|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guan WL, He Y and Xu RH: Gastric cancer
treatment: Recent progress and future perspectives. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Joshi SS and Badgwell BD: Current
treatment and recent progress in gastric cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
71:264–279. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chuang TW, Lee KM and Tarn WY: Function
and pathological implications of exon junction complex factor Y14.
Biomolecules. 5:343–355. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bai R, Wan R, Wang L, Xu K, Zhang Q, Lei J
and Shi Y: Structure of the activated human minor spliceosome.
Science. 371:eabg08792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhan X, Yan C, Zhang X, Lei J and Shi Y:
Structure of a human catalytic step I spliceosome. Science.
359:537–545. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noble CG and Song H: mlN51 stimulates the
RNA-helicase activity of eIF4AIII. PLoS One. 2:e3032007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hosoda N, Kim YK, Lejeune F and Maquat LE:
CBP80 promotes interaction of Upf1 with Upf2 during
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammalian cells. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 12:893–901. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Isken O and Maquat LE: The multiple lives
of nMD factors: Balancing roles in gene and genome regulation. Nat
Rev Genet. 9:699–712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Woeller CF, Gaspari M, Isken O and Maquat
LE: nMD resulting from encephalomyocarditis virus IRES-directed
translation initiation seems to be restricted to CBP80/20-bound
mRNA. EMBO Rep. 9:446–451. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kashima I, Yamashita A, Izumi N, Kataoka
N, Morishita R, Hoshino S, Ohno M, Dreyfuss G and Ohno S: Binding
of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction
complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA
decay. Genes Dev. 20:355–367. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
López-Perrote A, Castaño R, Melero R,
Zamarro T, Kurosawa H, Ohnishi T, Uchiyama A, Aoyagi K, Buchwald G,
Kataoka N, et al: Human nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor UPF2
interacts directly with eRF3 and the SURF complex. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:1909–1923. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Behm-Ansmant I and Izaurralde E: Quality
control of gene expression: A stepwise assembly pathway for the
surveillance complex that triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.
Genes Dev. 20:391–398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kervestin S and Jacobson A: nMD: A
multifaceted response to premature translational termination. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:700–712. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mei N, Chen H, Zhao N, Yi Y and Li C: A
comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of RBM8A based on data mining. J
Oncol. 2021:99833542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin Y, Wei L, Hu B, Zhang J, Wei J, Qian Z
and Zou D: RBM8A promotes glioblastoma growth and invasion through
the notch/STAT3 pathway. Front Oncol. 11:7369412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li F, Wang X, Zhang J, Zhang J, Jing X,
Jiang Q, Zhou J, Cao L, Peng H, Tong D and Huang C: RBM8A, a new
target of TEAD4, promotes breast cancer progression by regulating
IGF1R and IRS-2. J Transl Med. 22:8232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang R, Lin Y, Ye JZ, Yan XX, Liu ZH, Li
YQ, Luo XL and Ye HH: High expression of RBM8A predicts poor
patient prognosis and promotes tumor progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 37:2167–2176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song T and Zhang H: RBM8A depletion
decreases the cisplatin resistance and represses the proliferation
and metastasis of breast cancer cells via AKT/mTOR pathway. Breast
J. 2022:45767892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao J, Senthil M, Ren B, Yan J, Xing Q, Yu
J, Zhang L and Yim JH: IRF-1 transcriptionally upregulates PUMA,
which mediates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in IRF-1-induced
apoptosis in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 17:699–709. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Peng H, Zhang W, Dong H, Yuan J, Li Y, Li
F, Yu D, Guan Y and Zhang F: CircFAT1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma
progression by sequestering miR-7 from repressing IRS2-ERK-mediated
CCND1 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 18:3944–3960. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
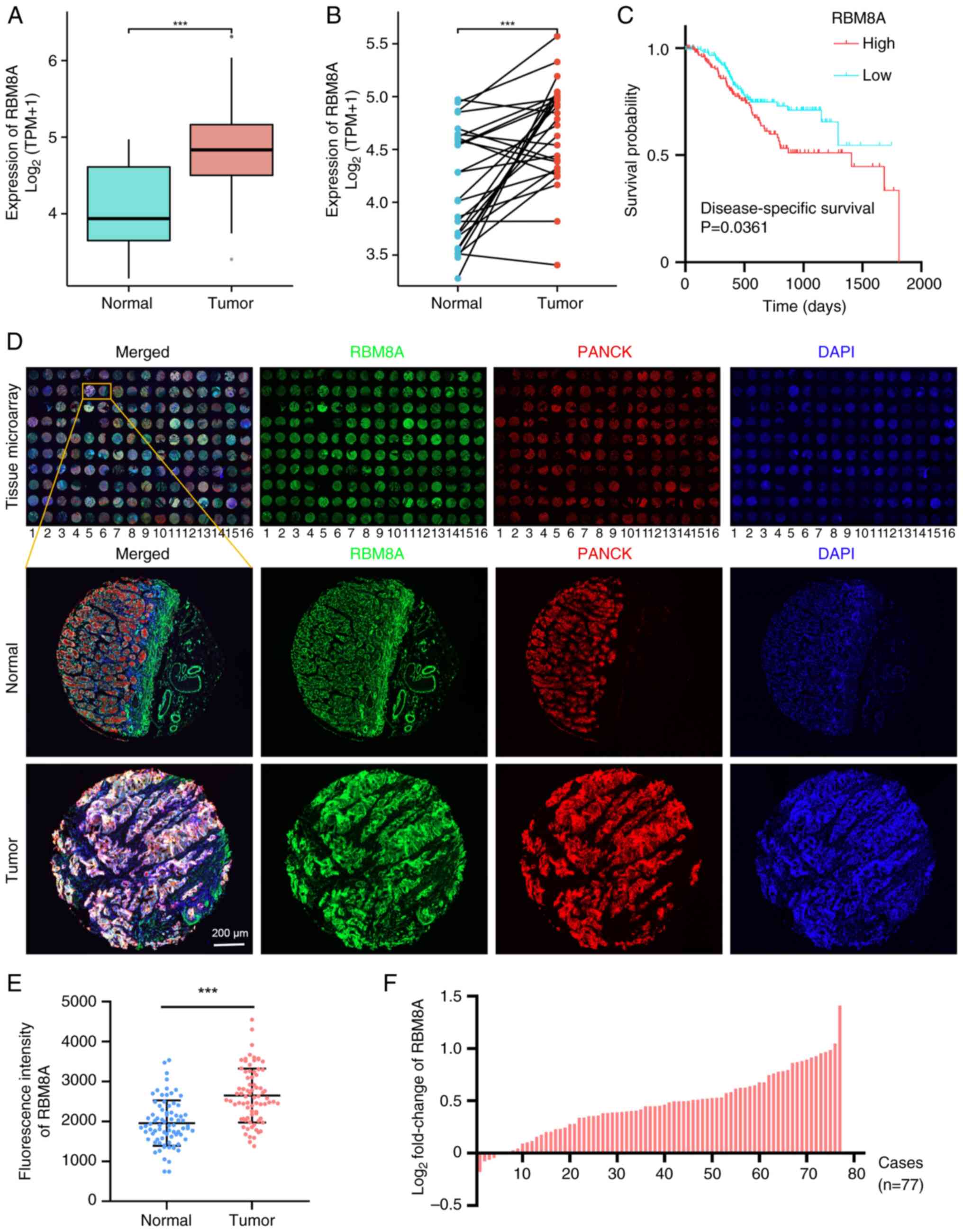
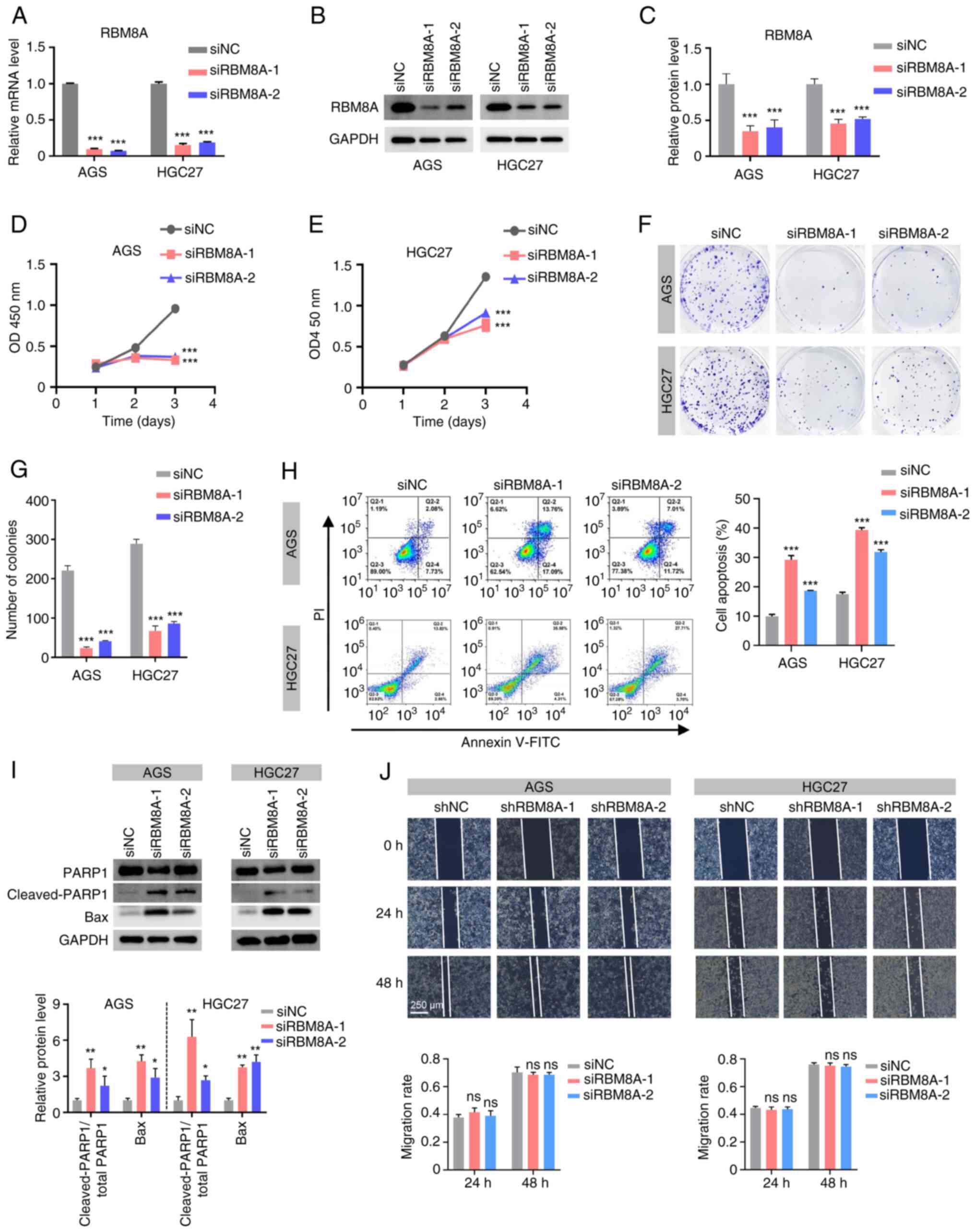
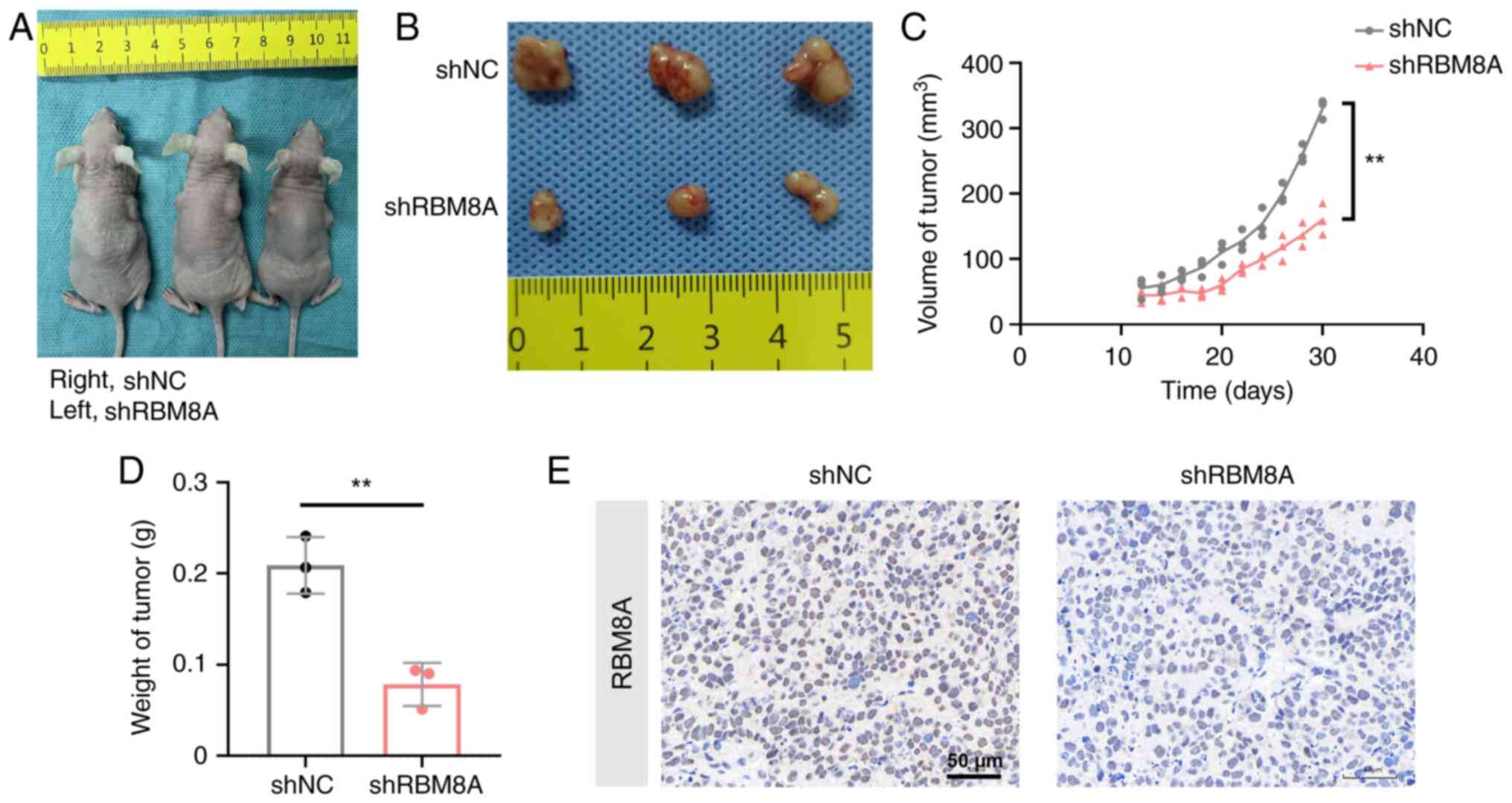
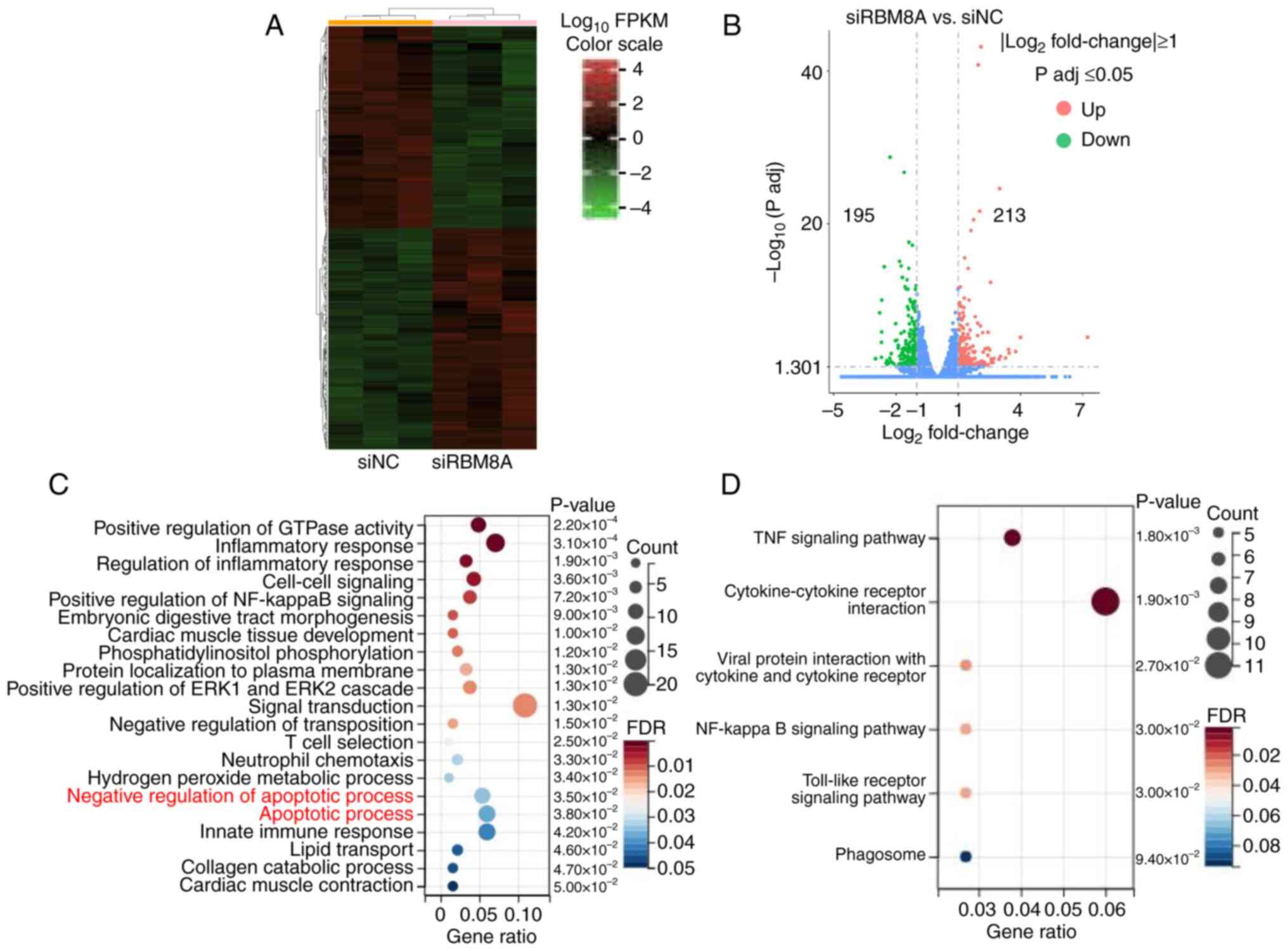
Lv X and Cheng H: Prognostic value of
increased expression of RBM8A in gastric cancer. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 53:e92902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu J and Zhang L: No PUMA, no death:
Implications for p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 4:248–249.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M: The role of P53 up-regulated
modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) in ovarian development,
cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Apoptosis.
26:235–247. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qiu L, Yao L, Hu P and He T: Analysis of
the detection rate and clinical characteristics of early gastric
cancer by painless gastroscopy and ordinary gastroscopy. Medicine
(Baltimore). 103:e381202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Obeng EA, Stewart C and Abdel-Wahab O:
Altered RNA processing in cancer pathogenesis and therapy. Cancer
Discov. 9:1493–1510. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin S, Liu H, Zhou Z, Xu X, Wang P, Chen
W, Deng G, Wang H, Yu H, Gu L, et al: PUM1 promotes tumor
progression by activating DEPTOR-meditated glycolysis in gastric
cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 10:e23011902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C, Yin Y, Tao R, Lin Y, Wang T, Shen Q,
Li R, Tao K and Liu W: ESRP1-driven alternative splicing of CLSTN1
inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Discov.
9:4642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Wei H, Yue A, Zhang H, Zheng Y,
Sun W, Zhou Y and Wang Y: KPNA2 promotes the progression of gastric
cancer by regulating the alternative splicing of related genes. Sci
Rep. 14:171402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ,
Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman pM, Day CL, Adams JM and Huang DC:
Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their
BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell.
17:393–403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE,
Bonzon C, Sullivan BA, Green DR and Newmeyer DD: BH3 domains of
BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated
mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and
indirectly. Mol Cell. 17:525–535. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD,
Sorcinelli MD, Weiler S and Korsmeyer SJ: Distinct BH3 domains
either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as
prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2:183–192. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mérino D, Giam M, Hughes PD, Siggs OM,
Heger K, O'Reilly LA, Adams JM, Strasser A, Lee EF, Fairlie WD and
Bouillet P: The role of BH3-only protein Bim extends beyond
inhibiting Bcl-2-like prosurvival proteins. J Cell Biol.
186:355–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Z, Sun J, Liu B, Zhao M, Xing E and
Dang C: miRNA-222 promotes liver cancer cell proliferation,
migration and invasion and inhibits apoptosis by targeting BBC3.
Int J Mol Med. 42:141–148. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Buchwald G, Ebert J, Basquin C, Sauliere
J, Jayachandran U, Bono F, Le Hir H and Conti E: Insights into the
recruitment of the nMD machinery from the crystal structure of a
core EJC-UPF3b complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:10050–10055.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Celik A, Kervestin S and Jacobson A: nMD:
At the crossroads between translation termination and ribosome
recycling. Biochimie. 114:2–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Chan WK, Huang L, Gudikote JP, Chang YF,
Imam JS, MacLean JA II and Wilkinson MF: An alternative branch of
the nonsense-mediated decay pathway. EMBO J. 26:1820–1830. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chamieh H, Ballut L, Bonneau F and Le Hir
H: nMD factors UPF2 and UPF3 bridge UPF1 to the exon junction
complex and stimulate its RNA helicase activity. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 15:85–93. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jones SH and Wilkinson M: RNA decay,
evolution, and the testis. RNA Biol. 14:146–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Karam R, Wengrod J, Gardner LB and
Wilkinson MF: Regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay:
Implications for physiology and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1829:624–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lykke-Andersen S and Jensen TH:
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: An intricate machinery that shapes
transcriptomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:665–677. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Goetz AE and Wilkinson M: Stress and the
nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci.
74:3509–3531. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hou B, Shu M, Liu C, Du Y, Xu C, Jiang H,
Hou J, Chen X, Wang L and Wu X: Unveiling the role of UPF3B in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential therapeutic target. Cancer Sci.
115:2646–2658. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang H, Qian D, Wang J, Liu Y, Luo W,
Zhang H, Cheng J, Li H, Wu Y, Li W, et al: HnRNPR-mediated UPF3B
mRNA splicing drives hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Adv
Res. 68:257–270. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Ma J, Chen T, Wu S, Yang C, Bai M, Shu K,
Li K, Zhang G, Jin Z, He F, et al: iProX: An integrated proteome
resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D1211–D121. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Chen T, Ma J, Liu Y, Chen Z, Xiao N, Lu Y,
Fu Y, Yang C, Li M, Wu S, et al: iProX in 2021: Connecting
proteomics data sharing with big data. Nucleic Acids Res.
50:D1522–D1527. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|