|
1
|
American Diabetes Association: 2.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care
in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 44(Suppl 1): S15–S33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M,
Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et
al: IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 183:1091192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Harding JL, Pavkov ME, Magliano DJ, Shaw
JE and Gregg EW: Global trends in diabetes complications: A review
of current evidence. Diabetologia. 62:3–16. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prasad RB and Groop L: Genetics of type 2
diabetes-pitfalls and possibilities. Genes (Basel). 6:87–123. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lyssenko V and Laakso M: Genetic screening
for the risk of type 2 diabetes: Worthless or valuable? Diabetes
Care. 36(Suppl 2): S120–S126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vassy JL and Meigs JB: Is Genetic testing
useful to predict type 2 diabetes? Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 26:189–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miranda-Lora AL, Vilchis-Gil J,
Juárez-Comboni DB, Cruz M and Klünder-Klünder M: A genetic risk
score improves the prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus in
mexican youths but has lower predictive utility compared with
non-genetic factors. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:6478642021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Willems SM, Mihaescu R, Sijbrands EJG, Van
Duijn CM and Janssens AC: A methodological perspective on genetic
risk prediction studies in type 2 diabetes: Recommendations for
future research. Curr Diab Rep. 11:511–518. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fava S and Hattersley AT: The role of
genetic susceptibility in diabetic nephropathy: evidence from
family studies. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17:1543–1546. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Szymañski M, Barciszewska MZ, Zywicki M
and Barciszewski J: Noncoding RNA transcripts. J Appl Genet.
44:1–19. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK,
Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF and Sharpless NE: Circular RNAs are
abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA.
19:141–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P,
Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss,
et al: Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant,
conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 58:870–885. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H and Bartel DP:
Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular
RNAs. Genome Biol. 15:4092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL and
Brown PO: Cell-Type specific features of circular RNA expression.
PLoS Genet. 9:e10037772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xiang JF, Yin
QF, Xing YH, Zhu S, Yang L and Chen LL: Circular intronic long
noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 51:792–806. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song P, Yang F, Jin H and Wang X: The
regulation of protein translation and its implications for cancer.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liao W, Du J, Wang Z, Feng Q, Liao M, Liu
H, Yuan K and Zeng Y: The role and mechanism of noncoding RNAs in
regulation of metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Cancer. 151:337–347. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J:
Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 14:1035–1045. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Chen LL: The biogenesis and emerging roles
of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:205–211. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qu S, Zhong Y, Shang R, Zhang X, Song W,
Kjems J and Li H: The emerging landscape of circular RNA in life
processes. RNA Biol. 14:992–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Barrett SP and Salzman J: Circular RNAs:
Analysis, expression and potential functions. Development.
143:1838–1847. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu CX and Chen LL: Circular RNAs:
Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell.
185:2016–2034. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chi T, Lin J, Wang M, Zhao Y, Liao Z and
Wei P: Non-Coding RNA as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes development
and clinical management. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12:6300322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang F and Zhang M: Circ_001209 aggravates
diabetic retinal vascular dysfunction through regulating
miR-15b-5p/COL12A1. J Transl Med. 19:2942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan W, Pang H, Xie Z, Huang G and Zhou Z:
Circular RNAs in diabetes mellitus and its complications. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8856502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patil NS, Feng B, Su Z, Castellani CA and
Chakrabarti S: Circular RNA mediated gene regulation in chronic
diabetic complications. Sci Rep. 11:237662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tu C, Wang L, Wei L and Jiang Z: The role
of circular RNA in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Med Sci. 19:916–923.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu R, Zhang M and Ge Y: Circular RNA
HIPK3 exacerbates diabetic nephropathy and promotes proliferation
by sponging miR-185. Gene. 765:1450652021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
van Zonneveld AJ, Kölling M, Bijkerk R and
Lorenzen JM: Circular RNAs in kidney disease and cancer. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 17:814–826. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lasda E and Parker R: Circular RNAs:
Diversity of form and function. RNA. 20:1829–1842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Petkovic S and Müller S: RNA
circularization strategies in vivo and in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:2454–2465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamazaki T, Fujiwara N, Yukinaga H,
Ebisuya M, Shiki T, Kurihara T, Kioka N, Kambe T, Nagao M, Nishida
E and Masuda S: The Closely Related RNA helicases, UAP56 and URH49,
Preferentially Form Distinct mRNA Export Machineries and
Coordinately Regulate Mitotic Progression. Mol Biol Cell.
21:2953–2965. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang C, Liang D, Tatomer DC and Wilusz
JE: A length-dependent evolutionarily conserved pathway controls
nuclear export of circular RNAs. Genes Dev. 32:639–644. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ren L, Jiang Q, Mo L, Tan L, Dong Q, Meng
L, Yang N and Li G: Mechanisms of circular RNA degradation. Commun
Biol. 5:13552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, Ruan S, Zhou
Z, Huang K, Ji F, Ma Z, Hou B and He X: YTHDF2 promotes the liver
cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4
expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene. 39:4507–4518. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang W and Wang J: Exosomes and their
noncoding RNA cargo are emerging as new modulators for diabetes
mellitus. Cells. 8:8532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hentze MW and Preiss T: Circular RNAs:
Splicing's enigma variations. EMBO J. 32:923–925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang
W, Wang G, Wu P, Wang H, Jiang L, et al: Exosomal circRNAs:
Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer.
18:1162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen XT, Li ZW, Zhao X, Li ML, Hou PF, Chu
SF, Zheng JN and Bai J: Role of Circular RNA in kidney-related
diseases. Front Pharmacol. 12:6158822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang H, Gao X, Yu S, Wang W, Liu G, Jiang
X and Sun D: Circular RNAs regulate parental gene expression: A new
direction for molecular oncology research. Front Oncol.
12:9477752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu N, Yuan Z, Du KY, Fang L, Lyu J, Zhang
C, He A, Eshaghi E, Zeng K, Ma J, et al: Translation of
yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA
via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation
machinery. Cell Death Differ. 26:2758–2773. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando
M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, Fatica A, Santini T, Andronache A, Wade
M, et al: Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that Can Be translated and
functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell. 66:22–37.e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Z, Yang T and Xiao J: Circular RNAs:
Promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine. 34:267–274.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR,
Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N and
Kadener S: CircRNA Biogenesis competes with Pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 56:55–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Du WW, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P
and Yang BB: Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via
forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:2846–2858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schneider T, Hung LH, Schreiner S, Starke
S, Eckhof H, Rossbach O, Reich S, Medenbach J and Bindereif A:
CircRNA-protein complexes: IMP3 protein component defines subfamily
of circRNPs. Sci Rep. 6:313132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Holdt LM, Stahringer A, Sass K, Pichler G,
Kulak NA, Wilfert W, Kohlmaier A, Herbst A, Northoff BH, Nicolaou
A, et al: Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA
maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat Commun. 7:124292016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Das A, Sinha T, Shyamal S and Panda AC:
Emerging role of circular RNA-protein interactions. Noncoding RNA.
7:482021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Castello A, Fischer B, Eichelbaum K, Horos
R, Beckmann BM, Strein C, Davey NE, Humphreys DT, Preiss T,
Steinmetz LM, et al: Insights into RNA Biology from an Atlas of
Mammalian mRNA-Binding Proteins. Cell. 149:1393–1406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yar Saglam SA, Alp E and Ilke Onen H:
Circular RNAs and its biological functions in health and disease.
Gene Expression and Phenotypic Traits. Chen YC and Chen SJ:
IntechOpen; pp. 1–37. 2020
|
|
53
|
Yang Q, Li F, He AT and Yang BB: Circular
RNAs: Expression, localization, and therapeutic potentials. Mol
Ther. 29:1683–1702. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang Y, Lu T, Wang Q, Liu J and Jiao W:
Circular RNAs: Crucial regulators in the human body (Review). Oncol
Rep. 40:3119–3135. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang M, Yu F, Wu W, Zhang Y, Chang W,
Ponnusamy M, Wang K and Li P: Circular RNAs: A novel type of
non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral
immunity. Int J Biol Sci. 13:1497–1506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang L, Fu J and Zhou Y: Circular RNAs and
their emerging roles in immune regulation. Front Immunol.
9:29772018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Shao T, Pan YH and Xiong XD: Circular RNA:
an important player with multiple facets to regulate its parental
gene expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:369–376. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chen N, Zhao G, Yan X, Lv Z, Yin H, Zhang
S, Song W, Li X, Li L, Du Z, et al: A novel FLI1 exonic circular
RNA promotes metastasis in breast cancer by coordinately regulating
TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol. 19:2182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu Y, Song J, Liu Y, Zhou Z and Wang X:
Transcription activation of circ-STAT3 induced by Gli2 promotes the
progression of hepatoblastoma via acting as a sponge for
miR-29a/b/c-3p to upregulate STAT3/Gli2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:1012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Okholm TLH, Nielsen MM, Hamilton MP,
Christensen LL, Vang S, Hedegaard J, Hansen TB, Kjems J, Dyrskjøt L
and Pedersen JS: Circular RNA expression is abundant and correlated
to aggressiveness in early-stage bladder cancer. NPJ Genom Med.
2:362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Selby NM and Taal MW: An updated overview
of diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and
latest guidelines. Diabetes Obes Metab. 22(Suppl 1): S3–S15. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Gheith O, Farouk N, Nampoory N, Halim MA
and Al-Otaibi T: Diabetic kidney disease: Worldwide difference of
prevalence and risk factors. J Nephropharmacol. 5:49–56.
2015.eCollection 2016.
|
|
63
|
Brosius FC, Khoury CC, Buller CL and Chen
S: Abnormalities in signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy.
Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 5:51–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cooper ME: Interaction of metabolic and
haemodynamic factors in mediating experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetologia. 44:1957–1972. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Makita Z, Radoff S, Rayfield EJ, Yang Z,
Skolnik E, Delaney V, Friedman EA, Cerami A and Vlassara H:
Advanced glycosylation end products in patients with diabetic
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 325:836–842. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Busch M, Franke S, Rüster C and Wolf G:
Advanced glycation end-products and the kidney. Eur J Clin Invest.
40:742–755. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ramasamy R, Yan SF and Schmidt AM:
Receptor for AGE (RAGE): Signaling mechanisms in the pathogenesis
of diabetes and its complications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1243:88–102.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Kay AM, Simpson CL and Stewart JA Jr: The
role of AGE/RAGE signaling in diabetes-mediated vascular
calcification. J Diabetes Res. 2016:68097032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yun J, Ren J, Liu Y, Dai L, Song L, Ma X,
Luo S and Song Y: Circ-ACTR2 aggravates the high glucose-induced
cell dysfunction of human renal mesangial cells through mediating
the miR-205-5p/HMGA2 axis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetol Metab
Syndr. 13:722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang Q, Cang Z, Shen L, Peng W, Xi L,
Jiang X, Ge X, Xu B and Huang S: circ_0037128/miR-17-3p/AKT3 axis
promotes the development of diabetic nephropathy. Gene.
765:1450762021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Feng T, Li W, Li T, Jiao W and Chen S:
Circular RNA_0037128 aggravates high glucose-induced damage in HK-2
cells via regulation of microRNA-497-5p/nuclear factor of activated
T cells 5 axis. Bioengineered. 12:10959–10970. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fang R, Cao X, Zhu Y and Chen Q:
Hsa_circ_0037128 aggravates high glucose-induced podocytes injury
in diabetic nephropathy through mediating miR-31-5p/KLF9.
Autoimmunity. 55:254–263. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tang B, Li W, Ji TT, Li XY, Qu X, Feng L
and Bai S: Circ-AKT3 inhibits the accumulation of extracellular
matrix of mesangial cells in diabetic nephropathy via modulating
miR-296-3p/E-cadherin signals. J Cell Mol Med. 24:8779–8788. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu W, Han Q, Zhao L and Wang L: Circular
RNA circRNA_15698 aggravates the extracellular matrix of diabetic
nephropathy mesangial cells via miR-185/TGF-β1. J Cell Physiol.
234:1469–1476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Mou X, Chen JW, Zhou DY, Liu K, Chen LJ,
Zhou D and Hu YB: A novel identified circular RNA, circ-0000491,
aggravates the extracellular matrix of diabetic nephropathy
glomerular mesangial cells through suppressing miR-101b by
targeting TGFβRI. Mol Med Rep. 22:3785–3794. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bai S, Xiong X, Tang B, Ji T, Li X, Qu X
and Li W: Exosomal circ_DLGAP4 promotes diabetic kidney disease
progression by sponging miR-143 and targeting ERBB3/NF-κB/MMP-2
axis. Cell Death Dis. 11:10082020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Xu B, Wang Q, Li W, Xia L, Ge X, Shen L,
Cang Z, Peng W, Shao K and Huang S: Circular RNA circEIF4G2
aggravates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by sponging
miR-218. J Cell Mol Med. 26:1799–1805. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yao T, Zha D, Hu C and Wu X: Circ_0000285
promotes podocyte injury through sponging miR-654-3p and activating
MAPK6 in diabetic nephropathy. Gene. 747:1446612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Qiu B, Qi X and Wang J: CircTLK1
downregulation attenuates high glucose-induced human mesangial cell
injury by blocking the AKT/NF-κB pathway through sponging
miR-126-5p/miR-204-5p. Biochem Genet. 60:1471–1487. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Chen B, Li Y, Liu Y and Xu Z: circLRP6
regulates high glucose-induced proliferation, oxidative stress, ECM
accumulation, and inflammation in mesangial cells. J Cell Physiol.
234:21249–21259. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Feng F, Yang J, Wang G, Huang P, Li Y and
Zhou B: Circ_0068087 promotes high glucose-induced human renal
tubular cell injury through regulating miR-106a-5p/ROCK2 pathway.
Nephron. 147:212–222. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhuang L, Wang Z, Hu X, Yang Q, Pei X and
Jin G: CircHIPK3 alleviates high glucose toxicity to human renal
tubular epithelial HK-2 cells through regulation of
miR-326/miR-487a-3p/SIRT1. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 14:729–740.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liu H, Wang X, Wang ZY and Li L:
Circ_0080425 inhibits cell proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic
nephropathy via sponging miR-24-3p and targeting fibroblast growth
factor 11. J Cell Physiol. 235:4520–4529. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Wang W, Feng J, Zhou H and Li Q:
Circ_0123996 promotes cell proliferation and fibrosis in mouse
mesangial cells through sponging miR-149-5p and inducing Bach1
expression. Gene. 761:1449712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Li G, Qin Y, Qin S, Zhou X, Zhao W and
Zhang D: Circ_WBSCR17 aggravates inflammatory responses and
fibrosis by targeting miR-185-5p/SOX6 regulatory axis in high
glucose-induced human kidney tubular cells. Life Sci.
259:1182692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
An L, Ji D, Hu W, Wang J, Jin X, Qu Y and
Zhang N: Interference of hsa_circ_0003928 alleviates high
glucose-induced cell apoptosis and inflammation in HK-2 cells via
mir-151-3p/anxa2. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 13:3157–3168. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Liu Q, Cui Y, Ding N and Zhou C: Knockdown
of circ_0003928 ameliorates high glucose-induced dysfunction of
human tubular epithelial cells through the miR-506-3p/HDAC4 pathway
in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Med Res. 27:552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ge X, Xi L, Wang Q, Li H, Xia L, Cang Z,
Peng W and Huang S: Circular RNA Circ_0000064 promotes the
proliferation and fibrosis of mesangial cells via miR-143 in
diabetic nephropathy. Gene. 758:1449522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sun L, Han Y, Shen C, Luo H and Wang Z:
Emodin alleviates high glucose-induced oxidative stress,
inflammation and extracellular matrix accumulation of mesangial
cells by the circ_0000064/miR-30c-5p/Lmp7 axis. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 42:302–312. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wang H, Huang S, Hu T, Fei S and Zhang H:
Circ_0000064 promotes high glucose-induced renal tubular epithelial
cells injury to facilitate diabetic nephropathy progression through
miR-532-3p/ROCK1 axis. BMC Endocr Disord. 22:672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li J, Min Y and Zhao Q: Circ_0000064
knockdown attenuates high glucose-induced proliferation,
inflammation and extracellular matrix deposition of mesangial cells
through miR-424-5p-mediated WNT2B inhibition in cell models of
diabetic nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 26:943–954. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Peng F, Gong W, Li S, Yin B, Zhao C, Liu
W, Chen X, Luo C, Huang Q, Chen T, et al: circRNA_010383 Acts as a
Sponge for miR-135a, and its downregulated expression contributes
to renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 70:603–615.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang Y, Qi Y, Ji T, Tang B, Li X, Zheng P
and Bai S: Circ_LARP4 regulates high glucose-induced cell
proliferation, apoptosis, and fibrosis in mouse mesangial cells.
Gene. 765:1451142021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Sun A, Sun N, Liang X and Hou Z:
Circ-FBXW12 aggravates the development of diabetic nephropathy by
binding to miR-31-5p to induce LIN28B. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
13:1412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu R, Niu Z, Ren G, Ruan L and Sun L:
CircSMAD4 alleviates high glucose-induced inflammation,
extracellular matrix deposition and apoptosis in mouse glomerulus
mesangial cells by relieving miR-377-3p-mediated BMP7 inhibition.
Diabetol Metab Syndr. 13:1372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liu J, Duan P, Xu C, Xu D, Liu Y and Jiang
J: CircRNA circ-ITCH improves renal inflammation and fibrosis in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by regulating the
miR-33a-5p/SIRT6 axis. Inflamm Res. 70:835–846. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhao L, Chen H, Zeng Y, Yang K, Zhang R,
Li Z, Yang T and Ruan H: Circular RNA circ_0000712 regulates high
glucose-induced apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and
fibrosis in (DN) by targeting the miR-879-5p/SOX6 axis. Endocr J.
68:1155–1164. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhu Y, Zha F, Tang B, Ji TT, Li XY, Feng L
and Bai SJ: Exosomal hsa_circ_0125310 promotes cell proliferation
and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via sponging miR-422a and
targeting the IGF1R/p38 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 26:151–162. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Jin J, Wang Y, Zheng D, Liang M and He Q:
A Novel Identified Circular RNA, mmu_mmu_circRNA_0000309, Involves
in Germacrone-Mediated Improvement of Diabetic Nephropathy Through
Regulating Ferroptosis by Targeting miR-188-3p/GPX4 Signaling Axis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 36:740–759. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Chen S: Circ_000166/miR-296 aggravates the
process of diabetic renal fibrosis by regulating the SGLT2
signaling pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. Dis Markers.
2022:61030862022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang D, Zhang Z, Si Z and Wang L: Circ
0006282/miR-155 reduced inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via
expression of SIRT1/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Food Sci Technol
(Campinas). 42:e395202022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Li Y, Yu W, Xiong H and Yuan F:
Circ_0000181 regulates miR-667-5p/NLRC4 axis to promote pyroptosis
progression in diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. 12:119942022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhuang L, Jin G, Qiong W, Ge X and Pei X:
Circular RNA COL1A2 mediates high glucose-induced oxidative stress
and pyroptosis by regulating MiR-424-5p/SGK1 in diabetic
nephropathy. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 195:7652–7667. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Liu X and Wu Y: Circ_0000953 deficiency
exacerbates podocyte injury and autophage through targeting
mir-655/atg4b in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Rep. 8:S198–S199.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Rashad NM, Sherif MH, El-Shal AS and
Abdelsamad MAE: The expression profile of circANKRD36 and ANKRD36
as diagnostic biomarkers of chronic kidney disease in patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 22:432021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Zhang K, Wan X, Khan MA, Sun X, Yi X, Wang
Z, Chen K and Peng L: Peripheral Blood circRNA microarray profiling
identities hsa_circ_0001831 and hsa_circ_0000867 as two novel
circrna biomarkers for early type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 15:2789–2801. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Badr AM, Elkholy O, Said M, Fahim SA,
El-Khatib M, Sabry D and Gaber RM: Diagnostic Significance of
hsa_circ_0000146 and hsa_circ_0000072 biomarkers for diabetic
kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med
Biochem. 42:239–248. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Ling L, Tan Z, Zhang C, Gui S, Cui Y, Hu Y
and Chen L: CircRNAs in exosomes from high glucose-treated
glomerular endothelial cells activate mesangial cells. Am J Transl
Res. 11:4667–4682. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Liu M and Zhao J: Circular RNAs in
diabetic nephropathy: Updates and perspectives. Aging Dis.
13:1365–1380. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Loganathan TS, Sulaiman SA, Abdul Murad
NA, Shah SA, Abdul Gafor AH, Jamal R and Abdullah N: Interactions
Among Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front Pharmacol.
11:1912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Xiong X, Liu C, Shen M, Yang Q, Zhao Q, Li
X, Zhong X and Wang Z: Circular RNA expression profile in
transgenic diabetic mouse kidneys. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 26:252021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Bai YH, Wang JP, Yang M, Zeng Y and Jiang
HY: SiRNA-HMGA2 weakened AGEs-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in tubular epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
457:730–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Birchmeier W and Behrens J: Cadherin
expression in carcinomas: Role in the formation of cell junctions
and the prevention of invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1198:11–26. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li JH, Wang W, Huang XR, Oldfield M,
Schmidt AM, Cooper ME and Lan HY: Advanced glycation end products
induce tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transition through the
RAGE-ERK1/2 MAP kinase signaling pathway. Am J Pathol.
164:1389–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Guria A, Sharma P, Natesan S and Pandi G:
Circular RNAs-The road less traveled. Front Mol Biosci. 6:1462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ikeda Y, Morikawa S, Nakashima M,
Yoshikawa S, Taniguchi K, Sawamura H, Suga N, Tsuji A and Matsuda
S: CircRNAs and RNA-Binding proteins involved in the pathogenesis
of cancers or central nervous system disorders. Noncoding RNA.
9:232023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zeng Y, Du WW, Wu Y, Yang Z, Awan FM, Li
X, Yang W, Zhang C, Yang Q, Yee A, et al: A circular RNA binds to
and activates AKT phosphorylation and nuclear localization reducing
apoptosis and enhancing cardiac repair. Theranostics. 7:3842–3855.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Stoll L, Rodríguez-Trejo A, Guay C, Brozzi
F, Bayazit MB, Gattesco S, Menoud V, Sobel J, Marques AC, Venø MT,
et al: A circular RNA generated from an intron of the insulin gene
controls insulin secretion. Nat Commun. 11:56112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Hou L, Wei Y, Lin Y, Wang X, Lai Y, Yin M,
Chen Y, Guo X, Wu S, Zhu Y, et al: Concurrent binding to DNA and
RNA facilitates the pluripotency reprogramming activity of Sox2.
Nucleic Acids Res. 48:3869–3887. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang C, Han X, Yang L, Fu J, Sun C, Huang
S, Xiao W, Gao Y, Liang Q, Wang X, et al: Circular RNA circPPM1F
modulates M1 macrophage activation and pancreatic islet
inflammation in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Theranostics.
10:10908–10924. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Livi CM, Klus P, Delli Ponti R and
Tartaglia GG: CatRAPID signature: Identification of
ribonucleoproteins and RNA-binding regions. Bioinformatics.
32:773–775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
122
|
Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE and Noble
WS: The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(W1): W39–W49. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gupta S, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Bailey TL
and Noble WS: Quantifying similarity between motifs. Genome Biol.
8:R242007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Muppirala UK, Honavar VG and Dobbs D:
Predicting RNA-Protein interactions using only sequence
information. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:4892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Pan X, Fang Y, Li X, Yang Y and Shen HB:
RBPsuite: RNA-protein binding sites prediction suite based on deep
learning. BMC Genomics. 21:8842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Lin YC, Boone M, Meuris L, Lemmens I, Van
Roy N, Soete A, Reumers J, Moisse M, Plaisance S, Drmanac R, et al:
Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in
response to cell biology manipulations. Nat Commun. 5:47672014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhou WY, Cai ZR, Liu J, Wang DS, Ju HQ and
Xu RH: Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with
proteins. Mol Cancer. 19:1722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Kreisberg JI, Radnik RA, Ayo SH, Garoni J
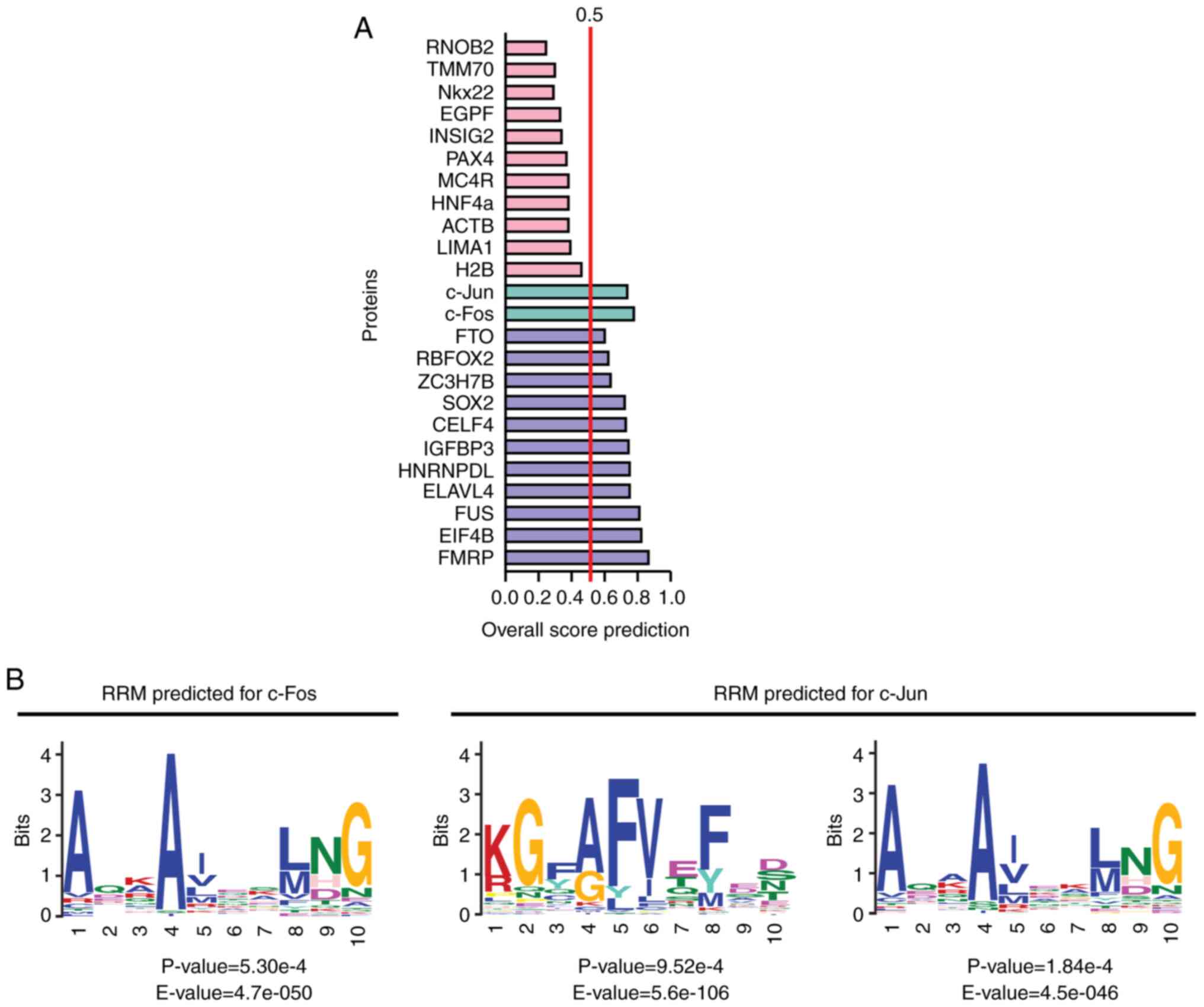
and Saikumar P: High glucose elevates c-fos and c-jun transcripts
and proteins in mesangial cell cultures. Kidney Int. 46:105–112.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Xu YX, Pu SD, Li X, Yu ZW, Zhang YT, Tong
XW, Shan YY and Gao XY: Exosomal ncRNAs: Novel therapeutic target
and biomarker for diabetic complications. Pharmacol Res.
178:1061352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Feng S, LV L, Liu B, Zhu X and Jing J:
MO619: Landscape RNA Profiling of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in
Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis
Transplantation. 37:2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Sinha N, Kumar V, Puri V, Nada R, Rastogi
A, Jha V and Puri S: Urinary exosomes: Potential biomarkers for
diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 25:881–887. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Xie Y, Jia Y, Cuihua X, Hu F, Xue M and
Xue Y: Urinary exosomal MicroRNA profiling in incipient type 2
diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Res. 2017:69789842017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Zhao Y, Shen A, Guo F, Song Y, Jing N,
Ding X, Pan M, Zhang H, Wang J, Wu L, et al: Urinary Exosomal
MiRNA-4534 as a novel diagnostic biomarker for diabetic kidney
disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11:5902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Cao Y, Shi Y, Yang Y, Wu Z, Peng N, Xiao
J, Dou F, Xu J, Pei W, Fu C, et al: Urinary exosomes derived
circRNAs as biomarkers for chronic renal fibrosis. Ann Med.
54:1966–1976. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Ma H, Xu Y, Zhang R, Guo B, Zhang S and
Zhang X: Differential expression study of circular RNAs in exosomes
from serum and urine in patients with idiopathic membranous
nephropathy. Arch Med Sci. 15:738–753. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Luan R, Tian G, Ci X, Zheng Q, Wu L and Lu
X: Differential expression analysis of urinary exosomal circular
RNAs in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton).
26:432–441. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|