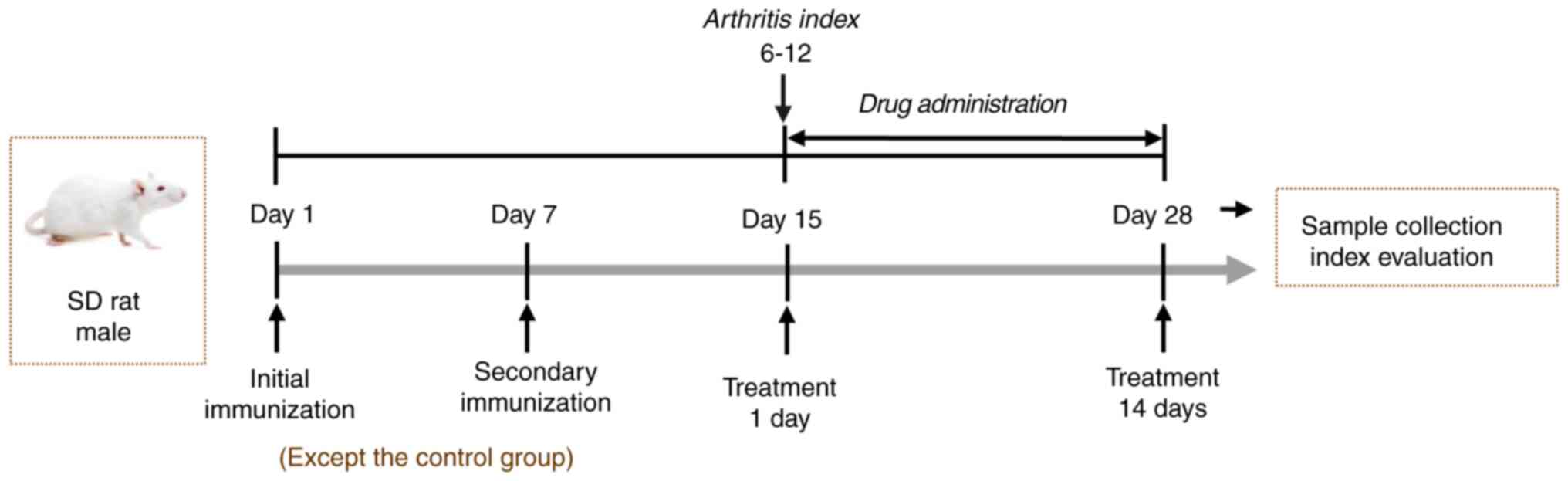
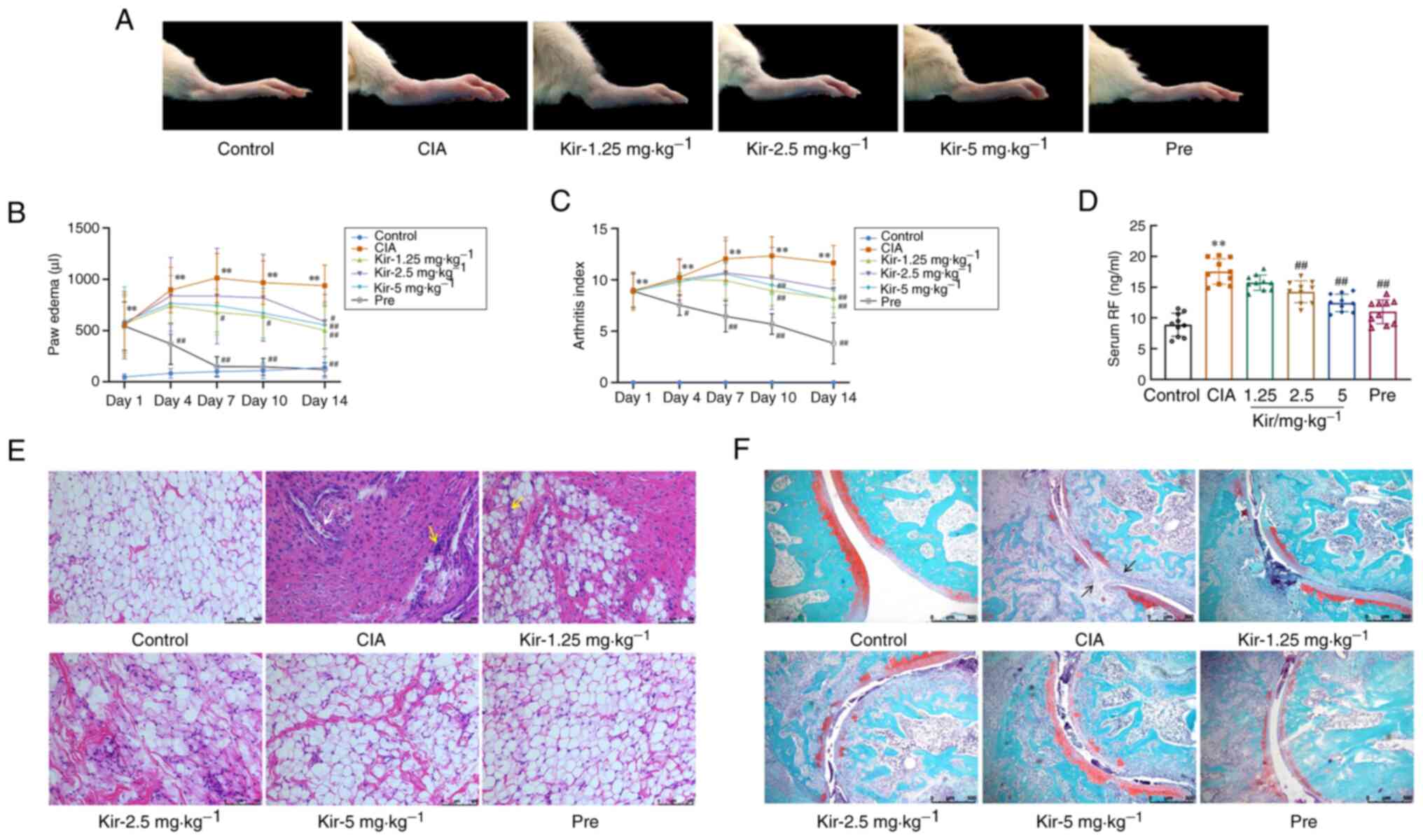
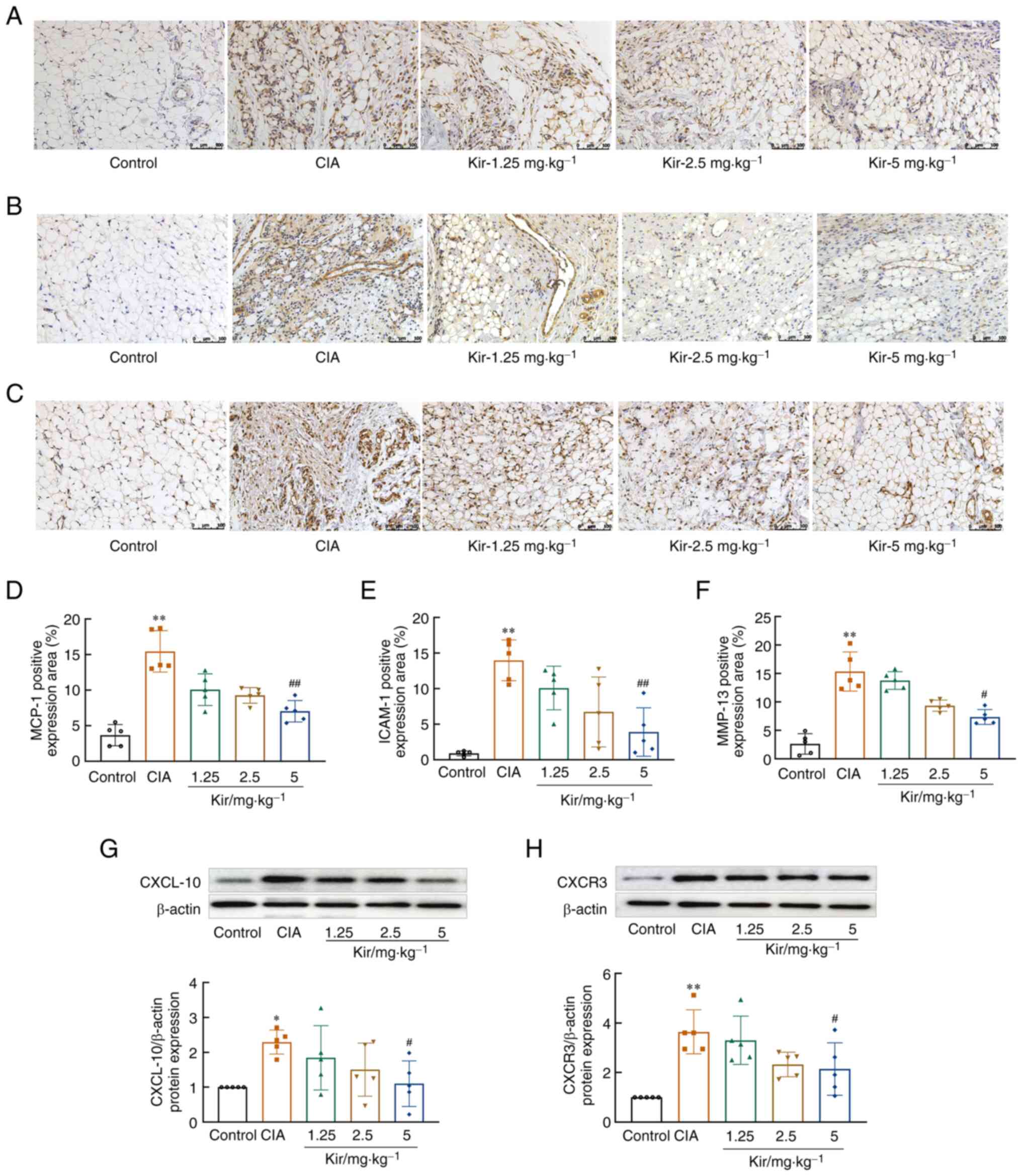
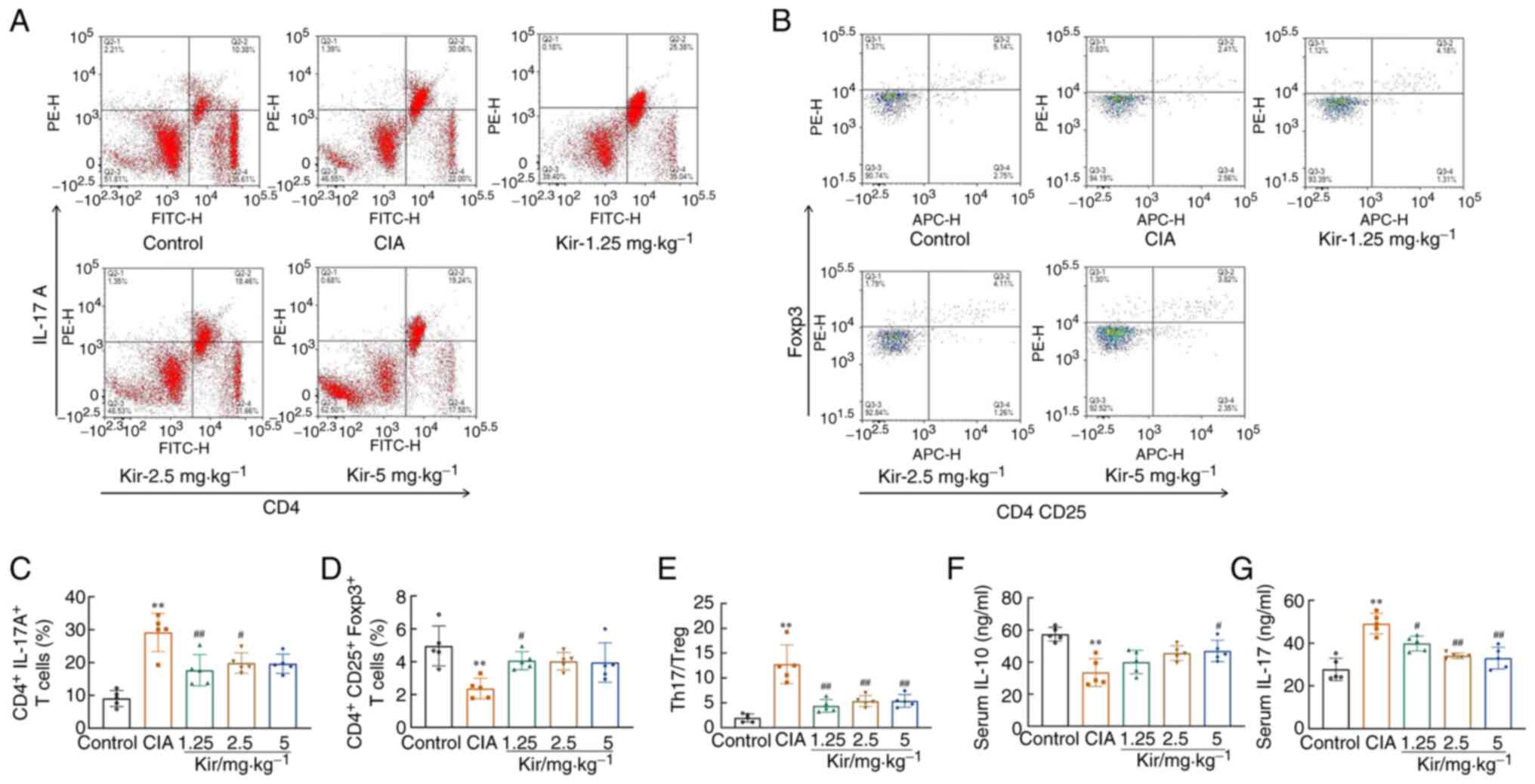
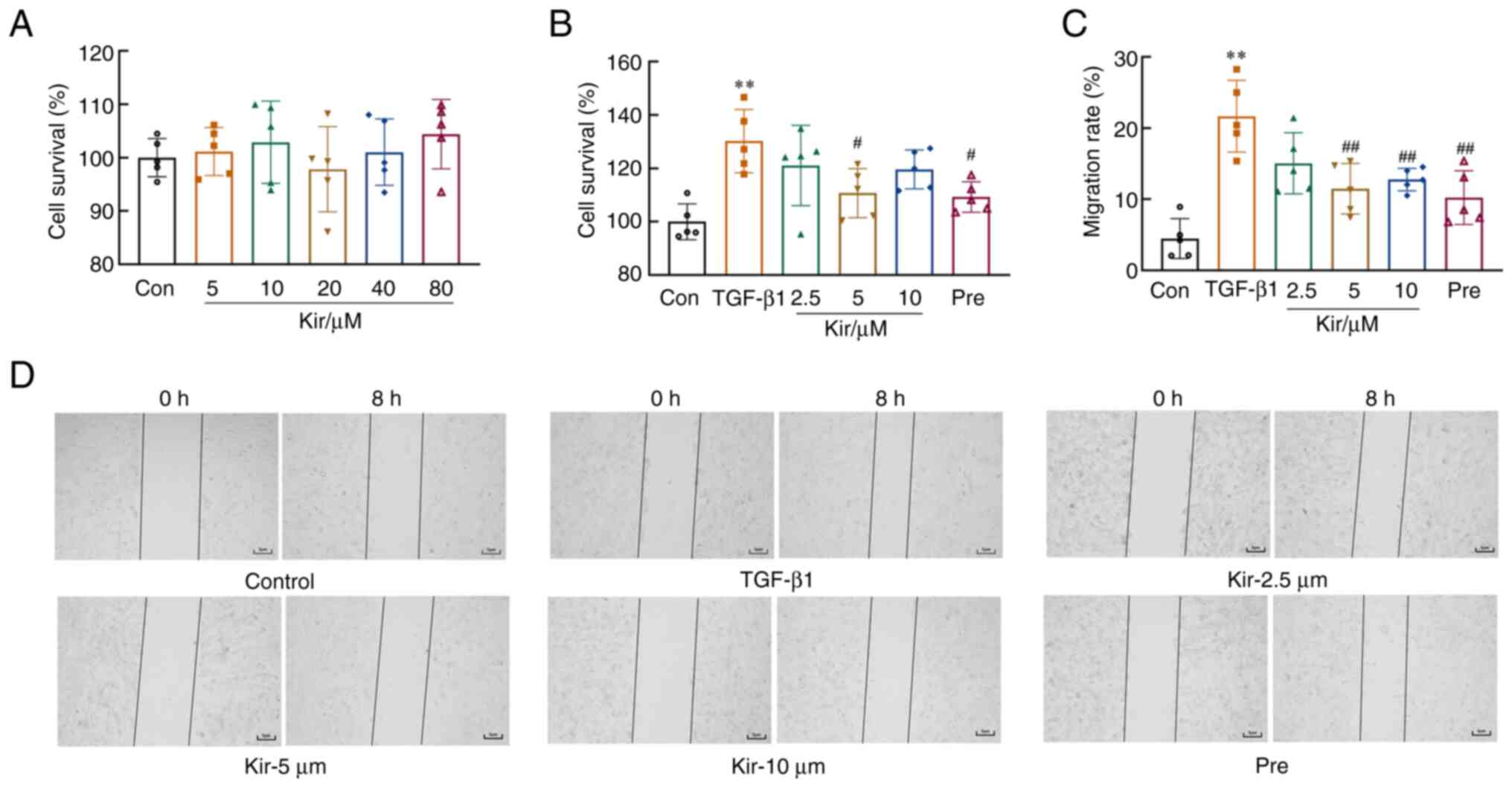
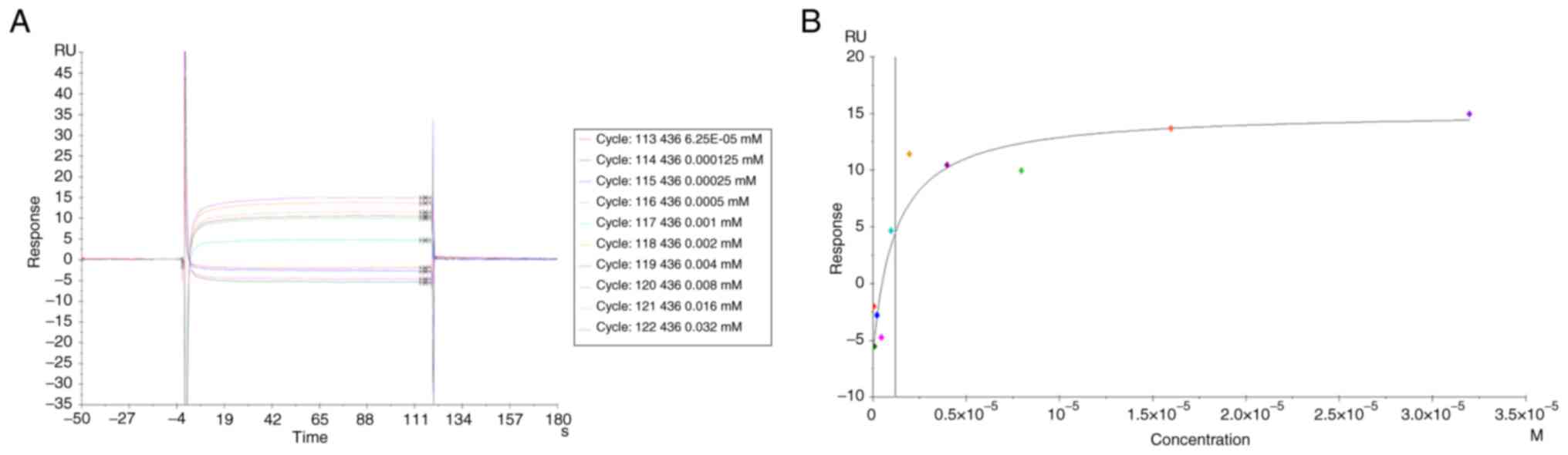
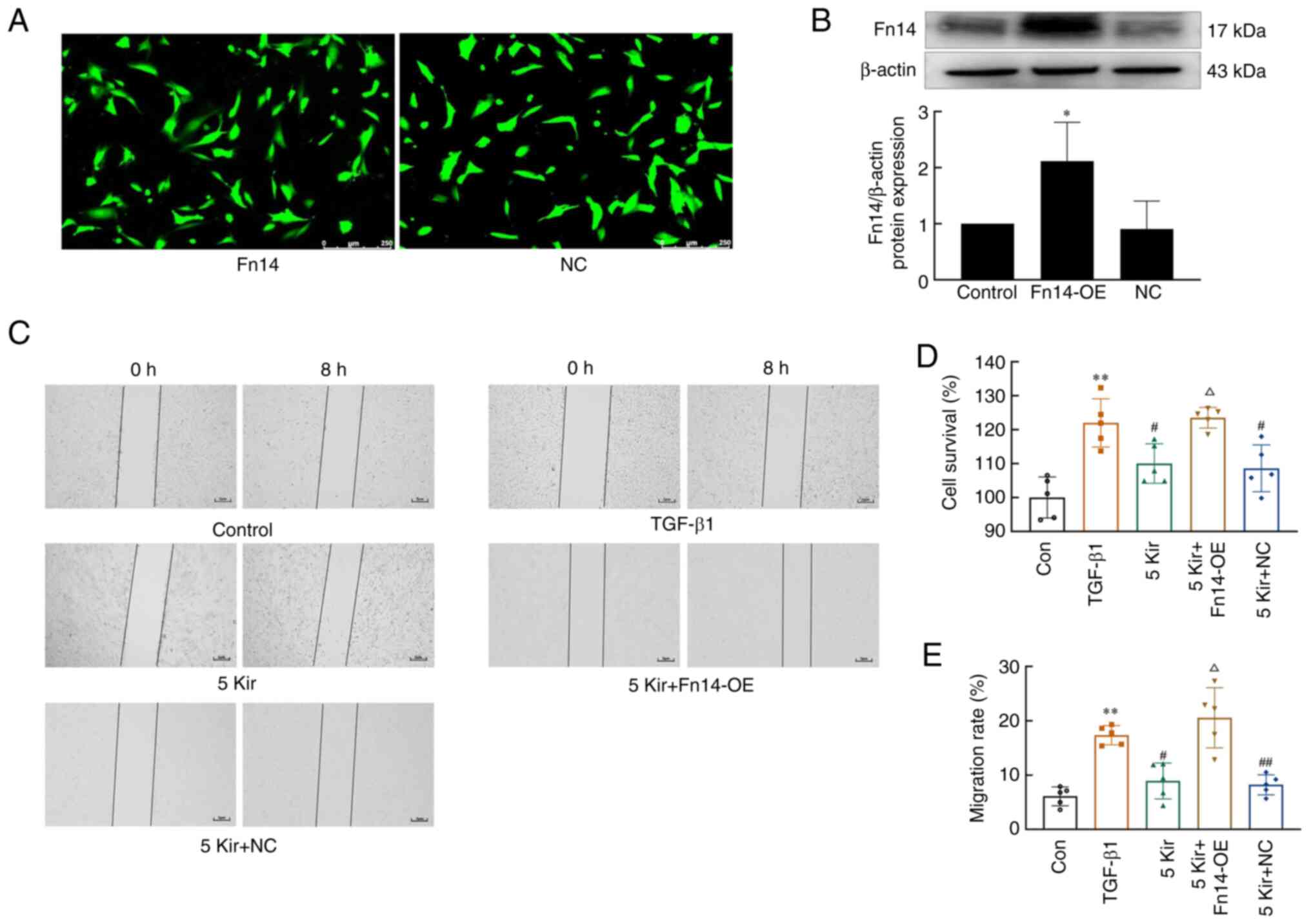
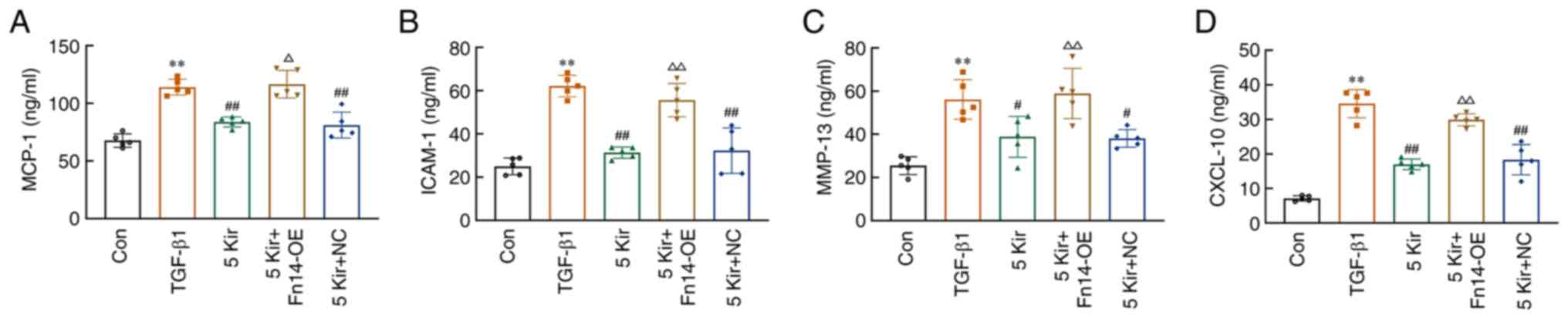
|
1
|
Macáková K, Illésová J, Mlynáriková V,
Lesayová A, Konečná B, Vlková B, Celec P and Šteňová E: The
dynamics of extracellular DNA associates with treatment response in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 12:210992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weyand CM and Goronzy JJ: The immunology
of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 22:10–18. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Modarresi Chahardehi A, Masoumi SA,
Bigdeloo M, Arsad H and Lim V: The effect of exercise on patients
with rheumatoid arthritis on the modulation of inflammation. Clin
Exp Rheumatol. 40:1420–1431. 2022.
|
|
4
|
Finckh A, Gilbert B, Hodkinson B, Bae SC,
Thomas R, Deane KD, Alpizar-Rodriguez D and Lauper K: Global
epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
18:591–602. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nii T, Maeda Y, Motooka D, Naito M,
Matsumoto Y, Ogawa T, Oguro-Igashira E, Kishikawa T, Yamashita M,
Koizumi S, et al: Genomic repertoires linked with pathogenic
potency of arthritogenic Prevotella copri isolated from the gut of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 82:621–629.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garcia-Carbonell R, Divakaruni AS, Lodi A,
Vicente-Suarez I, Saha A, Cheroutre H, Boss GR, Tiziani S, Murphy
AN and Guma M: Critical role of glucose metabolism in rheumatoid
arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol.
68:1614–1626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao X, Kang X, Lu H, Xue E, Chen R, Pan J
and Ma J: Piceatannol suppresses inflammation and promotes
apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast-like synoviocytes by
inhibiting the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep.
25:1802022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nygaard G and Firestein GS: Restoring
synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 16:316–333. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Kuijk AW, Wijbrandts CA, Vinkenoog M,
Zheng TS, Reedquist KA and Tak PP: TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 in
the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to
psoriatic arthritis and its response to tumour necrosis factor
blockade. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:301–304. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rodríguez-Muguruza S, Altuna-Coy A,
Castro-Oreiro S, Poveda-Elices MJ, Fontova-Garrofé R and Chacón MR:
A serum biomarker panel of exomiR-451a, exomiR-25-3p and soluble
TWEAK for early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol.
12:7908802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kamijo S, Nakajima A, Kamata K, Kurosawa
H, Yagita H and Okumura K: Involvement of TWEAK/Fn14 interaction in
the synovial inflammation of RA. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:442–450.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JS, Park MK, Lee SY, Oh HJ, Lim MA,
Cho WT, Kim EK, Ju JH, Park YW, Park SH, et al: TWEAK promotes the
production of interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine.
60:143–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Drosos AA, Pelechas E, Kaltsonoudis E and
Voulgari PV: Therapeutic options and cost-effectiveness for
rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 22:442020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Crofford LJ: Use of NSAIDs in treating
patients with arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 15 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):
S22013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Radu AF and Bungau SG: Management of
rheumatoid arthritis: An overview. Cells. 10:28572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang Z, Yu QH, Cheng Y and Guo XJ:
Simultaneous quantification of eight major constituents in Herba
Siegesbeckiae by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray
ionization time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 55:452–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ibrahim SRM, Altyar AE, Sindi IA, El-Agamy
DS, Abdallah HM, Mohamed SGA and Mohamed GA: Kirenol: A promising
bioactive metabolite from siegesbeckia species: A detailed review.
J Ethnopharmacol. 281:1145522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Y, Xiao J, Wu ZW, Wang ZM, Hu J, Fu HZ,
Chen YY and Qian RQ: Kirenol exerts a potent anti-arthritic effect
in collagen-induced arthritis by modifying the T cells balance.
Phytomedicine. 19:882–889. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang ZM, Zhu SG, Wu ZW, Lu Y, Fu HZ and
Qian RQ: Kirenol upregulates nuclear annexin-1 which interacts with
NF-κB to attenuate synovial inflammation of collagen-induced
arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:774–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu W, Mao C and Sheng W: The protective
effect of kirenol in osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study.
J Orthop Surg Res. 17:1952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu S: Anti-rheumatic drug Kirenol's
preparations and reasearch. Master thesis. Guangzhou University of
Chinese Medicine; 2014, In Chinese.
|
|
22
|
Nan LH, Liu YF, Huang M, Xu W, Li H, Chu
KD and Yang L: Effects of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. F. before
and after processing on CIA model rats. Chin J Tradit Chin Med
Pharm. 35:5795–5799. 2020.In Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Han L, Zhang XZ, Wang C, Tang XY, Zhu Y,
Cai XY, Wu YJ, Shu JL, Wang QT, Chen JY, et al: IgD-Fc-Ig fusion
protein, a new biological agent, inhibits T cell function in CIA
rats by inhibiting IgD-IgDR-Lck-NF-κB signaling pathways. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 41:800–812. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu YJ, Xu WH, Fan LM, Zhang YQ, Xu W,
Chen YP, Chen LL, Chen L, Xu W, Wang Y, et al: Polydatin alleviates
DSS- and TNBS-induced colitis by suppressing Th17 cell
differentiation via directly inhibiting STAT3. Phytother Res.
36:3662–3671. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Asquith DL, Miller AM, McInnes IB and Liew
FY: Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol.
39:2040–2044. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Che Q, Kou Y, Rong X, Zhang X, Li
M and Shu Q: A novel drug combination of Tofacitinib and Iguratimod
alleviates rheumatoid arthritis and secondary osteoporosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 124:1109132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Togashi T, Ishihara R, Watanabe R, Shiomi
M, Yano Y, Fujisawa Y, Katsushima M, Fukumoto K, Yamada S and
Hashimoto M: Rheumatoid factor: Diagnostic and prognostic
performance and therapeutic implications in rheumatoid arthritis. J
Clin Med. 14:15292025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Steiner G and Toes REM: Autoantibodies in
rheumatoid arthritis-rheumatoid factor, anticitrullinated protein
antibodies and beyond. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 36:217–224. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Han T, Guo Z, Li X, Zhang X and
Peng W: Editorial: Immunomodulatory roles of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol.
15:14156722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cho ML, Yoon BY, Ju JH, Jung YO, Jhun JY,
Park MK, Park SH, Cho CS and Kim HY: Expression of CCR2A, an
isoform of MCP-1 receptor, is increased by MCP-1, CD40 ligand and
TGF-beta in fibroblast like synoviocytes of patients with RA. Exp
Mol Med. 39:499–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao S, Wang Y, Hou L, Wang Y, Xu N and
Zhang N: Pentraxin 3 inhibits fibroblast growth factor 2 induced
osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother.
131:1106282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jia Q, Wang T, Wang X, Xu H, Liu Y, Wang
Y, Shi Q and Liang Q: Astragalin suppresses inflammatory responses
and bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis and in
human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front Pharmacol. 10:942019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li H, Wang D, Yuan Y and Min J: New
insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of
early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu Q and Ecker M: Overview of MMP-13 as a
promising target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:17422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paradowska-Gorycka A, Wajda A,
Romanówska-Prochnicka K, Walczuk E, Kuca-Warnawin E, Kmiolek T,
Stypinska B, Rzeszotarska E, Majewski D, Jagodzinski PP and Pawlik
A: Th17/Treg-related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine
profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol.
11:5728582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gautam S, Kumar R, Kumar U, Kumar S,
Luthra K and Dada R: Yoga maintains Th17/Treg cell homeostasis and
reduces the rate of T cell aging in rheumatoid arthritis: A
randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 13:149242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Godessart N and Kunkel SL: Chemokines in
autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 13:670–675. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Iwamoto T, Okamoto H, Toyama Y and
Momohara S: Molecular aspects of rheumatoid arthritis: Chemokines
in the joints of patients. FEBS J. 275:4448–4455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Groom JR and Luster AD: CXCR3 in T cell
function. Exp Cell Res. 317:620–631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Christen U, McGavern DB, Luster AD, von
Herrath MG and Oldstone MB: Among CXCR3 chemokines,
IFN-gammainducible protein of 10 kDa (CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL)
10) but not monokine induced by IFN-gamma (CXCL9) imprints a
pattern for the subsequent development of autoimmune disease. J
Immunol. 171:6838–6845. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Ge M, Lu S, Shi J, Li X, Wang M,
Huang J, Shao Y, Huang Z, Zhang J, et al: Pro-inflammatory effects
of the Th1 chemokine CXCL10 in acquired aplastic anaemia. Cytokine.
94:45–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Siegmund D, Zaitseva O and Wajant H: Fn14
and TNFR2 as regulators of cytotoxic TNFR1 signaling. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 11:12678372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Madhavan A, Kok BP, Rius B, Grandjean JMD,
Alabi A, Albert V, Sukiasyan A, Powers ET, Galmozzi A, Saez E and
Wiseman RL: Pharmacologic IRE1/XBP1s activation promotes systemic
adaptive remodeling in obesity. Nat Commun. 13:6082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin CC, Lin WN, Cho RL, Wang CY, Hsiao LD
and Yang CM: TNF-α-induced cPLA2 expression via NADPH
oxidase/reactive oxygen species-dependent NF-κB cascade on human
pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Front Pharmacol.
7:4472016.
|
|
45
|
O'Dea E and Hoffmann A: NF-κB signaling.
Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 1:107–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sun SC: Non-canonical NF-κB signaling
pathway. Cell Res. 21:71–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dohi T and Burkly LC: The TWEAK/Fn14
pathway as an aggravating and perpetuating factor in inflammatory
diseases: Focus on inflammatory bowel diseases. J Leukoc Biol.
92:265–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|