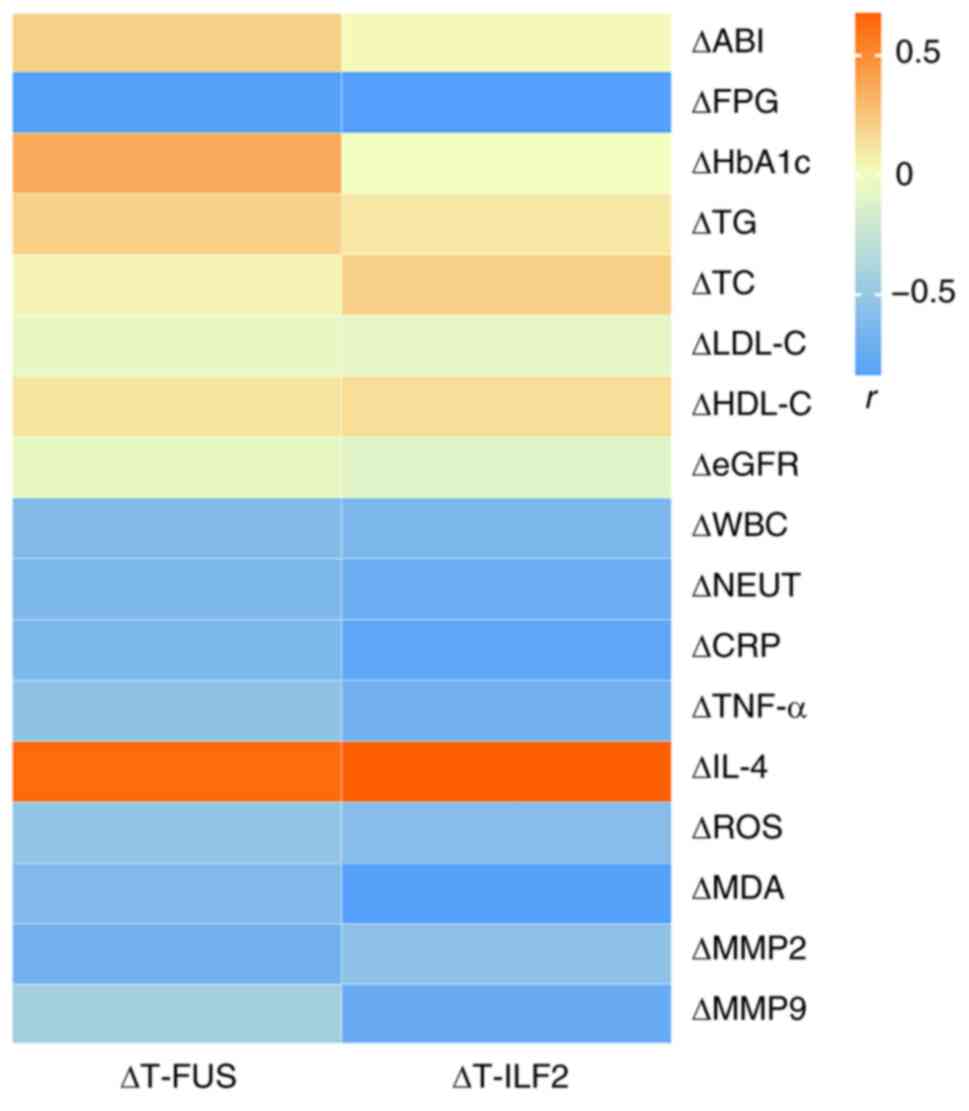
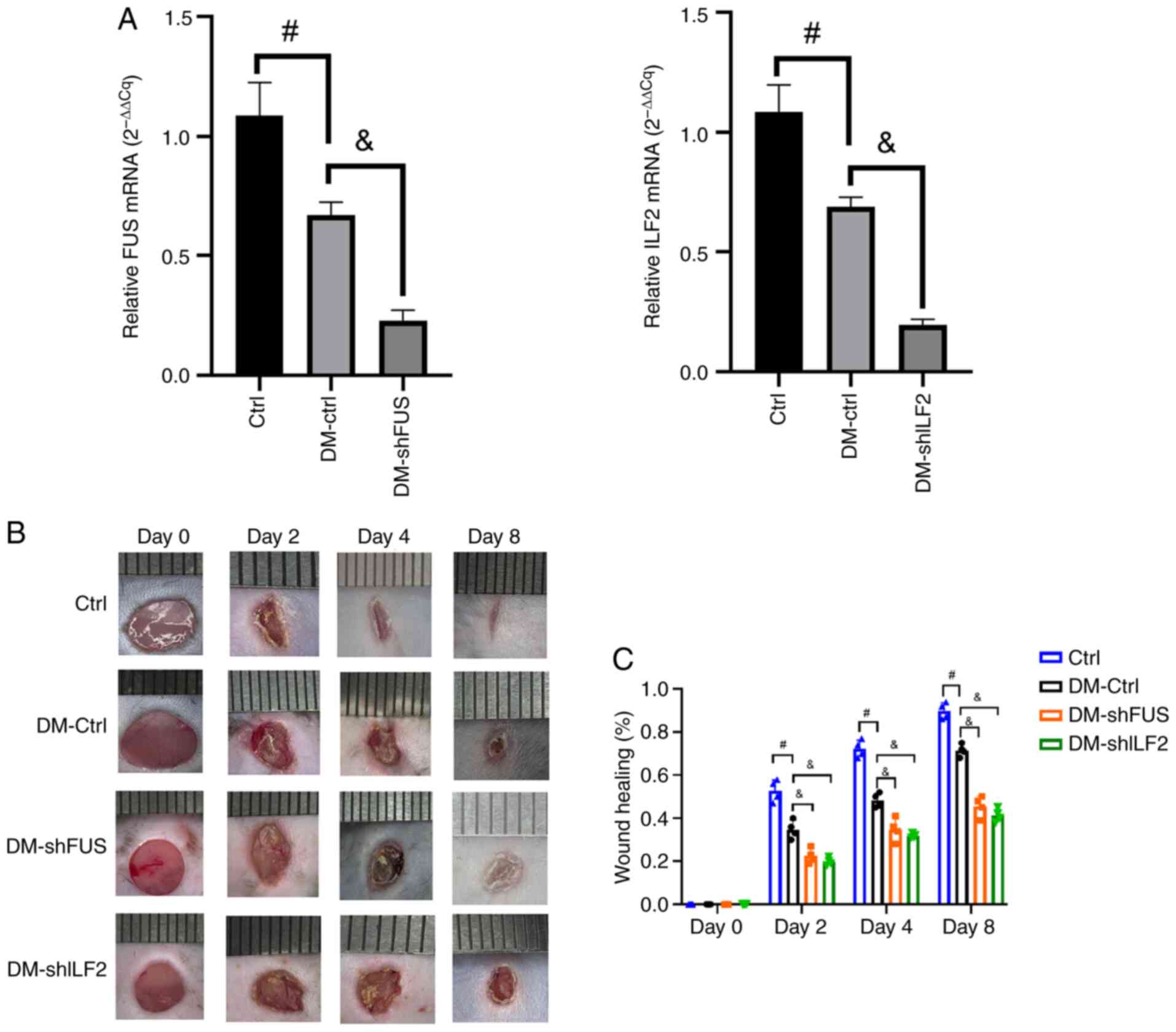
|
1
|
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M,
Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, et
al: IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes
prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 183:1091192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Senneville É, Albalawi Z, van Asten SA,
Abbas ZG, Allison G, Aragón-Sánchez J, Embil JM, Lavery LA, Alhasan
M, Oz O, et al: IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and
treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023).
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 40:e36872024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Meloni M, Izzo V, Giurato L,
Lázaro-Martínez JL and Uccioli L: Prevalence, clinical aspects and
outcomes in a large cohort of persons with diabetic foot disease:
Comparison between neuropathic and ischemic ulcers. J Clin Med.
9:17802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hassanshahi A, Moradzad M, Ghalamkari S,
Fadaei M, Cowin AJ and Hassanshahi M: Macrophage-mediated
inflammation in skin wound healing. Cells. 11:29532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davis FM, Kimball A, Boniakowski A and
Gallagher K: Dysfunctional wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers:
New crossroads. Curr Diab Rep. 18:22018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao X, Xu M, Tang Y, Xie D, Deng L, Chen
M and Wang Y: Decreased expression of miR-204-3p in peripheral
blood and wound margin tissue associated with the onset and poor
wound healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 20:413–429.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hu SCS and Lan CEE: High-glucose
environment disturbs the physiologic functions of keratinocytes:
Focusing on diabetic wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 84:121–127.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salem ESB, Vonberg AD, Borra VJ, Gill RK
and Nakamura T: RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in immuno-metabolic
homeostasis and diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 6:1062019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Assoni AF, Foijer F and Zatz M:
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, FUS and protein synthesis defects.
Stem Cell Rev Rep. 19:625–638. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao H, Kong H, Wang B, Wu S, Chen T and
Cui Y: RNA-binding proteins and alternative splicing genes are
coregulated in human retinal endothelial cells treated with high
glucose. J Diabetes Res. 2022:76805132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang G, Wu H, Liang P, He X and Liu D: Fus
knockdown inhibits the profibrogenic effect of cardiac fibroblasts
induced by angiotensin II through targeting Pax3 thereby regulating
TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Bioengineered. 12:1415–1425. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garikipati VNS, Verma SK, Cheng Z, Liang
D, Truongcao MM, Cimini M, Yue Y, Huang G, Wang C, Benedict C, et
al: Circular RNA CircFndc3b modulates cardiac repair after
myocardial infarction via FUS/VEGF-A axis. Nat Commun. 10:43172019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du H, Le Y, Sun F, Li K and Xu Y: ILF2
directly binds and stabilizes CREB to stimulate malignant
phenotypes of liver cancer cells. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst).
2019:15750312019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao M, Liu Y, Chang J, Qi J, Liu R, Hou
Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Qiao L and Ren L: ILF2 cooperates with E2F1 to
maintain mitochondrial homeostasis and promote small cell lung
cancer progression. Cancer Biol Med. 16:771–783. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xi Z, Huang H, Hu J, Yu Y, Ma X, Xu M,
Ming J, Li L, Zhang H, Chen H and Huang T: LINC00571 drives
tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism in triple-negative breast
cancer through HNRNPK/ILF2/IDH2 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
43:222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin J, Li A, Wang W and Wu J:
Interleukin-enhanced binding factor 2 interacts with NLRP3 to
inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 500:398–404. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ji S, Liu X, Huang J, Bao J, Chen Z, Han
C, Hao D, Hong J, Hu D, Jiang Y, et al: Consensus on the
application of negative pressure wound therapy of diabetic foot
wounds. Burns Trauma. 9:tkab0182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saraiya HA and Shah MN: Use of
indigenously made negative-pressure wound therapy system for
patients with diabetic foot. Adv Skin Wound Care. 26:74–77. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maranna H, Lal P, Mishra A, Bains L,
Sawant G, Bhatia R, Kumar P and Beg MY: Negative pressure wound
therapy in grade 1 and 2 diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized
controlled study. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 15:365–371. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang N, Liu Y, Yan W and Liu F: The
effect of negative pressure wound therapy on the outcome of
diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis. Int Wound J. 21:e148862024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Campitiello F, Mancone M, Corte AD,
Guerniero R and Canonico S: Expanded negative pressure wound
therapy in healing diabetic foot ulcers: A prospective randomised
study. J Wound Care. 30:121–129. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeon BJ, Choi HJ, Kang JS, Tak MS and Park
ES: Comparison of five systems of classification of diabetic foot
ulcers and predictive factors for amputation. Int Wound J.
14:537–545. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mu S, Hua Q, Jia Y, Chen MW, Tang Y, Deng
D, He Y, Zuo C, Dai F and Hu H: Effect of negative-pressure wound
therapy on the circulating number of peripheral endothelial
progenitor cells in diabetic patients with mild to moderate degrees
of ischaemic foot ulcer. Vascular. 27:381–389. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Oh SS and Narver HL: Mouse and rat
anesthesia and analgesia. Curr Protoc. 4:e9952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dutton JW II, Artwohl JE, Huang X and
Fortman JD: Assessment of pain associated with the injection of
sodium pentobarbital in laboratory mice (Mus musculus). J Am Assoc
Lab Anim Sci. 58:373–379. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Caudron-Herger M, Jansen RE, Wassmer E and
Diederichs S: RBP2GO: A comprehensive pan-species database on
RNA-binding proteins, their interactions and functions. Nucleic
Acids Res. 49(D1): D425–D436. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Smith MR and Costa G: RNA-binding proteins
and translation control in angiogenesis. FEBS J. 289:7788–7809.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gerstberger S, Hafner M and Tuschl T: A
census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 15:829–845.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Lazzarini PA, McPhail SM, van
Netten JJ, Armstrong DG and Pacella RE: Global disability burdens
of diabetes-related lower-extremity complications in 1990 and 2016.
Diabetes Care. 43:964–974. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM and Bus SA:
Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med.
376:2367–2375. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Armstrong DG, Tan TW, Boulton AJM and Bus
SA: Diabetic foot ulcers: A review. JAMA. 330:62–75. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tricco AC, Antony J, Vafaei A, Khan PA,
Harrington A, Cogo E, Wilson C, Perrier L, Hui W and Straus SE:
Seeking effective interventions to treat complex wounds: An
overview of systematic reviews. BMC Med. 13:892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eneroth M and van Houtum WH: The value of
debridement and vacuum-assisted closure (V.A.C.) therapy in
diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 24(Suppl 1): S76–S80.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raphael A and Gonzales J: Use of
cryopreserved umbilical cord with negative pressure wound therapy
for complex diabetic ulcers with osteomyelitis. J Wound Care.
26(Sup10): S38–S44. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Namgoong S, Jung SY, Han SK, Kim AR and
Dhong ES: Clinical experience with surgical debridement and
simultaneous meshed skin grafts in treating biofilm-associated
infection: An exploratory retrospective pilot study. J Plast Surg
Hand Surg. 54:47–54. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Armstrong DG and Lavery LA; Diabetic Foot
Study Consortium: Negative pressure wound therapy after partial
diabetic foot amputation: A multicentre, randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 366:1704–1710. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu L, Chen R, Jia Z, Li X, Tang Y, Zhao
X, Zhang S, Luo L, Fang Z, Zhang Y and Chen M: Downregulation of
hsa-miR-203 in peripheral blood and wound margin tissue by negative
pressure wound therapy contributes to wound healing of diabetic
foot ulcers. Microvasc Res. 139:1042752022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu Z, Dumville JC, Hinchliffe RJ, Cullum
N, Game F, Stubbs N, Sweeting M and Peinemann F: Negative pressure
wound therapy for treating foot wounds in people with diabetes
mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 10:CD0103182018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen L, Zhang S, Da J, Wu W, Ma F, Tang C,
Li G, Zhong D and Liao B: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
efficacy and safety of negative pressure wound therapy in the
treatment of diabetic foot ulcer. Ann Palliat Med. 10:10830–10839.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McDermott K, Fang M, Boulton AJM, Selvin E
and Hicks CW: Etiology, Epidemiology, and disparities in the burden
of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 46:209–221. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Seghieri G, Policardo L, Gualdani E,
Anichini R and Francesconi P: Gender difference in the risk for
cardiovascular events or mortality of patients with diabetic foot
syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 56:561–567. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Iacopi E, Pieruzzi L, Riitano N,
Abbruzzese L, Goretti C and Piaggesi A: The weakness of the strong
sex: Differences between men and women affected by diabetic foot
disease. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 22:19–26. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jarl G, Alnemo J, Tranberg R and Lundqvist
LO: Gender differences in attitudes and attributes of people using
therapeutic shoes for diabetic foot complications. J Foot Ankle
Res. 12:212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sorber R and Abularrage CJ: Diabetic foot
ulcers: Epidemiology and the role of multidisciplinary care teams.
Semin Vasc Surg. 34:47–53. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kotlinowski J, Dulak J and Józkowicz A:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus impairs endothelial progenitor cells
functions. Postepy Biochem. 59:257–266. 2013.In Polish.
|
|
47
|
Fernando ME, Seneviratne RM, Tan YM,
Lazzarini PA, Sangla KS, Cunningham M, Buttner PG and Golledge J:
Intensive versus conventional glycaemic control for treating
diabetic foot ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2016:CD0107642016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Markuson M, Hanson D, Anderson J, Langemo
D, Hunter S, Thompson P, Paulson R and Rustvang D: The relationship
between hemoglobin A(1c) values and healing time for lower
extremity ulcers in individuals with diabetes. Adv Skin Wound Care.
22:365–372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Christman AL, Selvin E, Margolis DJ,
Lazarus GS and Garza LA: Hemoglobin A1c predicts healing rate in
diabetic wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 131:2121–2127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hemmingsen B, Lund SS, Gluud C, Vaag A,
Almdal TP, Hemmingsen C and Wetterslev J: Targeting intensive
glycaemic control versus targeting conventional glycaemic control
for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
CD0081432013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang WL, Yan WJ, Sun B and Zou ZP:
Synergistic effects of atorvastatin and rosiglitazone on
endothelium protection in rats with dyslipidemia. Lipids Health
Dis. 13:1682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zangiabadi N, Shafiee K, Alavi KH, Assadi
AR and Damavandi M: Atorvastatin treatment improves diabetic
polyneuropathy electrophysiological changes in non-insulin
dependent diabetic patients: A double blind, randomized clinical
trial. Minerva Endocrinol. 37:195–200. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xie X, Bao Y, Ni L, Liu D, Niu S, Lin H,
Li H, Duan C, Yan L, Huang S and Luo Z: Bacterial profile and
antibiotic resistance in patients with diabetic foot ulcer in
Guangzhou, Southern China: Focus on the differences among different
Wagner's grades, IDSA/IWGDF grades, and ulcer types. Int J
Endocrinol. 2017:86949032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tang Y, Liu L, Jie R, Tang Y, Zhao X, Xu M
and Chen M: Negative pressure wound therapy promotes wound healing
of diabetic foot ulcers by up-regulating PRDX2 in wound margin
tissue. Sci Rep. 13:161922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qin G, Song Y, Guo Y, Sun Y and Zeng W:
LincRNA TINCR facilitates excessive proliferation and inflammation
in post-burn skin fibroblasts by directly binding with SND1 protein
and inducing SND1-mediated TGF-β1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 509:903–910. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Meder L, König K, Dietlein F, Macheleidt
I, Florin A, Ercanoglu MS, Rommerscheidt-Fuss U, Koker M, Schön G,
Odenthal M, et al: LIN28B enhanced tumorigenesis in an
autochthonous KRASG12V-driven lung carcinoma mouse model. Oncogene.
37:2746–2756. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guo L and Huang X, Liang P, Zhang P, Zhang
M, Ren L, Zeng J, Cui X and Huang X: Role of XIST/miR-29a/LIN28A
pathway in denatured dermis and human skin fibroblasts (HSFs) after
thermal injury. J Cell Biochem. 119:1463–1474. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ayerst BI, Merry CLR and Day AJ: The good
the bad and the ugly of glycosaminoglycans in tissue engineering
applications. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 10:542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rohani MG and Parks WC: Matrix remodeling
by MMPs during wound repair. Matrix Biol. 44-46:113–121. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lobmann R, Ambrosch A, Schultz G, Waldmann
K, Schiweck S and Lehnert H: Expression of
matrix-metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the wounds of
diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 45:1011–1016.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Y, Min D, Bolton T, Nubé V, Twigg SM,
Yue DK and McLennan SV: Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9
predicts poor wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers: Response to
Muller et al. Diabetes Care. 32:e1372009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chang M: Restructuring of the
extracellular matrix in diabetic wounds and healing: A perspective.
Pharmacol Res. 107:243–248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cui YH, Feng QY, Liu Q, Li HY, Song XL, Hu
ZX, Xu ZY, Li JH, Li MJ, Zheng WL, et al: Posttranscriptional
regulation of MMP-9 by HuR contributes to IL-1β-induced pterygium
fibroblast migration and invasion. J Cell Physiol. 235:5130–5140.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chen Q, Zhou L, Ma D, Hou J, Lin Y, Wu J
and Tao M: LncRNA GAS6-AS1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis
of colorectal cancer by regulating TRIM14 through
miR-370-3p/miR-1296-5p and FUS. J Transl Med. 20:3562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang T, Shen P, Chen Q, Wu P, Yuan H, Ge
W, Meng L, Huang X, Fu Y, Zhang Y, et al: FUS-induced circRHOBTB3
facilitates cell proliferation via miR-600/NACC1 mediated autophagy
response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 40:2612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang Q, Yang Y, Fu X, Wang Z, Liu Y, Li M,
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li PF, Yu T and Chu XM: Long noncoding RNA
XXYLT1-AS2 regulates proliferation and adhesion by targeting the
RNA binding protein FUS in HUVEC. Atherosclerosis. 298:58–69. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ghanbarpanah E, Kohanpour MA,
Hosseini-Beheshti F, Yari L and Keshvari M: Structure and function
of FUS gene in prostate cancer. Bratisl Lek Listy. 119:660–663.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jia Y, Li X, Nan A, Zhang N, Chen L, Zhou
H, Zhang H, Qiu M, Zhu J, Ling Y and Jiang Y: Circular RNA 406961
interacts with ILF2 to regulate PM2.5-induced
inflammatory responses in human bronchial epithelial cells via
activation of STAT3/JNK pathways. Environ Int. 141:1057552020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Huang W, Liu J, Yan J, Huang Z, Zhang X,
Mao Y and Huang X: LncRNA LINC00470 promotes proliferation through
association with NF45/NF90 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum
Cell. 33:131–139. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Li Y, Wang M, Yang M, Xiao Y, Jian Y, Shi
D, Chen X, Ouyang Y, Kong L, Huang X, et al: Nicotine-induced ILF2
facilitates nuclear mRNA export of pluripotency factors to promote
stemness and chemoresistance in human esophageal cancer. Cancer
Res. 81:3525–3538. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chiu CL, Li CG, Verschueren E, Wen RM,
Zhang D, Gordon CA, Zhao H, Giaccia AJ and Brooks JD: NUSAP1 binds
ILF2 to modulate R-loop accumulation and DNA damage in prostate
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:62582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yin X, Yang Z, Zhu M, Chen C, Huang S, Li
X, Zhong H, Wen H, Sun Q, Yu X, et al: ILF2 contributes to
hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and skin inflammation in a
KLHDC7B-DT-dependent manner in psoriasis. Front Genet.
13:8906242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Du Y, Chen W, Li Y, Liang D and Liu G:
Study on the regulatory effect of Panax notoginseng saponins
combined with bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on
IRAK1/TRAF6-NF-κB pathway in patients with diabetic cutaneous
ulcers. J Orthop Surg Res. 18:802023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Yen YH, Pu CM, Liu CW, Chen YC, Chen YC,
Liang CJ, Hsieh JH, Huang HF and Chen YL: Curcumin accelerates
cutaneous wound healing via multiple biological actions: The
involvement of TNF-α, MMP-9, α-SMA, and collagen. Int Wound J.
15:605–617. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|