|
1
|
Miguel V, Alcalde-Estévez E, Sirera B,
Rodríguez-Pascual F and Lamas S: Metabolism and bioenergetics in
the pathophysiology of organ fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
222:85–105. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan Z, El Sharkway R, Bayoumi A, Metwally
M, Gloss BS, Brink R, Lu DB, Liddle C, Alqahtani SA, Yu J, et al:
Inhibition of MERTK reduces organ fibrosis in mouse models of
fibrotic disease. Sci Transl Med. 16:eadj01332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao X, Kwan JYY, Yip K, Liu PP and Liu
FF: Targeting metabolic dysregulation for fibrosis therapy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 19:57–75. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Antar SA, Ashour NA, Marawan ME and
Al-Karmalawy AA: Fibrosis: Types, effects, markers, mechanisms for
disease progression, and its relation with oxidative stress,
immunity, and inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 24:40042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palmer JE, Wilson N, Son SM, Obrocki P,
Wrobel L, Rob M, Takla M, Korolchuk VI and Rubinsztein DC:
Autophagy, aging, and age-related neurodegeneration. Neuron.
113:29–48. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liang S, Wu YS, Li DY, Tang JX and Liu HF:
Autophagy and renal fibrosis. Aging Dis. 13:712–731. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo D, Lu X, Li H, Li Y, Wang Y, Jiang S,
Li G, Xu Y, Wu K, Dou X, et al: The spermine oxidase/spermine axis
coordinates ATG5-Mediated autophagy to orchestrate renal senescence
and fibrosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23069122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Wu X, Wang Y and Guo Y: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy are involved in adipocyte-induced
fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
476:2527–2538. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wen JH, Li DY, Liang S, Yang C, Tang JX
and Liu HF: Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization,
chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front Immunol.
13:9468322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Tan J, Wang Y, Gong Y, Zhang X,
Yuan Z, Lu X, Tang H, Zhang Z, Jiang X, et al: Atg5 deficiency in
macrophages protects against kidney fibrosis via the CCR6-CCL20
axis. Cell Commun Signal. 22:2232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Ping Z, Gao H, Liu Z, Xv Q, Jiang
X and Yu W: LYC inhibits the AKT signaling pathway to activate
autophagy and ameliorate TGFB-induced renal fibrosis. Autophagy.
20:1114–1133. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamamoto H and Matsui T: Molecular
mechanisms of macroautophagy, microautophagy, and
chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Nippon Med Sch. 91:2–9. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li WW, Li J and Bao JK: Microautophagy:
Lesser-known self-eating. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:1125–1136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu Y, Qian C, Wang Q, Song L, He Z, Liu W
and Wan W: Deacetylation of ATG7 drives the induction of
macroautophagy and LC3-associated microautophagy. Autophagy.
20:1134–1146. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tukaj C: The significance of
macroautophagy in health and disease. Folia Morphol (Warsz).
72:87–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakahira K, Pabon Porras MA and Choi AM:
Autophagy in pulmonary diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
194:1196–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zachari M and Ganley IG: The mammalian
ULK1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. 61:585–596.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N and Ohsumi
Y: Formation of the approximately 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5.Apg16
multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential
for autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem. 277:18619–18625. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Silva VR, Neves SP, Santos LS, Dias RB and
Bezerra DP: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities of autophagy
in cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:34612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barth S, Glick D and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Assays and artifacts. J Pathol. 221:117–124. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pugsley HR: Quantifying autophagy:
Measuring LC3 puncta and autolysosome formation in cells using
multispectral imaging flow cytometry. Methods. 112:147–156. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Agrotis A, Pengo N, Burden JJ and Ketteler
R: Redundancy of human ATG4 protease isoforms in autophagy and
LC3/GABARAP processing revealed in cells. Autophagy. 15:976–997.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saftig P, Beertsen W and Eskelinen EL:
LAMP-2: A control step for phagosome and autophagosome maturation.
Autophagy. 4:510–512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kroemer G, Mariño G and Levine B:
Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 40:280–293.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao XC, Livingston MJ, Liang XL and Dong
Z: Cell apoptosis and autophagy in renal fibrosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1165:557–584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
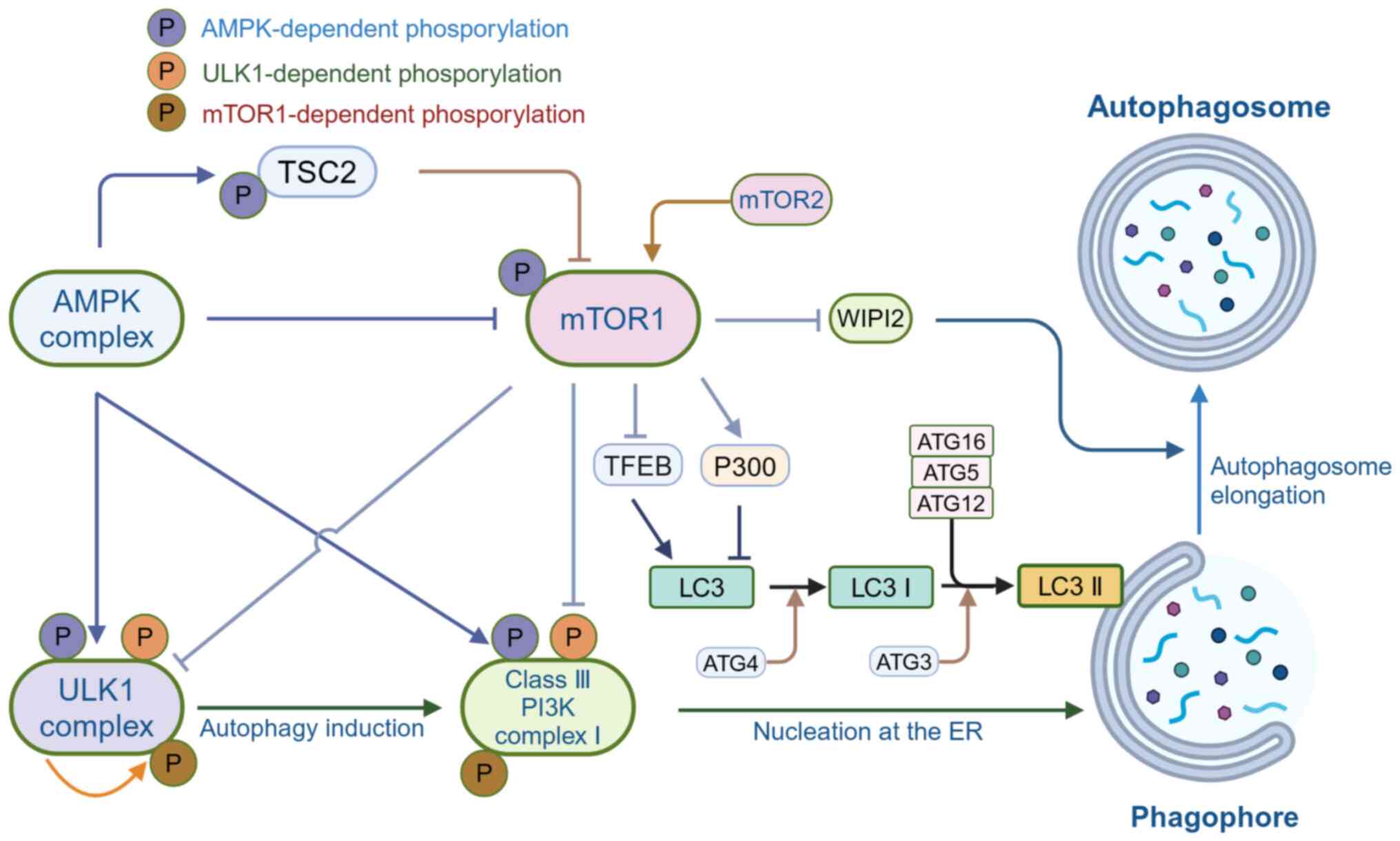
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C,
Takamura A, Miura Y, Iemura S, Natsume T, Takehana K, Yamada N, et
al: Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the
ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell.
20:1981–1991. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y and Zhang H: Regulation of
autophagy by mTOR signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1206:67–83.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wan W, You Z, Xu Y, Zhou L, Guan Z, Peng
C, Wong CCL, Su H, Zhou T, Xia H and Liu W: mTORC1 Phosphorylates
Acetyltransferase p300 to regulate autophagy and lipogenesis. Mol
Cell. 68:323–335.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dooley HC, Razi M, Polson HE, Girardin SE,
Wilson MI and Tooze SA: WIPI2 links LC3 conjugation with PI3P,
autophagosome formation, and pathogen clearance by recruiting
Atg12-5-16L1. Mol Cell. 55:238–252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roczniak-Ferguson A, Petit CS, Froehlich
F, Qian S, Ky J, Angarola B, Walther TC and Ferguson SM: The
transcription factor TFEB links mTORC1 signaling to transcriptional
control of lysosome homeostasis. Sci Signal. 5:ra422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Settembre C, Di Malta C, Polito VA, Garcia
Arencibia M, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Erdin SU, Huynh T, Medina D,
Colella P, et al: TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis.
Science. 332:1429–1433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Wang H, Qu T, Luo J, An P, Ren F,
Luo Y and Li Y: mTORC2: A multifaceted regulator of autophagy. Cell
Commun Signal. 21:42023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herzig S and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Guardian of
metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:121–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Tamargo-Gómez I and Mariño G: AMPK:
Regulation of metabolic dynamics in the context of autophagy. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:38122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang H, Yu Z, Chen X, Li J, Li N, Cheng J,
Gao N, Yuan HX, Ye D, Guan KL and Xu Y: Structural insights into
TSC complex assembly and GAP activity on Rheb. Nat Commun.
12:3392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang NC: Autophagy and stem cells:
Self-eating for self-renewal. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:1382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang S, Li H, Yuan M, Fan H and Cai Z:
Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front Physiol. 13:10155002022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Kim J, Kim YC, Fang C, Russell RC, Kim JH,
Fan W, Liu R, Zhong Q and Guan KL: Differential regulation of
distinct Vps34 complexes by AMPK in nutrient stress and autophagy.
Cell. 152:290–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F,
Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A and
Altucci L: Sirtuin functions and modulation: from chemistry to the
clinic. Clin Epigenetics. 8:612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Begum MK, Konja D, Singh S, Chlopicki S
and Wang Y: Endothelial SIRT1 as a target for the prevention of
arterial aging: Promises and challenges. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
78(Suppl 6): S63–S77. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Joo SY, Aung JM, Shin M, Moon EK, Kong HH,
Goo YK, Chung DI and Hong Y: The role of the Acanthamoeba
castellanii Sir2-like protein in the growth and encystation of
Acanthamoeba. Parasit Vectors. 13:3682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
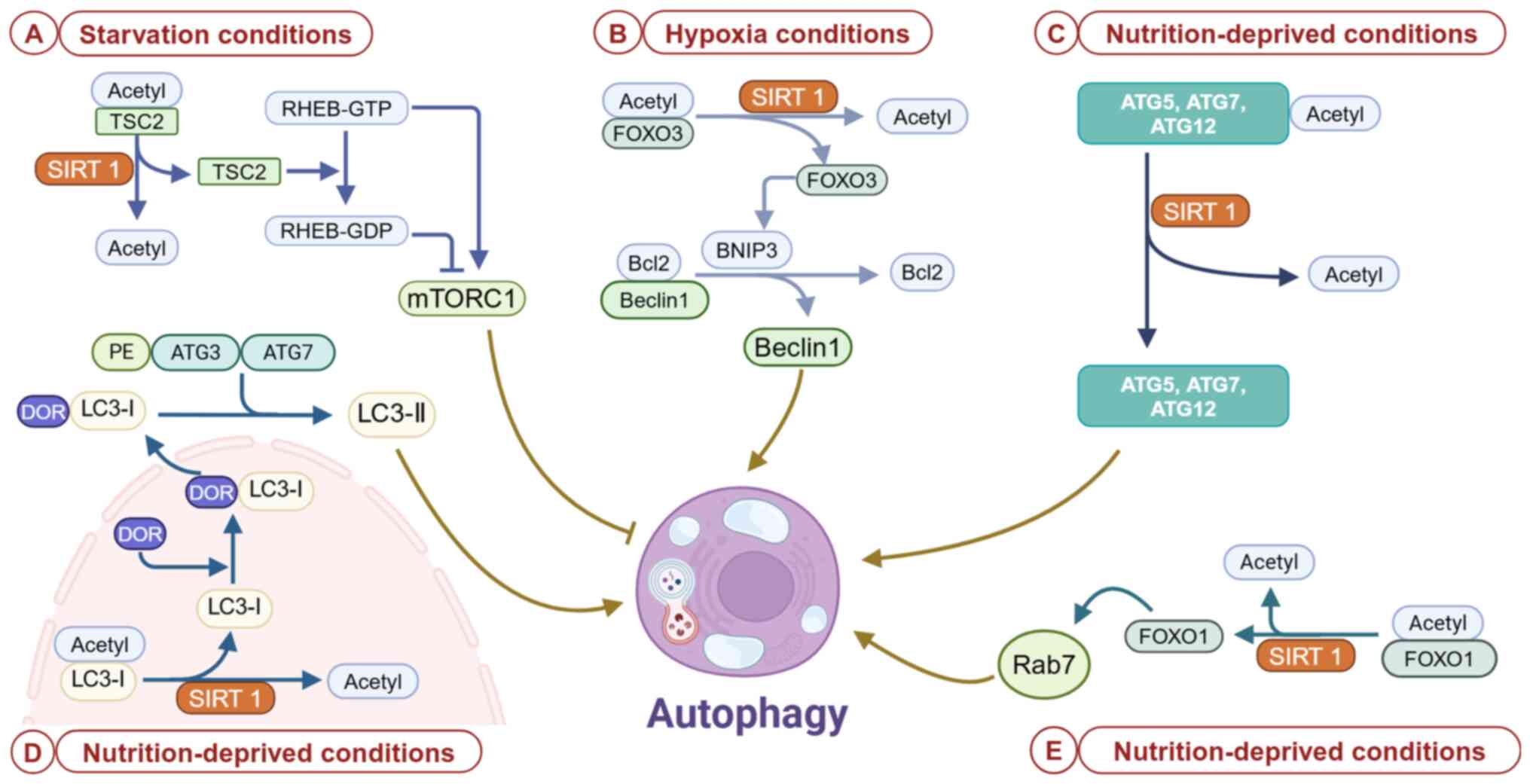
Ding X, Zhu C, Wang W, Li M, Ma C and Gao
B: SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy: Implications for the
progression and treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.
Pharmacol Res. 199:1069572024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang Q, Wang SY, Fleuriel C, Leprince D,
Rocheleau JV, Piston DW and Goodman RH: Metabolic regulation of
SIRT1 transcription via a HIC1:CtBP corepressor complex. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:829–833. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yu H, Gan D, Luo Z, Yang Q, An D, Zhang H,
Hu Y, Ma Z, Zeng Q, Xu D and Ren H: α-Ketoglutarate improves
cardiac insufficiency through NAD(+)-SIRT1 signaling-mediated
mitophagy and ferroptosis in pressure overload-induced mice. Mol
Med. 30:152024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Gao Y, Kim K, Vitrac H, Salazar RL, Gould
BD, Soedkamp D, Spivia W, Raedschelders K, Dinh AQ, Guzman AG, et
al: Autophagic signaling promotes systems-wide remodeling in
skeletal muscle upon oncometabolic stress by D2-HG. Mol Metab.
86:1019692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang J, Wang H, Li B, Liu J, Zhang X, Wang
Y, Peng J, Gao L, Wang X, Hu S, et al: Inhibition of ACSS2 triggers
glycolysis inhibition and nuclear translocation to activate
SIRT1/ATG5/ATG2B deacetylation axis, promoting autophagy and
reducing malignancy and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer.
Metabolism. 162:1560412025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li X, Zhao C, Mao C, Sun G, Yang F, Wang L
and Wang X: Oleic and linoleic acids promote chondrocyte apoptosis
by inhibiting autophagy via downregulation of SIRT1/FOXO1
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1870:1670902024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang Q, Sun K, Gao T, Gao Y, Yang Y, Li Z
and Zuo D: SIRT1 silencing promotes EMT and Crizotinib resistance
by regulating autophagy through AMPK/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway in
EML4-ALK L1196M and EML4-ALK G1202R mutant non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 63:2133–2144. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
He C: Balancing nutrient and energy demand
and supply via autophagy. Curr Biol. 32:R684–r696. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baeken MW: Sirtuins and their influence on
autophagy. J Cell Biochem. 125:e303772024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim JY, Mondaca-Ruff D, Singh S and Wang
Y: SIRT1 and autophagy: Implications in endocrine disorders. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9309192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ghosh HS, McBurney M and Robbins PD: SIRT1
negatively regulates the mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS One.
5:e91992010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Corradetti MN, Inoki K and Guan KL:
TSC2: filling the GAP in the mTOR signaling pathway. Trends Biochem
Sci. 29:32–38. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kume S, Uzu T, Horiike K, Chin-Kanasaki M,
Isshiki K, Araki S, Sugimoto T, Haneda M, Kashiwagi A and Koya D:
Calorie restriction enhances cell adaptation to hypoxia through
Sirt1-dependent mitochondrial autophagy in mouse aged kidney. J
Clin Invest. 120:1043–1055. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yang X, Jiang T, Wang Y and Guo L: The
role and mechanism of SIRT1 in resveratrol-regulated osteoblast
autophagy in osteoporosis rats. Sci Rep. 9:184242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bánréti A, Sass M and Graba Y: The
emerging role of acetylation in the regulation of autophagy.
Autophagy. 9:819–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB,
Liu J, Bruns NE, Tsokos M, Alt FW and Finkel T: A role for the
NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3374–3379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Huang R, Xu Y, Wan W, Shou X, Qian J, You
Z, Liu B, Chang C, Zhou T, Lippincott-Schwartz J and Liu W:
Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under
starvation. Mol Cell. 57:456–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hyttinen JM, Niittykoski M, Salminen A and
Kaarniranta K: Maturation of autophagosomes and endosomes: A key
role for Rab7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:503–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lee J, Kim J, Lee JH, Choi YM, Choi H, Cho
HD, Cha GH, Lee YH, Jo EK, Park BH and Yuk JM: SIRT1 promotes host
protective immunity against toxoplasma gondii by controlling the
FoxO-autophagy axis via the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:135782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu C, Wang L, Fozouni P, Evjen G, Chandra
V, Jiang J, Lu C, Nicastri M, Bretz C, Winkler JD, et al: SIRT1 is
downregulated by autophagy in senescence and ageing. Nat Cell Biol.
22:1170–1179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wei F, Wang Y, Yao J, Mei L, Huang X, Kong
H, Chen J, Chen X, Liu L, Wang Z, et al: ZDHHC7-mediated
S-palmitoylation of ATG16L1 facilitates LC3 lipidation and
autophagosome formation. Autophagy. 20:2719–2737. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Valdor R and Macian F: Autophagy and the
regulation of the immune response. Pharmacol Res. 66:475–483. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hu YX, Han XS and Jing Q: Autophagy in
Development and Differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1206:469–487.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Adelipour M, Saleth LR, Ghavami S,
Alagarsamy KN, Dhingra S and Allameh A: The role of autophagy in
the metabolism and differentiation of stem cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1868:1664122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pohl C and Dikic I: Cellular quality
control by the ubiquitinproteasome system and autophagy. Science.
366:818–822. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Henderson NC, Rieder F and Wynn TA:
Fibrosis: From mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 587:555–566. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sun C, Zhang H, Wang X and Liu X:
Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways,
cellular mechanisms, and future directions. FASEB J. 34:9854–9868.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wynn TA and Ramalingam TR: Mechanisms of
fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med.
18:1028–1040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Schuster R, Younesi F, Ezzo M and Hinz B:
The role of myofibroblasts in physiological and pathological tissue
repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 15:a0412312023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Humphreys BD: Mechanisms of renal
fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 80:309–326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S and Tacke F:
Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms
and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med. 65:2–15. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Piersma B, Bank RA and Boersema M:
Signaling in fibrosis: TGF-β, WNT, and YAP/TAZ converge. Front Med
(Lausanne). 2:592015.
|
|
83
|
Burgy O and Königshoff M: The WNT
signaling pathways in wound healing and fibrosis. Matrix Biol.
68-69:67–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:325–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Noguchi S, Saito A and Nagase T: YAP/TAZ
signaling as a molecular link between fibrosis and cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:36742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Habibie H, Adhyatmika A, Schaafsma D and
Melgert BN: The role of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in fibrosis: Its
potential as a biomarker and/or biological target for the treatment
of fibrotic diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 228:1079412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Williams L, Layton T, Yang N, Feldmann M
and Nanchahal J: Collagen VI as a driver and disease biomarker in
human fibrosis. FEBS J. 289:3603–3629. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Bai L, Li A, Gong C, Ning X and Wang Z:
Protective effect of rutin against bleomycin induced lung fibrosis:
Involvement of TGF-β1/α-SMA/Col I and III pathway. BioFactors.
46:637–644. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ge M, Zou H, Chen J, Zhang Q, Li C, Yang
J, Wu J, Xie X, Liu J, Lei L, et al: Cellular fibronectin-targeted
fluorescent aptamer probes for early detection and staging of liver
fibrosis. Acta Biomater. 190:579–592. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Biel C, Faber KN, Bank RA and Olinga P:
Matrix metalloproteinases in intestinal fibrosis. J Crohns Colitis.
18:462–478. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Liu H, Yan W, Ma C, Zhang K, Li K, Jin R,
Xu H, Xu R, Tong J, Yang Z and Guo Y: Early detection of cardiac
fibrosis in diabetic mice by targeting myocardiopathy and matrix
metalloproteinase 2. Acta Biomater. 176:367–378. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhou D, Tian Y, Sun L, Zhou L, Xiao L, Tan
RJ, Tian J, Fu H, Hou FF and Liu Y: Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is a
urinary biomarker and pathogenic mediator of kidney fibrosis. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 28:598–611. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Patel V and Noureddine L: MicroRNAs and
fibrosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 21:410–416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Duan ZY, Bu R, Liang S, Chen XZ, Zhang C,
Zhang QY, Li JJ, Chen XM and Cai GY: Urinary miR-185-5p is a
biomarker of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy.
Front Immunol. 15:13260262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhao X, Xue X, Cui Z, Kwame Amevor F, Wan
Y, Fu K, Wang C, Peng C and Li Y: microRNAs-based diagnostic and
therapeutic applications in liver fibrosis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 14:e17732023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Xuan Y, Wu D, Zhang Q, Yu Z, Yu J and Zhou
D: Elevated ALT/AST ratio as a marker for NAFLD risk and severity:
insights from a cross-sectional analysis in the United States.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 15:14575982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Amernia B, Moosavy SH, Banookh F and Zoghi
G: FIB-4, APRI, and AST/ALT ratio compared to FibroScan for the
assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in Bandar Abbas, Iran. BMC Gastroenterol. 21:4532021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cylwik B, Bauer A, Gruszewska E, Gan K,
Kazberuk M and Chrostek L: The diagnostic value of fibrotest and
hepascore as non-invasive markers of liver fibrosis in primary
sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). J Clin Med. 12:75522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Dzudzor B, Hammond H, Tachi K, Alisi A,
Vento S, Gyasi RK and Aheto JMK: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and
hyaluronic acid levels as markers of fibrosis in patients with
chronic liver disease at the main tertiary referral hospital in
Ghana: A case-control study design. Health Sci Rep. 6:e11012023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Soccio P, Moriondo G, d'Alessandro M,
Scioscia G, Bergantini L, Gangi S, Tondo P, Foschino Barbaro MP,
Cameli P, Bargagli E and Lacedonia D: Role of BAL and Serum Krebs
von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) in patients with pulmonary fibrosis.
Biomedicines. 12:2692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jehn LB, Costabel U, Boerner E, Wälscher
J, Theegarten D, Taube C and Bonella F: Serum KL-6 as a biomarker
of progression at any time in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. J
Clin Med. 12:11732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chiba S, Ohta H, Abe K, Hisata S, Ohkouchi
S, Hoshikawa Y, Kondo T and Ebina M: The diagnostic value of the
interstitial biomarkers KL-6 and SP-D for the degree of fibrosis in
combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Pulm Med.
2012:4929602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
White ES, Xia M, Murray S, Dyal R,
Flaherty CM, Flaherty KR, Moore BB, Cheng L, Doyle TJ, Villalba J,
et al: Plasma surfactant protein-D, matrix metalloproteinase-7, and
osteopontin index distinguishes idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from
other idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 194:1242–1251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ikeda K, Chiba H, Nishikiori H, Azuma A,
Kondoh Y, Ogura T, Taguchi Y, Ebina M, Sakaguchi H, Miyazawa S, et
al: Serum surfactant protein D as a predictive biomarker for the
efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: A post-hoc analysis of the phase 3 trial in Japan. Respir
Res. 21:3162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Saito H, Tanaka T, Tanaka S, Higashijima
Y, Yamaguchi J, Sugahara M, Ito M, Uchida L, Hasegawa S, Wakashima
T, et al: Persistent expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated
lipocalin and M2 macrophage markers and chronic fibrosis after
acute kidney injury. Physiol Rep. 6:e137072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hijmans RS, Rasmussen DG, Yazdani S, Navis
G, van Goor H, Karsdal MA, Genovese F and van den Born J: Urinary
collagen degradation products as early markers of progressive renal
fibrosis. J Transl Med. 15:632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Papasotiriou M, Genovese F, Klinkhammer
BM, Kunter U, Nielsen SH, Karsdal MA, Floege J and Boor P: Serum
and urine markers of collagen degradation reflect renal fibrosis in
experimental kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
30:1112–1121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Karabinowska-Małocha A, Dziewięcka E,
Szymańska M, Banyś P, Urbańczyk-Zawadzka M, Krupiński M, Mielnik M,
Wiśniowska-Śmiałek S, Podolec P, Budkiewicz A, et al: Link between
fibrosis-specific biomarkers and interstitial fibrosis in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Kardiol Pol. 81:692–699. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Scisciola L, Paolisso P, Belmonte M,
Gallinoro E, Delrue L, Taktaz F, Fontanella RA, Degrieck I,
Pesapane A, Casselman F, et al: Myocardial sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2 expression and cardiac remodelling in patients with
severe aortic stenosis: The BIO-AS study. Eur J Heart Fail.
26:471–482. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Al Ali L, Meijers WC, Beldhuis IE, Groot
HE, Lipsic E, van Veldhuisen DJ, Voors AA, van der Horst ICC, de
Boer RA and van der Harst P: Association of fibrotic markers with
diastolic function after STEMI. Sci Rep. 14:191222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
de Jong S, van Veen TA, de Bakker JM, Vos
MA and van Rijen HV: Biomarkers of myocardial fibrosis. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 57:522–535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yan L, Wang J, Cai X, Liou YC, Shen HM,
Hao J, Huang C, Luo G and He W: Macrophage plasticity: Signaling
pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration. MedComm (2020).
5:e6582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Luo M, Zhao F, Cheng H, Su M and Wang Y:
Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory
diseases. Front Immunol. 15:13529462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ge Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Hu F and Xie L:
Macrophage polarization and its impact on idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Immunol. 15:14449642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N and Gordon S:
Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor
activity: A marker of alternative immunologic macrophage
activation. J Exp Med. 176:287–292. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wang C, Ma C, Gong L, Guo Y, Fu K, Zhang
Y, Zhou H and Li Y: Macrophage polarization and its role in liver
disease. Front Immunol. 12:8030372021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
118
|
Wu MY and Lu JH: Autophagy and macrophage
functions: Inflammatory response and phagocytosis. Cells. 9:702019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Rockey DC, Bell PD and Hill JA: Fibrosis-a
common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med.
372:1138–1149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wang Y, Jiao L, Qiang C, Chen C, Shen Z,
Ding F, Lv L, Zhu T, Lu Y and Cui X: The role of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 in fibrosis diseases and its molecular
mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 171:1161162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ogawa T, Shichino S, Ueha S and Matsushima
K: Macrophages in lung fibrosis. Int Immunol. 33:665–671. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Huang WJ and Tang XX: Virus infection
induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Transl Med. 19:4962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tian Y, Lv J, Su Z, Wu T, Li X, Hu X,
Zhang J and Wu L: LRRK2 plays essential roles in maintaining lung
homeostasis and preventing the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21066851182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mornex JF, Cordier G and Revillard JP:
Markers of lymphocyte activation in interstitial pulmonary disease.
Rev Fr Mal Respir. 11:293–300. 1983.In Frence.
|
|
125
|
Du S, Li C, Lu Y, Lei X, Zhang Y, Li S,
Liu F, Chen Y, Weng D and Chen J: Dioscin alleviates crystalline
silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through
promoting alveolar macrophage autophagy. Theranostics. 9:1878–1892.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Li C, Lu Y, Du S, Li S, Zhang Y, Liu F,
Chen Y, Weng D and Chen J: Dioscin exerts protective effects
against crystalline silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
Theranostics. 7:4255–4275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhong Y, Jin R, Luo R, Liu J, Ren L, Zhang
Y, Shan Z and Peng X: Diosgenin targets CaMKK2 to alleviate type II
diabetic nephropathy through improving autophagy, mitophagy and
mitochondrial dynamics. Nutrients. 15:35542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Qian Q, Ma Q, Wang B, Qian Q, Zhao C, Feng
F and Dong X: MicroRNA-205-5p targets E2F1 to promote autophagy and
inhibit pulmonary fibrosis in silicosis through impairing
SKP2-mediated Beclin1 ubiquitination. J Cell Mol Med. 25:9214–9227.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Jessop F, Hamilton RF, Rhoderick JF, Shaw
PK and Holian A: Autophagy deficiency in macrophages enhances NLRP3
inflammasome activity and chronic lung disease following silica
exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 309:101–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Tan S and Chen S: Macrophage autophagy and
silicosis: Current perspective and latest insights. Int J Mol Sci.
22:4532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Tang PM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
Macrophages: Versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 15:144–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
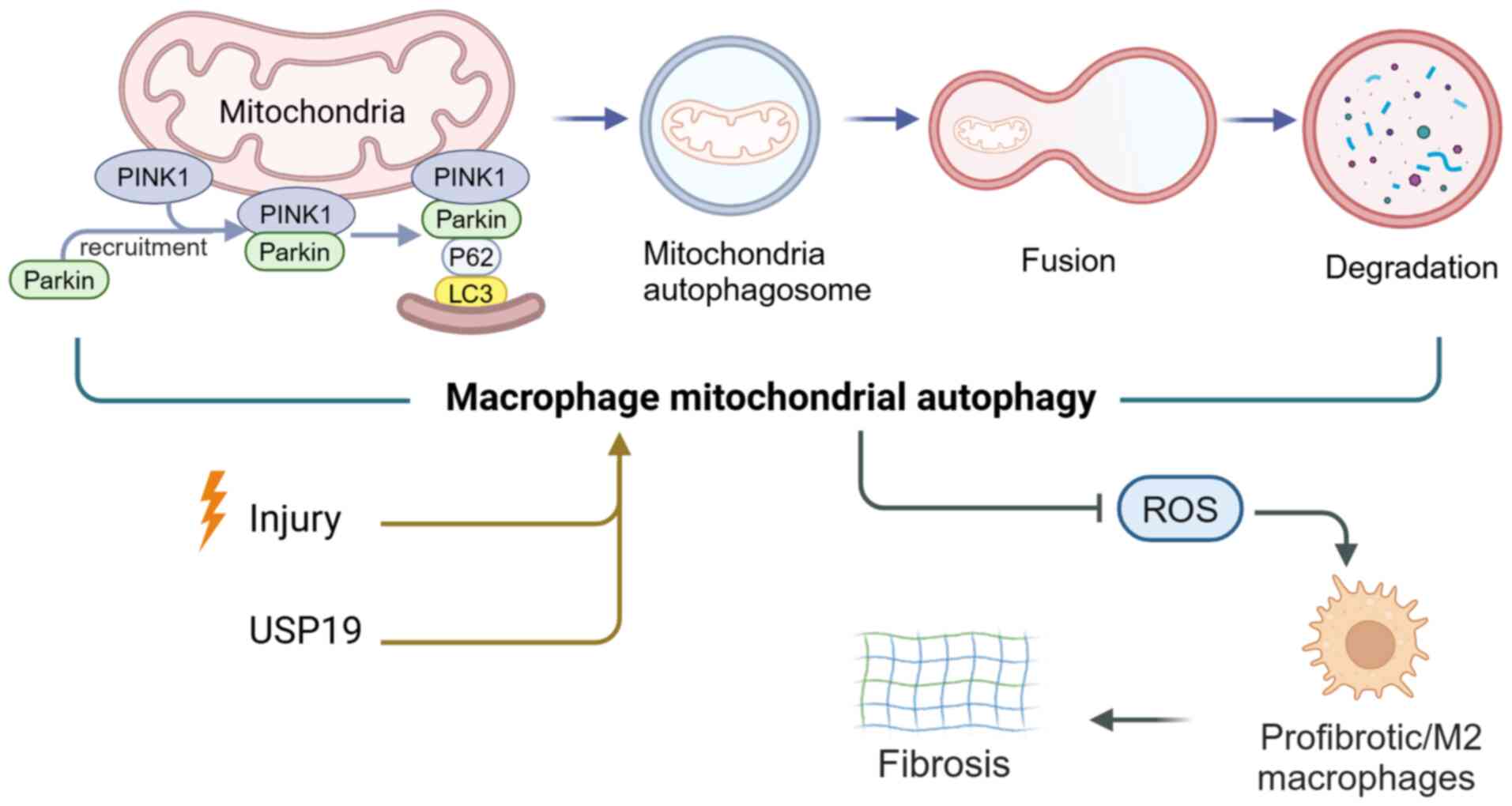
Liu K, Zhao E, Ilyas G, Lalazar G, Lin Y,
Haseeb M, Tanaka KE and Czaja MJ: Impaired macrophage autophagy
increases the immune response in obese mice by promoting
proinflammatory macrophage polarization. Autophagy. 11:271–284.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu T, Wang L, Liang P, Wang X, Liu Y, Cai
J, She Y, Wang D, Wang Z, Guo Z, et al: USP19 suppresses
inflammation and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by
manipulating NLRP3 function via autophagy. Cell Mol Immunol.
18:2431–2442. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
134
|
Bhatia D, Chung KP, Nakahira K, Patino E,
Rice MC, Torres LK, Muthukumar T, Choi AM, Akchurin OM and Choi ME:
Mitophagy-dependent macrophage reprogramming protects against
kidney fibrosis. JCI Insight. 4:e1328262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Li L, Liang X, Cheng P,
Li Q, Chang X, Wang K, Huang S, Li Y, et al: Lymphangiogenesis in
renal fibrosis arises from macrophages via VEGF-C/VEGFR3-dependent
autophagy and polarization. Cell Death Dis. 12:1092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Lodder J, Denaës T, Chobert MN, Wan J,
El-Benna J, Pawlotsky JM, Lotersztajn S and Teixeira-Clerc F:
Macrophage autophagy protects against liver fibrosis in mice.
Autophagy. 11:1280–1292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
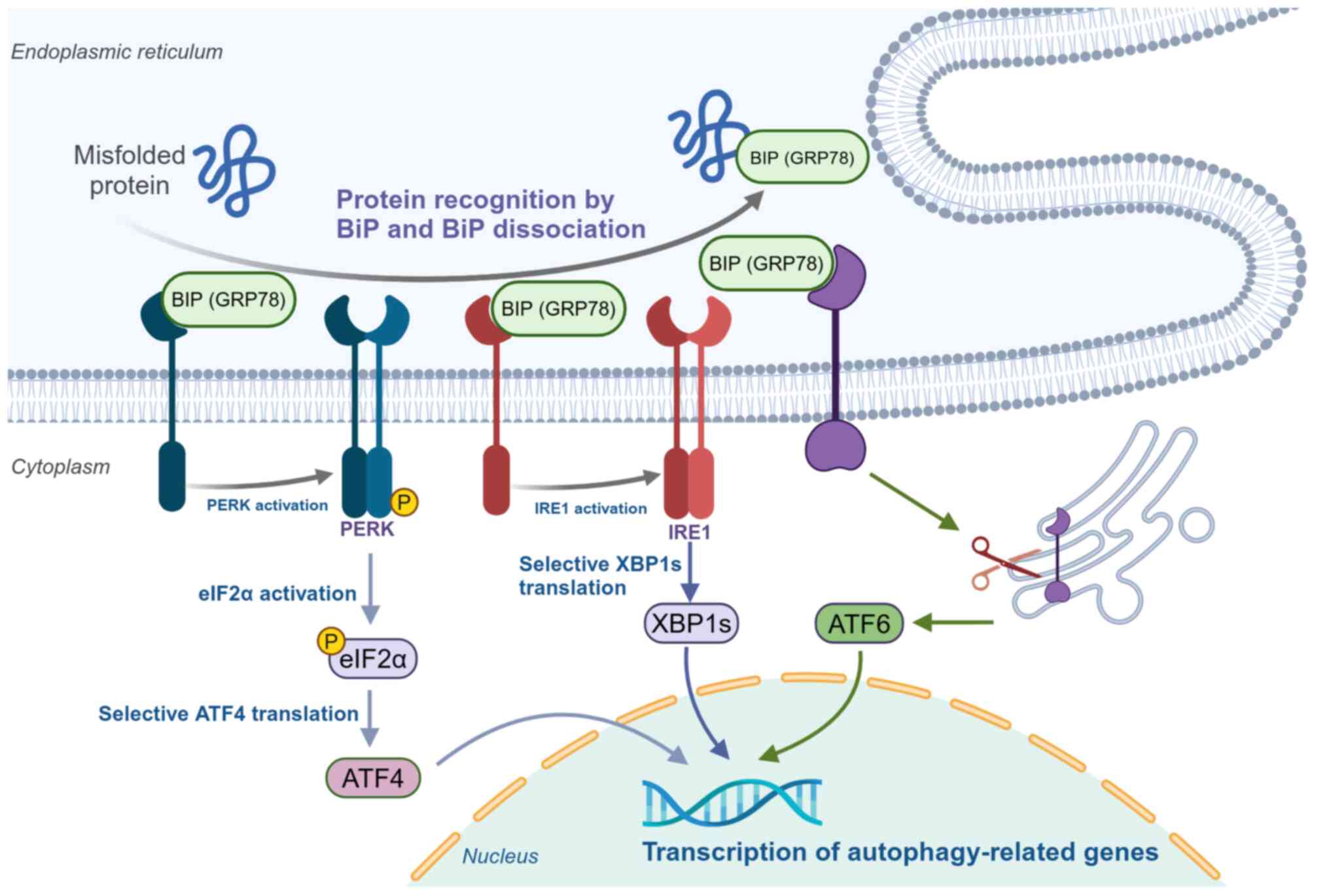
Oakes SA and Papa FR: The role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:173–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Senft D and Ronai ZA: UPR, autophagy, and
mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends
Biochem Sci. 40:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C,
Kroemer G, Kaufman RJ, Malhi H and Ren J: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress in liver diseases. Hepatology. 77:619–639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Chen X, Shi C, He M, Xiong S and Xia X:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic
targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ernst R, Renne MF, Jain A and von der
Malsburg A: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane homeostasis and the
unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
16:a0414002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Gong J, Wang XZ, Wang T, Chen JJ, Xie XY,
Hu H, Yu F, Liu HL, Jiang XY and Fan HD: Molecular signal networks
and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 18:1–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Xia SW, Wang ZM, Sun SM, Su Y, Li ZH, Shao
JJ, Tan SZ, Chen AP, Wang SJ, Zhang ZL, et al: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and protein degradation in chronic liver disease.
Pharmacol Res. 161:1052182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Benedetti R, Romeo MA, Arena A, Gilardini
Montani MS, D'Orazi G and Cirone M: ATF6 supports lysosomal
function in tumor cells to enable ER stress-activated
macroautophagy and CMA: Impact on mutant TP53 expression.
Autophagy. 20:1854–1867. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Chen L, Wei M, Zhou B, Wang K, Zhu E and
Cheng Z: The roles and mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated autophagy in animal viral infections. Vet Res.
55:1072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Shi Y, Jiang B and Zhao J: Induction
mechanisms of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury, inflammatory bowel disease,
and colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 170:1159842024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Feng S, Ji J, Li H and Zhang X:
H2S alleviates renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by
suppressing ERS-induced autophagy. Transpl Immunol. 83:1020062024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
He L, Li H, Li C, Liu ZK, Lu M, Zhang RY,
Wu D, Wei D, Shao J, Liu M, et al: HMMR alleviates endoplasmic
reticulum stress by promoting autophagolysosomal activity during
endoplasmic reticulum stress-driven hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cancer Commun (Lond). 43:981–1002. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Habshi T, Shelke V, Kale A, Anders HJ and
Gaikwad AB: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in
the transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease.
J Cell Physiol. 238:82–93. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Liao H, Liu S, Ma Q, Huang H, Goel A,
Torabian P, Mohan CD and Duan C: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
induced autophagy in cancer and its potential interactions with
apoptosis and ferroptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1872:1198692025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Baek AR, Hong J, Song KS, Jang AS, Kim DJ,
Chin SS and Park SW: Spermidine attenuates bleomycin-induced lung
fibrosis by inducing autophagy and inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress (ERS)-induced cell death in mice. Exp Mol Med. 52:2034–2045.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Ma C, Liu Y and Fu Z: Implications of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in aging and
cardiovascular diseases. Front Pharmacol. 15:14138532024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhou L, Liu Z, Chen S, Qiu J, Li Q, Wang
S, Zhou W, Chen D, Yang G and Guo L: Transcription factor
EB-mediated autophagy promotes dermal fibroblast differentiation
and collagen production by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
and autophagy-dependent secretion. Int J Mol Med. 47:547–560. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Wu W, Zhao Y, Hu T, Long Y, Zeng Y, Li M,
Peng S, Hu J and Shen Y: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is
upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease and contributed TLR2
pathway-mediated inflammatory response. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 46:192–198. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Shi Y, Gao Z, Xu B, Mao J, Wang Y, Liu Z
and Wang J: Protective effect of naringenin on cadmium
chloride-induced renal injury via alleviating oxidative stress,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy in chickens. Front
Pharmacol. 15:14408772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Feng J, Chen Y, Lu B and Sun X, Zhu H and
Sun X: Autophagy activated via GRP78 to alleviate endoplasmic
reticulum stress for cell survival in blue light-mediated damage of
A2E-laden RPEs. BMC Ophthalmol. 19:2492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Shu S, Wang H, Zhu J, Liu Z, Yang D, Wu W,
Cai J, Chen A, Tang C and Dong Z: Reciprocal regulation between ER
stress and autophagy in renal tubular fibrosis and apoptosis. Cell
Death Dis. 12:10162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Xiong X, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xie J, Bian Y,
Yin Q, Tong R, Yu D and Pan L: Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)
ATPase (SERCA)-mediated ER stress crosstalk with autophagy is
involved in tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate stress-induced cardiac
fibrosis. J Inorg Biochem. 236:1119722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Ren Y, Cui Q, Zhang J, Liu W, Xu M, Lv Y,
Wu Z, Zhang Y and Wu R: Milk fat globule-egf factor 8 alleviates
pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting ER stress-induced
chaperone-mediated autophagy in mice. Front Pharmacol.
12:7072592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zheng Y, Zhang D, Su L, Wen Y and Wang Y:
FAM172A supervises ER (endoplasmic reticulum) stress-triggered
autophagy in the epidural fibrosis process. JOR Spine. 5:e12032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Singh A, Bhatt KS, Nguyen HC, Frisbee JC
and Singh KK: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
cardiovascular pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 25:61802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Jimenez SA and Piera-Velazquez S:
Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis
of Systemic Sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Myth or reality? Matrix Biol. 51:26–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z and Jimenez SA:
Role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the
pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol. 179:1074–1080.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Singh B, Cui K, Eisa-Beygi S, Zhu B, Cowan
DB, Shi J, Wang DZ, Liu Z, Bischoff J and Chen H: Elucidating the
crosstalk between endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT)
and endothelial autophagy in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
Vascul Pharmacol. 155:1073682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Jackson AO, Zhang J, Jiang Z and Yin K:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: A novel therapeutic target
for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 27:383–393.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Lu X, Gong J, Dennery PA and Yao H:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: Pathogenesis and therapeutic
targets for chronic pulmonary and vascular diseases. Biochem
Pharmacol. 168:100–107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Bischoff J: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Circ Res. 124:1163–1165. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zhang L, He J, Wang J, Liu J, Chen Z, Deng
B, Wei L, Wu H, Liang B, Li H, et al: Knockout RAGE alleviates
cardiac fibrosis through repressing endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition (EndMT) mediated by autophagy. Cell Death Dis.
12:4702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Pan JA, Zhang H, Lin H, Gao L, Zhang HL,
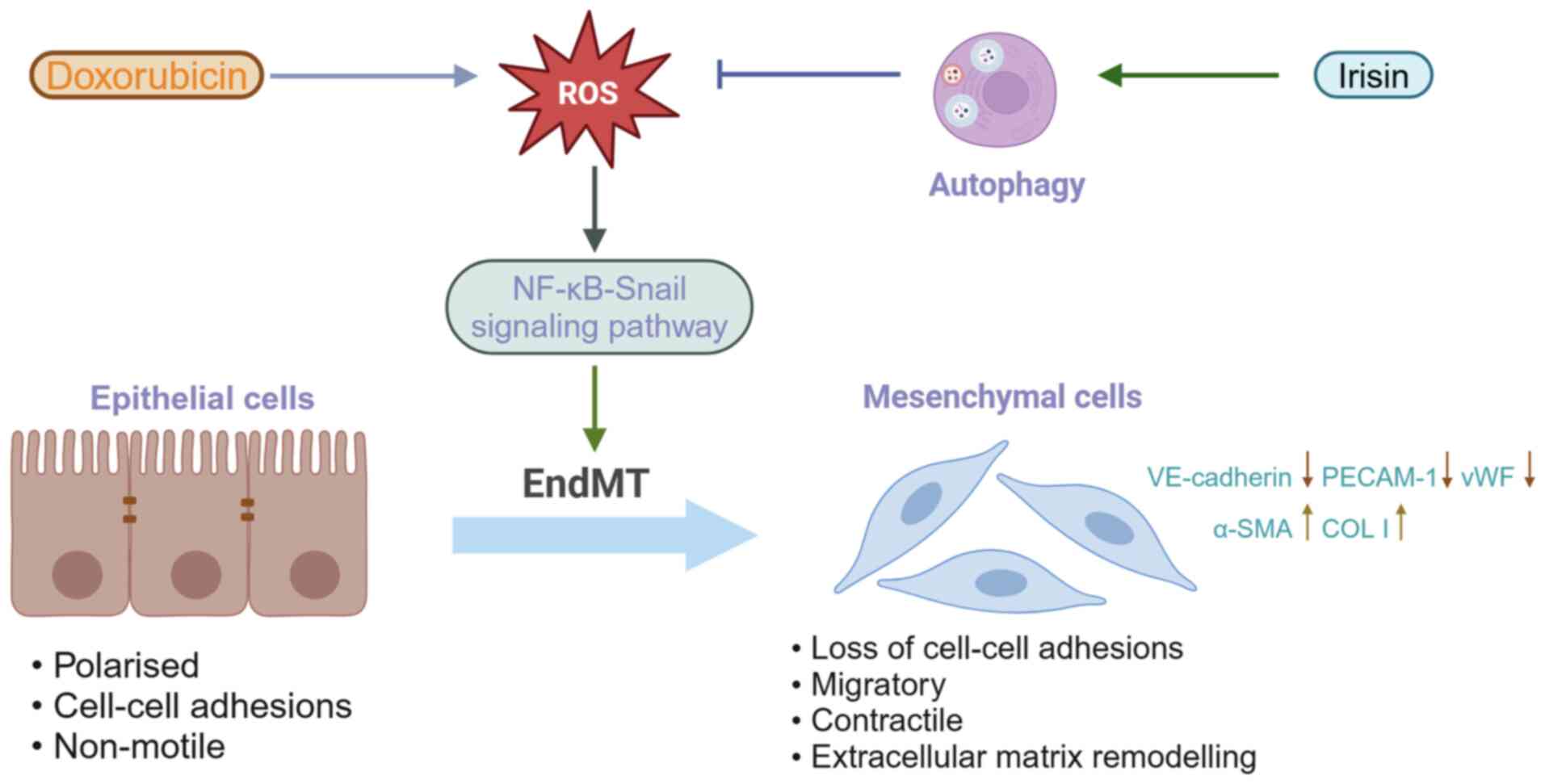
Zhang JF, Wang CQ and Gu J: Irisin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced
cardiac perivascular fibrosis through inhibiting
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by regulating ROS
accumulation and autophagy disorder in endothelial cells. Redox
Biol. 46:1021202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Zhou Z, Wang H, Zhang X, Song M, Yao S,
Jiang P, Liu D, Wang Z, Lv H, Li R, et al: Defective autophagy
contributes to endometrial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
intrauterine adhesions. Autophagy. 18:2427–2442. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Singh KK, Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Ramadan
A, Matkar PN, Ehsan M, Sandhu P, Mantella LE, Gupta N, et al: The
essential autophagy gene ATG7 modulates organ fibrosis via
regulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
290:2547–2559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
173
|
Livingston MJ, Shu S, Fan Y, Li Z, Jiao Q,
Yin XM, Venkatachalam MA and Dong Z: Tubular cells produce FGF2 via
autophagy after acute kidney injury leading to fibroblast
activation and renal fibrosis. Autophagy. 19:256–277. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
174
|
Nam SA, Kim WY, Kim JW, Park SH, Kim HL,
Lee MS, Komatsu M, Ha H, Lim JH, Park CW, et al: Autophagy
attenuates tubulointerstital fibrosis through regulating
transforming growth factor-β and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10:782019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Liu X, Tan S, Liu H, Jiang J, Wang X, Li L
and Wu B: Hepatocyte-derived MASP1-enriched small extracellular
vesicles activate HSCs to promote liver fibrosis. Hepatology.
77:1181–1197. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Li S, Liu G, Gu M, Li Y, Li Y, Ji Z, Li K
and Wang Y, Zhai H and Wang Y: A novel therapeutic approach for
IPF: Based on the 'Autophagy-Apoptosis' balance regulation of
Zukamu Granules in alveolar macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
297:1155682022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Chen M, Menon MC, Wang W, Fu J, Yi Z, Sun
Z, Liu J, Li Z, Mou L, Banu K, et al: HCK induces macrophage
activation to promote renal inflammation and fibrosis via
suppression of autophagy. Nat Commun. 14:42972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Liu XY, Zhang W, Ma BF, Sun MM and Shang
QH: Advances in research on the effectiveness and mechanism of
active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine in regulating
hepatic stellate cells autophagy against hepatic fibrosis. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 18:2715–2727. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|