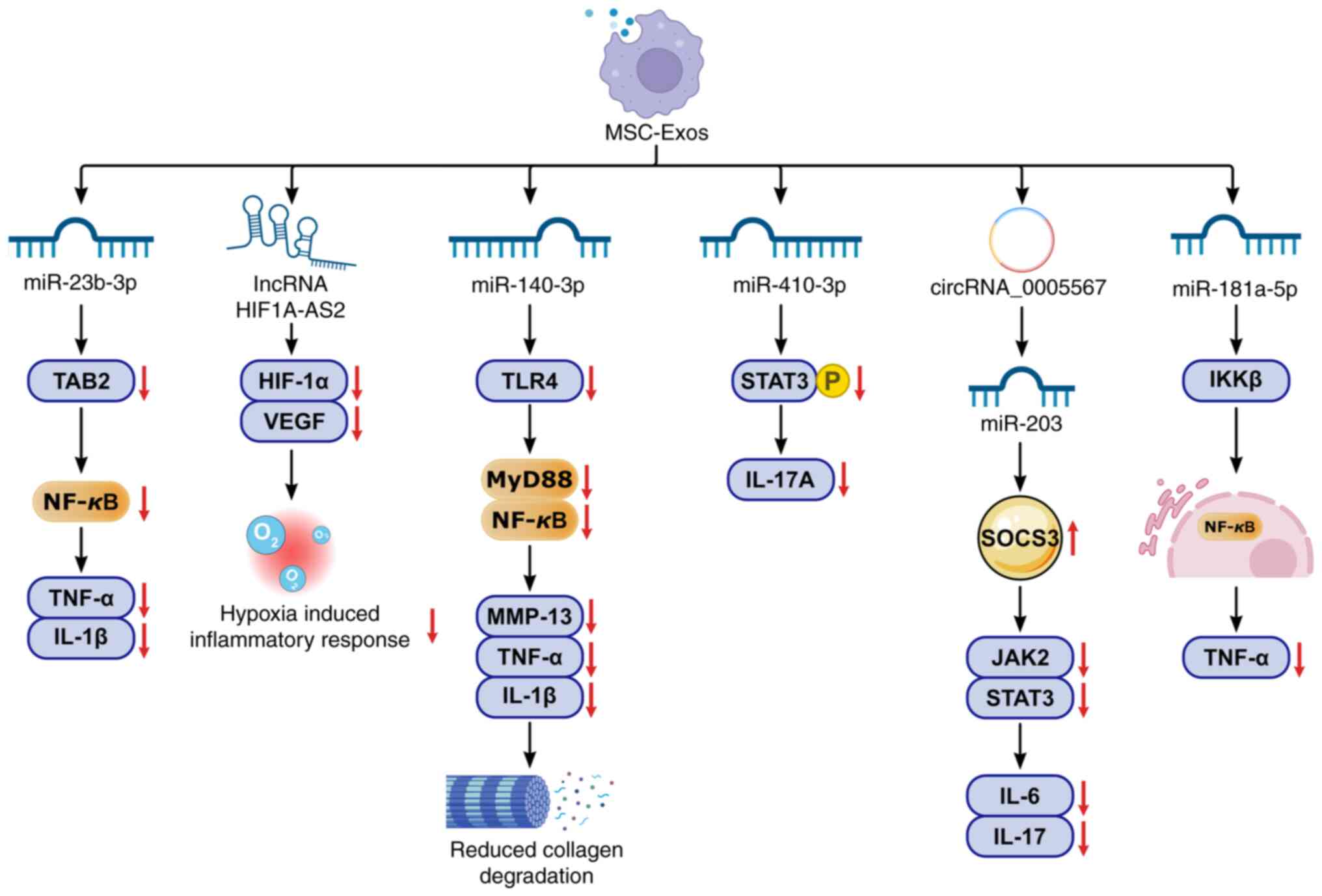
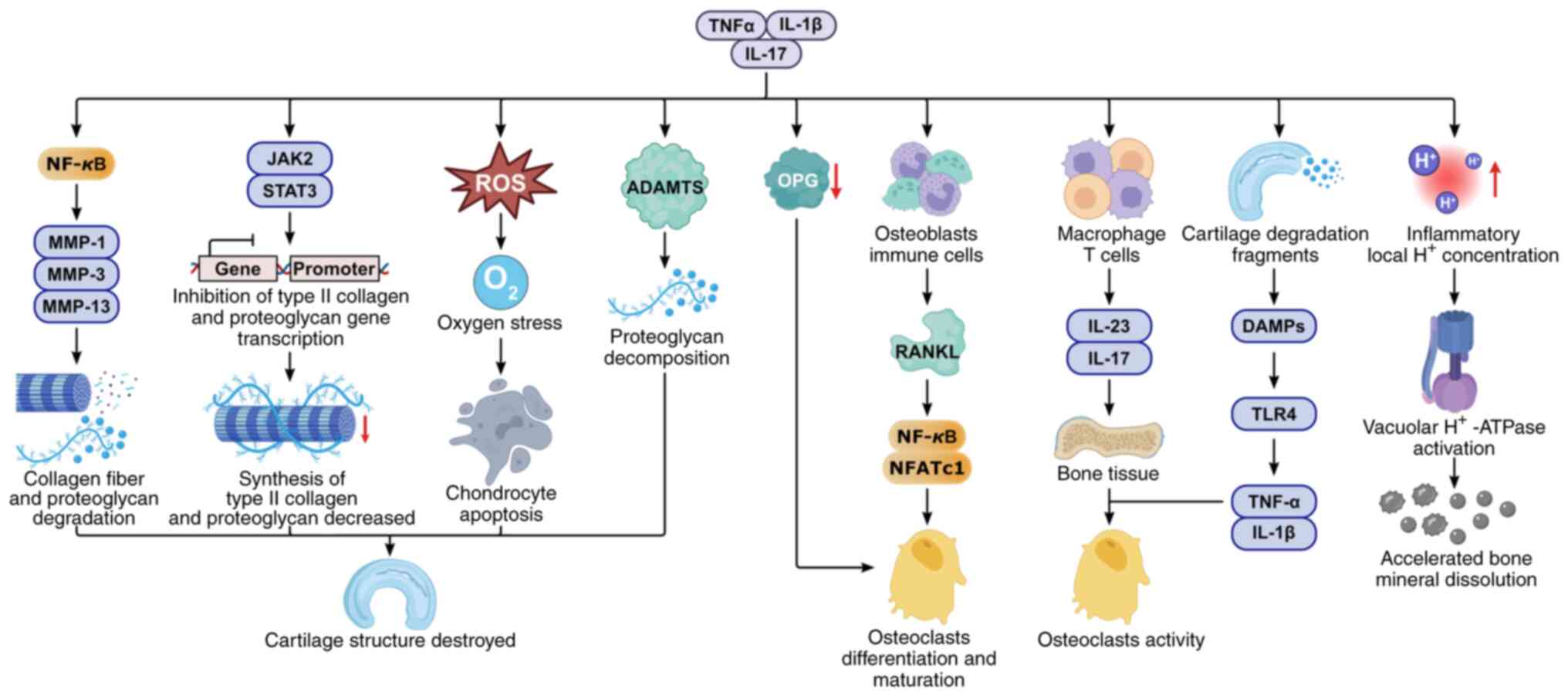
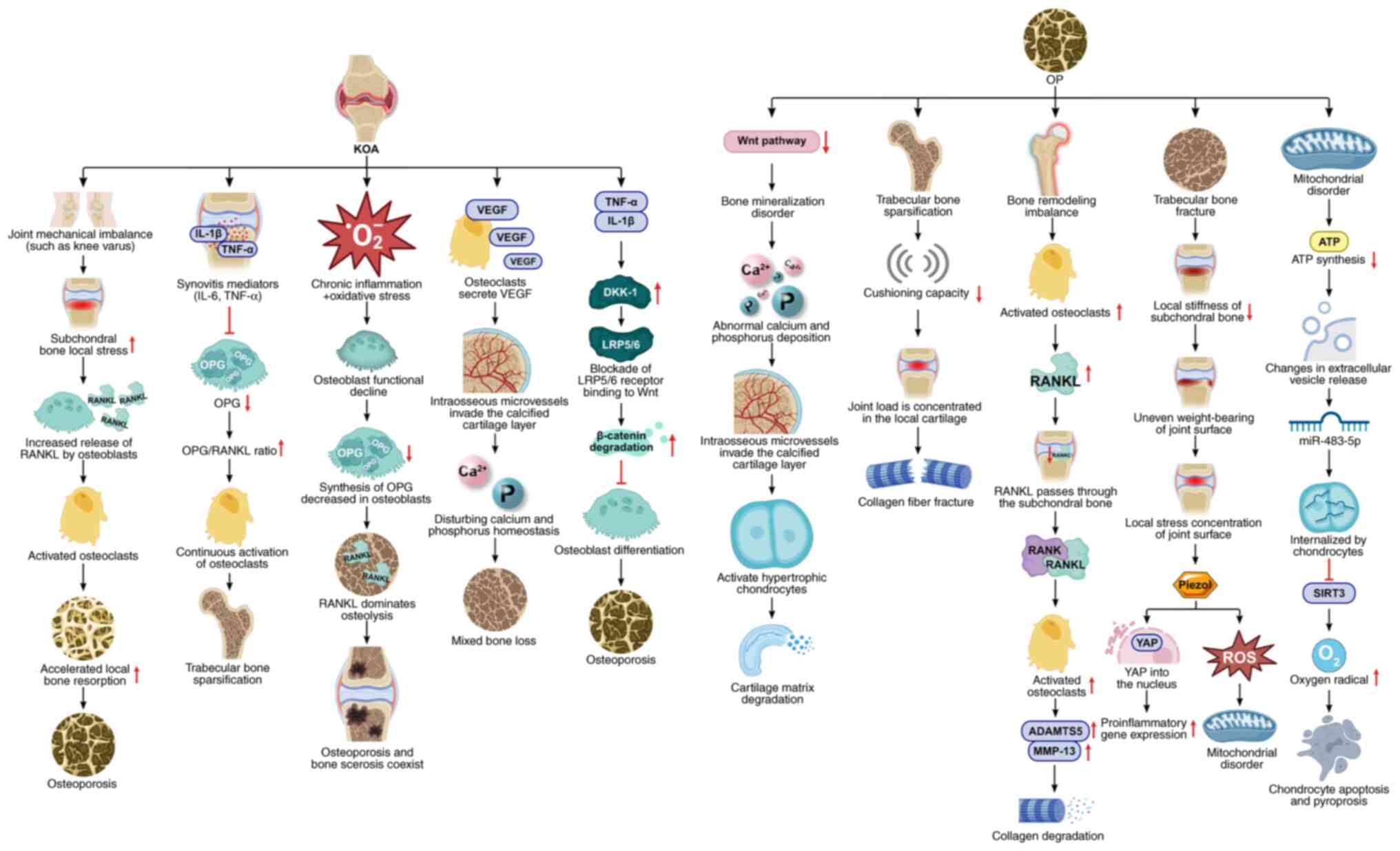
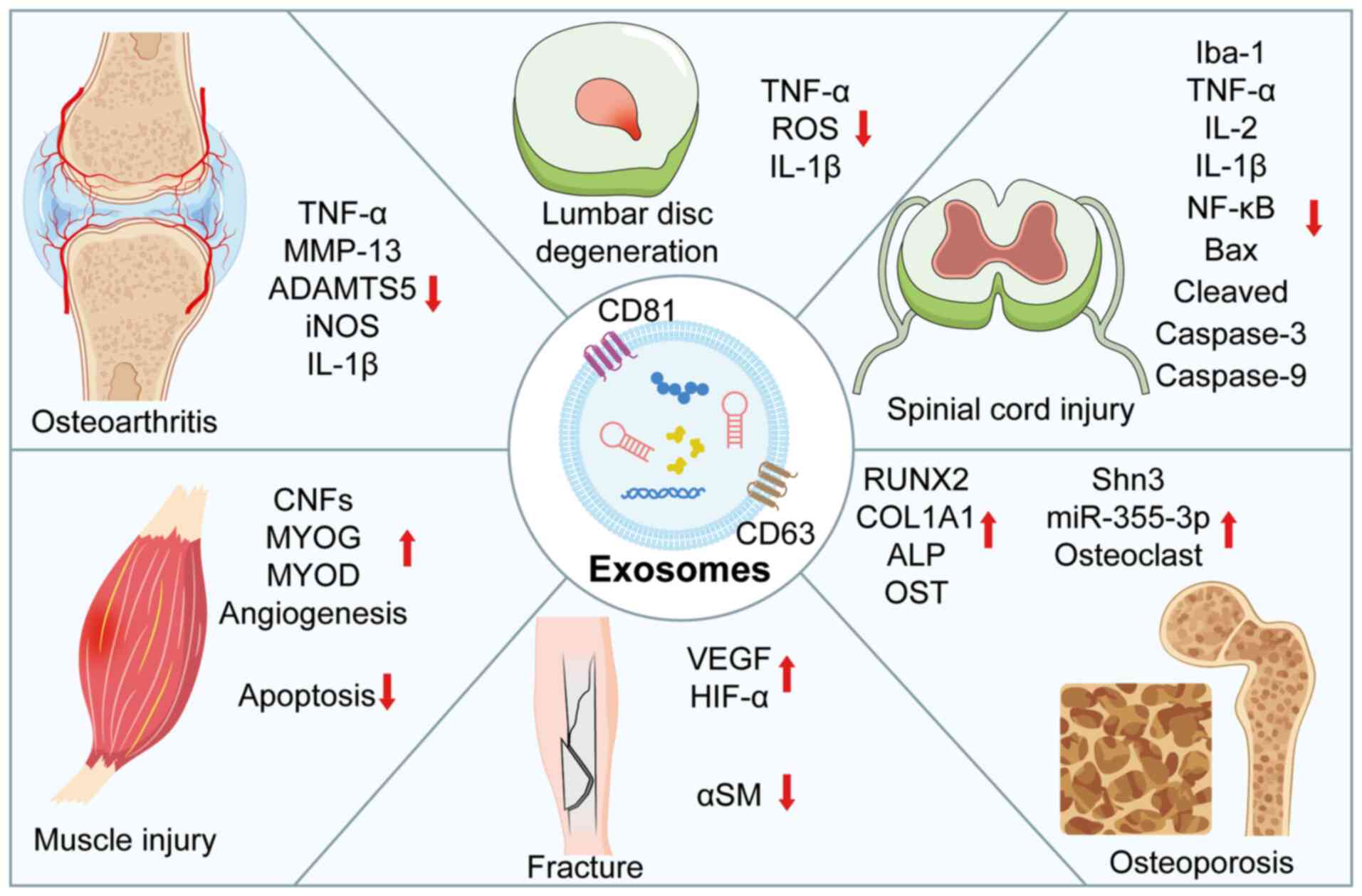
|
1
|
Curry ZA, Beling A and Borg-Stein J: Knee
osteoarthritis in midlife women: Unique considerations and
comprehensive management. Menopause. 29:748–755. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ren JL, Yang J and Hu W: The global burden
of osteoarthritis knee: A secondary data analysis of a
population-based study. Clin Rheumatol. 44:1769–1810. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lv Y, Sui L, Lv H, Zheng J, Feng H and
Jing F: Burden of knee osteoarthritis in China and globally from
1992 to 2021, and projections to 2030: A systematic analysis from
the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Front Public Health.
13:15431802025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muñoz M, Robinson K and Shibli-Rahhal A:
Bone health and osteoporosis prevention and treatment. Clin Obstet
Gynecol. 63:770–787. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou G, Zhang X, Gu Z, Zhao J, Luo M and
Liu J: Research progress on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis
combined with osteoporosis by single-herb Chinese medicine and
compound. Front Med (Lausanne). 10:12540862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qu Y, Chen S, Han M, Gu Z, Zhang Y, Fan T,
Zeng M, Ruan G, Cao P, Yang Q, et al: Osteoporosis and
osteoarthritis: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.
Arthritis Res Ther. 25:2422023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zamzam M, Alamri MS, Aldarsouni FG, Al
Zaid H and Al Ofair AA: Impact of osteoporosis in postmenopausal
women with primary knee osteoarthritis. Cureus.
15:e406452023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zafeiris EP, Babis GC, Zafeiris CP and
Chronopoulos E: Association of vitamin D, BMD and knee
osteoarthritis in postmenopausal women. J Musculoskelet Neuronal
Interact. 21:509–516. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai CJ, Wang YW, Chen JF, Chou CK, Huang
CC and Chen YC: Factors associated with osteoarthritis in
menopausal women: A registry study of osteoporosis sarcopenia and
osteoarthritis. J Family Med Prim Care. 12:1859–1863. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li D, Wan Y, Sun Y and Wu X: Clinical
study of correlation between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis of
knee joint using gold nanomaterial contrast agent. J Nanosci
Nanotechnol. 20:7761–7768. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshimura N, Muraki S, Oka H, Mabuchi A,
En-Yo Y, Yoshida M, Saika A, Yoshida H, Suzuki T, Yamamoto S, et
al: Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, lumbar spondylosis, and
osteoporosis in Japanese men and women: The research on
osteoarthritis/osteoporosis against disability study. J Bone Miner
Metab. 27:620–628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, Tanaka K, Smith ER, Müller H,
Wang X, González C, Kim M, Rossi F, Patel J, Nguyen T, et al:
Global burden of osteoporosis in knee osteoarthritis: A multicenter
analysis of 32,000 patients from 15 countries. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 33:411–428. 2025.
|
|
13
|
Tanaka K, Zhang L, Kim M, Nguyen T, Wong
ML, Chen W, Patel J, Johnson DA and Saito H: Vitamin D deficiency
and osteoporosis risk in Asian KOA populations: Substudy of KOA-OP
global consortium. J Bone Miner Res. 32:409–425. 2025.
|
|
14
|
Du X, Liu ZY, Tao XX, Mei YL, Zhou DQ,
Cheng K, Gao SL, Shi HY, Song C and Zhang XM: Research progress on
the pathogenesis of knee osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 15:2213–2224.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rizzoli R, Reginster JY, Bruyère O, Cooper
C, Kanis JA, Al-Daghri N, Brandi ML, Cavalier E and Sambrook PN:
Role of vitamin D and calcium supplementation in the management of
osteoporosis: An evidence-based consensus. Aging Clin Exp Res.
32:1873–1887. 2020.
|
|
16
|
Neptune E, Kraus VB, Sharma L, Guermazi A,
Roemer F, Nevitt M, Torner J, Felson D, Lewis CE, Lynch J, et al:
MRI-based cartilage thickness loss predicts knee replacement within
5 years: A longitudinal analysis from the Osteoarthritis
Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 81:331–338. 2022.
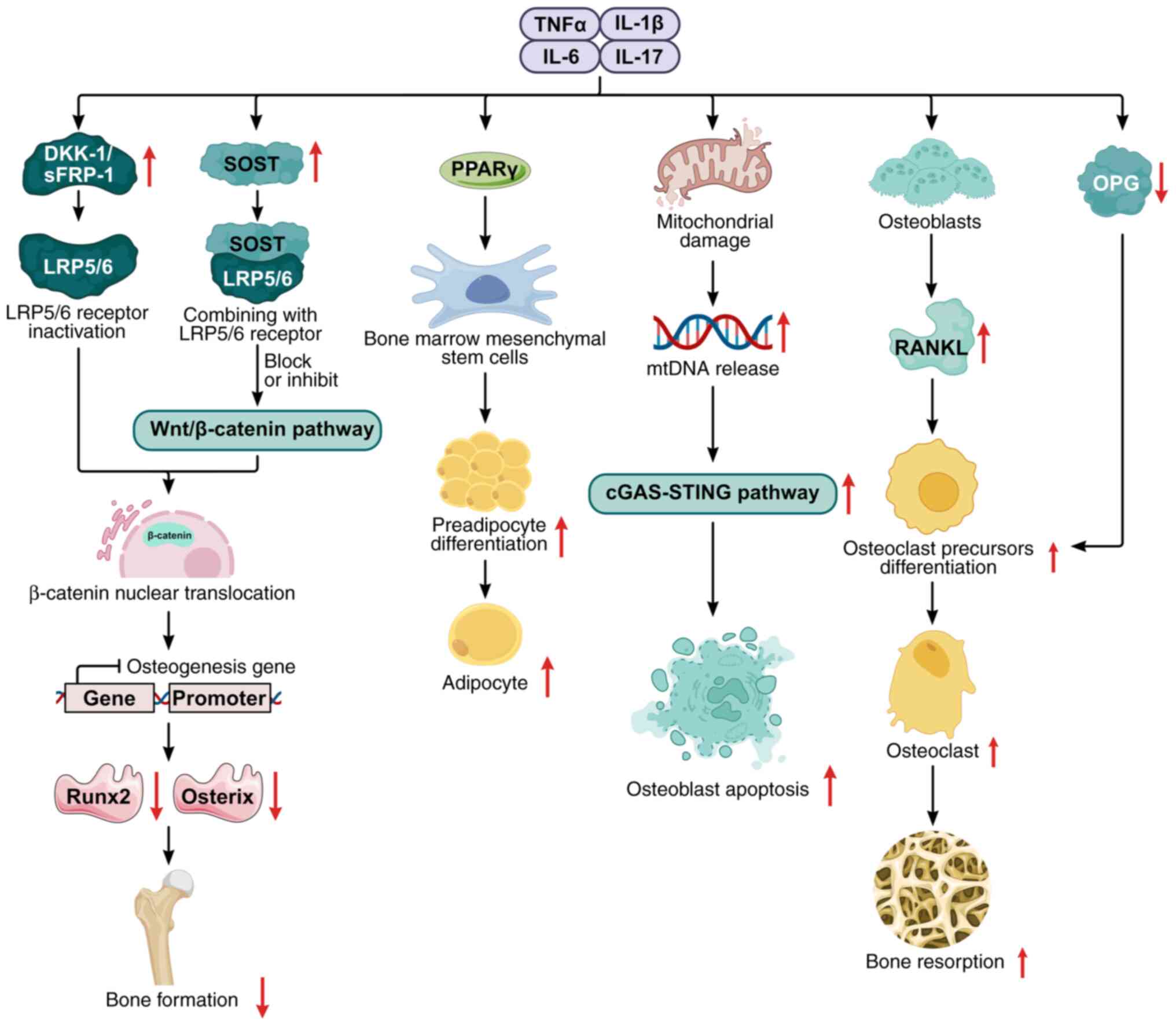
|
|
17
|
Kawaguchi H, Tanaka S, Yoshimura N, Muraki
S, Akune T, Nishimura Y, Oka H, Nakamura K, Cooper CB, Sowers MF,
et al: The biomechanical-metabolic paradox in coexisting
osteoporosis and knee osteoarthritis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
108:e678–e689. 2023.
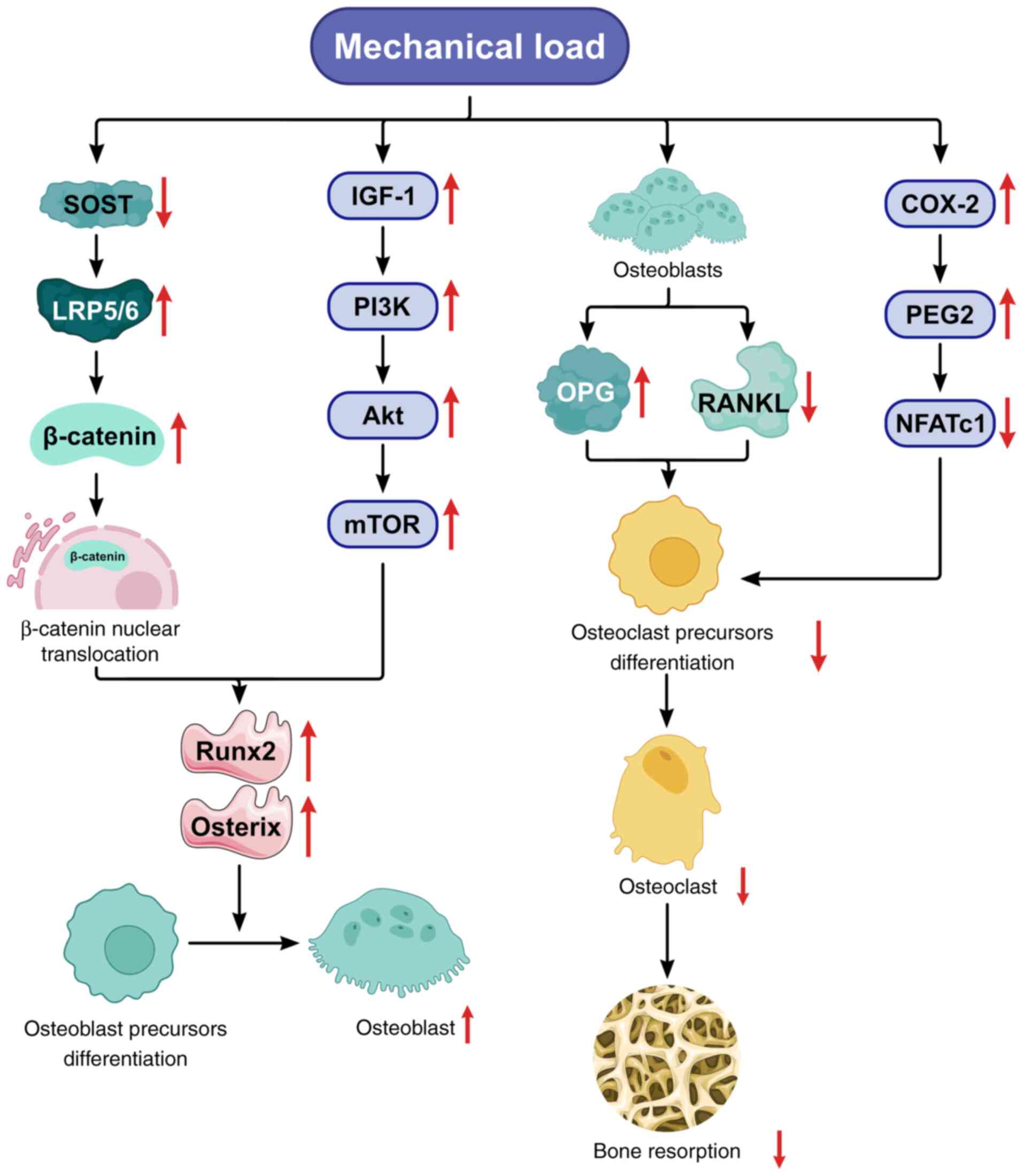
|
|
18
|
Wilson DR, Baker EL, Chen CX, Fritz MJ,
Phillips LS, Schwartz AV, Smith KE and York JD: Polygenic risk
score combines with EHR imaging to predict TKA: A machine learning
framework. Nat Med. 29:978–989. 2023.
|
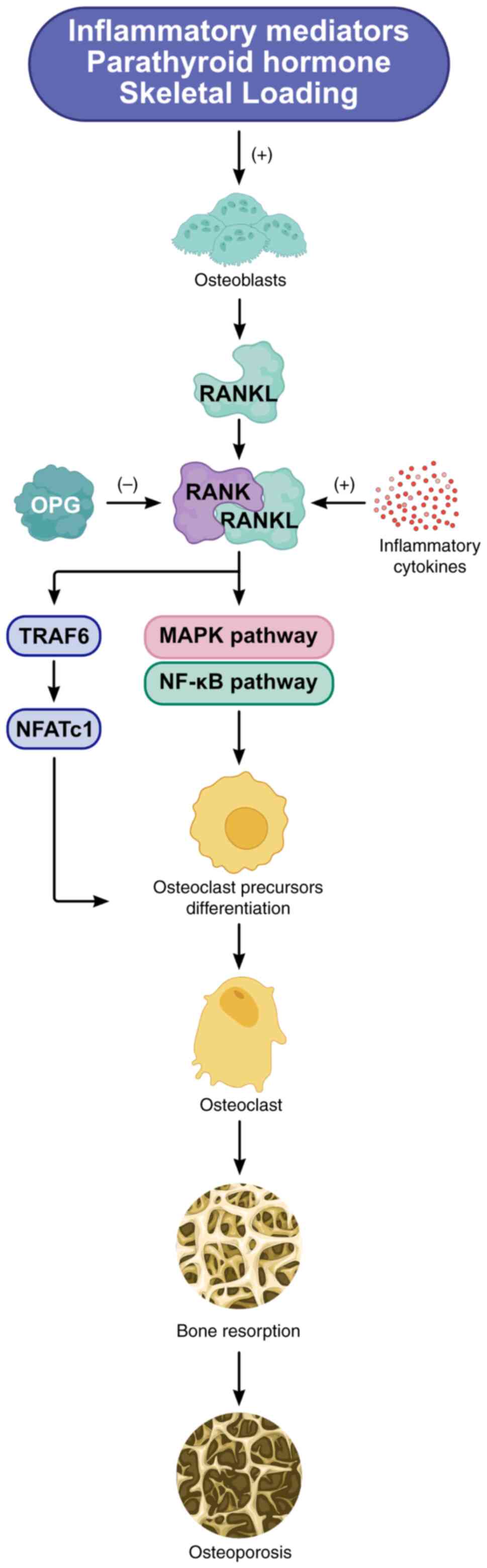
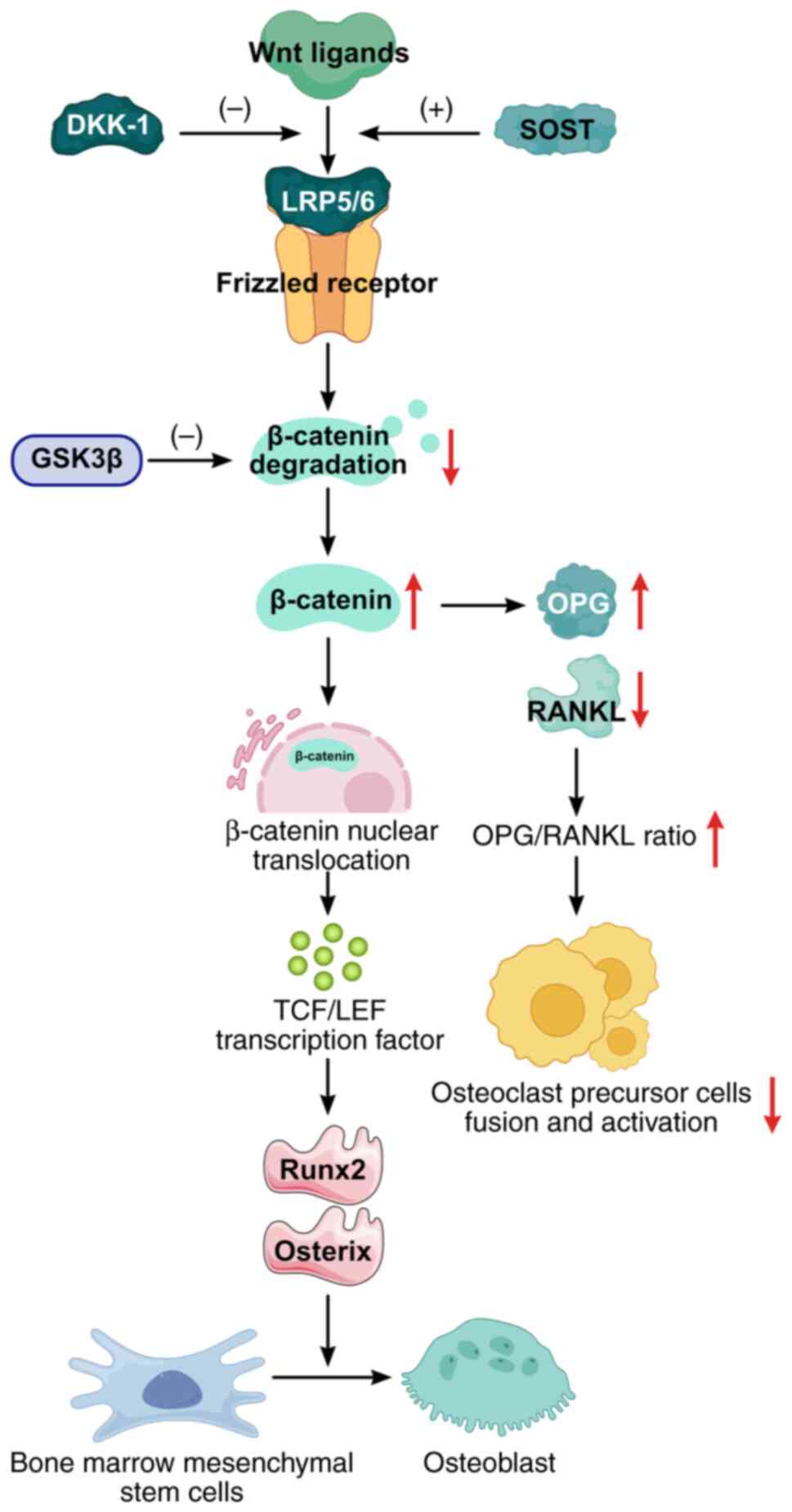
|
19
|
Li M, Zhang ZL, Xia WB, Lin H, Cheng XG,
Li YZ, Xie ZJ, Wang L, Xu YJ and Liu Y: Prevalence and risk factors
of osteoporosis in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A multicenter
registry study. Chin J Orthop. 42:1001–1008. 2022.
|
|
20
|
Rousseau MC, Feydy A, Boutron I, Chapurlat
R, Bousson V, Vital JM, Beaudoin C, Rannou F, Arden N, Maggi S, et
al: Longitudinal association between knee osteoarthritis
progression and bone mineral density loss: Results from the French
OSTEOLAR cohort. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 32:621–632. 2024.
|
|
21
|
Luyten FP, Kraus VB, Guermazi A, Arden NK,
Bierma-Zeinstra S, Pelletier JP, Hazes J, Lohmander S, Hunter D,
Kloppenburg M, et al: ROBUST-Knee: A prospective multicenter
registry for biomarker discovery in knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum
Dis. 82:1557–1567. 2023.
|
|
22
|
Zhao J, Yang W, Liang G, Luo M, Pan J, Liu
J and Zeng L: The efficacy and safety of Jinwu Gutong capsule in
the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. J Ethnopharmacol. 293:1152472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao PL, Hsu CJ, Ma YG, Liu D, Peng R, Xu
XH and Lu HD: Prevalence and treatment rate of osteoporosis in
patients undergoing total knee and hip arthroplasty: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Arch Osteoporos. 17:162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ozen G, Kamen DL, Mikuls TR, England BR,
Wolfe F and Michaud K: Trends and determinants of osteoporosis
treatment and screening in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
compared to osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).
70:713–723. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vuori IM: Dose-response of physical
activity and low back pain, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis. Med
Sci Sports Exerc. 33(6 Suppl): S551–S86. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma R, Wu M, Li Y, Wang J, Yang P, Chen Y,
Wang W, Song J and Wang K: The use of bone turnover markers for
monitoring the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal females
undergoing total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized study.
J Orthop Surg Res. 16:1952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jeyaraman M, Muthu S, Shehabaz S,
Jeyaraman N, Rajendran RL, Hong CM, Nallakumarasamy A,
Packkyarathinam RP, Sharma S, Ranjan R, et al: Current
understanding of MSC-derived exosomes in the management of knee
osteoarthritis. Exp Cell Res. 418:1132742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Yuan L, Cao H, Guo J, Zhou X and
Zeng Z: Application and molecular mechanisms of extracellular
vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 44:6346–6367. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang M, Xu X, Su L, Zeng Y, Lin J, Li W,
Zou Y, Li S, Lin B, Li Z, et al: Oral administration of Sophora
Flavescens-derived exosomes-like nanovesicles carrying CX5461
ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice. J Nanobiotechnology.
22:6072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He X, Wang Y, Liu Z, Weng Y, Chen S, Pan
Q, Li Y, Wang H, Lin S and Yu H: Osteoporosis treatment using stem
cell-derived exosomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu L, Sui B, Fan W, Lei L, Zhou L, Yang L,
Diao Y, Zhang Y, Li Z, Liu J and Hao X: Exosomes derived from
osteogenic tumor activate osteoclast differentiation and
concurrently inhibit osteogenesis by transferring COL1A1-targeting
miRNA-92a-1-5p. J Extracell Vesicles. 10:e120562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hadvina R, Lotfy Khaled M, Akoto T, Zhi W,
Karamichos D and Liu Y: Exosomes and their miRNA/protein profile in
keratoconus-derived corneal stromal cells. Exp Eye Res.
236:1096422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang Y, Xu C, Meng L, Dong X, Qi M and
Jiang D: Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based
scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory
properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater.
18:26–41. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He L, He T, Xing J, Zhou Q, Fan L, Liu C,
Chen Y, Wu D, Tian Z, Liu B and Rong L: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve
knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 11:2762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun Y, Chen P and Zhao B: Role of
extracellular vesicles associated with microRNAs and their
interplay with cuproptosis in osteoporosis. Noncoding RNA Res.
9:715–719. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lou G, Chen Z, Zheng M and Liu Y:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic
strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 49:e3462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Q, Wei S, Wang H, Li Y, Fan S, Cao Y
and Wang C: T cell-derived exosomes in tumor immune modulation and
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 14:11300332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bouchareychas L, Duong P, Covarrubias S,
Alsop E, Phu TA, Chung A, Gomes M, Wong D, Meechoovet B, Capili A,
et al: Macrophage exosomes resolve atherosclerosis by regulating
hematopoiesis and inflammation via MicroRNA cargo. Cell Rep.
32:1078812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tienda-Vázquez MA, Hanel JM,
Márquez-Arteaga EM, Salgado-Álvarez AP, Scheckhuber CQ,
Alanis-Gómez JR, Espinoza-Silva JI, Ramos-Kuri M, Hernández-Rosas
F, Melchor-Martínez EM and Parra-Saldívar R: Exosomes: A promising
strategy for repair, regeneration and treatment of skin disorders.
Cells. 12:16252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pegtel DM and Gould SJ: Exosomes. Annu Rev
Biochem. 88:487–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chu DT, Phuong TNT, Tien NLB, Tran DK,
Thanh VV, Quang TL, Truong DT, Pham VH, Ngoc VTN, Chu-Dinh T and
Kushekhar K: An update on the progress of isolation, culture,
storage, and clinical application of human bone marrow mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:7082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Galipeau J and Sensébé L: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Clinical challenges and therapeutic opportunities.
Cell Stem Cell. 22:824–833. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qin C, Bai L, Li Y and Wang K: The
functional mechanism of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
in the treatment of animal models with Alzheimer's disease:
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther.
13:902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang ZG, He ZY, Liang S, Yang Q, Cheng P
and Chen AM: Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived
from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:5112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li X, Wang M, Jing X, Guo W, Hao C, Zhang
Y, Gao S, Chen M, Zhang Z, Zhang X, et al: Bone Marrow- and adipose
Tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Characterization,
differentiation, and applications in cartilage tissue engineering.
Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 28:285–310. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhu X, Xu X, Shen M, Wang Y, Zheng T, Li
H, Wang X and Meng J: Transcriptomic heterogeneity of human
mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, dental pulp,
adipose tissue, and umbilical cord. Cell Reprogram. 25:162–170.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Naji A, Eitoku M, Favier B, Deschaseaux F,
Rouas-Freiss N and Suganuma N: Biological functions of mesenchymal
stem cells and clinical implications. Cell Mol Life Sci.
76:3323–3348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Varzideh F, Gambardella J, Kansakar U,
Jankauskas SS and Santulli G: Molecular mechanisms underlying
pluripotency and Self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:83862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Guo X, Yao H, Zhang Z and Zhao H:
Epigenetic control of dental stem cells: Progress and prospects in
multidirectional differentiation. Epigenetics Chromatin. 17:372024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dong L, Li X, Leng W, Guo Z, Cai T, Ji X,
Xu C, Zhu Z and Lin J: Adipose stem cells in tissue regeneration
and repair: From bench to bedside. Regen Ther. 24:547–560. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li N, Gao J, Mi L, Zhang G, Zhang L, Zhang
N, Huo R, Hu J and Xu K: Synovial membrane mesenchymal stem cells:
Past life, current situation, and application in bone and joint
diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:3812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang Y, Fang J, Liu B, Shao C and Shi Y:
Reciprocal regulation of mesenchymal stem cells and immune
responses. Cell Stem Cell. 29:1515–1530. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang L, Dong H, Cao H, Ji X, Luan S and
Liu J: Exosomes in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Med Sci Monit. 25:3329–3335. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gonda A, Kabagwira J, Senthil GN and Wall
NR: Internalization of exosomes through Receptor-mediated
endocytosis. Mol Cancer Res. 17:337–347. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Krylova SV and Feng D: The machinery of
exosomes: Biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int J Mol Sci.
24:13372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tan F, Li X, Wang Z, Li J, Shahzad K and
Zheng J: Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nishiyama Y, Ohmichi T, Kazami S, Iwasaki
H, Mano K, Nagumo Y, Kudo F, Ichikawa S, Iwabuchi Y, Kanoh N, et
al: Vicenistatin induces early Endosome-derived vacuole formation
in mammalian cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 80:902–910. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Scott CC, Vacca F and Gruenberg J:
Endosome maturation transport and functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
31:2–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hessvik NP and Llorente A: Current
knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:193–208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y and Wang B: Exosome
theranostics: Biology and translational medicine. Theranostics.
8:237–255. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu D, Zhao X, Zhang Q, Zhou F and Tong X:
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote
osteoblast proliferation, migration and inhibit apoptosis by
regulating KLF3-AS1/miR-338-3p. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
25:1222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Huang Y, Zhang X, Zhan J, Yan Z, Chen D,
Xue X and Pan X: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal
miR-206 promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in
osteoarthritis by reducing Elf3. J Cell Mol Med. 25:7734–7745.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li Z, Zhang B, Shang J, Wang Y, Jia L, She
X, Xu X, Zhang D, Guo J and Zhang F: Diabetic and nondiabetic
BMSC-derived exosomes affect bone regeneration via regulating
miR-17-5p/SMAD7 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 125:1111902023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Su H, Yang Y, Lv W, Li X and Zhao B: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-382 promotes
osteogenesis in osteoblast via regulation of SLIT2. J Orthop Surg
Res. 18:1852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yan L, Liu G and Wu X: The umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves
osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl
Med. 11:e2552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang S, Lu C, Zheng S and Hong G:
Hydrogel loaded with bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes
promotes bone regeneration by inhibiting inflammatory responses and
angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells. 16:499–511. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qi X, Zhang J, Yuan H, Xu Z, Li Q, Niu X,
Hu B, Wang Y and Li X: Exosomes secreted by Human-induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair
critical-sized bone defects through enhanced angiogenesis and
osteogenesis in osteoporotic rats. Int J Biol Sci. 12:836–849.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jiang Y, Zhang J, Li Z and Jia G: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem Cell-derived exosomal miR-25 regulates the
ubiquitination and degradation of Runx2 by SMURF1 to promote
fracture healing in mice. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:5775782020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Yu H, Zhang J, Liu X and Li Y:
microRNA-136-5p from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes facilitates fracture healing by targeting LRP4 to activate
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bone Joint Res. 10:744–758. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tang Y, Sun Y, Zeng J, Yuan B, Zhao Y,
Geng X, Jia L, Zhou S and Chen X: Exosomal miR-140-5p inhibits
osteogenesis by targeting IGF1R and regulating the mTOR pathway in
ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J
Nanobiotechnol. 20:4522022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lu H, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Wang J, Mi T, Jin
L, Wu X, Luo J, Liu Y, Liu J, et al: Human mesenchymal stem
Cells-derived exosome mimetic vesicles regulation of the MAPK
pathway and ROS levels inhibits Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in
osteoblasts. Stem Cells Int. 2023:55376102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hu H, Wang D, Li L, Yin H, He G and Zhang
Y: Role of microRNA-335 carried by bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells-derived extracellular vesicles in bone fracture recovery.
Cell Death Dis. 12:1562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lu GD, Cheng P, Liu T and Wang Z:
BMSC-derived exosomal miR-29a promotes angiogenesis and
osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:6085212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Jia D, Li Y, Han R, Wang K, Cai G, He C
and Yang L: miR-146a-5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4
antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF-1-induced cartilage
degradation. Mol Med Rep. 19:4388–4400. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang X and Thomsen P: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived small extracellular vesicles and bone regeneration.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 128:18–36. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Nicolini A, Ferrari P and Biava PM:
Exosomes and cell communication: From Tumour-derived exosomes and
their role in tumour progression to the use of exosomal cargo for
cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel). 13:8222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Asgarpour K, Shojaei Z, Amiri F, Ai J,
Mahjoubin-Tehran M, Ghasemi F, ArefNezhad R, Hamblin MR and Mirzaei
H: Exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells:
Cell-to-cell messages. Cell Commun Signal. 18:1492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cui Y, Guo Y, Kong L, Shi J, Liu P, Li R,
Geng Y, Gao W, Zhang Z and Fu D: A bone-targeted engineered exosome
platform delivering siRNA to treat osteoporosis. Bioact Mater.
10:207–221. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shen Z, Huang W, Liu J, Tian J, Wang S and
Rui K: Effects of mesenchymal stem Cell-derived exosomes on
autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 12:7491922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xie QH, Zheng JQ, Ding JY, Wu YF, Liu L,
Yu ZL and Chen G: Exosome-mediated immunosuppression in tumor
microenvironments. Cells. 11:19462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shahir M, Mahmoud Hashemi S, Asadirad A,
Varahram M, Kazempour-Dizaji M, Folkerts G, Garssen J, Adcock I and
Mortaz E: Effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on the
induction of mouse tolerogenic dendritic cells. J Cell Physiol.
235:7043–7055. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Bolandi Z, Mokhberian N, Eftekhary M,
Sharifi K, Soudi S, Ghanbarian H and Hashemi SM: Adipose derived
mesenchymal stem cell exosomes loaded with miR-10a promote the
differentiation of Th17 and Treg from naive CD4+ T cell. Life Sci.
259:1182182020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Tavasolian F, Hosseini AZ, Rashidi M,
Soudi S, Abdollahi E, Momtazi-Borojeni AA, Sathyapalan T and
Sahebkar A: The impact of immune cell-derived exosomes on immune
response initiation and immune system function. Curr Pharm Des.
27:197–205. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Yu J, Xue J, Liu C, Zhang A, Qin L, Liu J
and Yang Y: MiR-146a-5p accelerates sepsis through dendritic cell
activation and glycolysis via targeting ATG7. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 36:e231512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sun W, Yan S, Yang C, Yang J, Wang H, Li
C, Zhang L, Zhao L, Zhang J, Cheng M, et al: Mesenchymal stem
Cells-derived exosomes ameliorate lupus by inducing M2 macrophage
polarization and regulatory T cell expansion in MRL/lpr mice.
Immunol Invest. 51:1785–1803. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Khare D, Or R, Resnick I, Barkatz C,
Almogi-Hazan O and Avni B: Mesenchymal stromal Cell-derived
exosomes Affect mRNA expression and function of B-lymphocytes.
Front Immunol. 9:30532018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Wang R and Xu B: TGF-β1-modified
MSC-derived exosomal miR-135b attenuates cartilage injury via
promoting M2 synovial macrophage polarization by targeting MAPK6.
Cell Tissue Res. 384:113–127. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li H, Zhang P, Lin M, Li K, Zhang C, He X
and Gao K: Pyroptosis: Candidate key targets for mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes for the treatment of Bone-related diseases.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 16:682025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bhaskara M, Anjorin O and Wang M:
Mesenchymal stem Cell-derived exosomal microRNAs in cardiac
regeneration. Cells. 12:28152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li J, Deng X, Ji X, Shi X, Ying Z, Shen K,
Xu D and Cheng Z: Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reverse acute lung
injury through Nrf-2/ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways. PeerJ.
8:e99282020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Hu Y, Qu H, He J, Zhong H, He S, Zhao P,
Zhang L, Chen J and Deng C: Human placental mesenchymal stem cell
derived exosomes exhibit anti-inflammatory effects via
TLR4-mediated NF-κB/MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways. Pharmazie.
77:112–117. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu L, Wu Y, Wang P, Shi M, Wang J, Ma H
and Sun D: PSC-MSC-Derived exosomes protect against kidney fibrosis
in vivo and in vitro through the SIRT6/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Int J Stem Cells. 14:310–319. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sevimli M, Inan U, Seyidova N, Guluzade L,
Ahmadova Z, Gulec K, Topal AE and Semerci Sevimli T: In vitro
chondrogenic induction promotes the expression level of IL-10 via
the TGF-β/SMAD and Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in
exosomes secreted by human adipose Tissue-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 82:3741–3750. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Zhao B, Li J, Zhang X, Dai Y, Yang N, Bao
Z, Chen Y and Wu X: Exosomal miRNA-181a-5p from the cells of the
hair follicle dermal papilla promotes the hair follicle growth and
development via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Biol
Macromol. 207:110–120. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang R and Xu B: TGFβ1-modified
MSC-derived exosome attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting PDGF-BB
secretion and H-type vessel activity in the subchondral bone. Acta
Histochem. 124:1519332022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Zhang Y, Xie Y, Hao Z, Zhou P, Wang P,
Fang S, Li L, Xu S and Xia Y: Umbilical mesenchymal stem
Cell-derived Exosome-encapsulated hydrogels accelerate bone repair
by enhancing angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
13:18472–18487. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhang J, Liu X, Li H, Chen C, Hu B, Niu X,
Li Q, Zhao B, Xie Z and Wang Y: Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate
combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 7:1362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhang S, Chuah SJ, Lai RC, Hui JHP, Lim SK
and Toh WS: MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing
proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune
reactivity. Biomaterials. 156:16–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Chen JY, Feng L, Zhang HL, Li JC, Yang XW,
Cao XL, Liu L, Qin HY, Liang YM and Han H: Differential regulation
of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial
outgrowth cells by the Notch signaling pathway. PLoS One.
7:e436432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Simon TM and Jackson DW: Articular
cartilage: Injury pathways and treatment options. Sports Med
Arthrosc Rev. 26:31–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Yu Y and Zhao J: Modulated autophagy by
MicroRNAs in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int.
2019:14841522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kan HS, Chan PK, Chiu KY, Yan CH, Yeung
SS, Ng YL, Shiu KW and Ho T: Nonsurgical treatment of knee
osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 25:127–133. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Schulze-Tanzil G: Intraarticular ligament
degeneration is interrelated with cartilage and bone destruction in
osteoarthritis. Cells. 8:9902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhao Z, Bi B, Cheng G, Zhao Y, Wu H, Zheng
M and Cao Z: Melatonin ameliorates osteoarthritis rat cartilage
injury by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases and JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 31:359–368. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Kuchynsky K, Stevens P, Hite A, Xie W,
Diop K, Tang S, Pietrzak M, Khan S, Walter B and Purmessur D:
Transcriptional profiling of human cartilage endplate cells
identifies novel genes and cell clusters underlying degenerated and
non-degenerated phenotypes. Arthritis Res Ther. 26:122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Radenska-Lopovok SG: Immunomorphological
characteristics of the synovial membrane in rheumatic diseases.
Arkh Patol. 78:64–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Shakoor D, Demehri S, Roemer FW, Loeuille
D, Felson DT and Guermazi A: Are contrast-enhanced and non-contrast
MRI findings reflecting synovial inflammation in knee
osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 28:126–136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Sanchez-Lopez E, Coras R, Torres A, Lane
NE and Guma M: Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 18:258–275. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Alivernini S, MacDonald L, Elmesmari A,
Finlay S, Tolusso B, Gigante MR, Petricca L, Di Mario C, Bui L,
Perniola S, et al: Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets
regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat
Med. 26:1295–1306. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sanchez-Lopez E, Coras R, Torres A, Lane
NE and Guma M: Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 18:258–275. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Harris AB, Lantieri MA, Agarwal AR,
Golladay GJ and Thakkar SC: Osteoporosis and total knee
arthroplasty: Higher 5-year Implant-Related complications. J
Arthroplasty. 39:948–953.e1. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Iizawa N, Oshima Y, Kataoka T, Watanabe H,
Majima T and Takai S: Relationship between severity of varus
osteoarthritis of the knee and contracture of medial structures. J
Nippon Med Sch. 89:108–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Roemer FW, Jarraya M, Collins JE, Kwoh CK,
Hayashi D, Hunter DJ and Guermazi A: tructural phenotypes of knee
osteoarthritis: Potential clinical and research relevance. Skeletal
Radiol. 52:2021–2030. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Chen X, Wang Z, Duan N, Zhu G, Schwarz EM
and Xie C: Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res.
59:99–107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Wang LT, Chen LR and Chen KH:
Hormone-related and Drug-induced osteoporosis: A cellular and
molecular overview. Int J Mol Sci. 24:58142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Xie Y, Zhou J, Tian L, Dong Y, Yuan H, Zhu
E, Li X and Wang B: miR-196b-5p regulates osteoblast and osteoclast
differentiation and bone homeostasis by targeting SEMA3A. J Bone
Miner Res. 38:1175–1191. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhao G, Luo WD, Yuan Y, Lin F, Guo LM, Ma
JJ, Chen HB, Tang H and Shu J: LINC02381, a sponge of miR-21,
weakens osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs through
KLF12-mediated Wnt4 transcriptional repression. J Bone Miner Metab.
40:66–80. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Brown JP: Long-term treatment of
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 36:544–552.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kimmel DB, Vennin S, Desyatova A, Turner
JA, Akhter MP, Lappe JM and Recker RR: Bone architecture, bone
material properties, and bone turnover in nonosteoporotic
postmenopausal women with fragility fracture. Osteoporos Int.
33:1125–1136. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Jonasson G and Rythén M: Alveolar bone
loss in osteoporosis: A loaded and cellular affair? Clin Cosmet
Investig Dent. 8:95–103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Gorwa J, Zieliński J, Wolański W, Michnik
R, Larysz D, Dworak LB and Kusy K: Decreased bone mineral density
in forearm vs loaded skeletal sites in professional ballet dancers.
Med Probl Perform Art. 34:25–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Whyne CM, Ferguson D, Clement A, Rangrez M
and Hardisty M: Biomechanical properties of metastatically involved
osteolytic bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 18:705–715. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wu H, Yin G, Pu X, Wang J, Liao X and
Huang Z: Coordination of osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis
by the bone marrow mesenchymal stem Cell-derived extracellular
matrix to promote bone regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater.
5:2913–2927. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Levin VA, Jiang X and Kagan R: Estrogen
therapy for osteoporosis in the modern era. Osteoporos Int.
29:1049–1055. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Chen T, Wang Y, Hao Z, Hu Y and Li J:
Parathyroid hormone and its related peptides in bone metabolism.
Biochem Pharmacol. 192:1146692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Fang J, Zhang X, Chen X, Wang Z, Zheng S,
Cheng Y, Liu S and Hao L: The role of insulin-like growth factor-1
in bone remodeling: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 238:1241252023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Kong Q, Gao S, Li P, Sun H, Zhang Z, Yu X,
Deng F and Wang T: Calcitonin gene-related peptide-modulated
macrophage phenotypic alteration regulates angiogenesis in early
bone healing. Int Immunopharmacol. 130:1117662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Che Ahmad Tantowi NA, Lau SF and Mohamed
S: Ficus deltoidea prevented bone loss in preclinical
Osteoporosis/osteoarthritis model by suppressing inflammation.
Calcif Tissue Int. 103:388–399. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Warmink K, Rios JL, van Valkengoed DR,
Korthagen NM and Weinans H: Sprague dawley rats show more severe
bone loss, osteophytosis and inflammation compared towistar han
rats in a high-Fat, High-sucrose diet model of joint damage. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:37252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Watanabe S, Matsushita T, Nishida K, Nagai
K, Hoshino Y, Matsumoto T and Kuroda R: Knee osteotomy decreases
joint inflammation based on synovial histology and synovial fluid
analysis. Arthroscopy. 40:830–843. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Yuce P, Hosgor H, Rencber SF and Yazir Y:
Effects of Intra-articular resveratrol injections on cartilage
destruction and synovial inflammation in experimental
temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
79:344.e1–344.e12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Iantomasi T, Romagnoli C, Palmini G,
Donati S, Falsetti I, Miglietta F, Aurilia C, Marini F, Giusti F
and Brandi ML: Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis:
Molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:37722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Bai RJ, Li YS and Zhang FJ: Osteopontin, a
bridge links osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:10125082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Aubonnet R, Ramos J, Recenti M, Jacob D,
Ciliberti F, Guerrini L, Gislason MK, Sigurjonsson O, Tsirilaki M,
Jónsson H Jr and Gargiulo P: Toward new assessment of knee
cartilage degeneration. Cartilage. 14:351–374. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
135
|
Mehana EE, Khafaga AF and El-Blehi SS: The
role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis:
An updated review. Life Sci. 234:1167862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Yao Q, Wu X, Tao C, Gong W, Chen M, Qu M,
Zhong Y, He T, Chen S and Xiao G: Osteoarthritis: Pathogenic
signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Mukherjee A and Das B: The role of
inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the
progression of osteoarthritis. Biomater Biosyst.
13:1000902024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhou Q, Ren Q, Jiao L, Huang J, Yi J, Chen
J, Lai J, Ji G and Zheng T: The potential roles of JAK/STAT
signaling in the progression of osteoarthritis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:10690572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Fukuda K, Miura Y, Maeda T, Hayashi S,
Matsumoto T and Kuroda R: Expression profiling of genes in
rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulated by Fas ligand via
cDNA microarray analysis. Exp Ther Med. 22:10002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Yang Y, Cheng R, Liu J, Fang J, Wang X,
Cui Y, Zhang P and Du B: Linarin protects against Cadmium-induced
osteoporosis via reducing oxidative stress and inflammation and
altering RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res.
200:3688–3700. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Wang L, You X, Zhang L, Zhang C and Zou W:
Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 10:162022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Koyama Y, Tateuchi H, Araki K, Fujita K,
Umehara J, Kobayashi M and Ichihashi N: Mechanical energy
efficiency for stepping up and down in persons with medial knee
osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 69:143–149. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Chen L, Zhang Z and Liu X: Role and
mechanism of mechanical load in the homeostasis of the subchondral
bone in knee osteoarthritis: A comprehensive review. J Inflamm Res.
17:9359–9378. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Yokota S, Ishizu H, Miyazaki T, Takahashi
D, Iwasaki N and Shimizu T: Osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and
subchondral insufficiency fracture: Recent insights. Biomedicines.
12:8432024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Im GI and Kim MK: The relationship between
osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 32:101–109.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Wada H, Aso K, Izumi M and Ikeuchi M: The
effect of post-menopausal osteoporosis on subchondral bone
pathology in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis. Sci Rep.
13:29262023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Fujita H, Ochi M, Ono M, Aoyama E, Ogino
T, Kondo Y and Ohuchi H: Glutathione accelerates osteoclast
differentiation and inflammatory bone destruction. Free Radic Res.
53:226–236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Da W, Tao L and Zhu Y: The role of
osteoclast energy metabolism in the occurrence and development of
osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:6753852021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Li J, Zhang Z and Huang X: l-Arginine and
allopurinol supplementation attenuates inflammatory mediators in
human Osteoblasts-osteoarthritis cells. Int J Biol Macromol.
118:716–721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Kovács B, Vajda E and Nagy EE: Regulatory
effects and interactions of the wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling at
the Bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
20:46532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Trojian T and Naik H: Arthritis: Knee and
hip osteoarthritis. FP Essent. 548:6–12. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Fujii Y, Liu L, Yagasaki L, Inotsume M,
Chiba T and Asahara H: Cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:63162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Geng R, Li J, Yu C, Zhang C, Chen F, Chen
J, Ni H, Wang J, Kang K, Wei Z, et al: Knee osteoarthritis: Current
status and research progress in treatment (review). Exp Ther Med.
26:4812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Herrero-Beaumont G, Roman-Blas JA, Bruyère
O, Cooper C, Kanis J, Maggi S, Rizzoli R and Reginster JY: Clinical
settings in knee osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology guides treatment.
Maturitas. 96:54–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Klemm P, Schulz N, Lange U and Bühring B:
Diagnostics and treatment of osteoporosis in 2025: An update on
current guidelines. Inn Med (Heidelb). 66:603–614. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Boyde A: Scanning electron microscopy and
bone. Methods Mol Biol. 2885:621–670. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Geusens PP and van den Bergh JP:
Osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: Shared mechanisms and
epidemiology. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 28:97–103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Musyuni P, Kumar D, Pandita D, Jain GK,
Nagpal M and Aggarwal G: Application of nutraceuticals in managing
osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric.
12:88–103. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S and Okada Y:
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation.
Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:325–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zheng H, Qu L, Yang L, Xie X, Song L and
Xie Q: An injectable hydrogel loaded with Icariin attenuates
cartilage damage in rabbit knee osteoarthritis via Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 145:1137252025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Smith AE, Sigurbjörnsdóttir ES,
Steingrímsson E and Sigurbjörnsdóttir S: Hedgehog signalling in
bone and osteoarthritis: The role of Smoothened and cholesterol.
FEBS J. 290:3059–3075. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Scotece M, Koskinen-Kolasa A, Pemmari A,
Leppänen T, Hämäläinen M, Moilanen T, Moilanen E and Vuolteenaho K:
Novel adipokine associated with OA: Retinol binding protein 4
(RBP4) is produced by cartilage and is correlated with MMPs in
osteoarthritis patients. Inflamm Res. 69:415–421. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Xu F, Zhong JY, Guo B, Lin X, Wu F, Li FX,
Shan SK, Zheng MH, Wang Y, Xu QS, et al: H19 promotes osteoblastic
transition by acting as ceRNA of miR-140-5p in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:7743632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Udagawa N, Koide M, Nakamura M, Nakamichi
Y, Yamashita T, Uehara S, Kobayashi Y, Furuya Y, Yasuda H, Fukuda C
and Tsuda E: Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling
pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 39:19–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Nassar ES, Elnemr R, Shaaban A, Elhameed
AA and Taleb RSZ: Association between AXIN1 gene polymorphism
(rs9921222) of WNT signaling pathway and susceptibility to
osteoporosis in Egyptian patients: A case-control study. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 24:5272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Falchetti A: Genetics of osteoarticular
disorders, Florence, Italy, 22-23 February 2002. Arthritis Res.
4:326–331. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Findlay DM and Atkins GJ:
Osteoblast-chondrocyte interactions in osteoarthritis. Curr
Osteoporos Rep. 12:127–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Delgado-Calle J, Fernández AF, Sainz J,
Zarrabeitia MT, Sañudo C, García-Renedo R, Pérez-Núñez MI,
García-Ibarbia C, Fraga MF and Riancho JA: Genome-wide profiling of
bone reveals differentially methylated regions in osteoporosis and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 65:197–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Boroňová I, Bernasovská J, Mačeková S,
Petrejčíková E, Tomková Z, Kľoc J, Poráčová J, Blaščáková MM and
Litavcová E: TNFRSF11B gene polymorphisms, bone mineral density,
and fractures in Slovak postmenopausal women. J Appl Genet.
56:57–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Marozik P, Rudenka A, Kobets K and Rudenka
E: Vitamin D status, bone mineral density, and VDR gene
polymorphism in a cohort of belarusian postmenopausal women.
Nutrients. 13:8372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Carlson KM, Yamaga KM, Reinker KA, Hsia
YE, Carpenter C, Abe LM, Perry AK, Person DA, Marchuk DA and Raney
EM: Precocious osteoarthritis in a family with recurrent COL2A1
mutation. J Rheumatol. 33:1133–1116. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
van der Kraan PM: Factors that influence
outcome in experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
25:369–375. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Ntanasis-Stathopoulos J, Tzanninis JG,
Philippou A and Koutsilieris M: Epigenetic regulation on gene
expression induced by physical exercise. J Musculoskelet Neuronal
Interact. 13:133–146. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Czogała W, Czogała M, Strojny W, Wątor G,
Wołkow P, Wójcik M, Bik Multanowski M, Tomasik P, Wędrychowicz A,
Kowalczyk W, et al: Methylation and expression of FTO and PLAG1
genes in childhood obesity: Insight into anthropometric parameters
and Glucose-lipid metabolism. Nutrients. 13:16832021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Gilbert SJ, Jones R, Egan BJ, Bonnet CS,
Evans SL and Mason DJ: Investigating mechanical and inflammatory
pathological mechanisms in osteoarthritis using MSC-derived
osteocyte-like cells in 3D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
15:13590522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Zhang L, Liu W, Zhao J, Ma X, Shen L,
Zhang Y, Jin F and Jin Y: Mechanical stress regulates osteogenic
differentiation and RANKL/OPG ratio in periodontal ligament stem
cells by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1860:2211–2219. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Gao YH, Zhao CW, Liu B, Dong N, Ding L, Li
YR, Liu JG, Feng W, Qi X and Jin XH: An update on the association
between metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis and on the potential
role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Cytokine. 129:1550432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Sun X, Sun B, Sammani S, Dudek SM,
Belvitch P, Camp SM, Zhang D, Bime C and Garcia JGN: Genetic and
epigenetic regulation of cortactin (CTTN) by inflammatory factors
and mechanical stress in human lung endothelial cells. Biosci Rep.
44:BSR202319342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Kania K, Colella F, Riemen AHK, Wang H,
Howard KA, Aigner T, Dell'Accio F, Capellini TD, Roelofs AJ and De
Bari C: Regulation of Gdf5 expression in joint remodelling, repair
and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 10:1572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhang C, Zhang X, Xia T,
Han J, Song S, Xu C and Chen F: Effects of icariin on the fracture
healing in young and old rats and its mechanism. Pharm Biol.
59:1245–1255. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Stathopoulou MG, Dedoussis GV, Trovas G,
Katsalira A, Hammond N, Deloukas P and Lyritis GP: Low-density
lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 polymorphisms are associated
with bone mineral density in Greek postmenopausal women: An
interaction with calcium intake. J Am Diet Assoc. 110:1078–1083.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Tao Y, Zhou J, Wang Z, Tao H, Bai J, Ge G,
Li W, Zhang W, Hao Y, Yang X and Geng D: Human bone mesenchymal
stem cells-derived exosomal miRNA-361-5p alleviates osteoarthritis
by downregulating DDX20 and inactivating the NF-κB signaling
pathway. Bioorg Chem. 113:1049782021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Qiu B, Xu X, Yi P and Hao Y: Curcumin
reinforces MSC-derived exosomes in attenuating osteoarthritis via
modulating the miR-124/NF-kB and miR-143/ROCK1/TLR9 signalling
pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 24:10855–10865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Lou C, Jiang H, Lin Z, Xia T, Wang W, Lin
C, Zhang Z, Fu H, Iqbal S, Liu H, et al: MiR-146b-5p enriched
bioinspired exosomes derived from fucoidan-directed induction
mesenchymal stem cells protect chondrocytes in osteoarthritis by
targeting TRAF6. J Nanobiotechnol. 21:4862023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Liu Y, Lin L, Zou R, Wen C, Wang Z and Lin
F: MSC-derived exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis
of chondrocytes via lncRNA-KLF3-AS1/miR-206/GIT1 axis in
osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 17:2411–2422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Jammes M, Cassé F, Velot E, Bianchi A,
Audigié F, Contentin R and Galéra P: Pro-inflammatory cytokine
priming and purification method modulate the impact of exosomes
derived from equine bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells on equine
articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 24:141692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Cosenza S, Ruiz M, Toupet K, Jorgensen C
and Noël D: Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and
microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in
osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 7:162142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Qi H, Liu DP, Xiao DW, Tian DC, Su YW and
Jin SF: Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit
mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via
p38, ERK, and Akt pathways. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
55:203–210. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Wang Y, Yu D, Liu Z, Zhou F, Dai J, Wu B,
Zhou J, Heng BC, Zou XH, Ouyang H and Liu H: Exosomes from
embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through
balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular
matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:1892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Jin Z, Ren J and Qi S: Exosomal miR-9-5p
secreted by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviates
osteoarthritis by inhibiting syndecan-1. Cell Tissue Res.
381:99–114. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Chen LQ, Ma S, Yu J, Zuo DC, Yin ZJ, Li
FY, He X, Peng HT, Shi XQ, Huang WJ, et al: Human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-199a-3p inhibits the
MAPK4/NF-κB signaling pathway to relieve osteoarthritis. World J
Stem Cells. 17:1039192025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Sotozawa M, Kumagai K, Ishikawa K, Yamada
S, Inoue Y and Inaba Y: Bevacizumab suppressed degenerative changes
in articular cartilage explants from patients with osteoarthritis
of the knee. J Orthop Surg Res. 18:252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Adam MS, Zhuang H, Ren X, Zhang Y and Zhou
P: The metabolic characteristics and changes of chondrocytes in
vivo and in vitro in osteoarthritis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
15:13935502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Jiang K, Jiang T, Chen Y and Mao X:
Mesenchymal stem Cell-derived exosomes modulate chondrocyte
glutamine metabolism to alleviate osteoarthritis progression.
Mediators Inflamm. 2021:29791242021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Bao C and He C: The role and therapeutic
potential of MSC-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 710:1090022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Zou J, Yang W, Cui W, Li C, Ma C, Ji X,
Hong J, Qu Z, Chen J, Liu A and Wu H: Therapeutic potential and
mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive
materials in tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:142023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Xie L, Chen Z, Liu M, Huang W, Zou F, Ma
X, Tao J, Guo J, Xia X, Lyu F, et al: MSC-Derived exosomes protect
vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and calcification
via the miR-31-5p/ATF6 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:601–614.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Liu Y, Zou R, Wang Z, Wen C, Zhang F and
Lin F: Exosomal KLF3-AS1 from hMSCs promoted cartilage repair and
chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. Biochem J.
475:3629–3638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Zhang Z, Zhao S, Sun Z, Zhai C, Xia J, Wen
C and Zhang Y and Zhang Y: Enhancement of the therapeutic efficacy
of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Cell
Mol Biol Lett. 28:752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Jiang S, Tian G, Yang Z, Gao X, Wang F, Li
J, Tian Z, Huang B, Wei F, Sang X, et al: Enhancement of acellular
cartilage matrix scaffold by Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes to promote osteochondral regeneration. Bioact
Mater. 6:2711–2728. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Tao SC, Yuan T, Zhang YL, Yin WJ, Guo SC
and Zhang CQ: Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human
synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue
regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model.
Theranostics. 7:180–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Wu M, Wu S, Chen W and Li YP: The roles
and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and
cartilage development, homeostasis and disease. Cell Res.
34:101–123. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Sani M, Hosseinie R, Latifi M, Shadi M,
Razmkhah M, Salmannejad M, Parsaei H and Talaei-Khozani T:
Engineered artificial articular cartilage made of decellularized
extracellular matrix by mechanical and IGF-1 stimulation. Biomater
Adv. 139:2130192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Löfvall H, Newbould H, Karsdal MA,
Dziegiel MH, Richter J, Henriksen K and Thudium CS: Osteoclasts
degrade bone and cartilage knee joint compartments through
different resorption processes. Arthritis Res Ther. 20:672018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Ma L, Liu Y, Xu F, Shen R, Wang M, Zhang
Y, Liu C and Zheng G: IL-27-induced, MSC-derived exosomes promote
MMP3 expression through the miR-206/L3MBTL4 axis in synovial
fibroblasts. Altern Ther Health Med. 29:680–688. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Ungsudechachai T, Honsawek S, Jittikoon J
and Udomsinprasert W: Clusterin is associated with systemic and
synovial inflammation in knee osteoarthritis. Cartilage.
13(1_Suppl): S1557S–S1565S. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Vilá S: Inflammation in osteoarthritis. P
R Health Sci J. 36:123–129. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Rosini S, Saviola G, Comini L and Molfetta
L: Mesenchymal cells are a promising-But Still
Unsatisfying-Anti-Inflammatory therapeutic strategy for
osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 19:287–293.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Qiu M, Liu D and Fu Q: MiR-129-5p shuttled
by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves
IL-1β induced osteoarthritis by targeting HMGB1. Life Sci.
269:1189872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Chen YH, Hsieh SC, Chen WY, Li KJ, Wu CH,
Wu PC, Tsai CY and Yu CL: Spontaneous resolution of acute gouty
arthritis is associated with rapid induction of the
anti-inflammatory factors TGFβ1, IL-10 and soluble TNF receptors
and the intracellular cytokine negative regulators CIS and SOCS3.
Ann Rheum Dis. 70:1655–1663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Yang J, Yang L, Tian L, Ji X, Yang L and
Li L: Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P Receptor2/3 axis promotes
inflammatory M1 polarization of bone Marrow-Derived
Monocyte/Macrophagevia G(α)i/o/PI3K/JNK pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 49:1677–1693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Ruiz-Miyazawa KW, Staurengo-Ferrari L,
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Fattori V, Zaninelli TH, Badaro-Garcia S, Borghi
SM, Andrade KC, Clemente-Napimoga JT, Alves-Filho JC, et al:
15d-PGJ2-loaded nanocapsules ameliorate experimental
gout arthritis by reducing pain and inflammation in a
PPAR-gamma-sensitive manner in mice. Sci Rep. 8:139792018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
213
|
Hao F, Wang Q, Liu L, Wu LB, Cai RL, Sang
JJ, Hu J, Wang J, Yu Q, He L, et al: Effect of moxibustion on
autophagy and the inflammatory response of synovial cells in
rheumatoid arthritis model rat. J Tradit Chin Med. 42:73–82.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Xu X, Liang Y, Li X, Ouyang K, Wang M, Cao
T, Li W, Liu J, Xiong J, Li B, et al: Exosome-mediated delivery of
kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal
stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials.
269:1205392021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Bruckner S, Capria VM, Zeno B,
Leblebicioglu B, Goyal K, Vasileff WK, Awan H, Willis WL, Ganesan
LP and Jarjour WN: The therapeutic effects of gingival mesenchymal
stem cells and their exosomes in a chimeric model of rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 25:2112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Mathiessen A and Conaghan PG: Synovitis in
osteoarthritis: Current understanding with therapeutic
implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Wang Y, Hou L, Yuan X, Xu N, Zhao S, Yang
L and Zhang N: LncRNA NEAT1 targets Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
rheumatoid arthritis via the miR-410-3p/YY1 Axis. Front Immunol.
11:19752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Qiu M, Xie Y, Tan G, Wang X, Huang P and
Hong L: Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-485-3p
relieves cartilage damage in osteoarthritis by targeting the
NRP1-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway: Exosomal miR-485-3p relieves
cartilage damage. Heliyon. 10:e240422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Ichise Y, Saegusa J, Tanaka-Natsui S, Naka
I, Hayashi S, Kuroda R and Morinobu A: Soluble CD14 induces
pro-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synovial cells via toll-like receptor 4. Cells. 9:16892020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Qi H, Shen E, Shu X, Liu D and Wu C:
ERK-estrogen receptor α signaling plays a role in the process of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protecting
against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Orthop Surg Res.
18:2502023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
221
|
Wei Y, Ma Z, Li Z, Kang J, Liao T, Jie L,
Liu D, Shi L, Wang P, Mao J and Wu P: Gentiopicroside ameliorates
synovial inflammation and fibrosis in KOA rats by modulating the
HMGB1-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling axis. Int Immunopharmacol.
147:1139732025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Meng S, Zhang X, Yu Y, Tong M, Yuan Y, Cao
Y, Zhang W, Shi X and Liu K: New-QiangGuYin-containing serum
inhibits osteoclast-Derived exosome secretion and down-regulates
notum to promote osteoblast differentiation. Adv Biol (Weinh).
9:e24001662025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
223
|
Liu Z, Jian H, Peng Z, Xiong S and Zhang
Z: Association between dietary inflammatory index and osteoporosis
in the US population: Evidence from NHANES 2003-2010. Front Nutr.
12:15081272025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Huang S, Wa Q, Pan J, Peng X, Ren D, Huang
Y, Chen X and Tang Y: Downregulation of miR-141-3p promotes bone
metastasis via activating NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 36:1732017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Yang S, Zhang W, Cai M, Zhang Y, Jin F,
Yan S, Baloch Z, Fang Z, Xue S, Tang R, et al: Suppression of bone
resorption by miR-141 in aged rhesus monkeys. J Bone Miner Res.
33:1799–1812. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Ye Y, Li SL, Ma YY, Diao YJ, Yang L, Su
MQ, Li Z, Ji Y, Wang J, Lei L, et al: Exosomal miR-141-3p regulates
osteoblast activity to promote the osteoblastic metastasis of
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 8:94834–94849. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Longfei H, Wenyuan H, Weihua F, Peng P,
Sun L, Kun L, Mincong H, Fan Y, Wei H and Qiushi W: Exosomes in
cartilage microenvironment regulation and cartilage repair. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 13:14604162025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Helaehil JV, Huang B, Bartolo P,
Santamaria M Jr and Caetano GF: Bone regeneration: The influence of
composite HA/TCP scaffolds and electrical stimulation on TGF/BMP
and RANK/RANKL/OPG pathways. Injury. 56:1121582025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Hu Z, Deshmukh M, Jarneborn A, Bollmann M,
Corciulo C, Kopparapu PK, Ali A, Svensson MND, Engdahl C, Pullerits
R, et al: Combination treatment with anti-RANKL and antibiotics for
preventing joint destruction in septic arthritis. JCI Insight.
10:e1849542025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Kurihara T, Shimamura M, Etani Y, Noguchi
T, Fukuda Y, Ochiai N, Goshima A, Miura T, Hirao M, Sugimoto A, et
al: RANKL-derived peptide MHP1-AcN attenuates ovariectomy-induced
osteoporosis by targeting RANK and TNFR1 in mice. Bone.
194:1174402025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Pei B, Teng Y, Dong D and Liu L:
OPG/RANK/RANKL Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in rheumatoid
arthritis: Associations with disease susceptibility, bone mineral
density, and clinical manifestations in a Chinese Han population.
Int J Gen Med. 18:815–824. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Liao T, Kang J, Ma Z, Jie L, Feng M, Liu
D, Mao J, Wang P and Xing R: Total glucosides of white paeony
capsule alleviate articular cartilage degeneration and aberrant
subchondral bone remodeling in knee osteoarthritis. Phytother Res.
39:1758–1775. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Li J, Ding Z, Li Y, Wang W, Wang J, Yu H,
Liu A, Miao J, Chen S, Wu T and Cao Y: BMSCs-derived exosomes
ameliorate pain via abrogation of aberrant nerve invasion in
subchondral bone in lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis. J Orthop
Res. 38:670–679. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
234
|
Wei Z, Zhou J, Shen J, Sun D, Gao T, Liu
Q, Wu H, Wang X, Wang S, Xiao S, et al: Osteostaticytes: A novel
osteoclast subset couples bone resorption and bone formation. J
Orthop Translat. 47:144–160. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Wan Y, Nemoto YL, Oikawa T, Takano K,
Fujiwara TK, Tsujita K and Itoh T: Mechanical control of osteoclast
fusion by Membrane-cortex attachment and BAR proteins. J Cell Biol.
224:e2024110242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Shao Y, Zhang H, Guan H, Wu C, Qi W, Yang
L, Yin J, Zhang H, Liu L, Lu Y, et al: PDZK1 protects against
mechanical overload-induced chondrocyte senescence and
osteoarthritis by targeting mitochondrial function. Bone Res.
12:412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Chen N, Diao CY, Huang X, Tan WX, Chen YB,
Qian XY, Gao J and Zhao DB: RhoA promotes synovial proliferation
and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis through Wnt/PCP pathway.
Mediators Inflamm. 2023:50570092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Zhang W, Wu X, Li W, Zhang H, Wang Y, Xu
J, Li W, Qin Y, Wu Z, Ge G, et al: Pinosylvin inhibits inflammatory
and osteoclastogenesis via NLRP3 inflammasome. Adv Sci (Weinh).
e015322025. View Article : Google Scholar : Epub ahead of
print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Cafferata EA, Monasterio G, Castillo F,
Carvajal P, Flores G, Díaz W, Fuentes AD and Vernal R:
Overexpression of MMPs, cytokines, and RANKL/OPG in
temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and their association with
joint pain, mouth opening, and bone degeneration: A preliminary
report. Oral Dis. 27:970–980. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
240
|
Wu P, Jiao F, Huang H, Liu D, Tang W,
Liang J and Chen W: Morinda officinalis polysaccharide enable
suppression of osteoclastic differentiation by exosomes derived
from rat mesenchymal stem cells. Pharm Biol. 60:1303–1316. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Gostage J, Kostenuik P, Goljanek-Whysall
K, Bellantuono I, McCloskey E and Bonnet N: Extra-osseous roles of
the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis with a focus on skeletal muscle. Curr
Osteoporos Rep. 22:632–650. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Hu Y, Wang Z, Fan C, Gao P, Wang W, Xie Y
and Xu Q: Human gingival mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
cross-regulate the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signalling pathways in
the periodontal inflammation microenvironment. J Clin Periodontol.
50:796–806. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Li L, Huang R, Gao X, Li Z, Lin Y, Zhang
H, Jiang Y and Fan P: Prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with
knee osteoarthritis awaiting total knee arthroplasty is similar to
that in the general population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
26:2172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Fischer V and Haffner-Luntzer M:
Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 123:14–21. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
245
|
Li Y, Ling J and Jiang Q: Inflammasomes in
alveolar bone loss. Front Immunol. 12:6910132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
El-Ali Z, El-Kassas G, Ziade FM, Shivappa
N, Hébert JR, Zmerly H and Bissar N: Evaluation of circulating
levels of Interleukin-10 and Interleukin-16 and dietary
inflammatory index in Lebanese knee osteoarthritis patients.
Heliyon. 7:e075512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Piao X, Kim JW, Hyun M, Wang Z, Park SG,
Cho IA, Ryu JH, Lee BN, Song JH and Koh JT: Boeravinone B, a
natural rotenoid, inhibits osteoclast differentiation through
modulating NF-κB, MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. BMB Rep.
56:545–550. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Zheng X, Qiu J, Gao N, Jiang T, Li Z,
Zhang W, Gong Y, Hong Z and Hong H: Paroxetine attenuates
chondrocyte pyroptosis and inhibits osteoclast formation by
inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation to delay osteoarthritis
progression. Drug Des Devel Ther. 17:2383–2399. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
249
|
Xu J, Jiao W, Wu DB, Yu JH, Liu LJ, Zhang
MY and Chen GX: Yishen Tongbi decoction attenuates inflammation and
bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating
JAK/STAT3/SOCS3 pathway. Front Immunol. 15:13818022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Ma J, Kitaura H, Ogawa S, Ohori F, Noguchi
T, Marahleh A, Nara Y, Pramusita A, Kinjo R, Kanou K, et al:
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation
and orthodontic tooth movement through GPR120. Front Immunol.
13:9296902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
251
|
Yang J, Shuai J, Siow L, Lu J, Sun M, An
W, Yu M, Wang B and Chen Q: MicroRNA-146a-loaded magnesium silicate
nanospheres promote bone regeneration in an inflammatory
microenvironment. Bone Res. 12:22024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Hua T, Yang M, Song H, Kong E, Deng M, Li
Y, Li J, Liu Z, Fu H, Wang Y and Yuan H: Huc-MSCs-derived exosomes
attenuate inflammatory pain by regulating microglia pyroptosis and
autophagy via the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis. J Nanobiotechnology.
20:3242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Li XY, Zhang W, Chen J, Yamamoto KJ, Smith
JD, Liu F, Garcia MA, Kim SH, Patel RJ, Dubois N, et al:
AAV9-delivered miR-146a Reprograms osteoimmune microenvironment via
dual suppression of TRAF6/NF-κB axis in postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Nat Metab. 37:857–872. 2025.
|
|
254
|
Chen J, Liu F, Yamamoto K, Smith JD, Wang
YC, Zhang W, Garcia MA, Patel R and Tanaka H: miR-21 drives
osteoclastogenesis via PDCD4-mediated control of IKKβ
Phosphorylation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Cell Rep.
42:103541–103556. 2025.
|
|
255
|
Zhang J, Rong Y, Luo C and Cui W: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent
osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization.
Aging (Albany NY). 12:25138–25152. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Han Y, An M, Yang L, Li L, Rao S and Cheng
Y: Effect of acid or base interventions on bone health: A
systematic review, Meta-analysis, and Meta-regression. Adv Nutr.
12:1540–1557. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
He LH, Liu M, He Y, Xiao E, Zhao L, Zhang
T, Yang HQ and Zhang Y: TRPV1 deletion impaired fracture healing
and inhibited osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation. Sci Rep.
7:423852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Gong S, Ma J, Tian A, Lang S, Luo Z and Ma
X: Effects and mechanisms of microenvironmental acidosis on
osteoclast biology. Biosci Trends. 16:58–72. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Disthabanchong S, Radinahamed P,
Stitchantrakul W, Hongeng S and Rajatanavin R: Chronic metabolic
acidosis alters osteoblast differentiation from human mesenchymal
stem cells. Kidney Int. 71:201–209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
260
|
Xu Y, Lu Z, Ling Y, Hou R, Tao J, Deng G,
Xu X, Chen X, Ruan J, Zhang Y, et al: Acid sensor ASIC1a induces
synovial fibroblast proliferation via Wnt/beta-catenin/c-Myc
pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol.
113:1093282022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
261
|
Chan EL, MacDonald D, Ho SC and
Swaminathan R: Potassium intake and urinary calcium excretion in
healthy subjects. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 19:36–38.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Lin L, Luo P, Yang M, Wang J, Hou W and Xu
P: Causal relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A
two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13:10112462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Wang Y, Sun L, Dong Z, Zhang T, Wang L,
Cao Y, Xu H, Liu C and Chen B: Targeted inhibition of ferroptosis
in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by engineered exosomes
alleviates bone loss in smoking-related osteoporosis. Mater Today
Bio. 31:1015012025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Zhang D, Xiao W, Liu C, Wang Z, Liu Y, Yu
Y, Jian C and Yu A: Exosomes derived from adipose stem cells
enhance bone fracture healing via the activation of the
Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 24:48522023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
265
|
Sun W, Qu S, Ji M, Sun Y and Hu B: BMP-7
modified exosomes derived from synovial mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate osteoarthritis by M2 polarization of macrophages.
Heliyon. 9:e199342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Li X, Fang S, Wang S, Xie Y, Xia Y, Wang
P, Hao Z, Xu S and Zhang YJ: Hypoxia preconditioning of adipose
stem cell-derived exosomes loaded in gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)
promote type H angiogenesis and osteoporotic fracture repair.
Nanobiotechnology. 22:1122024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
267
|
Lee AE, Choi JG, Shi SH, He P, Zhang QZ
and Le AD: DPSC-derived extracellular vesicles promote rat jawbone
regeneration. J Dent Res. 102:313–321. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
268
|
Luo D, Xie W, He X, Zhou X, Ye P and Wang
P: Exosomal miR-590-3p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells promotes osteoblast differentiation and osteogenesis by
targeting TGFBR1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 61:46–58. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
269
|
Zhang Y, Cao X, Li P, Fan Y, Zhang L, Ma
X, Sun R, Liu Y and Li W: microRNA-935-modified bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes enhance osteoblast
proliferation and differentiation in osteoporotic rats. Life Sci.
272:1192042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Marini F, Giusti F, Palmini G and Brandi
ML: Role of Wnt signaling and sclerostin in bone and as therapeutic
targets in skeletal disorders. Osteoporos Int. 34:213–238. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
271
|
Komori T: Bone development by Hedgehog and
Wnt signaling, Runx2, and Sp7. J Bone Miner Metab. 43:33–38. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
272
|
Samman WA, Mosalam EM, Saif DS, Abdallah
MS, Zidan AA, Sallam AS, Abdelsattar S, Khalil FO, Elashkar AE,
Mohamed SM, et al: Deciphering the role of Wnt/β-catenin and
miR-214 in knee osteoarthritis: Molecular and clinical insights.
Front Pharmacol. 16:15076932025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
273
|
Danz JC and Degen M: Selective modulation
of the bone remodeling regulatory system through orthodontic tooth
movement-a review. Front Oral Health. 6:14727112025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Coombs CV, Greeves JP, Young CD, Irving
AS, Eisenhauer A, Kolevica A, Heuser A, Tang JCY, Fraser WD and
O'Leary TJ: The effect of calcium supplementation on bone calcium
balance and calcium and bone metabolism during load carriage in
women: A randomized controlled crossover trial. J Bone Miner Res.
13:zjaf0042025.
|
|
275
|
Rummler M, Ziouti F, Snyder L, Zimmermann
EA, Lynch M, Donnelly E, Wagermaier W, Jundt F and Willie BM: Bone
mechanical properties were altered in a mouse model of multiple
myeloma bone disease. Biomater Adv. 166:2140472025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
276
|
Cai G, Lu Y, Zhong W, Wang T, Li Y, Ruan
X, Chen H, Sun L, Guan Z, Li G, et al: Piezo1-mediated M2
macrophage mechanotransduction enhances bone formation through
secretion and activation of transforming growth factor-β1. Cell
Prolif. 56:e134402023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
277
|
Zhang J, Tong Y, Liu Y, Lin M, Xiao Y and
Liu C: Mechanical loading attenuated negative effects of nucleotide
analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitor TDF on bone repair via
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bone. 161:1164492022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
278
|
Hiasa M, Endo I and Matsumoto T: Bone-fat
linkage via interleukin-11 in response to mechanical loading. J
Bone Miner Metab. 42:447–454. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Bullock WA, Pavalko FM and Robling AG:
Osteocytes and mechanical loading: The Wnt connection. Orthod
Craniofac Res. 22(Suppl 1): S175–S179. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
280
|
Simic MK, Mohanty ST, Xiao Y, Cheng TL,
Taylor VE, Charlat O, Croucher PI and McDonald MM: Multi-Targeting
DKK1 and LRP6 prevents bone loss and improves fracture resistance
in multiple myeloma. J Bone Miner Res. 38:814–828. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Xun J, Li C, Liu M, Mei Y, Zhou Q, Wu B,
Xie F, Liu Y and Dai R: Serum exosomes from young rats improve the
reduced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in aged rats with
osteoporosis after fatigue loading in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12:4242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Qi J, Zhang R and Wang Y: Exosomal
miR-21-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting PIK3R1. J
Cell Mol Med. 25:11016–11030. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Liu W, Li L, Rong Y, Qian D, Chen J, Zhou
Z, Luo Y, Jiang D, Cheng L, Zhao S, et al: Hypoxic mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer
of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 103:196–212. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
284
|
Neogi T and Colloca L: Placebo effects in
osteoarthritis: Implications for treatment and drug development.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 19:613–626. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Olansen J, Dyke JP and Aaron RK: Is
osteoarthritis a vascular disease? Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
29:1132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Zaussinger M, Schwaiger K, Schwarzbauer J,
Bachleitner K, Holzbauer M, Ehebruster G and Schmidt M:
Three-dimensional planning for vascularized bone grafts:
Implementation and surgical application for complex bone
reconstruction in the hand and forearm. J Clin Med. 14:4402025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Song LL, Tang YP, Qu YQ, Yun YX, Zhang RL,
Wang CR, Wong VKW, Wang HM, Liu MH, Qu LQ, et al: Exosomal delivery
of rapamycin modulates Blood-brain barrier penetration and VEGF
axis in glioblastoma. J Control Release. 381:1136052025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Anderson JD, Johansson HJ, Graham CS,
Vesterlund M, Pham MT, Bramlett CS, Montgomery EN, Mellema MS,
Bardini RL, Contreras Z, et al: Comprehensive proteomic analysis of
mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reveals modulation of angiogenesis
via nuclear Factor-KappaB signaling. Stem Cells. 34:601–613. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
289
|
Vyas KS, Kaufman J, Munavalli GS,
Robertson K, Behfar A and Wyles SP: Exosomes: The latest in
regenerative aesthetics. Regen Med. 18:181–194. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
290
|
Shen K, Duan A, Cheng J, Yuan T, Zhou J,
Song H, Chen Z, Wan B, Liu J, Zhang X, et al: Exosomes derived from
hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells laden in a silk
hydrogel promote cartilage regeneration via the miR-205-5p/PTEN/AKT
pathway. Acta Biomater. 143:173–188. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Wang Y, Kong Y, Du J, Qi L, Liu M, Xie S,
Hao J, Li M, Cao S, Cui H, et al: Injection of human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells exosomes for the treatment of knee
osteoarthritis: From preclinical to clinical research. J Transl
Med. 23:6412025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
Rajabloo Y, Al-Asady AM, Avan A, Khazaei
M, Ryzhikov M and Hassanian SM: Unlocking therapeutic potential:
Mesenchymal stem Cells-derived exosomes in IUA treatment, current
status and perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 31:1663–1672. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Infante A and Rodríguez CI: Osteogenesis
and aging: Lessons from mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
9:2442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Liu S, Liu D, Chen C, Hamamura K,
Moshaverinia A, Yang R, Liu Y, Jin Y and Shi S: MSC transplantation
improves osteopenia via epigenetic regulation of Notch signaling in
lupus. Cell Metab. 22:606–618. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
295
|
Zhang L, Jiao G, Ren S, Zhang X, Li C, Wu
W, Wang H, Liu H, Zhou H and Chen Y: Exosomes from bone marrow mes
enchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through the promotion
of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of nonunion. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 11:382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
296
|
Chen S, Tang Y, Liu Y, Zhang P, Lv L,
Zhang X, Jia L and Zhou Y: Exosomes derived from
miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote
bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 52:e126692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
297
|
Zhou QF, Cai YZ and Lin XJ: The dual
character of exosomes in osteoarthritis: Antagonists and
therapeutic agents. Acta Biomater. 105:15–25. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Chen P, Zheng L, Wang Y, Tao M, Xie Z, Xia
C, Gu C, Chen J, Qiu P, Mei S, et al: Desktop-stereolithography 3D
printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal
stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration.
Theranostics. 9:2439–2459. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
299
|
Liu X, Yang Y, Li Y, Niu X, Zhao B, Wang
Y, Bao C, Xie Z, Lin Q and Zhu L: Integration of stem cell-derived
exosomes with in situ hydrogel glue as a promising tissue patch for
articular cartilage regeneration. Nanoscale. 9:4430–4438. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Li W, Liu Y, Zhang P, Tang Y, Zhou M,
Jiang W, Zhang X, Wu G and Zhou Y: Tissue-engineered bone
immobilized with human adipose stem cells-derived exosomes promotes
bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 10:5240–5254. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
301
|
Ni Z, Zhou S, Li S, Kuang L, Chen H, Luo
X, Ouyang J, He M, Du X and Chen L: Exosomes: Roles and therapeutic
potential in osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 8:252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
302
|
Rudiansyah M, El-Sehrawy AA, Ahmad I,
Terefe EM, Abdelbasset WK, Bokov DO, Salazar A, Rizaev JA, Muthanna
FMS and Shalaby MN: Osteoporosis treatment by mesenchymal
stromal/stem cells and their exosomes: Emphasis on signaling
pathways and mechanisms. Life Sci. 306:1207172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
303
|
Zhang L, Wang Q, Su H and Cheng J:
Exosomes from adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate
diabetic osteoporosis in rats through suppressing NLRP3
inflammasome activation in osteoclasts. J Biosci Bioeng.
131:671–678. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
304
|
Liang Y, Xu X, Li X, Xiong J, Li B, Duan
L, Wang D and Xia J: Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by
engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS
Appl Mater Interfaces. 12:36938–36947. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
He L, He T, Xing J, Zhou Q, Fan L, Liu C,
Chen Y, Wu D, Tian Z, Liu B and Rong L: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieveknee
osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 11:2762020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
306
|
Lu M, Lou A, Gao J, Li S, He L, Fan W and
Zhao L: Quercetin-primed MSC exosomes synergistically attenuate
osteoarthritis progression. J Orthop Surg Res. 20:3732025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
307
|
Chen Q, Lin Y, Li W, Zhang X, Asahara H,
Zheng M, Zhang YC, Xie T, Sun LY, Chang J, et al: Engineered
cartilage-targeting extracellular vesicles deliver
anti-inflammatory RNAi therapy for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci
Transl Med. 17:eabn02592025.
|
|
308
|
Zhang Y, Kirkland JL, Chen W, Qin L, Chen
X, Yang H, Zhang T, Lin JH, Zhang ZM, Cao X, et al: Systemically
administered exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells mitigate
bone loss by targeting osteogenesis in postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Nat Commun. 15:32182024.
|
|
309
|
Yoo J, Lee SK, Lim M, Sheen D, Choi EH and
Kim SA: Exosomal amyloid A and lymphatic vessel endothelial
hyaluronic acid receptor-1 proteins are associated with disease
activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:1192017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
310
|
Zhao Y and Xu J: Synovial fluid-derived
exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as biomarker for the different stages of
osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 42:2865–2872. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
311
|
Zhang Y, Cai F, Liu J, Chang H, Liu L,
Yang A and Liu X: Transfer RNA-derived fragments as potential
exosome tRNA-derived fragment biomarkers for osteoporosis. Int J
Rheum Dis. 21:1659–1669. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
312
|
Wang L, Wang C, Jia X and Yu J:
Circulating exosomal miR-17 inhibits the induction of regulatory T
cells via suppressing TGFBR II expression in rheumatoid arthritis.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:1754–1763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Xia B, Di Chen, Zhang J, Hu S, Jin H and
Tong P: Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: A review of molecular
mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int. 95:495–505. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
314
|
Zhang E, Chen L, Wang YF, Smith JR,
Yamamoto HE and Johnson SK: Cryopreservation of exosomes with
enhanced bioactivity using liquid nitrogen and novel
cryoprotectants. Nat Commun. 15:1238–1256. 2024.
|
|
315
|
Stevenson J; Medical advisory council of
the British Menopause Society: Prevention and treatment of
osteoporosis in women. Post Reprod Health. 29:11–14. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
316
|
Galanis A, Dimopoulou S, Karampinas P,
Vavourakis M, Papagrigorakis E, Sakellariou E, Karampitianis S,
Zachariou D, Theodora M, Antsaklis P, et al: The correlation
between transient osteoporosis of the hip and pregnancy: A review.
Medicine (Baltimore). 102:e354752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Gehrke B, Alves Coelho MC, Brasil d'Alva C
and Madeira M: Long-term consequences of osteoporosis therapy with
bisphosphonates. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 68:e2203342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
318
|
Yu S, Chen H and Gao B: Potential
therapeutic effects of exosomes in regenerative endodontics. Arch
Oral Biol. 120:1049462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
319
|
Munagala R, Aqil F, Jeyabalan J and Gupta
RC: Bovine Milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett.
371:48–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
320
|
Zhang S, Wong KL, Ren X, Teo KYW, Afizah
H, Choo ABH, Lai RC, Lim SK, Hui JHP and Toh WS: Mesenchymal stem
cell exosomes promote functional osteochondral repair in a
clinically relevant porcine model. Am J Sports Med. 50:788–800.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|