Cord blood (CB) has been a significant source of
haematopoietic stem cells. The therapeutic value of CB has been
examined since the late 90s when the first transplantation
effectively treated a 5-year-old patient with Fanconi anaemia
(1). Considering the potential of
CB and its viability for autologous use, the practice of CB banking
has been extensively embraced to maintain the CB unit from birth,
either through government-funded organisations or private companies
with a storage charge (2).
However, such an approach has also been affected by the high
running cost, the actual clinical utilisation and new emergent
alternatives (3), thus prompting
the cell banking endeavour and its sustainability to be carefully
revisited.
Strategies have been introduced to keep the cell
banking endeavour relevant, including the introduction of criteria
for CB cryopreservation, CB cell expansion, use in allogeneic
transplantation and exploring novel medicinal uses. However, the
use of CB in the clinic is predominantly focused on treating
haematological diseases, which hinders the progress of cell banking
initiatives aimed at achieving broader storage and clinical
benefits.
There is an increasing interest in converting CB
into hiPSCs as an approach to resolve the underutilized CB unit in
the cell bank (4,5), since hiPSCs present with greater
therapeutic value and applications. This could potentially enhance
the utility of CB and satisfy the rising need for hiPSCs, which
could redefine the future of regenerative medicine.
The present review discusses the rise and fall of CB
usage and banking for clinical transplantation, including the early
discovery of CB characteristics and therapeutic value, the
development of past trials that subsequently promoted the growth of
the CB bank and industry, the challenge of using low total
nucleated cells (TNCs) in CB and the strategy to expand the cells
for autologous transplantation, the change in trends of application
from intended autologous to allogeneic use, and lastly, the shift
of preference to haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
transplantation from using allogeneic CB. The review also
summarizes the considerations in reprogramming CB into hiPSCs,
including the reprogramming methods, the advantages of using CB as
the choice of somatic cells for reprogramming, as well as the
disadvantages, and the latest strategies for overcoming iPSC
allogenicity. Lastly, the prospect of using CB-iPSC banking and the
opportunity that it creates is discussed.
HSCs, which can differentiate into any type of blood
cell, are found in umbilical CB. Just 0.02–1.43% of the
mononucleated cells in CB are CD34+ HSCs, which is a
density that is higher than that found in the peripheral blood (PB)
(<0.01%) but lower than that found in the bone marrow (0.5–5.0%)
(6). The colony-forming cell
content has not only been found to be associated with the
CD34+ cell number, but is also associated with the
gestational age of the newborn (7). CB-derived HSCs exhibit a greater
growth response to known mitogens and cytokines, and are less
reliant on the support of stromal cells (8). These properties allow CB-HSCs to
exit the G0/G1 phase and divide more rapidly
than HSCs from other adult tissues under the same culture
conditions (9).
The first CB transplantation to a 5-year-old patient
with severe Fanconi anaemia was performed in 1988 (1), establishing precedence for
subsequent use of CB in transplantation between identical siblings
after cryopreservation (18).
Complete haematopoietic reconstitution has also been shown to be
possible following CB transplantation in HLA mismatched siblings or
unrelated patients with leukaemia, as documented in previous
studies (18,19). Broxmeyer et al (20) reported that nucleated HSCs were
found to remain effective and functional even after being frozen
for 23 years. CD34+ cells isolated from cryopreserved CB
were also capable of successful integration and functioning after 6
months in primary and secondary immunodeficient mice, suggesting
that cryopreservation does not affect the function of injected HSCs
in the long term (20). The
growing banking service for CB worldwide has garnered a substantial
number of transplantable units for use in clinical
transplantation.
According to the World Marrow Donor Association, the
global inventory of CB has grown by >800,000 units in 2022
(21), and >40,000 CB
transplantations have been performed in both paediatric and adult
patients (9), for treating either
malignant or non-malignant haematological diseases. In leukemic
paediatric patients, the transplantation of complete HLA-matched CB
has shown to have comparable effects with bone marrow from sibling
donors (22). In children with
haematopoietic malignancies, related HLA-identical CB
transplantation achieved neutrophil recovery in 90% in patients
with a median age of 5 years, and the incidence of GvHD was only
10–12% at 2 years post-transplant (23), with non-relapse mortality at 9%
and relapse at 47% at 5 years post-transplant. It was also
highlighted that transplanted CB units with higher TNCs contributed
to greater neutrophil recovery and a greater disease-free survival
rate. Similarly, 2-loci mismatched, unrelated CB units also
demonstrated similar therapeutic effects compared with matched
adult marrow transplants (24,25).
It was also found that the higher the HLA disparity
and mismatch, the lower the 5-year survival rate observed in
paediatric donor-recipient pairs who received single unit CB graft
(26). The relative risk of CB
transplant-related mortality has shown to rise with increasing HLA
mismatch (26), despite the lower
rate of relapse (25,27,28). This evidence collectively suggests
that CB transplantation is the ideal option in paediatric patients
provided that the CB unit is sufficiently HLA-matched and the
therapeutic cell number is adequate. In conclusion, successful
transplantation, especially in pediatric patients, relies on
sufficient cell numbers in CB units. Higher TNCs improve outcomes,
while proper HLA matching and cell quantity reduce GvHD. Even
mismatched CB units can perform similarly to matched adult
transplants, highlighting the importance of stem cell numbers for
engraftment and survival.
CB from an allogenic source remains the most used in
clinical transplantation compared with CB from an autologous source
(29). In a survey by the
European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, it was shown
that, of the 119 patients transfused with CB, 75% of the
transplanted grafts were from unrelated donors. As patients are
unrelated, HLA matching between the donor CB unit and the recipient
patient is important to minimize graft rejection and increase the
eventual patient survival time (29). Based on the National Marrow Donor
Program and The Centre for International Blood and Marrow
Transplant Research (CIBMTR) guidelines, patients and donor CB
grafts should be HLA typed for HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C and HLA-DRB1, as
well as the confirmatory typing for DQB1 and DPB1, at high
resolution using DNA methods (30). However, the availability of such
fully HLA-matched CB units (6/6 loci) is only ~10%, and is highly
dependent on the race and ethnic group of the CB donor (31). Mismatched CB units at one or two
HLA loci could be considered and have been previously been found to
work in all patients <20 years old and in 75% of patients ≥20
years old (31–33).
Another factor that determines the outcome of the
transplantation is the number of TNCs in CB unit. Table I (30,34–37) summarizes the minimum cell number
required for single- or double-unit infusion. The Center for
International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR),
Eurocord and the European Group for Blood and Marrow
Transplantation collaborative group recommended a 2×107
TNCs/kg of recipient for a single unit, and this was found to be
associated with sufficient engraftment of progenitor cells and
successful transplantation (27).
A TNC number <2×107 TNCs/kg proved to have a lower
therapeutic value, including delayed engraftment and lower
transplant-related mortality (38). Furthermore, a high TNC number
(>5.0×107/kg) could subdue the effect of two HLA
mismatches, and HLA matching can compensate for the disadvantage of
a low TNC number (39). More
notably, improved event-free survival rate was found to correlate
with higher CD34+ cells in the CB unit but was not
associated with TNC number (19).
Considering the pros and cons, recommendations are
made to ensure the minimum level of both the TNCs and
CD34+ cells in each cryopreserved CB unit are met
(Table I) in order to balance the
cost and the therapeutic benefit. Collected CB units that fail to
meet these requirements are discarded. These ‘unqualified’ CB units
account for ~36–39% of the total collected CB units (40). This practice not only incurs
substantial operational costs involving steps from CB collection to
cell analysis, but also involves sacrificing CB units of high
therapeutic or research value, especially from donors with rare
blood types or diseases (41).
Hence, to address low TNC numbers in CB units, the logical and
immediate solutions to increase the cell number for transplantation
are as follows: i) Combining two CB grafts (42,43); and ii) expanding the autologous
cells to a therapeutically meaningful number in vitro.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 9
controlled clinical trials (phase I–III) involving 1,146 patients
who underwent umbilical CB transplantation (UCBT) (44–52) using ex vivo expanded or
unmanipulated grafts was conducted by Saiyin et al (2023)
(53). The expansion strategies
employed in the included studies consisted of cytokine cocktails
combined with small molecules such as UM171, nicotinamide (NiCord),
copper chelation, Notch ligand or Stem regenin-1 (SR-1) (Table II) (49,50,52,54–56) or coculture with mesenchymal
stromal cells or double unit transplantation. The meta-analysis
concluded that transplantation using ex vivo expanded CB
significantly reduced neutrophil recovery time in patients compared
to transplantation with unmanipulated units. Notably, the infused
cell dose did not correlate with time to neutrophil and platelet
recovery. Additionally, patients receiving expanded CB transplants
exhibited a significant decrease in the risk of death at the study
endpoint, and graft failure only occurred in 0 to 10% of patients
using expanded cells. Moreover, with the transplantation of
expanded CB units using mesenchymal stromal cells or Notch
ligand-expanded cells in combination with a second unmanipulated
CB, the expanded population were found to be overtaken by
unmanipulated CB at 1-year post-transplantation. SR-1 and NiCord
expanded CB units achieved graft dominance after a year if double
units were used in the transplantation, but this was only seen in
35 and 78% of the patients, respectively (49,51). Nonetheless, the overall CB
expansion and time to initial neutrophil recovery do not always
improve survival, and there is no statistical difference in the
risk of acute GvHD between patients administered ex vivo
expanded CB units and controls (57). A study has also found that
excellent overall survival rate was observed in patients with
unmanipulated CB despite the low medium infusion of TNCs and the
slower engraftment (45).
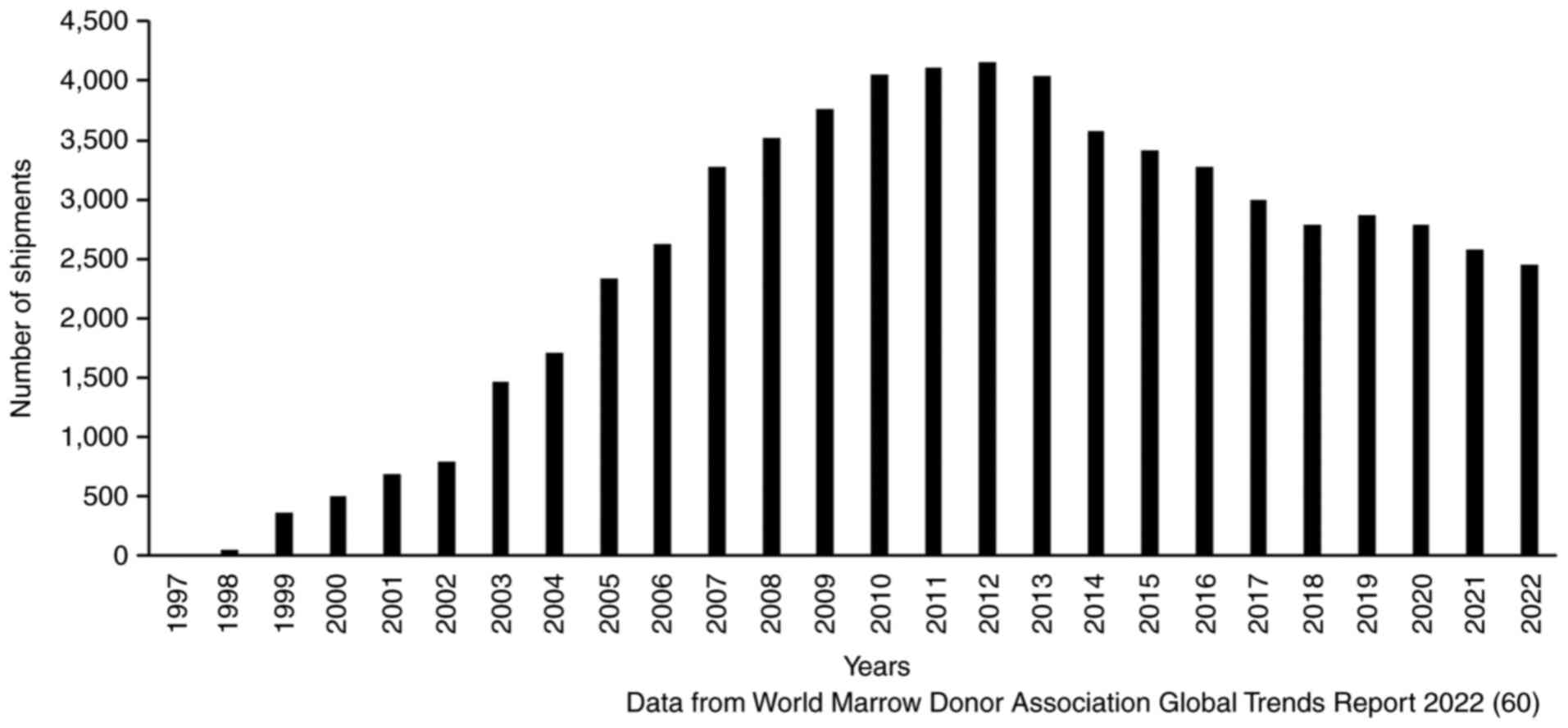
The growing banking service for CB worldwide has
garnered substantial transplantable units for use in clinical
transplantation. Despite the promising growth in the global
inventory of CB (21), the total
number of units dispensed has reduced from 4,150 units in 2012 to
2,450 units in 2022, a reduction of 41.0% in the past decade
(Fig. 1). According to a special
report by Passweg et al studying the trends of
haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Europe in 2013, CB was
only used in 2 out of 22,998 autologous transplantations, while
only 5 out of 7,624 allogeneic transplantations involved related
family members and 666 out of 8,587 were transplanted to unrelated
patients (58). The decline in
using CB is also due to the marked increase in haploidentical
transplantation, and a similar trend was also observed by the Asia
Pacific Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group (59) and the Worldwide Network of Blood
and Marrow Transplantation (60).
Allogenic stem cell transplantation has become the treatment of
choice for high-risk haematological malignancies, and the
established sources of HSCs for these patients are either CB or
haploidentical donors when there is a lack of HLA-matched
donors.
Haploidentical donors are immediate family members
who possess tissue with half matching HLA haplotypes. The shift of
preference towards haploidentical HSC transplantation, particularly
from PB, is mainly due to the high cell source availability, fresh
HSC isolation from donors upon demand without the need for
cryopreservation, a shorter time to transplantation without the
need to mobilize or transport matched grafts from cell banks, such
as CB, and therefore a significantly lower cost per
transplantation. More importantly, there are no statistical
differences in the main outcomes between haplo-HSC and CB
transplantation, including relapse incidence, leukaemia-free
survival, 2-year non-relapse mortality rate and overall survival
rate (61,62). In some trials, CB transplantation
demonstrated more disadvantages than the haplo-graft
transplantation, including slow neutrophil recovery and a relative
higher risk of grade II–IV acute GvHD (63,64).
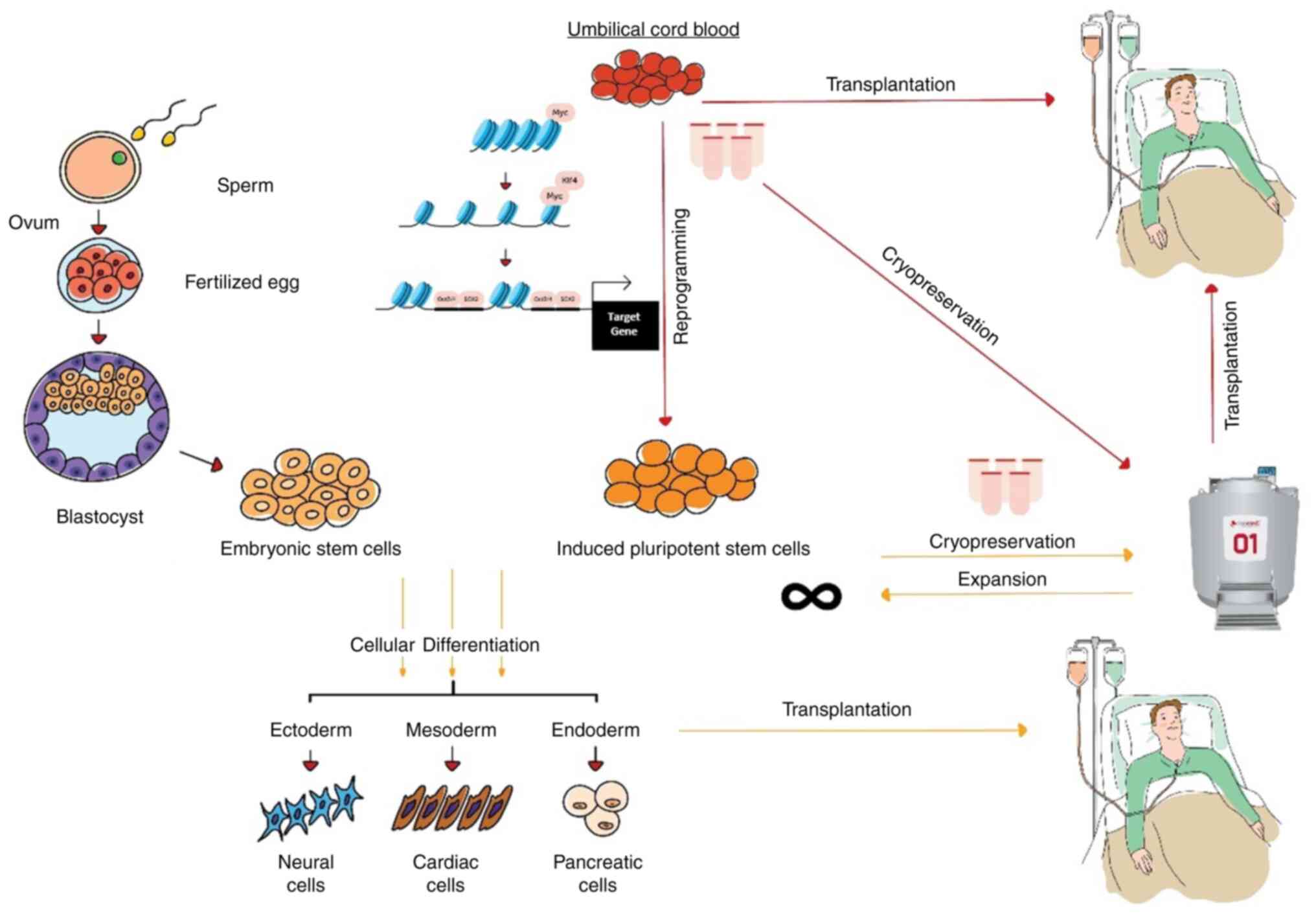
hiPSCs are cells that are created through cellular
reprogramming, a technology introduced by Takahashi and Yamanaka
(2006) to reverse the fate of differentiated cells back to the
pluripotent stage (65). The
invention enables the making of PSCs from any adult somatic cells
possible, and the cells possess the differentiation plasticity of
the embryonic stem cells. Recently, the induced PSCs were also
found to be capable of cultivating synthetic embryos (66), opening vast opportunities to study
complex embryology and early human development. Judging from the
enormous variety of applications and the therapeutic potential that
hiPSCs could offer, and the recent decline in CB transplantation in
clinics, several reports have proposed to convert cryopreserved CB
into hiPSCs (4,67) (Fig.
2). Efforts to revamp the cell banking industry and
revolutionize regenerative medicine have begun by promoting the use
of hiPSCs. The present review discusses and summarizes the
information, including the reprogramming methods assessed on CB,
the comparison between the use of CB and adult PB, and the advances
in establishing hiPSC haplobank or hypoimmunogenic lines as the
off-the-shelf cell source for clinical treatment.
Several reprograming and hiPSC generation methods
have been introduced since its discovery. In general, both
integrating and non-integrating methods have been used in
reprogramming CB (Table III)
(20,68–79). Evidence has shown that the
reprogramming of CB is possible even it has been frozen for 21
years (20). The outcome of this
was also confirmed to be comparable to that of fresh CB (70). The long-term cryopreservation of
CB did not impede the formation of embryoid bodies in both in
vivo and ex vivo studies, and the injection of hiPSCs
into testis capsules of immune-deficient mice demonstrating
spontaneous differentiation into cells of all three germ layers
(20). The present review
summarizes and emphasizes the reprogramming methods that have
previously successfully generated hiPSCs, namely use of
retroviruses and lentiviruses, episomal transfection of vectors,
and use of Sendai virus, self-replicative RNA (srRNA), microRNA
(miRNA/miR) or defined chemicals (Table III).
Retroviruses rely on the infectivity of host cells
via receptor-mediated endocytosis to achieve stable genomic
integration of the RNA reprogramming factors with the aid of the
reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes (80). The transgenes transduced into host
cells allow for stable expression and maintenance for 30 days
before generating the iPSCs. CD34+ cells that were
transduced with retroviruses carrying Yamanaka's factors and p53
short-hairpin RNA vectors enhanced the reprogramming efficiency.
p53 short hairpin RNA vectors are crucial in inhibiting the p53
pathway (69). However,
retroviruses are prone to insertional mutagenesis, raising the
safety concern over their use in the clinic (68).
Lentiviruses are RNA viruses that are capable of
infecting both dividing and non-dividing cells. After reverse
transcription, the lentiviral genome will be integrated into the
host cell genome, allowing long-term expression of the inserted
genes in the target cells in vitro. Haase et al
(70) successfully generated
iPSCs from proliferative CB endothelial cells and yielded better
results than with PB. Lentiviral vector-mediated transduction of
OCT3/4 and SOX2 alone was found to sufficiently
reprogram CB CD34+ cells into hiPSCs with an efficiency
of 2% (81), an outcome that was
higher by 1,000-fold than that of using a retrovirus. However,
early lentivirus vectors tend to integrate transgenes into target
cells, leading to host genome sequence changes (81). These transgenes were not silenced
in the generated hiPSCs and could result in tumour formation,
especially due to the high expression of c-Myc and
Klf4, known oncogenes. A safer, self-inactivating
third-generation lentiviral system has been introduced, with the
packaging system containing two plasmids: the Rev encoding and Gag
and Pol encoding plasmids. Multiple clinical trials have shown that
third-generation lentiviral vectors can introduce genes to HSCs to
treat hemoglobinopathies and primary immunodeficiencies (82,83). However, the use of
third-generation lentiviral systems is still not applied in iPSC
generation.
The non-integrating, self-replicating vector
delivery system using EBNA1/OriP, capable of long-term persistence
in cells to mediate nuclear import and retention of vector DNA,
allows hiPSC derivation from a single transfection. EBNA vectors
express the EBNA1 gene to deliver episomal vectors into somatic
cells. This method is a transgene-free approach, whereby episomal
vectors are removed from iPSCs without integration into genomic DNA
(72). A study using CB, which
has been cryopreserved for 13 years, demonstrated that transduction
with EBNA1/OriP resulted in a highly efficient generation of hiPSCs
obtained within 14 days, with 1,000 hiPSC colonies created per 2
million transfected cells. A parallel experiment with
PB-mononuclear cells indicated a 50-fold lower efficiency in
deriving hiPSCs compared with that for CB (73).
Also, the non-integrating method using the Sendai
virus vector (SeV) can generate hiPSCs without foreign gene
insertions into the host genome. This approach is highly applicable
for future clinical use, as SeV can be produced with
temperature-sensitive mutations, making the vectors easily
removable at non-permissive temperatures, thereby eliminating the
foreign genes in the mature hiPSCs (74). Another study demonstrated that
CD34+ CB could be reprogrammed with volumes as low as 5
ml for each procedure using a viral mixture of SeV
TS7-OCT3/4, -SOX2, -KLF4 and -c-MYC to
generate 10 independent hiPSCs per ml of blood (74). In 2019, the SeV reprogramming
method was used to reprogram the CB CD34+ cells of a
female child to create iPSCs (75). Recently, Kunitomi et al
(84) developed a more precise
and versatile SeV-KLF4 by modifying the vector to include L-MYC in
place of c-MYC, and also adjusted the temperature settings during
cell maintenance and reprogramming. Thus, naive hiPSCs showed a
significantly improved ability to differentiate into trilineage
lineages (85).
Reprogramming can also be achieved by using srRNA or
miRNA. The non-integrating srRNA that encodes Venezuelan equine
encephalitis (VEE) replicon carried the four reprogramming
transcription factors OCT3/4, SOX2, KLF4 and cMYC, or with GLIS1 in
replacement of cMYC, was found to successfully induce reprogramming
in newborn or adult fibroblasts (86). This reprogramming process was
facilitated by supplementing B18R recombinant protein, an essential
virus-encoded receptor, which increased cell viability during RNA
transfection, that neutralizes type 1 interferon induced by VEE RNA
(86). In addition, the ES
cell-specific cell cycle-regulating miRNAs miR-291-3p, miR-294 and
miR-295 also showed enhanced retrovirus-mediated expression of
OCT3/4, SOX2 and KLF4 (87). Similar mRNA-facilitated srRNA
reprogramming was also employed and assessed in a study that
compared the reprogramming efficiency of CB-derived endothelial
progenitor cells (CB-EPCs) with PB-EPCs. CB-EPCs were found to be
more efficiently reprogrammed than PB-EPCs, as shown by a 3.5-fold
increase in colony formation and cell number, along with results
from pluripotent gene expression microarrays (77).
An alternative reprogramming method has been
introduced using small molecules to replace the conventional
gene-mediated reprogramming method. In the study by Chou et
al (73), it was demonstrated
that the use of the small molecule compound VC6TFZ, consisting of 6
specific molecules [valproic acid sodium salt (VPA), CHIR99021,
616452, tranylcypromine, forskolin and 3-deazaneplanocin A
(DZNep)], followed by dual inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase
and mitogen-activated protein kinase, could efficiently generate
hiPSCs from mouse embryonic fibroblasts without the ectopic
expression of reprogramming genes (88). Nonetheless, this method has not
been used in reprogramming CB cells into hiPSCs, although direct
programming of CB erythroblasts to induced megakaryocytes was
demonstrated using Bix01294, PD0325901, VPA and RG108 (89).
The cellular reprogramming process involves
resetting the epigenetic landscape of a somatic cell and reverting
it back to a pluripotent state. Studies have shown that cellular
reprogramming and the subsequent differentiation efficiency are
affected by several factors, which include the age of the parental
somatic cells, cell origin, type of cell and the method of
reprogramming or differentiation (90–93). The types of parental somatic cells
used in reprogramming do not seem to have induced variability in
the resultant hiPSCs. For instance, a study that tested fibroblast
and blood cells from the same donor showed no major variability
between the produced hiPSCs, in terms of both reprogramming and
differentiation efficiency (94),
but evidence has proven that the retained residual epigenetic
memory in the generated iPSCs could make the cells prone to
differentiation towards their tissue of origin (91,92). Moreover, hiPSCs derived from cells
of genetically different donors revealed significant differences in
the hiPSC differentiation efficiency (90,94).
Additionally, higher reprogramming efficiency was
observed when younger, juvenescent somatic cells that possess less
epigenetic modifications were used (95). A study by Lo Sardo et al
(95) showed that hiPSCs
generated from the PB of young individuals in their twenties,
middle-aged individuals at 49–79 years old and the elderly at
86–100 years old showed no difference in reprogramming efficiency.
The study also reported that a significantly higher level of
methylation was found in donor cells from older individuals, with a
5% increase in the global methylation level at CpG sites (95). This makes the relative resistance
to demethylation in age-associated CpG sites higher during cellular
reprogramming in older donors. This is in line with the observation
reported in the study by Gao et al (2017) (77), which compared hiPSCs derived from
EPCs, CB and adult PB. The study showed that a higher reprogramming
efficiency was evident in CB-EPCs compared with that in PB-derived
cells. Furthermore, hiPSCs from aged donors retained an epigenetic
signature of age, which could be slowly reduced through in
vitro passaging, but the older the parental cells, the higher
the risk of exomic mutation present in the generated hiPSCs, as
evidenced by whole-exome sequencing analyses that demonstrated an
increased frequency of mutations correlating with donor age
(95).
The most discussed advantages of using CB as the
cell source for generating hiPSCs are the availability of the cells
in CB banks, the primitive nature of the cells (free from any
acquired mutations such as those found in other somatic cells) and
their young age. Studies have shown that the function of the
generated hiPSCs does not seem to be affected by the age of the
donor cells (96), as the
epigenetic signature of ageing in hiPSCs can be reduced with in
vitro passaging (95). In
general, CB-derived cells were more proliferative than those from
adult PB (70), and the advantage
of using youthful CB cells was evident in their reprogramming
efficiency (95). However, no
difference in differentiation was found when comparing the hiPSCs
from CB and PB (73). Other
studies have also concluded that the differentiated cells from
different hiPSCs donor sources possess no difference, or functional
superiority in in vivo heart function after transplantation
(92).
Nonetheless, a significant drawback in generating
hiPSCs from CB is the additional cost required for cell separation
to purify mononuclear cells or CD34-expressing HSCs, similar to the
situation in PB. This process is necessary, as attempts to
reprogram red blood cells into hiPSCs have not been successful due
to the lack of a nucleus in mature red blood cells.
The use of CB-iPSCs only for autologous means may
incur a substantial cost of preparation and maintenance, and it is
more applicable to personalized and precision testing, and
treatment in patients with specific conditions or family members.
Allogeneic use of the cells is, however, more likely to be the
option to reduce the cost of maintenance and to maximize the usage
across different patients. One of the strategies to lower the
immunogenicity of CB-hiPSC-derived cells is to identify HLA
haplotype homozygous CB donors. Research has shown that cells from
HLA haplotype homozygous donors can benefit significant numbers of
patients in the country or populations with low HLA diversity
(97,98). By using this method, off-the-shelf
allogenic CB-hiPSCs that are haploidentical to a good majority of
the population can be generated in large quantity and decrease the
time and cost when compared with individualized hiPSC
manufacturing.
In Japan, a clinical-grade hiPSC haplobank was
established with 27 hiPSC lines derived from 7 HLA-homozygous
donors, which was claimed capable of covering 40% of the Japanese
population (99). The haplobank
has provided the iPSCs for more than 10 clinical trials since 2015.
Similarly, in Spain, an iPSC haplobank was established through a
search of 32,000 bone marrow donors and CB donors from the Spanish
Bone Marrow Donor Registry (99).
A total of 10 CB units from homozygous donors stored were found to
meet HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-DRB1 matching for 28.23% of the
population (100). The efforts
also led to the formation of The Global Alliance for iPSC
Therapies, which consolidate and assess the feasibility in
developing the global haplobank partnership in the generation of
clinical grade hiPSCs (101).
Autologous cell transplantation is still a
favourable option considering its better graft engraftment and low
immunogenicity compared with allogenic cells post-transplantation.
However, generating hiPSCs processed from an autologous source can
be costly and time-consuming, while long-term immunosuppression may
be needed if hiPSCs from an allogeneic source are used, despite
some precedence of successful clinical translation (Table III). The major underlying cause
of the immune rejection is the highly polymorphic major
histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, the primary trigger of
T-cell-mediated cytotoxic responses upon the recognition of the
alloantigen presented on antigen-presenting cells.
Recently, a strategy to remove the MHC class I and
II expression, by gene-editing the B2m gene (a structural
component of MHC class-I molecules) and Ciita (the master
regulator of MHC class-II molecules), has been introduced to reduce
the cell-immunogenicity, cloaking the cells from the
immuno-surveillance by T cell-mediated adaptive responses (102). The cells were also engineered to
express CD47 transmembrane protein alone (103) or with immunoregulatory factors
inhibitors, such as program death-ligand 1 and human leucocyte
antigen-G, to better prevent both the T cell- and natural killer
cell-mediated immune responses, as well as macrophage engulfment
(104). These methods have
successfully created universal, allogenic hiPSCs with
‘hypoimmunogenic’, without compromising the cell pluripotency,
differentiation and post-differentiation cell functions, as
demonstrated in humanized animals (genetically or biologically
modified to express human genes or contain human cells, tissues or
organs) post-transplantation in the absence of immunosuppression
(103).
A critical issue concerning the clinical use of
patient-specific hiPSCs is the accumulation of somatic (stem) cell
mutations over an organism's lifetime. Acquired somatic mutations
are passed on to hiPSCs during reprogramming and may be associated
with the loss of cellular functions and cancer formation (105). Cell reprogramming has also been
associated with defective epigenetic reversion and gene expression
changes, which raise safety concerns and the possibility of
treatment failure. hiPSCs would inevitably retain a certain form of
epigenetic memory linked to their parental cells (91). The presence of these epigenetic
signatures would thus skew the differentiation potential of these
cells to their tissue of origin.
Additionally, other studies have determined that
modifications related to neoplastic gene methylation and altered
genomic imprinting are present in hiPSC lines, which can cause
malignant transformation and abnormal differentiation (106,107). Efforts to overcome the genomic
instability of hiPSCs centre on implementing two main approaches:
Genetic screening and the prevention of aberrations. These measures
are crucial in ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of study
outcomes, which at the right time determine the feasibility of
translating hiPSCs to clinical applications.
As abnormalities have been found at various levels
of the genetic hierarchy, the evaluation of hiPSCs is recommended
based on three pillars: Karyotyping for the detection of balanced
aberrations, chromosomal microarray for the identification of copy
number variants and next generation sequencing for the
determination of single nucleotide variants or indels. These
genetic assessments are ideally conducted on each hiPSC line before
being used for research or therapeutic purposes. In the endeavours
to prevent aberrations, recent research has discovered that adding
antioxidant supplements to the culture media of hiPSCs can reduce
genomic instability (108,109). This has been attributed to the
alleviation of the oxidative stress cells are subjected to during
the reprogramming and early passage cultures. Furthermore, research
using small molecules to reprogram cells indicated that this
approach could generate hiPSCs without compromising genomic
stability (110). The mechanism
of action leading to this observation is believed to stem from
initiating the expression of the Zscan4 gene and the
prevention of DNA double-strand breaks (111).
As with the case of reprogramming hiPSCs from CB,
this strategy to repurpose CB to hiPSCs is viewed as advantageous
to prevent genomic instability, as it can exclude any genetic
aberrations accumulated from adult cells, is void of most
epigenetic imprinting and retains the cellular age of a newborn,
thus preserving telomeric length for greater proliferative
capacity. Furthermore, a protocol has been developed to use two
reprogramming factors, OCT3/4 and SOX2, to generate
CB-hiPSCs (72). A recent study
also disclosed that using improved lentiviral vectors with high
efficiency (2–14%) achieved enhancements such as optimized promoter
design, and incorporated genome stabilizers, such as Zscan4, which
could reduce reprogramming-induced mutations (112). This method generated CB-iPSCs
that harbour an average of only 1.3 coding mutations per cell line,
as determined by whole-exome sequencing. These findings
significantly improve the generation and manufacturing procedures
of hiPSCs, and serve as a step forward to bring hiPSCs and their
derivatives to clinical use.
One of the most promising prospects is the
realization of autologous CB-hiPSCs. This will allow patients to
benefit from their own reprogrammed cells, reducing the risk of
immune rejection and improving treatment outcomes. Additionally,
CB-iPSC lines derived from donors with rare blood groups could pave
the way to manufacture blood cells of unique characteristics as
differentiation technologies advance, meeting the demand for
transfusion in patients in need of rare blood (40). Furthermore, analyzing primitive
CB-hiPSCs across different developmental stages may provide
valuable insights into commonly acquired mutations, enhancing our
understanding of genetic changes in human disease development and
aging.
hiPSC technology offers great promising in
regenerative medicine, judging from the pluripotent capability of
the cells to differentiate and regenerate tissues, including those
that were previously considered impossible to regrow. Reprogramming
CB cells into hiPSCs is a viable strategy to expand their use to a
wider range of diseases and reinvent the banking business that
limits the current growth of CB banking services. The formation of
an iPSC haplobank based on the existing cryopreserved CB donations
could serve as a good cell source for regenerative therapy, not
only in the context of allogeneic transplantation, but also as the
foundation for use in autologous tissue regeneration or organ
engineering in future.
Not applicable.
Funding was provided by the Universiti Sains Malaysia Research
University (grant no. 1001/CIPPT/8011101) and a Cryocord Sdn Bhd
Matching Grant (no. 304/CIPPT/6501002/C130).
Not applicable.
FFR, YXY, JJT, SKC, ZG, AP, GCO, KLT, KYT and MNA
contributed to the review conception and design, interpretation and
writing. FFR, YXY and JJT wrote the first draft. SKC, ZG, AP and
JJT reviewed, revised and proofread the manuscript. All authors
read and approved the manuscript. Data authentication is not
applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
JJT received research grants from Cryocord Sdn Bhd
and ALPS Global Holding Bhd. Other authors declare the absence of
any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed
as a potential conflict of interest.
|
1
|
Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HA, Auerbach AD,
Friedman HS, Douglas GW, Devergie A, Esperou H, Thierry D, Socie G,
Lehn P, et al: Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with
Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an
HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 321:1174–1178. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ballen KK, Verter F and Kurtzberg J:
Umbilical cord blood donation: Public or private? Bone Marrow
Transplant. 50:1271–1278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
O'Donnell PV, Brunstein CG, Fuchs EJ,
Zhang MJ, Allbee-Johnson M, Antin JH, Leifer ES, Elmariah H,
Grunwald MR, Hashmi H, et al: Umbilical cord blood or
HLA-haploidentical transplantation: Real-world outcomes versus
randomized trial outcomes. Transplant Cell Ther. 28:109.e1–109.e8.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Álvarez-Palomo B, Veiga A, Raya A,
Codinach M, Torrents S, Ponce Verdugo L, Rodriguez-Aierbe C,
Cuellar L, Alenda R, Arbona C, et al: Public cord blood banks as a
source of starting material for clinical grade HLA-homozygous
induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 13:4082022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Abberton K, Tian P, Elefanty A, Stanley E,
Leslie S, Youngson J, Diviney M, Holdsworth R, Tiedemann K, Little
M and Elwood N: Banked cord blood is a potential source of cells
for deriving induced pluripotent stem cell lines suitable for
cellular therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 7 (Suppl):S132018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hordyjewska A, Popiołek Ł and Horecka A:
Characteristics of hematopoietic stem cells of umbilical cord
blood. Cytotechnology. 67:387–396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Faivre L, Couzin C, Boucher H, Domet T,
Desproges A, Sibony O, Bechard M, Vanneaux V, Larghero J and Cras
A: Associated factors of umbilical cord blood collection quality.
Transfusion. 58:520–531. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nies C and Gottwald E: Artificial
hematopoietic stem cell niches-dimensionality matters. Adv Tissue
Eng Regen Med Open Access. 2:236–247. 2017.
|
|
9
|
Mayani H, Wagner JE and Broxmeyer HE: Cord
blood research, banking, and transplantation: Achievements,
challenges, and perspectives. Bone Marrow Transplant. 55:48–61.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bowie MB, Kent DG, Dykstra B, McKnight KD,
McCaffrey L, Hoodless PA and Eaves CJ: Identification of a new
intrinsically timed developmental checkpoint that reprograms key
hematopoietic stem cell properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:5878–5882. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jung JJ, Buisman SC and de Haan G: Do
hematopoietic stem cells get old? Leukemia. 31:529–531. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jaing TH: Is the benefit-risk ratio for
patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia treated by
unrelated cord blood transplantation favorable? Int J Mol Sci.
18:24722017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Roura S, Pujal JM, Gálvez-Montón C and
Bayes-Genis A: The role and potential of umbilical cord blood in an
era of new therapies: A review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1232015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Szabolcs P, Park KD, Reese M, Marti L,
Broadwater G and Kurtzberg J: Coexistent naïve phenotype and higher
cycling rate of cord blood T cells as compared to adult peripheral
blood. Exp Hematol. 31:708–714. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chalmers IM, Janossy G, Contreras M and
Navarrete C: Intracellular cytokine profile of cord and adult blood
lymphocytes. Blood. 92:11–18. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gluckman E, Rocha V, Arcese W, Michel G,
Sanz G, Chan KW, Takahashi TA, Ortega J, Filipovich A, Locatelli F,
et al: Factors associated with outcomes of unrelated cord blood
transplant: Guidelines for donor choice. Exp Hematol. 32:397–407.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wagner JE and Gluckman E: Umbilical cord
blood transplantation: The first 20 years. Semin Hematol. 47:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kurtzberg J, Laughlin M, Graham ML, Smith
C, Olson JF, Halperin EC, Ciocci G, Carrier C, Stevens CE and
Rubinstein P: Placental blood as a source of hematopoietic stem
cells for transplantation into unrelated recipients. N Engl J Med.
335:157–166. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, Koc ON,
Rizzieri DA, Wagner JE, Gerson SL, Lazarus HM, Cairo M, Stevens CE,
et al: Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients
of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med.
344:1815–1822. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Broxmeyer HE, Lee MR, Hangoc G, Cooper S,
Prasain N, Kim YJ, Mallett C, Ye Z, Witting S, Cornetta K, et al:
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells, and isolation of endothelial progenitors
from 21- to 23.5-year cryopreserved cord blood. Blood.
117:4773–4777. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
World Marrow Donor Association, . Global
Trend Report. 2022.Retrieved from. https://wmda.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/30052023-GTR-2022-Summary-slides.pdfJuly
17–2023
|
|
22
|
Rocha V, Kabbara N, Ionescu I, Ruggeri A,
Purtill D and Gluckman E: Pediatric related and unrelated cord
blood transplantation for malignant diseases. Bone Marrow
Transplant. 44:653–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Herr AL, Kabbara N, Bonfim CMS, Teira P,
Locatelli F, Tiedemann K, Lankester A, Jouet JP, Messina C,
Bertrand Y, et al: Long-term follow-up and factors influencing
outcomes after related HLA-identical cord blood transplantation for
patients with malignancies: An analysis on behalf of Eurocord-EBMT.
Blood. 116:1849–1856. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Marks DI, Woo KA, Zhong X, Appelbaum FR,
Bachanova V, Barker JN, Brunstein CG, Gibson J, Kebriaei P, Lazarus
HM, et al: Unrelated umbilical cord blood transplant for adult
acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first and second complete
remission: A comparison with allografts from adult unrelated
donors. Haematologica. 99:322–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Eapen M, Rubinstein P, Zhang MJ, Stevens
C, Kurtzberg J, Scaradavou A, Loberiza FR, Champlin RE, Klein JP,
Horowitz MM and Wagner JE: Outcomes of transplantation of unrelated
donor umbilical cord blood and bone marrow in children with acute
leukaemia: A comparison study. Lancet. 369:1947–1954. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Eapen M, Wang T, Veys PA, Boelens JJ, St
Martin A, Spellman S, Bonfim CS, Brady C, Cant AJ, Dalle JH, et al:
Allele-level HLA matching for umbilical cord blood transplantation
for non-malignant diseases in children: A retrospective analysis.
Lancet Haematol. 4:e325–e333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Eapen M, Klein JP, Ruggeri A, Spellman S,
Lee SJ, Anasetti C, Arcese W, Barker JN, Baxter-Lowe LA, Brown M,
et al: Impact of allele-level HLA matching on outcomes after
myeloablative single unit umbilical cord blood transplantation for
hematologic malignancy. Blood. 123:133–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Eapen M, Klein JP, Sanz GF, Spellman S,
Ruggeri A, Anasetti C, Brown M, Champlin RE, Garcia-Lopez J,
Hattersely G, et al: Effect of donor-recipient HLA matching at HLA
A, B, C, and DRB1 on outcomes after umbilical-cord blood
transplantation for leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: A
retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 12:1214–1221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Chabannon C,
Basak GW, de la Cámara R, Corbacioglu S, Dolstra H, Duarte R, Glass
B, Greco R, et al: Hematopoietic cell transplantation and cellular
therapy survey of the EBMT: Monitoring of activities and trends
over 30 years. Bone Marrow Transplant. 56:1651–1664. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dehn J, Spellman S, Hurley CK, Shaw BE,
Barker JN, Burns LJ, Confer DL, Eapen M, Fernandez-Vina M, Hartzman
R, et al: Selection of unrelated donors and cord blood units for
hematopoietic cell transplantation: Guidelines from the
NMDP/CIBMTR. Blood. 134:924–934. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gragert L, Eapen M, Williams E, Freeman J,
Spellman S, Baitty R, Hartzman R, Rizzo JD, Horowitz M, Confer D
and Maiers M: HLA match likelihoods for hematopoietic stem-cell
grafts in the U.S. registry. N Engl J Med. 371:339–348. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kanda J, Ichinohe T, Kato S, Uchida N,
Terakura S, Fukuda T, Hidaka M, Ueda Y, Kondo T, Taniguchi S, et
al: Unrelated cord blood transplantation vs related transplantation
with HLA 1-antigen mismatch in the graft-versus-host direction.
Leukemia. 27:286–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Laughlin MJ, Eapen M, Rubinstein P, Wagner
JE, Zhang MJ, Champlin RE, Stevens C, Barker JN, Gale RP, Lazarus
HM, et al: Outcomes after transplantation of cord blood or bone
marrow from unrelated donors in adults with leukemia. N Engl J Med.
351:2265–2275. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Politikos I, Davis E, Nhaissi M, Wagner
JE, Brunstein CG, Cohen S, Shpall EJ, Milano F, Scaradavou A and
Barker JN; American Society for Transplantation and Cellular
Therapy Cord Blood Special Interest Group, : Guidelines for cord
blood unit selection. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 26:2190–2196.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rocha V and Gluckman E; Eurocord-Netcord
registry, European Blood and Marrow Transplant Group, : Improving
outcomes of cord blood transplantation: HLA matching, cell dose and
other graft- and transplantation-related factors. Br J Haematol.
147:262–274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ruggeri A: Optimizing cord blood
selection. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2019:522–531.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Querol S, Mufti GJ, Marsh SG, Pagliuca A,
Little AM, Shaw BE, Jeffery R, Garcia J, Goldman JM and Madrigal
JA: Cord blood stem cells for hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation in the UK: How big should the bank be?
Haematologica. 94:536–541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wagner JE, Barker JN, DeFor TE, Baker KS,
Blazar BR, Eide C, Goldman A, Kersey J, Krivit W, MacMillan ML, et
al: Transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood in 102
patients with malignant and nonmalignant diseases: influence of
CD34 cell dose and HLA disparity on treatment-related mortality and
survival. Blood. 100:1611–1618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Barker JN, Scaradavou A and Stevens CE:
Combined effect of total nucleated cell dose and HLA match on
transplantation outcome in 1061 cord blood recipients with
hematologic malignancies. Blood. 115:1843–1849. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tan JJ: Cord blood with low cell count:
Re-use, rather than discard. Single Cell Biol. 6:32017.
|
|
41
|
Magalon J, Maiers M, Kurtzberg J,
Navarrete C, Rubinstein P, Brown C, Schramm C, Larghero J,
Katsahian S, Chabannon C, et al: Banking or bankrupting: Strategies
for sustaining the economic future of public cord blood banks. PLoS
One. 10:e01434402015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Marotta D, Rao C and Fossati V: Human
induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) handling protocols:
Maintenance, expansion, and cryopreservation. In: Induced
pluripotent stem (iPS) cells: Methods and protocols. Springer; New
York, NY: pp. 1–15. 2021
|
|
43
|
Natunen S, Satomaa T, Pitkänen V, Salo H,
Mikkola M, Natunen J, Otonkoski T and Valmu L: The binding
specificity of the marker antibodies Tra-1–60 and Tra-1–81 reveals
a novel pluripotency-associated type 1 lactosamine epitope.
Glycobiology. 21:1125–1130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Horwitz ME, Stiff PJ, Cutler C, Brunstein
C, Hanna R, Maziarz RT, Rezvani AR, Karris NA, McGuirk J, Valcarcel
D, et al: Omidubicel vs standard myeloablative umbilical cord blood
transplantation: Results of a phase 3 randomized study. Blood.
138:1429–1440. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cohen S, Roy J, Lachance S, Delisle JS,
Marinier A, Busque L, Roy DC, Barabé F, Ahmad I, Bambace N, et al:
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using single UM171-expanded
cord blood: a single-arm, phase 1–2 safety and feasibility study.
Lancet Haematol. 7:e134–e145. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Stiff PJ, Montesinos P, Peled T, Landau E,
Goudsmid NR, Mandel J, Hasson N, Olesinski E, Glukhman E, Snyder
DA, et al: Cohort-controlled comparison of umbilical cord blood
transplantation using carlecortemcel-L, a single
progenitor-enriched cord blood, to double cord blood unit
transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 24:1463–1470. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Anand S, Thomas S, Hyslop T, Adcock J,
Corbet K, Gasparetto C, Lopez R, Long GD, Morris AK, Rizzieri DA,
et al: Transplantation of ex vivo expanded umbilical cord blood
(NiCord) decreases early infection and hospitalization. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant. 23:1151–1157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Horwitz ME, Wease S, Blackwell B,
Valcarcel D, Frassoni F, Boelens JJ, Nierkens S, Jagasia M, Wagner
JE, Kuball J, et al: Phase I/II study of stem-cell transplantation
using a single cord blood unit expanded ex vivo with nicotinamide.
J Clin Oncol. 37:367–374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wagner JE Jr, Brunstein CG, Boitano AE,
DeFor TE, McKenna D, Sumstad D, Blazar BR, Tolar J, Le C, Jones J,
et al: Phase I/II trial of stemregenin-1 expanded umbilical cord
blood hematopoietic stem cells supports testing as a stand-alone
graft. Cell Stem Cell. 18:144–155. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
de Lima M, McNiece I, Robinson SN, Munsell
M, Eapen M, Horowitz M, Alousi A, Saliba R, McMannis JD, Kaur I, et
al: Cord-blood engraftment with ex vivo mesenchymal-cell coculture.
N Engl J Med. 367:2305–2315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Horwitz ME, Chao NJ, Rizzieri DA, Long GD,
Sullivan KM, Gasparetto C, Chute JP, Morris A, McDonald C,
Waters-Pick B, et al: Umbilical cord blood expansion with
nicotinamide provides long-term multilineage engraftment. J Clin
Invest. 124:3121–3128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Delaney C, Heimfeld S, Brashem-Stein C,
Voorhies H, Manger RL and Bernstein ID: Notch-mediated expansion of
human cord blood progenitor cells capable of rapid myeloid
reconstitution. Nat Med. 16:232–236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Saiyin T, Kirkham AM, Bailey AJM, Shorr R,
Pineault N, Maganti HB and Allan DS: Clinical outcomes of umbilical
cord blood transplantation using ex vivo expansion: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Transplant Cell
Ther. 29:129.e1–129.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Fares I, Chagraoui J, Gareau Y, Gingras S,
Rjean R, Csaszar E, Cohen S, Anne M, Zandstra PW and Sauvageau G:
UM171 is a novel and potent agonist of human hematopoietic stem
cell renewal. Blood. 122:7982013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Peled T, Shoham H, Aschengrau D, Yackoubov
D, Frei G, Rosenheimer GN, Lerrer B, Cohen HY, Nagler A, Fibach E
and Peled A: Nicotinamide, a SIRT1 inhibitor, inhibits
differentiation and facilitates expansion of hematopoietic
progenitor cells with enhanced bone marrow homing and engraftment.
Exp Hematol. 40:342–355.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
de Lima M, McMannis J, Gee A, Komanduri K,
Couriel D, Andersson BS, Hosing C, Khouri I, Jones R, Champlin R,
et al: Transplantation of ex vivo expanded cord blood cells using
the copper chelator tetraethylenepentamine: a phase I/II clinical
trial. Bone Marrow Transplant. 41:771–778. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Mehta RS, Saliba RM, Cao K, Kaur I,
Rezvani K, Chen J, Olson A, Parmar S, Shah N, Marin D, et al: Ex
vivo mesenchymal precursor cell-expanded cord blood transplantation
after reduced-intensity conditioning regimens improves time to
neutrophil recovery. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 23:1359–1366.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Bregni M, Cesaro
S, Dreger P, Duarte RF, Falkenburg JH, Kröger N, Farge-Bancel D,
Gaspar HB, et al: Hematopoietic SCT in Europe: Data and trends in
2011. Bone Marrow Transplant. 48:1161–1167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Iida M, Dodds A, Akter M, Srivastava A,
Moon JH, Dung PC, Bravo MR, Gyi AA, Jayathilake D, Liu K, et al:
The 2016 APBMT activity survey report: Trends in haploidentical and
cord blood transplantation in the Asia-Pacific region. Blood Cell
Ther. 4:20–28. 2021.
|
|
60
|
Niederwieser D, Baldomero H, Bazuaye N,
Bupp C, Chaudhri N, Corbacioglu S, Elhaddad A, Frutos C, Galeano S,
Hamad N, et al: One and a half million hematopoietic stem cell
transplants: Continuous and differential improvement in worldwide
access with the use of non-identical family donors. Haematologica.
107:1045–1053. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Fuchs EJ, O'Donnell PV, Eapen M, Logan B,
Antin JH, Dawson P, Devine S, Horowitz MM, Horwitz ME, Karanes C,
et al: Double unrelated umbilical cord blood vs HLA-haploidentical
bone marrow transplantation: the BMT CTN 1101 trial. Blood.
137:420–428. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Savani B,
Paviglianiti A, Blaise D, Volt F, Ciceri F, Bacigalupo A, Tischer
J, Chevallier P, et al: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
with unrelated cord blood or haploidentical donor grafts in adult
patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia, a comparative study
from Eurocord and the ALWP EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant.
54:1987–1994. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Konuma T, Kanda J, Yamasaki S, Harada K,
Shimomura Y, Terakura S, Mizuno S, Uchida N, Tanaka M, Doki N, et
al: Single cord blood transplantation versus unmanipulated
haploidentical transplantation for adults with acute myeloid
leukemia in complete remission. Transplant Cell Ther.
27:334.e1–334.e11. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wieduwilt MJ, Metheny L, Zhang MJ, Wang
HL, Estrada-Merly N, Marks DI, Al-Homsi AS, Muffly L, Chao N,
Rizzieri D, et al: Haploidentical vs sibling, unrelated, or cord
blood hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Blood Adv. 6:339–357. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tarazi S, Aguilera-Castrejon A, Joubran C,
Ghanem N, Ashouokhi S, Roncato F, Wildschutz E, Haddad M, Oldak B,
Gomez-Cesar E, et al: Post-gastrulation synthetic embryos generated
ex utero from mouse naive ESCs. Cell. 185:3290–3306.e25. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Abberton KM, McDonald TL, Diviney M,
Holdsworth R, Leslie S, Delatycki MB, Liu L, Klamer G, Johnson P
and Elwood NJ: Identification and Re-consent of existing cord blood
donors for creation of induced pluripotent stem cell lines for
potential clinical applications. Stem Cells Transl Med.
11:1052–1060. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ye Z, Zhan H, Mali P, Dowey S, Williams
DM, Jang YY, Dang CV, Spivak JL, Moliterno AR and Cheng L:
Human-induced pluripotent stem cells from blood cells of healthy
donors and patients with acquired blood disorders. Blood.
114:5473–5480. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Takenaka C, Nishishita N, Takada N, Jakt
LM and Kawamata S: Effective generation of iPS cells from CD34+
cord blood cells by inhibition of p53. Exp Hematol. 38:154–162.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Haase A, Olmer R, Schwanke K, Wunderlich
S, Merkert S, Hess C, Zweigerdt R, Gruh I, Meyer J, Wagner S, et
al: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord
blood. Cell Stem Cell. 5:434–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Dorn I, Klich K, Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Radstaak
M, Santourlidis S, Ghanjati F, Radke TF, Psathaki OE, Hargus G,
Kramer J, et al: Erythroid differentiation of human induced
pluripotent stem cells is independent of donor cell type of origin.
Haematologica. 100:32–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Giorgetti A, Montserrat N, Rodriguez-Piza
I, Azqueta C, Veiga A and Izpisúa Belmonte JC: Generation of
induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood cells with
only two factors: Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Protoc. 5:811–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chou BK, Mali P, Huang X, Ye Z, Dowey SN,
Resar LM, Zou C, Zhang YA, Tong J and Cheng L: Efficient human iPS
cell derivation by a non-integrating plasmid from blood cells with
unique epigenetic and gene expression signatures. Cell Res.
21:518–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ban H, Nishishita N, Fusaki N, Tabata T,
Saeki K, Shikamura M, Takada N, Inoue M, Hasegawa M, Kawamata S and
Nishikawa S: Efficient generation of transgene-free human induced
pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by temperature-sensitive Sendai
virus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:14234–14239. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Arellano-Viera E, Zabaleta L, Castaño J,
Azkona G, Carvajal-Vergara X and Giorgetti A: Generation of two
transgene-free human iPSC lines from CD133+ cord blood
cells. Stem Cell Res. 36:1014102019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Tian P, Elefanty A, Stanley EG, Durnall
JC, Thompson LH and Elwood NJ: Creation of GMP-compliant iPSCs from
banked umbilical cord blood. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8353212022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Gao X, Yourick JJ and Sprando RL:
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of endothelial progenitor cells
derived from umbilical cord blood and adult peripheral blood:
Implications for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells.
Stem Cell Res. 25:202–212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Gao X, Yourick JJ and Sprando RL:
Generation of nine induced pluripotent stem cell lines as an ethnic
diversity panel. Stem Cell Res. 31:193–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Wang Q, Wang Y, Chang C, Ma F, Peng D,
Yang S, An Y, Deng Q, Wang Q, Gao F, et al: Comparative analysis of
mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from human induced
pluripotent stem cells and the cognate umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells. Heliyon. 9:e126832023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Kane NM, Nowrouzi A, Mukherjee S, Blundell
MP, Greig JA, Lee WK, Houslay MD, Milligan G, Mountford JC, von
Kalle C, et al: Lentivirus-mediated reprogramming of somatic cells
in the absence of transgenic transcription factors. Mol Ther.
18:2139–2145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Shadid M, Shrestha A and Malik P:
Preclinical safety assessment of modified gamma globin lentiviral
vector-mediated autologous hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for
hemoglobinopathies. PLoS One. 19:e03067192024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Thompson AA, Walters MC, Kwiatkowski J,
Rasko JEJ, Ribeil JA, Hongeng S, Magrin E, Schiller GJ, Payen E,
Semeraro M, et al: Gene therapy in patients with
transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 378:1479–1493.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Kunitomi A, Hirohata R, Arreola V, Osawa
M, Kato TM, Nomura M, Kawaguchi J, Hara H, Kusano K, Takashima Y,
et al: Improved Sendai viral system for reprogramming to naive
pluripotency. Cell Rep Methods. 2:1003172022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Kunitomi A, Hirohata R, Osawa M, Washizu
K, Arreola V, Saiki N, Kato TM, Nomura M, Kunitomi H, Ohkame T, et
al: H1FOO-DD promotes efficiency and uniformity in reprogramming to
naive pluripotency. Stem Cell Reports. 19:710–728. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Yoshioka N, Gros E, Li HR, Kumar S, Deacon
DC, Maron C, Muotri AR, Chi NC, Fu XD, Yu BD and Dowdy SF:
Efficient generation of human iPSCs by a synthetic self-replicative
RNA. Cell Stem Cell. 13:246–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Judson RL, Babiarz JE, Venere M and
Blelloch R: Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced
pluripotency. Nat Biotechnol. 27:459–461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu C, Guan J, Li H,
Zhao T, Ye J, Yang W, Liu K, et al: Pluripotent stem cells induced
from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds. Science.
341:651–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Qin J, Zhang J, Jiang J, Zhang B, Li J,
Lin X, Wang S, Zhu M, Fan Z, Lv Y, et al: Direct chemical
reprogramming of human cord blood erythroblasts to induced
megakaryocytes that produce platelets. Cell Stem Cell.
29:1229–1245.e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Kajiwara M, Aoi T, Okita K, Takahashi R,
Inoue H, Takayama N, Endo H, Eto K, Toguchida J, Uemoto S and
Yamanaka S: Donor-dependent variations in hepatic differentiation
from human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:12538–12543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Kim K, Zhao R, Doi A, Ng K, Unternaehrer
J, Cahan P, Huo H, Loh YH, Aryee MJ, Lensch MW, et al: Donor cell
type can influence the epigenome and differentiation potential of
human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 29:1117–1119.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Sanchez-Freire V, Lee AS, Hu S, Abilez OJ,
Liang P, Lan F, Huber BC, Ong SG, Hong WX, Huang M and Wu JC:
Effect of human donor cell source on differentiation and function
of cardiac induced pluripotent stem cells. J Am Coll Cardiol.
64:436–448. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Streckfuss-Bömeke K, Wolf F, Azizian A,
Stauske M, Tiburcy M, Wagner S, Hübscher D, Dressel R, Chen S,
Jende J, et al: Comparative study of human-induced pluripotent stem
cells derived from bone marrow cells, hair keratinocytes, and skin
fibroblasts. Eur Heart J. 34:2618–2629. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Kyttälä A, Moraghebi R, Valensisi C,
Kettunen J, Andrus C, Pasumarthy KK, Nakanishi M, Nishimura K,
Ohtaka M, Weltner J, et al: Genetic variability overrides the
impact of parental cell type and determines iPSC differentiation
potential. Stem Cell Reports. 6:200–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Lo Sardo V, Ferguson W, Erikson GA, Topol
EJ, Baldwin KK and Torkamani A: Influence of donor age on induced
pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 35:69–74. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Chang CJ, Mitra K, Koya M, Velho M,
Desprat R, Lenz J and Bouhassira EE: Production of embryonic and
fetal-like red blood cells from human induced pluripotent stem
cells. PLoS One. 6:e257612011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Lee S, Huh JY, Turner DM, Lee S, Robinson
J, Stein JE, Shim SH, Hong CP, Kang MS, Nakagawa M, et al:
Repurposing the cord blood bank for haplobanking of HLA-homozygous
iPSCs and their usefulness to multiple populations. Stem Cells.
36:1552–1566. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Shin S, Song EY, Kwon YW, Oh S, Park H,
Kim NH and Roh EY: Usefulness of the hematopoietic stem cell donor
pool as a source of HLA-homozygous induced pluripotent stem cells
for haplobanking: Combined analysis of the cord blood inventory and
bone marrow donor registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.
26:e202–e208. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Yoshida S, Kato TM, Sato Y, Umekage M,
Ichisaka T, Tsukahara M, Takasu N and Yamanaka S: A clinical-grade
HLA haplobank of human induced pluripotent stem cells matching
approximately 40% of the Japanese population. Med. 4:51–66.e10.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Alvarez-Palomo B, Garcia-Martinez I,
Gayoso J, Raya A, Veiga A, Abad ML, Eiras A, Guzmán-Fulgencio M,
Luis-Hidalgo M, Eguizabal C, et al: Evaluation of the Spanish
population coverage of a prospective HLA haplobank of induced
pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:2332021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Sullivan S, Ginty P, McMahon S, May M,
Solomon SL, Kurtz A, Stacey GN, Bennaceur Griscelli A, Li RA, Barry
J, et al: The global alliance for iPSC therapies (GAiT). Stem Cell
Res. 49:1020362020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Meissner TB, Schulze HS and Dale SM:
Immune editing: Overcoming immune barriers in stem cell
transplantation. Curr Stem Cell Rep. 8:206–218. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Deuse T, Hu X, Gravina A, Wang D,
Tediashvili G, De C, Thayer WO, Wahl A, Garcia JV, Reichenspurner
H, et al: Hypoimmunogenic derivatives of induced pluripotent stem
cells evade immune rejection in fully immunocompetent allogeneic
recipients. Nat Biotechnol. 37:252–258. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Han X, Wang M, Duan S, Franco PJ, Kenty
JH, Hedrick P, Xia Y, Allen A, Ferreira LMR, Strominger JL, et al:
Generation of hypoimmunogenic human pluripotent stem cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:10441–10446. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Popp B, Krumbiegel M, Grosch J, Sommer A,
Uebe S, Kohl Z, Plötz S, Farrell M, Trautmann U, Kraus C, et al:
Need for high-resolution genetic analysis in iPSC: Results and
lessons from the ForIPS consortium. Sci Rep. 8:172012018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Ohm JE, Mali P, Van Neste L, Berman DM,
Liang L, Pandiyan K, Briggs KJ, Zhang W, Argani P, Simons B, et al:
Cancer-related epigenome changes associated with reprogramming to
induced pluripotent stem cells. Cancer Res. 70:7662–7673. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Pick M, Stelzer Y, Bar-Nur O, Mayshar Y,
Eden A and Benvenisty N: Clone- and gene-specific aberrations of
parental imprinting in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem
Cells. 27:2686–2690. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Ji J, Sharma V, Qi S, Guarch ME, Zhao P,
Luo Z, Fan W, Wang Y, Mbabaali F, Neculai D, et al: Antioxidant
supplementation reduces genomic aberrations in human induced
pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2:44–51. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Luo L, Kawakatsu M, Guo CW, Urata Y, Huang
WJ, Ali H, Doi H, Kitajima Y, Tanaka T, Goto S, et al: Effects of
antioxidants on the quality and genomic stability of induced
pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep. 4:37792014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Park HS, Hwang I, Choi KA, Jeong H, Lee JY
and Hong S: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without
genetic defects by small molecules. Biomaterials. 39:47–58. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Akiyama T, Ishiguro KI, Chikazawa N, Ko
SBH, Yukawa M and Ko MSH: ZSCAN4-binding motif-TGCACAC is conserved
and enriched in CA/TG microsatellites in both mouse and human
genomes. DNA Res. 31:dsad0292024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Su RJ, Yang Y, Neises A, Payne KJ, Wang J,
Viswanathan K, Wakeland EK, Fang X and Zhang XB: Few single
nucleotide variations in exomes of human cord blood induced
pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 8:e599082013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Butler MG and Menitove JE: Umbilical cord
blood banking: An update. J Assist Reprod Genet. 28:669–676. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|