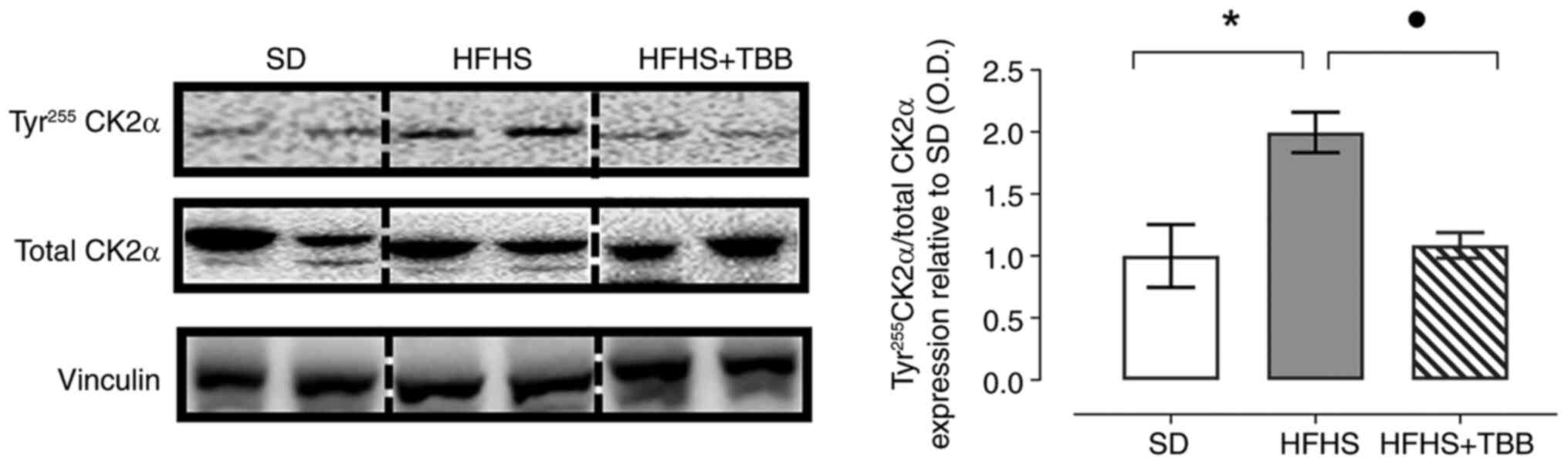
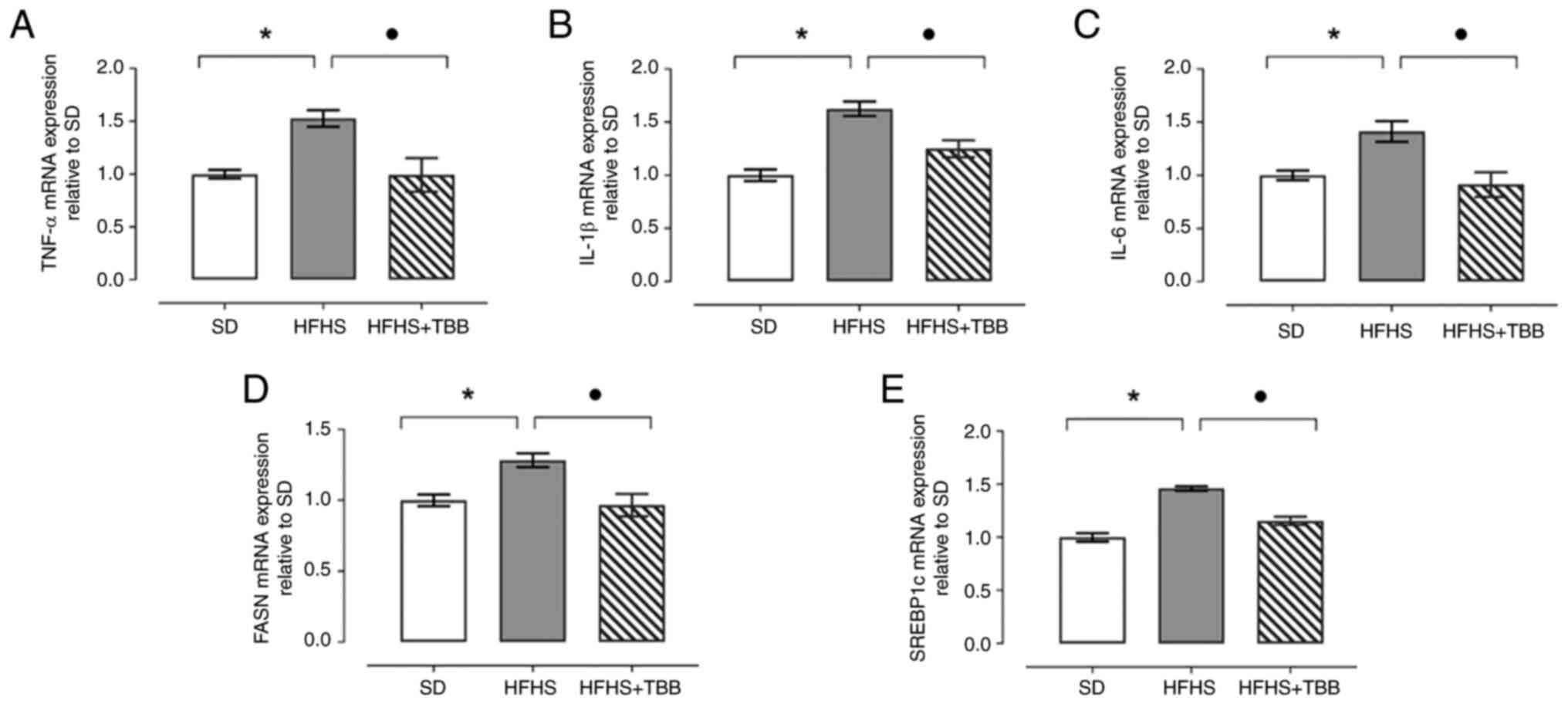
|
1
|
Budreviciute A, Damiati S, Sabir DK, Onder
K, Schuller-Goetzburg P, Plakys G, Katileviciute A, Khoja S and
Kodzius R: Management and prevention strategies for
non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and their risk factors. Front
Public Health. 8:5741112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Christ A and Latz E: The western lifestyle
has lasting effects on metaflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 19:267–268.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malesza IJ, Malesza M, Walkowiak J, Mussin
N, Walkowiak D, Aringazina R, Bartkowiak-Wieczorek J and Mądry E:
High-fat, western-style diet, systemic inflammation, and gut
microbiota: A narrative review. Cells. 10:31642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hotamisligil GS: Inflammation,
metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. 542:177–185.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ramos-Lopez O, Martinez-Urbistondo D,
Vargas-Nuñez JA and Martinez JA: The role of nutrition on
meta-inflammation: Insights and potential targets in communicable
and chronic disease management. Curr Obes Rep. 11:305–335. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van de Vyver M: Immunology of chronic
low-grade inflammation: Relationship with metabolic function. J
Endocrinol. 257:e2202712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YS and Olefsky J: Chronic tissue
inflammation and metabolic disease. Genes Dev. 35:307–328. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Caputo T, Gilardi F and Desvergne B: From
chronic overnutrition to metaflammation and insulin resistance:
Adipose tissue and liver contributions. FEBS Lett. 591:3061–3088.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nandipati KC, Subramanian S and Agrawal
DK: Protein kinases: Mechanisms and downstream targets in
inflammation-mediated obesity and insulin resistance. Mol Cell
Biochem. 426:27–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Collotta D, Hull W, Mastrocola R, Chiazza
F, Cento AS, Murphy C, Verta R, Alves GF, Gaudioso G, Fava F, et
al: Baricitinib counteracts metaflammation, thus protecting against
diet-induced metabolic abnormalities in mice. Mol Metab.
39:1010092020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Bako HY, Ibrahim MA, Isah MS and Ibrahim
S: Inhibition of JAK-STAT and NF-κB signalling systems could be a
novel therapeutic target against insulin resistance and type 2
diabetes. Life Sci. 239:1170452019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Borgo C, D'Amore C, Sarno S, Salvi M and
Ruzzene M: Protein kinase CK2: A potential therapeutic target for
diverse human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:1832021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roffey SE and Litchfield DW: CK2
regulation: Perspectives in 2021. Biomedicines. 9:13612021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barroga CF, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM and
Verma IM: Constitutive phosphorylation of IκBα by casein kinase II
(NF-κB/Rel/transcription/PEST/protein purification). Proc Natl
Acad. 92:7637–7641. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McElhinny JA, Trushin SA, Bren GD, Chester
N and Paya CV: Casein kinase II phosphorylates I kappa B alpha at
S-283, S-289, S-293, and T-291 and is required for its degradation.
Mol Cell Biol. 16:899–906. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin R, Beauparlant P, Makris C, Meloche S
and Hiscott J: Phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha in the C-terminal
PEST domain by casein kinase II affects intrinsic protein
stability. Mol Cell Biol. 16:1401–1409. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heilker R, Freuler F, Pulfer R, Di Padova
F and Eder J: All three IkappaB isoforms and most Rel family
members are stably associated with the IkappaB kinase 1/2 complex.
Eur J Biochem. 259:253–261. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chantôme A, Pance A, Gauthier N, Vandroux
D, Chenu J, Solary E, Jeannin JF and Reveneau S: Casein kinase
II-mediated phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit enhances
inducible nitric-oxide synthase gene transcription in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 279:23953–23960. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Manni S, Brancalion A, Mandato E, Tubi LQ,
Colpo A, Pizzi M, Cappellesso R, Zaffino F, Di Maggio SA, Cabrelle
A, et al: Protein kinase CK2 inhibition down modulates the NF-κB
and STAT3 survival pathways, enhances the cellular proteotoxic
stress and synergistically boosts the cytotoxic effect of
bortezomib on multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma cells. PLoS
One. 8:e752802013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lan YC, Wang YH, Chen HH, Lo SF, Chen SY
and Tsai FJ: Effects of casein kinase 2 alpha 1 gene expression on
mice liver susceptible to type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Int
J Med Sci. 17:13–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shinoda K, Ohyama K, Hasegawa Y, Chang HY,
Ogura M, Sato A, Hong H, Hosono T, Sharp LZ, Scheel DW, et al:
Phosphoproteomics identifies CK2 as a negative regulator of beige
adipocyte thermogenesis and energy expenditure. Cell Metab.
22:997–1008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Borgo C, Milan G, Favaretto F, Stasi F,
Fabris R, Salizzato V, Cesaro L, Belligoli A, Sanna M, Foletto M,
et al: CK2 modulates adipocyte insulin-signaling and is
up-regulated in human obesity. Sci Rep. 7:175692017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Buchwald LM, Neess D, Hansen D, Doktor TK,
Ramesh V, Steffensen LB, Blagoev B, Litchfield DW, Andresen BS,
Ravnskjaer K, et al: Body weight control via protein kinase CK2:
Diet-induced obesity counteracted by pharmacological targeting.
Metabolism. 162:1560602025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sanna M, Borgo C, Compagnin C, Favaretto
F, Vindigni V, Trento M, Bettini S, Comin A, Belligoli A, Rugge M,
et al: White adipose tissue expansion in multiple symmetric
lipomatosis is associated with upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:79332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Varghese Z and Ruan XZ: The
molecular pathogenic role of inflammatory stress in dysregulation
of lipid homeostasis and hepatic steatosis. Genes Dis. 1:106–112.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ke B, Zhao Z, Ye X, Gao Z, Manganiello V,
Wu B and Ye J: Inactivation of NF-κB p65 (RelA) in liver improves
insulin sensitivity and inhibits cAMP/PKA pathway. Diabetes.
64:3355–3362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai D, Yuan M, Frantz DF, Melendez PA,
Hansen L, Lee J and Shoelson SE: Local and systemic insulin
resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and
NF-kappaB. Nat Med. 11:183–190. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang H, Lee SH, Sousa-Lima I, Kim SS,
Hwang WM, Dagon Y, Yang WM, Cho S, Kang MC, Seo JA, et al:
Rho-kinase/AMPK axis regulates hepatic lipogenesis during
overnutrition. J Clin Invest. 128:5335–5350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S,
Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U,
Emerson M, et al: Reporting animal research: Explanation and
elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol.
18:e30004112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Directive 2010/63/EU of the European
parliament and of the council of 22 september 2010 on the
protection of animals used for scientific purposes (Text with EEA
relevance). 2010.
|
|
31
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
32
|
Collino M, Mastrocola R, Nigro D, Chiazza
F, Aragno M, D'Antona G and Minetto MA: Variability in myosteatosis
and insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet in mouse skeletal
muscles. Biomed Res Int. 2014:5696232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xia B, Zhu R, Zhang H, Chen B, Liu Y, Dai
X, Ye Z, Zhao D, Mo F, Gao S, et al: Lycopene improves bone quality
and regulates AGE/RAGE/NF-кB signaling pathway in high-fat
diet-induced obese mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:36970672022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chiazza F, Couturier-Maillard A, Benetti
E, Mastrocola R, Nigro D, Cutrin JC, Serpe L, Aragno M, Fantozzi R,
Ryffel B, et al: Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome to reduce
diet-induced metabolic abnormalities in mice. Mol Med.
21:1025–1037. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang J, Chen Z, Li J, Chen Q, Li J, Gong
W, Huang J, Liu P and Huang H: Protein kinase CK2α catalytic
subunit ameliorates diabetic renal inflammatory fibrosis via NF-κB
signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 132:102–117. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Z, Chen Q, Huang J, Gong W, Zou Y,
Zhang L, Liu P and Huang H: CK2α promotes advanced glycation end
products-induced expressions of fibronectin and intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 via activating MRTF-A in glomerular mesangial
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 148:41–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Brehme H, Kirschstein T, Schulz R and
Köhling R: In vivo treatment with the casein kinase 2 inhibitor
4,5,6,7-tetrabromotriazole augments the slow afterhyperpolarizing
potential and prevents acute epileptiform activity. Epilepsia.
55:175–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
National Centre for the Replacement
Refinement and Reduction of Aninals in Research: Microsampling.
https://nc3rs.org.uk/3rs-resources/microsampling#microsampling-study-designs.
Accessed June 17, 2025
|
|
39
|
National Institutes of Health (NIH);
Animal Research Advisory Committee (ARAC); National Institutes of
Health (NIH); Animal Research Advisory Committee (ARAC): Guidelines
for Survival Blood Collection in Mice and Rats. https://oacu.oir.nih.gov/system/files/media/file/2022-12/b2-Survival_Blood_Collection_Mice_Rats.pdf.
Accessed June 17, 2025
|
|
40
|
University of Kentucky: Guidelines for
Blood Collection in Laboratory Animals. https://research.uky.edu/division-laboratory-animal-resources/guidelines-blood-collection-laboratory-animals.
Accessed June 17, 2025
|
|
41
|
Swiss Animal Welfare Officer Network
(AWON): Guideline on blood collection techniques in rodents and
rabbits. https://portal-cdn.scnat.ch/asset/aa5ba763-49be-5603-b964-c59d0cbd932f/AWON%20Blood%20coll%20Guideline%20Final%20Publ.pdf?b=eb714836-a777-530c-89db-69ff16d3774e&v=313fdd66-5ae2-5085-8364-bd2045117053_0&s=Mf4vKYyAmFEoqPTJTfB7z0RwOdBNqZWEXv_XpVGu6jl8wJ0B_Mjy-0ga8ZrOJX0zLnOPTg1yKb7h9Gh9Cx_oLPBsZ9Taub11Xb7QSBMar0KPHPp59VkUMj99iiOCdRDeZ124RZBfS0ceD0IuZLR6SNV6S2El4DGP-d-AIomqFEQ.
Accessed June 17, 2025
|
|
42
|
O'Donnell KL, Knopick PL, Larsen R, Sarkar
S, Nilles ML and Bradley DS: Difference in strain pathogenicity of
septicemic yersinia pestis infection in a TLR2−/− mouse
model. Infect Immun. 88:e00792–19. 2020.
|
|
43
|
Kovalski V, Prestes AP, Oliveira JG, Alves
GF, Colarites DF, Mattos JE, Sordi R, Vellosa JC and Fernandes D:
Protective role of cGMP in early sepsis. Eur J Pharmacol.
807:174–181. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Aimaretti E, Porchietto E, Mantegazza G,
Gargari G, Collotta D, Einaudi G, Ferreira Alves G, Marzani E,
Algeri A, Dal Bello F, et al: Anti-glycation properties of
zinc-enriched Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) contribute to
prevention of metaflammation in a diet-induced obese mouse model.
Nutrients. 16:5522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fornelli C, Sofia Cento A, Nevi L,
Mastrocola R, Ferreira Alves G, Caretti G, Collino M and Penna F:
The BET inhibitor JQ1 targets fat metabolism and counteracts
obesity. J Adv Res. 68:403–413. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Jiang L, Wang Q, Yu Y, Zhao F, Huang P,
Zeng R, Qi RZ, Li W and Liu Y: Leptin contributes to the adaptive
responses of mice to high-fat diet intake through suppressing the
lipogenic pathway. PLoS One. 4:e68842009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Serino M, Luche E, Gres S, Baylac A, Bergé
M, Cenac C, Waget A, Klopp P, Iacovoni J, Klopp C, et al: Metabolic
adaptation to a high-fat diet is associated with a change in the
gut microbiota. Gut. 61:543–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lo YH, Ho PC, Chen MS, Hugo E,
Ben-Jonathan N and Wang SC: Phosphorylation at tyrosine 114 of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is required for
adipogenesis in response to high fat diet. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 430:43–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yu H, Liu Y, Wang M, Restrepo RJ, Wang D,
Kalogeris TJ, Neumann WL, Ford DA and Korthuis RJ: Myeloperoxidase
instigates proinflammatory responses in a cecal ligation and
puncture rat model of sepsis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
319:H705–H721. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schleh MW, Caslin HL, Garcia JN,
Mashayekhi M, Srivastava G, Bradley AB and Hasty AH: Metaflammation
in obesity and its therapeutic targeting. Sci Transl Med.
15:eadf93822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A,
Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM and Dixit
VD: The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation
and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 17:179–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Purvis GSD, Collino M, Aranda-Tavio H,
Chiazza F, O'Riordan CE, Zeboudj L, Mohammad S, Collotta D, Verta
R, Guisot NES, et al: Inhibition of Bruton's TK regulates
macrophage NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in metabolic
inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 177:4416–4432. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li Y, Zhao J, Wu Y and Xia L: Btk knockout
attenuates the liver inflammation in STZ-induced diabetic mice by
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 549:75–82. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yamada M, Katsuma S, Adachi T, Hirasawa A,
Shiojima S, Kadowaki T, Okuno Y, Koshimizu TA, Fujii S, Sekiya Y,
et al: Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 prevents the progression of
glomerulonephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:7736–7741. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Durak A, Bitirim CV and Turan B: Titin and
CK2α are new intracellular targets in acute insulin
application-associated benefits on electrophysiological parameters
of left ventricular cardiomyocytes from insulin-resistant metabolic
syndrome rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 34:487–501. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Drygin D, Ho CB, Omori M, Bliesath J,
Proffitt C, Rice R, Siddiqui-Jain A, O'Brien S, Padgett C, Lim JK,
et al: Protein kinase CK2 modulates IL-6 expression in inflammatory
breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:163–167. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ye H, Fu D, Fang X, Xie Y, Zheng X, Fan W,
Hu F and Li Z: Casein kinase II exacerbates rheumatoid arthritis
via promoting Th1 and Th17 cell inflammatory responses. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 25:1017–1024. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang W, Zheng X, Huang Q, Weng D, Yao S,
Zhou C, Li Q, Hu Y, Xu W and Huang K: Protein kinase CK2 promotes
proliferation, abnormal differentiation, and proinflammatory
cytokine production of keratinocytes via regulation of STAT3 and
Akt pathways in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. 193:567–578. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ferreira Alves G, Aimaretti E, da Silveira
Hahmeyer ML, Einaudi G, Porchietto E, Rubeo C, Marzani E, Aragno M,
da Silva-Santos JE, Cifani C, et al: Pharmacological inhibition of
CK2 by silmitasertib mitigates sepsis-induced circulatory collapse,
thus improving septic outcomes in mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
178:1171912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ampofo E, Rudzitis-Auth J, Dahmke IN,
Rössler OG, Thiel G, Montenarh M, Menger MD and Laschke MW:
Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 suppresses tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:2123–2136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yadav AK and Jang BC: Anti-adipogenic and
pro-lipolytic effects on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by CX-4945, an
inhibitor of casein kinase 2. Int J Mol Sci. 23:72742022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ka SO, Hwang HP, Jang JH, Hyuk Bang I, Bae
UJ, Yu HC, Cho BH and Park BH: The protein kinase 2 inhibitor
tetrabromobenzotriazole protects against renal ischemia reperfusion
injury. Sci Rep. 5:148162015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Dixit D, Ahmad F, Ghildiyal R, Joshi SD
and Sen E: CK2 inhibition induced PDK4-AMPK axis regulates
metabolic adaptation and survival responses in glioma. Exp Cell
Res. 344:132–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and
inflammation: impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2:170232017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Niu T, De Rosny C, Chautard S, Rey A,
Patoli D, Groslambert M, Cosson C, Lagrange B, Zhang Z, Visvikis O,
et al: NLRP3 phosphorylation in its LRR domain critically regulates
inflammasome assembly. Nat Commun. 12:58622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pack M, Gulde TN, Völcker MV, Boewe AS,
Wrublewsky S, Ampofo E, Montenarh M and Götz C: Protein kinase CK2
contributes to glucose homeostasis by targeting
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1. Int J Mol Sci. 24:4282022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Guerra B and Issinger OG: Role of protein
kinase CK2 in aberrant lipid metabolism in cancer. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 13:2922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Peterson TR, Sengupta SS, Harris TE,
Carmack AE, Kang SA, Balderas E, Guertin DA, Madden KL, Carpenter
AE, Finck BN and Sabatini DM: mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1
localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell. 146:408–420. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hennessy M, Granade ME, Hassaninasab A,
Wang D, Kwiatek JM, Han GS, Harris TE and Carman GM: Casein kinase
II-mediated phosphorylation of lipin 1β phosphatidate phosphatase
at Ser-285 and Ser-287 regulates its interaction with 14-3-3β
protein. J Biol Chem. 294:2365–2374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Viscarra JA, Wang Y, Hong IH and Sul HS:
Transcriptional activation of lipogenesis by insulin requires
phosphorylation of MED17 by CK2. Sci Signal. 10:eaai85962017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Guerra B, Jurcic K, van der Poel R,
Cousineau SL, Doktor TK, Buchwald LM, Roffey SE, Lindegaard CA,
Ferrer AZ, Siddiqui MA, et al: Protein kinase CK2 sustains de novo
fatty acid synthesis by regulating the expression of SCD-1 in human
renal cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 24:4322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pagano MA, Bain J, Kazimierczuk Z, Sarno
S, Ruzzene M, Di Maira G, Elliott M, Orzeszko A, Cozza G, Meggio F
and Pinna LA: The selectivity of inhibitors of protein kinase CK2:
An update. Biochem J. 415:353–365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sarno S, Reddy H, Meggio F, Ruzzene M,
Davies SP, Donella-Deana A, Shugar D and Pinna LA: Selectivity of
4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, an ATP site-directed inhibitor of
protein kinase CK2 ('casein kinase-2'). FEBS Lett. 496:44–48. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|