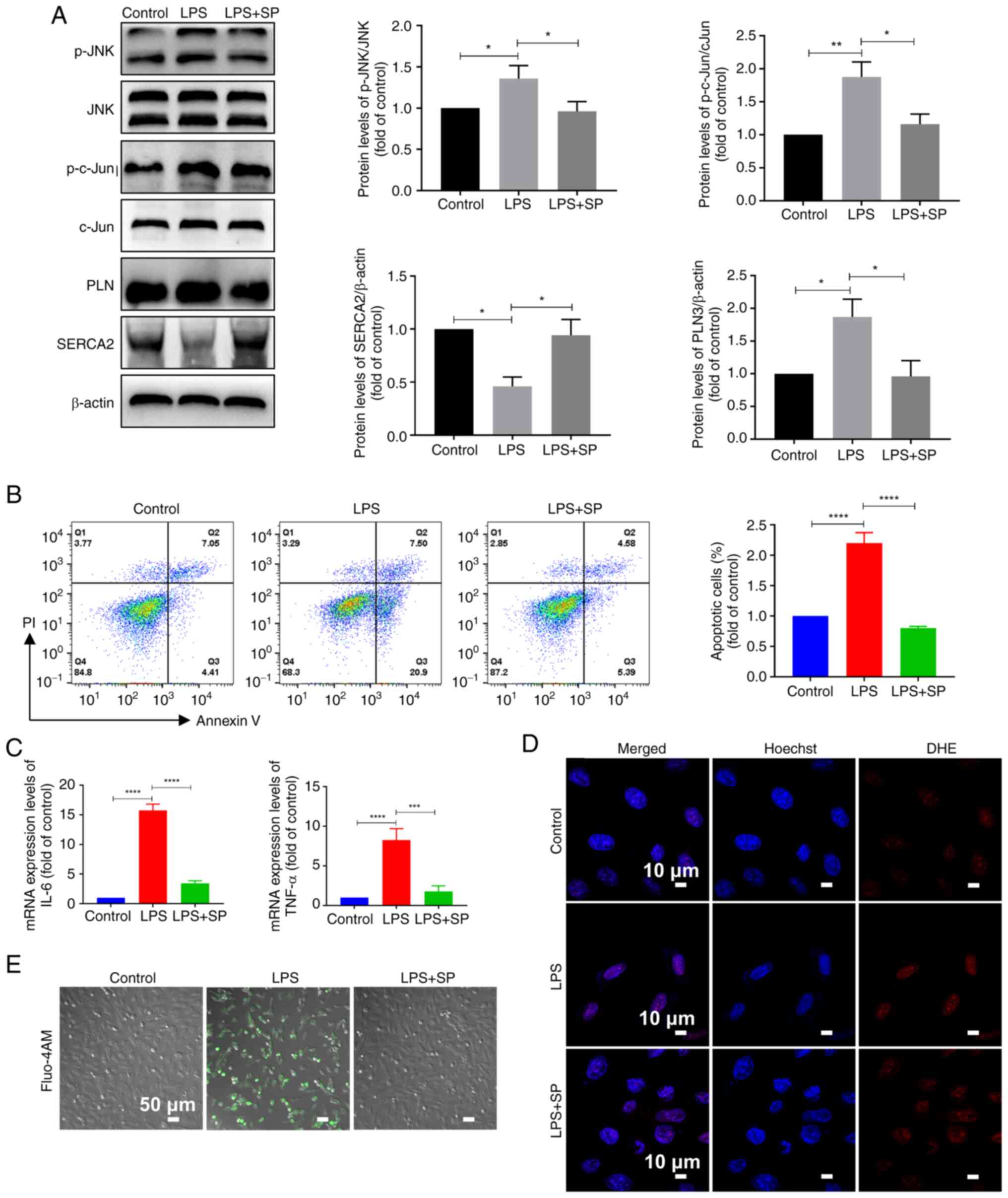
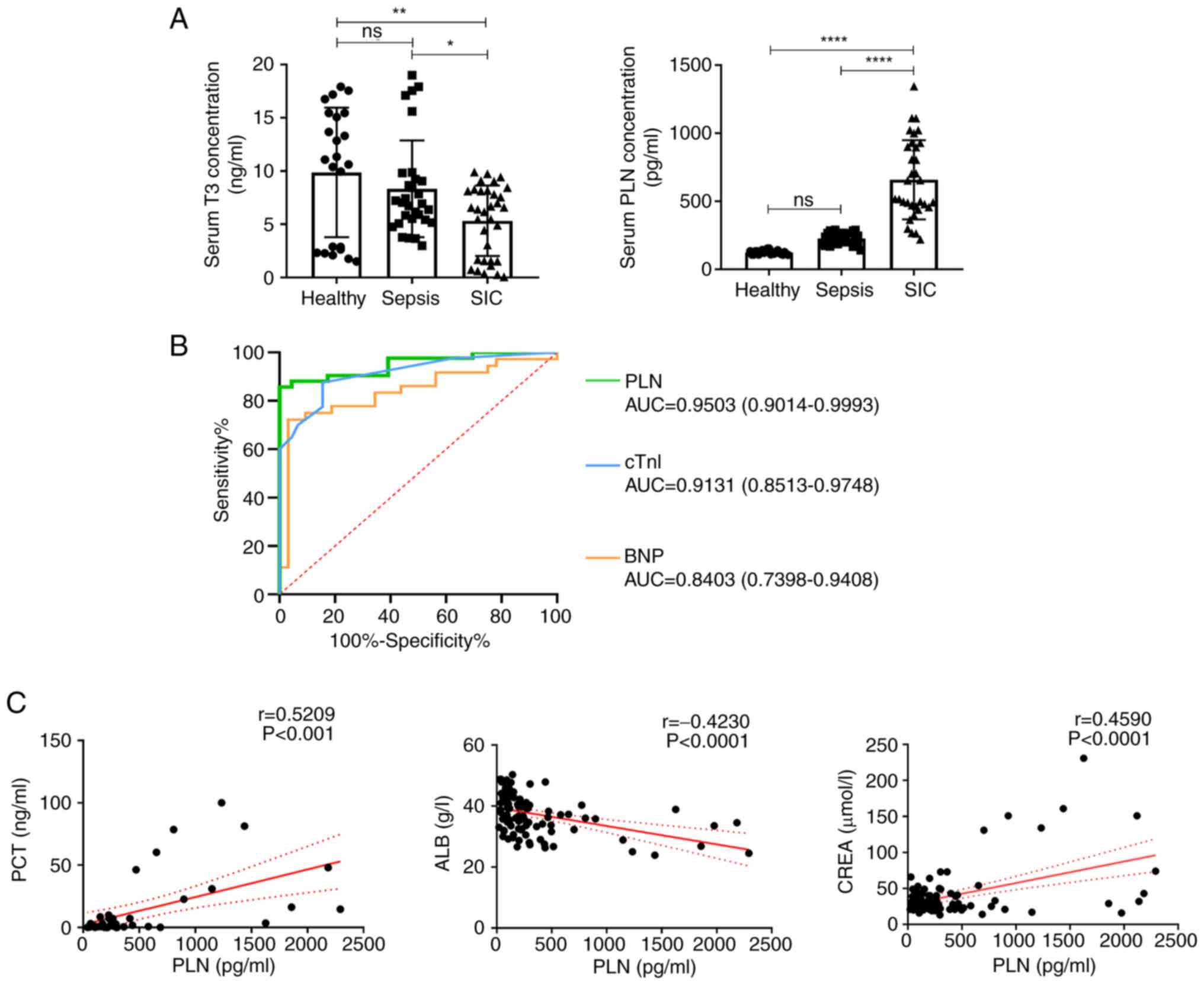
|
1
|
Singh S, Mohan S and Singhal R:
Definitions for sepsis and septic shock. JAMA. 316:4582016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gohil SK, Cao C, Phelan M, Tjoa T, Rhee C,
Platt R and Huang SS: Impact of policies on the rise in sepsis
incidence, 2000-2010. Clin Infect Dis. 62:695–703. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mahla RS, Vincent JL and Sakr Y; ICON and
SOAP Investigators: Sepsis is a global burden to human health:
Incidences are underrepresented: Discussion on 'comparison of
European ICU patients in 2012 (ICON) versus 2002 (SOAP)'. Intensive
Care Med. 44:1197–1198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki T, Suzuki Y, Okuda J, Kurazumi T,
Suhara T, Ueda T, Nagata H and Morisaki H: Sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction and β-adrenergic blockade therapy for sepsis. J
Intensive Care. 5:222017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Allison SJ: Sepsis: NET-induced
coagulation induces organ damage in sepsis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
13:1332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weiss SL, Peters MJ, Alhazzani W, Agus
MSD, Flori HR, Inwald DP, Nadel S, Schlapbach LJ, Tasker RC, Argent
AC, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for
the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ
dysfunction in children. Intensive Care Med. 46(Suppl 1): S10–S67.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hollenberg SM and Singer M:
Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol.
18:424–434. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ehrman RR, Sullivan AN, Favot MJ, Sherwin
RL, Reynolds CA, Abidov A and Levy PD: Pathophysiology,
echocardiographic evaluation, biomarker findings, and prognostic
implications of septic cardiomyopathy: A review of the literature.
Crit Care. 22:1122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Melis MJ, Miller M, Peters VBM and Singer
M: The role of hormones in sepsis: An integrated overview with a
focus on mitochondrial and immune cell dysfunction. Clin Sci
(Lond). 137:707–725. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Das BK, Agarwal P, Agarwal JK and Mishra
OP: Serum cortisol and thyroid hormone levels in neonates with
sepsis. Indian J Pediatr. 69:663–665. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vidart J, Axelrud L, Braun AC, Marschner
RA and Wajner SM: Relationship among low T3 levels, type 3
deiodinase, oxidative stress, and mortality in sepsis and septic
shock: Defining patient outcomes. Int J Mol Sci. 24:39352023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jongejan RMS, Meima ME, Visser WE,
Korevaar TIM, Van Den Berg SAA, Peeters RP and de Rijke YB: Binding
characteristics of thyroid hormone distributor proteins to thyroid
hormone metabolites. Thyroid. 32:990–999. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salas-Lucia F and Bianco AC: T3 levels and
thyroid hormone signaling. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13:10446912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cokkinos DV and Chryssanthopoulos S:
Thyroid hormones and cardiac remodeling. Heart Fail Rev.
21:365–372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mastorci F, Sabatino L, Vassalle C and
Pingitore A: Cardioprotection and thyroid hormones in the clinical
setting of heart failure. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:9272020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang R, Xu Y, Fang Y, Wang C, Xue Y, Wang
F, Cheng J, Ren H, Wang J, Guo W, et al: Pathogenetic mechanisms of
septic cardiomyopathy. J Cell Physiol. 237:49–58. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shankar TS, Ramadurai DKA, Steinhorst K,
Sommakia S, Badolia R, Thodou Krokidi A, Calder D, Navankasattusas
S, Sander P, Kwon OS, et al: Cardiac-specific deletion of voltage
dependent anion channel 2 leads to dilated cardiomyopathy by
altering calcium homeostasis. Nat Commun. 12:45832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Capasso JM, Sonnenblick EH and Anversa P:
Chronic calcium channel blockade prevents the progression of
myocardial contractile and electrical dysfunction in the
cardiomyopathic Syrian hamster. Circ Res. 67:1381–1393. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Selnø ATH, Sumbayev VV and Gibbs BF:
IgE-dependent human basophil responses are inversely associated
with the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA).
Front Immunol. 13:10522902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Myles RC, Lee IJ, Bers DM and
Ripplinger CM: Role of reduced sarco-endoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+-ATPase function on sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ alternans in the intact rabbit heart. Front
Physiol. 12:6565162021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Carlson CR, Aronsen JM, Bergan-Dahl A,
Moutty MC, Lunde M, Lunde PK, Jarstadmarken H, Wanichawan P,
Pereira L, Kolstad TRS, et al: AKAP18δ anchors and regulates CaMKII
activity at phospholamban-SERCA2 and RYR. Circ Res. 130:27–44.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hamstra SI, Whitley KC, Baranowski RW,
Kurgan N, Braun JL, Messner HN and Fajardo VA: The role of
phospholamban and GSK3 in regulating rodent cardiac SERCA function.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 319:C694–C699. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kranias EG and Hajjar RJ: Modulation of
cardiac contractility by the phospholamban/SERCA2a regulatome. Circ
Res. 110:1646–1660. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sivakumaran V, Stanley BA, Tocchetti CG,
Ballin JD, Caceres V, Zhou L, Keceli G, Rainer PP, Lee DI, Huke S,
et al: HNO enhances SERCA2a activity and cardiomyocyte function by
promoting redox-dependent phospholamban oligomerization. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 19:1185–1197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lygren B, Carlson CR, Santamaria K,
Lissandron V, McSorley T, Litzenberg J, Lorenz D, Wiesner B,
Rosenthal W, Zaccolo M, et al: AKAP complex regulates Ca2+
re-uptake into heart sarcoplasmic reticulum. EMBO Rep. 8:1061–1067.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Steinberg C, Roston TM, Van der Werf C,
Sanatani S, Chen SRW, Wilde AAM and Krahn AD:
RYR2-ryanodinopathies: From calcium overload to calcium deficiency.
Europace. 25:euad1562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strubbe-Rivera JO, Schrad JR, Pavlov EV,
Conway JF, Parent KN and Bazil JN: The mitochondrial permeability
transition phenomenon elucidated by cryo-EM reveals the genuine
impact of calcium overload on mitochondrial structure and function.
Sci Rep. 11:10372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reddy LG, Autry JM, Jones LR and Thomas
DD: Co-reconstitution of phospholamban mutants with the Ca-ATPase
reveals dependence of inhibitory function on phospholamban
structure. J Biol Chem. 274:7649–7655. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin J, Zhang J, Lin L, Haji-Ghassemi O,
Lin Z, Woycechowsky KJ, Van Petegem F, Zhang Y and Yuchi Z:
Structures of PKA-phospholamban complexes reveal a mechanism of
familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Elife. 11:e753462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Feyen DAM, Perea-Gil I, Maas RGC,
Harakalova M, Gavidia AA, Arthur Ataam J, Wu TH, Vink A, Pei J,
Vadgama N, et al: Unfolded protein response as a compensatory
mechanism and potential therapeutic target in PLN R14del
cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 144:382–392. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sinha RA and Yen PM: Metabolic messengers:
Thyroid hormones. Nat Metab. 6:639–650. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLoS Boil. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Feng X, Wang L, Zhou R, Zhou R, Chen L,
Peng H, Huang Y, Guo Q, Luo X and Zhou H: Senescent immune cells
accumulation promotes brown adipose tissue dysfunction during
aging. Nat Commun. 14:32082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang J, Zhou D, Zhang A, Yu W, Du L, Yuan
H, Zhang C, Wang Z, Jia X, Zhang ZN and Luan B: Thermogenic
adipocyte-derived zinc promotes sympathetic innervation in male
mice. Nat Metab. 5:481–494. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mahmood SR, Xie X, Hosny El Said N, Venit
T, Gunsalus KC and Percipalle P: β-actin dependent chromatin
remodeling mediates compartment level changes in 3D genome
architecture. Nat Commun. 12:52402021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hunter T and Garrels JI: Characterization
of the mRNAs for alpha-, beta- and gamma-actin. Cell. 12:767–781.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang L and Elias JE: Relative protein
quantification using tandem mass tag mass spectrometry. Methods Mol
Biol. 1550:185–198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pantos C, Malliopoulou V, Paizis I,
Moraitis P, Mourouzis I, Tzeis S, Karamanoli E, Cokkinos DD,
Carageorgiou H, Varonos D and Cokkinos DV: Thyroid hormone and
cardioprotection: study of p38 MAPK and JNKs during ischaemia and
at reperfusion in isolated rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem.
242:173–180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lieder HR, Braczko F, Gedik N, Stroetges
M, Heusch G and Kleinbongard P: Cardioprotection by
post-conditioning with exogenous triiodothyronine in isolated
perfused rat hearts and isolated adult rat cardiomyocytes. Basic
Res Cardiol. 116:272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vafiadaki E, Haghighi K, Arvanitis DA,
Kranias EG and Sanoudou D: Aberrant PLN-R14del protein interactions
intensify SERCA2a inhibition, driving impaired Ca2+
handling and arrhythmogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:69472022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stege NM, de Boer RA, Makarewich CA, van
der Meer P and Silljé HHW: Reassessing the mechanisms of PLN-R14del
cardiomyopathy: From calcium dysregulation to S/ER malformation.
JACC Basic Transl Sci. 9:1041–1052. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dong J, Gao C, Liu J, Cao Y and Tian L:
TSH inhibits SERCA2a and the PKA/PLN pathway in rat cardiomyocytes.
Oncotarget. 7:39207–39215. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gaique TG, Lopes BP, Souza LL, Paula GSM,
Pazos-Moura CC and Oliveira KJ: Cinnamon intake reduces serum T3
level and modulates tissue-specific expression of thyroid hormone
receptor and target genes in rats. J Sci Food Agric. 96:2889–2895.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mattiazzi A, Tardiff JC and Kranias EG:
Stress seats a new guest at the table of PLN/SERCA and their
partners. Circ Res. 128:471–473. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zeng B, Liao X, Liu L, Zhang C, Ruan H and
Yang B: Thyroid hormone mediates cardioprotection against
postinfarction remodeling and dysfunction through the
IGF-1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Life Sci. 267:1189772021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
de Castro AL, Fernandes RO, Ortiz VD,
Campos C, Bonetto JH, Fernandes TR, Conzatti A, Siqueira R, Tavares
AV, Schenkel PC, et al: Thyroid hormones improve cardiac function
and decrease expression of pro-apoptotic proteins in the heart of
rats 14 days after infarction. Apoptosis. 21:184–194. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Brennan A, Leech JT, Kad NM and Mason JM:
Selective antagonism of cJun for cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 39:1842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vernia S, Morel C, Madara JC,
Cavanagh-Kyros J, Barrett T, Chase K, Kennedy NJ, Jung DY, Kim JK,
Aronin N, et al: Excitatory transmission onto AgRP neurons is
regulated by cJun NH2-terminal kinase 3 in response to metabolic
stress. Elife. 5:e100312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Manieri E, Folgueira C, Rodríguez ME,
Leiva-Vega L, Esteban-Lafuente L, Chen C, Cubero FJ, Barrett T,
Cavanagh-Kyros J, Seruggia D, et al: JNK-mediated disruption of
bile acid homeostasis promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:16492–16499. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang J, Do-Umehara HC, Zhang Q, Wang H,
Hou C, Dong H, Perez EA, Sala MA, Anekalla KR, Walter JM, et al:
miR-221-5p-mediated downregulation of JNK2 aggravates acute lung
injury. Front Immunol. 12:7009332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jaeschke A, Karasarides M, Ventura JJ,
Ehrhardt A, Zhang C, Flavell RA, Shokat KM and Davis RJ: JNK2 is a
positive regulator of the cJun transcription factor. Mol Cell.
23:899–911. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chin KY, Silva LS, Darby IA, Ng DCH and
Woodman OL: Protection against reperfusion injury by
3′,4′-dihydroxyflavonol in rat isolated hearts involves inhibition
of phospholamban and JNK2. Int J Cardiol. 254:265–271. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Song Q, Schmidt AG, Hahn HS, Carr AN,
Frank B, Pater L, Gerst M, Young K, Hoit BD, McConnell BK, et al:
Rescue of cardiomyocyte dysfunction by phospholamban ablation does
not prevent ventricular failure in genetic hypertrophy. J Clin
Invest. 111:859–867. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sundqvist A, Voytyuk O, Hamdi M, Popeijus
HE, van der Burgt CB, Janssen J, Martens JWM, Moustakas A, Heldin
CH, Ten Dijke P and van Dam H: JNK-dependent cJun phosphorylation
mitigates TGFβ- and EGF-induced pre-malignant breast cancer cell
invasion by suppressing AP-1-mediated transcriptional responses.
Cells. 8:14812019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Martin L, Derwall M, Al Zoubi S,
Zechendorf E, Reuter DA, Thiemermann C and Schuerholz T: The septic
heart: Current understanding of molecular mechanisms and clinical
implications. Chest. 155:427–437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Funk F, Kronenbitter A, Hackert K, Oebbeke
M, Klebe G, Barth M, Koch D and Schmitt JP: Phospholamban
pentamerization increases sensitivity and dynamic range of cardiac
relaxation. Cardiovasc Res. 119:1568–1582. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Babić Leko M, Gunjača I, Pleić N and
Zemunik T: Environmental factors affecting thyroid-stimulating
hormone and thyroid hormone levels. Int J Mol Sci. 22:65212021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Silvestri E, Lombardi A, de Lange P,
Schiavo L, Lanni A, Goglia F, Visser TJ and Moreno M: Age-related
changes in renal and hepatic cellular mechanisms associated with
variations in rat serum thyroid hormone levels. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 294:E1160–E1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|