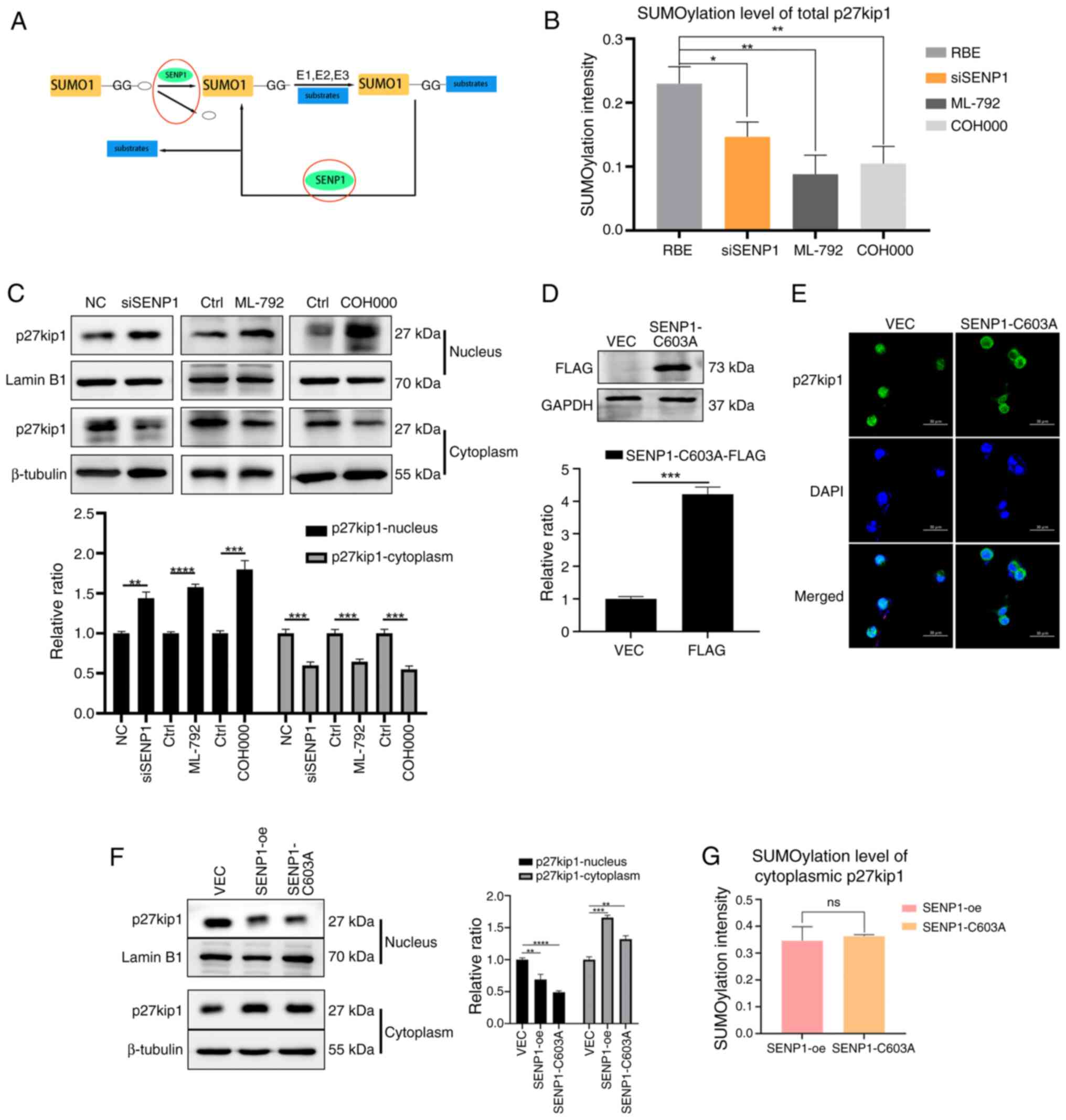
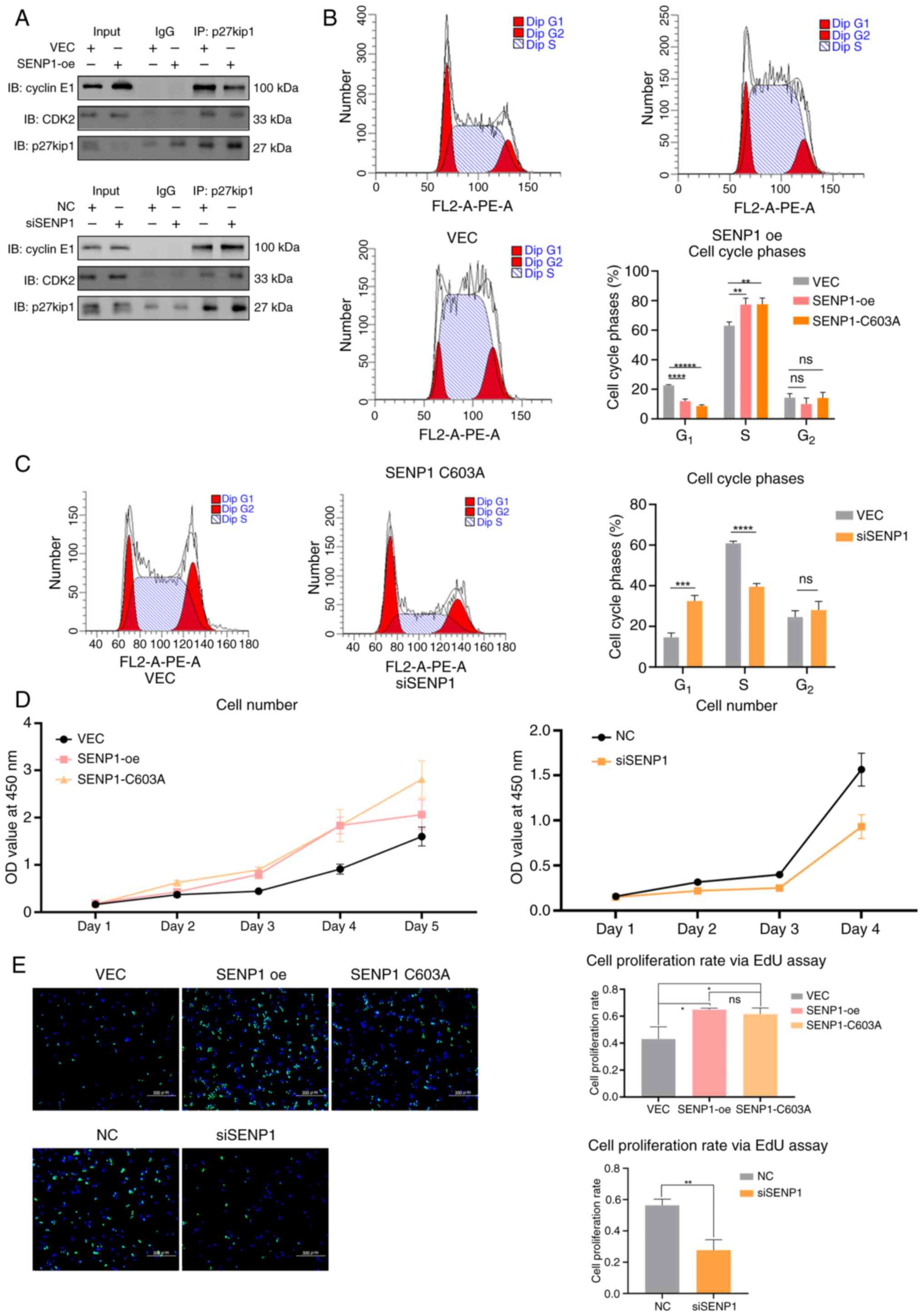
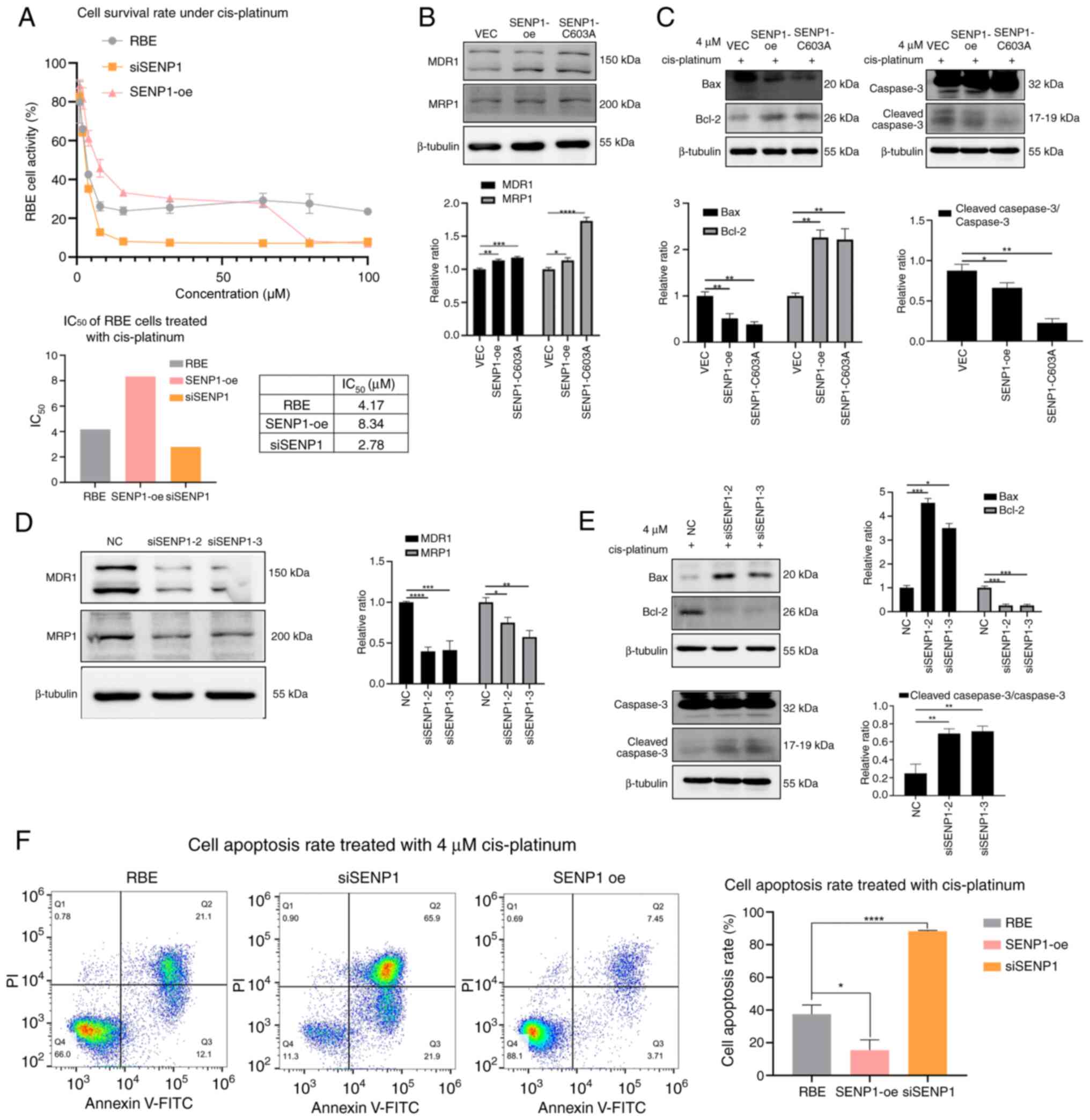
|
1
|
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A,
Rodrigues PM, Khan SA, Roberts LR, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Andersen
JB, Braconi C, et al: Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in
mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:557–588. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Darwish Murad S, Kim WR, Harnois DM,
Douglas DD, Burton J, Kulik LM, Botha JF, Mezrich JD, Chapman WC,
Schwartz JJ, et al: Efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiation,
followed by liver transplantation, for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
at 12 US centers. Gastroenterology. 143:88–98.e3. e142012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chu IM, Hengst L and Slingerland JM: The
Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: Prognostic potential and
relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:253–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Razavipour SF, Harikumar KB and
Slingerland JM: p27 as a transcriptional regulator: New roles in
development and cancer. Cancer Res. 80:3451–3458. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jeannot P, Nowosad A, Perchey RT, Callot
C, Bennana E, Katsube T, Mayeux P, Guillonneau F, Manenti S and
Besson A: p27Kip1 promotes invadopodia turnover and
invasion through the regulation of the PAK1/Cortactin pathway.
Elife. 6:e222072017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li N, Zeng J, Sun F, Tong X, Meng G, Wu C,
Ding X, Liu L, Han M, Lu C and Dai F: p27 inhibits CDK6/CCND1
complex formation resulting in cell cycle arrest and inhibition of
cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 17:2335–2348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McKay LK and White JP: The
AMPK/p27Kip1 pathway as a novel target to promote
autophagy and resilience in aged cells. Cells. 10:14302021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chang HM and Yeh ETH: SUMO: From bench to
bedside. Physiol Rev. 100:1599–1619. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Flotho A and Melchior F: Sumoylation: A
regulatory protein modification in health and disease. Annu Rev
Biochem. 82:357–385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vertegaal AC: SUMO chains: Polymeric
signals. Biochem Soc Trans. 38:46–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tokarz P and Woźniak K: SENP proteases as
potential targets for cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:20592021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kunz K, Piller T and Müller S:
SUMO-specific proteases and isopeptidases of the SENP family at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 131:jcs2119042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang J, Liu Y, Wang B, Lan H, Liu Y, Chen
F, Zhang J and Luo J: Sumoylation in p27kip1 via RanBP2 promotes
cancer cell growth in cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939. BMC Mol
Biol. 18:232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang J, Tan X, Liu Y, Jiang K and Luo J:
Knockdown of UBE2I inhibits tumorigenesis and enhances
chemosensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma via modulating p27kip1
nuclear export. Mol Carcinog. 62:700–715. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng J, Kang X, Zhang S and Yeh ET:
SUMO-specific protease 1 is essential for stabilization of
HIF1alpha during hypoxia. Cell. 131:584–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao Y, Wang R, Liu J, Zhao K, Qian X, He X
and Liu H: SENP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer invasion
and metastasis via enhancing CSN5 transcription mediated by GATA1
deSUMOylation. Int J Biol Sci. 18:2186–2201. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, Wu R, Yung MMH, Sun J, Li Z, Yang H,
Zhang Y, Liu SS, Cheung ANY, Ngan HYS, et al: SENP1-mediated
deSUMOylation of JAK2 regulates its kinase activity and platinum
drug resistance. Cell Death Dis. 12:3412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu S, Hu J, Cui Y, Liang S, Gao X, Zhang
J and Jia W: Knockdown of SENP1 inhibits HIF-1α SUMOylation and
suppresses oncogenic CCNE1 in Wilms tumor. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
23:355–366. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, et al: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 22.
8th. Springer International Publishing: American Joint Commission
on Cancer; Chicago: pp. 287–293. 2017
|
|
20
|
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla
PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne
U, et al: UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis
platform. Neoplasia. 25:18–27. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Rodriguez IP, Chakravarthi BVSK and Varambally
S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression
and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Tang Z, Zhang W, Ye Z and Liu F:
GEPIA2021: Integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into
GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:W242–W246. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Specht E, Kaemmerer D, Sänger J, Wirtz RM,
Schulz S and Lupp A: Comparison of immunoreactive score, HER2/neu
score and H score for the immunohistochemical evaluation of
somatostatin receptors in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine
neoplasms. Histopathology. 67:368–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Luo Y, Yu L, Lin Y, Luo D, Zhang H,
He Y, Kim YO, Kim Y, Tang S and Min W: SENP1 mediates TNF-induced
desumoylation and cytoplasmic translocation of HIPK1 to enhance
ASK1-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 15:739–750. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Xiang J, Ji F, Deng Y,
Tang C, Yang S, Xi Q, Liu R and Di W: Knockdown of CRM1 inhibits
the nuclear export of p27(Kip1) phosphorylated at serine 10 and
plays a role in the pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Cancer Lett. 343:6–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Connor MK, Kotchetkov R, Cariou S, Resch
A, Lupetti R, Beniston RG, Melchior F, Hengst L and Slingerland JM:
CRM1/Ran-mediated nuclear export of p27(Kip1) involves a nuclear
export signal and links p27 export and proteolysis. Mol Biol Cell.
14:201–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He X, Riceberg J, Soucy T, Koenig E,
Minissale J, Gallery M, Bernard H, Yang X, Liao H, Rabino C, et al:
Probing the roles of SUMOylation in cancer cell biology by using a
selective SAE inhibitor. Nat Chem Biol. 13:1164–1171. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Z, Chau SF, Lam KH, Chan HY, Ng TB and
Au SWN: Crystal structure of the SENP1 mutant C603S-SUMO complex
reveals the hydrolytic mechanism of SUMO-specific protease. Biochem
J. 398:345–352. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu Z and Au SWN: Mapping residues of SUMO
precursors essential in differential maturation by SUMO-specific
protease, SENP1. Biochem J. 386:325–330. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Elvevi A, Laffusa A, Scaravaglio M, Rossi
RE, Longarini R, Stagno AM, Cristoferi L, Ciaccio A, Cortinovis DL,
Invernizzi P and Massironi S: Clinical treatment of
cholangiocarcinoma: An updated comprehensive review. Ann Hepatol.
27:1007372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Song Y and Liu S: The new insight of
treatment in cholangiocarcinoma. J Cancer. 13:450–464. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Macias RIR, Rimassa L and Lamarca A: The
promise of precision medicine: How biomarkers are shaping the
future of cholangiocarcinoma treatment. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr.
12:457–461. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan J, Luo K, Zhang L, Cheville JC and
Lou Z: USP10 regulates p53 localization and stability by
deubiquitinating p53. Cell. 140:384–396. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen JH, Zhang P, Chen WD, Li DD, Wu XQ,
Deng R, Jiao L, Li X, Ji J, Feng GK, et al: ATM-mediated PTEN
phosphorylation promotes PTEN nuclear translocation and autophagy
in response to DNA-damaging agents in cancer cells. Autophagy.
11:239–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan BZ, Jefferson AM, Millecchia L,
Popescu NC and Reynolds SH: Morphological changes and nuclear
translocation of DLC1 tumor suppressor protein precede apoptosis in
human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res.
313:3868–3880. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rivera MN, Kim WJ, Wells J, Stone A,
Burger A, Coffman EJ, Zhang J and Haber DA: The tumor suppressor
WTX shuttles to the nucleus and modulates WT1 activity. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:8338–8343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luo J, Chen Y, Li Q, Wang B, Zhou Y and
Lan H: CRM-1 knockdown inhibits extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
tumor growth by blocking the nuclear export of p27Kip1. Int J Mol
Med. 38:381–390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee J and Kim SS: The function of p27 KIP1
during tumor development. Exp Mol Med. 41:765–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burdelski C, Menan D, Tsourlakis MC, Kluth
M, Hube-Magg C, Melling N, Minner S, Koop C, Graefen M, Heinzer H,
et al: The prognostic value of SUMO1/Sentrin specific peptidase 1
(SENP1) in prostate cancer is limited to ERG-fusion positive tumors
lacking PTEN deletion. BMC Cancer. 15:5382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hay RT: SUMO: A history of modification.
Mol Cell. 18:1–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Palancade B and Doye V: Sumoylating and
desumoylating enzymes at nuclear pores: Underpinning their
unexpected duties? Trends Cell Biol. 18:174–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu H, Yan S, Ding J, Yu TT and Cheng SY:
DeSUMOylation of gli1 by SENP1 attenuates sonic hedgehog signaling.
Mol Cell Biol. 37:e00579–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hang J and Dasso M: Association of the
human SUMO1 protease SENP2 with the nuclear pore. J Biol Chem.
277:19961–19966. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ball JR and Ullman KS: Versatility at the
nuclear pore complex: Lessons learned from the nucleoporin Nup153.
Chromosoma. 114:319–330. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shin EJ, Shin HM, Nam E, Kim WS, Kim JH,
Oh BH and Yun Y: DeSUMOylating isopeptidase: A second class of SUMO
protease. EMBO Rep. 13:339–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|