|
1
|
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M,
Herrlich P, Schütz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M,
Chambon P and Evans RM: The nuclear receptor superfamily: The
second decade. Cell. 83:835–839. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE,
Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW,
et al: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by
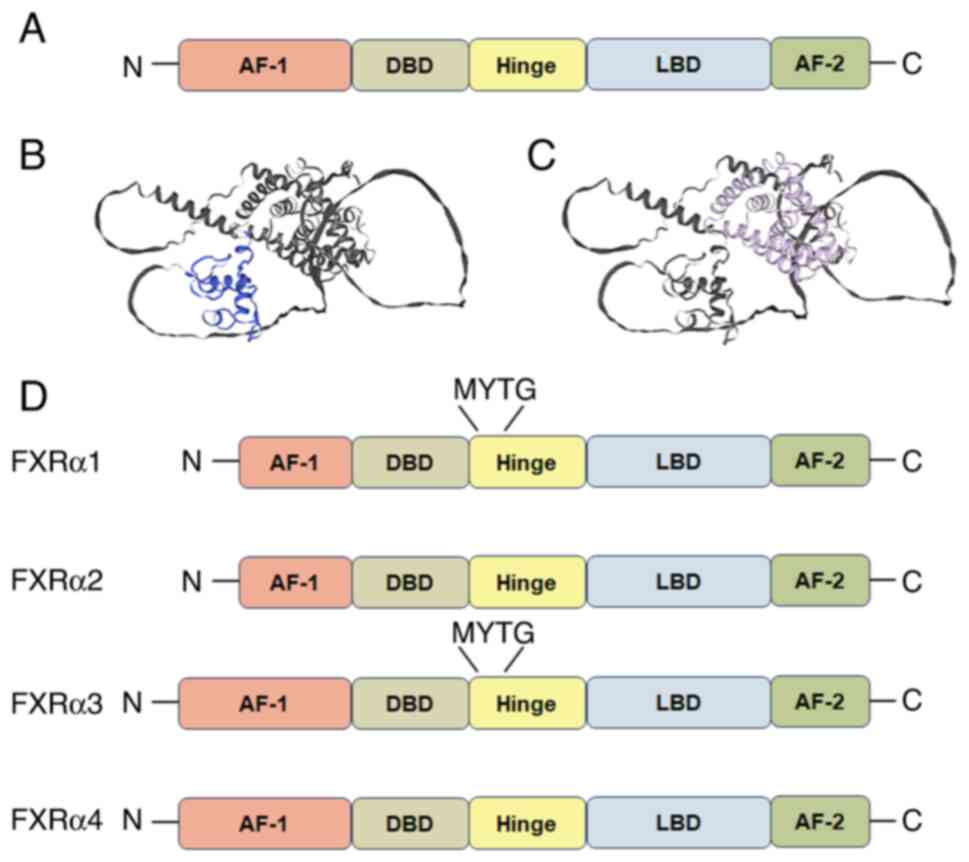
farnesol metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK,
Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki
AM, Moore DD and Lehmann JM: Bile acids: Natural ligands for an
orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 284:1365–1368. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC and
Forman BM: Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear
receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell. 3:543–553. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chávez-Talavera O, Tailleux A, Lefebvre P
and Staels B: Bile acid control of metabolism and inflammation in
obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Gastroenterology. 152:1679–1694.e3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
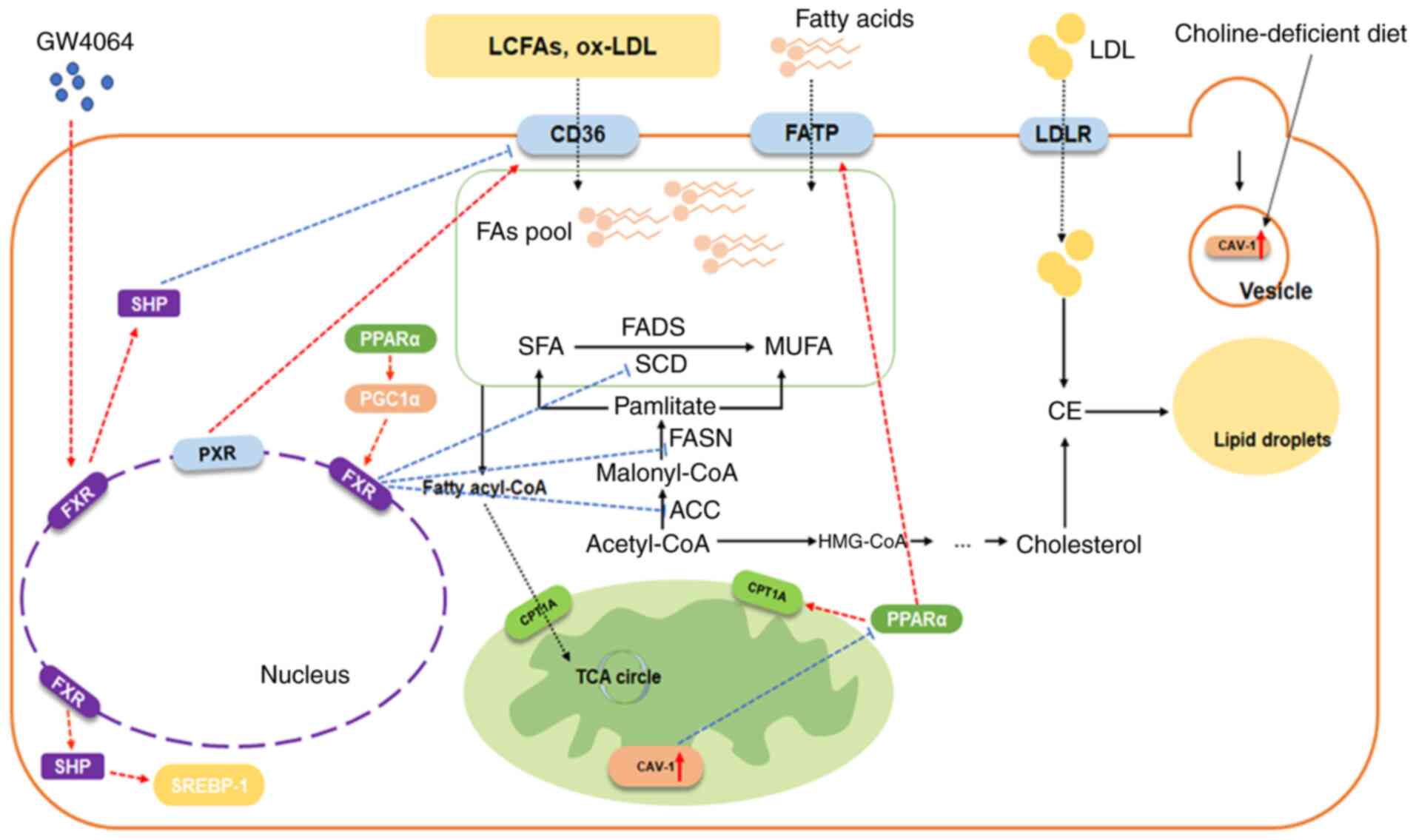
6
|
Mencarelli A and Fiorucci S: FXR an
emerging therapeutic target for the treatment of atherosclerosis. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:79–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Q, Sun L, Hu X, Wang X, Xu F, Chen B,
Liang X, Xia J, Wang P, Aibara D, et al: Suppressing the intestinal
farnesoid X receptor/sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 axis
decreases atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 131:e1428652021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Glass CK: Differential recognition of
target genes by nuclear receptor monomers, dimers, and
heterodimers. Endocr Rev. 15:391–407. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Downes M, Verdecia MA, Roecker AJ, Hughes
R, Hogenesch JB, Kast-Woelbern HR, Bowman ME, Ferrer JL, Anisfeld
AM, Edwards PA, et al: A chemical, genetic, and structural analysis
of the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR. Mol Cell. 11:1079–1092.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
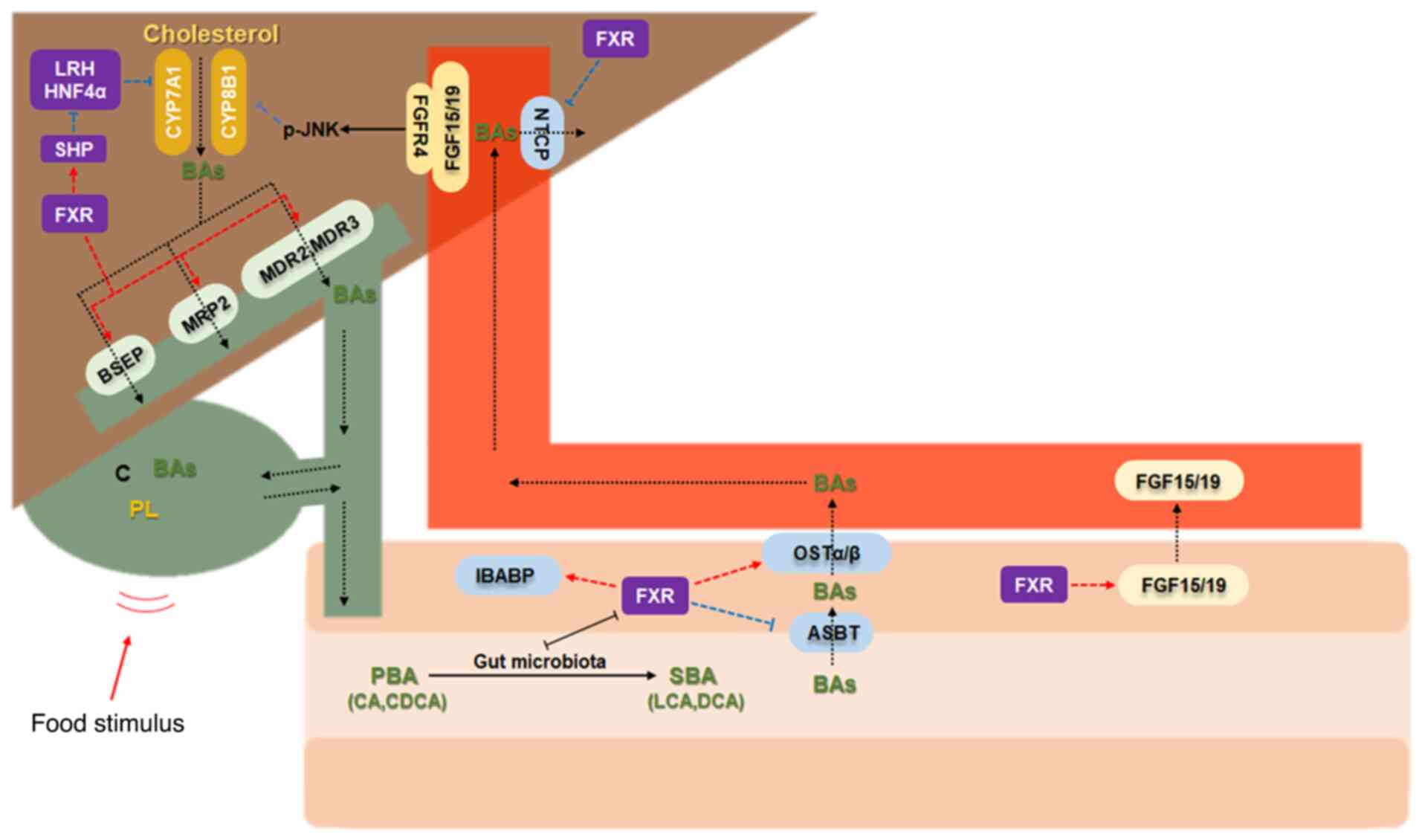
|
|
10
|
Mi LZ, Devarakonda S, Harp JM, Han Q,
Pellicciari R, Willson TM, Khorasanizadeh S and Rastinejad F:
Structural basis for bile acid binding and activation of the
nuclear receptor FXR. Mol Cell. 11:1093–1100. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
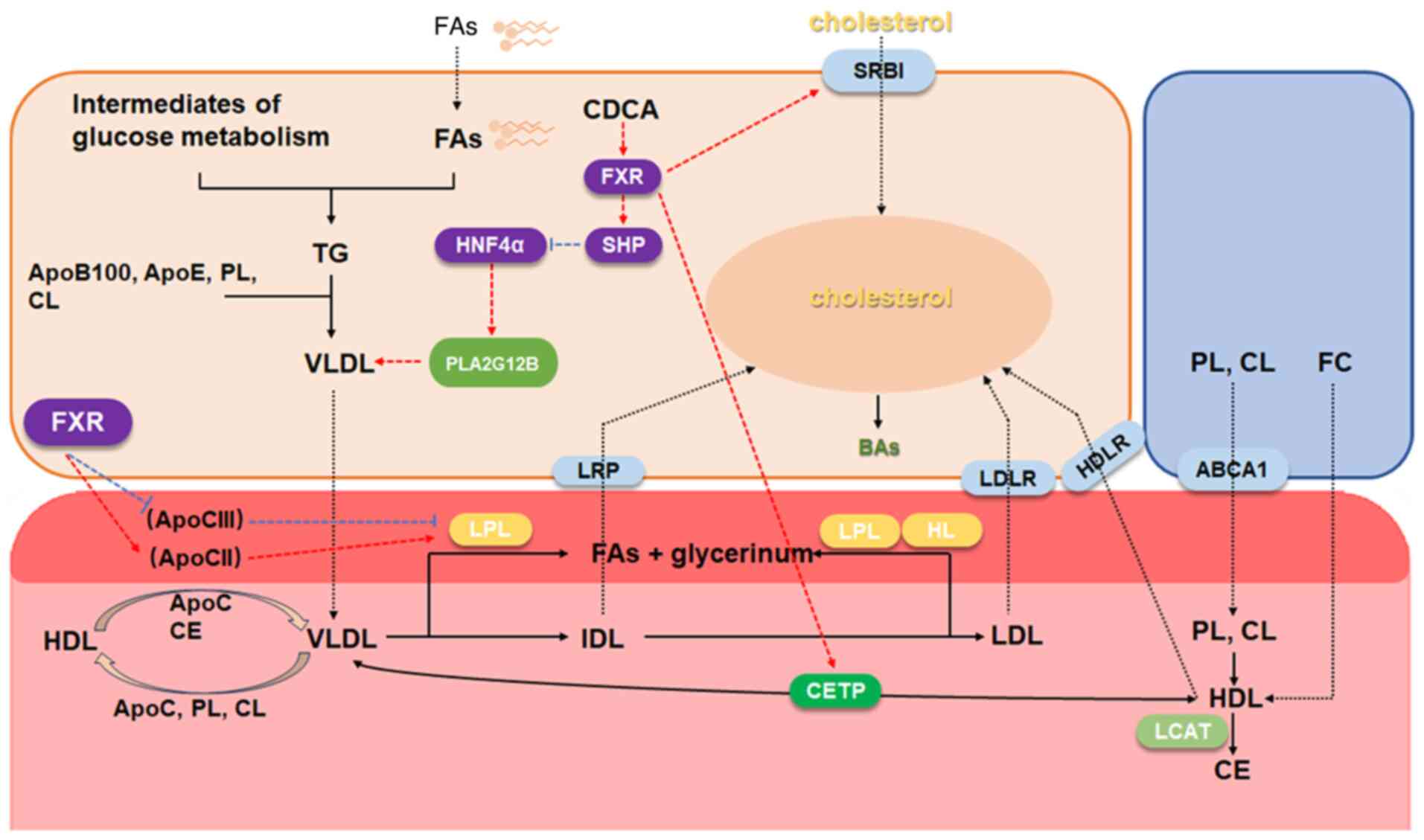
11
|
Jiang L, Zhang H, Xiao D, Wei H and Chen
Y: Farnesoid X receptor (FXR): Structures and ligands. Comput
Struct Biotechnol J. 19:2148–2159. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian SY, Chen SM, Pan CX and Li Y: FXR:
Structures, biology, and drug development for NASH and fibrosis
diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 43:1120–1132. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Otte K, Kranz H, Kober I, Thompson P,
Hoefer M, Haubold B, Remmel B, Voss H, Kaiser C, Albers M, et al:
Identification of farnesoid X receptor beta as a novel mammalian
nuclear receptor sensing lanosterol. Mol Cell Biol. 23:864–872.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huber RM, Murphy K, Miao B, Link JR,
Cunningham MR, Rupar MJ, Gunyuzlu PL, Haws TF, Kassam A, Powell F,
et al: Generation of multiple farnesoid-X-receptor isoforms through
the use of alternative promoters. Gene. 290:35–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Kast-Woelbern HR and Edwards PA:
Natural structural variants of the nuclear receptor farnesoid X
receptor affect transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem.
278:104–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vaquero J, Monte MJ, Dominguez M, Muntané
J and Marin JJ: Differential activation of the human farnesoid X
receptor depends on the pattern of expressed isoforms and the bile
acid pool composition. Biochem Pharmacol. 86:926–939. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Y, Song X, Valanejad L, Vasilenko A,
More V, Qiu X, Chen W, Lai Y, Slitt A, Stoner M, et al: Bile salt
export pump is dysregulated with altered farnesoid X receptor
isoform expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 57:1530–1541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Correia JC, Massart J, de Boer JF,
Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Martínez-Redondo V, Agudelo LZ, Sinha I,
Meierhofer D, Ribeiro V, Björnholm M, et al: Bioenergetic cues
shift FXR splicing towards FXRα2 to modulate hepatic lipolysis and
fatty acid metabolism. Mol Metab. 4:891–902. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Massafra V and van Mil SWC: Farnesoid X
receptor: A 'homeostat' for hepatic nutrient metabolism. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:45–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marzolini C, Tirona RG, Gervasini G,
Poonkuzhali B, Assem M, Lee W, Leake BF, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG and
Kim RB: A common polymorphism in the bile acid receptor farnesoid X
receptor is associated with decreased hepatic target gene
expression. Mol Endocrinol. 21:1769–1780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ruscica M, Busnelli M, Runfola E, Corsini
A and Sirtori CR: Impact of PPAR-Alpha polymorphisms-the case of
metabolic disorders and atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci.
20:43782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meirhaeghe A and Amouyel P: Impact of
genetic variation of PPARgamma in humans. Mol Genet Metab.
83:93–102. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valdivielso JM and Fernandez E: Vitamin D
receptor polymorphisms and diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 371:1–12.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dahlman I, Nilsson M, Jiao H, Hoffstedt J,
Lindgren CM, Humphreys K, Kere J, Gustafsson JA, Arner P and
Dahlman-Wright K: Liver X receptor gene polymorphisms and adipose
tissue expression levels in obesity. Pharmacogenet Genomics.
16:881–889. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishigori H, Tomura H, Tonooka N, Kanamori
M, Yamada S, Sho K, Inoue I, Kikuchi N, Onigata K, Kojima I, et al:
Mutations in the small heterodimer partner gene are associated with
mild obesity in Japanese subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:575–580. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vaxillaire M, Rouard M, Yamagata K, Oda N,
Kaisaki PJ, Boriraj VV, Chevre JC, Boccio V, Cox RD, Lathrop GM, et
al: Identification of nine novel mutations in the hepatocyte
nuclear factor 1 alpha gene associated with maturity-onset diabetes
of the young (MODY3). Hum Mol Genet. 6:583–586. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamagata K, Furuta H, Oda N, Kaisaki PJ,
Menzel S, Cox NJ, Fajans SS, Signorini S, Stoffel M and Bell GI:
Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene in
maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1). Nature. 384:458–460.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van Mil SW, Milona A, Dixon PH, Mullenbach
R, Geenes VL, Chambers J, Shevchuk V, Moore GE, Lammert F, Glantz
AG, et al: Functional variants of the central bile acid sensor FXR
identified in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
Gastroenterology. 133:507–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Edwards PA, Kast HR and Anisfeld AM:
BAREing it all: The adoption of LXR and FXR and their roles in
lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 43:2–12. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laffitte BA, Kast HR, Nguyen CM, Zavacki
AM, Moore DD and Edwards PA: Identification of the DNA binding
specificity and potential target genes for the farnesoid
X-activated receptor. J Biol Chem. 275:10638–10647. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen WD, Wang YD, Zhang L, Shiah S, Wang
M, Yang F, Yu D, Forman BM and Huang W: Farnesoid X receptor
alleviates age-related proliferation defects in regenerating mouse
livers by activating forkhead box m1b transcription. Hepatology.
51:953–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gautier T, de Haan W, Grober J, Ye D, Bahr
MJ, Claudel T, Nijstad N, Van Berkel TJC, Havekes LM, Manns MP, et
al: Farnesoid X receptor activation increases cholesteryl ester
transfer protein expression in humans and transgenic mice. J Lipid
Res. 54:2195–2205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Anisfeld AM, Kast-Woelbern HR, Meyer ME,
Jones SA, Zhang Y, Williams KJ, Willson T and Edwards PA:
Syndecan-1 expression is regulated in an isoform-specific manner by
the farnesoid-X receptor. J Biol Chem. 278:20420–20428. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thomas AM, Hart SN, Kong B, Fang J, Zhong
XB and Guo GL: Genome-wide tissue-specific farnesoid X receptor
binding in mouse liver and intestine. Hepatology. 51:1410–1419.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Panzitt K and Wagner M: FXR in liver
physiology: Multiple faces to regulate liver metabolism. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1867:1661332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Anisfeld AM, Kast-Woelbern HR, Lee H,
Zhang Y, Lee FY and Edwards PA: Activation of the nuclear receptor
FXR induces fibrinogen expression: A new role for bile acid
signaling. J Lipid Res. 46:458–468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao A, Lew JL, Huang L, Yu J, Zhang T,
Hrywna Y, Thompson JR, de Pedro N, Blevins RA, Peláez F, et al:
Human kininogen gene is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor.
J Biol Chem. 278:28765–28770. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang X, Huang S, Gao M, Liu J, Jia X, Han
Q, Zheng S, Miao Y, Li S, Weng H, et al: Farnesoid X receptor (FXR)
gene deficiency impairs urine concentration in mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 111:2277–2282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiang T, Wang XX, Scherzer P, Wilson P,
Tallman J, Takahashi H, Li J, Iwahashi M, Sutherland E, Arend L and
Levi M: Farnesoid X receptor modulates renal lipid metabolism,
fibrosis, and diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 56:2485–2493. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Glatz JFC and Luiken J: Dynamic role of
the transmembrane glycoprotein CD36 (SR-B2) in cellular fatty acid
uptake and utilization. J Lipid Res. 59:1084–1093. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wilson CG, Tran JL, Erion DM, Vera NB,
Febbraio M and Weiss EJ: Hepatocyte-specific disruption of CD36
attenuates fatty liver and improves insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed
mice. Endocrinology. 157:570–585. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Zhou J, Febbraio M, Wada T, Zhai Y, Kuruba
R, He J, Lee JH, Khadem S, Ren S, Li S, et al: Hepatic fatty acid
transporter Cd36 is a common target of LXR, PXR, and PPARgamma in
promoting steatosis. Gastroenterology. 134:556–567. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma Y, Huang Y, Yan L, Gao M and Liu D:
Synthetic FXR agonist GW4064 prevents diet-induced hepatic
steatosis and insulin resistance. Pharm Res. 30:1447–1457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen S, Sun S, Feng Y, Li X, Yin G, Liang
P, Yu W, Meng D, Zhang X, Liu H and Zhang F: Diosgenin attenuates
nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the hepatic
FXR-SHP-SREBP1C/PPARα/CD36 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
952:1758082023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mastrodonato M, Calamita G, Rossi R,
Mentino D, Bonfrate L, Portincasa P, Ferri D and Liquori GE:
Altered distribution of caveolin-1 in early liver steatosis. Eur J
Clin Invest. 41:642–651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fernández-Rojo MA, Restall C, Ferguson C,
Martel N, Martin S, Bosch M, Kassan A, Leong GM, Martin SD, McGee
SL, et al: Caveolin-1 orchestrates the balance between glucose and
lipid-dependent energy metabolism: Implications for liver
regeneration. Hepatology. 55:1574–1584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fernández-Rojo MA, Gongora M, Fitzsimmons
RL, Martel N, Martin SD, Nixon SJ, Brooks AJ, Ikonomopoulou MP,
Martin S, Lo HP, et al: Caveolin-1 is necessary for hepatic
oxidative lipid metabolism: Evidence for crosstalk between
caveolin-1 and bile acid signaling. Cell Rep. 4:238–247. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Motojima K, Passilly P, Peters JM,
Gonzalez FJ and Latruffe N: Expression of putative fatty acid
transporter genes are regulated by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha and gamma activators in a
tissue- and inducer-specific manner. J Biol Chem. 273:16710–16744.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Acharya R, Shetty SS and Kumari NS: Fatty
acid transport proteins (FATPs) in cancer. Chem Phys Lipids.
250:1052692023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hirsch D, Stahl A and Lodish HF: A family
of fatty acid transporters conserved from mycobacterium to man.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:8625–8629. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Falcon A, Doege H, Fluitt A, Tsang B,
Watson N, Kay MA and Stahl A: FATP2 is a hepatic fatty acid
transporter and peroxisomal very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. Am
J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E384–E393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee Y, Kim BR, Kang GH, Lee GJ, Park YJ,
Kim H, Jang HC and Choi SH: The effects of PPAR agonists on
atherosclerosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in
ApoE-/-FXR-/- mice. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 36:1243–1253. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Savage DB, Choi CS, Samuel VT, Liu ZX,
Zhang D, Wang A, Zhang XM, Cline GW, Yu XX, Geisler JG, et al:
Reversal of diet-induced hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin
resistance by antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors of acetyl-CoA
carboxylases 1 and 2. J Clin Invest. 116:817–824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dentin R, Benhamed F, Hainault I, Fauveau
V, Foufelle F, Dyck JR, Girard J and Postic C: Liver-specific
inhibition of ChREBP improves hepatic steatosis and insulin
resistance in ob/ob mice. Diabetes. 55:2159–2170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yahagi N, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka
T, Ide T, Yoshikawa T, Amemiya-Kudo M, Tomita S, Okazaki H, Tamura
Y, et al: Absence of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1
(SREBP-1) ameliorates fatty livers but not obesity or insulin
resistance in Lep(ob)/Lep(ob) mice. J Biol Chem. 277:19353–19357.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ma K, Saha PK, Chan L and Moore DD:
Farnesoid X receptor is essential for normal glucose homeostasis. J
Clin Invest. 116:1102–1109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Wang L, Moschetta
A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Heyman RA, Moore DD and Auwerx J: Bile acids
lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and
SREBP-1c. J Clin Invest. 113:1408–1418. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Iizuka K, Takao K and Yabe D:
ChREBP-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism: Involvement of the
gut microbiota, liver, and adipose tissue. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 11:5871892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Caron S, Huaman Samanez C, Dehondt H,
Ploton M, Briand O, Lien F, Dorchies E, Dumont J, Postic C, Cariou
B, et al: Farnesoid X receptor inhibits the transcriptional
activity of carbohydrate response element binding protein in human
hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 33:2202–2211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kliewer SA and Mangelsdorf DJ: Bile acids
as hormones: The FXR-FGF15/19 pathway. Dig Dis. 33:327–331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Beenken A and Mohammadi M: The FGF family:
biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:235–253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Montagner A, Polizzi A, Fouché E, Ducheix
S, Lippi Y, Lasserre F, Barquissau V, Régnier M, Lukowicz C,
Benhamed F, et al: Liver PPARα is crucial for whole-body fatty acid
homeostasis and is protective against NAFLD. Gut. 65:1202–1214.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Prawitt J, Abdelkarim M, Stroeve JH,
Popescu I, Duez H, Velagapudi VR, Dumont J, Bouchaert E, van Dijk
TH, Lucas A, et al: Farnesoid X receptor deficiency improves
glucose homeostasis in mouse models of obesity. Diabetes.
60:1861–1871. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pineda Torra I, Claudel T, Duval C, Kosykh
V, Fruchart JC and Staels B: Bile acids induce the expression of
the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene via
activation of the farnesoid X receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 17:259–272.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu J, Li Y, Chen WD, Xu Y, Yin L, Ge X,
Jadhav K, Adorini L and Zhang Y: Hepatic carboxylesterase 1 is
essential for both normal and farnesoid X receptor-controlled lipid
homeostasis. Hepatology. 59:1761–1771. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Liu Y, Song A, Yang X, Zhen Y, Chen W,
Yang L, Wang C and Ma H: Farnesoid X receptor agonist decreases
lipid accumulation by promoting hepatic fatty acid oxidation in
db/db mice. Int J Mol Med. 42:1723–1731. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Fernandez-Marcos PJ and Auwerx J:
Regulation of PGC-1alpha, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial
biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:884s–890s. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang C, Deng J, Liu D, Tuo X, Xiao L, Lai
B, Yao Q, Liu J, Yang H and Wang N: Nuciferine ameliorates hepatic
steatosis in high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced diabetic mice
through a PPARα/PPARγ coactivator-1α pathway. Br J Pharmacol.
175:4218–4228. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang Y, Castellani LW, Sinal CJ, Gonzalez
FJ and Edwards PA: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) regulates triglyceride metabolism
by activation of the nuclear receptor FXR. Genes Dev. 18:157–169.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Rizzolo D, Kong B, Taylor RE, Brinker A,
Goedken M, Buckley B and Guo GL: Bile acid homeostasis in female
mice deficient in Cyp7a1 and Cyp27a1. Acta Pharm Sin B.
11:3847–3856. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA,
McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, et al:
A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1
represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 6:517–526. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chiang JY: Bile acid regulation of gene
expression: Roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev.
23:443–463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kong B, Wang L, Chiang JY, Zhang Y,
Klaassen CD and Guo GL: Mechanism of tissue-specific farnesoid X
receptor in suppressing the expression of genes in bile-acid
synthesis in mice. Hepatology. 56:1034–1043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lee FY, Lee H, Hubbert ML, Edwards PA and
Zhang Y: FXR, a multipurpose nuclear receptor. Trends Biochem Sci.
31:572–580. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cai SY and Boyer JL: FXR: A target for
cholestatic syndromes? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 10:409–421. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kast HR, Goodwin B, Tarr PT, Jones SA,
Anisfeld AM, Stoltz CM, Tontonoz P, Kliewer S, Willson TM and
Edwards PA: Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2
(ABCC2) by the nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor farnesoid
X-activated receptor and constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol
Chem. 277:2908–2915. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Huang L, Zhao A, Lew JL, Zhang T, Hrywna
Y, Thompson JR, de Pedro N, Royo I, Blevins RA, Peláez F, et al:
Farnesoid X receptor activates transcription of the phospholipid
pump MDR3. J Biol Chem. 278:51085–51090. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM,
Lambert G and Gonzalez FJ: Targeted disruption of the nuclear
receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell.
102:731–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Denke MA and Grundy SM:
Hypertriglyceridemia: A relative contraindication to the use of
bile acid-binding resins? Hepatology. 8:974–975. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hirokane H, Nakahara M, Tachibana S,
Shimizu M and Sato R: Bile acid reduces the secretion of very low
density lipoprotein by repressing microsomal triglyceride transfer
protein gene expression mediated by hepatocyte nuclear factor-4. J
Biol Chem. 279:45685–45692. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu Q, Yang M, Fu X, Liu R, Sun C, Pan H,
Wong CW and Guan M: Activation of farnesoid X receptor promotes
triglycerides lowering by suppressing phospholipase A2 G12B
expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 436:93–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Giammanco A, Spina R, Cefalù AB and Averna
M: APOC-III: A gatekeeper in controlling triglyceride metabolism.
Curr Atheroscler Rep. 25:67–76. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Claudel T, Inoue Y, Barbier O,
Duran-Sandoval D, Kosykh V, Fruchart J, Fruchart JC, Gonzalez FJ
and Staels B: Farnesoid X receptor agonists suppress hepatic
apolipoprotein CIII expression. Gastroenterology. 125:544–555.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kast HR, Nguyen CM, Sinal CJ, Jones SA,
Laffitte BA, Reue K, Gonzalez FJ, Willson TM and Edwards PA:
Farnesoid X-activated receptor induces apolipoprotein C-II
transcription: A molecular mechanism linking plasma triglyceride
levels to bile acids. Mol Endocrinol. 15:1720–1728. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Mak PA, Kast-Woelbern HR, Anisfeld AM and
Edwards PA: Identification of PLTP as an LXR target gene and apoE
as an FXR target gene reveals overlapping targets for the two
nuclear receptors. J Lipid Res. 43:2037–2041. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Urizar NL, Dowhan DH and Moore DD: The
farnesoid X-activated receptor mediates bile acid activation of
phospholipid transfer protein gene expression. J Biol Chem.
275:39313–39317. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim I, Morimura K, Shah Y, Yang Q, Ward JM
and Gonzalez FJ: Spontaneous hepatocarcinogenesis in farnesoid X
receptor-null mice. Carcinogenesis. 28:940–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Yang F, Huang X, Yi T, Yen Y, Moore DD and
Huang W: Spontaneous development of liver tumors in the absence of
the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor. Cancer Res.
67:863–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Su H, Ma C, Liu J, Li N, Gao M, Huang A,
Wang X, Huang W and Huang X: Downregulation of nuclear receptor FXR
is associated with multiple malignant clinicopathological
characteristics in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303:G1245–G1253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Takahashi S, Tanaka N, Fukami T, Xie C,
Yagai T, Kim D, Velenosi TJ, Yan T, Krausz KW, Levi M and Gonzalez
FJ: Role of Farnesoid X Receptor and Bile Acids in Hepatic Tumor
Development. Hepatol Commun. 2:1567–1582. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kong B, Zhu Y, Li G, Williams JA, Buckley
K, Tawfik O, Luyendyk JP and Guo GL: Mice with hepatocyte-specific
FXR deficiency are resistant to spontaneous but susceptible to
cholic acid-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 310:G295–G302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Degirolamo C, Modica S, Vacca M, Di Tullio
G, Morgano A, D'Orazio A, Kannisto K, Parini P and Moschetta A:
Prevention of spontaneous hepatocarcinogenesis in farnesoid X
receptor-null mice by intestinal-specific farnesoid X receptor
reactivation. Hepatology. 61:161–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Li G, Kong B, Zhu Y, Zhan L, Williams JA,
Tawfik O, Kassel KM, Luyendyk JP, Wang L and Guo GL: Small
heterodimer partner overexpression partially protects against liver
tumor development in farnesoid X receptor knockout mice. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 272:299–305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Režen T, Rozman D, Kovács T, Kovács P,
Sipos A, Bai P and Mikó E: The role of bile acids in
carcinogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:2432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Ooi GJ, Meikle PJ, Huynh K, Earnest A,
Roberts SK, Kemp W, Parker BL, Brown W, Burton P and Watt MJ:
Hepatic lipidomic remodeling in severe obesity manifests with
steatosis and does not evolve with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J
Hepatol. 75:524–535. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Nobili V, Alisi A, Mosca A, Della Corte C,
Veraldi S, De Vito R, De Stefanis C, D'Oria V, Jahnel J, Zohrer E,
et al: Hepatic farnesoid X receptor protein level and circulating
fibroblast growth factor 19 concentration in children with NAFLD.
Liver Int. 38:342–349. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Aguilar-Olivos NE, Carrillo-Córdova D,
Oria-Hernández J, Sánchez-Valle V, Ponciano-Rodríguez G,
Ramírez-Jaramillo M, Chablé-Montero F, Chávez-Tapia NC, Uribe M and
Méndez-Sánchez N: The nuclear receptor FXR, but not LXR,
up-regulates bile acid transporter expression in non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol. 14:487–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Loomba R, Sanyal
AJ, Lavine JE, Van Natta ML, Abdelmalek MF, Chalasani N, Dasarathy
S, Diehl AM and Hameed B, et al: Farnesoid X nuclear receptor
ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 385:956–965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Tully DC, Rucker PV, Chianelli D, Williams
J, Vidal A, Alper PB, Mutnick D, Bursulaya B, Schmeits J, Wu X, et
al: Discovery of tropifexor (LJN452), a highly potent non-bile acid
FXR agonist for the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases and
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). J Med Chem. 60:9960–9973.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhang S, Wang J, Liu Q and Harnish DC:
Farnesoid X receptor agonist WAY-362450 attenuates liver
inflammation and fibrosis in murine model of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 51:380–388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang J, Yang N and Xu Y: Natural products
in the modulation of farnesoid X receptor against nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Am J Chin Med. 52:291–314. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Huang W, Cao Z, Wang W, Yang Z, Jiao S,
Chen Y, Chen S, Zhang L and Li Z: Discovery of LH10, a novel
fexaramine-based FXR agonist for the treatment of liver disease.
Bioorg Chem. 143:1070712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Qin X, Tan Y, Ren W, Zhou W, Niu R, Liang
L, Li J, Cao K, Wei G, Zhu X and Huang M: Elevated expression of
LCN13 through FXR activation ameliorates hepatocellular lipid
accumulation and inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 131:1118122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Huang XF, Zhao WY and Huang WD: FXR and
liver carcinogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:37–43. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
105
|
Sayin SI, Wahlström A, Felin J, Jäntti S,
Marschall HU, Bamberg K, Angelin B, Hyötyläinen T, Orešič M and
Bäckhed F: Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by
reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally
occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 17:225–235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Qu R, Zhou X, Sun L, Wang
K, Jiang C, Zhang Z and Fu W: Promotion of Deoxycholic acid effect
on colonic cancer cell lines in vitro by altering the mucosal
microbiota. Microorganisms. 10:24862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Bailey AM, Zhan L, Maru D, Shureiqi I,
Pickering CR, Kiriakova G, Izzo J, He N, Wei C, Baladandayuthapani
V, et al: FXR silencing in human colon cancer by DNA methylation
and KRAS signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
306:G48–G58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
108
|
Guo S, Peng Y, Lou Y, Cao L, Liu J, Lin N,
Cai S, Kang Y, Zeng S and Yu L: Downregulation of the farnesoid X
receptor promotes colorectal tumorigenesis by facilitating
enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis colonization. Pharmacol Res.
177:1061012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chung L, Thiele Orberg E, Geis AL, Chan
JL, Fu K, DeStefano Shields CE, Dejea CM, Fathi P, Chen J, Finard
BB, et al: Bacteroides fragilis toxin coordinates a
pro-carcinogenic inflammatory cascade via targeting of colonic
epithelial cells. Cell Host Microbe. 23:203–214.e5. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S,
Wu X, Yen HR, Huso DL, Brancati FL, Wick E, McAllister F, et al: A
human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation
of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med. 15:1016–1022. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Dong X, Qi M, Cai C, Zhu Y, Li Y, Coulter
S, Sun F, Liddle C, Uboha NV, Halberg R, et al: Farnesoid X
receptor mediates macrophage-intrinsic responses to suppress
colitis-induced colon cancer progression. JCI Insight.
9:e1704282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Gadaleta RM, van Erpecum KJ, Oldenburg B,
Willemsen EC, Renooij W, Murzilli S, Klomp LW, Siersema PD,
Schipper ME, Danese S, et al: Farnesoid X receptor activation
inhibits inflammation and preserves the intestinal barrier in
inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 60:463–472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Absil L, Journé F, Larsimont D, Body JJ,
Tafforeau L and Nonclercq D: Farnesoid X receptor as marker of
osteotropism of breast cancers through its role in the
osteomimetism of tumor cells. BMC Cancer. 20:6402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Silva J, Dasgupta S, Wang G, Krishnamurthy
K, Ritter E and Bieberich E: Lipids isolated from bone induce the
migration of human breast cancer cells. J Lipid Res. 47:724–733.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Krishnamurthy K, Wang G, Rokhfeld D and
Bieberich E: Deoxycholate promotes survival of breast cancer cells
by reducing the level of pro-apoptotic ceramide. Breast Cancer Res.
10:R1062008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Swales KE, Korbonits M, Carpenter R, Walsh
DT, Warner TD and Bishop-Bailey D: The farnesoid X receptor is
expressed in breast cancer and regulates apoptosis and aromatase
expression. Cancer Res. 66:10120–10126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Alasmael N, Mohan R, Meira LB, Swales KE
and Plant NJ: Activation of the Farnesoid X-receptor in breast
cancer cell lines results in cytotoxicity but not increased
migration potential. Cancer Lett. 370:250–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Giordano C, Catalano S, Panza S, Vizza D,
Barone I, Bonofiglio D, Gelsomino L, Rizza P, Fuqua SA and Andò S:
Farnesoid X receptor inhibits tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast
cancer cell growth through downregulation of HER2 expression.
Oncogene. 30:4129–4140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Giordano C, Barone I, Vircillo V, Panza S,
Malivindi R, Gelsomino L, Pellegrino M, Rago V, Mauro L, Lanzino M,
et al: Activated FXR inhibits leptin signaling and counteracts
tumor-promoting activities of cancer-associated fibroblasts in
breast malignancy. Sci Rep. 6:217822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Strauss P, Rivedal M, Scherer A, Eikrem Ø,
Nakken S, Beisland C, Bostad L, Flatberg A, Skandalou E, Beisvåg V,
et al: A multiomics disease progression signature of low-risk
ccRCC. Sci Rep. 12:135032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Fujino T, Sakamaki R, Ito H, Furusato Y,
Sakamoto N, Oshima T and Hayakawa M: Farnesoid X receptor regulates
the growth of renal adenocarcinoma cells without affecting that of
a normal renal cell-derived cell line. J Toxicol Sci. 42:259–265.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Huang S, Hou Y, Hu M, Hu J and Liu X:
Clinical significance and oncogenic function of NR1H4 in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 22:9952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tan SK, Hougen HY, Merchan JR, Gonzalgo ML
and Welford SM: Fatty acid metabolism reprogramming in ccRCC:
Mechanisms and potential targets. Nat Rev Urol. 20:48–60. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Zhang CJ, Zhu N, Wang YX, Liu LP, Zhao TJ,
Wu HT, Liao DF and Qin L: Celastrol attenuates lipid accumulation
and stemness of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via CAV-1/LOX-1
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:6580922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Xu GH, Lou N, Shi HC, Xu YC, Ruan HL, Xiao
W, Liu L, Li X, Xiao HB, Qiu B, et al: Up-regulation of SR-BI
promotes progression and serves as a prognostic biomarker in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 18:882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Riscal R, Bull CJ, Mesaros C, Finan JM,
Carens M, Ho ES, Xu JP, Godfrey J, Brennan P, Johansson M, et al:
Cholesterol auxotrophy as a targetable vulnerability in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 11:3106–3125. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chao F, Gong W, Zheng Y, Li Y, Huang G,
Gao M, Li J, Kuruba R, Gao X, Li S and He F: Upregulation of
scavenger receptor class B type I expression by activation of FXR
in hepatocyte. Atherosclerosis. 213:443–448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Cariello M, Ducheix S, Maqdasy S, Baron S,
Moschetta A and Lobaccaro JA: LXRs, SHP, and FXR in prostate
cancer: Enemies or ménage à quatre with AR? Nucl Recept Signal.
15:15507629188010702018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Liu J, Tong SJ, Wang X and Qu LX:
Farnesoid X receptor inhibits LNcaP cell proliferation via the
upregulation of PTEN. Exp Ther Med. 8:1209–1212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Liu N, Zhao J, Wang J, Teng H, Fu Y and
Yuan H: Farnesoid X receptor ligand CDCA suppresses human prostate
cancer cells growth by inhibiting lipid metabolism via targeting
sterol response element binding protein 1. Am J Transl Res.
8:5118–5124. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Urizar NL, Liverman AB, Dodds DT, Silva
FV, Ordentlich P, Yan Y, Gonzalez FJ, Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ and
Moore DD: A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an
antagonist ligand for FXR. Science. 296:1703–1706. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Burris TP, Montrose C, Houck KA, Osborne
HE, Bocchinfuso WP, Yaden BC, Cheng CC, Zink RW, Barr RJ, Hepler
CD, et al: The hypolipidemic natural product guggulsterone is a
promiscuous steroid receptor ligand. Mol Pharmacol. 67:948–954.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Bijsmans IT, Guercini C, Ramos Pittol JM,
Omta W, Milona A, Lelieveld D, Egan DA, Pellicciari R, Gioiello A
and van Mil SW: The glucocorticoid mometasone furoate is a novel
FXR ligand that decreases inflammatory but not metabolic gene
expression. Sci Rep. 5:140862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Dussault I, Beard R, Lin M, Hollister K,
Chen J, Xiao JH, Chandraratna R and Forman BM: Identification of
gene-selective modulators of the bile acid receptor FXR. J Biol
Chem. 278:7027–7033. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Chang Y, Lin TY, Lu CW, Huang SK, Wang YC
and Wang SJ: Xanthohumol-induced presynaptic reduction of glutamate
release in the rat hippocampus. Food Funct. 7:212–226. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Liu W and Wong C: Oleanolic acid is a
selective farnesoid X receptor modulator. Phytother Res.
24:369–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Fang S, Suh JM, Reilly SM, Yu E, Osborn O,
Lackey D, Yoshihara E, Perino A, Jacinto S, Lukasheva Y, et al:
Intestinal FXR agonism promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces
obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 21:159–165. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Pellicciari R, Passeri D, De Franco F,
Mostarda S, Filipponi P, Colliva C, Gadaleta RM, Franco P, Carotti
A, Macchiarulo A, et al: Discovery of
3α,7α,11β-Trihydroxy-6α-ethyl-5β-cholan-2 4-oic Acid (TC-100), a
novel bile acid as potent and highly selective FXR agonist for
enterohepatic disorders. J Med Chem. 59:9201–9214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Jin L, Wang R, Zhu Y, Zheng W, Han Y, Guo
F, Ye FB and Li Y: Selective targeting of nuclear receptor FXR by
avermectin analogues with therapeutic effects on nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Sci Rep. 5:172882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Li G, Lin W, Araya JJ, Chen T, Timmermann
BN and Guo GL: A tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, is a
unique modulator of the farnesoid X receptor. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 258:268–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|