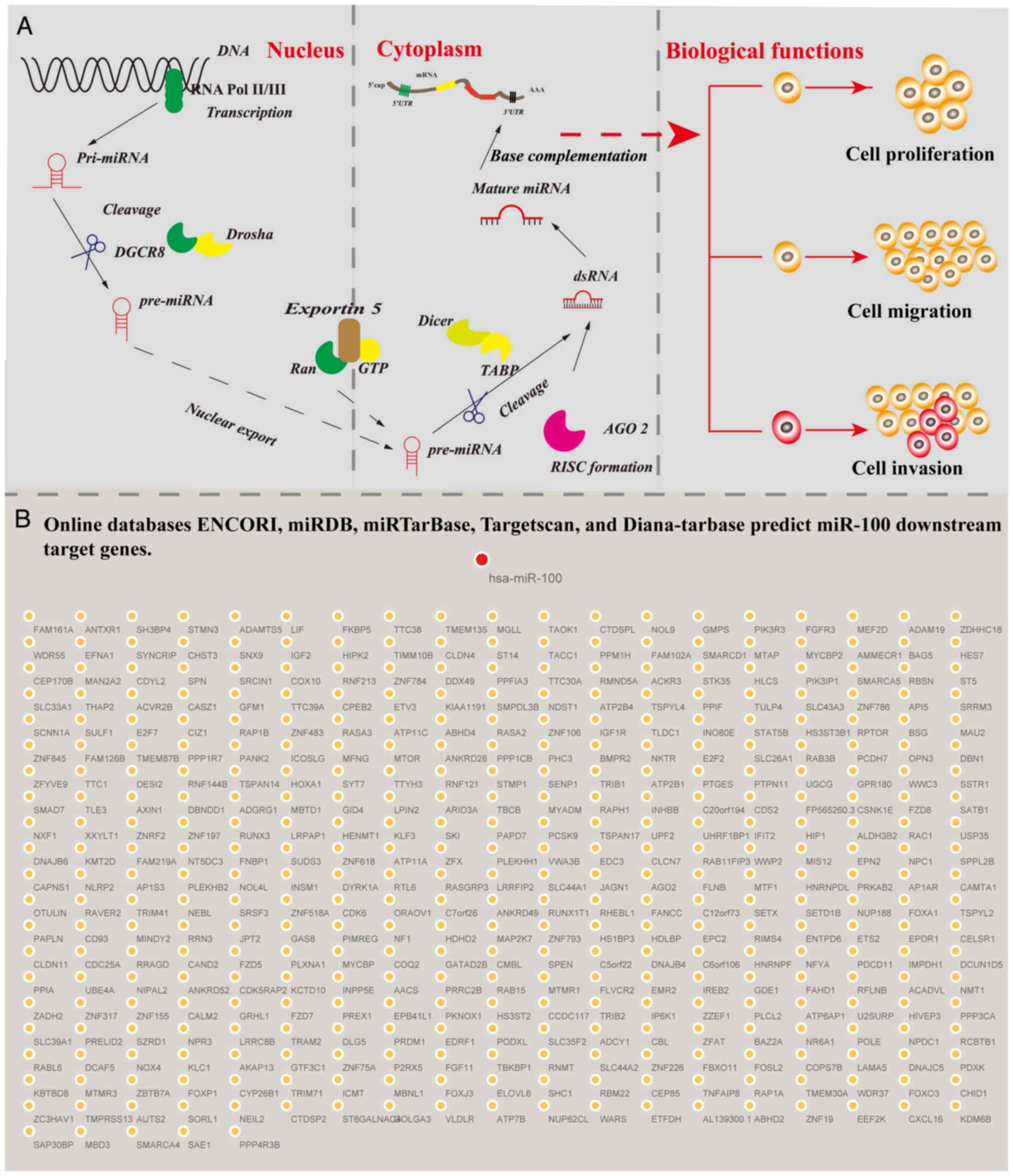
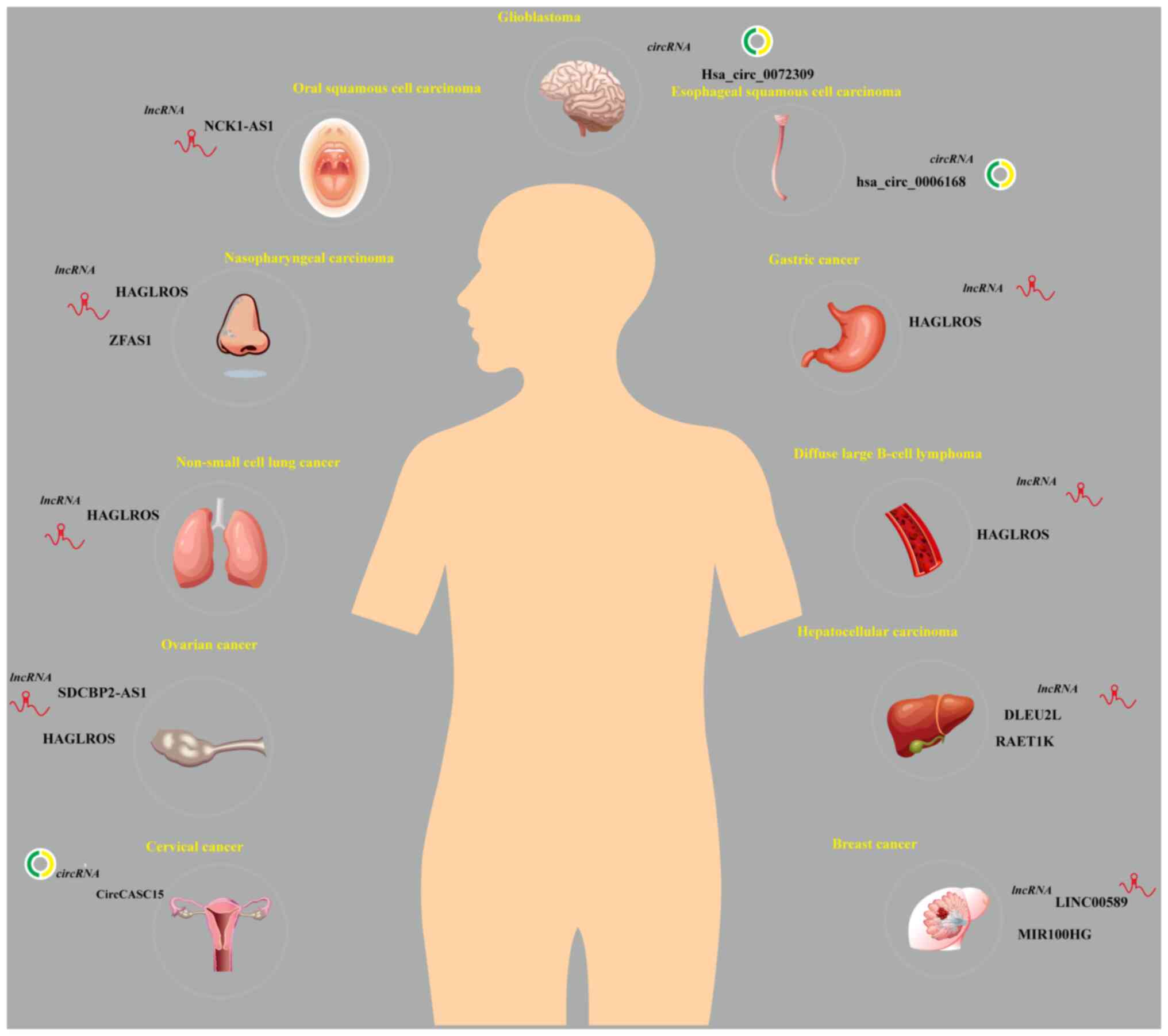
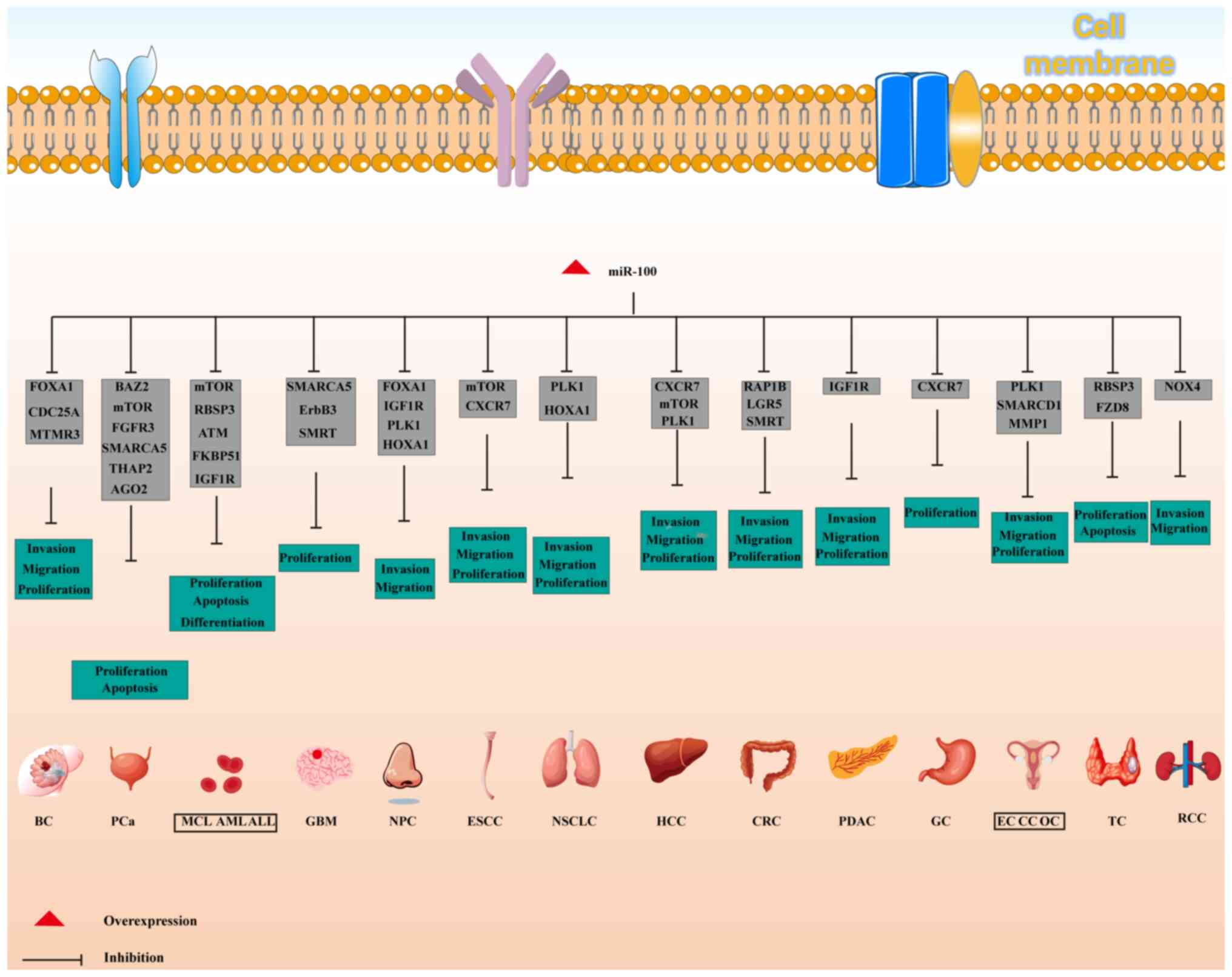
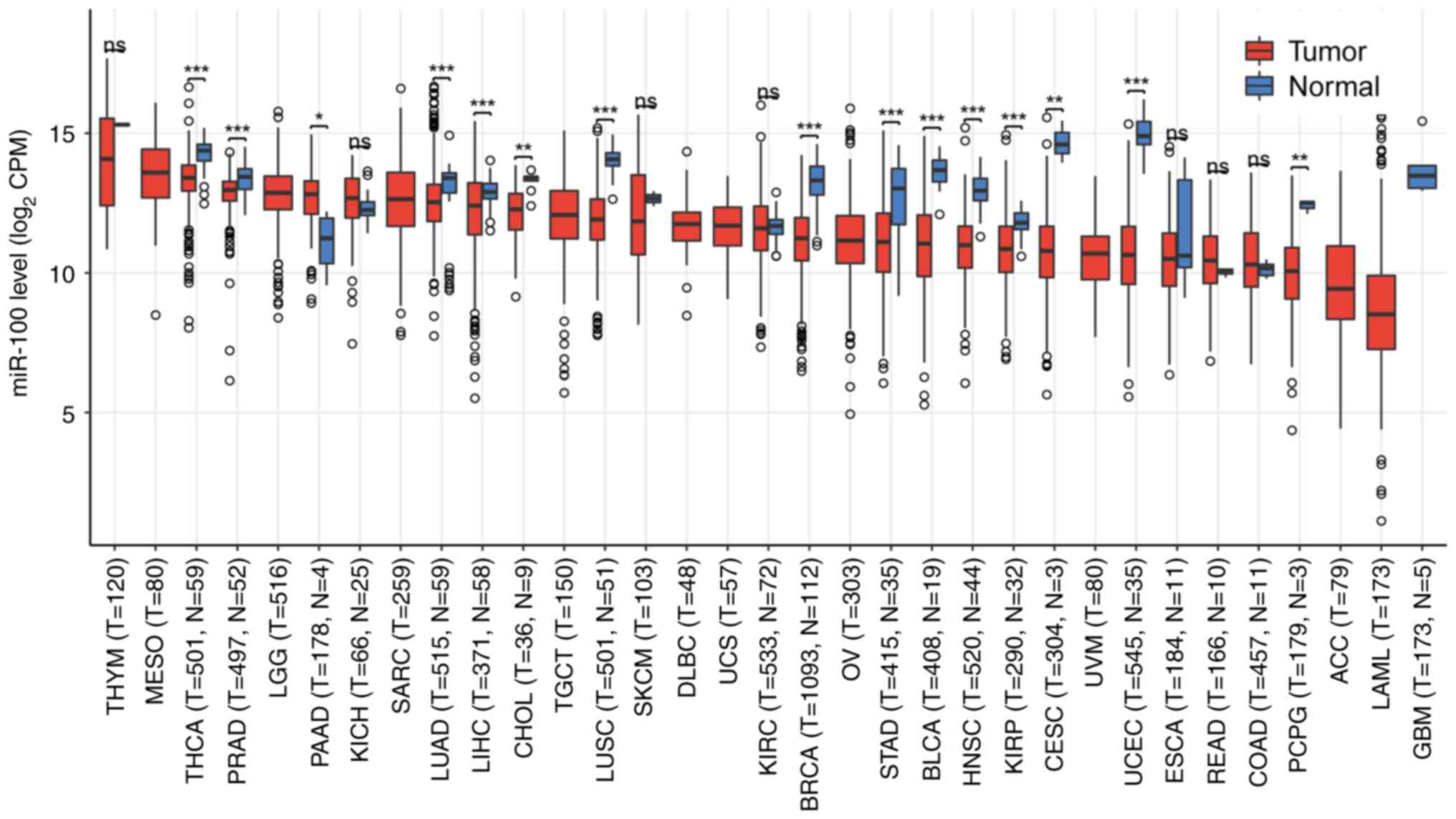
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–148. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao M, Li H, Sun D and Chen W: Cancer
burden of major cancers in China: A need for sustainable actions.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 40:205–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N and Chen WQ:
Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A
secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J
(Engl). 134:783–791. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Toden S, Zumwalt TJ and Goel A: Non-coding
RNAs and potential therapeutic targeting in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1875:1884912021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Chen B, Dragomir MP, Yang C, Li Q, Horst D
and Calin GA: Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy
resistance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saw PE, Xu X, Chen J and Song EW:
Non-coding RNAs: The new central dogma of cancer biology. Sci China
Life Sci. 64:22–50. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wightman B, Ha I and Ruvkun G:
Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by
lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell.
75:855–862. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li C, Gao Y, Zhang K, Chen J, Han S, Feng
B, Wang R and Chen L: Multiple roles of microRNA-100 in human
cancer and its therapeutic potential. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:2143–2159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang S, Deng B, Zhang Y and Jiang N:
Expression of miR-100 and RBSP3 in FTC-133 cells after exposure to
131I. Nucl Med Commun. 35:932–938. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S, Xue S, Dai Y, Yang J, Chen Z, Fang
X, Zhou W, Wu W and Li Q: Reduced expression of microRNA-100
confers unfavorable prognosis in patients with bladder cancer.
Diagn Pathol. 7:1592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang G, Yang L, Hu M, Hu R, Wang Y, Chen
B, Jiang X and Cui R: Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic
significance of Hsa-miR-100-5p and its related gene signature in
stomach adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7362742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang XD, Xu XH, Zhang SY, Wu Y, Xing CG,
Ru G, Xu HT and Cao JP: Role of miR-100 in the radioresistance of
colorectal cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 5:5452015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin X, Yu S, Zhou L, Shi M, Hu Y, Xu X,
Shen B, Liu S, Yan D and Feng J: Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer
cell-derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient
cells in exosomal miR-100-5p-dependent manner. Int J Nanomedicine.
12:3721–3733. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai Y, Xie CH, Neis JP, Fan CY, Vural E
and Spring PM: MicroRNA expression profiles of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma with docetaxel-induced multidrug
resistance. Head Neck. 33:786–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeng J, Wang L, Zhao J, Zheng Z, Peng J,
Zhang W, Wen T, Nie J, Ding L and Yi D: MiR-100-5p regulates
cardiac hypertrophy through activation of autophagy by targeting
mTOR. Hum Cell. 34:1388–1397. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Huang Y, Hu K, Zhang Z, Yang J and
Wang Z: HIF1A activates the transcription of lncRNA RAET1K to
modulate hypoxia-induced glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via miR-100-5p. Cell Death Dis. 11:1762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Assmann TS, Recamonde-Mendoza M, De Souza
BM and Crispim D: MicroRNA expression profiles and type 1 diabetes
mellitus:systematic review and bioinformatic analysis. Endocr
Connect. 6:773–790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pek SL, Sum CF, Lin MX, Cheng AK, Wong MT,
Lim SC and Tavintharan S: Circulating and visceral adipose miR-100
is down-regulated in patients with obesity and Type 2 diabetes. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 427:112–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ai L, Yi W, Chen L, Wang H and Huang Q:
Xian-Ling-Gu-Bao protects osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast
differentiation by targeting miR-100-5p/KDM6B/RUNX2 axis. In Vitro
Cell Dev Biol Anim. 57:3–9. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kelch S, Balmayor ER, Seeliger C, Vester
H, Kirschke JS and van Griensven M: miRNAs in bone tissue correlate
to bone mineral density and circulating miRNAs are gender
independent in osteoporotic patients. Sci Rep. 7:158612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu J, Kuang L, Chen C, Yang J, Zeng WN, Li
T, Chen H, Huang S, Fu Z, Li J, et al: miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes
derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage
and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in
osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 206:87–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang YS, Chang YC, Chen PH, Li CY, Wu WC
and Kao YH: MicroRNA-100 mediates hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis of human retinal pigment epithelium ARPE-19 cells.
Pharmaceuticals. 14:3142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tan Q, Shi S, Liang J, Cao D, Wang S and
Wang Z: Endometrial cell-derived small extracellular vesicle
miR-100-5p promotes functions of trophoblast during embryo
implantation. Mol Ther-Nucleic Acids. 23:217–231. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang YL, Huang GY, Lv J, Pan LN, Luo X
and Shen J: miR-100 promotes the proliferation of spermatogonial
stem cells via regulating Stat3. Mol Reprod Dev. 84:693–701. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sempere LF, Sokol NS, Dubrovsky EB, Berger
EM and Ambros V: Temporal regulation of microRNA expression in
Drosophila melanogaster mediated by hormonal signals and
broad-Complex gene activity. Dev Biol. 259:9–18. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Henson BJ, Bhattacharjee S, O'Dee DM,
Feingold E and Gollin SM: Decreased expression of miR-125b and
miR-100 in oral cancer cells contributes to malignancy. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 48:569–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao S, Liu S, Wei W, Qi Y and Meng F:
Advances in targeting of miR-10-associated lncRNAs/circRNAs for the
management of cancer. Oncolo Lett. 25:892023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Zhong L, Li P and Zhao P:
MicroRNA-100 enhances autophagy and suppresses migration and
invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells via disruption of
NOX4-dependent mTOR pathway. Clin Transl Sci. 15:567–575. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhou MK, Liu XJ, Zhao ZG and Cheng YM:
MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting Lgr5
expression in colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:2947–2952. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Qi X, Zhang DH, Wu N, Xiao JH, Wang X and
Ma W: ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical
implications. J Med Genet. 52:710–718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Basera A, Hull R, Demetriou D, Bates DO,
Kaufmann AM, Dlamini Z and Marima R: Competing Endogenous RNA
(ceRNA) Networks and Splicing Switches in Cervical Cancer: HPV
Oncogenesis, Clinical Significance and Therapeutic Opportunities.
Microorganisms. 10:18522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang C, Zhou Y, Zhang B, Sheng Z, Sun N,
Yuan B and Wu X: Identification of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA
expression profiles and ceRNA Networks in small cell lung cancer.
BMC Genomics. 24:2172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qin L, Li B, Wang S, Tang Y, Fahira A, Kou
Y, Li T, Hu Z and Huang Z: Construction of an Immune-related
prognostic signature and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in acute
myeloid leukaemia. J Leukoc Biol. 116:146–165. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang W, Zhang Y and Xi S: Upregulation of
lncRNA HAGLROS enhances the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
via modulating miR-100/ATG14 axis-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signals.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:3043–3052. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L, Zhu H, Li X, Ke Y, Yang S and Cheng
Q: Long non-coding RNA HAGLROS facilitates the malignant phenotypes
of NSCLC cells via repressing miR-100 and up-regulating SMARCA5.
Biomed J. 44(6 Suppl 2): S305–S315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang M, Zhai Z, Zhang Y and Wang Y:
Clinical significance and oncogene function of long noncoding RNA
HAGLROS overexpression in ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
300:703–710. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shu L, Guo K, Lin ZH and Liu H: Long
non-coding RNA HAGLROS promotes the development of diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma via suppressing miR-100. J Clin Lab Anal.
36:e241682022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu X, Liu C, Zhang A, Wang Q, Ge J, Li Q
and Xiao J: Long non-coding RNA SDCBP2-AS1 delays the progression
of ovarian cancer via microRNA-100-5p-targeted EPDR1. World J Surg
Oncol. 19:1992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen F, Wu P, Xia R, Yang J, Huo XY, Gu
DY, Tang CJ, De W and Yang F: STAT3-induced lncRNA HAGLROS
overexpression contributes to the malignant progression of gastric
cancer cells via mTOR signal-mediated inhibition of autophagy. Mol
Cancer. 17:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peng J, Zheng H, Liu F, Wu Q and Liu S:
The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 affects autophagy and progression
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the stability of lncRNA
ZFAS1. Infect Agent Cancer. 17:12022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Le F, Ou Y, Luo P and Zhong X: LncRNA
NCK1-AS1 in plasma distinguishes oral ulcer from early-stage oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 27:162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi Y, Zhang DD, Liu JB, Yang XL, Xin R,
Jia CY, Wang HM, Lu GX, Wang PY, Liu Y, et al: Comprehensive
analysis to identify DLEU2L/TAOK1 axis as a prognostic biomarker in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:702–718. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bai W, Peng H, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Li Z, Feng
X, Zhang J, Liang F, Wang L, Zhang N, et al: LINC00589-dominated
ceRNA networks regulate multiple chemoresistance and cancer stem
cell-like properties in HER2+breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer.
8:1152022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lu Y, Zhao X, Liu Q, Li C, Graves-Deal R,
Cao Z, Singh B, Franklin JL, Wang J, Hu H, et al: lncRNA
MIR100HG-derived miR-100 and miR-125b mediate cetuximab resistance
via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nat Med. 23:1331–1341. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shi Y, Guo Z, Fang N, Jiang W, Fan Y, He
Y, Ma Z and Chen Y: hsa_circ_0006168 sponges miR-100 and regulates
mTOR to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1091512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yuan F, Zhang S, Sun Q, Ye L, Xu Y, Xu Z,
Deng G, Zhang S, Liu B and Chen Q: Hsa_circ_0072309 enhances
autophagy and TMZ sensitivity in glioblastoma. CNS Neurosci Ther.
28:897–912. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yao T, Yao Y, Chen Z, Peng Y, Zhong G,
Huang C, Li J and Li R: CircCASC15-miR-100-mTOR may influence the
cervical cancer radioresistance. Cancer Cell Int. 22:1652022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hill M and Tran N: miRNA interplay:
Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0476622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Silkenstedt E, Linton K and Dreyling M:
Mantle cell lymphoma-advances in molecular biology, prognostication
and treatment approaches. Br J Haematol. 195:162–173. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin L, Huang Y, Zhuang W, Lin P and Ma X:
miR-100 inhibits cell proliferation in mantle cell lymphoma by
targeting mTOR. Exp Hematol Oncol. 9:252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nepstad I, Hatfield KJ, Grønningsæter IS
and Reikvam H: The PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in human acute
myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:29072020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun Y, Wang H and Luo C: MiR-100 regulates
cell viability and apoptosis by targeting ATM in pediatric acute
myeloid leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 522:855–861. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zheng YS, Zhang H, Zhang XJ, Feng DD, Luo
XQ, Zeng CW, Lin KY, Zhou H, Qu LH, Zhang P and Chen YQ: MiR-100
regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting RBSP3, a
phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncogene. 31:80–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Chang JH, Poppe MM, Hua CH, Marcus KJ and
Esiashvili N: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
68(Suppl 2): e283712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li XJ, Luo XQ, Han BW, Duan FT, Wei PP and
Chen YQ: MicroRNA-100/99a, deregulated in acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia, suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis by
regulating the FKBP51 and IGF1R/mTOR signalling pathways. Br J
Cancer. 109:2189–2198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ou A, Yung WKA and Majd N: Molecular
mechanisms of treatment resistance in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci.
22:3512020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Alrfaei BM, Clark P, Vemuganti R and Kuo
JS: MicroRNA miR-100 decreases glioblastoma growth by targeting
SMARCA5 and ErbB3 in tumor-initiating cells. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 19:15330338209607482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Alrfaei BM, Vemuganti R and Kuo JS:
microRNA-100 targets SMRT/NCOR2, reduces proliferation, and
improves survival in glioblastoma animal models. PLoS One.
8:e808652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guo R, Mao YP, Tang LL, Chen L, Sun Y and
Ma J: The evolution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma staging. Br J
Radiol. 92:201902442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lee HM, Okuda KS, González FE and Patel V:
Current perspectives on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1164:11–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Peng Q, Zhang L, Li J, Wang W, Cai J, Ban
Y, Zhou Y, Hu M, Mei Y, Zeng Z, et al: FOXA1 suppresses the growth,
migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through
repressing miR-100-5p and miR-125b-5p. J Cancer. 11:2485–2495.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
He W, Huang Y, Jiang CC, Zhu Y, Wang L,
Zhang W, Huang W, Zhou T and Tang S: miR-100 inhibits cell growth
and proliferation by targeting HOXA1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:593–602. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun X, Liu X, Wang Y, Yang S, Chen Y and
Yuan T: miR-100 inhibits the migration and invasion of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting IGF1R. Oncol Lett.
15:8333–8338. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shi W, Alajez NM, Bastianutto C, Hui AB,
Mocanu JD, Ito E, Busson P, Lo KW, Ng R, Waldron J, et al:
Significance of Plk1 regulation by miR-100 in human nasopharyngeal
cancer. Int J Cancer. 126:2036–2048. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Alexander M, Kim SY and Cheng H: Update
2020: Management of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung. 198:897–907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu J, Lu KH, Liu ZL, Sun M, De W and Wang
ZX: MicroRNA-100 is a potential molecular marker of non-small cell
lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting
polo-like kinase 1. BMC Cancer. 12:5192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Han W, Ren X, Yang Y, Li H, Zhao L and Lin
Z: microRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell
lung cancer via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
Wnt/β-catenin by targeting HOXA1. Thorac Cancer. 11:1679–1688.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Nagata Y, Yamamoto S and Kato K: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors in esophageal cancer: Clinical development
and perspectives. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 18:21431772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang N, Fu H, Song L, Ding Y, Wang X,
Zhao C and Zhao Y, Jiao F and Zhao Y: MicroRNA-100 promotes
migration and invasion through mammalian target of rapamycin in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 32:1409–1418. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhou F, Tan F, Gao Y, Sun N, Xu X, Shao K
and He J: MicroRNA-99a/100 promotes apoptosis by targeting mTOR in
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:4112013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhou SM, Zhang F, Chen XB, Jun CM, Jing X,
Wei DX, Xia Y, Zhou YB, Xiao XQ, Jia RQ, et al: miR-100 suppresses
the proliferation and tumor growth of esophageal squamous cancer
cells via targeting CXCR7. Oncol Rep. 35:3453–3459. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou S, Yang B, Zhao Y, Xu S, Zhang H and
Li Z: Prognostic value of microRNA-100 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Surg Res. 192:515–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nagaraju GP, Dariya B, Kasa P, Peela S and
El-Rayes BF: Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer
Biol. 86:622–632. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Ren Z, Ma X, Duan Z and Chen X: Diagnosis,
therapy, and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal Cell
Pathol (Amst). 2020:81574062020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ge Y, Shu J, Shi G, Yan F, Li Y and Ding
H: miR-100 suppresses the proliferation, invasion, and migration of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting CXCR7. J Immunol Res.
2021:99207862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhou HC, Fang JH, Shang LR, Zhang ZJ, Sang
Y, Xu L, Yuan Y, Chen MS, Zheng L, Zhang Y and Zhuang S: MicroRNAs
miR-125b and miR-100 suppress metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by disrupting the formation of vessels that encapsulate
tumour clusters. J Pathol. 240:450–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen P, Zhao X and Ma L: Downregulation of
microRNA-100 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 383:49–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski
R and Sitarz R: Gastric cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors,
classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:40122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wei L, Sun J, Zhang N, Zheng Y, Wang X, Lv
L, Liu J, Xu Y, Shen Y and Yang M: Noncoding RNAs in gastric
cancer: Implications for drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 19:622020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cao Y, Song J, Ge J, Song Z, Chen J and Wu
C: MicroRNA-100 suppresses human gastric cancer cell proliferation
by targeting CXCR7. Oncol Lett. 15:453–458. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chen Z, Liu X, Hu Z, Wang Y, Liu M, Liu X,
Li H, Ji R, Guo Q and Zhou Y: Identification and characterization
of tumor suppressor and oncogenic miRNAs in gastric cancer. Oncol
Lett. 10:329–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang N, Hu X, Du Y and Du J: The role of
miRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and chemoradiotherapy.
Biomed Pharmacother. 134:1110992021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Zhao W, Dai S, Yue L, Xu F, Gu J, Dai X
and Qian X: Emerging mechanisms progress of colorectal cancer liver
metastasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10815852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Czauderna C, Luley K, von Bubnoff N and
Marquardt JU: Tailored systemic therapy for colorectal cancer liver
metastases. Int J Mol Sci. 22:117802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Peng H, Luo J, Hao H, Hu J, Xie SK, Ren D
and Rao B: MicroRNA-100 regulates SW620 colorectal cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting RAP1B. Oncol Rep.
31:2055–2062. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fujino Y, Takeishi S, Nishida K, Okamoto
K, Muguruma N, Kimura T, Kitamura S, Miyamoto H, Fujimoto A,
Higashijima J, et al: Downregulation of micro RNA-100/micro
RNA-125b is associated with lymph node metastasis in early
colorectal cancer with submucosal invasion. Cancer Sci.
108:390–397. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
89
|
Wood LD, Canto MI, Jaffee EM and Simeone
DM: Pancreatic cancer: Pathogenesis, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Gastroenterology. 163:386–402.e1. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Jiang S, Fagman JB, Ma Y, Liu J, Vihav C,
Engstrom C, Liu B and Chen C: A comprehensive review of pancreatic
cancer and its therapeutic challenges. Aging (Albany NY).
14:7635–7649. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Huang JS, Egger ME, Grizzle WE and McNally
LR: MicroRNA-100 regulates IGF1-receptor expression in metastatic
pancreatic cancer cells. Biotech Histochem. 88:397–402. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Dobre M, Herlea V, Vlăduţ C, Ciocîrlan M,
Balaban VD, Constantinescu G, Diculescu M and Milanesi E:
Dysregulation of miRNAs targeting the IGF-1R pathway in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Cells. 10:18562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B,
Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Crouzet L, Laguerre B,
Belaud-Rotureau MA, et al: Immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma:
The future is now. Int J Mol Sci. 21:25322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li F, Aljahdali IAM, Zhang R, Nastiuk KL,
Krolewski JJ and Ling X: Kidney cancer biomarkers and targets for
therapeutics: Survivin (BIRC5), XIAP, MCL-1, HIF1α, HIF2α, NRF2,
MDM2, MDM4, p53, KRAS and AKT in renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 40:2542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Chen P, Lin C, Quan J, Lai Y, He T, Zhou
L, Pan X, Wu X, Wang Y, Ni L, et al: Oncogenic miR-100-5p is
associated with cellular viability, migration and apoptosis in
renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 16:5023–5030. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Adamaki M and Zoumpourlis V: Prostate
cancer biomarkers: From diagnosis to prognosis and precision-guided
therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 228:1079322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST,
Sousa-Canavez JM, Sañudo A, Dall'Oglio MF, Camara-Lopes LH and
Srougi M: MicroRNA-100 expression is independently related to
biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. J Urol. 185:1118–1122.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Leite KR, Morais DR, Reis ST, Viana N,
Moura C, Florez MG, Silva IA, Dip N and Srougi M: MicroRNA 100: A
context dependent miRNA in prostate cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
68:797–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wang M, Ren D, Guo W, Wang Z, Huang S, Du
H, Song L and Peng X: Loss of miR-100 enhances migration, invasion,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties in
prostate cancer cells through targeting Argonaute 2. Int J Oncol.
45:362–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Nabavi N, Saidy NRN, Venalainen E, Haegert
A, Parolia A, Xue H, Wang Y, Wu R, Dong X, Collins C, et al:
miR-100-5p inhibition induces apoptosis in dormant prostate cancer
cells and prevents the emergence of castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Sci Rep. 7:40792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ye Y, Li SL and Wang JJ: miR-100-5p
downregulates mTOR to suppress the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of prostate cancer cells. Front Oncol. 10:5789482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chen DW, Lang BHH, McLeod DSA, Newbold K
and Haymart MR: Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 401:1531–1544. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Şah Ünal FT, Gökçay Canpolat A, Elhan AH,
Sevim S, Sak SD, Emral R, Demir Ö, Güllü S, Erdoğan MF, Çorapçıoğlu
D and Şahin M: Cancer rates and characteristics of thyroid nodules
with macrocalcification. Endocrine. 84:1021–1029. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Ma P and Han J: Overexpression of
miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via
targeting FZD8. Open Med (Wars). 17:1172–1182. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Trapani D, Ginsburg O, Fadelu T, Lin NU,
Hassett M, Ilbawi AM, Anderson BO and Curigliano G: Global
challenges and policy solutions in breast cancer control. Cancer
Treat Rev. 104:1023392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xie H, Xiao R, He Y, He L, Xie C, Chen J
and Hong Y: MicroRNA-100 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation,
invasion and migration by targeting FOXA1. Oncol Lett. 22:8162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Gebeshuber CA and Martinez J: miR-100
suppresses IGF2 and inhibits breast tumorigenesis by interfering
with proliferation and survival signaling. Oncogene. 32:3306–3310.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Li X, Ren Y, Liu D, Yu X and Chen K: Role
of miR-100-5p and CDC25A in breast carcinoma cells. PeerJ.
9:e122632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Gong Y, He T, Yang L, Yang G, Chen Y and
Zhang X: The role of miR-100 in regulating apoptosis of breast
cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:116502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Throwba H PK, Unnikrishnan L, Pangath M,
Vasudevan K, Jayaraman S, Li M, Iyaswamy A, Palaniyandi K and
Gnanasampanthapandian D: The epigenetic correlation among ovarian
cancer, endometriosis and PCOS: A review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
180:1038522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Volkova LV, Pashov AI and Omelchuk NN:
Cervical carcinoma: Oncobiology and biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci.
22:125712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Schoutrop E, Moyano-Galceran L, Lheureux
S, Mattsson J, Lehti K, Dahlstrand H and Magalhaes I: Molecular,
cellular and systemic aspects of epithelial ovarian cancer and its
tumor microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol. 86:207–223. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Huang C, Qin X, Zhao N, Jin H, Zhang S and
Yang H: Erratum: MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor in
cervical cancer via downregulating the SATB1 expression and
regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncol Lett. 22:7412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Li BH, Zhou JS, Ye F, Cheng XD, Zhou CY,
Lu WG and Xie X: Reduced miR-100 expression in cervical cancer and
precursors and its carcinogenic effect through targeting PLK1
protein. Eur J Cancer. 47:2166–2174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Crosbie EJ, Kitson SJ, McAlpine JN,
Mukhopadhyay A, Powell ME and Singh N: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
399:1412–1428. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Chen C, Zhang Q and Kong B: miRNA-576-5p
promotes endometrial cancer cell growth and metastasis by targeting
ZBTB4. Clin Transl Oncol. 25:706–720. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
118
|
Takebayashi K, Nasu K, Okamoto M, Aoyagi
Y, Hirakawa T and Narahara H: hsa-miR-100-5p, an overexpressed
miRNA in human ovarian endometriotic stromal cells, promotes
invasion through attenuation of SMARCD1 expression. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 18:312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Valihrach L, Androvic P and Kubista M:
Circulating miRNA analysis for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Mol
Aspects Med. 72:1008252020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
O'Neill RS and Stoita A: Biomarkers in the
diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: Are we closer to finding the golden
ticket? World J Gastroenterol. 27:4045–40875. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Wang H, Meng Q, Qian J, Li M, Gu C and
Yang Y: RNA-based diagnostic markers discovery and therapeutic
targets development in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 234:1081232022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Wang S, Li L, Yang M, Wang X, Zhang H, Wu
N, Jia K, Wang J, Li M, Wei L and Liu J: Identification of three
circulating MicroRNAs in plasma as clinical biomarkers for breast
cancer detection. J Clin Med. 12:3222022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Fuso P, Di Salvatore M, Santonocito C,
Guarino D, Autilio C, Mulè A, Arciuolo D, Rinninella A, Mignone F,
Ramundo M, et al: Let-7a-5p, miR-100-5p, miR-101-3p, and
miR-199a-3p hyperexpression as potential predictive biomarkers in
early breast cancer patients. J Pers Med. 11:8162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Jin Y, Wong YS, Goh BKP, Chan CY, Cheow
PC, Chow PKH, Lim TKH, Goh GBB, Krishnamoorthy TL, Kumar R, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic
biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 9:104642019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Qureshi A, Fahim A, Kazi N, Farsi Kazi SA
and Nadeem F: Expression of miR-100 as a novel ancillary
non-invasive biomarker for early detection of bladder carcinoma. J
Pak Med Assoc. 68:759–763. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Ludwig N, Nourkami-Tutdibi N, Backes C,
Lenhof HP, Graf N, Keller A and Meese E: Circulating serum miRNAs
as potential biomarkers for nephroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
62:1360–1367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Blanca A, Sanchez-Gonzalez A, Requena MJ,
Carrasco-Valiente J, Gomez-Gomez E, Cheng L, Cimadamore A,
Montironi R and Lopez-Beltran A: Expression of miR-100 and miR-138
as prognostic biomarkers in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
APMIS. 127:545–553. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Yamanaka Z, Sasaki T, Yamanaka A, Kato K
and Nishi H: Circulating and tissue miR-100 acts as a potential
diagnostic biomarker for cervical cancer. Cancer Biomark.
32:551–558. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Bahnassy AA, Salem SE, El-Sayed M,
Khorshid O, Abdellateif MS, Youssef AS, Mohanad M, Hussein M, Zekri
AN and Ali NM: MiRNAs as molecular biomarkers in stage II egyptian
colorectal cancer patients. Exp Mol Pathol. 105:260–271. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wang X, Chen L, Jin H, Wang S, Zhang Y,
Tang X and Tang G: Screening miRNAs for early diagnosis of
colorectal cancer by small RNA deep sequencing and evaluation in a
Chinese patient population. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1159–1166.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gong Y, Yang G, Wang Q, Wang Y and Zhang
X: NME2 is a master suppressor of apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
via transcriptional regulation of miR-100 and other survival
factors. Mol Cancer Res. 18:287–299. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Damodaran M, Chinambedu Dandapani M, Raj
Simon Durai, Sundaram Sandhya, VenkatRamanan S, Ramachandran I and
Venkatesan V: Differentially expressed miR-20, miR-21, miR-100,
miR-125a and miR-146a as a potential biomarker for prostate cancer.
Mol Biol Rep. 48:3349–3356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Jakob M, Mattes LM, Küffer S, Unger K,
Hess J, Bertlich M, Haubner F, Ihler F, Canis M, Weiss BG and Kitz
J: MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma:
Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for
oral cancer. Head Neck. 41:3499–3515. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Zhao JY, Wang F, Li Y, Zhang XB, Yang L,
Wang W, Xu H, Liu DZ and Zhang LY: Five miRNAs considered as
molecular targets for predicting esophageal cancer. Med Sci Monit.
21:32222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang HC and Tang KF: Clinical value of
integrated-signature miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Cancer Med.
6:1893–1903. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wang G, Chen L, Meng J, Chen M, Zhuang L
and Zhang L: Overexpression of microRNA-100 predicts an unfavorable
prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 45:373–379.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Liu HT, Wang YW, Xing AY, Shi DB, Zhang H,
Guo XY, Xu J and Gao P: Prognostic value of microRNA signature in
patients with gastric cancers. Sci Rep. 7:428062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
He QL, Qin SY, Tao L, Ning HJ and Jiang
HX: Prognostic value and prospective molecular mechanism of
miR-100-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive study based
on 1,258 samples. Oncol Lett. 18:6126–6142. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Hassan NM, Refaat LA, Ismail GN,
Abdellateif M, Fadel SA and AbdelAziz RS: Diagnostic, prognostic
and predictive values of miR-100 and miR-210 in pediatric acute
lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematology. 25:405–413. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Nussinov R, Tsai CJ and Jang H: Anticancer
drug resistance: An update and perspective. Drug Resist Updat.
59:1007962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Bukowski K, Kciuk M and Kontek R:
Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:32332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Luan Y, Zhang S, Zuo L and Zhou L:
Overexpression of miR-100 inhibits cell proliferation, migration,
and chemosensitivity in human glioblastoma through FGFR3. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:3391–3400. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Xiao F, Bai Y, Chen Z, Li Y, Luo L, Huang
J, Yang J, Liao H and Guo L: Downregulation of HOXA1 gene affects
small cell lung cancer cell survival and chemoresistance under the
regulation of miR-100. Eur J Cancer. 50:1541–1554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Feng B, Wang R and Chen LB: MiR-100
resensitizes docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells
(SPC-A1) to docetaxel by targeting Plk1. Cancer Lett. 317:184–191.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Guo P, Xiong X, Zhang S and Peng D:
miR-100 resensitizes resistant epithelial ovarian cancer to
cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 36:3552–3558. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Liu Y, Zhu ST, Wang X, Deng J, Li WH,
Zhang P and Liu BS: MiR-100 inhibits osteosarcoma cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion and enhances
chemosensitivity by targeting IGFIR. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
15:NP40–NP48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Lai Y, Kacal M, Kanony M, Stukan I, Jatta
K, Kis L, Norberg E, Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H, Lewensohn R,
Hydbring P and Ekman S: miR-100-5p confers resistance to ALK
tyrosine kinase inhibitors Crizotinib and Lorlatinib in EML4-ALK
positive NSCLC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 511:260–265. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Lobert S, Jefferson B and Morris K:
Regulation of β-tubulin isotypes by micro-RNA 100 in MCF7 breast
cancer cells. Cytoskeleton. 68:355–362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Moqadam FA, Lange-Turenhout EAM, Ariës IM,
Pieters R and den Boer ML: MiR-125b, miR-100 and miR-99a
co-regulate vincristine resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Leuk Res. 37:1315–1321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Ng WL, Yan D, Zhang X, Mo YY and Wang Y:
Over-expression of miR-100 is responsible for the low-expression of
ATM in the human glioma cell line: M059J. DNA Repair (Amst).
9:1170–1175. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Zhou B, Lin W, Long Y, Yang Y, Zhang H, Wu
K and Chu Q: Notch signaling pathway: Architecture, disease, and
therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lee YJ, Kim WR, Park EG, Lee DH, Kim JM,
Shin HJ, Jeong HS, Roh HY and Kim HS: Exploring the key signaling
pathways and ncRNAs in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
25:45482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Peng WX, Koirala P and Mo YY:
LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene.
36:5661–5667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Park JH, Pyun WY and Park HW: Cancer
metabolism: Phenotype, signaling and therapeutic targets. Cells.
9:23082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Song SK, Jung WY, Park SK, Chung CW and
Park Y: Significantly different expression levels of microRNAs
associated with vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma and
their prognostic significance after surgical resection. PLoS One.
14:e02168472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Chen D, Sun Y, Yuan Y, Han Z, Zhang P,
Zhang J, You MJ, Teruya-Feldstein J, Wang M, Gupta S, et al:
miR-100 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition but suppresses
tumorigenesis, migration and invasion. PLoS Genet. 10:e10041772014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Yang J, Chen Z, Wang X, Xu M, Fang H, Li
F, Liu Y, Jiang Y, Ding Y, Li J and Wang S: Inactivation of miR-100
combined with arsenic treatment enhances the malignant
transformation of BEAS-2B cells via stimulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:965–973.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Huang C, Qin X, Zhao N, Jin H, Zhang S and
Yang H: (Corrigendum) MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor
in cervical cancer via downregulating the SATB1 expression and
regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncol Lett. 22:2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Song P, Gao Z, Bao Y, Chen L, Huang Y, Liu
Y, Dong Q and Wei X: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in
carcinogenesis and cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 17:462024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Peng CW, Yue LX, Zhou YQ, Tang S, Kan C,
Xia LM, Yang F and Wang SY: miR-100-3p inhibits cell proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through targeting to
BMPR2. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3542019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
162
|
Yang G, Gong Y, Wang Q, Wang Y and Zhang
X: The role of miR-100-mediated Notch pathway in apoptosis of
gastric tumor cells. Cell Signal. 27:1087–1101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Huang C, Qin X, Zhao N, Jin H, Zhang S and
Yang H: MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor in cervical
cancer via downregulating the SATB1 expression and regulating
AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncol Lett. 20:1336–1344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Morgos DT, Stefani C, Miricescu D, Greabu
M, Stanciu S, Nica S, Stanescu-Spinu II, Balan DG,
Balcangiu-Stroescu AE, Coculescu EC, et al: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR
and MAPK signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
25:18482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Qin C, Huang RY and Wang ZX: Potential
role of miR-100 in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Tumour
Biol. 36:1403–1409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Wei X, Feng Y, Fu Y, Liu F, Chen Q, Zhang
W, Zhao Y, Huang X, Chen Y, Li Q and Zhang Q: miR-100-5p is
upregulated in multiple myeloma and involves in the pathogenesis of
multiple myeloma through targeting MTMR3. Hematology.
28:21968572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Eniafe J and Jiang S: MicroRNA-99 family
in cancer and immunity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 12:e16352021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Gu L, Li H, Chen L, Ma X, Gao Y, Li X,
Zhang Y, Fan Y and Zhang X: MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular
signatures in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:32545–32560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Glassy MC, Abak A, Hussen
BM, Niazi V and Taheri M: The interaction between miRNAs/lncRNAs
and Notch pathway in human disorders. Biomed Pharmacother.
138:1114962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Servín-González LS, Granados-López AJ and
López JA: Families of microRNAs expressed in clusters regulate cell
signaling in cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:12773–12790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Shemesh R, Laufer-Geva S, Gorzalczany Y,
Anoze A, Sagi-Eisenberg R, Peled N and Roisman LC: The interaction
of mast cells with membranes from lung cancer cells induces the
release of extracellular vesicles with a unique miRNA signature.
Sci Rep. 13:215442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Jamali L, Tofigh R, Tutunchi S, Panahi G,
Borhani F, Akhavan S, Nourmohammadi P, Ghaderian SMH, Rasouli M and
Mirzaei H: Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic
biomarkers in gastric and esophageal cancers. J Cell Physiol.
233:8538–8550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Farasati Far B, Vakili K, Fathi M,
Yaghoobpoor S, Bhia M and Naimi-Jamal MR: The role of microRNA-21
(miR-21) in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis of
gastrointestinal cancers: A review. Life Sci. 316:1213402023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Grimaldi AM, Nuzzo S, Condorelli G,
Salvatore M and Incoronato M: Prognostic and clinicopathological
significance of miR-155 in breast cancer: A systematic review. Int
J Mol Sci. 21:58342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Seyhan AA: Trials and tribulations of
microRNA therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 25:14692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Qian H, Maghsoudloo M, Kaboli PJ,
Babaeizad A, Cui Y, Fu J, Wang Q and Imani S: Decoding the promise
and challenges of miRNA-based cancer therapies: An essential update
on miR-21, miR-34, and miR-155. Int J Med Sci. 21:2781–2798. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|