|
1
|
Qin F, Luo M, Xiong Y, Zhang N, Dai Y,
Kuang W and Cen X: Prevalence and associated factors of cognitive
impairment among the elderly population: A nationwide
cross-sectional study in China. Front Public Health.
10:10326662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feng X, Zhan F, Luo D, Hu J, Wei G, Hua F
and Xu G: LncRNA 4344 promotes NLRP3-related neuroinflammation and
cognitive impairment by targeting miR-138-5p. Brain Behav Immun.
98:283–298. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang X, Luo L, Zhao J, Guo X, Tao L, Zhang
F, Liu X, Gao B and Luo Y: Associations between sleep duration
trajectories and cognitive decline: A longitudinal cohort study in
China. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 124:1054452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharifi-Rad J, Quispe C, Shaheen S, El
Haouari M, Azzini E, Butnariu M, Sarac I, Pentea M, Ramírez-Alarcón
K, Martorell M, et al: Flavonoids as potential anti-platelet
aggregation agents: From biochemistry to health promoting
abilities. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:8045–8058. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhao C, Noble JM, Marder K, Hartman JS, Gu
Y and Scarmeas N: Dietary patterns, physical activity, sleep, and
risk for dementia and cognitive decline. Curr Nutr Rep. 7:335–345.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tian Q, Li Z, Yan Z, Jiang S, Zhao X, Wang
L and Li M: Inflammatory role of S100A8/A9 in the central nervous
system non-neoplastic diseases. Brain Res Bull. 218:1111002024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tampé JF, Monni E, Palma-Tortosa S,
Brogårdh E, Böiers C, Lindgren AG and Kokaia Z: Human monocyte
subtype expression of neuroinflammation- and regeneration-related
genes is linked to age and sex. PLoS One. 19:e03009462024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen B and Di B: Endogenous ligands of
TLR4 in microglia: Potential targets for related neurological
diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 25:953–970. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng Y, Kim WK, Wellman LL, Sanford LD
and Guo ML: Short-term sleep fragmentation dysregulates autophagy
in a brain Region-specific manner. Life (Basel).
11:10982021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zera KA and Buckwalter MS: The local and
peripheral immune responses to stroke: Implications for therapeutic
development. Neurotherapeutics. 17:414–435. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P and
Amor S: Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology.
154:204–219. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bowman GL, Dayon L, Kirkland R, Wojcik J,
Peyratout G, Severin IC, Henry H, Oikonomidi A, Migliavacca E,
Bacher M and Popp J: Blood-brain barrier breakdown,
neuroinflammation, and cognitive decline in older adults.
Alzheimers Dement. 14:1640–1650. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang R, Hou L, Lu H, Zhang Y, Guo T, Zhou
B, Zhao H and Xing M: Unveiling the interplay of MAPK/NF-κB/MLKL
axis in brain health: Omega-3 as a promising candidates against
copper neurotoxicity. J Environ Manage. 370:1227912024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang D, Yin K, Zhang Y, Lu H, Hou L, Zhao
H and Xing M: Fluoride induces neutrophil extracellular traps and
aggravates brain inflammation by disrupting neutrophil calcium
homeostasis and causing ferroptosis. Environ Pollut.
331:1218472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Zhao H, Yang X, Mu M, Zong H, Luo
L and Xing M: Excessive Cu2+ deteriorates arsenite-induced
apoptosis in chicken brain and resulting in immunosuppression, not
in homeostasis. Chemosphere. 239:1247582020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tao Q, Qiu X, Li C, Zhou J, Gu L, Zhang L,
Pang J, Zhang L, Yin S, Jiang Y and Peng J: S100A8 regulates
autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in microglia after experimental
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 357:1141712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Woodburn SC, Bollinger JL and Wohleb ES:
The semantics of microglia activation: Neuroinflammation,
homeostasis, and stress. J Neuroinflammation. 18:2582021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cerón JJ, Ortín-Bustillo A, López-Martínez
MJ, Martínez-Subiela S, Eckersall PD, Tecles F, Tvarijonaviciute A
and Muñoz-Prieto A: S-100 proteins: Basics and applications as
biomarkers in animals with special focus on calgranulins (S100A8,
A9, and A12). Biology (Basel). 12:8812023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Muñoz-Grajales C, Barraclough ML,
Diaz-Martinez JP, Su J, Bingham K, Kakvan M, Kretzmann RP,
Tartaglia MC, Ruttan L, Choi MY, et al: Serum S100A8/A9 and MMP-9
levels are elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with
cognitive impairment. Front Immunol. 14:13267512023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rayes HA, Tani C, Kwan A, Marzouk S,
Colosimo K, Medina-Rosas J, Mustafa A, Su J, Lambiris P, Mosca M
and Touma Z: What is the prevalence of cognitive impairment in
lupus and which instruments are used to measure it? A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 48:240–255. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng F and Xie W: High-sensitivity
C-reactive protein and cognitive decline: The English Longitudinal
study of ageing. Psychol Med. 48:1381–1389. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Iadecola C: The pathobiology of vascular
dementia. Neuron. 80:844–866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong J, Wang S, Hu Z and Gong L:
Extracellular proteins as potential biomarkers in Sepsis-related
cerebral injury. Front Immunol. 14:11284762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gofton TE and Young GB: Sepsis-associated
encephalopathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 8:557–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiong Y, Liang W, Wang X, Zhu H, Yi P, Wei
G, Liu H, Lin Y, Zhang L, Ying J and Hua F: S100A8 knockdown
activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to inhibit microglial
autophagy and improve cognitive impairment mediated by chronic
sleep deprivation. Int Immunopharmacol. 143:1133752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su X, Xie L, Li J, Tian X, Lin B and Chen
M: Exploring molecular signatures related to the mechanism of aging
in different brain regions by integrated bioinformatics. Front Mol
Neurosci. 16:11331062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen L, Liao L, Chen C, Guo Y, Song D,
Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang K, Ying M, Li S, et al: Proteomics analysis
of blood serums from Alzheimer's disease patients using iTRAQ
labeling technology. J Alzheimers Dis. 56:361–378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Ouyang Y, Li Z, Wang X and Ma J:
S100A8 and S100A9 in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1878:1888912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shabani F, Farasat A, Mahdavi M and Gheibi
N: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9): A key protein between inflammation
and cancer. Inflamm Res. 67:801–812. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mondet J, Chevalier S and Mossuz P:
Pathogenic roles of S100A8 and S100A9 proteins in acute myeloid and
lymphoid leukemia: Clinical and therapeutic impacts. Molecules.
26:13232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia V, Perera YR and Chazin WJ: A
structural perspective on calprotectin as a ligand of receptors
mediating inflammation and potential drug target. Biomolecules.
12:1592022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pan S, Hu Y, Hu M, Xu Y, Chen M, Du C, Cui
J, Zheng P, Lai J, Zhang Y, et al: S100A8 facilitates
cholangiocarcinoma metastasis via upregulation of VEGF through
TLR4/NF-κB pathway activation. Int J Oncol. 56:101–112. 2020.
|
|
33
|
Mondet J, Laurin D, Lo Presti C, Jacob MC,
Meunier M, Giraudon E, Lefebvre C, Berthier S, Leer AM, Park S and
Mossuz P: Increased S100A8 expression in bone marrow plasma by
monocytic cells from acute myeloid leukemia patients. Hematol
Oncol. 38:114–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gomes LH, Raftery MJ, Yan WX, Goyette JD,
Thomas PS and Geczy CL: S100A8 and S100A9-oxidant scavengers in
inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med. 58:170–186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwon MS: Advanced therapeutic strategies
targeting microglia: Beyond neuroinflammation. Arch Pharm Res.
45:618–630. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Orihuela R, McPherson CA and Harry GJ:
Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br J Pharmacol.
173:649–665. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Blom AB, van den Bosch MH, Blaney Davidson
EN, Roth J, Vogl T, van de Loo FA, Koenders M, van der Kraan PM,
Geven EJ and van Lent PL: The alarmins S100A8 and S100A9 mediate
acute pain in experimental synovitis. Arthritis Res Ther.
22:1992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bach M, Moon J, Moore R, Pan T, Nelson JL
and Lood C: A neutrophil activation biomarker panel in prognosis
and monitoring of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 72:47–56. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schenten V, Melchior C, Steinckwich N,
Tschirhart EJ and Bréchard S: Sphingosine kinases regulate NOX2
activity via p38 MAPK-dependent translocation of S100A8/A9. J
Leukoc Biol. 89:587–596. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park IH, Yeon SI, Youn JH, Choi JE, Sasaki
N, Choi IH and Shin JS: Expression of a novel secreted splice
variant of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)
in human brain astrocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Mol Immunol. 40:1203–1211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yan SF, Yan SD, Ramasamy R and Schmidt AM:
Tempering the wrath of RAGE: An emerging therapeutic strategy
against diabetic complications, neurodegeneration, and
inflammation. Ann Med. 41:408–422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fang F, Lue LF, Yan S, Xu H, Luddy JS,
Chen D, Walker DG, Stern DM, Yan S, Schmidt AM, et al:
RAGE-dependent signaling in microglia contributes to
neuroinflammation, Abeta accumulation, and impaired learning/memory
in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 24:1043–1055.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu G, Cheng Z, Lin C, Hoffman RM, Huang
Y, Singh SR, Zheng W, Yang S and Ye J: MyD88 regulates LPS-induced
NF-ĸB/MAPK cytokines and promotes inflammation and malignancy in
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 16:409–419.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu K, Zhu X, Sun S, Yang W, Liu S, Tang
Z, Zhang R, Li J, Shen T and Hei M: Inhibition of TLR4 prevents
hippocampal hypoxic-ischemic injury by regulating ferroptosis in
neonatal rats. Exp Neurol. 345:1138282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou H, Zhao C, Shao R, Xu Y and Zhao W:
The functions and regulatory pathways of S100A8/A9 and its
receptors in cancers. Front Pharmacol. 14:11877412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun Y, Xu H, Gao W, Deng J, Song X, Li J
and Liu X: S100a8/A9 proteins: Critical regulators of inflammation
in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 11:13941372024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Flemmig J, Zámocký M and Alia A: Amyloid β
and free heme: Bloody new insights into the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Neural Regen Res. 13:1170–1174. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang S, Song R, Wang Z, Jing Z, Wang S and
Ma J: S100A8/A9 in inflammation. Front Immunol. 9:12982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pruenster M, Vogl T, Roth J and Sperandio
M: S100A8/A9: From basic science to clinical application. Pharmacol
Ther. 167:120–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lodeiro M, Puerta E, Ismail MA,
Rodriguez-Rodriguez P, Rönnbäck A, Codita A, Parrado-Fernandez C,
Maioli S, Gil-Bea F, Merino-Serrais P and Cedazo-Minguez A:
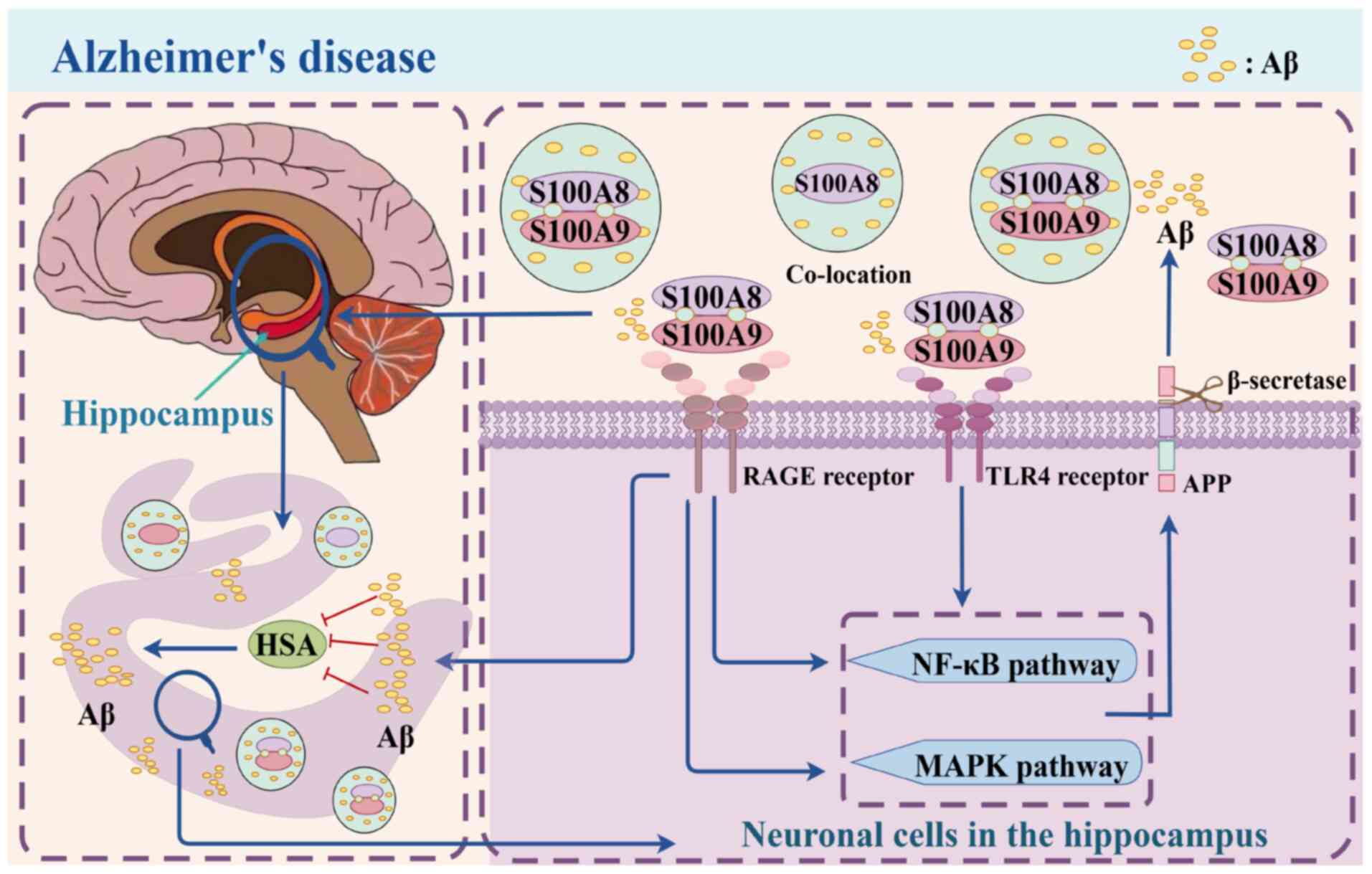
Aggregation of the inflammatory S100A8 precedes Aβ plaque formation
in transgenic APP mice: Positive feedback for S100A8 and Aβ
productions. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 72:319–328. 2017.
|
|
52
|
Zheng J, Wang J, Liu H, Chen F, Wang H,
Chen S, Xie J, Zheng Z and Li Z: Alarmins S100A8/A9 Promote
intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation-related pain in a
rat model through toll-like receptor-4 and activation of the NF-κB
signaling pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 30:998–1011. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
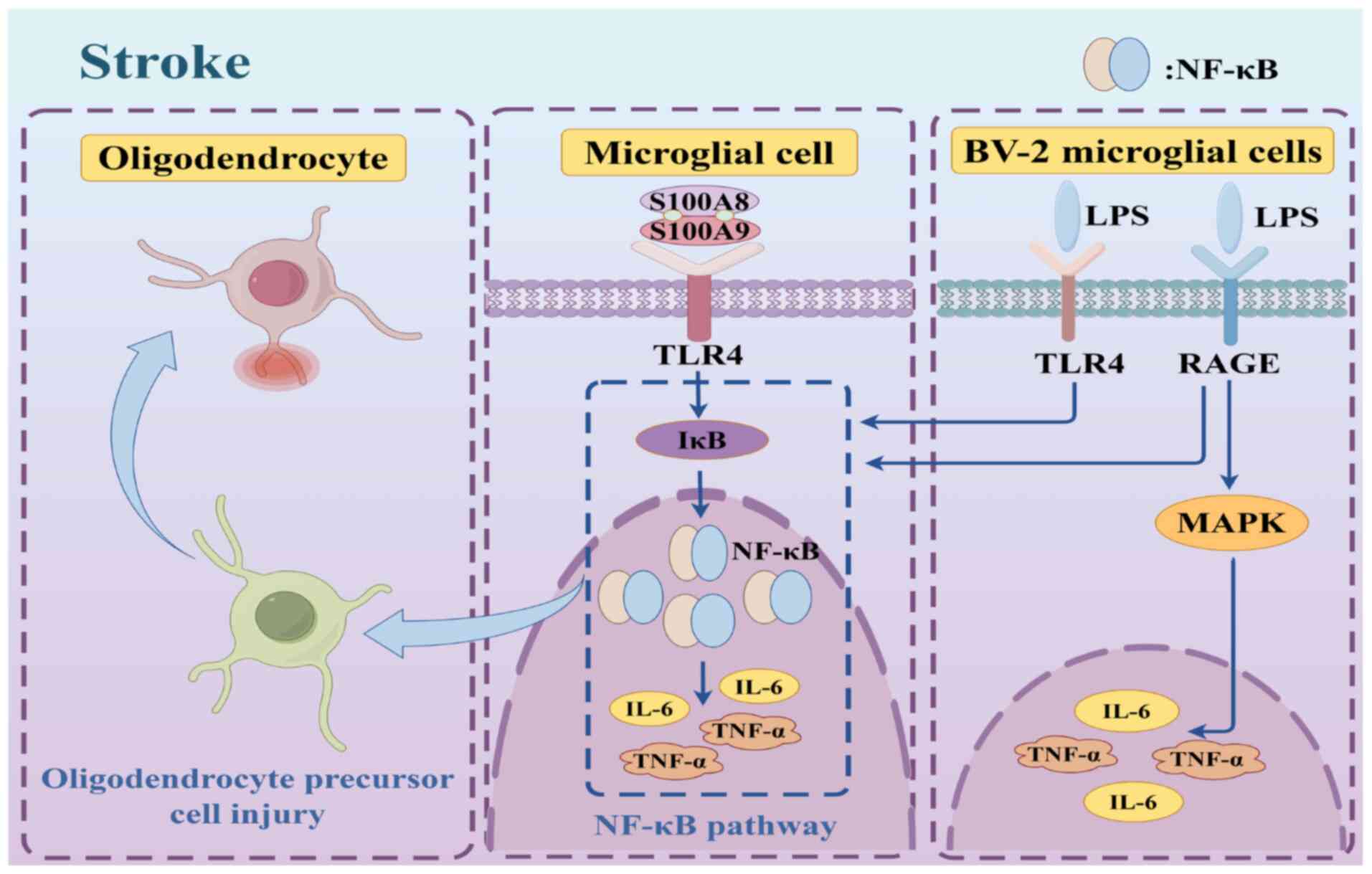
Wu M, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhou N, Zhen F, Zhang
Y, Qu X, Fan H, Liu S, Chen Y and Yao R: S100A8/A9 induces
microglia activation and promotes the apoptosis of oligodendrocyte
precursor cells by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Brain
Res Bull. 143:234–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Barbosa-Silva MC, Lima MN, Battaglini D,
Robba C, Pelosi P, Rocco PRM and Maron-Gutierrez T: Infectious
disease-associated encephalopathies. Crit Care. 25:2362021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Litus EA, Shevelyova MP, Vologzhannikova
AA, Deryusheva EI, Machulin AV, Nemashkalova EL, Permyakova ME,
Sokolov AS, Alikova VD, Uversky VN and Permyakov SE: Binding of
Pro-inflammatory proteins S100A8 or S100A9 to Amyloid-β peptide
suppresses its fibrillation. Biomolecules. 15:4312025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Stephan JR, Yu F, Costello RM, Bleier BS
and Nolan EM: Oxidative Post-translational modifications accelerate
proteolytic degradation of calprotectin. J Am Chem Soc.
140:17444–17455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hou Z, Sun A, Li Y, Song X, Liu S, Hu X,
Luan Y, Guan H, He C, Sun Y and Chen J: What are the reliable
plasma biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment? A clinical 4D
proteomics study and validation. Mediators Inflamm.
2024:77092772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gratuze M, Chen Y, Parhizkar S, Jain N,
Strickland MR, Serrano JR, Colonna M, Ulrich JD and Holtzman DM:
Activated microglia mitigate Aβ-associated tau seeding and
spreading. J Exp Med. 218:e202105422021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Mancuso R, Fryatt G, Cleal M, Obst J, Pipi
E, Monzón-Sandoval J, Ribe E, Winchester L, Webber C, Nevado A, et
al: CSF1R inhibitor JNJ-40346527 attenuates microglial
proliferation and neurodegeneration in P301S mice. Brain.
142:3243–3264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bhaskar K, Konerth M, Kokiko-Cochran ON,
Cardona A, Ransohoff RM and Lamb BT: Regulation of tau pathology by
the microglial fractalkine receptor. Neuron. 68:19–31. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gruel R, Bijnens B, Van Den Daele J, Thys
S, Willems R, Wuyts D, Van Dam D, Verstraelen P, Verboven R, Roels
J, et al: S100A8-enriched microglia populate the brain of
tau-seeded and accelerated aging mice. Aging Cell. 23:e141202024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue
B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L, Lin C, Yu J, et al:
RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain
barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med. 9:907–913. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Santiago JA, Bottero V and Potashkin JA:
Transcriptomic and network analysis identifies shared and unique
pathways across dementia spectrum disorders. Int J Mol Sci.
21:20502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update: A report from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 125:e2–e220. 2012.
|
|
65
|
Ge X, Zheng M, Hu M, Fang X, Geng D, Liu
S, Wang L, Zhang J, Guan L, Zheng P, et al: Butyrate ameliorates
quinolinic acid-induced cognitive decline in obesity models. J Clin
Invest. 133:e1546122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Metcalf TU, Wilkinson PA, Cameron MJ,
Ghneim K, Chiang C, Wertheimer AM, Hiscott JB, Nikolich-Zugich J
and Haddad EK: Human monocyte subsets are transcriptionally and
functionally altered in aging in response to pattern recognition
receptor agonists. J Immunol. 199:1405–1417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gülke E, Gelderblom M and Magnus T: Danger
signals in stroke and their role on microglia activation after
ischemia. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 11:17562864187742542018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shichita T, Ito M and Yoshimura A:
Post-ischemic inflammation regulates neural damage and protection.
Front Cell Neurosci. 8:3192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Marta-Enguita J, Navarro-Oviedo M,
Rubio-Baines I, Aymerich N, Herrera M, Zandio B, Mayor S, Rodriguez
JA, Páramo JA, Toledo E, et al: Association of calprotectin with
other inflammatory parameters in the prediction of mortality for
ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 18:32021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Denstaedt SJ, Spencer-Segal JL, Newstead
MW, Laborc K, Zhao AP, Hjelmaas A, Zeng X, Akil H, Standiford TJ
and Singer BH: S100A8/A9 drives neuroinflammatory priming and
protects against Anxiety-like behavior after sepsis. J Immunol.
200:3188–3200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ge R, Tornero D, Hirota M, Monni E,
Laterza C, Lindvall O and Kokaia Z: Choroid plexus-cerebrospinal
fluid route for monocyte-derived macrophages after stroke. J
Neuroinflammation. 14:1532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wattananit S, Tornero D, Graubardt N,
Memanishvili T, Monni E, Tatarishvili J, Miskinyte G, Ge R,
Ahlenius H, Lindvall O, et al: Monocyte-derived macrophages
contribute to spontaneous Long-term functional recovery after
stroke in mice. J Neurosci. 36:4182–4195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nacken W, Roth J, Sorg C and Kerkhoff C:
S100A9/S100A8: Myeloid representatives of the S100 protein family
as prominent players in innate immunity. Microsc Res Tech.
60:569–580. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Guo D, Zhu Z, Xu T, Zhong C, Wang A, Xie
X, Peng Y, Peng H, Li Q, Ju Z, et al: Plasma S100A8/A9
concentrations and clinical outcomes of ischemic stroke in 2
independent multicenter cohorts. Clin Chem. 66:706–717. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li L, Dong L, Xiao Z, He W, Zhao J, Pan H,
Chu B, Cheng J and Wang H: Integrated analysis of the proteome and
transcriptome in a MCAO mouse model revealed the molecular
landscape during stroke progression. J Adv Res. 24:13–27. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chen L, Chen X, Wang Y, Li S, Huang S, Wu
Z, He J, Chen S, Deng F, Zhu P, et al: Polymorphisms of calgranulin
genes and ischemic stroke in a Chinese population. J Inflamm Res.
15:3355–3368. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Carrión-Barberà I, Salman-Monte TC,
Vílchez-Oya F and Monfort J: Neuropsychiatric involvement in
systemic lupus erythematosus: A review. Autoimmun Rev.
20:1027802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hanly JG: Diagnosis and management of
neuropsychiatric SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:338–347. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wakiya R, Kameda T, Ueeda K, Nakashima S,
Shimada H, Mansour MF, Kato M, Miyagi T, Miyatake N, Kadowaki N and
Dobashi H: Hydroxychloroquine modulates elevated expression of S100
proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 28:826–833. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Šumová B, Cerezo LA, Szczuková L,
Nekvindová L, Uher M, Hulejová H, Moravcová R, Grigorian M, Pavelka
K, Vencovský J, et al: Circulating S100 proteins effectively
discriminate SLE patients from healthy controls: A cross-sectional
study. Rheumatol Int. 39:469–478. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Tydén H, Lood C, Gullstrand B, Jönsen A,
Ivars F, Leanderson T and Bengtsson AA: Pro-inflammatory S100
proteins are associated with glomerulonephritis and anti-dsDNA
antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 26:139–149.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Tydén H, Lood C, Gullstrand B, Jönsen A,
Nived O, Sturfelt G, Truedsson L, Ivars F, Leanderson T and
Bengtsson AA: Increased serum levels of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 are
associated with cardiovascular disease in patients with inactive
systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:2048–2055.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Soyfoo MS, Roth J, Vogl T, Pochet R and
Decaux G: Phagocyte-specific S100A8/A9 protein levels during
disease exacerbations and infections in systemic lupus
erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 36:2190–2194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wu CY, Bawa KK, Ouk M, Leung N, Yu D,
Lanctôt KL, Herrmann N, Pakosh M and Swardfager W: Neutrophil
activation in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of protein markers in blood and
cerebrospinal fluid. Ageing Res Rev. 62:1011302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bracko O, Njiru BN, Swallow M, Ali M,
Haft-Javaherian M and Schaffer CB: Increasing cerebral blood flow
improves cognition into late stages in Alzheimer's disease mice. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 40:1441–1452. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Volkman R, Ben-Zur T, Kahana A, Garty BZ
and Offen D: Myeloperoxidase Deficiency inhibits cognitive decline
in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci.
13:9902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cruz Hernández JC, Bracko O, Kersbergen
CJ, Muse V, Haft-Javaherian M, Berg M, Park L, Vinarcsik LK, Ivasyk
I, Rivera DA, et al: Neutrophil adhesion in brain capillaries
reduces cortical blood flow and impairs memory function in
Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Nat Neurosci. 22:413–420. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Jönsen A, Bengtsson AA, Nived O, Ryberg B
and Sturfelt G: Outcome of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus
erythematosus within a defined Swedish population: Increased
morbidity but low mortality. Rheumatology (Oxford). 41:1308–1312.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Walker DG, Link J, Lue LF,
Dalsing-Hernandez JE and Boyes BE: Gene expression changes by
amyloid beta peptide-stimulated human postmortem brain microglia
identify activation of multiple inflammatory processes. J Leukoc
Biol. 79:596–610. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Stanek A, Brożyna-Tkaczyk K and Myśliński
W: Oxidative stress markers among obstructive sleep apnea patients.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:96815952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ha JS, Choi HR, Kim IS, Kim EA, Cho SW and
Yang SJ: Hypoxia-induced S100A8 expression activates microglial
inflammation and promotes neuronal apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci.
22:12052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fei W, Jiao W, Feng X, Chen X and Wang Y:
Intermittent hypoxia mimicking obstructive sleep apnea aggravates
early brain injury following ICH via neuroinflammation and
apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 24:8242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zeng X, Guo R, Dong M, Zheng J, Lin H and
Lu H: Contribution of TLR4 signaling in intermittent
hypoxia-mediated atherosclerosis progression. J Transl Med.
16:1062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Akinnusi M, Jaoude P, Kufel T and El-Solh
AA: Toll-like receptor activity in patients with obstructive sleep
apnea. Sleep Breath. 17:1009–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Chaput JP, McHill AW, Cox RC, Broussard
JL, Dutil C, da Costa BGG, Sampasa-Kanyinga H and Wright KP: The
role of insufficient sleep and circadian misalignment in obesity.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 19:82–97. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Korte SM and Straub RH: Fatigue in
inflammatory rheumatic disorders: Pathophysiological mechanisms.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 58(Suppl 5): v35–v50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Singer BH, Dickson RP, Denstaedt SJ,
Newstead MW, Kim K, Falkowski NR, Erb-Downward JR, Schmidt TM,
Huffnagle GB and Standiford TJ: Bacterial dissemination to the
brain in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 197:747–756. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
98
|
Lamar CD, Hurley RA and Taber KH:
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Review of the neuropsychiatric
manifestations and cognitive outcome. J Neuropsychiatry Clin
Neurosci. 23:237–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lamers KJ, Vos P, Verbeek MM, Rosmalen F,
van Geel WJ and van Engelen BG: Protein S-100B, neuron-specific
enolase (NSE), myelin basic protein (MBP) and glial fibrillary
acidic protein (GFAP) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood of
neurological patients. Brain Res Bull. 61:261–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ghavami S, Eshragi M, Ande SR, Chazin WJ,
Klonisch T, Halayko AJ, McNeill KD, Hashemi M, Kerkhoff C and Los
M: S100A8/A9 induces autophagy and apoptosis via ROS-mediated
cross-talk between mitochondria and lysosomes that involves BNIP3.
Cell Res. 20:314–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N,
Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA, Nacken W, Foell D, van der Poll T, Sorg
C and Roth J: Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like
receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med.
13:1042–1049. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lv J, Wang Z, Wang B, Deng C, Wang W and
Sun L: S100A9 induces macrophage M2 polarization and
immunomodulatory role in the lesion site after spinal cord injury
in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 61:5525–5540. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Huang N, Tang J, Yi X, Zhang M, Li B,
Cheng Y and Chen J: Glioma-derived S100A9 polarizes M2 microglia to
inhibit CD8+T lymphocytes for immunosuppression via αvβ3
integrin/AKT1/TGFβ1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1871:1196192024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Lu SM, Yu CJ, Liu YH, Dong HQ, Zhang X,
Zhang SS, Hu LQ, Zhang F, Qian YN and Gui B: S100A8 contributes to
postoperative cognitive dysfunction in mice undergoing tibial
fracture surgery by activating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Brain Behav
Immun. 44:221–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Cao Y, Yang Y, Wu H, Lu Y, Wu S, Liu L,
Wang C, Huang F, Shi H, Zhang B, et al: Stem-leaf saponins from
Panax notoginseng counteract aberrant autophagy and apoptosis in
hippocampal neurons of mice with cognitive impairment induced by
sleep deprivation. J Ginseng Res. 44:442–452. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Uddin MS, Tewari D, Mamun AA, Kabir MT,
Niaz K, Wahed MII, Barreto GE and Ashraf GM: Circadian and sleep
dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 60:1010462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Liu Y, Zhang T, Meng D, Sun L, Yang G, He
Y and Zhang C: Involvement of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in depression and
cognitive impairment induced by chronic unpredictable stress and
relevant underlying mechanism. Behav Brain Res. 381:1123712020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Quick JD, Silva C, Wong JH, Lim KL,
Reynolds R, Barron AM, Zeng J and Lo CH: Lysosomal acidification
dysfunction in microglia: An emerging pathogenic mechanism of
neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation.
20:1852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Franceschi C, Garagnani P, Parini P,
Giuliani C and Santoro A: Inflammaging: A new immune-metabolic
viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:576–590.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Swindell WR, Johnston A, Xing X, Little A,
Robichaud P, Voorhees JJ, Fisher G and Gudjonsson JE: Robust shifts
in S100a9 expression with aging: A novel mechanism for chronic
inflammation. Sci Rep. 3:12152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hamasaki MY, Severino P, Puga RD, Koike
MK, Hernandes C, Barbeiro HV, Barbeiro DF, Machado MCC, Reis EM and
Pinheiro da Silva F: Short-term effects of sepsis and the impact of
aging on the transcriptional profile of different brain regions.
Inflammation. 42:1023–1031. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Hoyaux D, Decaestecker C, Heizmann CW,
Vogl T, Schäfer BW, Salmon I, Kiss R and Pochet R: S100 proteins in
Corpora amylacea from normal human brain. Brain Res. 867:280–288.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhang K, Mizuma H, Zhang X, Takahashi K,
Jin C, Song F, Gao Y, Kanayama Y, Wu Y, Li Y, et al: PET imaging of
neural activity, β-amyloid, and tau in normal brain aging. Eur J
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 48:3859–3871. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ding L, Lu L, Zheng S, Zhang Z, Huang X,
Ma R, Zhang M, Xu Z, Chen M, Guo Z, et al: Usp14 deficiency removes
α-synuclein by regulating S100A8/A9 in Parkinson's disease. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 81:2322024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Yi W, Zhu R, Hou X, Wu F and Feng R:
Integrated analysis reveals S100a8/a9 Regulates autophagy and
apoptosis through the MAPK and PI3K-AKT signaling pathway in the
early stage of myocardial infarction. Cells. 11:19112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang C, Klechikov AG, Gharibyan AL,
Wärmländer SK, Jarvet J, Zhao L, Jia X, Narayana VK, Shankar SK,
Olofsson A, et al: The role of pro-inflammatory S100A9 in
Alzheimer's disease amyloid-neuroinflammatory cascade. Acta
Neuropathol. 127:507–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Zheng X, Wang M, Liu S, Chen H, Li Y, Yuan
F, Yang L, Qiu S, Wang H, Xie Z and Xiang M: A lncRNA-encoded
mitochondrial micropeptide exacerbates microglia-mediated
neuroinflammation in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell
Death Dis. 14:1262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Bonora BM, Palano MT, Testa G, Fadini GP,
Sangalli E, Madotto F, Persico G, Casciaro F, Vono R, Colpani O, et
al: Hematopoietic progenitor cell liabilities and alarmins
S100A8/A9-related inflammaging associate with frailty and predict
poor cardiovascular outcomes in older adults. Aging Cell.
21:e135452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Gong X, Shen H, Guo L, Huang C, Su T, Wang
H, Feng S, Yang S, Huo F, Liu H, et al: Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits
myeloid differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells by binding S100
calcium binding protein A8 to improve cognition in aged mice. Immun
Ageing. 20:122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ding S, Khan AI, Cai X, Song Y, Lyu Z, Du
D, Dutta P and Lin Y: Overcoming blood-brain barrier transport:
Advances in nanoparticle-based drug delivery strategies. Mater
Today (Kidlington). 37:112–125. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Wu SK, Tsai CL, Huang Y and Hynynen K:
Focused ultrasound and Microbubbles-mediated drug delivery to brain
tumor. Pharmaceutics. 13:152021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
122
|
Song KH, Harvey BK and Borden MA:
State-of-the-art of microbubble-assisted blood-brain barrier
disruption. Theranostics. 8:4393–4408. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Keller LA, Merkel O and Popp A: Intranasal
drug delivery: Opportunities and toxicologic challenges during drug
development. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 12:735–757. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Shah P, Lalan M and Barve K: Intranasal
delivery: An attractive route for the administration of nucleic
acid based therapeutics for CNS disorders. Front Pharmacol.
13:9746662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Ma L, Sun P, Zhang JC, Zhang Q and Yao SL:
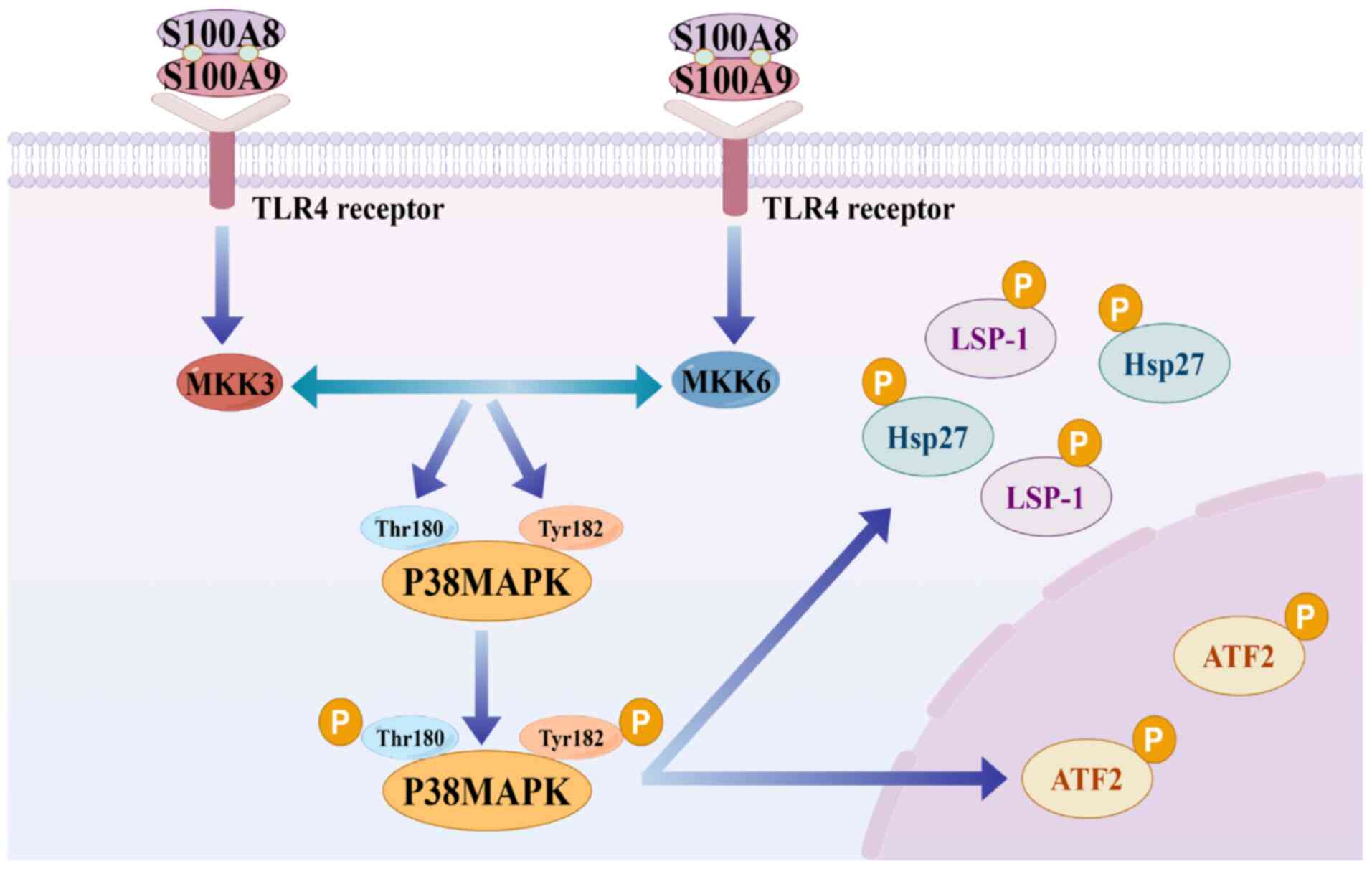
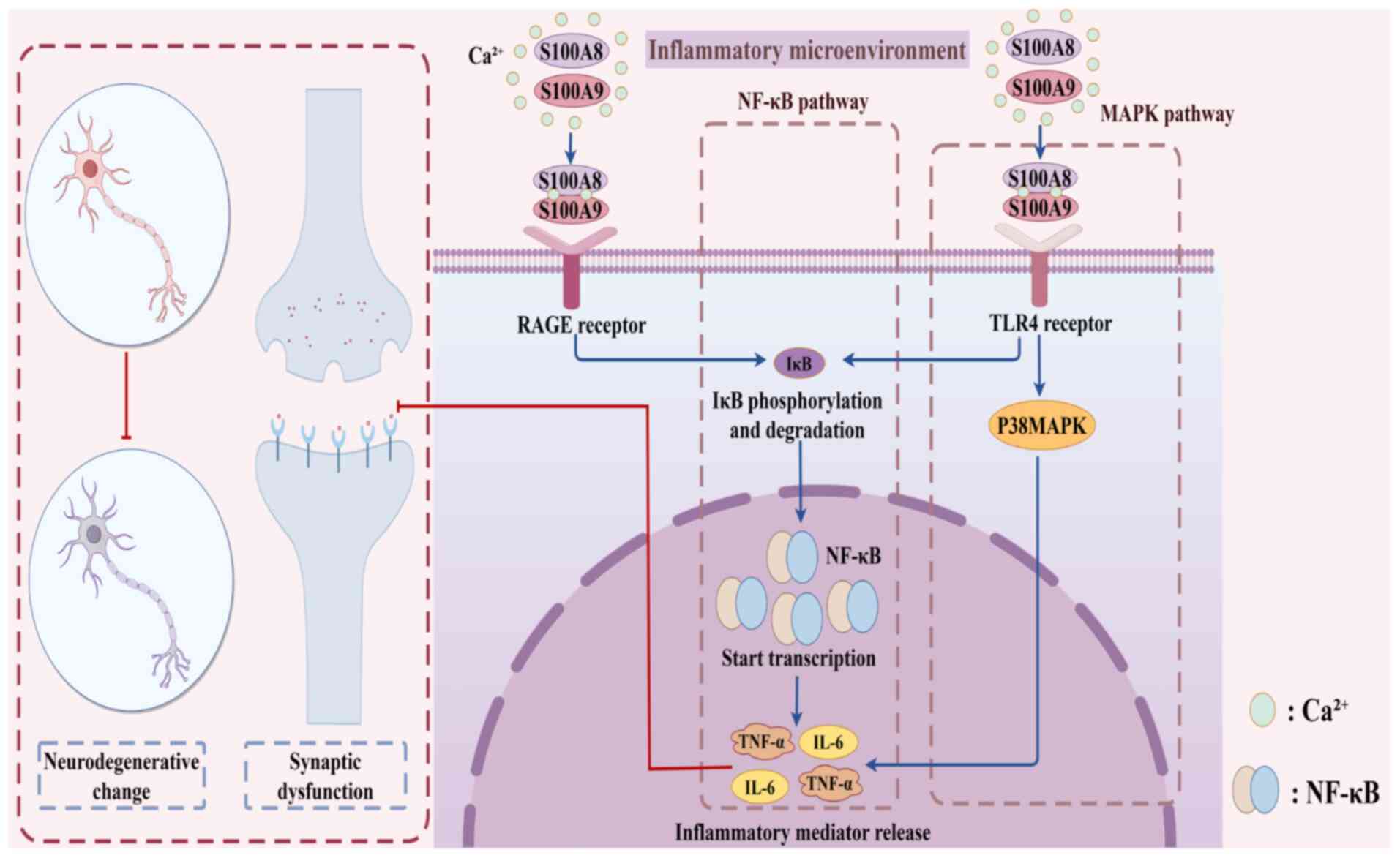
Proinflammatory effects of S100A8/A9 via TLR4 and RAGE signaling
pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Med. 40:31–38. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|