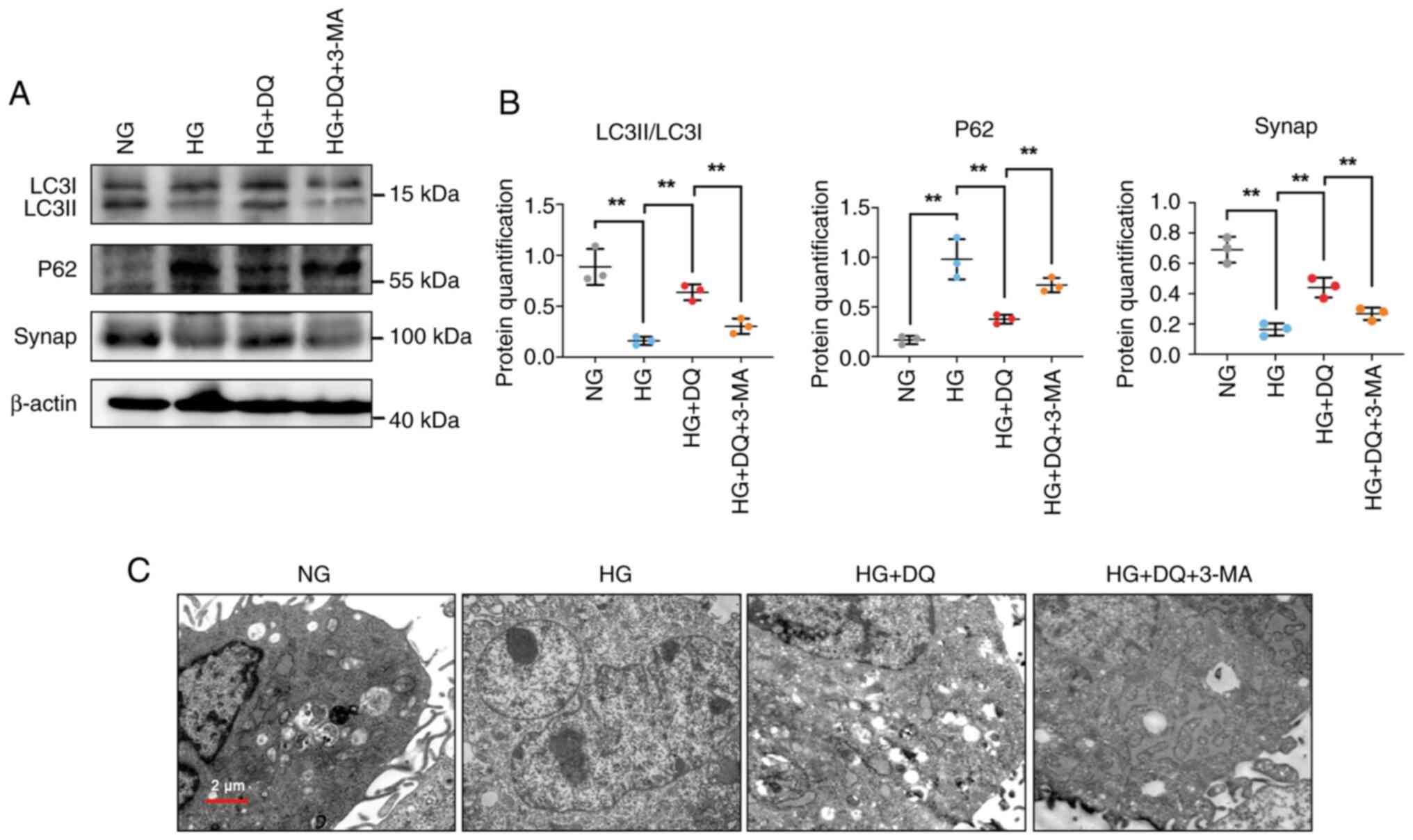
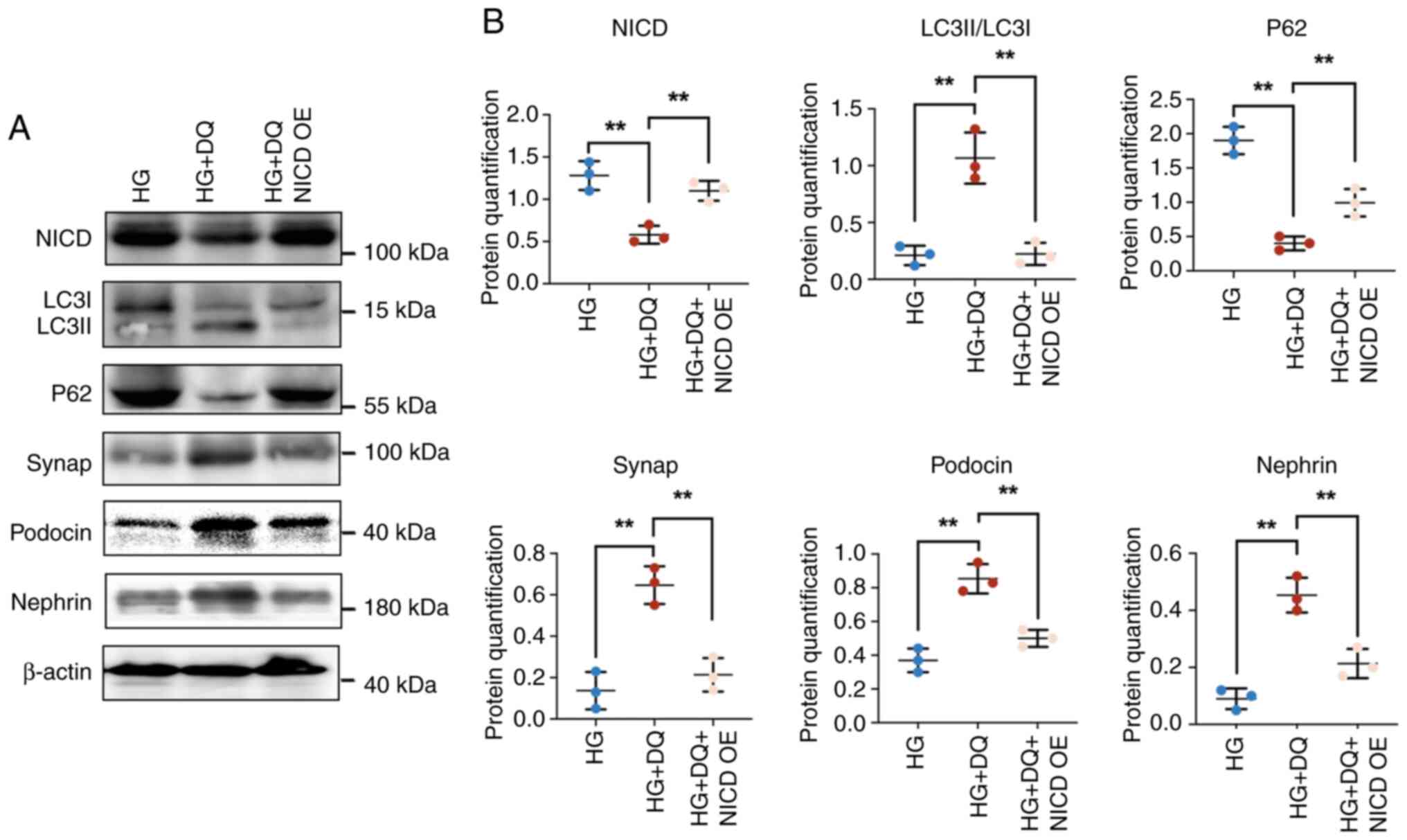
|
1
|
Reutens AT: Epidemiology of diabetic
kidney disease. Med Clin North Am. 97:1–18. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Hoogeveen EK: The epidemiology of diabetic
kidney disease. Kidney Dial. 2:433–442. 2022.
|
|
3
|
Lv JC and Zhang LX: Prevalence and disease
burden of chronic kidney disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1165:3–15.
2019.
|
|
4
|
Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, Bakris
GL, Brosius FC, Kolkhof P and Uribarri J: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
102:248–260. 2022.
|
|
5
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Yamazaki T, Mimura I, Tanaka T and Nangaku
M: Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: Current and future.
Diabetes Metab J. 45:11–26. 2021.
|
|
7
|
Zou H, Zhou B and Xu G: SGLT2 inhibitors:
A novel choice for the combination therapy in diabetic kidney
disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:652017.
|
|
8
|
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint
S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull
S, et al: Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 380:2295–2306. 2019.
|
|
9
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Hartleben B, Gödel M, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Liu S, Ulrich T, Köbler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ,
Lindenmeyer MT, et al: Autophagy influences glomerular disease
susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J
Clin Invest. 120:1084–1096. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Zhang C, Li W, Wen J and Yang Z: Autophagy
is involved in mouse kidney development and podocyte
differentiation regulated by Notch signalling. J Cell Mol Med.
21:1315–1328. 2017.
|
|
12
|
Yasuda-Yamahara M, Kume S, Tagawa A,
Maegawa H and Uzu T: Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy. 11:2385–2386.
2015.
|
|
13
|
Gonzales MM, Garbarino VR, Marques Zilli
E, Petersen RC, Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Musi N, Seshadri S, Craft
S and Orr ME: Senolytic therapy to modulate the progression of
Alzheimer's disease (SToMP-AD): A pilot clinical trial. J Prev
Alzheimers Dis. 9:22–29. 2022.
|
|
14
|
Novais EJ, Tran VA, Johnston SN, Darris
KR, Roupas AJ, Sessions GA, Shapiro IM, Diekman BO and Risbud MV:
Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs dasatinib and quercetin
ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice.
Nat Commun. 12:52132021.
|
|
15
|
Krzystyniak A, Wesierska M, Petrazzo G,
Gadecka A, Dudkowska M, Bielak-Zmijewska A, Mosieniak G, Figiel I,
Wlodarczyk J and Sikora E: Combination of dasatinib and quercetin
improves cognitive abilities in aged male Wistar rats, alleviates
inflammation and changes hippocampal synaptic plasticity and
histone H3 methylation profile. Aging (Albany NY). 14:572–595.
2022.
|
|
16
|
Saccon TD, Nagpal R, Yadav H, Cavalcante
MB, Nunes ADC, Schneider A, Gesing A, Hughes B, Yousefzadeh M,
Tchkonia T, et al: Senolytic combination of dasatinib and quercetin
alleviates intestinal senescence and inflammation and modulates the
gut microbiome in aged mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
76:1895–1905. 2021.
|
|
17
|
Levêque D, Becker G, Bilger K and
Natarajan-Amé S: Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of
dasatinib. Clin Pharmacokinet. 59:849–856. 2020.
|
|
18
|
Banerjee S, Sarkar R, Mukherjee A, Miyoshi
SI, Kitahara K, Halder P, Koley H and Chawla-Sarkar M: Quercetin, a
flavonoid, combats rotavirus infection by deactivating
rotavirus-induced pro-survival NF-κB pathway. Front Microbiol.
13:9517162022.
|
|
19
|
Hickson LJ, Langhi Prata LGP, Bobart SA,
Evans TK, Giorgadze N, Hashmi SK, Herrmann SM, Jensen MD, Jia Q,
Jordan KL, et al: Senolytics decrease senescent cells in humans:
Preliminary report from a clinical trial of dasatinib plus
quercetin in individuals with diabetic kidney disease.
EBioMedicine. 47:446–456. 2019.
|
|
20
|
Palmer AK, Xu M, Zhu Y, Pirtskhalava T,
Weivoda MM, Hachfeld CM, Prata LG, van Dijk TH, Verkade E,
Casaclang-Verzosa G, et al: Targeting senescent cells alleviates
obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction. Aging Cell.
18:e129502019.
|
|
21
|
Kumari R, Bettermann K, Willing L, Sinha K
and Simpson IA: The role of neutrophils in mediating stroke injury
in the diabetic db/db mouse brain following hypoxia-ischemia.
Neurochem Int. 139:1047902020.
|
|
22
|
You YK, Huang XR, Chen HY, Lyu XF, Liu HF
and Lan HY: C-reactive protein promotes diabetic kidney disease in
db/db mice via the CD32b-Smad3-mTOR signaling pathway. Sci Rep.
6:267402016.
|
|
23
|
You YK, Wu WF, Huang XR, Li HD, Ren YP,
Zeng JC, Chen H and Lan HY: Deletion of Smad3 protects against
C-reactive protein-induced renal fibrosis and inflammation in
obstructive nephropathy. Int J Biol Sci. 17:3911–3922. 2021.
|
|
24
|
Xu L, Fan Q, Wang X, Li L, Lu X, Yue Y,
Cao X, Liu J, Zhao X and Wang L: Ursolic acid improves podocyte
injury caused by high glucose. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
32:1285–1293. 2017.
|
|
25
|
Dungan CM, Murach KA, Zdunek CJ, Tang ZJ,
Nolt GL, Brightwell CR, Hettinger Z, Englund DA, Liu Z, Fry CS, et
al: Deletion of SA β-Gal+ cells using senolytics improves muscle
regeneration in old mice. Aging Cell. 21:e135282022.
|
|
26
|
Kong ZL, Che K, Hu JX, Chen Y, Wang YY,
Wang X, Lü WS, Wang YG and Chi JW: Orientin protects podocytes from
high glucose induced apoptosis through mitophagy. Chem Biodivers.
17:e19006472020.
|
|
27
|
Zhu X, Zhang C, Shi M, Li H, Jiang X and
Wang L: IL-6/STAT3-mediated autophagy participates in the
development of age-related glomerulosclerosis. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 35:e226982021.
|
|
28
|
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z,
Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY and Yang CW: Chronic kidney
disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 382:260–272.
2013.
|
|
29
|
Huang Y, Wang B, Hassounah F, Price SR,
Klein J, Mohamed TMA, Wang Y, Park J, Cai H, Zhang X and Wang XH:
The impact of senescence on muscle wasting in chronic kidney
disease. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 14:126–141. 2023.
|
|
30
|
Li C, Shen Y, Huang L, Liu C and Wang J:
Senolytic therapy ameliorates renal fibrosis postacute kidney
injury by alleviating renal senescence. FASEB J. 35:e212292021.
|
|
31
|
Cavalcante MB, Saccon TD, Nunes ADC,
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Schneider A and Masternak MM: Dasatinib
plus quercetin prevents uterine age-related dysfunction and
fibrosis in mice. Aging (Albany NY). 12:2711–2722. 2020.
|
|
32
|
Adeva-Andany MM and Carneiro-Freire N:
Biochemical composition of the glomerular extracellular matrix in
patients with diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes.
13:498–520. 2022.
|
|
33
|
Kolset SO, Reinholt FP and Jenssen T:
Diabetic nephropathy and extracellular matrix. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:976–986. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Canney AL, Cohen RV, Elliott JA, M Aboud
C, Martin WP, Docherty NG and le Roux CW: Improvements in diabetic
albuminuria and podocyte differentiation following Roux-en-Y
gastric bypass surgery. Diab Vasc Dis Res.
17:14791641198790392020.
|
|
35
|
Weil EJ, Lemley KV, Mason CC, Yee B, Jones
LI, Blouch K, Lovato T, Richardson M, Myers BD and Nelson RG:
Podocyte detachment and reduced glomerular capillary endothelial
fenestration promote kidney disease in type 2 diabetic nephropathy.
Kidney Int. 82:1010–1017. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Nagata M: Podocyte injury and its
consequences. Kidney Int. 89:1221–1230. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Mundel P, Heid HW, Mundel TM, Krüger M,
Reiser J and Kriz W: Synaptopodin: An actin-associated protein in
telencephalic dendrites and renal podocytes. J Cell Biol.
139:193–204. 1997.
|
|
38
|
Harvey SJ, Jarad G, Cunningham J, Goldberg
S, Schermer B, Harfe BD, McManus MT, Benzing T and Miner JH:
Podocyte-specific deletion of dicer alters cytoskeletal dynamics
and causes glomerular disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:2150–2158.
2008.
|
|
39
|
Li X, Chuang PY, D'Agati VD, Dai Y, Yacoub
R, Fu J, Xu J, Taku O, Premsrirut PK, Holzman LB and He JC: Nephrin
preserves podocyte viability and glomerular structure and function
in adult kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:2361–2377. 2015.
|
|
40
|
Nishibori Y, Liu L, Hosoyamada M, Endou H,
Kudo A, Takenaka H, Higashihara E, Bessho F, Takahashi S, Kershaw
D, et al: Disease-causing missense mutations in NPHS2 gene alter
normal nephrin trafficking to the plasma membrane. Kidney Int.
66:1755–1765. 2004.
|
|
41
|
ElShaarawy A, Behairy MA, Bawady SA,
Abdelsattar HA and Shadad E: Urinary podocin level as a predictor
of diabetic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 8:e262019.
|
|
42
|
Baisantry A, Bhayana S, Wrede C, Hegermann
J, Haller H, Melk A and Schmitt R: The impact of autophagy on the
development of senescence in primary tubular epithelial cells. Cell
Cycle. 15:2973–2979. 2016.
|
|
43
|
Gewirtz DA: Autophagy and senescence: A
partnership in search of definition. Autophagy. 9:808–812.
2013.
|
|
44
|
Gonzalez CD, Carro Negueruela MP, Nicora
Santamarina C, Resnik R and Vaccaro MI: Autophagy dysregulation in
diabetic kidney disease: From pathophysiology to pharmacological
interventions. Cells. 10:24972021.
|
|
45
|
Yang D, Livingston MJ, Liu Z, Dong G,
Zhang M, Chen JK and Dong Z: Autophagy in diabetic kidney disease:
Regulation, pathological role and therapeutic potential. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 75:669–688. 2018.
|
|
46
|
Huber TB, Edelstein CL, Hartleben B, Inoki
K, Jiang M, Koya D, Kume S, Lieberthal W, Pallet N, Quiroga A, et
al: Emerging role of autophagy in kidney function, diseases and
aging. Autophagy. 8:1009–1031. 2012.
|
|
47
|
Barbosa Júnior Ade A, Zhou H,
Hültenschmidt D, Totovic V, Jurilj N and Pfeifer U: Inhibition of
cellular autophagy in proximal tubular cells of the kidney in
streptozotocin-diabetic and uninephrectomized rats. Virchows Arch B
Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 61:359–366. 1992.
|
|
48
|
Vallon V, Rose M, Gerasimova M, Satriano
J, Platt KA, Koepsell H, Cunard R, Sharma K, Thomson SC and Rieg T:
Knockout of Na-glucose transporter SGLT2 attenuates hyperglycemia
and glomerular hyperfiltration but not kidney growth or injury in
diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 304:F156–F167.
2013.
|
|
49
|
Matboli M, Eissa S, Ibrahim D, Hegazy MGA,
Imam SS and Habib EK: Caffeic acid attenuates diabetic kidney
disease via modulation of autophagy in a high-fat
diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Sci Rep. 7:22632017.
|
|
50
|
Ren H, Shao Y, Wu C, Ma X, Lv C and Wang
Q: Metformin alleviates oxidative stress and enhances autophagy in
diabetic kidney disease via AMPK/SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 500:1106282020.
|
|
51
|
Zheng D, Tao M, Liang X, Li Y, Jin J and
He Q: p66Shc regulates podocyte autophagy in high glucose
environment through the Notch-PTEN-PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Histol
Histopathol. 35:405–415. 2020.
|
|
52
|
Yoshida G, Kawabata T, Takamatsu H, Saita
S, Nakamura S, Nishikawa K, Fujiwara M, Enokidani Y, Yamamuro T,
Tabata K, et al: Degradation of the NOTCH intracellular domain by
elevated autophagy in osteoblasts promotes osteoblast
differentiation and alleviates osteoporosis. Autophagy.
18:2323–2332. 2022.
|
|
53
|
Niranjan T, Bielesz B, Gruenwald A, Ponda
MP, Kopp JB, Thomas DB and Susztak K: The Notch pathway in
podocytes plays a role in the development of glomerular disease.
Nat Med. 14:290–298. 2008.
|
|
54
|
Walsh DW, Roxburgh SA, McGettigan P,
Berthier CC, Higgins DG, Kretzler M, Cohen CD, Mezzano S, Brazil DP
and Martin F: Co-regulation of Gremlin and Notch signalling in
diabetic nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:10–21. 2008.
|
|
55
|
Waters AM, Wu MYJ, Onay T, Scutaru J, Liu
J, Lobe CG, Quaggin SE and Piscione TD: Ectopic notch activation in
developing podocytes causes glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:1139–1157. 2008.
|
|
56
|
Wang C, Kang Y, Liu P, Liu W, Chen W,
Hayashi T, Mizuno K, Hattori S, Fujisaki H and Ikejima T: Combined
use of dasatinib and quercetin alleviates overtraining-induced
deficits in learning and memory through eliminating senescent cells
and reducing apoptotic cells in rat hippocampus. Behav Brain Res.
440:1142602023.
|
|
57
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752.
2007.
|
|
58
|
Scarlatti F, Granata R, Meijer AJ and
Codogno P: Does autophagy have a license to kill mammalian cells?
Cell Death Differ. 16:12–20. 2009.
|
|
59
|
Rubinstein AD and Kimchi A: Life in the
balance-a mechanistic view of the crosstalk between autophagy and
apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 125:5259–5268. 2012.
|