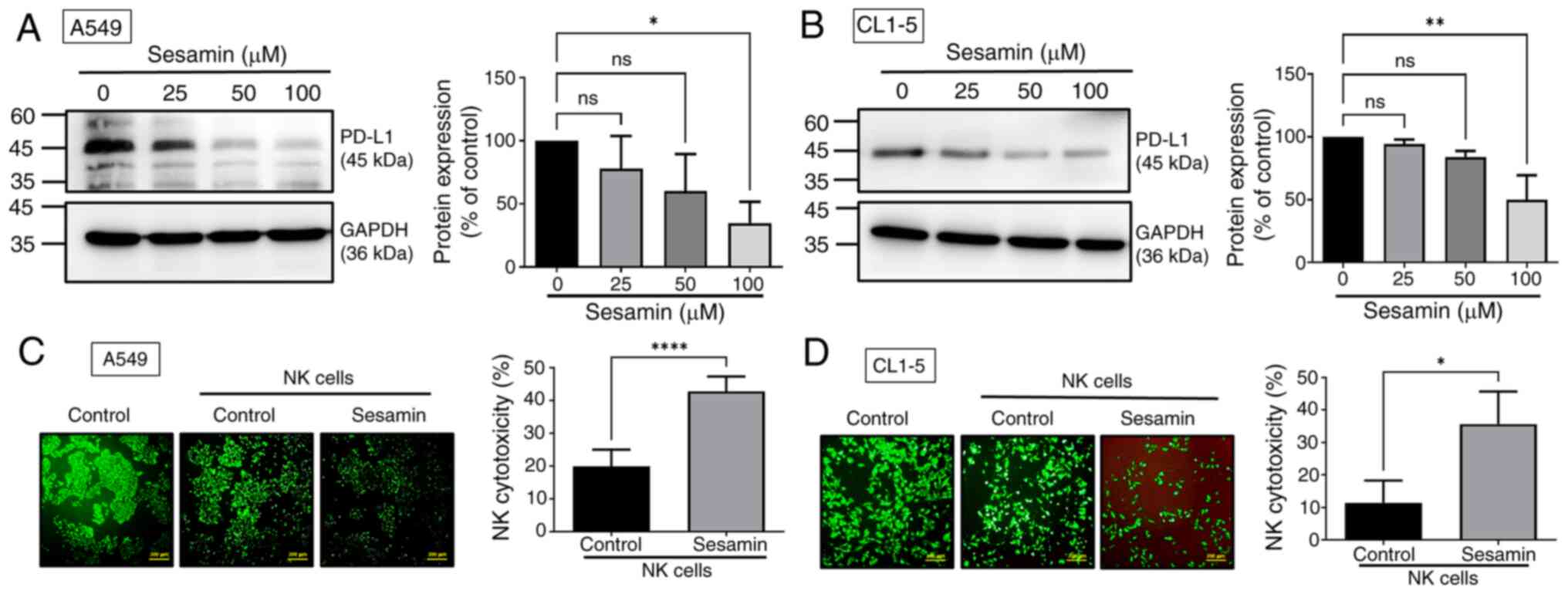
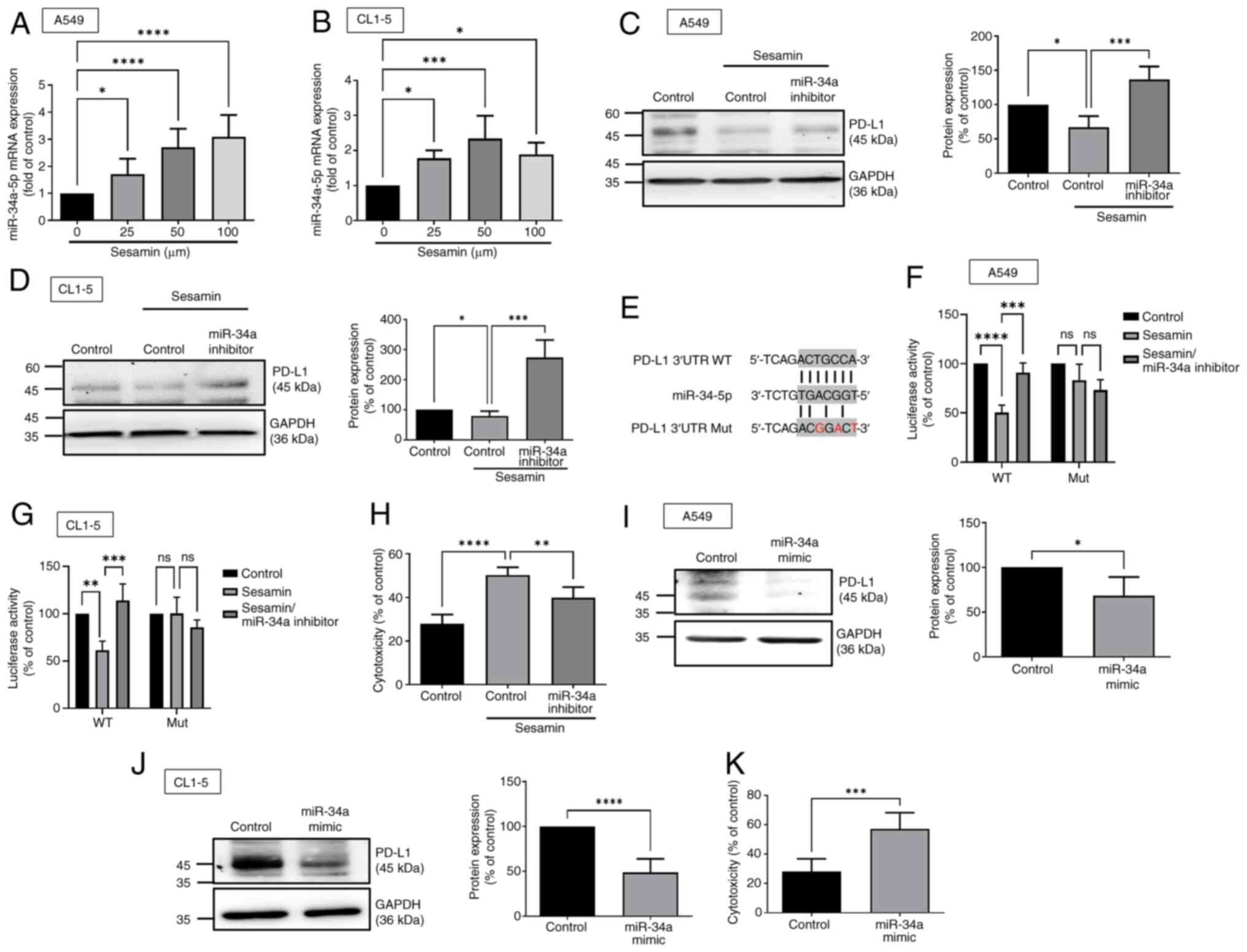
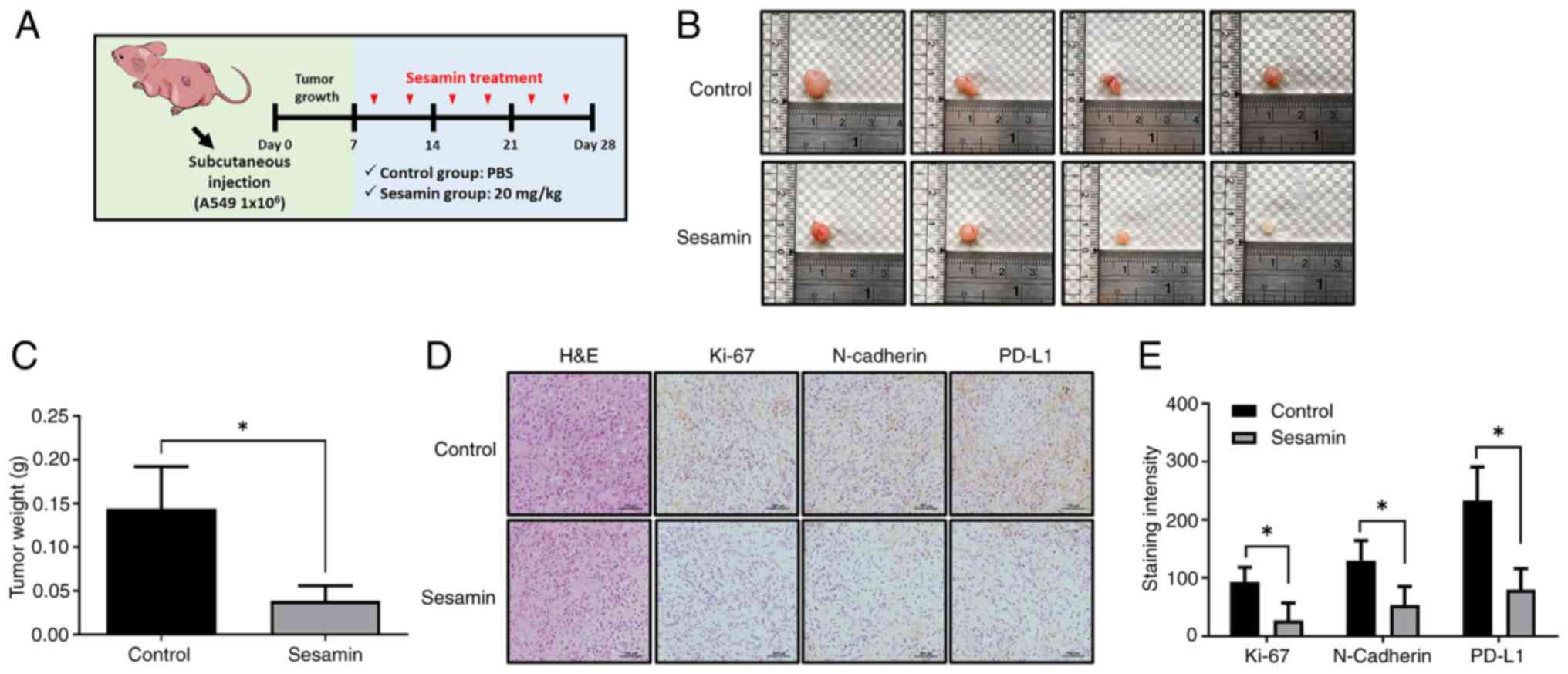
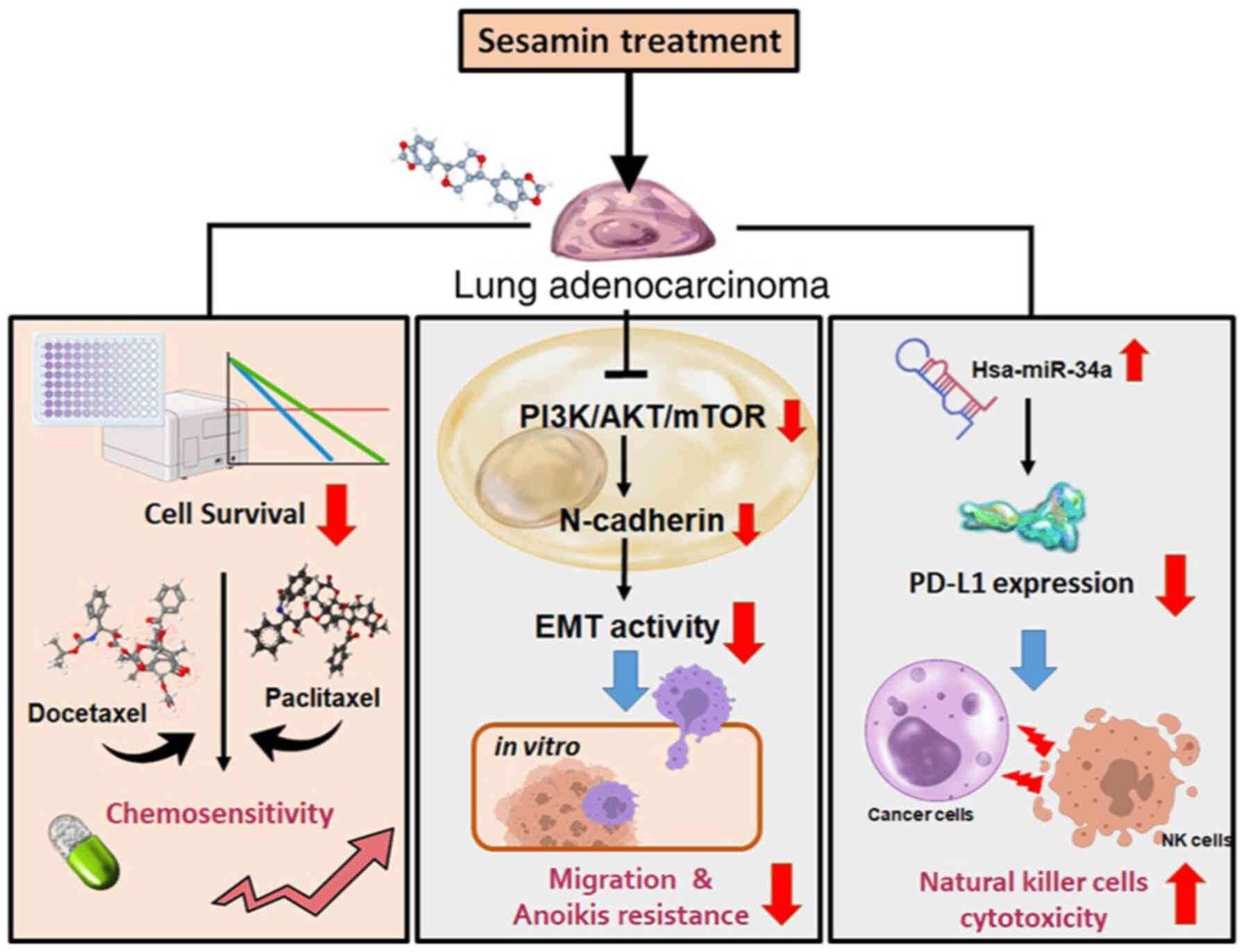
|
1
|
Myers DJ and Wallen JM: Lung
adenocarcinoma. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing;
Treasure, Island FL: 2023
|
|
2
|
Lu TP, Tsai MH, Lee JM, Hsu CP, Chen PC,
Lin CW, Shih JY, Yang PC, Hsiao CK, Lai LC and Chuang EY:
Identification of a novel biomarker, sema5a, for non-small cell
lung carcinoma in nonsmoking women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 19:2590–2597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsai SC, Liu YC, Li CP, Huang TS and Lee
CC: Sesamin inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth and
angiogenic activity of lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Cancer Mol.
2:199–205. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Kong X, Ma MZ, Zhang Y, Weng MZ, Gong W,
Guo LQ, Zhang JX, Wang GD, Su Q, Quan ZW and Yang JR:
Differentiation therapy: Sesamin as an effective agent in targeting
cancer stem-like side population cells of human gallbladder
carcinoma. BMC Complement Alternat Med. 14:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Majdalawieh AF, Massri M and Nasrallah GK:
A comprehensive review on the anti-cancer properties and mechanisms
of action of sesamin, a lignan in sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum).
Eur J Pharmacol. 815:512–521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ye H, Sun L, Li J, Wang Y, Bai J, Wu L,
Han Q, Yang Z and Li L: Sesamin attenuates carrageenan-induced lung
inflammation through upregulation of A20 and TAX1BP1 in rats. Int
Immunopharmacol. 88:1070092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang S, Li X, Dou H, Hu Y, Che C and Xu D:
Sesamin induces A549 cell mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis via
a reactive oxygen species-mediated reduction in mitochondrial
membrane potential. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 24:223–232. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dou H, Yang S, Hu Y, Xu D, Liu L and Li X:
Sesamin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis and activates
autophagy in cervical cancer cells. Life Sci. 200:87–93. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Siriwarin B and Weerapreeyakul N: Sesamol
induced apoptotic effect in lung adenocarcinoma cells through both
intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 254:109–116.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Acar V, Fernandez FL, Buscariolo FF,
Novais AA, Pereira RA and de Campos Zuccari DAP:
Immunohistochemical evaluation of PARP and caspase-3 as prognostic
markers in prostate carcinomas. Clin Med Res. 19:183–191. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Son H and Moon A: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cell invasion. Toxicol Res. 26:245–252. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mottaghi S and Abbaszadeh H: A
comprehensive mechanistic insight into the dietary and estrogenic
lignans, arctigenin and sesamin as potential anticarcinogenic and
anticancer agents. Current status, challenges, and future
perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:7301–7318. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH and Samarakoon
SR: Role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ovarian cancer:
Biological and therapeutic significance. Semin Cancer Biol.
59:147–160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fang Q, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Song M, Gao G and
Zhou Z: Suppression of cyclooxygenase 2 increases chemosensitivity
to sesamin through the Akt-PI3K signaling pathway in lung cancer
cells. Int J Mol Med. 43:507–516. 2019.
|
|
15
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kongtawelert P, Wudtiwai B, Shwe TH,
Pothacharoen P and Phitak T: Inhibition of programmed death ligand
1 (PD-L1) expression in breast cancer cells by sesamin. Int
Immunopharmacol. 86:1067592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL and Hung
MC: Mechanisms controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell.
76:359–370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cortez MA, Ivan C, Valdecanas D, Wang X,
Peltier HJ, Ye Y, Araujo L, Carbone DP, Shilo K, Giri DK, et al:
PDL1 regulation by p53 via miR-34. J Natl Cancer Inst.
108:djv3032016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Danbaran GR, Aslani S, Sharafkandi N,
Hemmatzadeh M, Hosseinzadeh R, Azizi G, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Babaie F
and Mohammadi H: How microRNAs affect the PD-L1 and its synthetic
pathway in cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin M, Zhang Z and Wang Y: Anti-tumor
effects of miR-34a by regulating immune cells in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Med. 12:11602–11610. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Li J, Dong K, Lin F, Long M,
Ouyang Y, Wei J, Chen X, Weng Y, He T and Zhang H: Tumor suppressor
miR-34a targets PD-L1 and functions as a potential
immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Signal.
27:443–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chu YW, Yang PC, Yang SC, Shyu YC, Hendrix
MJ, Wu R and Wu CW: Selection of invasive and metastatic
subpopulations from a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 17:353–360. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsai HC, Chang AC, Tsai CH, Huang YL, Gan
L, Chen CK, Liu SC, Huang TY, Fong YC and Tang CH: CCN2 promotes
drug resistance in osteosarcoma by enhancing ABCG2 expression. J
Cell Physiol. 234:9297–9307. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu HS, Wang SW, Chang AC, Tai HC, Yeh HI,
Lin YM and Tang CH: Bradykinin promotes vascular endothelial growth
factor expression and increases angiogenesis in human prostate
cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:243–253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu MH, Lo JF, Kuo CH, Lin JA, Lin YM, Chen
LM, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Huang CY and Tang CH: Endothelin-1 promotes
MMP-13 production and migration in human chondrosarcoma cells
through FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. J Cell Physiol. 227:3016–3026.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chang AC, Chen PC, Lin YF, Su CM, Liu JF,
Lin TH, Chuang SM and Tang CH: Osteoblast-secreted WISP-1 promotes
adherence of prostate cancer cells to bone via the VCAM-1/integrin
α4β1 system. Cancer Lett. 426:47–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun X and Kaufman PD: Ki-67: More than a
proliferation marker. Chromosoma. 127:175–186. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Ahmadi Z, Mohamadi N,
Zarrabi A, Abasi S, Dehghannoudeh G, Tamaddondoust RN, Khanbabaei
H, Mohammadinejad R and Thakur VK: Chitosan-based advanced
materials for docetaxel and paclitaxel delivery: Recent advances
and future directions in cancer theranostics. Int J Biol Macromol.
145:282–300. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hou RC, Huang HM, Tzen JT and Jeng KC:
Protective effects of sesamin and sesamolin on hypoxic neuronal and
PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res. 74:123–133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Loh CY, Chai JY, Tang TF, Wong WF, Sethi
G, Shanmugam MK, Chong PP and Looi CY: The E-cadherin and
N-cadherin switch in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells.
8:11182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou J, Yang S, Zhu D, Li H, Miao X, Gu M,
Xu W, Zhang Y, Tang W, Shen R, et al: The crosstalk between anoikis
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and their synergistic roles
in predicting prognosis in colon adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol.
13:11842152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zuo Y, Zheng W, Liu J, Tang Q, Wang SS and
Yang XS: MiR-34a-5p/PD-L1 axis regulates cisplatin chemoresistance
of ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasma. 67:93–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Deng S, Wang M, Wang C, Zeng Y, Qin X, Tan
Y, Liang B and Cao Y: p53 downregulates PD-L1 expression via
miR-34a to inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer
cells: A potential clinical immunotherapeutic target. Mol Biol Rep.
50:577–587. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang Y and Wang L: miR-34a attenuates
glioma cells progression and chemoresistance via targeting PD-L1.
Biotechnol Lett. 39:1485–1492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Verweij J, Clavel M and Chevalier B:
Paclitaxel (TaxolTM) and docetaxel (TaxotereTM): Not simply two of
a kind. Ann Oncol. 5:495–505. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN and
McCann A: Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:96–132. 2008.
|
|
38
|
Cenik M, Abas BI, Kocabiyik B, Demirbolat
GM and Cevik O: Development of a new drug delivery system from
hela-derived exosomes and the effect of docetaxel-loaded exosomes
on mitochondrial apoptosis. J Pharm Innov. 17:931–939. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Mirzaei S, Hashemi F,
Zarrabi A, Zabolian A, Saleki H, Sharifzadeh SO, Soleymani L,
Daneshi S, Hushmandi K, et al: New insight towards development of
paclitaxel and docetaxel resistance in cancer cells: EMT as a novel
molecular mechanism and therapeutic possibilities. Biomed
Pharmacother. 141:1118242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Li H, Zhang W, Qi W, Lu C, Huang
H, Yang Z, Liu B and Zhang L: Sesamin suppresses NSCLC cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis via Akt/p53 pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 387:1148482020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu M, Jiang Z, Duan H, Sun L, Zhang S,
Chen M, Wang Y, Gao Q, Song Y, Zhu X and Zhang L:
Deoxypodophyllotoxin triggers necroptosis in human non-small cell
lung cancer NCI-H460 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:701–706. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Choi JY, Hong WG, Cho JH, Kim EM, Kim J,
Jung CH, Hwang SG, Um HD and Park JK: Podophyllotoxin acetate
triggers anticancer effects against non-small cell lung cancer
cells by promoting cell death via cell cycle arrest, ER stress and
autophagy. Int J Oncol. 47:1257–1265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kuo TN, Lin CS, Li GD, Kuo CY and Kao SH:
Sesamin inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation by promoting
p53/PTEN-mediated apoptosis. Int J Med Sci. 17:2292–2298. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Siao AC, Hou CW, Kao YH and Jeng KC:
Effect of sesamin on apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human
breast cancer mcf-7 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:3779–3783.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Harikumar KB, Sung B, Tharakan ST, Pandey
MK, Joy B, Guha S, Krishnan S and Aggarwal BB: Sesamin manifests
chemopreventive effects through the suppression of NF-kappa
B-regulated cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenic
gene products. Mol Cancer Res. 8:751–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang RY, Wong MK, Tan TZ, Kuay KT, Ng AH,
Chung VY, Chu YS, Matsumura N, Lai HC, Lee YF, et al: An EMT
spectrum defines an anoikis-resistant and spheroidogenic
intermediate mesenchymal state that is sensitive to e-cadherin
restoration by a src-kinase inhibitor, saracatinib (AZD0530). Cell
Death Dis. 4:e9152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cao ZQ, Wang Z and Leng P: Aberrant
N-cadherin expression in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1093202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Abufaraj M, Shariat SF, Haitel A, Moschini
M, Foerster B, Chłosta P, Gust K, Babjuk M, Briganti A, Karakiewicz
PI and Albrecht W: Prognostic role of N-cadherin expression in
patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urol Oncol.
35:264–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Su Y, Li J, Shi C, Hruban RH and Radice
GL: N-cadherin functions as a growth suppressor in a model of
K-ras-induced PanIN. Oncogene. 35:3335–3341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Lammens T, Swerts K, Derycke L, De Craemer
A, De Brouwer S, De Preter K, Van Roy N, Vandesompele J, Speleman
F, Philippé J, et al: N-cadherin in neuroblastoma disease:
Expression and clinical significance. PLoS One. 7:e312062012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
He J, Hu Y, Hu M and Li B: Development of
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor immune microenvironment and treatment
for non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 5:131102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu H, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Li Y, Jain A,
Barve A, Jin W, Liu Y, Fetse J and Cheng K: Discovery of
low-molecular weight anti-PD-L1 peptides for cancer immunotherapy.
J Immunother Cancer. 7:2702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu MS, Aquino LBB, Barbaza MYU, Hsieh CL,
Castro-Cruz KA, Yang LL and Tsai PW: Anti-Inflammatory and
anticancer properties of bioactive compounds from sesamum indicum
L.-A review. Molecules. 24:44262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim JH and Lee JK: Sesamolin enhances NK
cell lysis activity by increasing the expression of NKG2D ligands
on Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:977–984. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang Q, Lin W, Tang X, Li S, Guo L, Lin Y
and Kwok HF: The roles of microRNAs in regulating the expression of
PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Int J Mol Sci. 18:25402017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hwang TI, Cuiu YC, Chen YC, Chen PC, Tsai
TF, Chou KY, Ho CY, Chen HE, Chang PH and Chang AC: Tumor
suppressive functions of hsa-miR-34a on cell cycle, migration and
protective autophagy in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 62:662023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz
GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y, et al:
TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment
promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 22:291–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shin J, Xie D and Zhong XP: MicroRNA-34a
enhances T cell activation by targeting diacylglycerol kinase ζ.
PLoS One. 8:e779832013. View Article : Google Scholar
|