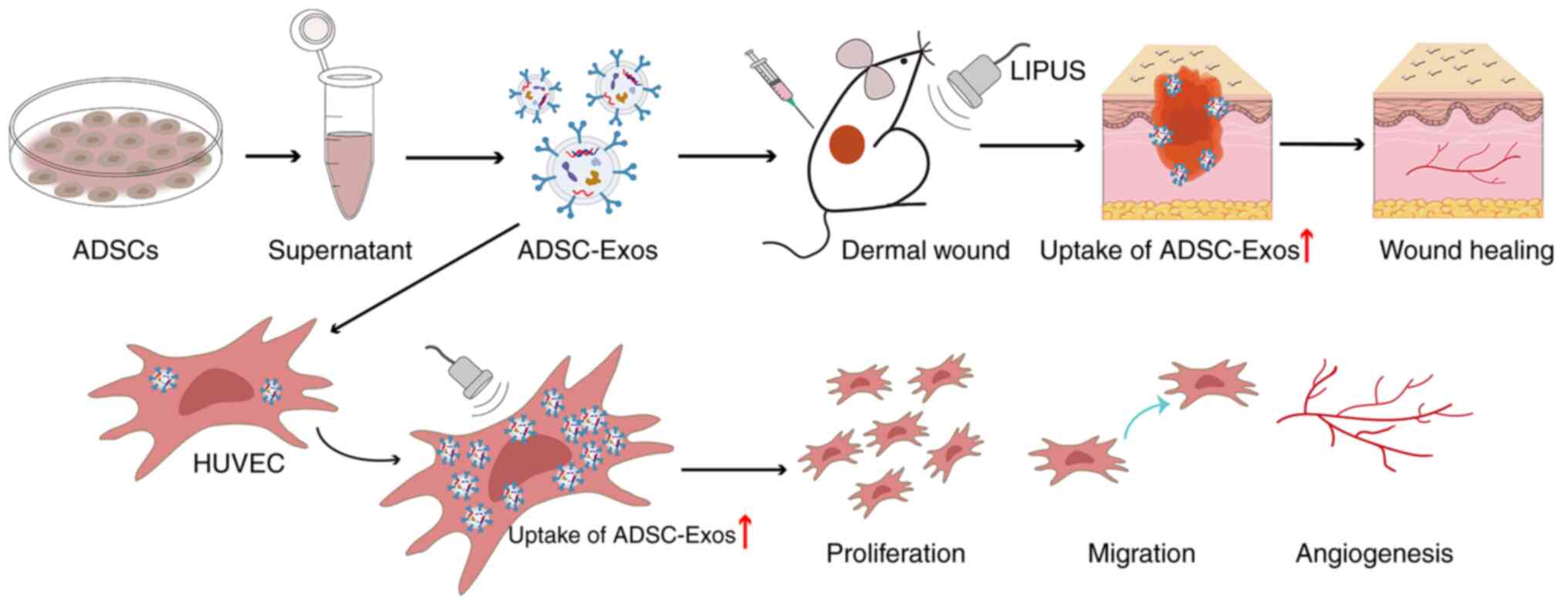
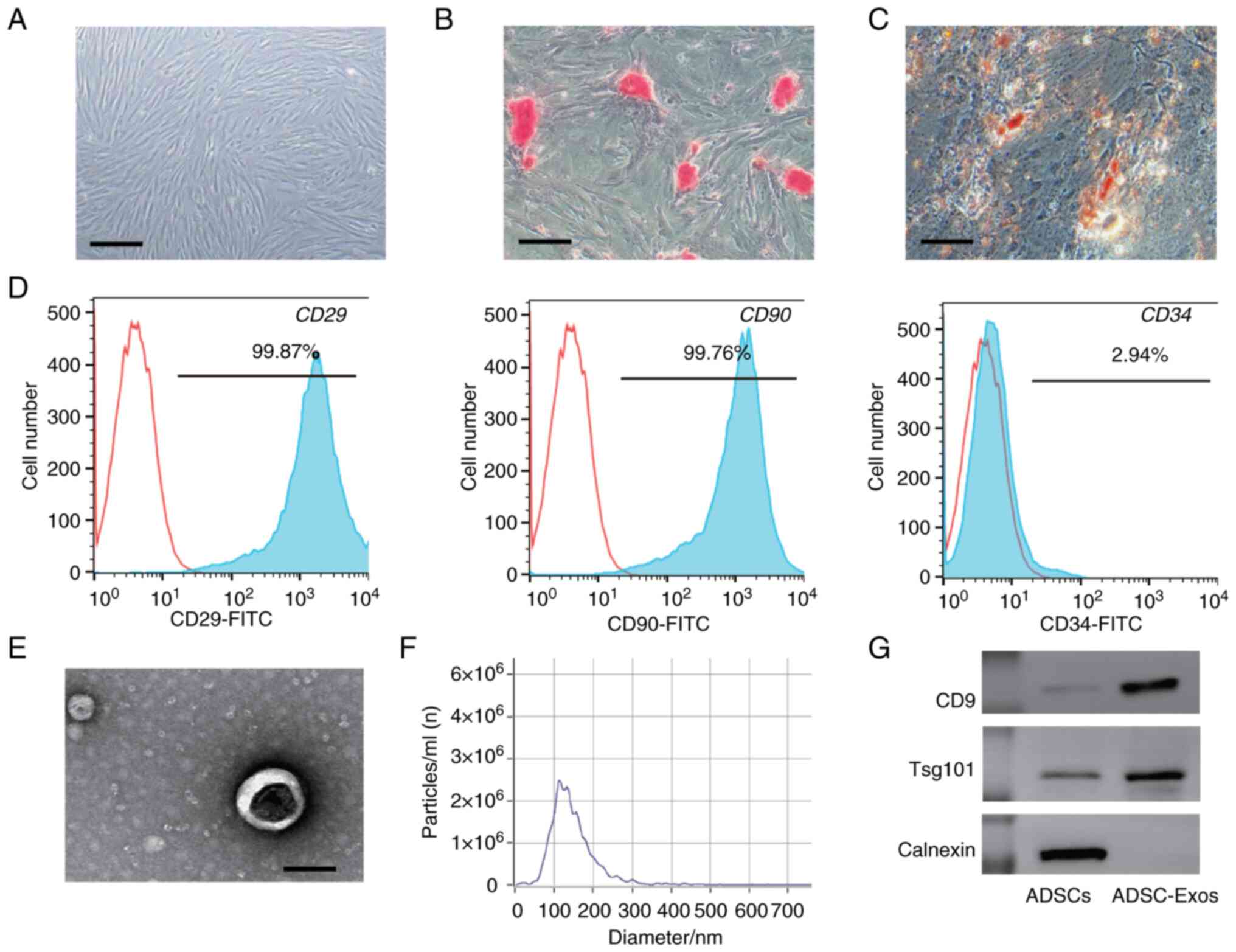
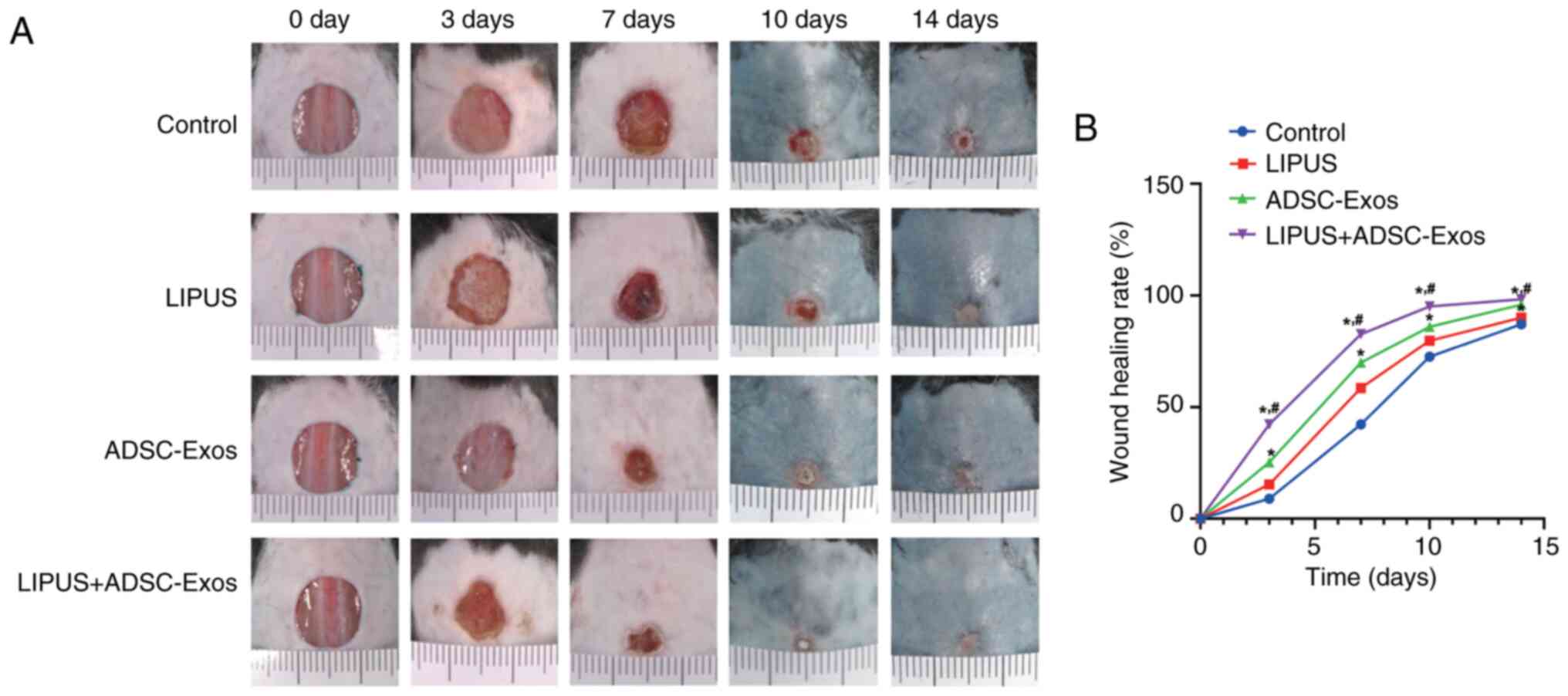
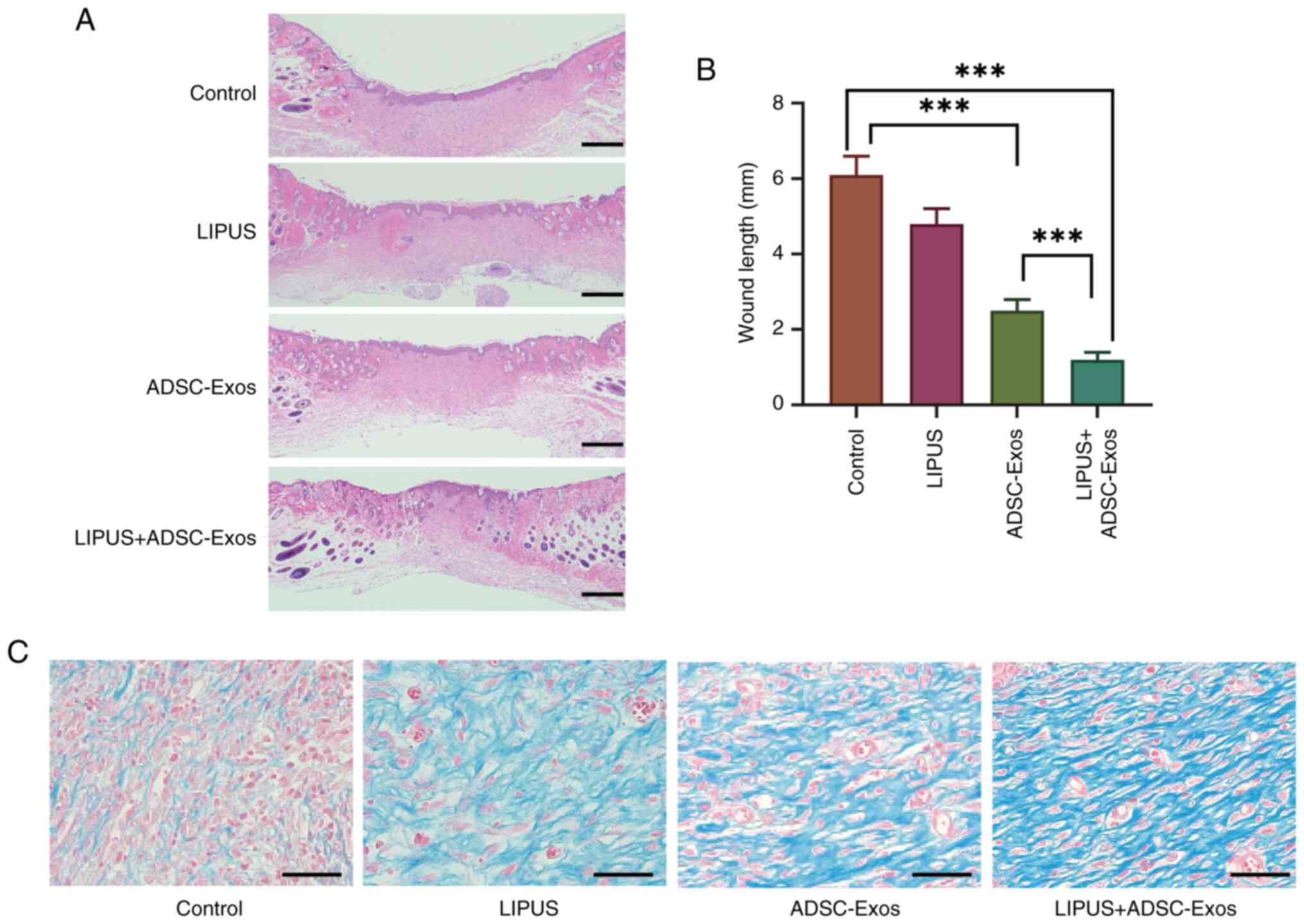
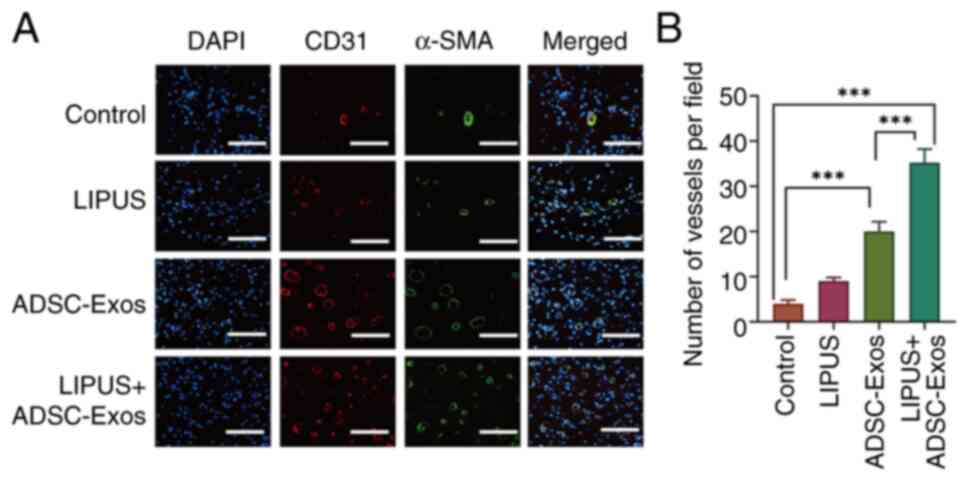
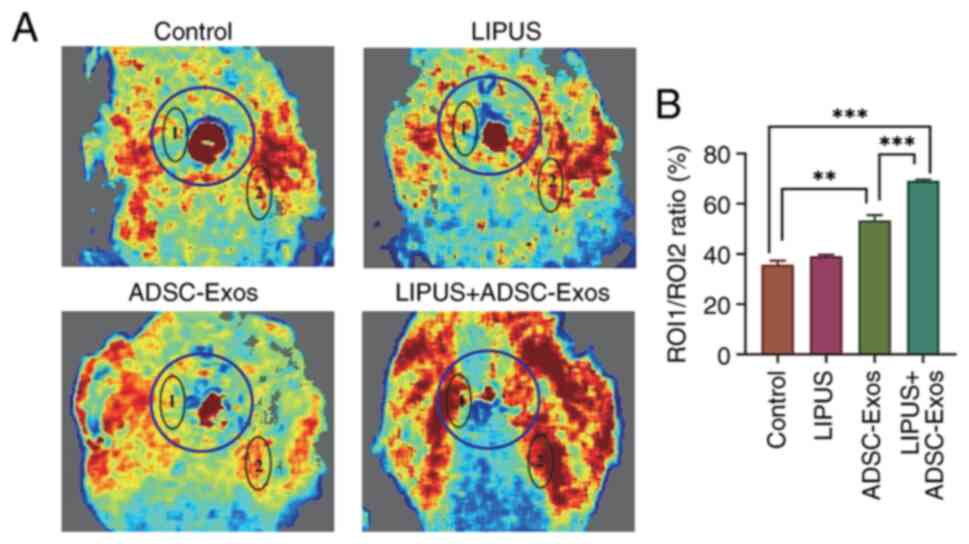
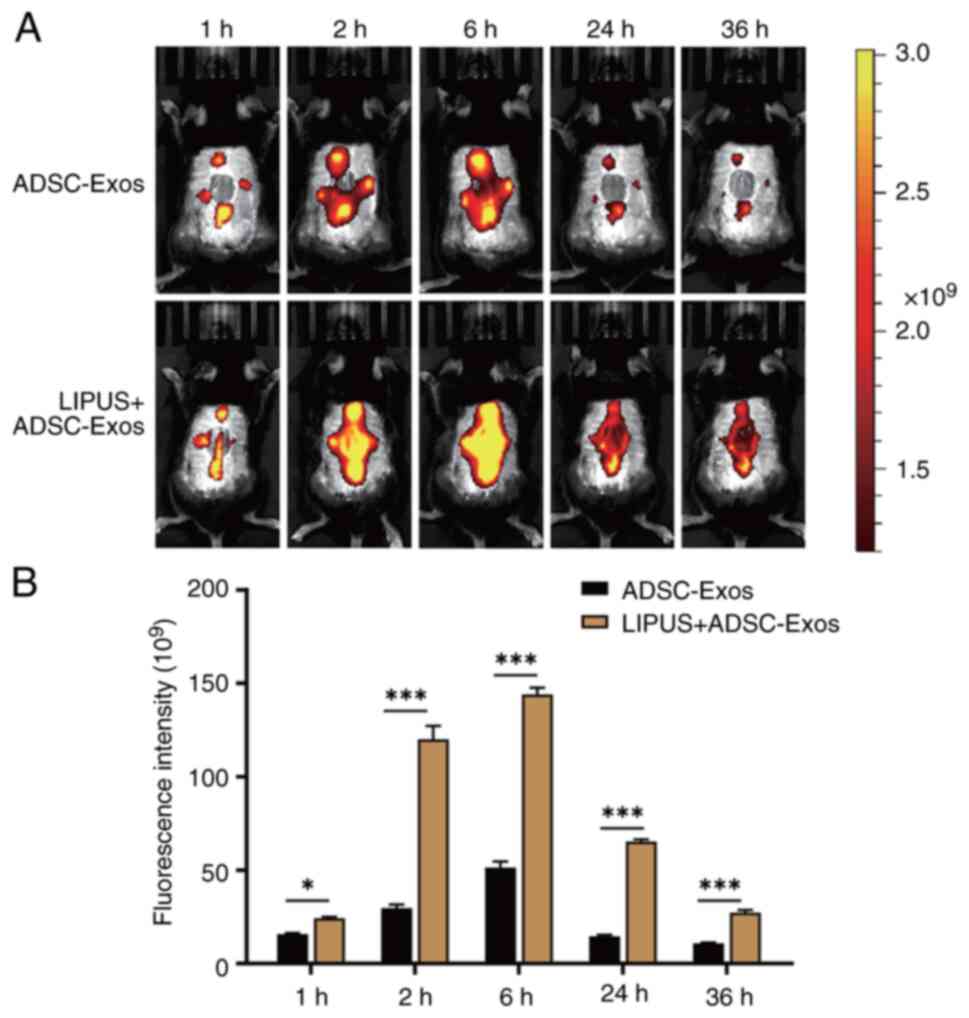
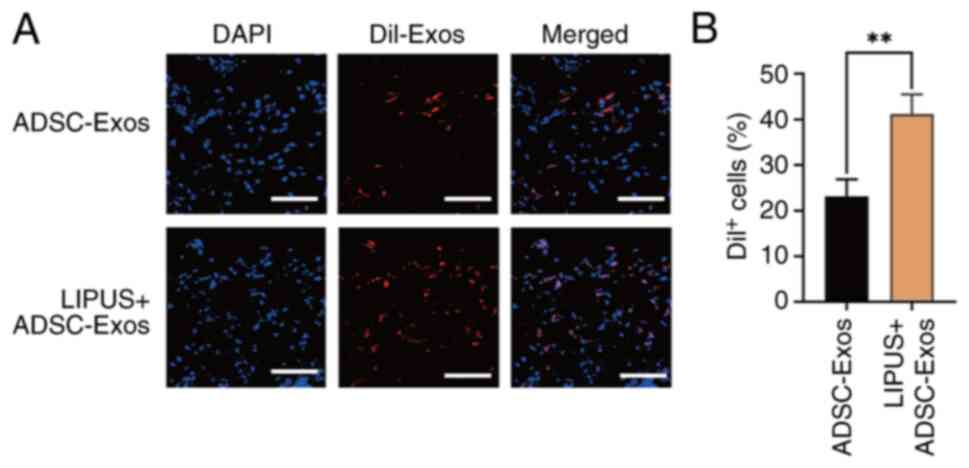
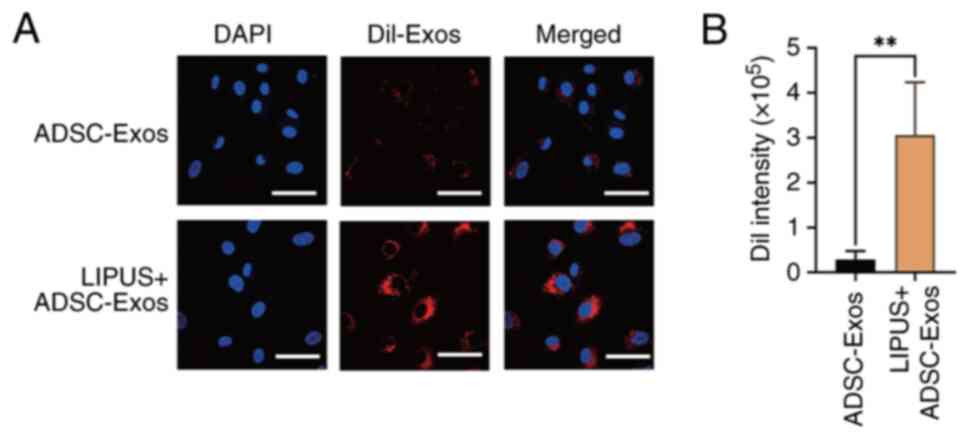
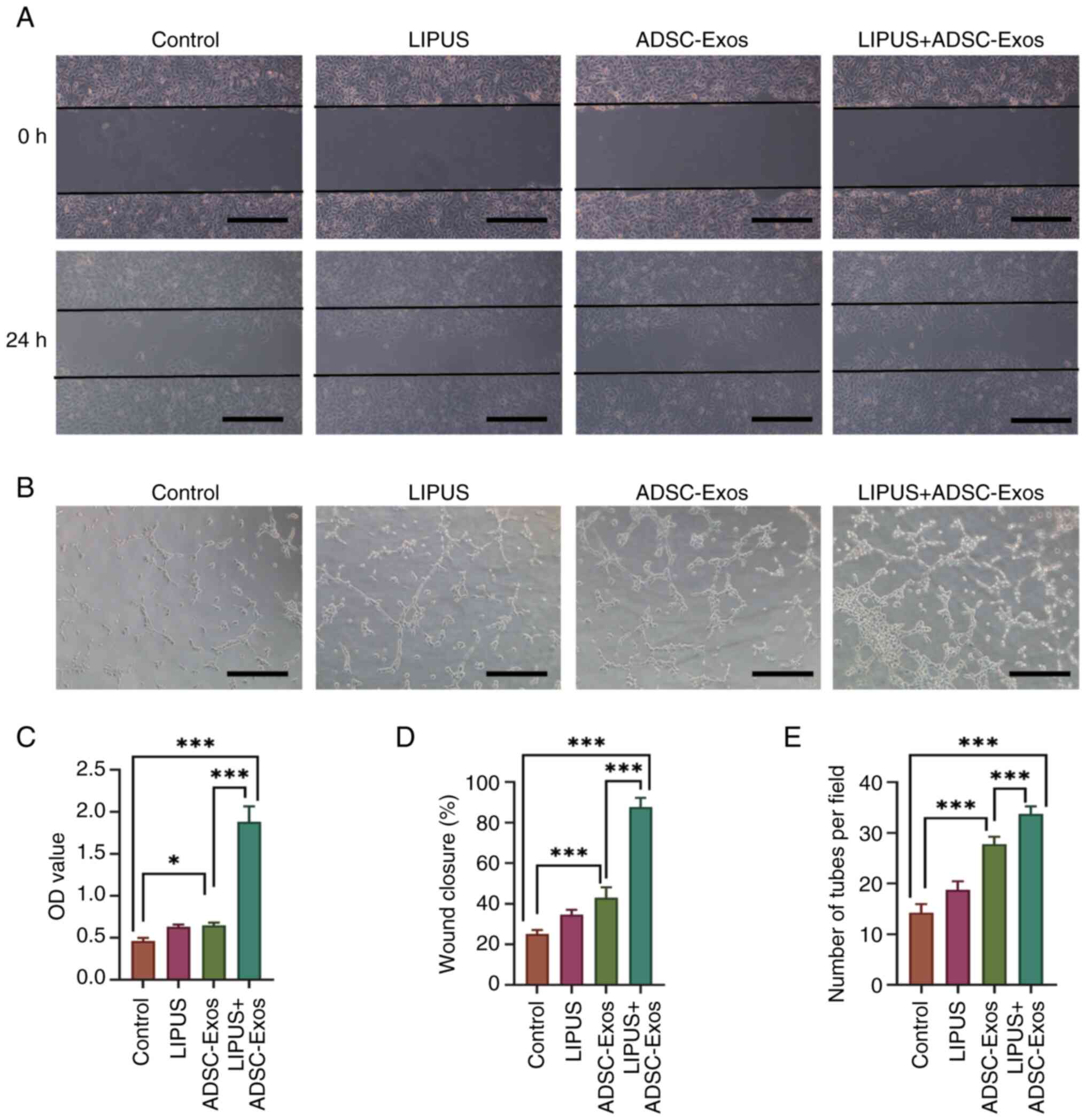
|
1
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157:1078432019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
International Working Group on the
Diabetic Foot: IWGDF Guidelines on the prevention and management of
diabetic foot disease. International Working Group on the Diabetic
Foot; Maastricht: 2019
|
|
3
|
National Institute of Health: Diabetic
Foot Consortium. Diabetic Foot Consortium; 2020
|
|
4
|
International Working Group of the
Diabetic Foot: Diabetic Foot-Epidemiology, Psychosocial, and
Economic Factors. IWGoD; Maastricht: 2012
|
|
5
|
CDC Diabetes Report Card: Services UDoHaH.
Centers for Disease Control Prevention; Arlington, VA: 2017
|
|
6
|
Dayya D, O'Neill OJ, Huedo-Medina TB,
Habib N, Moore J and Iyer K: Debridement of Diabetic Foot Ulcers.
Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 11:666–686. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Baronski S and Ayello EA: Wound Care
Essentials Principles and Practice. Wilkins LW: Philadelphia:
Wolters Kluwer; 2008
|
|
8
|
den Dekker A, Davis FM, Kunkel SL and
Gallagher KA: Targeting epigenetic mechanisms in diabetic wound
healing. Transl Res. 204:39–50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Wilkinson HN and Hardman MJ: Wound
healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol.
10:2002232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geng K, Ma X, Jiang Z, Huang W, Gao C, Pu
Y, Luo L and Xu Y and Xu Y: Innate immunity in diabetic wound
healing: Focus on the mastermind hidden in chronic inflammatory.
Front Pharmacol. 12:6539402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Cao Z, Wei Q, Ma K, Hu W, Huang Q,
Su J, Li H, Zhang C and Fu X: VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles
released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic
wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta
Biomater. 147:342–355. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deptuła M, Brzezicka A, Skoniecka A,
Zieliński J and Pikuła M: Adipose-derived stromal cells for
nonhealing wounds: Emerging opportunities and challenges. Med Res
Rev. 41:2130–2171. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nalisa DL, Moneruzzaman M, Changwe GJ,
Mobet Y, Li LP, Ma YJ and Jiang HW: Stem cell therapy for diabetic
foot ulcers: Theory and practice. J Diabetes Res. 2022:60287432022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Xie X, Lian W, Shi R, Han S, Zhang
H, Lu L and Li M: Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells
overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting
vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med.
50:1–14. 2018.
|
|
15
|
Lv Q, Deng J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Liu B and
Liu J: Engineered human adipose stem-cell-derived exosomes loaded
with miR-21-5p to promote diabetic cutaneous wound healing. Mol
Pharm. 17:1723–1733. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An Y, Lin S, Tan X, Zhu S, Nie F, Zhen Y,
Gu L, Zhang C, Wang B, Wei W, et al: Exosomes from adipose-derived
stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Prolif.
54:e129932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Wu H, Peng Y, Zhao Y, Qin Y, Zhang
Y and Xiao Z: Hypoxia adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promote
high-quality healing of diabetic wound involves activation of
PI3K/Akt pathways. J Nanobiotechnology. 19:2022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo H, Wang Y, Su Y, Liu D, Xiao H, Wu M,
Zhao Y and Xue F: Paracrine effects of adipose-derived stem cells
in cutaneous wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
J Wound Care. 31(Suppl 3): S29–S38. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Zhang B, Yang Y, Jiang Q, Li T,
Gong J, Tang H and Zhang Q: Stem cell-derived exosomes: Emerging
therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther.
14:1072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rezaie J, Feghhi M and Etemadi T: A review
on exosomes application in clinical trials: Perspective, questions,
and challenges. Cell Commun Signal. 20:1452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poolman RW, Agoritsas T, Siemieniuk RA,
Harris IA, Schipper IB, Mollon B, Smith M, Albin A, Nador S, Sasges
W, et al: Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for bone healing:
A clinical practice guideline. BMJ. 356:j5762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Elmajee M, Munasinghe C, Nasser AAH,
Nagappa S and Mahmood A: The perceptions of clinicians using
low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for orthopaedic pathology:
A national qualitative study. Injury. 53:3214–3219. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lai WC, Iglesias BC, Mark BJ and Wang D:
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound augments tendon, Ligament, and
bone-soft tissue healing in preclinical animal models: A systematic
review. Arthroscopy. 37:2318–2333. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sabbagh A, Beccaria K, Ling X, Marisetty
A, Ott M, Caruso H, Barton E, Kong LY, Fang D, Latha K, et al:
Opening of the blood-brain barrier using low-intensity pulsed
utrasound enhances responses to immunotherapy in preclinical glioma
models. Clin Cancer Res. 27:4325–4337. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Truong TT, Chiu WT, Lai YS, Huang H, Jiang
X and Huang CC: Ca2+ signaling-mediated low-intensity pulsed
ultrasound-induced proliferation and activation of motor neuron
cells. Ultrasonics. 124:1067392022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu Y, Gao Q, Zhu S, Wu Q, Zhu R, Zhong H,
Xing C, Qu H, Wang D, Li B, et al: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound
regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells
through notch signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
526:793–798. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Lin Q, Zhang T, Wang X, Cheng K,
Gao M, Xia P and Li X: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes
chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells via regulation of
autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bunnell BA, Flaat M, Gagliardi C, Patel B
and Ripoll C: Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and
differentiation. Methods. 45:115–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsu HH, Wang AYL, Loh CYY, Pai AA and Kao
HK: Therapeutic potential of exosomes derived from diabetic adipose
stem cells in cutaneous wound healing of db/db mice. Pharmaceutics.
14:12062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Foster DS, Januszyk M, Yost KE, Chinta MS,
Gulati GS, Nguyen AT, Burcham AR, Salhotra A, Ransom RC, Henn D, et
al: Integrated spatial multiomics reveals fibroblast fate during
tissue repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21100251182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Geng X, Qi Y, Liu X, Shi Y, Li H and Zhao
L: A multifunctional antibacterial and self-healing hydrogel laden
with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for
accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 133:1126132022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu Y, Tao R, Chen L, Xiong Y, Xue H, Hu L,
Yan C, Xie X, Lin Z, Panayi AC, et al: Exosomes derived from
pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing
through enhancing angiogenesis. J Nanobiotechnology. 19:1502021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan C, Xv Y, Lin Z, Endo Y, Xue H, Hu Y,
Hu L, Chen L, Cao F, Zhou W, et al: Human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate diabetic wound
healing via ameliorating oxidative stress and promoting
angiogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 10:8298682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pomatto M, Gai C, Negro F, Cedrino M,
Grange C, Ceccotti E, Togliatto G, Collino F, Tapparo M, Figliolini
F, et al: Differential therapeutic effect of extracellular vesicles
derived by bone marrow and adipose mesenchymal stem cells on wound
healing of diabetic ulcers and correlation to their cargoes. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:38512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xia P, Shi Y, Wang X and Li X: Advances in
the application of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound to mesenchymal
stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 13:2142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lucchetti D, Perelli L, Colella F,
Ricciardi-Tenore C, Scoarughi GL, Barbato G, Boninsegna A, De Maria
R and Sgambato A: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound affects growth,
differentiation, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition of colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
235:5363–5377. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang D, Gao Y, Wang S, Zhang W, Cao H,
Zheng L, Chen Y, Zhang S and Chen J: Impact of low-intensity pulsed
ultrasound on transcription and metabolite compositions in
proliferation and functionalization of human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci Rep. 10:136902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cao Y, Gong Y, Liu L, Zhou Y, Fang X,
Zhang C, Li Y and Li J: The use of human umbilical vein endothelial
cells (HUVECs) as an in vitro model to assess the toxicity of
nanoparticles to endothelium: A review. J Appl Toxicol.
37:1359–1369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cheng M, Li F, Han T, Yu ACH and Qin P:
Effects of ultrasound pulse parameters on cavitation properties of
flowing microbubbles under physiologically relevant conditions.
Ultrason Sonochem. 52:512–521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Atherton P, Lausecker F, Harrison A and
Ballestrem C: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes cell
motility through vinculin-controlled Rac1 GTPase activity. J Cell
Sci. 130:2277–2291. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang X, Savchenko O, Li Y, Qi S, Yang T,
Zhang W and Chen J: A Review of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound for
Therapeutic Applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 66:2704–2718.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Harrison A and Alt V: Low-intensity pulsed
ultrasound (LIPUS) for stimulation of bone healing-A narrative
review. Injury. 52(Suppl): S91–S96. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Razavi M, Zheng F, Telichko A, Ullah M,
Dahl J and Thakor AS: Effect of pulsed focused ultrasound on the
native pancreas. Ultrasound Med Biol. 46:630–638. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Burks SR, Ziadloo A, Hancock HA, Chaudhry
A, Dean DD, Lewis BK, Frenkel V and Frank JA: Investigation of
cellular and molecular responses to pulsed focused ultrasound in a
mouse model. PLoS One. 6:e247302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoon CW, Jung H, Goo K, Moon S, Koo KM,
Lee NS, Weitz AC and Shung KK: Low-intensity ultrasound modulates
Ca2+ dynamics in human mesenchymal stem cells via connexin 43
hemichannel. Ann Biomed Eng. 46:48–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
King AJ: The use of animal models in
diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol. 166:877–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|