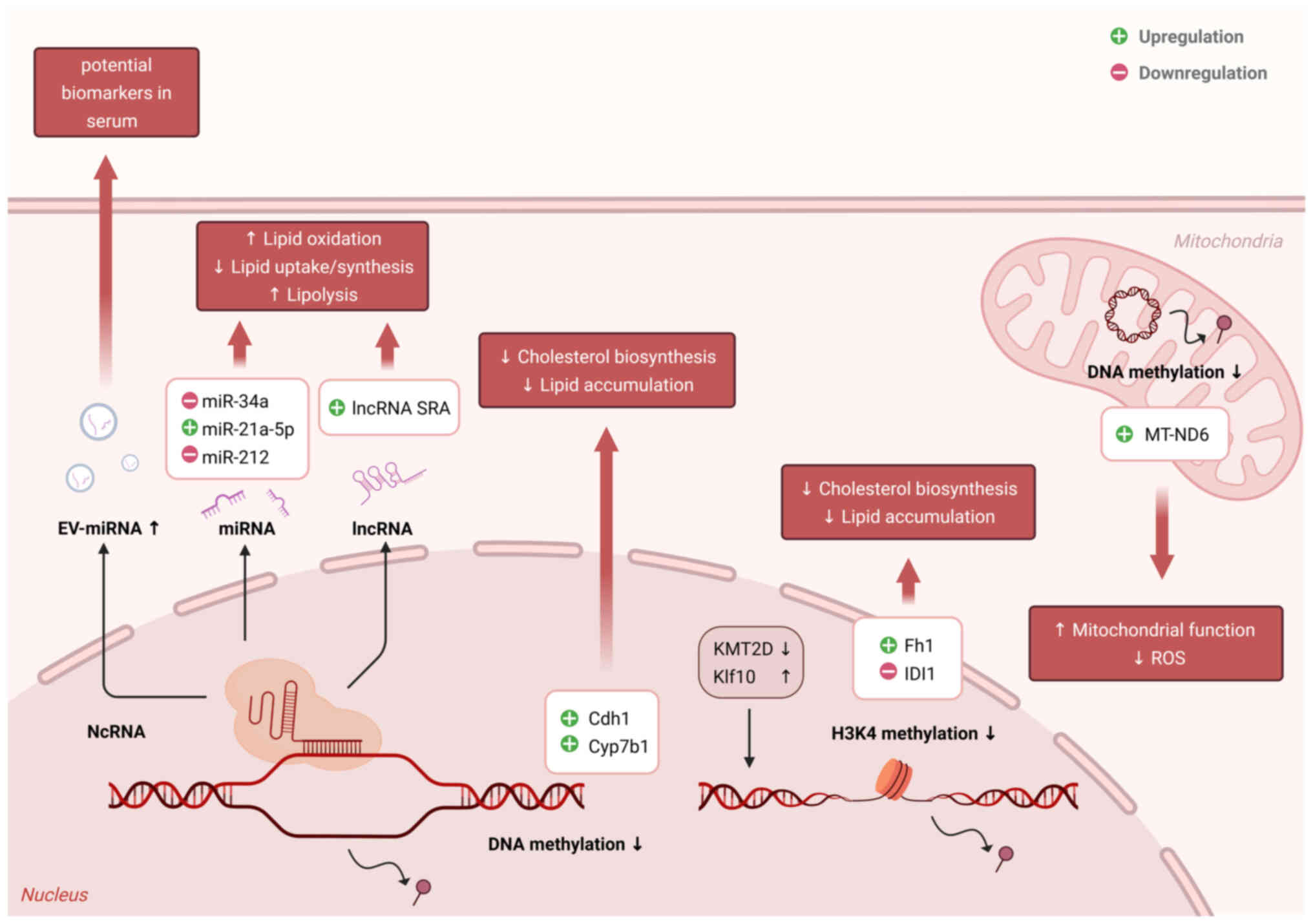
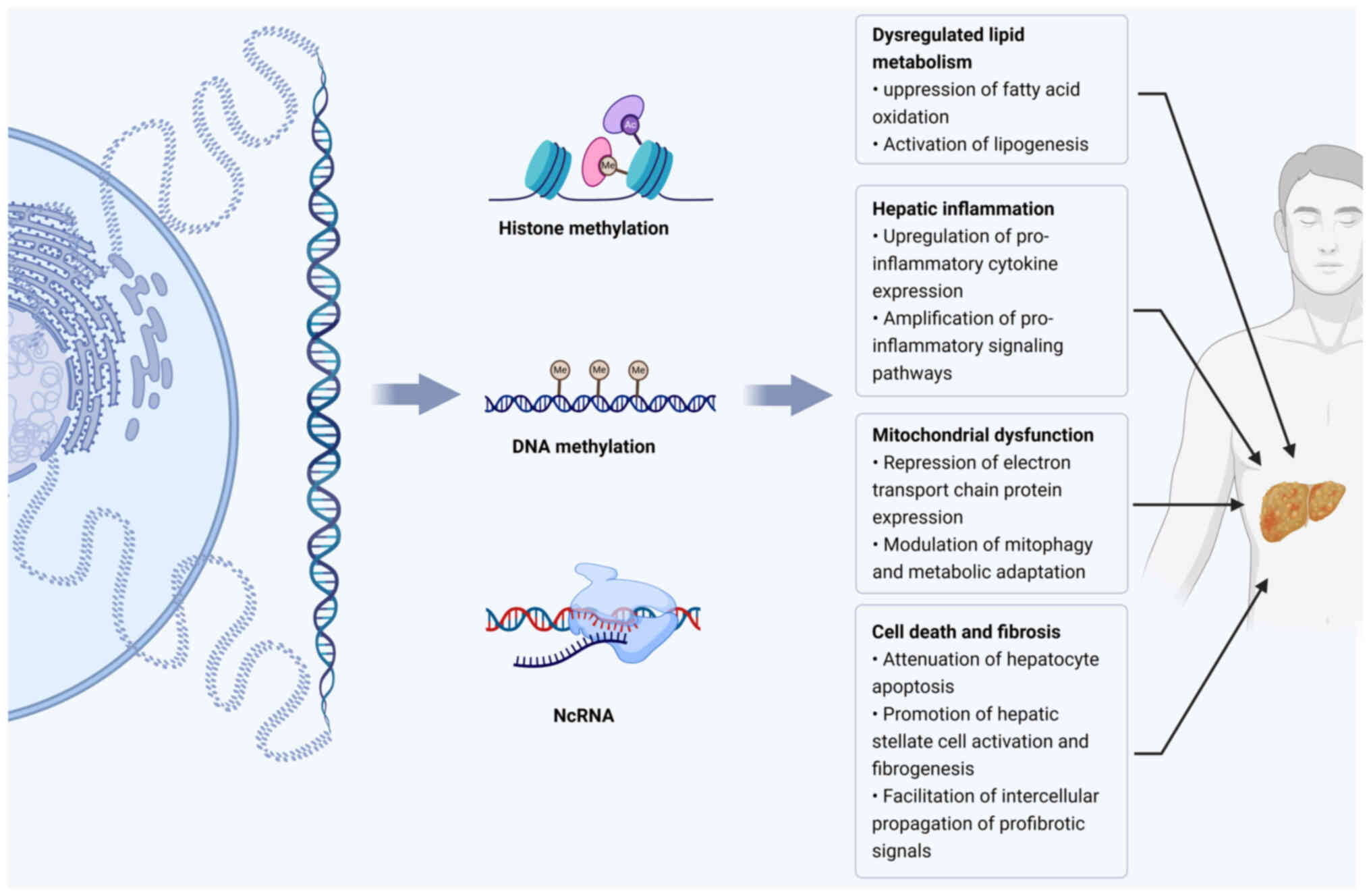
|
1
|
Chen G, Ni Y, Nagata N, Xu L and Ota T:
Micronutrient anti-oxidants and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:13792016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Byrne CD and Targher G: NAFLD: A
multisystem disease. J Hepatol. 62(Suppl 1): S47–S64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eslam M, Valenti L and Romeo S: Genetics
and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact. J Hepatol.
68:268–279. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schwimmer JB: Definitive diagnosis and
assessment of risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children
and adolescents. Semin Liver Dis. 27:312–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J and Mantzoros CS:
Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology
to therapeutics. Metabolism. 92:82–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Targher G, Tilg H and Byrne CD:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multisystem disease requiring
a multidisciplinary and holistic approach. Lancet Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 6:578–588. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Younossi ZM: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease-A global public health perspective. J Hepatol. 70:531–544.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Keskin M, Hayıroğlu M, Uzun AO, Güvenç TS,
Şahin S and Kozan Ö: Effect of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on
in-hospital and Long-term outcomes in patients with ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 120:1720–1726. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA,
Rinella M and Sanyal AJ: Mechanisms of NAFLD development and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 24:908–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Romero-Gómez M, Zelber-Sagi S and Trenell
M: Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J
Hepatol. 67:829–846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kwak MS and Kim D: Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and lifestyle modifications, focusing on physical
activity. Korean J Intern Med. 33:64–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Malkova D, Evans RD, Frayn KN, Humphreys
SM, Jones PR and Hardman AE: Prior exercise and postprandial
substrate extraction across the human leg. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 279:E1020–E1028. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yaskolka Meir A, Keller M, Müller L,
Bernhart SH, Tsaban G, Zelicha H, Rinott E, Kaplan A, Gepner Y,
Shelef I, et al: Effects of lifestyle interventions on epigenetic
signatures of liver fat: Central randomized controlled trial. Liver
Int. 41:2101–2111. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barrès R, Yan J, Egan B, Treebak JT,
Rasmussen M, Fritz T, Caidahl K, Krook A, O'Gorman DJ and Zierath
JR: Acute exercise remodels promoter methylation in human skeletal
muscle. Cell Metab. 15:405–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Li L, Wu W, Liu Z, Huang Y, Yang
L, Luo Q, Chen J, Hou Y and Song G: Exercise protects proliferative
muscle satellite cells against exhaustion via the Igfbp7-Akt-mTOR
axis. Theranostics. 10:6448–6466. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fiorito G, Caini S, Palli D, Bendinelli B,
Saieva C, Ermini I, Valentini V, Assedi M, Rizzolo P, Ambrogetti D,
et al: DNA methylation-based biomarkers of aging were slowed down
in a two-year diet and physical activity intervention trial: The
DAMA study. Aging Cell. 20:e134392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Lu Q and Chang C: Epigenetics in
health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1253:3–55. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goldberg AD, Allis CD and Bernstein E:
Epigenetics: A landscape takes shape. Cell. 128:635–638. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stefanska B, Karlic H, Varga F,
Fabianowska-Majewska K and Haslberger A: Epigenetic mechanisms in
anti-cancer actions of bioactive food components-the implications
in cancer prevention. Br J Pharmacol. 167:279–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dehan P, Kustermans G, Guenin S, Horion J,
Boniver J and Delvenne P: DNA methylation and cancer diagnosis: New
methods and applications. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 9:651–657. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao Q, Liu J, Deng H, Ma R, Liao JY,
Liang H, Hu J, Li J, Guo Z, Cai J, et al: Targeting
Mitochondria-located circRNA SCAR alleviates NASH via reducing mROS
output. Cell. 183:76–93.e22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Y, Cai J, Yang X, Wang K, Sun K, Yang
Z, Zhang L, Yang L, Gu C, Huang X, et al: Dysregulated m6A
modification promotes lipogenesis and development of Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther.
30:2342–2353. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Z, Zhang S, Liu X, Shu R, Shi W, Qu
W, Liu D, Cai Z, Wang Y, Cheng X, et al: Histone demethylase KDM1A
promotes hepatic steatosis and inflammation by increasing chromatin
accessibility in NAFLD. J Lipid Res. 65:1005132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Farzanegi P, Dana A, Ebrahimpoor Z, Asadi
M and Azarbayjani MA: Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise
training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of
oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur J Sport Sci. 19:994–1003.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stevanović J, Beleza J, Coxito P, Ascensão
A and Magalhães J: Physical exercise and liver 'fitness': Role of
mitochondrial function and epigenetics-related mechanisms in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Metab. 32:1–14. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Peixoto P, Cartron PF, Serandour AA and
Hervouet E: From 1957 to Nowadays: A brief history of epigenetics.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:75712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jablonka E: Epigenetic variations in
heredity and evolution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 92:683–688. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Coulondre C, Miller JH, Farabaugh PJ and
Gilbert W: Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in
Escherichia coli. Nature. 274:775–780. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bird AP: DNA methylation and the frequency
of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8:1499–1504. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Antequera F and Bird A: CpG islands as
genomic footprints of promoters that are associated with
replication origins. Curr Biol. 9:R661–R667. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wolf SF, Dintzis S, Toniolo D, Persico G,
Lunnen KD, Axelman J and Migeon BR: Complete concordance between
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and hypomethylation of
3′CpG clusters: Implications for X chromosome dosage compensation.
Nucleic Acids Res. 12:9333–9348. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morgan RK, Wang K, Svoboda LK, Rygiel CA,
Lalancette C, Cavalcante R, Bartolomei MS, Prasasya R, Neier K,
Perera BPU, et al: Effects of developmental lead and phthalate
exposures on DNA methylation in adult mouse blood, brain, and
liver: A focus on genomic imprinting by tissue and sex. Environ
Health Perspect. 132:670032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Yin J, Gao Y, Li Y, Bai D,
He W, Li X, Zhang P, Li R, et al: Distinct H3K9me3 and DNA
methylation modifications during mouse spermatogenesis. J Biol
Chem. 294:18714–18725. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yen RW, Vertino PM, Nelkin BD, Yu JJ,
el-Deiry W, Cumaraswamy A, Lennon GG, Trask BJ, Celano P and Baylin
SB: Isolation and characterization of the cDNA encoding human DNA
methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 20:2287–2291. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lian H, Li WB and Jin WL: The emerging
insights into catalytic or Non-catalytic roles of TET proteins in
tumors and neural development. Oncotarget. 7:64512–64525. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lyko F: The DNA methyltransferase family:
A versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation. Nat Rev Genet.
19:81–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li E and Zhang Y: DNA methylation in
mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:a0191332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Melamed P, Yosefzon Y, David C, Tsukerman
A and Pnueli L: Tet enzymes, variants, and differential effects on
function. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tábara LC, Burr SP, Frison M, Chowdhury
SR, Paupe V, Nie Y, Johnson M, Villar-Azpillaga J, Viegas F, Segawa
M, et al: MTFP1 controls mitochondrial fusion to regulate inner
membrane quality control and maintain mtDNA levels. Cell.
187:3619–3637.e27. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Menger KE, Rodríguez-Luis A, Chapman J and
Nicholls TJ: Controlling the topology of mammalian mitochondrial
DNA. Open Biol. 11:2101682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Devall M, Soanes DM, Smith AR, Dempster
EL, Smith RG, Burrage J, Iatrou A, Hannon E, Troakes C, Moore K, et
al: Genome-wide characterization of mitochondrial DNA methylation
in human brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10591202022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Patil V, Cuenin C, Chung F, Aguilera JRR,
Fernandez-Jimenez N, Romero-Garmendia I, Bilbao JR, Cahais V,
Rothwell J and Herceg Z: Human mitochondrial DNA is extensively
methylated in a non-CpG context. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:10072–10085.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tessarz P and Kouzarides T: Histone core
modifications regulating nucleosome structure and dynamics. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 15:703–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou VW, Goren A and Bernstein BE:
Charting histone modifications and the functional organization of
mammalian genomes. Nat Rev Genet. 12:7–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hansen JC: Linking genome structure and
function through specific histone acetylation. ACS Chem Biol.
1:69–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Black JC, Van Rechem C and Whetstine JR:
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: Establishment, regulation, and
biological impact. Mol Cell. 48:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hyun K, Jeon J, Park K and Kim J: Writing,
erasing and reading histone lysine methylations. Exp Mol Med.
49:e3242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Qu P, Li L, Jin Q, Liu D, Qiao Y, Zhang Y,
Sun Q, Ran S, Li Z, Liu T and Peng L: Histone methylation
modification and diabetic kidney disease: Potential molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic approaches (Review). Int J Mol Med.
54:1042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xiong J, Nie M, Fu C, Chai X, Zhang Y, He
L and Sun S: Hypoxia enhances HIF1 α transcription activity by
upregulating KDM4A and mediating H3K9me3, thus inducing ferroptosis
resistance in cervical cancer cells. Stem Cells Int.
2022:16088062022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Song Y, Wu F and Wu J: Targeting histone
methylation for cancer therapy: Enzymes, inhibitors, biological
activity and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. 9:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gong F and Miller KM: Histone methylation
and the DNA damage response. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 780:37–47.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nimura K, Ura K and Kaneda Y: Histone
methyltransferases: Regulation of transcription and contribution to
human disease. J Mol Med (Berl). 88:1213–1220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Allis CD, Bowen JK, Abraham GN, Glover CV
and Gorovsky MA: Proteolytic processing of histone H3 in chromatin:
A physiologically regulated event in Tetrahymena micronuclei. Cell.
20:55–64. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P,
Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA and Shi Y: Histone demethylation
mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell.
119:941–953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shen H, Xu W and Lan F: Histone lysine
demethylases in mammalian embryonic development. Exp Mol Med.
49:e3252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li L, Chen K, Wang T, Wu Y, Xing G, Chen
M, Hao Z, Zhang C, Zhang J, Ma B, et al: Glis1 facilitates
induction of pluripotency via an epigenome-metabolome-epigenome
signalling cascade. Nat Metab. 2:882–892. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hu Z, Lu Y, Cao J, Lin L, Chen X, Zhou Z,
Pu J, Chen G, Ma X, Deng Q, et al: N-acetyltransferase NAT10
controls cell fates via connecting mRNA cytidine acetylation to
chromatin signaling. Sci Adv. 10:eadh98712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kronfol MM, Jahr FM, Dozmorov MG,
Phansalkar PS, Xie LY, Aberg KA, McRae M, Price ET, Slattum PW,
Gerk PM and McClay JL: DNA methylation and histone acetylation
changes to cytochrome P450 2E1 regulation in normal aging and
impact on rates of drug metabolism in the liver. Geroscience.
42:819–832. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lin Y, Lin A, Cai L, Huang W, Yan S, Wei
Y, Ruan X, Fang W, Dai X, Cheng J, et al: ACSS2-dependent histone
acetylation improves cognition in mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. Mol Neurodegener. 18:472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu Y, Tang L, Huang H, Yu Q, Hu B, Wang G,
Ge F, Yin T, Li S and Yu X: Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
activates PKM2 to phosphorylate histone H3T11 and attenuate
cellular senescence. Nat Commun. 14:13232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen G, Zhu X, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang X,
Zhang R, Qin X, Chen X, Wang J, Liao W, et al: Celastrol inhibits
lung cancer growth by triggering histone acetylation and acting
synergically with HDAC inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 185:1064872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Turner BM: Histone acetylation and an
epigenetic code. Bioessays. 22:836–845. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shen Y, Wei W and Zhou DX: Histone
acetylation enzymes coordinate metabolism and gene expression.
Trends Plant Sci. 20:614–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang P, Wang Z and Liu J: Role of HDACs in
normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Mol Cancer. 19:52020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wessels HH, Stirn A, Méndez-Mancilla A,
Kim EJ, Hart SK, Knowles DA and Sanjana NE: Prediction of on-target
and off-target activity of CRISPR-Cas13d guide RNAs using deep
learning. Nat Biotechnol. 42:628–637. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lodde V, Murgia G, Simula ER, Steri M,
Floris M and Idda ML: Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs in
autoimmune diseases. Biomolecules. 10:10442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL and Huarte M:
Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological
functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:96–118. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function
and role in human diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Bratkovič T, Božič J and Rogelj B:
Functional diversity of small nucleolar RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.
48:1627–1651. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Yao Q, He T, Liao JY, Liao R, Wu X, Lin L
and Xiao G: Noncoding RNAs in skeletal development and disorders.
Biol Res. 57:162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Horvitz HR and Sulston JE: Isolation and
genetic characterization of cell-lineage mutants of the nematode
Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 96:435–454. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Röszer T: MicroRNA profile of mouse
Adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles. Cells. 13:12982024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kingreen T, Kewitz-Hempel S, Rohde C,
Hause G, Sunderkötter C and Gerloff D: Extracellular vesicles from
highly invasive melanoma subpopulations increase the invasive
capacity of less invasive melanoma cells through mir-1246-mediated
inhibition of CCNG2. Cell Commun Signal. 22:4422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kmiotek-Wasylewska K, Bobis-Wozowicz S,
Karnas E, Orpel M, Woźnicka O, Madeja Z, Dawn B and Zuba-Surma EK:
Anti-inflammatory, Anti-fibrotic and Pro-cardiomyogenic effects of
genetically engineered extracellular vesicles enriched in miR-1 and
miR-199a on human cardiac fibroblasts. Stem Cell Rev Rep.
19:2756–2773. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li Y, Meng Y, Zhu X, Van Wijnen A, Eirin A
and Lerman LO: Metabolic syndrome is associated with altered mRNA
and miRNA content in human circulating extracellular vesicles.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:6875862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Venkatesh J, Wasson MD, Brown JM, Fernando
W and Marcato P: LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: Novel points
of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett. 509:81–88. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Han JJ: LncRNAs: The missing link to
senescence nuclear architecture. Trends Biochem Sci. 48:618–628.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Herman AB, Tsitsipatis D and Gorospe M:
Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation.
Mol Cell. 82:2252–2266. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang X, Asllanaj E, Amiri M,
Portilla-Fernandez E, Bramer WM, Nano J, Voortman T, Pan Q and
Ghanbari M: Deciphering the role of epigenetic modifications in
fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Eur J Clin Invest.
51:e134792021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Wei L, Yang X, Wang J, Wang Z, Wang Q,
Ding Y and Yu A: H3K18 lactylation of senescent microglia
potentiates brain aging and Alzheimer's disease through the NFκB
signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 20:2082023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Huang MY, Xuan F, Liu W and Cui HJ: MINA
controls proliferation and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by
epigenetically regulating cyclins and CDKs via H3K9me3
demethylation. Oncogene. 36:387–396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Miao F, Gonzalo IG, Lanting L and
Natarajan R: In vivo chromatin remodeling events leading to
inflammatory gene transcription under diabetic conditions. J Biol
Chem. 279:18091–18097. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Bricambert J, Miranda J, Benhamed F,
Girard J, Postic C and Dentin R: Salt-inducible kinase 2 links
transcriptional coactivator p300 phosphorylation to the prevention
of ChREBP-dependent hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
120:4316–4331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Brunt EM, Wong VW, Nobili V, Day CP,
Sookoian S, Maher JJ, Bugianesi E, Sirlin CB, Neuschwander-Tetri BA
and Rinella ME: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 1:150802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Tryndyak VP, Han T, Muskhelishvili L,
Fuscoe JC, Ross SA, Beland FA and Pogribny IP: Coupling global
methylation and gene expression profiles reveal key
pathophysiological events in liver injury induced by a
methyl-deficient diet. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:411–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lee JH, Friso S and Choi SW: Epigenetic
mechanisms underlying the link between non-alcoholic fatty liver
diseases and nutrition. Nutrients. 6:3303–3325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sookoian S, Rosselli MS, Gemma C, Burgueño
AL, Fernández Gianotti T, Castaño GO and Pirola CJ: Epigenetic
regulation of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Impact of liver methylation of the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α promoter.
Hepatology. 52:1992–2000. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Pirola CJ, Gianotti TF, Burgueño AL,
Rey-Funes M, Loidl CF, Mallardi P, Martino JS, Castaño GO and
Sookoian S: Epigenetic modification of liver mitochondrial DNA is
associated with histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Gut. 62:1356–1363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Zeybel M, Hardy T, Robinson SM, Fox C,
Anstee QM, Ness T, Masson S, Mathers JC, French J, White S and Mann
J: Differential DNA methylation of genes involved in fibrosis
progression in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic
liver disease. Clin Epigenetics. 7:252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Nishida N, Yada N, Hagiwara S, Sakurai T,
Kitano M and Kudo M: Unique features associated with hepatic
oxidative DNA damage and DNA methylation in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:1646–1653. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Baumeier C, Schlüter L, Saussenthaler S,
Laeger T, Rödiger M, Alaze SA, Fritsche L, Häring HU, Stefan N,
Fritsche A, et al: Elevated hepatic DPP4 activity promotes insulin
resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Metab.
6:1254–1263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Baumeier C, Saussenthaler S, Kammel A,
Jähnert M, Schlüter L, Hesse D, Canouil M, Lobbens S, Caiazzo R,
Raverdy V, et al: Hepatic DPP4 DNA methylation associates with
fatty liver. Diabetes. 66:25–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zhang RN, Pan Q, Zheng RD, Mi YQ, Shen F,
Zhou D, Chen GY, Zhu CY and Fan JG: Genome-wide analysis of DNA
methylation in human peripheral leukocytes identifies potential
biomarkers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med.
42:443–452. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ahrens M, Ammerpohl O, von Schönfels W,
Kolarova J, Bens S, Itzel T, Teufel A, Herrmann A, Brosch M,
Hinrichsen H, et al: DNA methylation analysis in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease suggests Distinct disease-specific and remodeling
signatures after bariatric surgery. Cell Metab. 18:296–302. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Sun C, Fan JG and Qiao L: Potential
epigenetic mechanism in non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:5161–5179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Emmett MJ and Lazar MA: Integrative
regulation of physiology by histone deacetylase 3. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 20:102–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Sun Z, Miller RA, Patel RT, Chen J, Dhir
R, Wang H, Zhang D, Graham MJ, Unterman TG, Shulman GI, et al:
Hepatic Hdac3 promotes gluconeogenesis by repressing lipid
synthesis and sequestration. Nat Med. 18:934–942. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wang RH, Li C and Deng CX: Liver steatosis
and increased ChREBP expression in mice carrying a liver specific
SIRT1 null mutation under a normal feeding condition. Int J Biol
Sci. 6:682–690. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Jin M, Shen Y, Pan T, Zhu T, Li X, Xu F,
Betancor MB, Jiao L, Tocher DR and Zhou Q: Dietary betaine
mitigates hepatic steatosis and inflammation induced by a
High-Fat-Diet by modulating the Sirt1/Srebp-1/Pparα pathway in
juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). Front Immunol.
12:6947202021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Zeng C and Chen M: Progress in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: SIRT family regulates
mitochondrial biogenesis. Biomolecules. 12:10792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Nassir F and Ibdah JA: Sirtuins and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol.
22:10084–10092. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kim JH, Jung DY, Kim HR and Jung MH:
Histone H3K9 demethylase JMJD2B plays a role in LXRα-dependent
lipogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:83132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Pogribny IP, Tryndyak VP, Bagnyukova TV,
Melnyk S, Montgomery B, Ross SA, Latendresse JR, Rusyn I and Beland
FA: Hepatic epigenetic phenotype predetermines individual
susceptibility to hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic
methyl-deficient diet. J Hepatol. 51:176–186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gjorgjieva M, Sobolewski C, Dolicka D,
Correia de Sousa M and Foti M: miRNAs and NAFLD: From
pathophysiology to therapy. Gut. 68:2065–2079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Bandiera S, Pfeffer S, Baumert TF and
Zeisel MB: miR-122-a key factor and therapeutic target in liver
disease. J Hepatol. 62:448–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Cheung O, Puri P, Eicken C, Contos MJ,
Mirshahi F, Maher JW, Kellum JM, Min H, Luketic VA and Sanyal AJ:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic
MicroRNA expression. Hepatology. 48:1810–1820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Pirola CJ, Fernández Gianotti T, Castaño
GO, Mallardi P, San Martino J, Mora Gonzalez Lopez Ledesma M,
Flichman D, Mirshahi F, Sanyal AJ and Sookoian S: Circulating
microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From serum
Non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut.
64:800–812. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Hsu SH, Wang B, Kota J, Yu J, Costinean S,
Kutay H, Yu L, Bai S, La Perle K, Chivukula RR, et al: Essential
metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of
miR-122 in liver. J Clin Invest. 122:2871–2883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ,
Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF, et al: MicroRNA-122
plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 122:2884–2897. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Liu CH, Ampuero J, Gil-Gómez A,
Montero-Vallejo R, Rojas Á, Muñoz-Hernández R, Gallego-Durán R and
Romero-Gómez M: miRNAs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol.
69:1335–1348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Liu XL, Pan Q, Zhang RN, Shen F, Yan SY,
Sun C, Xu ZJ, Chen YW and Fan JG: Disease-specific miR-34a as
diagnostic marker of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in a Chinese
population. World J Gastroenterol. 22:9844–9852. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ding J, Li M, Wan X, Jin X, Chen S, Yu C
and Li Y: Effect of miR-34a in regulating steatosis by targeting
PPARα expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep.
5:137292015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Xu Y, Zalzala M, Xu J, Li Y, Yin L and
Zhang Y: A metabolic stress-inducible miR-34a-HNF4α pathway
regulates lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Nat Commun. 6:74662015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Calo N, Ramadori P, Sobolewski C, Romero
Y, Maeder C, Fournier M, Rantakari P, Zhang FP, Poutanen M, Dufour
JF, et al: Stress-activated miR-21/miR-21* in hepatocytes promotes
lipid and glucose metabolic disorders associated with High-fat diet
consumption. Gut. 65:1871–1881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Loyer X, Paradis V, Hénique C, Vion AC,
Colnot N, Guerin CL, Devue C, On S, Scetbun J, Romain M, et al:
Liver microRNA-21 is overexpressed in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
and contributes to the disease in experimental models by inhibiting
PPARα expression. Gut. 65:1882–1894. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Wu H, Ng R, Chen X, Steer CJ and Song G:
MicroRNA-21 is a potential link between non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease and hepatocellular carcinoma via modulation of the
HBP1-p53-Srebp1c pathway. Gut. 65:1850–1860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Atic AI, Thiele M, Munk A and Dalgaard LT:
Circulating miRNAs associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 324:C588–C602. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Hendy OM, Rabie H, El Fouly A,
Abdel-Samiee M, Abdelmotelb N, Elshormilisy AA, Allam M, Ali ST,
Bahaa El-Deen NM, Abdelsattar S and Mohamed SM: The circulating
Micro-RNAs (-122, -34a and -99a) as predictive biomarkers for
Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
12:2715–2723. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Liu XL, Pan Q, Cao HX, Xin FZ, Zhao ZH,
Yang RX, Zeng J, Zhou H and Fan JG: Lipotoxic Hepatocyte-derived
exosomal MicroRNA 192-5p activates macrophages through
Rictor/Akt/Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 72:454–469. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Becker PP, Rau M, Schmitt J, Malsch C,
Hammer C, Bantel H, Müllhaupt B and Geier A: Performance of Serum
microRNAs-122, -192 and -21 as biomarkers in patients with
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 10:e01426612015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Li M, Guo Y, Wang XJ, Duan BH and Li L:
HOTAIR participates in hepatic insulin resistance via regulating
SIRT1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:7883–7890. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhu X, Wu YB, Zhou J and Kang DM:
Upregulation of lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic insulin resistance via
increasing FoxO1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
469:319–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Zhu X, Li H, Wu Y, Zhou J, Yang G and Wang
W: lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic insulin resistance by serving as a
competing endogenous RNA of miR-214 to regulate ATF4 expression.
Int J Mol Med. 43:345–357. 2019.
|
|
129
|
Zhao XY, Xiong X, Liu T, Mi L, Peng X, Rui
C, Guo L, Li S, Li X and Lin JD: Long noncoding RNA licensing of
obesity-linked hepatic lipogenesis and NAFLD pathogenesis. Nat
Commun. 9:29862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Yan C, Chen J and Chen N: Long noncoding
RNA MALAT1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by
increasing nuclear SREBP-1c protein stability. Sci Rep.
6:226402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Ma M, Duan R, Shen L, Liu M, Ji Y, Zhou H,
Li C, Liang T, Li X and Guo L: The lncRNA Gm15622 stimulates
SREBP-1c expression and hepatic lipid accumulation by sponging the
miR-742-3p in mice. J Lipid Res. 61:1052–1064. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zhang N, Geng T, Wang Z, Zhang R, Cao T,
Camporez JP, Cai SY, Liu Y, Dandolo L, Shulman GI, et al: Elevated
hepatic expression of H19 long noncoding RNA contributes to
diabetic hyperglycemia. JCI Insight. 3:e1203042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Wang J, Yang W, Chen Z, Chen J, Meng Y,
Feng B, Sun L, Dou L, Li J, Cui Q and Yang J: Long noncoding RNA
lncSHGL recruits hnRNPA1 to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis and
lipogenesis. Diabetes. 67:581–593. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Li D, Cheng M, Niu Y, Chi X, Liu X, Fan J,
Fan H, Chang Y and Yang W: Identification of a novel human long
non-coding RNA that regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by
inhibiting SREBP-1c. Int J Biol Sci. 13:349–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang B, Li H, Li D, Sun H, Li M and Hu H:
Long noncoding RNA Mirt2 upregulates USP10 expression to suppress
hepatic steatosis by sponging miR-34a-5p. Gene. 700:139–148. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Berzigotti A, Saran U and Dufour JF:
Physical activity and liver diseases. Hepatology. 63:1026–1040.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Hayıroğlu M, Çınar T, Cilli Hayıroğlu S,
Şaylık F, Uzun M and Tekkeşin A: The role of smart devices and
mobile application on the change in peak VO2 in patients
with high cardiovascular risk: A sub-study of the LIGHT randomised
clinical trial. Acta Cardiol. 78:1000–1005. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Hayıroğlu M, Çınar T, Çinier G, Karakaya
A, Yıldırım M, Güney BÇ, Öz A, Gündoğmuş PD, Ösken A, Özkan A, et
al: The effect of 1-year mean step count on the change in the
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk calculation in patients
with high cardiovascular risk: A sub-study of the LIGHT randomized
clinical trial. Kardiol Pol. 79:1140–1142. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Su P, Chen JG and Tang DH: Exercise
against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Possible role and
mechanism of lipophagy. Life Sci. 327:1218372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR,
Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC and Swain DP; American
College of Sports Medicine: American College of Sports Medicine
position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and
maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor
fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing
exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 43:1334–1359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Simpson RJ, Campbell JP, Gleeson M, Krüger
K, Nieman DC, Pyne DB, Turner JE and Walsh NP: Can exercise affect
immune function to increase susceptibility to infection? Exerc
Immunol Rev. 26:8–22. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Carbone S, Del Buono MG, Ozemek C and
Lavie CJ: Obesity, risk of diabetes and role of physical activity,
exercise training and cardiorespiratory fitness. Prog Cardiovasc
Dis. 62:327–333. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Liu S, Liu Y, Liu Z, Hu Y and Jiang M: A
review of the signaling pathways of aerobic and anaerobic exercise
on atherosclerosis. J Cell Physiol. 238:866–879. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
McKie GL and Wright DC: Biochemical
adaptations in white adipose tissue following aerobic exercise:
From mitochondrial biogenesis to browning. Biochem J.
477:1061–1081. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Richter EA and Hargreaves M: Exercise,
GLUT4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiol Rev.
93:993–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
El Assar M, Álvarez-Bustos A, Sosa P,
Angulo J and Rodríguez-Mañas L: Effect of physical
Activity/exercise on oxidative stress and inflammation in muscle
and vascular aging. Int J Mol Sci. 23:87132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Guo R, Liong EC, So KF, Fung ML and Tipoe
GL: Beneficial mechanisms of aerobic exercise on hepatic lipid
metabolism in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 14:139–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Mohammad Rahimi GR and Attarzadeh Hosseini
SR: Effect of aerobic exercise alone or in conjunction with diet on
liver function, insulin resistance and lipids in Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Biol Res Nurs. 24:259–276. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Diniz TA, de Lima Junior EA, Teixeira AA,
Biondo LA, da Rocha LAF, Valadão IC, Silveira LS, Cabral-Santos C,
de Souza CO and Rosa Neto JC: Aerobic training improves NAFLD
markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in
obese mice. Life Sci. 266:1188682021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Keating SE, Hackett DA, George J and
Johnson NA: Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 57:157–166. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Hajighasem A, Farzanegi P and Mazaheri Z:
Effects of combined therapy with resveratrol, continuous and
interval exercises on apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory
biomarkers in the liver of old rats with Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 125:142–149. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Sohet FM, Neyrinck AM, Pachikian BD, de
Backer FC, Bindels LB, Niklowitz P, Menke T, Cani PD and Delzenne
NM: Coenzyme Q10 supplementation lowers hepatic oxidative stress
and inflammation associated with diet-induced obesity in mice.
Biochem Pharmacol. 78:1391–1400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Xiao J, Ching YP, Liong EC, Nanji AA, Fung
ML and Tipoe GL: Garlic-derived S-allylmercaptocysteine is a
hepato-protective agent in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in
vivo animal model. Eur J Nutr. 52:179–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
154
|
Xiao J, Ho CT, Liong EC, Nanji AA, Leung
TM, Lau TY, Fung ML and Tipoe GL: Epigallocatechin gallate
attenuates fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rat model through TGF/SMAD, PI3
K/Akt/FoxO1, and NF-kappa B pathways. Eur J Nutr. 53:187–199. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Qi F, Li T, Deng Q and Fan A: The impact
of aerobic and anaerobic exercise interventions on the management
and outcomes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Physiol Res.
73:671–686. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Li H, Dun Y, Zhang W, You B, Liu Y, Fu S,
Qiu L, Cheng J, Ripley-Gonzalez JW and Liu S: Exercise improves
lipid droplet metabolism disorder through activation of
AMPK-mediated lipophagy in NAFLD. Life Sci. 273:1193142021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zou YY, Tang XB, Chen ZL, Liu B, Zheng L,
Song MY, Xiao Q, Zhou ZQ, Peng XY and Tang CF: Exercise
intervention improves mitochondrial quality in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease zebrafish. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
14:11624852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
McLeod JC, Currier BS, Lowisz CV and
Phillips SM: The influence of resistance exercise training
prescription variables on skeletal muscle mass, strength, and
physical function in healthy adults: An umbrella review. J Sport
Health Sci. 13:47–60. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
159
|
Schoenfeld BJ, Ogborn D and Krieger JW:
Effects of resistance training frequency on measures of muscle
hypertrophy: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med.
46:1689–1697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Consitt LA, Dudley C and Saxena G: Impact
of endurance and resistance training on skeletal muscle glucose
metabolism in older adults. Nutrients. 11:26362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Fedewa MV, Gist NH, Evans EM and Dishman
RK: Exercise and insulin resistance in youth: A meta-analysis.
Pediatrics. 133:e163–e174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Ivy JL: Muscle insulin resistance amended
with exercise training: Role of GLUT4 expression. Med Sci Sports
Exerc. 36:1207–1211. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Mazur-Bialy AI, Pocheć E and Zarawski M:
Anti-inflammatory properties of irisin, mediator of physical
activity, are connected with TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
activation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:7012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Hashida R, Kawaguchi T, Bekki M, Omoto M,
Matsuse H, Nago T, Takano Y, Ueno T, Koga H, George J, et al:
Aerobic vs. resistance exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease: A systematic review. J Hepatol. 66:142–152. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Xue Y, Peng Y, Zhang L, Ba Y, Jin G and
Liu G: Effect of different exercise modalities on nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Sci Rep. 14:62122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Takahashi A, Abe K, Usami K, Imaizumi H,
Hayashi M, Okai K, Kanno Y, Tanji N, Watanabe H and Ohira H: Simple
resistance exercise helps patients with Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Int J Sports Med. 36:848–852. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Yang HJ, Hong YP, Yoon TY, Ryoo JH, Choi
JM and Oh CM: Independent and synergistic associations of aerobic
physical activity and resistance exercise with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Gut Liver. 17:600–609. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Gripp F, Nava RC, Cassilhas RC, Esteves
EA, Magalhães COD, Dias-Peixoto MF, de Castro Magalhães F and
Amorim FT: HIIT is superior than MICT on cardiometabolic health
during training and detraining. Eur J Appl Physiol. 121:159–172.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Ryan BJ, Schleh MW, Ahn C, Ludzki AC,
Gillen JB, Varshney P, Van Pelt DW, Pitchford LM, Chenevert TL,
Gioscia-Ryan RA, et al: Moderate-intensity exercise and
High-intensity interval training affect insulin sensitivity
similarly in obese adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
105:e2941–e2959. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Han C, Lu P and Yan SZ: Effects of
high-intensity interval training on mitochondrial supercomplex
assembly and biogenesis, mitophagy, and the AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway in the soleus muscle of aged female rats. Exp
Gerontol. 158:1116482022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Wadley AJ, Chen YW, Lip GY, Fisher JP and
Aldred S: Low volume-high intensity interval exercise elicits
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in humans. J Sports Sci.
34:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Su L, Fu J, Sun S, Zhao G, Cheng W, Dou C
and Quan M: Effects of HIIT and MICT on cardiovascular risk factors
in adults with overweight and/or obesity: A meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 14:e02106442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Gu S, Du X, Wang D, Yu Y and Guo S:
Effects of high intensity interval training versus moderate
intensity continuous training on exercise capacity and quality of
life in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and
Meta-analysis. PLoS One. 18:e02903622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
de Brito JN, McDonough DJ, Mathew M,
VanWagner LB, Schreiner PJ, Gabriel KP, Jacobs DR Jr, Terry JG,
Carr JJ and Pereira MA: Young adult physical activity trajectories
and midlife nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. JAMA Netw Open.
6:e23389522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Fredrickson G, Barrow F, Dietsche K,
Parthiban P, Khan S, Robert S, Demirchian M, Rhoades H, Wang H,
Adeyi O and Revelo XS: Exercise of high intensity ameliorates
hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol Metab.
53:1012702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Zhang HJ, He J, Pan LL, Ma ZM, Han CK,
Chen CS, Chen Z, Han HW, Chen S, Sun Q, et al: Effects of moderate
and vigorous exercise on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A
Randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 176:1074–1082. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Harden JE, Tabacu L and Reynolds LJ:
Physical activity intensity and markers of inflammation in those
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
207:1110472024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Yuan Z, Xiao-Wei L, Juan W, Xiu-Juan L,
Nian-Yun Z and Lei S: HIIT and MICT attenuate high-fat diet-induced
hepatic lipid accumulation and ER stress via the PERK-ATF4-CHOP
signaling pathway. J Physiol Biochem. 78:641–652. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Hyun J and Jung Y: DNA Methylation in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 21:81382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Moore LD, Le T and Fan G: DNA methylation
and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 38:23–38. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Jones MJ, Goodman SJ and Kobor MS: DNA
methylation and healthy human aging. Aging Cell. 14:924–932. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Kim YN, Hwang JH and Cho YO: The effects
of exercise training and acute exercise duration on plasma folate
and vitamin B12. Nutr Res Pract. 10:161–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Brunaud L, Alberto JM, Ayav A, Gérard P,
Namour F, Antunes L, Braun M, Bronowicki JP, Bresler L and Guéant
JL: Effects of vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies on DNA
methylation and carcinogenesis in rat liver. Clin Chem Lab Med.
41:1012–1019. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Hunter DJ, James L, Hussey B, Wadley AJ,
Lindley MR and Mastana SS: Impact of aerobic exercise and fatty
acid supplementation on global and gene-specific DNA methylation.
Epigenetics. 14:294–309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Robson-Ansley PJ, Saini A, Toms C, Ansley
L, Walshe IH, Nimmo MA and Curtin JA: Dynamic changes in dna
methylation status in peripheral blood Mononuclear cells following
an acute bout of exercise: Potential impact of exercise-induced
elevations in interleukin-6 concentration. J Biol Regul Homeost
Agents. 28:407–417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Zhou D, Hlady RA, Schafer MJ, White TA,
Liu C, Choi JH, Miller JD, Roberts LR, LeBrasseur NK and Robertson
KD: High fat diet and exercise lead to a disrupted and pathogenic
DNA methylome in mouse liver. Epigenetics. 12:55–69. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
187
|
Zhang Y, Hashimoto S, Fujii C, Hida S, Ito
K, Matsumura T, Sakaizawa T, Morikawa M, Masuki S, Nose H, et al:
NFκB2 gene as a novel candidate that epigenetically responds to
interval walking training. Int J Sports Med. 36:769–775. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Światowy WJ, Drzewiecka H, Kliber M,
Sąsiadek M, Karpiński P, Pławski A and Jagodziński PP: Physical
Activity and DNA Methylation in Humans. Int J Mol Sci.
22:129892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
King-Himmelreich TS, Schramm S, Wolters
MC, Schmetzer J, Möser CV, Knothe C, Resch E, Peil J, Geisslinger G
and Niederberger E: The impact of endurance exercise on global and
AMPK gene-specific DNA methylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
474:284–290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Freitas-Dias R, Lima TI, Costa-Junior JM,
Gonçalves LM, Araujo HN, Paula FMM, Santos GJ, Branco RCS, Ou K,
Kaestner KH, et al: Offspring from trained male mice inherit
improved muscle mitochondrial function through PPAR co-repressor
modulation. Life Sci. 291:1202392022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
McGee SL and Hargreaves M: Epigenetics and
Exercise. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 30:636–645. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Mallett G: The effect of exercise and
physical activity on skeletal muscle epigenetics and metabolic
adaptations. Eur J Appl Physiol. 125:611–627. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Stols-Gonçalves D, Tristão LS, Henneman P
and Nieuwdorp M: Epigenetic markers and
Microbiota/Metabolite-Induced epigenetic modifications in the
pathogenesis of obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Diab Rep. 19:312019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Fan X, Wang H, Wang W, Shen J and Wang Z:
Exercise training alleviates cholesterol and lipid accumulation in
mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Reduction of
KMT2D-mediated histone methylation of IDI1. Exp Cell Res.
442:1142652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Luo HY, Mu WJ, Chen M, Zhu JY, Li Y, Li S,
Yan LJ, Li RY, Yin MT, Li X, et al: Hepatic Klf10-Fh1 axis promotes
exercise-mediated amelioration of NASH in mice. Metabolism.
155:1559162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Villanova L, Vernucci E, Pucci B,
Pellegrini L, Nebbioso M, Mauri C, Marfe G, Spataro A, Fini M,
Banfi G, et al: Influence of age and physical exercise on sirtuin
activity in humans. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 27:497–507.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Yang J, Félix-Soriano E, Martínez-Gayo A,
Ibañez-Santos J, Sáinz N, Martínez JA and Moreno-Aliaga MJ: SIRT1
and FOXO1 role on MASLD risk: Effects of DHA-rich n-3 PUFA
supplementation and exercise in aged obese female mice and in
Post-menopausal Overweight/obese women. J Physiol Biochem.
80:697–712. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Zhang Y, Shan M, Ding X, Sun H, Qiu F and
Shi L: Maternal exercise represses Nox4 via SIRT1 to prevent
vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in SHR
offspring. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:12191942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Nikroo H, Hosseini SRA, Fathi M, Sardar MA
and Khazaei M: The effect of aerobic, resistance, and combined
training on PPAR-α, SIRT1 gene expression, and insulin resistance
in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD male rats. Physiol Behav.
227:1131492020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Song MY, Han CY, Moon YJ, Lee JH, Bae EJ
and Park BH: Sirt6 reprograms myofibers to oxidative type through
CREB-dependent Sox6 suppression. Nat Commun. 13:18082022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Tian C, Huang R and Xiang M: SIRT1:
Harnessing multiple pathways to hinder NAFLD. Pharmacol Res.
203:1071552024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Hou T, Tian Y, Cao Z, Zhang J, Feng T, Tao
W, Sun H, Wen H, Lu X, Zhu Q, et al: Cytoplasmic SIRT6-mediated
ACSL5 deacetylation impedes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by
facilitating hepatic fatty acid oxidation. Mol Cell.
82:4099–4115.e4099. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Hall MM, Rajasekaran S, Thomsen TW and
Peterson AR: Lactate: Friend or Foe. PM R. 8(Suppl 3): S8–S15.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Harris RT and Dudley GA: Exercise alters
the distribution of ammonia and lactate in blood. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 66:313–317. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Han H, Zhao Y, Du J, Wang S, Yang X, Li W,
Song J, Zhang S, Zhang Z, Tan Y, et al: Exercise improves cognitive
dysfunction and neuroinflammation in mice through Histone H3
lactylation in microglia. Immun Ageing. 20:632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Widmann M, Nieß AM and Munz B: Physical
exercise and epigenetic modifications in skeletal muscle. Sports
Med. 49:509–523. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Dos Santos JAC, Veras ASC, Batista VRG,
Tavares MEA, Correia RR, Suggett CB and Teixeira GR: Physical
exercise and the functions of microRNAs. Life Sci. 304:1207232022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Antunes-Correa LM, Trevizan PF, Bacurau
AVN, Ferreira-Santos L, Gomes JLP, Urias U, Oliveira PA, Alves
MJNN, de Almeida DR, Brum PC, et al: Effects of aerobic and
inspiratory training on skeletal muscle microRNA-1 and
downstream-associated pathways in patients with heart failure. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 11:89–102. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q,
Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL and Wang DZ: The role of
microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and
differentiation. Nat Genet. 38:228–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Scisciola L, Benedetti R, Chianese U,
Fontanella RA, Del Gaudio N, Marfella R, Surina, Altucci L,
Barbieri M, Paolisso G, et al: The pivotal role of miRNA-21 in
myocardial metabolic flexibility in response to short- and
long-term high glucose treatment: Evidence in human cardiomyocyte
cell line. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 191:1100662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Da Silva ND Jr, Fernandes T, Soci UP,
Monteiro AW, Phillips MI and De Oliveira EM: Swimming training in
rats increases cardiac MicroRNA-126 expression and angiogenesis.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. 44:1453–1462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Wilson RA, Stathis CG, Hayes A and Cooke
MB: Intermittent fasting and High-intensity exercise elicit
Sexual-dimorphic and Tissue-specific adaptations in Diet-induced
obese mice. Nutrients. 12:17642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Kristensen MM, Davidsen PK, Vigelsø A,
Hansen CN, Jensen LJ, Jessen N, Bruun JM, Dela F and Helge JW:
miRNAs in human subcutaneous adipose tissue: Effects of weight loss
induced by hypocaloric diet and exercise. Obesity (Silver Spring).
25:572–580. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Lionett S, Kiel IA, Camera DM, Vanky E,
Parr EB, Lydersen S, Hawley JA and Moholdt T: Circulating and
adipose Tissue miRNAs in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and
responses to High-intensity interval training. Front Physiol.
11:9042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Xu B, Zhang Y, Du XF, Li J, Zi HX, Bu JW,
Yan Y, Han H and Du JL: Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes
to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 27:882–897. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Panera N, Gnani D, Crudele A, Ceccarelli
S, Nobili V and Alisi A: MicroRNAs as controlled systems and
controllers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:15079–15086. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Ghareghani P, Shanaki M, Ahmadi S,
Khoshdel AR, Rezvan N, Meshkani R, Delfan M and Gorgani-Firuzjaee
S: Aerobic endurance training improves nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD) features via miR-33 dependent autophagy induction
in high fat diet fed mice. Obes Res Clin Pract. 12:80–89. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Kalaki-Jouybari F, Shanaki M, Delfan M,
Gorgani-Firouzjae S and Khakdan S: High-intensity interval training
(HIIT) alleviated NAFLD feature via miR-122 induction in liver of
high-fat high-fructose diet induced diabetic rats. Arch Physiol
Biochem. 126:242–249. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Lu YL, Jing W, Feng LS, Zhang L, Xu JF,
You TJ and Zhao J: Effects of hypoxic exercise training on microRNA
expression and lipid metabolism in obese rat livers. J Zhejiang
Univ Sci B. 15:820–829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Xiao J, Bei Y, Liu J, Dimitrova-Shumkovska
J, Kuang D, Zhou Q, Li J, Yang Y, Xiang Y, Wang F, et al: miR-212
downregulation contributes to the protective effect of exercise
against non-alcoholic fatty liver via targeting FGF-21. J Cell Mol
Med. 20:204–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
221
|
Wang M, Xue Q, Li X, Krohn K, Ziesche S,
Ceglarek U, Blüher M, Keller M, Yaskolka Meir A, Heianza Y, et al:
Circulating levels of microRNA-122 and hepatic fat change in
response to Weight-Loss interventions: CENTRAL Trial. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 107:e1899–e1906. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
de Mendonça M, Rocha KC, de Sousa É,
Pereira BMV, Oyama LM and Rodrigues AC: Aerobic exercise training
regulates serum extracellular vesicle miRNAs linked to obesity to
promote their beneficial effects in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 319:E579–E591. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Xia L, Li J, Song M and
Yang C: Exercise-Induced ADAR2 protects against nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease through miR-34a. Nutrients. 15:1212022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Wu B, Ding J, Chen A, Song Y, Xu C, Tian F
and Zhao J: Aerobic exercise improves adipogenesis in diet-induced
obese mice via the lncSRA/p38/JNK/PPARγ pathway. Nutr Res.
105:20–32. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Wu B, Xu C, Tian Y, Zeng Y, Yan F, Chen A,
Zhao J and Chen L: Aerobic exercise promotes the expression of ATGL
and attenuates inflammation to improve hepatic steatosis via lncRNA
SRA. Sci Rep. 12:53702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Zhang Y, Wei Q, Geng X and Fang G:
Long-term aerobic exercise enhances hepatoprotection in MAFLD by
modulating exosomal miR-324 via ROCK1. Metabolites. 14:6922024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Zhao J, Song Y, Zeng Y, Chen L, Yan F,
Chen A, Wu B and Wang Y: Improvement of hyperlipidemia by aerobic
exercise in mice through a regulatory effect of miR-21a-5p on its
target genes. Sci Rep. 11:119662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Lou J, Wu J, Feng M, Dang X, Wu G, Yang H,
Wang Y, Li J, Zhao Y, Shi C, et al: Exercise promotes angiogenesis
by enhancing endothelial cell fatty acid utilization via
liver-derived extracellular vesicle miR-122-5p. Journal of sport
and health science. 11:495–508. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
229
|
Xia SF, Jiang YY, Qiu YY, Huang W and Wang
J: Role of diets and exercise in ameliorating obesity-related
hepatic steatosis: Insights at the microRNA-dependent thyroid
hormone synthesis and action. Life Sci. 242:1171822020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Abdelmalek MF: Nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Another leap forward. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:85–86. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Gruet M, Saynor ZL, Urquhart DS and Radtke
T: Rethinking physical exercise training in the modern era of
cystic fibrosis: A step towards optimising Short-term efficacy and
long-term engagement. J Cyst Fibros. 21:e83–e98. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
232
|
Stevanović-Silva J, Beleza J, Coxito P,
Costa RC, Ascensão A and Magalhães J: Fit mothers for a healthy
future: Breaking the intergenerational cycle of non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease with maternal exercise. Eur J Clin Invest.
52:e135962022. View Article : Google Scholar
|