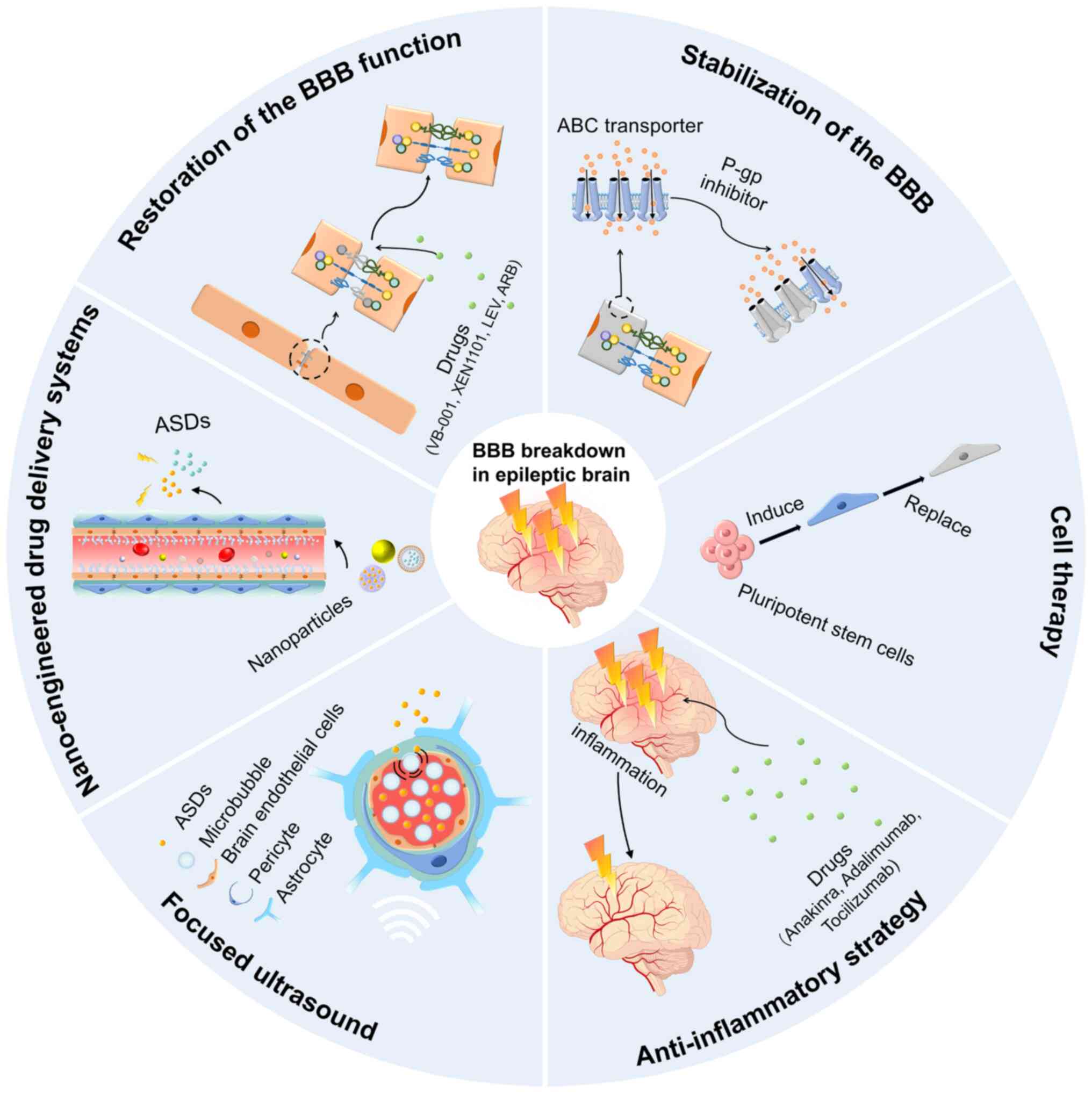
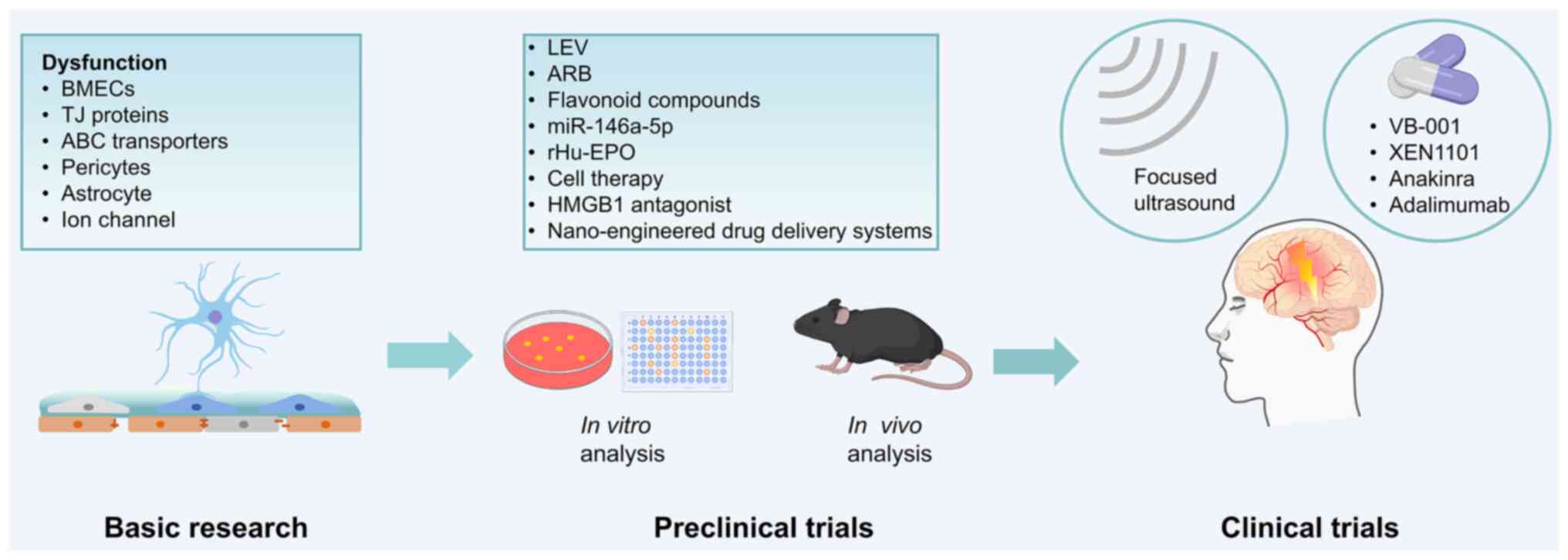
|
1
|
Thijs RD, Surges R, O'Brien TJ and Sander
JW: Epilepsy in adults. Lancet. 393:689–701. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization: Epilepsy: A
public health imperative: Summary. World Health Organization;
2019
|
|
3
|
Shao LR, Habela CW and Stafstrom CE:
Pediatric epilepsy mechanisms: Expanding the paradigm of
excitation/inhibition imbalance. Children (Basel).
6:232019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA, Higurashi
N, Hirsch E, Jansen FE, Lagae L, Moshé SL, Peltola J, Roulet Perez
E, et al: Operational classification of seizure types by the
international league against epilepsy: Position paper of the ILAE
commission for classification and terminology. Epilepsia.
58:522–530. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Z, Brodie MJ, Liew D and Kwan P:
Treatment outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy
treated with established and new antiepileptic drugs: A 30-year
longitudinal cohort study. JAMA Neurol. 75:279–286. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Cendes F, Sakamoto AC, Spreafico R,
Bingaman W and Becker AJ: Epilepsies associated with hippocampal
sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 128:21–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang Q and Han F:
The neurovascular unit dysfunction in the molecular mechanisms of
epileptogenesis and targeted therapy. Neurosci Bull. 40:621–634.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, O'Brien TJ, Jette
N, Scheffer IE, de Curtis M and Perucca P: Epilepsy Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 4:180242018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sultana B, Panzini MA, Veilleux Carpentier
A, Comtois J, Rioux B, Gore G, Bauer PR, Kwon CS, Jetté N,
Josephson CB and Keezer MR: Incidence and prevalence of
drug-resistant epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Neurology. 96:805–817. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kantanen AM, Reinikainen M, Parviainen I
and Kälviäinen R: Long-term outcome of refractory status
epilepticus in adults: A retrospective population-based study.
Epilepsy Res. 133:13–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Strzelczyk A, Griebel C, Lux W, Rosenow F
and Reese JP: The Burden of severely drug-refractory epilepsy: A
comparative longitudinal evaluation of mortality, morbidity,
resource use, and cost using german health insurance data. Front
Neurol. 8:7122017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang T, Wang J, Dou Y, Yan W, Ding D, Lu
G, Ma J, Zhou Y, Li T, Zhou S, et al: Clinical characteristics and
prognosis in a large paediatric cohort with status epilepticus.
Seizure. 80:5–11. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tian L, Li Y, Xue X, Wu M, Liu F, Hao X
and Zhou D: Super-refractory status epilepticus in West China. Acta
Neurol Scand. 132:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Al-Otaibi FA, Hamani C and Lozano AM:
Neuromodulation in epilepsy. Neurosurgery. 69:957–979. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dadas A and Janigro D: Breakdown of blood
brain barrier as a mechanism of post-traumatic epilepsy. Neurobiol
Dis. 123:20–26. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Baghirov H: Receptor-mediated transcytosis
of macromolecules across the blood-brain barrier. Expert Opin Drug
Deliv. 20:1699–1711. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chaves JCS, Dando SJ, White AR and Oikari
LE: Blood-brain barrier transporters: An overview of function,
dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and strategies for treatment.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1870:1669672024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Patabendige A and Janigro D: The role of
the blood-brain barrier during neurological disease and infection.
Biochem Soc Trans. 51:613–626. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vazana U, Veksler R, Pell GS, Prager O,
Fassler M, Chassidim Y, Roth Y, Shahar H, Zangen A, Raccah R, et
al: Glutamate-mediated blood-brain barrier opening: Implications
for neuroprotection and drug delivery. J Neurosci. 36:7727–7739.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leandro K, Bicker J, Alves G, Falcão A and
Fortuna A: ABC transporters in drug-resistant epilepsy: Mechanisms
of upregulation and therapeutic approaches. Pharmacol Res.
144:357–376. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Celentano C, Carotenuto L, Miceli F,
Carleo G, Corrado B, Baroli G, Iervolino S, Vecchione R,
Taglialatela M and Barrese V: Kv7 channel activation reduces brain
endothelial cell permeability and prevents kainic acid-induced
blood-brain barrier damage. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
326:C893–C904. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reimann F: Liver diseases and pernicious
anemia; clinical and physiopathological study of the behavior of
the anti-pernicious factor in the body. Blut. 4:261–279. 1958.In
German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bentivoglio M and Kristensson K: Tryps and
trips: Cell trafficking across the 100-year-old blood-brain
barrier. Trends Neurosci. 37:325–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reese TS and Karnovsky MJ: Fine structural
localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J
Cell Biol. 34:207–217. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Gan L, Cao F, Wang H, Gong P, Ma
C, Ren L, Lin Y and Lin X: The barrier and interface mechanisms of
the brain barrier, and brain drug delivery. Brain Res Bull.
190:69–83. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yan L, Moriarty RA and Stroka KM: Recent
progress and new challenges in modeling of human pluripotent stem
cell-derived blood-brain barrier. Theranostics. 11:10148–10170.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ushiyama A, Kataoka H and Iijima T:
Glycocalyx and its involvement in clinical pathophysiologies. J
Intensive Care. 4:592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iba T and Levy JH: Derangement of the
endothelial glycocalyx in sepsis. J Thromb Haemost. 17:283–294.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu R, Collier JM, Abdul-Rahman NH, Capuk
O, Zhang Z and Begum G: Dysregulation of Ion channels and
transporters and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in Alzheimer's
disease and vascular dementia. Aging Dis. 15:1748–1770.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen B, Bix G and Yao Y: Basal lamina
changes in neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurodegener.
16:812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Armulik A, Genové G, Mäe M, Nisancioglu
MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter
K, et al: Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature.
468:557–561. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gaceb A, Özen I, Padel T, Barbariga M and
Paul G: Pericytes secrete pro-regenerative molecules in response to
platelet-derived growth factor-BB. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
38:45–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Dabravolski SA, Andreeva ER, Eremin II,
Markin AM, Nadelyaeva II, Orekhov AN and Melnichenko AA: The role
of pericytes in regulation of innate and adaptive immunity.
Biomedicines. 11:6002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giovannoni F and Quintana FJ: The role of
astrocytes in CNS inflammation. Trends Immunol. 41:805–819. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L and Hansson E:
Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 7:41–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Díaz-Castro B, Robel S and Mishra A:
Astrocyte endfeet in brain function and pathology: Open questions.
Annu Rev Neurosci. 46:101–121. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alvarez JI, Dodelet-Devillers A, Kebir H,
Ifergan I, Fabre PJ, Terouz S, Sabbagh M, Wosik K, Bourbonnière L,
Bernard M, et al: The hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier
integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science. 334:1727–1731. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xing G, Zhao T, Zhang X, Li H, Li X, Cui
P, Li M, Li D, Zhang N and Jiang W: Astrocytic Sonic hedgehog
alleviates intracerebral hemorrhagic brain injury via modulation of
blood-brain barrier integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 14:5756902020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takahashi S: Metabolic contribution and
cerebral blood flow regulation by astrocytes in the neurovascular
unit. Cells. 11:8132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cornford EM and Oldendorf WH: Epilepsy and
the blood-brain barrier. Adv Neurol. 44:787–812. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Leroy C, Roch C, Koning E, Namer IJ and
Nehlig A: In the lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy, brain
lesions are not linked to changes in blood-brain barrier
permeability: An autoradiographic study in adult and developing
rats. Exp Neurol. 182:361–372. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Saija A, Princi P, Pisani A, Santoro G, De
Pasquale R, Massi M and Costa G: Blood-brain barrier dysfunctions
following systemic injection of kainic acid in the rat. Life Sci.
51:467–477. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Librizzi L, Noè F, Vezzani A, de Curtis M
and Ravizza T: Seizure-induced brain-borne inflammation sustains
seizure recurrence and blood-brain barrier damage. Ann Neurol.
72:82–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Michalak Z, Sano T, Engel T,
Miller-Delaney SFC, Lerner-Natoli M and Henshall DC:
Spatio-temporally restricted blood-brain barrier disruption after
intra-amygdala kainic acid-induced status epilepticus in mice.
Epilepsy Res. 103:167–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Löscher W: Epilepsy and alterations of the
blood-brain barrier: Cause or consequence of epileptic seizures or
both? Handb Exp Pharmacol. 273:331–350. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Castañeda-Cabral JL, Colunga-Durán A,
Ureña-Guerrero ME, Beas-Zárate C, Nuñez-Lumbreras MLA,
Orozco-Suárez S, Alonso-Vanegas M, Guevara-Guzmán R, Deli MA,
Valle-Dorado MG, et al: Expression of VEGF- and tight
junction-related proteins in the neocortical microvasculature of
patients with drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Microvasc Res.
132:1040592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Morin-Brureau M, Lebrun A, Rousset MC,
Fagni L, Bockaert J, de Bock F and Lerner-Natoli M: Epileptiform
activity induces vascular remodeling and zonula occludens 1
downregulation in organotypic hippocampal cultures: Role of VEGF
signaling pathways. J Neurosci. 31:10677–10688. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Soldner ELB, Sokola
BS, Alluri SR, Abner EL, Kryscio RJ, Pekcec A, Schlichtiger J and
Bauer B: Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated blood-brain barrier
dysfunction in epilepsy. J Neurosci. 38:4301–4315. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bronisz E, Cudna A, Wierzbicka A and
Kurkowska-Jastrzębska I: Blood-brain barrier-associated proteins
are elevated in serum of epilepsy patients. Cells. 12:3682023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lai M, Zou W, Han Z, Zhou L, Qiu Z, Chen
J, Zhang S, Lai P, Li K, Zhang Y, et al: Tsc1 regulates tight
junction independent of mTORC1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e20208911182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guo D, Zhang B, Han L, Rensing NR and Wong
M: Cerebral vascular and blood brain-barrier abnormalities in a
mouse model of epilepsy and tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia.
65:483–496. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Ogaki A, Ikegaya Y and Koyama R: Vascular
abnormalities and the role of vascular endothelial growth factor in
the epileptic brain. Front Pharmacol. 11:202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sweeney MD, Zhao Z, Montagne A, Nelson AR
and Zlokovic BV: Blood-brain barrier: From physiology to disease
and back. Physiol Rev. 99:21–78. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Klement W, Blaquiere M, Zub E, deBock F,
Boux F, Barbier E, Audinat E, Lerner-Natoli M and Marchi N: A
pericyte-glia scarring develops at the leaky capillaries in the
hippocampus during seizure activity. Epilepsia. 60:1399–1411. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Prager O, Kamintsky L, Hasam-Henderson LA,
Schoknecht K, Wuntke V, Papageorgiou I, Swolinsky J, Muoio V,
Bar-Klein G, Vazana U, et al: Seizure-induced microvascular injury
is associated with impaired neurovascular coupling and blood-brain
barrier dysfunction. Epilepsia. 60:322–336. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Q, Li QQ, Jia JN, Liu ZQ, Zhou HH and
Mao XY: Targeting gap junction in epilepsy: Perspectives and
challenges. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:57–65. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Haruwaka K, Ikegami A, Tachibana Y, Ohno
N, Konishi H, Hashimoto A, Matsumoto M, Kato D, Ono R, Kiyama H, et
al: Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability
induced by systemic inflammation. Nat Commun. 10:58162019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Park H, Choi SH, Kong MJ and Kang TC:
Dysfunction of 67-kDa laminin receptor disrupts bbb integrity via
impaired dystrophin/AQP4 complex and p38 MAPK/VEGF activation
following status epilepticus. Front Cell Neurosci. 13:2362019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu H, Dai R, Zhou Y, Fu H and Meng Q:
TLR2 ligand Pam3CSK4 regulates MMP-2/9 expression by MAPK/NF-κB
signaling pathways in primary brain microvascular endothelial
cells. Neurochem Res. 43:1897–1904. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yazarlou F, Lipovich L and Loeb JA:
Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in human epilepsy.
Epilepsia. 65:1491–1511. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Du Y, Chi X and An W: Downregulation of
microRNA-200c-3p reduces damage of hippocampal neurons in epileptic
rats by upregulating expression of RECK and inactivating the AKT
signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 307:223–233. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Meijer WC and Gorter JA: Role of
blood-brain barrier dysfunction in the development of poststroke
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 65:2519–2536. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ngo A, Royer J, Rodriguez-Cruces R, Xie K,
DeKraker J, Auer H, Tavakol S, Lam J, Schrader DV, Dudley RWR, et
al: Associations of cerebral blood flow patterns with gray and
white matter structure in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy.
Neurology. 103:e2095282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Musaeus CS, Kjaer TW, Lindberg U,
Vestergaard MB, Bo H, Larsson W, Press DZ, Andersen BB, Høgh P,
Kidmose P, et al: Subclinical epileptiform discharges in
Alzheimer's disease are associated with increased hippocampal blood
flow. Alzheimers Res Ther. 16:802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chai AB, Callaghan R and Gelissen IC:
Regulation of P-glycoprotein in the brain. Int J Mol Sci.
23:146672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tishler DM, Weinberg KI, Hinton DR,
Barbaro N, Annett GM and Raffel C: MDR1 gene expression in brain of
patients with medically intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia. 36:1–6.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lazarowski A, Ramos AJ, García-Rivello H,
Brusco A and Girardi E: Neuronal and glial expression of the
multidrug resistance gene product in an experimental epilepsy
model. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 24:77–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hartz AMS, Pekcec A, Soldner ELB, Zhong Y,
Schlichtiger J and Bauer B: P-gp protein expression and transport
activity in rodent seizure models and human epilepsy. Mol Pharm.
14:999–1011. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu JYW, Thom M, Catarino CB, Mar tinian
L, Figarella-Branger D, Bartolomei F, Koepp M and Sisodiya SM:
Neuropathology of the blood-brain barrier and pharmaco-resistance
in human epilepsy. Brain. 135:3115–3133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
van Vliet EA, Redeker S, Aronica E,
Edelbroek PM and Gorter JA: Expression of multidrug transporters
MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP shortly after status epilepticus, during the
latent period, and in chronic epileptic rats. Epilepsia.
46:1569–1580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Aronica E, Gorter JA, Redeker S, van Vliet
EA, Ramkema M, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, van der Valk P, Leenstra S,
Baayen JC, et al: Localization of breast cancer resistance protein
(BCRP) in microvessel endothelium of human control and epileptic
brain. Epilepsia. 46:849–857. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Aronica E, Gorter JA, Jansen GH, van
Veelen CW, van Rijen PC, Leenstra S, Ramkema M, Scheffer GL,
Scheper RJ and Troost D: Expression and cellular distribution of
multidrug transporter proteins in two major causes of medically
intractable epilepsy: Focal cortical dysplasia and glioneuronal
tumors. Neuroscience. 118:417–429. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ferreira A, Rodrigues M, Fortuna A, Falcão
A and Alves G: Flavonoid compounds as reversing agents of the
P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance: An in vitro
evaluation with focus on antiepileptic drugs. Food Res Int.
103:110–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gil-Martins E, Barbosa DJ, Silva V, Remião
F and Silva R: Dysfunction of ABC transporters at the blood-brain
barrier: Role in neurological disorders. Pharmacol Ther.
213:1075542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Vijay N and Morris ME: Role of
monocarboxylate transporters in drug delivery to the brain. Curr
Pharm Des. 20:1487–1498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Lauritzen F, Perez EL, Melillo ER, Roh JM,
Zaveri HP, Lee TS, Wang Y, Bergersen LH and Eid T: Altered
expression of brain monocarboxylate transporter 1 in models of
temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 45:165–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
77
|
van Vliet EA, Otte WM, Gorter JA,
Dijkhuizen RM and Wadman WJ: Longitudinal assessment of blood-brain
barrier leakage during epileptogenesis in rats. A quantitative MRI
study Neurobiol Dis. 63:74–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Bar-Klein G, Lublinsky S, Kamintsky L,
Noyman I, Veksler R, Dalipaj H, Senatorov VV Jr, Swissa E,
Rosenbach D, Elazary N, et al: Imaging blood-brain barrier
dysfunction as a biomarker for epileptogenesis. Brain.
140:1692–1705. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Scott G, Mahmud M, Owen DR and Johnson MR:
Microglial positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in epilepsy:
Applications, opportunities and pitfalls. Seizure. 44:42–47. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Gruenbaum BF, Zlotnik A, Fleidervish I,
Frenkel A and Boyko M: Glutamate neurotoxicity and destruction of
the blood-brain barrier: Key pathways for the development of
neuropsychiatric consequences of TBI and their potential treatment
strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 23:96282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Barker-Haliski M and White HS:
Glutamatergic mechanisms associated with seizures and epilepsy.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 5:a0228632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hogan-Cann AD and Anderson CM:
Physiological roles of non-neuronal NMDA receptors. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 37:750–767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kim KS, Jeon MT, Kim ES, Lee CH and Kim
DG: Activation of NMDA receptors in brain endothelial cells
increases transcellular permeability. Fluids Barriers CNS.
19:702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sharp CD, Hines I, Houghton J, Warren A,
Jackson TH IV, Jawahar A, Nanda A, Elrod JW, Long A, Chi A, et al:
Glutamate causes a loss in human cerebral endothelial barrier
integrity through activation of NMDA receptor. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 285:H2592–H2598. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen JT, Chen TG, Chang YC, Chen CY and
Chen RM: Roles of NMDARs in maintenance of the mouse
cerebrovascular endothelial cell-constructed tight junction
barrier. Toxicology. 339:40–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Yang T, Liu YW, Zhao L, Wang H, Yang N,
Dai SS and He F: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 deficiency
inhibits neutrophil infiltration after traumatic brain injury in
mice. Sci Rep. 7:99982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ren J, Yang T, Liu H, Ma P, Zhou M, Li J,
Li T, Sun J, He W, Xu L, et al: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5
promotes blood-brain barrier recovery after traumatic brain injury.
Exp Neurol. 374:1146912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Liu J, Feng X, Wang Y, Xia X and Zheng JC:
Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic cells in the brain. Front
Cell Neurosci. 16:8924972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kopeikina E, Dukhinova M, Yung AWY,
Veremeyko T, Kuznetsova IS, Lau TYB, Levchuk K and Ponomarev ED:
Platelets promote epileptic seizures by modulating brain serotonin
level, enhancing neuronal electric activity, and contributing to
neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Prog Neurobiol.
188:1017832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wang Y, Zhu Y, Wang J, Dong L, Liu S, Li S
and Wu Q: Purinergic signaling: A gatekeeper of blood-brain barrier
permeation. Front Pharmacol. 14:11127582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhao H, Zhang X, Dai Z, Feng Y, Li Q,
Zhang JH, Liu X, Chen Y and Feng H: P2X7 receptor suppression
preserves blood-brain barrier through inhibiting RhoA activation
after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Sci Rep.
6:232862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang K, Sun M, Juan Z, Zhang J, Sun Y,
Wang G, Wang C, Li Y, Kong W, Fan L, et al: The improvement of
sepsis-associated encephalopathy by P2X7R inhibitor through
inhibiting the Omi/HtrA2 apoptotic signaling pathway. Behav Neurol.
2022:37773512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
van Vliet EA, Otte WM, Wadman WJ, Aronica
E, Kooij G, de Vries HE, Dijkhuizen RM and Gorter JA: Blood-brain
barrier leakage after status epilepticus in rapamycin-treated rats
II: Potential mechanisms. Epilepsia. 57:70–78. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Feng L, Shu Y, Wu Q, Liu T, Long H, Yang
H, Li Y and Xiao B: EphA4 may contribute to microvessel remodeling
in the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 areas in a mouse model of temporal
lobe epilepsy. Mol Med Rep. 15:37–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Rigau V, Morin M, Rousset MC, de Bock F,
Lebrun A, Coubes P, Picot MC, Baldy-Moulinier M, Bockaert J,
Crespel A and Lerner-Natoli M: Angiogenesis is associated with
blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain.
130:1942–1956. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers
H, Van Oosterom AT and De Bruijn EA: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 56:549–580. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Waldbaum S and Patel M: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress: A contributing link to acquired
epilepsy? J Bioenerg Biomembr. 42:449–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ: Regulation of
angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat Med.
9:677–684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Marchi N, Granata T, Ghosh C and Janigro
D: Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and epilepsy: Pathophysiologic
role and therapeutic approaches. Epilepsia. 53:1877–1886. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wengert ER and Patel MK: The role of the
persistent sodium current in epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr. 21:40–47.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Di Cristo G, Awad PN, Hamidi S and Avoli
M: KCC2, epileptiform synchronization, and epileptic disorders.
Prog Neurobiol. 162:1–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Xu JH and Tang FR: Voltage-dependent
calcium channels, calcium binding proteins, and their interaction
in the pathological process of epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci.
19:27352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Dalal PJ, Muller WA and Sullivan DP:
Endothelial cell calcium signaling during barrier function and
inflammation. Am J Pathol. 190:535–542. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
104
|
Wu J, Yang J, Yu M, Sun W, Han Y, Lu X,
Jin C, Wu S and Cai Y: Lanthanum chloride causes blood-brain
barrier disruption through intracellular calcium-mediated RhoA/Rho
kinase signaling and myosin light chain kinase. Metallomics.
12:2075–2083. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Luh C, Feiler S, Frauenknecht K, Meyer S,
Lubomirov LT, Neulen A and Thal SC: The contractile apparatus is
essential for the integrity of the blood-brain barrier after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res.
10:534–545. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
Hubbard JA, Szu JI, Yonan JM and Binder
DK: Regulation of astrocyte glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1) and
aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression in a model of epilepsy. Exp Neurol.
283:85–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Alvestad S, Hammer J, Hoddevik EH, Skare
Ø, Sonnewald U, Amiry-Moghaddam M and Ottersen OP: Mislocalization
of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal
lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 105:30–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Salman MM, Sheilabi MA, Bhattacharyya D,
Kitchen P, Conner AC, Bill RM, Woodroofe MN, Conner MT and
Princivalle AP: Transcriptome analysis suggests a role for the
differential expression of cerebral aquaporins and the MAPK
signalling pathway in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci.
46:2121–2132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Vandebroek A and Yasui M: Regulation of
AQP4 in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 21:16032020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Bonosi L, Benigno UE, Musso S, Giardina K,
Gerardi RM, Brunasso L, Costanzo R, Paolini F, Buscemi F, Avallone
C, et al: The role of aquaporins in epileptogenesis-a systematic
review. Int J Mol Sci. 24:119232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zhu DD, Yang G, Huang YL, Zhang T, Sui AR,
Li N, Su WH, Sun HL, Gao JJ, Ntim M, et al: AQP4-A25Q point
mutation in mice depolymerizes orthogonal arrays of particles and
decreases polarized expression of AQP4 protein in astrocytic
endfeet at the blood-brain barrier. J Neurosci. 42:8169–8183. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Lin X, Peng Y, Guo Z, He W, Guo W, Feng J,
Lu L, Liu Q and Xu P: Short-chain fatty acids suppresses astrocyte
activation by amplifying Trp-AhR-AQP4 signaling in experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Cell Mol Life Sci. 81:2932024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Lee DJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM, Arellano JL and
Binder DK: Decreased expression of the glial water channel
aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of
epileptogenesis. Exp Neurol. 235:246–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Murphy TR, Davila D, Cuvelier N, Young LR,
Lauderdale K, Binder DK and Fiacco TA: Hippocampal and cortical
pyramidal neurons swell in parallel with astrocytes during acute
hypoosmolar stress. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:2752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Seiffert E, Dreier JP, Ivens S, Bechmann
I, Tomkins O, Heinemann U and Friedman A: Lasting blood-brain
barrier disruption induces epileptic focus in the rat somatosensory
cortex. J Neurosci. 24:7829–7836. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
van Vliet EA, da Costa Araújo S, Redeker
S, van Schaik R, Aronica E and Gorter JA: Blood-brain barrier
leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain.
130:521–534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Savotchenko A, Klymenko M, Shypshyna M and
Isaev D: The role of thrombin in early-onset seizures. Front Cell
Neurosci. 17:11010062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Greene C, Hanley N, Reschke CR, Reddy A,
Mäe MA, Connolly R, Behan C, O'Keeffe E, Bolger I, Hudson N, et al:
Microvascular stabilization via blood-brain barrier regulation
prevents seizure activity. Nat Commun. 13:20032022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Liu XX, Yang L, Shao LX, He Y, Wu G, Bao
YH, Lu NN, Gong DM, Lu YP, Cui TT, et al: Endothelial Cdk5 deficit
leads to the development of spontaneous epilepsy through
CXCL1/CXCR2-mediated reactive astrogliosis. J Exp Med.
217:e201809922020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
120
|
Salar S, Maslarova A, Lippmann K,
Nichtweiss J, Weissberg I, Sheintuch L, Kunz WS, Shorer Z, Friedman
A and Heinemann U: Blood-brain barrier dysfunction can contribute
to pharmacoresistance of seizures. Epilepsia. 55:1255–1263. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Lapilover EG, Lippmann K, Salar S,
Maslarova A, Dreier JP, Heinemann U and Friedman A: Peri-infarct
blood-brain barrier dysfunction facilitates induction of spreading
depolarization associated with epileptiform discharges. Neurobiol
Dis. 48:495–506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Frigerio F, Frasca A, Weissberg I,
Parrella S, Friedman A, Vezzani A and Noé FM: Long-lasting
pro-ictogenic effects induced in vivo by rat brain exposure to
serum albumin in the absence of concomitant pathology. Epilepsia.
53:1887–1897. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Salar S, Lapilover E, Müller J, Hollnagel
JO, Lippmann K, Friedman A and Heinemann U: Synaptic plasticity in
area CA1 of rat hippocampal slices following intraventricular
application of albumin. Neurobiol Dis. 91:155–165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Noé FM, Bellistri E, Colciaghi F,
Cipelletti B, Battaglia G, de Curtis M and Librizzi L: Kainic
acid-induced albumin leak across the blood-brain barrier
facilitates epileptiform hyperexcitability in limbic regions.
Epilepsia. 57:967–976. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Kinboshi M, Ikeda A and Ohno Y: Role of
astrocytic inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) 4.1 channels in
epileptogenesis. Front Neurol. 11:6266582020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Szu JI and Binder DK: Mechanisms
underlying aquaporin-4 subcellular mislocalization in epilepsy.
Front Cell Neurosci. 16:9005882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
David Y, Cacheaux LP, Ivens S, Lapilover
E, Heinemann U, Kaufer D and Friedman A: Astrocytic dysfunction in
epileptogenesis: Consequence of altered potassium and glutamate
homeostasis? J Neurosci. 29:10588–10599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Wallraff A, Köhling R, Heinemann U, Theis
M, Willecke K and Steinhäuser C: The impact of astrocytic gap
junctional coupling on potassium buffering in the hippocampus. J
Neurosci. 26:5438–5447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Vezzani A, Ravizza T, Bedner P, Aronica E,
Steinhäuser C and Boison D: Astrocytes in the initiation and
progression of epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 18:707–722. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Qiu YM, Zhang CL, Chen AQ, Wang HL, Zhou
YF, Li YN and Hu B: Immune cells in the BBB disruption after acute
ischemic stroke: Targets for immune therapy? Front Immunol.
12:6787442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Yang J, Ran M, Li H, Lin Y, Ma K, Yang Y,
Fu X and Yang S: New insight into neurological degeneration:
Inflammatory cytokines and blood-brain barrier. Front Mol Neurosci.
15:10139332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Broekaart DWM, Anink JJ, Baayen JC, Idema
S, de Vries HE, Aronica E, Gorter JA and van Vliet EA: Activation
of the innate immune system is evident throughout epileptogenesis
and is associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction and seizure
progression. Epilepsia. 59:1931–1944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Di Nunzio M, Di Sapia R, Sorrentino D,
Kebede V, Cerovic M, Gullotta GS, Bacigaluppi M, Audinat E, Marchi
N, Ravizza T and Vezzani A: Microglia proliferation plays distinct
roles in acquired epilepsy depending on disease stages. Epilepsia.
62:1931–1945. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Kamaşak T, Dilber B, Yaman SÖ, Durgut BD,
Kurt T, Çoban E, Arslan EA, Şahin S, Karahan SC and Cansu A:
HMGB-1, TLR4, IL-1R1, TNF-α, and IL-1β: Novel epilepsy markers?
Epileptic Disord. 22:183–193. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Greene C, Hanley N and Campbell M:
Claudin-5: Gatekeeper of neurological function. Fluids Barriers
CNS. 16:32019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Clark PR, Kim RK, Pober JS and Kluger MS:
Tumor necrosis factor disrupts claudin-5 endothelial tight junction
barriers in two distinct NF-κB-dependent phases. PLoS One.
10:e01200752015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Khan A, Ni W, Lopez-Giraldez F, Kluger MS,
Pober JS and Pierce RW: Tumor necrosis factor-induced ArhGEF10
selectively activates RhoB contributing to human microvascular
endothelial cell tight junction disruption. FASEB J. 35:e216272021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Tsai MM, Chen JL, Lee TH, Liu H, Shanmugam
V and Hsieh HL: Brain protective effect of resveratrol via
ameliorating interleukin-1β-induced MMP-9-mediated disruption of
ZO-1 arranged integrity. Biomedicines. 10:12702022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Manu DR, Slevin M, Barcutean L, Forro T,
Boghitoiu T and Balasa R: Astrocyte involvement in blood-brain
barrier function: A critical update highlighting novel, complex,
neurovascular interactions. Int J Mol Sci. 24:171462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Gardoni F,
Vezzani A, Behrens MM, Bartfai T, Binaglia M, Corsini E, Di Luca M,
Galli CL and Marinovich M: Interleukin-1beta enhances NMDA
receptor-mediated intracellular calcium increase through activation
of the Src family of kinases. J Neurosci. 23:8692–8700. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Mukhtar I: Inflammatory and immune
mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis and epilepsy: From
pathogenesis to treatment target. Seizure. 82:65–79. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Yang F, Zhao K, Zhang X, Zhang J and Xu B:
ATP induces disruption of tight junction proteins via IL-1
beta-dependent MMP-9 activation of human blood-brain barrier in
vitro. Neural Plast. 2016:89285302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Qiu J, Xu J, Zheng Y, Wei Y, Zhu X, Lo EH,
Moskowitz MA and Sims JR: High-mobility group box 1 promotes
metalloproteinase-9 upregulation through Toll-like receptor 4 after
cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 41:2077–2082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Kim EJ, Park SY, Baek SE, Jang MA, Lee WS,
Bae SS, Kim K and Kim CD: HMGB1 Increases IL-1β production in
vascular smooth muscle cells via NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Physiol.
9:3132018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
de Jong JM, Broekaart DWM, Bongaarts A,
Mühlebner A, Mills JD, van Vliet EA and Aronica E: Altered
extracellular matrix as an alternative risk factor for
epileptogenicity in brain tumors. Biomedicines. 10:24752022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Su J, Yin J, Qin W, Sha S, Xu J and Jiang
C: Role for pro-inflammatory cytokines in regulating expression of
GABA transporter type 1 and 3 in specific brain regions of kainic
acid-induced status epilepticus. Neurochem Res. 40:621–627. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Fu CY, He XY, Li XF, Zhang X, Huang ZW, Li
J, Chen M and Duan CZ: Nefiracetam attenuates pro-inflammatory
cytokines and GABA transporter in specific brain regions of rats
with post-ischemic seizures. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:2023–2031.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Olmos G and Lladó J: Tumor necrosis factor
alpha: A link between neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:8612312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Roseti C, van Vliet EA, Cifelli P, Ruffolo
G, Baayen JC, Di Castro MA, Bertollini C, Limatola C, Aronica E,
Vezzani A and Palma E: GABAA currents are decreased by IL-1β in
epileptogenic tissue of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy:
Implications for ictogenesis. Neurobiol Dis. 82:311–320. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Librizzi L, Vila Verde D, Colciaghi F,
Deleo F, Regondi MC, Costanza M, Cipelletti B and de Curtis M:
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation sustains seizure
activity. Epilepsia. 62:1715–1728. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Cresto N, Janvier A and Marchi N: From
neurons to the neuro-glio-vascular unit: Seizures and brain
homeostasis in networks. Rev Neurol (Paris). 179:308–315. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Thirupathi A and Chang YZ: Brain iron
metabolism and CNS diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1173:1–19. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Tang S, Gao P, Chen H, Zhou X, Ou Y and He
Y: The role of iron, its metabolism and ferroptosis in traumatic
brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 14:5907892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Chiueh CC: Iron overload, oxidative
stress, and axonal dystrophy in brain disorders. Pediatr Neurol.
25:138–147. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Willmore LJ, Sypert GW and Munson JB:
Recurrent seizures induced by cortical iron injection: a model of
posttraumatic epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 4:329–336. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Willmore LJ, Sypert GW, Munson JV and Hurd
RW: Chronic focal epileptiform discharges induced by injection of
iron into rat and cat cortex. Science. 200:1501–1503. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zimmer TS, David B, Broekaart DWM,
Schidlowski M, Ruffolo G, Korotkov A, van der Wel NN, van Rijen PC,
Mühlebner A, van Hecke W, et al: Seizure-mediated iron accumulation
and dysregulated iron metabolism after status epilepticus and in
temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. 142:729–759. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Ikeda M: Iron overload without the C282Y
mutation in patients with epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
70:551–553. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Dusek P, Hofer T, Alexander J, Roos PM and
Aaseth JO: Cerebral iron deposition in neurodegeneration.
Biomolecules. 12:7142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Bagwe-Parab S and Kaur G: Molecular
targets and therapeutic interventions for iron induced
neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull. 156:1–9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Wang F, Guo L, Wu Z, Zhang T, Dong D and
Wu B: The Clock gene regulates kainic acid-induced seizures through
inhibiting ferroptosis in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 74:1640–1650.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Mao XY, Zhou HH and Jin WL: Ferroptosis
induction in pentylenetetrazole kindling and pilocarpine-induced
epileptic seizures in mice. Front Neurosci. 13:7212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Huang L, Liu H and Liu S: Insight into the
role of ferroptosis in epilepsy. J Integr Neurosci. 23:1132024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T and Baram
TZ: The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:31–40.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Montagne A, Zhao Z and Zlokovic BV:
Alzheimer's disease: A matter of blood-brain barrier dysfunction? J
Exp Med. 214:3151–3169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Profaci CP, Munji RN, Pulido RS and
Daneman R: The blood-brain barrier in health and disease: Important
unanswered questions. J Exp Med. 217:e201900622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Lendahl U, Nilsson P and Betsholtz C:
Emerging links between cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative
diseases-a special role for pericytes. EMBO Rep. 20:e480702019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Sagare AP, Singh I,
LaRue B, Deane R and Zlokovic BV: Pericytes control key
neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain
and during brain aging. Neuron. 68:409–427. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Davalos D, Ryu JK, Merlini M, Baeten KM,
Le Moan N, Petersen MA, Deerinck TJ, Smirnoff DS, Bedard C,
Hakozaki H, et al: Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial
clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in
neuroinflammation. Nat Commun. 3:12272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Marchi N, Angelov L, Masaryk T, Fazio V,
Granata T, Hernandez N, Hallene K, Diglaw T, Franic L, Najm I and
Janigro D: Seizure-promoting effect of blood-brain barrier
disruption. Epilepsia. 48:732–742. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Oby E and Janigro D: The blood-brain
barrier and epilepsy. Epilepsia. 47:1761–1774. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
van Vliet EA, Ndode-Ekane XE, Lehto LJ,
Gorter JA, Andrade P, Aronica E, Gröhn O and Pitkänen A:
Long-lasting blood-brain barrier dysfunction and neuroinflammation
after traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 145:1050802020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Zhao Y, Liu Y, Xu Y, Li K, Zhou L, Qiao H,
Xu Q and Zhao J: The role of ferroptosis in blood-brain barrier
injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 43:223–236. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Yang LT, Anthony G and Kaufer D:
Inflammatory astrocytic TGFβ signaling induced by blood-brain
barrier dysfunction drives epileptogenesis. Noebels JL, Avoli M,
Rogawski MA, Vezzani A and Delgado-Escueta AV: Jasper's Basic
Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 5th edition. New York: Oxford
University Press; 2024
|
|
175
|
van Vliet EA, Aronica E and Gorter JA:
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction, seizures and epilepsy. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 38:26–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Belinskaia DA, Voronina PA, Shmurak VI,
Jenkins RO and Goncharov NV: Serum albumin in health and disease:
Esterase, antioxidant, transporting and signaling properties. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:103182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Wang Y: Leaky blood-brain barrier: A
double whammy for the brain. Epilepsy Currents. 20:165–167. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Luo WD, Min JW, Huang WX, Wang X, Peng YY,
Han S, Yin J, Liu WH, He XH and Peng BW: Vitexin reduces epilepsy
after hypoxic ischemia in the neonatal brain via inhibition of
NKCC1. J Neuroinflammation. 15:1862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Ahishali B, Kaya M, Orhan N, Arican N,
Ekizoglu O, Elmas I, Kucuk M, Kemikler G, Kalayci R and Gurses C:
Effects of levetiracetam on blood-brain barrier disturbances
following hyperthermia-induced seizures in rats with cortical
dysplasia. Life Sci. 87:609–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Shaikh TG, Hasan SFS, Ahmed H, Kazi AI and
Mansoor R: The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in treating
epilepsy: A review. Neurol Sci. 45:1437–1445. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Thorwald MA, Rodriguez
R, Mejias-Ortega M, Kieu Z, Maitra N, Hawkins C, Valenzuela J, Peng
M, Nishiyama A, et al: Angiotensin receptor blockade with
olmesartan alleviates brain pathology in obese OLETF rats. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 50:228–237. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
182
|
Pereira MGAG, Becari C, Oliveira JAC,
Salgado MCO, Garcia-Cairasco N and Costa-Neto CM: Inhibition of the
renin-angiotensin system prevents seizures in a rat model of
epilepsy. Clin Sci (Lond). 119:477–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Winkler EA, Sengillo JD, Sagare AP, Zhao
Z, Ma Q, Zuniga E, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Sullivan JS, Griffin JH, et al:
Blood-spinal cord barrier disruption contributes to early
motor-neuron degeneration in ALS-model mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:E1035–E1042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Cui J, Liu X and Chow LMC: Flavonoids as
P-gp inhibitors: A systematic review of SARs. Curr Med Chem.
26:4799–4831. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Deng X, Shao Y, Xie Y, Feng Y, Wu M, Wang
M and Chen Y: MicroRNA-146a-5p downregulates the expression of
P-glycoprotein in rats with lithium-pilocarpine-induced status
epilepticus. Biol Pharm Bull. 42:744–750. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Merelli A, Ramos AJ, Lazarowski A and
Auzmendi J: Convulsive stress mimics brain hypoxia and promotes the
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and erythropoietin receptor overexpression.
Recombinant human erythropoietin effect on P-gp activity. Front
Neurosci. 13:7502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Montanari F and Ecker GF: Prediction of
drug-ABC-transporter interaction-recent advances and future
challenges. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 86:17–26. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Yu J and Ragueneau-Majlessi I: In
Vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation of transporter inhibition data for
drugs approved by the US food and drug administration in 2018. Clin
Transl Sci. 13:693–699. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Faal T, Phan DTT, Davtyan H, Scarfone VM,
Varady E, Blurton-Jones M, Hughes CCW and Inlay MA: Induction of
mesoderm and neural crest-derived pericytes from human pluripotent
stem cells to study blood-brain barrier interactions. Stem Cell
Reports. 12:451–460. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Chen B: Cell therapy rejuvenates the
neuroglial-vascular unit. Neural Regen Res. 21: View Article : Google Scholar : 2025.
|
|
191
|
Dahalia M, Gupta S, Majid H, Vohora D and
Nidhi: Pirfenidone regulates seizures through the HMGB1/TLR4 axis
to improve cognitive functions and modulate oxidative stress and
neurotransmitters in PTZ-induced kindling in mice. Front Pharmacol.
15:15280322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wang Q, Qin B, Yu H, Yu H, Zhang X, Li M,
Zhou Y, Diao L and Liu H: Dingxian pill alleviates hippocampal
neuronal apoptosis in epileptic mice through TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling
pathway inhibition. J Ethnopharmacol. 334:1185792024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Chen S, Chen R, Luo M, Luo Y, Ma X, Zhao H
and Xu Z: Increased seizure susceptibility in the collagen-induced
arthritis mouse model depends on neuronal IL-1R1. Life Sci.
369:1235372025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Wu L, Zhu Y, Qin Y, Yuan H, Zhang L, Lu T,
Chen Q and Hu A: Conditional knockout of IL-1R1 in endothelial
cells attenuates seizures and neurodegeneration via inhibiting
neuroinflammation mediated by Nrf2/HO-1/NLRP3 signaling in status
epilepticus model. Mol Neurobiol. 61:4289–4303. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
195
|
Walker LE, Sills GJ, Jorgensen A,
Alapirtti T, Peltola J, Brodie MJ, Marson AG, Vezzani A and
Pirmohamed M: High-mobility group box 1 as a predictive biomarker
for drug-resistant epilepsy: A proof-of-concept study. Epilepsia.
63:e1–e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Zhao J, Zheng Y, Liu K, Chen J, Lai N, Fei
F, Shi J, Xu C, Wang S, Nishibori M, et al: HMGB1 is a therapeutic
target and biomarker in diazepam-refractory status epilepticus with
wide time window. Neurotherapeutics. 17:710–721. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
197
|
Rana A and Musto AE: The role of
inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation.
15:1442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K,
Taylor P, van Vollenhoven R, Heatley R, Walsh C, Lawson R, Reynolds
A and Emery P: Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor
inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:1895–1904.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Vezzani A, Balosso S and Ravizza T:
Neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarkers in
epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 15:459–472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Ravizza T and Vezzani A: Pharmacological
targeting of brain inflammation in epilepsy: Therapeutic
perspectives from experimental and clinical studies. Epilepsia
Open. 3(Suppl 2): S133–S142. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Soltani Khaboushan A, Yazdanpanah N and
Rezaei N: Neuroinflammation and proinflammatory cytokines in
epileptogenesis. Mol Neurobiol. 59:1724–1743. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Dilena R, Mauri E, Aronica E, Bernasconi
P, Bana C, Cappelletti C, Carrabba G, Ferrero S, Giorda R, Guez S,
et al: Therapeutic effect of Anakinra in the relapsing chronic
phase of febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome. Epilepsia
Open. 4:344–350. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Costagliola G, Depietri G, Michev A, Riva
A, Foiadelli T, Savasta S, Bonuccelli A, Peroni D, Consolini R,
Marseglia GL, et al: Targeting inflammatory mediators in epilepsy:
A systematic review of its molecular basis and clinical
applications. Front Neurol. 13:7412442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Zhong X, Na Y, Yin S, Yan C, Gu J, Zhang N
and Geng F: Cell membrane biomimetic nanoparticles with potential
in treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Molecules. 28:23362023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Qin Y, Fan W, Chen H, Yao N, Tang W, Tang
J, Yuan W, Kuai R, Zhang Z, Wu Y and He Q: In vitro and in vivo
investigation of glucose-mediated brain-targeting liposomes. J Drug
Target. 18:536–549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Xie F, Yao N, Qin Y, Zhang Q, Chen H, Yuan
M, Tang J, Li X, Fan W, Zhang Q, et al: Investigation of
glucose-modified liposomes using polyethylene glycols with
different chain lengths as the linkers for brain targeting. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:163–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Zhou Y, Zhu F, Liu Y, Zheng M, Wang Y,
Zhang D, Anraku Y, Zou Y, Li J, Wu H, et al: Blood-brain
barrier-penetrating siRNA nanomedicine for Alzheimer's disease
therapy. Sci Adv. 6:eabc70312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Anraku Y, Kuwahara H, Fukusato Y,
Mizoguchi A, Ishii T, Nitta K, Matsumoto Y, Toh K, Miyata K, Uchida
S, et al: Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier
crossing the BBB into the brain. Nat Commun. 8:10012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Fu X, Li J, Wu Y, Mao C and Jiang Y: PAR2
deficiency tunes inflammatory microenvironment to magnify STING
signalling for mitigating cancer metastasis via anionic CRISPR/Cas9
nanoparticles. J Control Release. 363:733–746. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Meng R, Hao S, Sun C, Hou Z, Hou Y, Wang
L, Deng P, Deng J, Yang Y, Xia H, et al: Reverse-QTY code design of
active human serum albumin self-assembled amphiphilic nanoparticles
for effective anti-tumor drug doxorubicin release in mice. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 120:e22201731202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Gu GJ, Chung H, Park JY, Yoo R, Im HJ,
Choi H, Lee YS and Seok SH: Mannosylated-serum albumin nanoparticle
imaging to monitor tumor-associated macrophages under anti-PD1
treatment. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Deng Z, Wang J, Xiao Y, Li F, Niu L, Liu
X, Meng L and Zheng H: Ultrasound-mediated augmented exosome
release from astrocytes alleviates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity.
Theranostics. 11:4351–4362. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
213
|
Qu F, Wang P, Zhang K, Shi Y, Li Y, Li C,
Lu J, Liu Q and Wang X: Manipulation of mitophagy by 'all-in-one'
nanosensitizer augments sonodynamic glioma therapy. Autophagy.
16:1413–1435. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Gasca-Salas C, Fernández-Rodríguez B,
Pineda-Pardo JA, Rodríguez-Rojas R, Obeso I, Hernández-Fernández F,
Del Álamo M, Mata D, Guida P, Ordás-Bandera C, et al: Blood-brain
barrier opening with focused ultrasound in Parkinson's disease
dementia. Nat Commun. 12:7792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Ozdas MS, Shah AS, Johnson PM, Patel N,
Marks M, Yasar TB, Stalder U, Bigler L, von der Behrens W, Sirsi SR
and Yanik MF: Non-invasive molecularly-specific
millimeter-resolution manipulation of brain circuits by
ultrasound-mediated aggregation and uncaging of drug carriers. Nat
Commun. 11:49292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Chen J, Yuan M, Madison CA, Eitan S and
Wang Y: Blood-brain barrier crossing using magnetic stimulated
nanoparticles. J Control Release. 345:557–571. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Gupta R, Chauhan A, Kaur T, Kuanr BK and
Sharma D: Transmigration of magnetite nanoparticles across the
blood-brain barrier in a rodent model: Influence of external and
alternating magnetic fields. Nanoscale. 14:17589–17606. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Zhang Q, Yang L, Zheng Y, Wu X, Chen X,
Fei F, Gong Y, Tan B, Chen Q, Wang Y, et al: Electro-responsive
micelle-based universal drug delivery system for on-demand therapy
in epilepsy. J Control Release. 360:759–771. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Zhang Y, Wu X, Ding J, Su B, Chen Z, Xiao
Z, Wu C, Wei D, Sun J, Luo F, et al: Wireless-powering deep brain
stimulation platform based on 1D-structured magnetoelectric
nanochains applied in antiepilepsy treatment. ACS Nano.
17:15796–15809. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Gao S, Zheng M, Ren X, Tang Y and Liang X:
Local hyperthermia in head and neck cancer: Mechanism, application
and advance. Oncotarget. 7:57367–57378. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Wu D, Fei F, Zhang Q, Wang X, Gong Y, Chen
X, Zheng Y, Tan B, Xu C, Xie H, et al: Nanoengineered on-demand
drug delivery system improves efficacy of pharmacotherapy for
epilepsy. Sci Adv. 8:eabm33812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Yang D, Ren Q, Nie J, Zhang Y, Wu H, Chang
Z, Wang B, Dai J and Fang Y: Black phosphorus flake-enabled
wireless neuromodulation for epilepsy treatment. Nano Lett.
24:1052–1061. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
223
|
Hou Q, Wang L, Xiao F, Wang L, Liu X, Zhu
L, Lu Y, Zheng W and Jiang X: Dual targeting nanoparticles for
epilepsy therapy. Chem Sci. 13:12913–12920. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Chen SG, Tsai CH, Lin CJ, Lee CC, Yu HY,
Hsieh TH and Liu HL: Transcranial focused ultrasound pulsation
suppresses pentylenetetrazol induced epilepsy in vivo. Brain
Stimul. 13:35–46. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Lee CC, Chou CC, Hsiao FJ, Chen YH, Lin
CF, Chen CJ, Peng SJ, Liu HL and Yu HY: Pilot study of focused
ultrasound for drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 63:162–175.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Gustafson HH, Holt-Casper D, Grainger DW
and Ghandehari H: Nanoparticle uptake: The phagocyte problem. Nano
Today. 10:487–510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Dobrovolskaia MA and McNeil SE:
Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat
Nanotechnol. 2:469–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
228
|
Singh N, Manshian B, Jenkins GJS,
Griffiths SM, Williams PM, Maffeis TGG, Wright CJ and Doak SH:
NanoGenotoxicology: The DNA damaging potential of engineered
nanomaterials. Biomaterials. 30:3891–3914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Zhang J, Yan F, Zhang W, He L, Li Y, Zheng
S, Wang Y, Yu T, Du L, Shen Y and He W: Biosynthetic gas vesicles
combined with focused ultrasound for blood-brain barrier opening.
Int J Nanomedicine. 17:6759–6772. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Mainprize T, Lipsman N, Huang Y, Meng Y,
Bethune A, Ironside S, Heyn C, Alkins R, Trudeau M, Sahgal A, et
al: Blood-brain barrier opening in primary brain tumors with
non-invasive MR-guided focused ultrasound: A clinical safety and
feasibility study. Sci Rep. 9:3212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Lipsman N, Meng Y, Bethune AJ, Huang Y,
Lam B, Masellis M, Herrmann N, Heyn C, Aubert I, Boutet A, et al:
Blood-brain barrier opening in Alzheimer's disease using MR-guided
focused ultrasound. Nat Commun. 9:23362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Pineda-Pardo JA, Gasca-Salas C,
Fernández-Rodríguez B, Rodríguez-Rojas R, Del Álamo M, Obeso I,
Hernández-Fernández F, Trompeta C, Martínez-Fernández R, Matarazzo
M, et al: Striatal blood-brain barrier opening in Parkinson's
disease dementia: A pilot exploratory study. Mov Disord.
37:2057–2065. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Gkountas AA, Polychronopoulos ND, Sofiadis
GN, Karvelas EG, Spyrou LA and Sarris IE: Simulation of magnetic
nanoparticles crossing through a simplified blood-brain barrier
model for Glioblastoma multiforme treatment. Comput Methods
Programs Biomed. 212:1064772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Bencsik A, Lestaevel P and Guseva Canu I:
Nano- and neuro-toxicology: An emerging discipline. Prog Neurobiol.
160:45–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Xiong X, Sun Y, Sattiraju A, Jung Y, Mintz
A, Hayasaka S and Li KC: Remote spatiotemporally controlled and
biologically selective permeabilization of blood-brain barrier. J
Control Release. 217:113–120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Chen W, Yu H, Hao Y, Liu W, Wang R, Huang
Y, Wu J, Feng L, Guan Y, Huang L and Qian K: Comprehensive
metabolic fingerprints characterize neuromyelitis optica spectrum
disorder by nanoparticle-enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass
spectrometry. ACS Nano. 17:19779–19792. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Lyu X, Liu J, Gou Y, Sun S, Hao J and Cui
Y: Development and validation of a machine learning-based model of
ischemic stroke risk in the Chinese elderly hypertensive
population. VIEW. 5:202400592024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
238
|
Yuan Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Li H, Qi Z, Du Z,
Chu YH, Feng D, Xie Q, Song J, et al: Multimodal data integration
using deep learning predicts overall survival of patients with
glioma. VIEW. 5:202400012024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
Ying X, Wang Y, Liang J, Yue J, Xu C, Lu
L, Xu Z, Gao J, Du Y and Chen Z: Angiopep-conjugated
electro-responsive hydrogel nanoparticles: Therapeutic potential
for epilepsy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:12436–12440. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Geng C, Ren X, Cao P, Chu X, Wei P, Liu Q,
Lu Y, Fu B, Li W, Li Y and Zhao G: Macrophage membrane-biomimetic
nanoparticles target inflammatory microenvironment for epilepsy
treatment. Theranostics. 14:6652–6670. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
241
|
Fang Z, Chen S, Qin J, Chen B, Ni G, Chen
Z, Zhou J, Li Z, Ning Y, Wu C and Zhou L: Pluronic P85-coated
poly(butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles overcome phenytoin
resistance in P-glycoprotein overexpressing rats with
lithium-pilocarpine-induced chronic temporal lobe epilepsy.
Biomaterials. 97:110–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Zybina A, Anshakova A, Malinovskaya J,
Melnikov P, Baklaushev V, Chekhonin V, Maksimenko O, Titov S,
Balabanyan V, Kreuter J, et al: Nanoparticle-based delivery of
carbamazepine: A promising approach for the treatment of refractory
epilepsy. Int J Pharm. 547:10–23. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Zhao J, Ye Z, Yang J, Zhang Q, Shan W,
Wang X, Wang Z, Ye S, Zhou X, Shao Z and Ren L: Nanocage
encapsulation improves antiepileptic efficiency of phenytoin.
Biomaterials. 240:1198492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Chu PC, Yu HY, Lee CC, Fisher R and Liu
HL: Pulsed-focused ultrasound provides long-term suppression of
epileptiform bursts in the kainic acid-induced epilepsy rat model.
Neurotherapeutics. 19:1368–1380. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Krishna V, Mindel J, Sammartino F, Block
C, Dwivedi AK, Van Gompel JJ, Fountain N and Fisher R: A phase 1
open-label trial evaluating focused ultrasound unilateral anterior
thalamotomy for focal onset epilepsy. Epilepsia. 64:831–842. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Choi T, Koo M, Joo J, Kim T, Shon YM and
Park J: Bidirectional neuronal control of epileptiform activity by
repetitive transcranial focused ultrasound stimulations. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:e23024042024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
247
|
Chu PC, Huang CS, Ing SZ, Yu HY, Fisher RS
and Liu HL: Pulsed focused ultrasound reduces hippocampal volume
loss and improves behavioral performance in the kainic acid rat
model of epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics. 20:502–517. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Zhang Y, Buckmaster PS, Qiu L, Wang J,
Keunen O, Ghobadi SN, Huang A, Hou Q, Li N, Narang S, et al:
Non-invasive, neurotoxic surgery reduces seizures in a rat model of
temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 343:1137612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Zhang M, Li B, Liu Y, Tang R, Lang Y,
Huang Q and He J: Different modes of low-frequency focused
ultrasound-mediated attenuation of epilepsy based on the
topological theory. Micromachines (Basel). 12. pp. 10012021,
View Article : Google Scholar
|