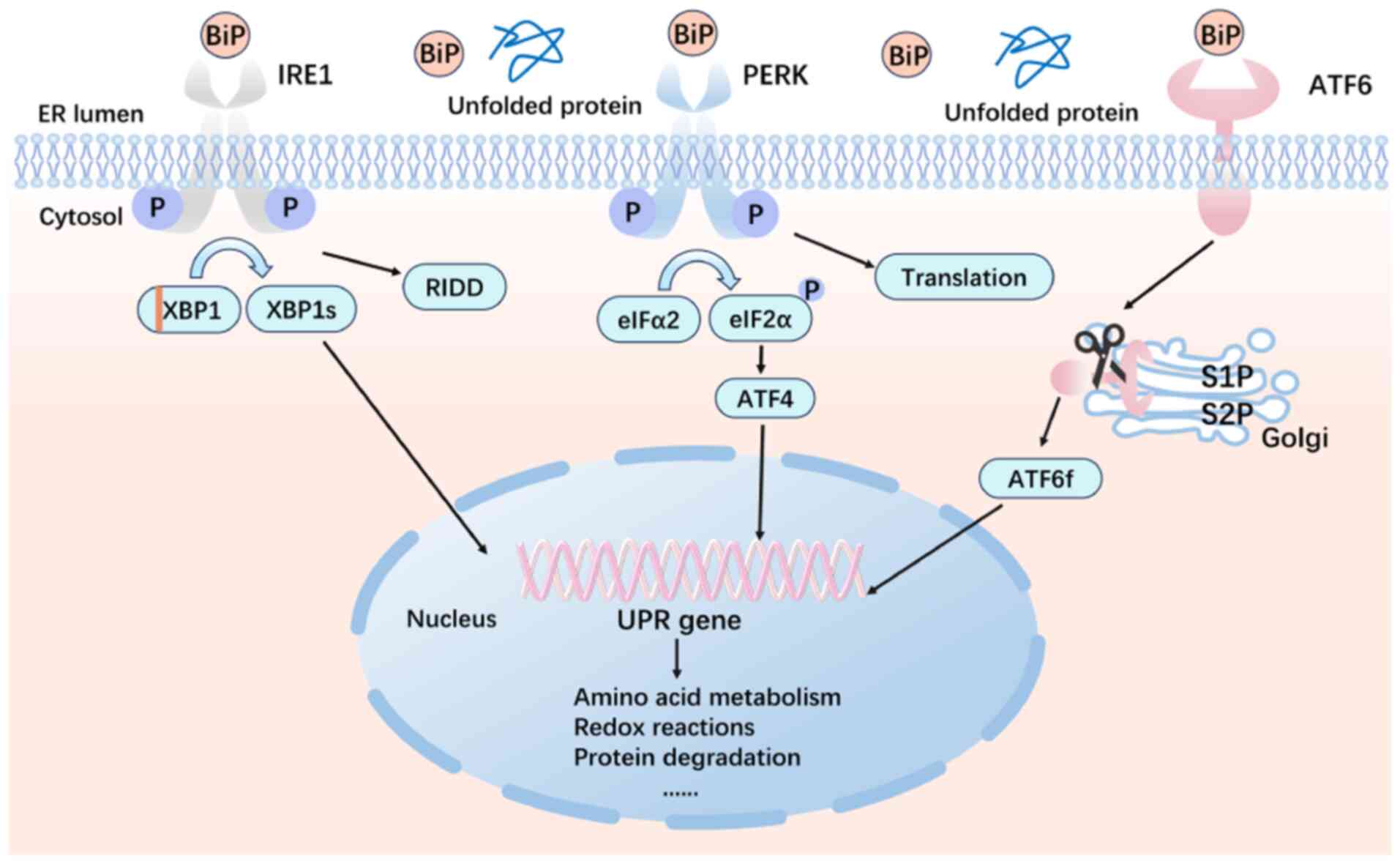
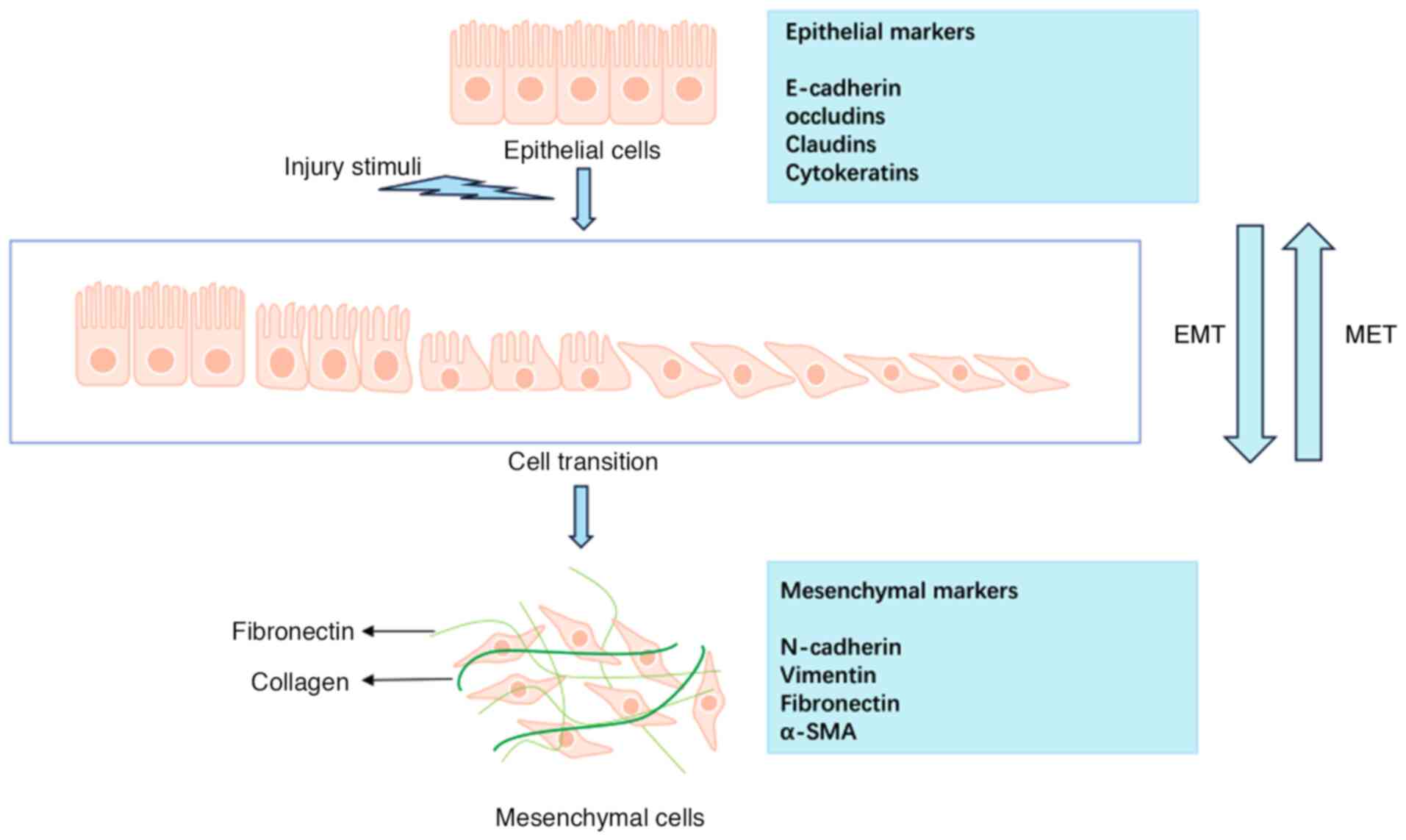
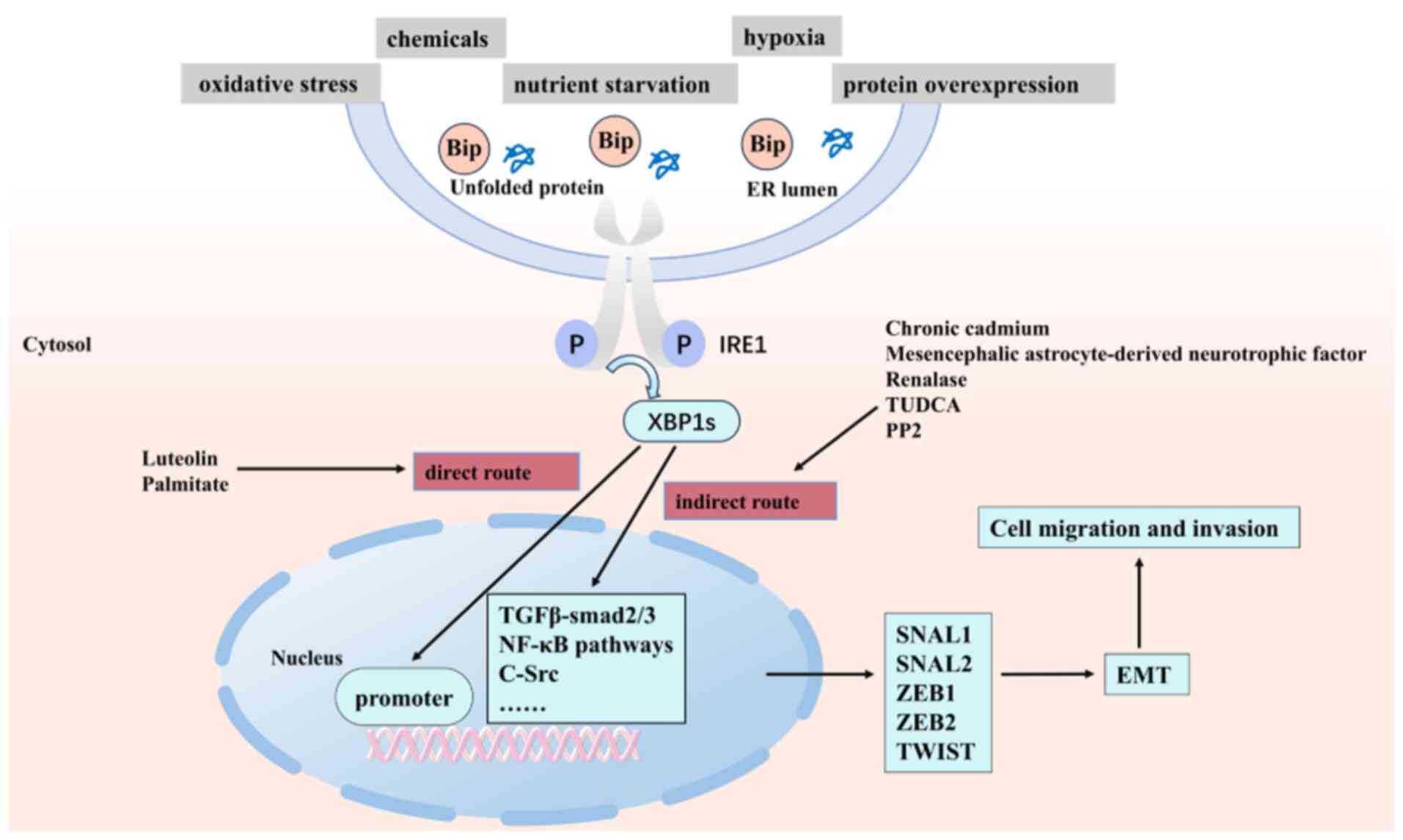
|
1
|
Santamaría PG, Mazón MJ, Eraso P and
Portillo F: UPR: An upstream signal to EMT induction in cancer. J
Clin Med. 8:6242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marconi GD, Fonticoli L, Rajan TS,
Pierdomenico SD, Trubiani O, Pizzicannella J and Diomede F:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): The type-2 EMT in wound
healing, tissue regeneration and organ fibrosis. Cells.
10:15872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brabletz S, Schuhwerk H, Brabletz T and
Stemmler MP: Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO
J. 40:e1086472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kropski JA and Blackwell TS: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disease. J Clin
Invest. 128:64–73. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uddin MS, Tewari D, Sharma G, Kabir MT,
Barreto GE, Bin-Jumah MN, Perveen A, Abdel-Daim MM and Ashraf GM:
Molecular mechanisms of ER stress and UPr in the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 57:2902–2919. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yap KN, Yamada K, Zikeli S, Kiaris H and
Hood WR: Evaluating endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded
protein response through the lens of ecology and evolution. Biol
Rev Camb Philos Soc. 96:541–556. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sims SG, Cisney RN, Lipscomb MM and Meares
GP: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in astrocytes. Glia.
70:5–19. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C and Yu S: The C/EBP
homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in
endoplasmic reticulum Stress-induced apoptosis and microbial
infection. Front Immunol. 9:30832018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang P, Li J, Tao J and Sha B: The luminal
domain of the ER stress sensor protein PERK binds misfolded
proteins and thereby triggers PERK oligomerization. J Biol Chem.
293:4110–4121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sato R, Semba T, Saya H and Arima Y:
Concise review: Stem cells and Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic targets. Stem
Cells. 34:1997–2007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu R, Won JY, Kim CH, Kim DE and Yim H:
Roles of the phosphorylation of transcriptional factors in
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Oncol. 2019:58104652019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tomecka P, Kunachowicz D, Górczyńska J,
Gebuza M, Kuźnicki J, Skinderowicz K and Choromańska A: Factors
determining Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Int J Mol Sci. 25:89722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin YT and Wu KJ: Epigenetic regulation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focusing on hypoxia and TGF-β
signaling. J Biomed Sci. 27:392020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sheikh KA, Amjad M, Irfan MT, Anjum S,
Majeed T, Riaz MU, Jassim AY, Sharif EAM and Ibrahim WN: Exploring
TGF-β signaling in cancer progression: Prospects and therapeutic
strategies. Onco Targets Ther. 18:233–262. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Ding C, Liu B, Yu T, Wang Z, Peng J, Gu Y
and Li Z: SIRT7 protects against liver fibrosis by suppressing
stellate cell activation via TGF-β/SMAD2/3 pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 180:1174772024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang YE: Non-smad signaling pathways of
the TGF-β family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 9:a0221292017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kahlert UD, Joseph JV and Kruyt FAE:
EMT-and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: Importance
for disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities.
Mol Oncol. 11:860–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Long Y, Niu Y, Liang K and Du Y:
Mechanical communication in fibrosis progression. Trends Cell Biol.
32:70–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang C and Ogawa R: The vascular
involvement in soft tissue Fibrosis-lessons learned from
pathological scarring. Int J Mol Sci. 21:25422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun Z, He W, Meng H, Ji Z, Qu J and Yu G:
Lactate activates ER stress to promote alveolar epithelial cells
apoptosis in pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 25:4012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bradley KL, Stokes CA, Marciniak SJ,
Parker LC and Condliffe AM: Role of unfolded proteins in lung
disease. Thorax. 76:92–99. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maiers JL, Kostallari E, Mushref M, de
Assuncao TM, Li H, Jalan-Sakrikar N, Huebert RC, Cao S, Malhi H and
Shah VH: The unfolded protein response mediates fibrogenesis and
collagen I secretion through regulating TANGO1 in mice. Hepatology.
65:983–998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li W, Liu P, Liu H, Zhang F and Fu Y:
Integrative analysis of genes reveals endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related immune responses involved in dilated cardiomyopathy
with fibrosis. Apoptosis. 28:14222023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Chen W and Wang Y: STING is an
essential regulator of heart inflammation and fibrosis in mice with
pathological cardiac hypertrophy via endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 125:1100222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghafoor H, Chu H, Huang J, Chen M, Wang S,
Wang J and Chao J: ZC3H4 promotes pulmonary fibrosis via an ER
stress-related positive feedback loop. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
435:1158562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Li C, Liu J, He Y, Wei Y and Chen
J: Inhibition of ER stress by targeting the IRE1α-TXNDC5 pathway
alleviates crystalline silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 95:1075192021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Cai W, Jin F, Wang X, Liu W, Li T,
Yang X, Liu H, Xu H and Yang F: Thalidomide alleviates pulmonary
fibrosis induced by silica in mice by inhibiting ER stress and the
TLR4-NF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 23:56562022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang X, Sun W, Jing X, Zhang Q, Huang H
and Xu Z: Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates the fate of lung
resident mesenchymal stem cell to myofibroblast via C/EBP
homologous protein during pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther.
13:2792022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C,
Kroemer G, Kaufman RJ, Malhi H and Ren J: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress in liver diseases. Hepatology. 77:619–639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Abdelfattah AM, Mahmoud SS, El-Wafaey DI,
Abdelgeleel HM and Abdelhamid AM: Diacerein ameliorates
cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis in rat via modulating
HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB/JNK pathway and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci
Rep. 13:114552023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu F, Yang J, Liu J, Wang Y, Mu J, Zeng Q,
Deng S and Zhou H: Signaling pathways in cancer-associated
fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 6:2182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wenxiu J, Mingyue Y, Fei H, Yuxin L,
Mengyao W, Chenyang L, Jia S, Hong Z, Shih DQ, Targan SR and
Xiaolan Z: Effect and mechanism of TL1A expression on
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition during chronic Colitis-related
intestinal fibrosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021:59270642021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu D, Zhang C and Zhang J, Xu GT and
Zhang J: Molecular pathogenesis of subretinal fibrosis in
neovascular AMD focusing on epithelial-mesenchymal transformation
of retinal pigment epithelium. Neurobiol Dis. 185:1062502023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peng D, Fu M, Wang M, Wei Y and Wei X:
Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer
therapy. Mol Cancer. 21:1042022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Hu X, Zhao Z, Chen Z,
Wang X, Zhang Z, Jin H and Zhang J: Luteolin inhibits subretinal
fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in laser-induced
mouse model via suppression of Smad2/3 and YAP signaling.
Phytomedicine. 116:1548652023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Lin R, Huang Y, Wang Z,
Xu S, Wang L, Chen F, Zhang J, Pan K and Yin Z: Lactate drives
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease via
the H3K14la/KLF5 pathway. Redox Biol. 75:1032462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yan Z, Zhu J, Liu Y, Li Z, Liang X, Zhou
S, Hou Y, Chen H, Zhou L, Wang P, et al: DNA-PKcs/AKT1 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition during radiation-induced
pulmonary fibrosis by inducing ubiquitination and degradation of
Twist1. Clin Transl Med. 14:e16902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagavally RR, Sunilkumar S, Akhtar M,
Trombetta LD and Ford SM: Chrysin ameliorates
Cyclosporine-A-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1-Induced
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Mol Sci. 22:102522021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang W, Shi Y, Oyang L, Cui S, Li S, Li
J, Liu L, Li Y, Peng M, Tan S, et al: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-a key guardian in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 10:3432024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao R, Lv Y, Feng T, Zhang R, Ge L, Pan
J, Han B, Song G and Wang L: ATF6α promotes prostate cancer
progression by enhancing PLA2G4A-mediated arachidonic acid
metabolism and protecting tumor cells against ferroptosis.
Prostate. 82:617–629. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ma X, Li Y and Zhao B: Ribosomal protein
L5 (RPL5)/E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) signaling suppresses
breast cancer progression via regulating endoplasmic reticulum
stress and autophagy. Bioengineered. 13:8076–8086. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pavlović N and Heindryckx F: Exploring the
role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma
through mining of the human protein atlas. Biology (Basel).
10:6402021.
|
|
43
|
Chen J, Lei C, Zhang H, Huang X, Yang Y,
Liu J, Jia Y, Shi H, Zhang Y, Zhang J and Du J: RPL11 promotes
non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by regulating
endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell autophagy. BMC Mol Cell Biol.
24:72023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oakes SA: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 190:934–946. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xue XC, Zhou YY, Xu LY, Wei LY, Hu YJ,
Yang J, Zhang XQ, Wang MY, Han YL and Chen JJ: Tongguanteng
injection exerts anti-osteosarcoma effects through the ER
stress-associated IRE1/CHOP pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther.
24:4002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bae H, Song G, Lee JY, Hong T, Chang MJ
and Lim W: Laminarin-derived from brown algae suppresses the growth
of ovarian cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction and ER
stress. Mar Drugs. 18:1522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Labrie M, Brugge JS, Mills GB and
Zervantonakis IK: Therapy resistance: Opportunities created by
adaptive responses to targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
22:323–339. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ang HL, Mohan CD, Shanmugam MK, Leong HC,
Makvandi P, Rangappa KS, Bishayee A, Kumar AP and Sethi G:
Mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer and its
regulation by natural compounds. Med Res Rev. 43:1141–1200. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huang Y, Hong W and Wei X: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression
and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fontana R, Mestre-Farrera A and Yang J:
Update on Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression.
Annu Rev Pathol. 19:133–156. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Liang H, Chen Z, Yang R, Huang Q, Chen H,
Chen W, Zou L, Wei P, Wei S, Yang Y and Zhang Y: Methyl gallate
suppresses the migration, invasion, and Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the AMPK/NF-κB
signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol.
13:8942852022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Melisi D, Garcia-Carbonero R, Macarulla T,
Pezet D, Deplanque G, Fuchs M, Trojan J, Oettle H, Kozloff M,
Cleverly A, et al: Galunisertib plus gemcitabine vs. gemcitabine
for first-line treatment of patients with unresectable pancreatic
cancer. Br J Cancer. 119:1208–1214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shah PP, Dupre TV, Siskind LJ and Beverly
LJ: Common cytotoxic chemotherapeutics induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) downstream of ER stress.
Oncotarget. 8:22625–22639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Delbrel E, Uzunhan Y, Soumare A, Gille T,
Marchant D, Planès C and Boncoeur E: ER stress is involved in
Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal transition of alveolar epithelial cells
exposed to a hypoxic micro-environment. Int J Mol Sci. 20:12992019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gong L, Liu G, Zhu H, Li C, Li P, Liu C,
Tang H, Wu K, Wu J, Liu D, et al: IL-32 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by triggering endoplasmic
reticulum stress in A549 cells. BMC Pulm Med. 20:2782020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liang X, Duan N, Wang Y, Shu S, Xiang X,
Guo T, Yang L, Zhang S, Tang X and Zhang J: Advanced oxidation
protein products induce endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
human renal glomerular endothelial cells through induction of
endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Diabetes Complications. 30:573–579.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Han J, Pang X, Shi X, Zhang Y, Peng Z and
Xing Y: Ginkgo biloba extract EGB761 ameliorates the extracellular
matrix accumulation and mesenchymal transformation of renal tubules
in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biomed Res Int. 2021:66572062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou S, Yang J, Wang M, Zheng D and Liu Y:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human lens epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 21:173–180.
2020.
|
|
59
|
Guo B, Cheng J, Jin X, He Y and Sun X:
Different calcium ion concentrations affect epithelial mesenchymal
transformation of human peritoneal mesothelial cells via
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 36:50–55. 2024.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bartoszewska S, Cabaj A, Dąbrowski M,
Collawn JF and Bartoszewski R: miR-34c-5p modulates X-box-binding
protein 1 (XBP1) expression during the adaptive phase of the
unfolded protein response. FASEB J. 33:11541–11554. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cuevas EP, Eraso P, Mazón MJ, Santos V,
Moreno-Bueno G, Cano A and Portillo F: LOXL2 drives
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of IRE1-XBP1
signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 7:449882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lhomond S, Avril T, Dejeans N, Voutetakis
K, Doultsinos D, McMahon M, Pineau R, Obacz J, Papadodima O, Jouan
F, et al: Dual IRE1 RNase functions dictate glioblastoma
development. EMBO Mol Med. 10:e79292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wu S, Du R, Gao C, Kang J, Wen J and Sun
T: The role of XBP1s in the metastasis and prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 500:530–537.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Qiao D, Skibba M, Xu X, Garofalo RP, Zhao
Y and Brasier AR: Paramyxovirus replication induces the hexosamine
biosynthetic pathway and mesenchymal transition via the IRE1α-XBP1s
arm of the unfolded protein response. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 321:L576–L594. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhu Y, Yang M, Li XH, Xu WJ, Gao W, Chen
YH, Li JD and Li Q: Nogo-B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in lung fibrosis via PERK branch of the endoplasmic
reticulum stress pathway. Ann Transl Med. 9:5632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Meng X, Liu K, Xie H, Zhu Y, Jin W, Lu J
and Wang R: Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the PERK signaling pathway in
paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Mol Med Rep. 24:5252021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Liu F, Chang L and Hu J: Activating
transcription factor 6 regulated cell growth, migration and
inhibiteds cell apoptosis and autophagy via MAPK pathway in
cervical cancer. J Reprod Immunol. 139:1031202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li R, Zhou H, Li M, Mai Q, Fu Z, Jiang Y,
Li C, Gao Y, Fan Y, Wu K, et al: Gremlin-1 promotes colorectal
cancer cell metastasis by activating ATF6 and inhibiting ATF4
pathways. Cells. 11:21362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ni YH, Deng HF, Zhou L, Huang CS, Wang NN,
Yue LX, Li GF, Yu HJ, Zhou W and Gao Y: Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorated
Bavachin-induced renal fibrosis via Suppressing Bip/eIF2α/CHOP
Signaling-Mediated EMT. Front Pharmacol. 13:8724742022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Luo R, Wei Y, Chen P, Zhang J, Wang L,
Wang W, Wang P and Tian W: Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition by modulating the IRE1α branch
of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Stem Cells Int.
2023:44837762023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Imran M, Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, Nadeem M,
Shariati MA, Khan IA, Imran A, Orhan IE, Rizwan M, Atif M, et al:
Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: A review. Biomed
Pharmacothe. 112:1086122019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Pan X, Phanish MK, Baines DL and Dockrell
MEC: High glucose-induced Smad3 linker phosphorylation and CCN2
expression are inhibited by dapagliflozin in a diabetic tubule
epithelial cell model. Biosci Rep. 41:BSR202039472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hao Y, Baker D and Ten Dijke P:
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 202:7672019.
|
|
74
|
Noshita S, Kubo Y, Kajiwara K, Okuzaki D,
Nada S and Okada M: A TGF-β-responsive enhancer regulates SRC
expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated cell
migration. J Cell Sci. 136:jcs2610012023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Liu H, Lai W, Nie H, Shi Y, Zhu L, Yang L,
Tian L, Li K, Bian L, Xi Z and Lin B: PM2.5 triggers autophagic
degradation of Caveolin-1 via endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) to
enhance the TGF-β1/Smad3 axis promoting pulmonary fibrosis. Environ
Int. 181:1082902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Borok Z, Horie M, Flodby P, Wang H, Liu Y,
Ganesh S, Firth AL, Minoo P, Li C, Beers MF, et al: Grp78 loss in
epithelial progenitors reveals an Age-linked role for endoplasmic
reticulum stress in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
201:198–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
77
|
Hu W, Xia M, Zhang C, Song B, Xia Z, Guo
C, Cui Y, Jiang W, Zhang S, Xu D and Fang J: Chronic cadmium
exposure induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate
cancer cells through a TGF-β-independent, endoplasmic reticulum
stress induced pathway. Toxicol Lett. 353:107–117. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bao M, Feng Q, Zou L, Huang J, Zhu C and
Xia W: Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes endometrial fibrosis
through the TGF-β/SMAD pathway. Reproduction. 165:171–182. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Takahashi N, Harada M, Hirota Y, Nose E,
Azhary JM, Koike H, Kunitomi C, Yoshino O, Izumi G, Hirata T, et
al: Activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in granulosa cells
from patients with polycystic ovary syndrome contributes to ovarian
fibrosis. Sci Rep. 7:108242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yi X, Wang H, Yang Y, Wang H, Zhang H, Guo
S, Chen J, Du J, Tian Y, Ma J, et al: SIRT7 orchestrates melanoma
progression by simultaneously promoting cell survival and immune
evasion via UPR activation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:1072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Adamson RJ, Payne NC, Bartual SG,
Mazitschek R and Bullock AN: Structural and biochemical
characterization establishes a detailed understanding of KEAP1-CUL3
complex assembly. Free Radic Biol Med. 215–225. 2004.
|
|
82
|
Raghunath A, Nagarajan R, Sundarraj K,
Palanisamy K and Perumal E: Identification of compounds that
inhibit the binding of Keap1a/Keap1b Kelch DGR domain with Nrf2
ETGE/DLG motifs in zebrafish. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
125:259–270. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang H, Feng Y, Si Y, Lu C, Wang J, Wang
S, Li L, Xie W, Yue Z, Yong J, et al: Shank3 ameliorates neuronal
injury after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via inhibiting oxidative
stress and inflammation. Redox Biol. 69:1029832024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Goswami D, Adiseshaiah PP,
Burgan W, Yi M, Guerin TM, Kozlov SV, Nissley DV and McCormick F:
Undermining glutaminolysis bolsters chemotherapy while NRF2
promotes chemoresistance in KRAS-driven pancreatic cancers. Cancer
Res. 80:1630–1643. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Adachi Y, Kimura R, Hirade K and Ebi H:
Escaping KRAS: Gaining autonomy and resistance to KRAS inhibition
in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancers (Basel). 13:50812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ferino A, Rapozzi V and Xodo LE: The
ROS-KRAS-Nrf2 axis in the control of the redox homeostasis and the
intersection with survival-apoptosis pathways: Implications for
photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B. 202:1116722020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Fu L, Zhao H, Xiang Y, Xiang HX, Hu B, Tan
ZX, Lu X, Gao L, Wang B, Wang H, et al: Reactive oxygen
species-evoked endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates
1-nitropyrene-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
pulmonary fibrosis. Environ Pollut. 283:1171342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Jin M, Wang J, Ji X, Cao H, Zhu J, Chen Y,
Yang J, Zhao Z, Ren T and Xing J: MCUR1 facilitates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via the
mitochondrial calcium dependent ROS/Nrf2/Notch pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1362019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gundamaraju R, Lu W, Paul MK, Jha NK,
Gupta PK, Ojha S, Chattopadhyay I, Rao PV and Ghavami S: Autophagy
and EMT in cancer and metastasis: Who controls whom? Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1868:1664312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kapuy O: Mechanism of decision making
between autophagy and apoptosis induction upon endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Int J Mol Sci. 25:43682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Si L, Yang Z, Ding L and Zhang D:
Regulatory effects of lncRNAs and miRNAs on the crosstalk between
autophagy and EMT in cancer: A new era for cancer treatment. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 148:547–564. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ and Tang
D: Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 17:2054–2081.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Zhou L, Lei Y, Zhang Y
and Huang C: Redox signaling and unfolded protein response
coordinate cell fate decisions under ER stress. Redox Biol.
25:1010472019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Leonardi A, Donato A, Rosani U, Di Stefano
A, Cavarzeran F and Brun P: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and
unfolded protein response in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 65:232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Beilankouhi EAV, Sajadi MA, Alipourfard I,
Hassani P, Valilo M and Safaralizadeh R: Role of the ER-induced UPR
pathway, apoptosis, and autophagy in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res
Practice. 248:1547062023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Chang TK, Lawrence DA, Lu M, Tan J,
Harnoss JM, Marsters SA, Liu P, Sandoval W, Martin SE and Ashkenazi
A: Coordination between two branches of the unfolded protein
response determines apoptotic cell fate. Mol Cell. 71:629–636.e5.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Zhao H, Liu T, Yang CE, Hu YH, Niu Y, Lei
SP, Chen L and Zhang MX: Poricoic acid A attenuates renal fibrosis
by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Braz
J Med Biol Res. 57:e142492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Golfinopoulos
S, Efthymiadi M, Poulianiti C, Polyzou Konsta MA, Liakopoulos V and
Stefanidis I: Routes of albumin overload toxicity in renal tubular
epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 24:96402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hetz C, Zhang K and Kaufman RJ:
Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein
response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:421–438. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Hsieh PC, Peng CK, Liu GT, Kuo CY, Tzeng
IS, Wang MC, Lan CC and Huang KL: Aqueous extract of descuraniae
semen attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and
apoptosis by regulating the proteasomal degradation and
IRE1α-dependent unfolded protein response in A549 cells. Front
Immunol. 13:9161022022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Wang WW, Liu YL, Wang MZ, Li H, Liu BH, Tu
Y, Yuan CC, Fang QJ, Chen JX, Wang J, et al: Inhibition of renal
tubular epithelial mesenchymal transition and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis with shenkang injection attenuates
diabetic tubulopathy. Front Pharmacol. 12:6627062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Strippoli R, Niayesh-Mehr R, Adelipour M,
Khosravi A, Cordani M, Zarrabi A and Allameh A: Contribution of
autophagy to epithelial mesenchymal transition induction during
cancer progression. Cancers. 16:8072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Chen HT, Liu H, Mao MJ, Tan Y, Mo XQ, Meng
XJ, Cao MT, Zhong CY, Liu Y, Shan H and Jiang GM: Crosstalk between
autophagy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its application
in cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 18:1012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen YM, Yang WQ, Gu CW, Fan YY, Liu YZ
and Zhao BS: Amlodipine inhibits the proliferation and migration of
esophageal carcinoma cells through the induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol. 30:367–380. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wu C, Qian Y, Jiang J, Li D and Feng L:
Piperine inhibits the proliferation of colorectal adenocarcinoma by
regulating ARL3-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomol
Biomed. 25:391–405. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
107
|
Gu W and Yang C: Zinc oxide nanoparticles
inhibit malignant progression and chemotherapy resistance of
ovarian cancer cells by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress and
promoting autophagy. Exp Ther Med. 26:5082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Cho W, Oh H, Choi SW, Abd El-Aty AM,
Birdal O, Jeong JH, Song JH and Jung TW: CTRP4 attenuates apoptosis
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in podocytes through
an AMPK/autophagy-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
682:104–110. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Jiang R, Han L, Gao Q and Chao J: ZC3H4
mediates silica-induced EndoMT via ER stress and autophagy. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 84:1036052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Han X, Duan X, Liu Z, Long Y, Liu C, Zhou
J, Li N, Qin J and Wang Y: ZEB1 directly inhibits GPX4
transcription contributing to ROS accumulation in breast cancer
cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 188:329–342. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yuan L, Zhou M, Wasan HS, Zhang K, Li Z,
Guo K, Shen F, Shen M and Ruan S: Jiedu Sangen decoction inhibits
the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by
regulating EMT through the hippo signaling pathway. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2019:14317262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Liu Z, Nan P, Gong Y, Tian L, Zheng Y and
Wu Z: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered ferroptosis via the
XBP1-Hrd1-Nrf2 pathway induces EMT progression in diabetic
nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacotherapy. 164:1148972023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Tan W, Liang Z, Tan X and Tan G:
Ginsenoside Rg1 improves cigarette smoke-induced ferroptosis in
COPD by regulating PERK/ATF4 axis to inhibit endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 739:1509462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ao Q, Hu H and Huang Y: Ferroptosis and
endoplasmic reticulum stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Front
Immunol. 15:14388032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhou R, Wei K, Li X, Yan B and Li L:
Mechanisms of ferroptosis and the relationship between ferroptosis
and ER stress after JEV and HSV infection. Front Microbiol.
15:14154172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Nie Z, Chen M, Wen X, Gao Y, Huang D, Cao
H, Peng Y, Guo N, Ni J and Zhang S: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
and tumor microenvironment in bladder cancer: The missing link.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6839402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Urra H, Aravena R, González-Johnson L and
Hetz C: The UPRising connection between endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer. 10:1161–1173.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu B, Yin X, Jiang G, Li Y, Jiang Z,
Qiang L, Chen N, Fan Y, Shen C, Dai L, et al: Identification of
endoplasmic reticulum stress-related subtypes, infiltration
analysis of tumor microenvironment, and construction of a
prognostic model in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel).
14:33262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Alvarez CL, Troncoso MF and Espelt MV:
Extracellular ATP and adenosine in tumor microenvironment: Roles in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell migration, and invasion. J
Cell Physiol. 237:389–400. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Yang H, Li J, Niu Y, Zhou T, Zhang P, Liu
Y and Li Y: Interactions between the metabolic reprogramming of
liver cancer and tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol.
16:14947882025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Daniel Y, Lelou E, Aninat C, Corlu A and
Cabillic F: Interplay between metabolism reprogramming and
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition in cancer stem cells. Cancers
(Basel). 13:19732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Balaji S, Kim U, Muthukkaruppan V and
Vanniarajan A: Emerging role of tumor microenvironment derived
exosomes in therapeutic resistance and metastasis through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Life Sci. 280:1197502021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Huang K, Han Y, Chen Y, Shen H, Zeng S and
Cai C: Tumor metabolic regulators: Key drivers of metabolic
reprogramming and the promising targets in cancer therapy. Mol
Cancer. 24:72025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hu C, Xin Z, Sun X, Hu Y, Zhang C, Yan R,
Wang Y, Lu M, Huang J, Du X, et al: Activation of ACLY by SEC63
deploys metabolic reprogramming to facilitate hepatocellular
carcinoma metastasis upon endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 42:1082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Tao J, Yin L, Wu A, Zhang J, Zhang J, Shi
H, Liu S, Niu L, Xu L, Feng Y, et al: PDIA2 bridges endoplasmic
reticulum stress and metabolic reprogramming during malignant
transformation of chronic colitis. Front Oncol. 12:8360872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Pathak T, Benson JC, Johnson MT, Xin P,
Abdelnaby AE, Walter V, Koltun WA, Yochum GS, Hempel N and Trebak
M: Loss of STIM2 in colorectal cancer drives growth and metastasis
through metabolic reprogramming and PERK-ATF4 endoplasmic reticulum
stress pathway. bioRxiv. Oct 3–2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Guimarães ES, Marinho FV, de Queiroz N,
Antunes MM and Oliveira SC: Impact of STING inflammatory signaling
during intracellular bacterial infections. Cells. 11:742021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Kang H, Kim H, Lee S, Youn H and Youn B:
Role of metabolic reprogramming in Epithelial-Mesenchymal
transition (EMT). Int J Mol Sci. 20:20422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Bhattacharya D and Scimè A: Metabolic
regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition: Implications
for endocrine cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:7732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Hua W, Ten Dijke P, Kostidis S, Giera M
and Hornsveld M: TGFβ-induced metabolic reprogramming during
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
77:2103–2123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Guo W, Duan Z, Wu J and Zhou BP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes metabolic reprogramming
to suppress ferroptosis. Semin Cancer Biol. 112:20–35. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Kandasamy T, Sarkar S and Ghosh SS:
Harnessing drug repurposing to combat breast cancer by targeting
altered metabolism and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition
pathways. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 7:3780–3794. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu B, Dan W, Wei Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Lei
Y, Hou T, Zhang Y and Gao Y: β-asarone inhibits the migration,
invasion, and EMT of bladder cancer through activating ER stress.
Cancer Med. 12:13610–13622. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Li CY, Chou TF and Lo YL: An innovative
nanoformulation utilizing tumor microenvironment-responsive
PEG-polyglutamic coating and dynamic charge adjustment for specific
targeting of ER stress inducer, microRNA, and immunoadjuvant in
pancreatic cancer: In vitro investigations. Int J Biol Macromol.
254:1279052024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Granados-Principal S, Liu Y, Guevara ML,
Blanco E, Choi DS, Qian W, Patel T, Rodriguez AA, Cusimano J, Weiss
HL, et al: Inhibition of iNOS as a novel effective targeted therapy
against triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
17:252025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu X, Lu S and
Hu X: A native Drug-free macromolecular therapeutic to trigger
mutual reinforcing of endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction for cancer treatment. ACS Nano.
17:11023–11038. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|